- 1Instituto de Química Rosario, Facultad de Ciencias Bioquímicas y Farmacéuticas, Universidad Nacional de Rosario-CONICET, Rosario, Argentina
- 2Università del Piemonte Orientale, Dipartimento di Scienze del Farmaco, Novara, Italy
The chemistry of phytocannabinoids has witnessed renewed interest these last decades as a consequence of reduced restrictions, research on the endocannabinoid system and the development of approved therapeutic treatments based on cannabinoids. The medicinal cannabinoid market constitutes a prolific scenario in current medicine. Most studies, however, have focused on only two major components of Cannabis sativa L., namely, cannabidiol (CBD, 2) and (−)-Δ9-trans-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-trans-THC, 6a), the latter being the main psychoactive compound of this plant. The cis-diastereoisomer of Δ9-trans-THC, Δ9-cis-THC, although also present in the same plant, has been less investigated in terms of biological, medicinal and synthetic perspectives. Interestingly, the cis-fused tetrahydrobenzo [c]chromene motif present in Δ9-cis-THC is embedded in many other natural products which also exhibit interesting biological activities such as anticancer, antifungal, and antiparasitic. This review discloses synthetic approaches that have been established towards the cis-fused tetrahydroisochromene system of Δ9-cis-THC.
Introduction
Plants of the genus Cannabis have been used by different cultures for millennia (Russo, 2014). Throughout history this plant has been used in religious acts, for recreational purposes, therapeutic uses for the treatment of pain and different disorders and even as a source of fibers for making cloth and cordage (Appendino, 2020). Its history has been as extensive as controversial, generally influenced by social belief around marijuana consumption as well as by all the legal restrictions imposed by different governments on the research and use of this plant and its phytocannabinoid components (Mechoulam, 1986). Investigations during the last century can be divided into three stages: a chemical one, the biochemical era and the current one focused on the commercialization and legal status. The chemical stage mainly dealt with the identification and characterization of the active components of the plant, having a milestone in 1964 with the isolation, structural elucidation and identification of (−)-Δ9-trans-tetrahydrocannabinol [(−)-Δ9-trans-THC, 6a, Figure 1] as the main psychoactive component of the plant by the group of Mechoulam (Gaoni and Mechoulam, 1964; Mechoulam and Hanuš, 2000). The biochemical era began with the identification of the first cannabinoid receptors leading later to the establishment of what today is known as the endocannabinoid system (ECS), which comprises the cannabinoid receptors, endogenous lipid mediators (endocannabinoids) and the corresponding metabolic enzymes (Mechoulam et al., 2014). The relevance that this system has been shown to possess, particularly on key physiological functions and dysfunctions, has promoted increased interest, a boost in research on cannabinoids and most importantly reduced restrictions opening the way for a commercial era involving the approval of medical treatments based on cannabinoids (Vemuri and Makriyannis, 2015). In this context, a plethora of pharmaceutical products and cosmetics appeared containing cannabidiol (CBD, 2) or Δ9-THC (6a). Since 1985, FDA has already approved four treatments based on cannabinoids: Marinol® and Syndros®, based on synthetic 6a as active ingredient, are indicated for the treatment of nausea associated with chemotherapy and anorexia in AIDS patients; Epidiolex®, which contains 2 as active principle, being the first FDA approved treatment to contain a purified extract of the plant and used for the treatment of seizures associated with two severe forms of epilepsy in patients over 2 years of age; and Cesamet®, based on drug nabilone, a synthetic analogue of 6a, is used to treat nausea and chemotherapy-induced vomit (Khalsa et al., 2022).
Phytocannabinoids are biologically active meroterpenoids of mixed polyketide and terpenoid biosynthetic origin (Degenhardt et al., 2017; Jamieson et al., 2021; Tahir et al., 2021; Purdy et al., 2022). Structurally isoprenylated resorcinols, main classes of cannabinoids include cannabigerol (1a, CBG), cannabidiol (2, CBD), cannabichromene (3, CBC), cannabinol (4, CBN), Δ8-tetrahydrocannabinol (5, Δ8-THC) and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinols (6, THCs) (Figure 1). To date, more than a hundred cannabinoids have been found to be produced by Cannabis sativa L. (Hanuš et al., 2016). Diversification in structure comprises oxidized and cyclized derivatives, analogues with variations in the length of the resorcinyl alkyl chain, and carboxylated versions called acidic cannabinoids which are metabolic precursors in their biosynthesis (e.g., cannabigerolic acid CBGA, 1b).
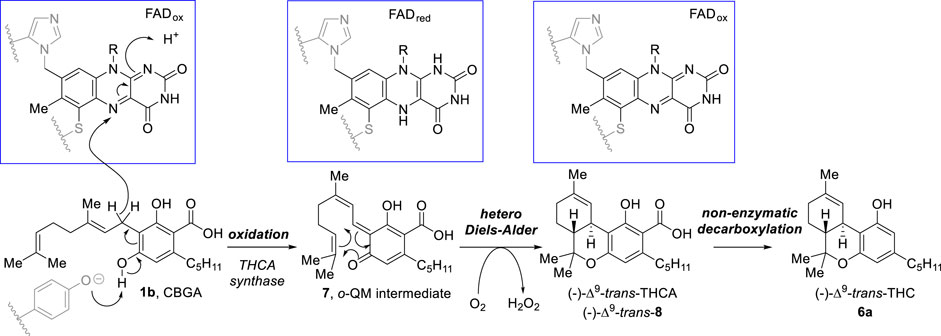
Although literature review reveals that most research studies have focused on only two major components of the plant [namely, CBD (2) and (−)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-trans-THC, 6a)] (Sampson, 2021), over the last two decades there has been an increase in interest in the occurrence, synthesis, and medicinal potential of minor components of the plant, known as “minor cannabinoids” or “rare cannabinoids”, probably as a result of reduced restrictions and approvals of cannabinoid-based therapeutic treatments (Walsh et al., 2021; Caprioglio et al., 2022; Maioli et al., 2022; Nguyen et al., 2022). Δ9-trans-THC, (6a) the main psychoactive constituent of Cannabis sativa, features a tetrahydrobenzo[c]chromene motif bearing two stereogenic centers at positions 6a and 10a and thus four stereoisomers can be conceived. Nevertheless, only one of these four compounds is produced in the plant via non-enzymatic decarboxylation of (−)-Δ9-trans-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid [(−)-Δ9-trans THCA, 8], formed in turn by enzyme tetrahydrocannabinolic acid synthase (THCA synthase) from cannabigerolic acid (1b) (Scheme 1). THCA synthase, with the aid of a doubly-covalent attached FAD cofactor (binding residues shown in grey), catalyzes the stereoselective oxidative cyclization of cannabigerolic acid (1b) through oxidized ortho-quinone intermediate 7, which undergoes an intramolecular hetero Diels–Alder reaction to deliver (−)-Δ9-trans-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid 8. While this particular cannabinoid has been assumed as the only relevant isomer since its identification in 1964, the cis-stereoisomers of 6a [(+)- and (−)-Δ9-cis-THC, 6b] have been both obtained via synthesis as well as identified in C. Sativa as minor constituents. The present review discloses the natural occurrence and bioactivity of these minor phytocannabinoids as well as all synthetic approaches that have been established to selectively prepare this medicinally promising enantiomeric pair of natural products.
Synthetic strategies toward Δ9-cis-THC
Shortly after the characterization and identification of (−)-Δ9-trans-THC as the main psychoactive component of Cannabis, cis-THC as a racemic mixture was first obtained by Taylor and co-workers in 1966 (Scheme 2) (Taylor et al., 1966). The group established a one-pot synthetic strategy based on the acid promoted condensation between olivetol (9) and citral (10), giving access to Δ8-trans-THC (which at the time had been identified in the plant as another psychoactive constituent) as well as Δ8-cis-THC and Δ9-cis-THC. In particular, treatment of the substrates with BF3.Et2O in benzene at 5°C–10°C led to the isolation of Δ8-cis-THC, Δ8-trans-THC and derivative Δ8-trans-11, in 20%, 20% and 10%–20% yields, respectively. On the other hand, when the condensation was carried out under milder acid conditions (HCl 0.0005 N) Δ9-cis-THC and Δ9-trans-THC were instead obtained as a mixture hard to separate (12% pure Δ9-cis-THC fraction, ca 25% mixture fraction). During this study, acid treatment was also shown to isomerize Δ9-THC isomers to the corresponding Δ8-THC products, as well as thermal treatment for the case of Δ9-trans-THC when using vapor phase partition chromatography (280°C) and based on these observations the group proposed that the effects of smoking Cannabis may be due to isomer Δ8-THC instead of Δ9-THC (Taylor et al., 1966). The same year, after this report, Gaoni and Mechoulam reevaluated these results and claimed that Δ9-cis-THC does not undergo acid-promoted isomerization toward Δ8-cis-THC and that the structure of the originally proposed product of this transformation (Δ8-cis-THC) should be reassigned to iso-THC (Δ4(8)-12) (Gaoni and Mechoulam, 1966). The researchers also indicated that Δ9-trans-THC does not undergo thermal isomerization to Δ8-trans-THC and that the isomerization found by Taylor and co-workers on vapor phase chromatography may have been promoted by the nature of the column support used. Mechoulam later demonstrated that both Δ9-cis-THC and Δ8-trans-THC were inert to oxidation conditions that converted Δ9-trans-THC to cannabinol (Mechoulam et al., 1968). This condensation of olivetol (9) and citral (10) using HCl in EtOH was reinvestigated by Crombie and Ponsford later under reflux conditions for 5 h to afford, after Florisil chromatography, a mixture of Δ9-cis-THC and Δ9-trans-THC in 19% yield (ca 5:1 by NMR analysis) (Crombie and Ponsford, 1971). Mechoulam and co-workers also repeated the BF3.Et2O promoted direct condensation and found that when the acid was used in low loading (1%) in CH2Cl2 for 1 h at room temperature, Δ9-trans-THC was obtained in 20% yield and isomer Δ9-cis-THC in 5% yield (Mechoulam et al., 1972).
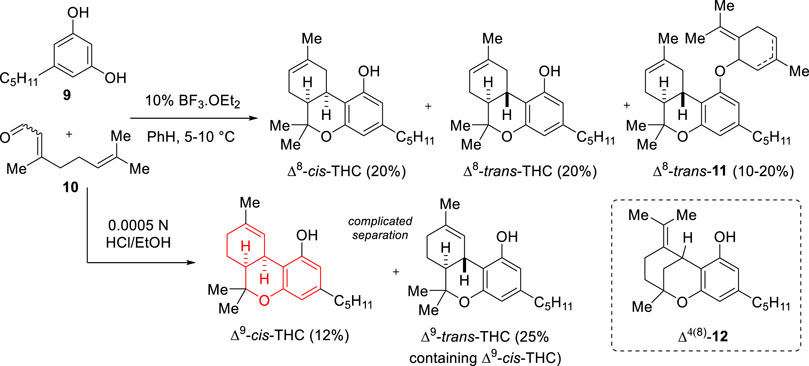
SCHEME 2. First synthesis of (±)-Δ9-cis-THC via condensation between olivetol (9) and citral (10) (1966).
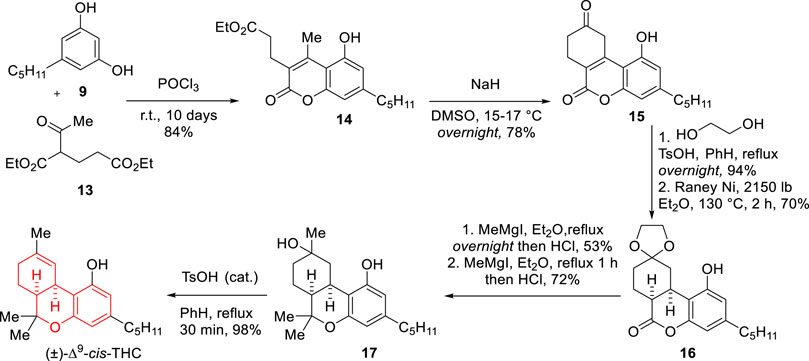
In 1967, Fahrenholtz and co-workers reported a novel synthetic approach towards many cannabinoids including Δ9-cis-THC, at the time considered an unnatural isomer of THC (Scheme 3) (Fahrenholtz et al., 1967). The synthetic strategy began with a von Pechmann condensation between olivetol (9) and diethyl 2-acetylglutarate (13) to afford a coumarin intermediate (14). Intramolecular condensation was then achieved using NaH in DMSO which led to a ketone intermediate (15) which was then protected as a cyclic ketal. Hydrogenation with Raney Ni under vigorous conditions afforded cis-lactone 16, which was treated with MeMgI followed by hydrolysis to afford a ketone intermediate that upon a new sequence of MeMgI treatment followed by hydrolysis yielded alcohol 17. Acid-catalyzed dehydration of this intermediate produced cis-THC in good yield.
In 1969, Razdan and Zitko reported that through treatment with p-toluenesulfonic acid (TsOH) in refluxing benzene, Δ9-cis-THC interconverted with cannabicitran (18) and iso-THC’s (12) leading to an equilibrium that favors the iso-THC´s (Scheme 4) (Razdan and Zitko, 1969). The acetylation of Δ9-cis-THC was shown to block this process. Cannabicitran (18) is established as an intermediate between Δ9-cis-THC and the iso-THC’s (12), a process that cannot take place with the trans-THC’s since a polycyclic system as cannabicitran cannot be formed with a trans-ring fusion. The group also found that BBr3 isomerizes Δ9-cis-THC to Δ8-trans-THC in 60% yield. The first proposed mechanism involves ionization of the ether linkage followed by epimerization at C-4 via elimination. Almost a decade after this report the group continued to investigate this isomerization making advances on the mechanistic interpretation (Uliss et al., 1978).
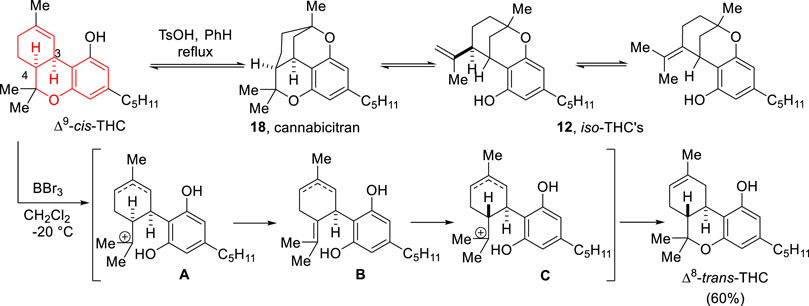
SCHEME 4. Isomerization of Δ9-cis-THC found by Razdan and Zitko (1969).
Also in 1969, Yagen and Mechoulam reported that on BF3.Et2O (5% in dichloromethane) treatment, cannabichromene (CBC, 3) gives rise to a low yield of Δ9-cis-THC (5%) among other isomers. A mechanism based on the intermediacy of cationic species was proposed to account for the transformation (Scheme 5) (Yagen and Mechoulam, 1969).
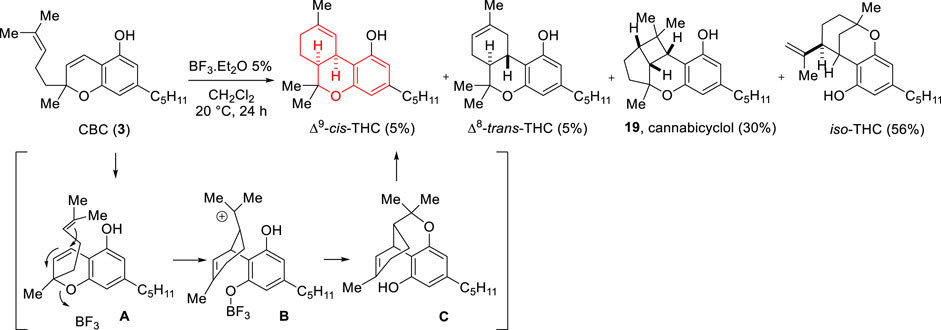
SCHEME 5. Acid-promoted isomerization of cannabichromene (3) by Yagen and Mechoulam (1969).
In 1970, Razdan and co-workers reported an asymmetric strategy towards THC-derivatives based on the use of a carene derivative (Scheme 6) (Razdan and Handrick, 1970). During their studies, they found that condensation between (+)-trans-2-carene oxide (20) and olivetol (9) promoted by 1% BF3.Et2O in dichloromethane at room temperature or p-toluenesulfonic acid in benzene (with a molar ratio of substrates 1.6:1) led to a mixture in which major products were (+)-Δ9-cis-THC and (−)-Δ9-trans-THC (28%).
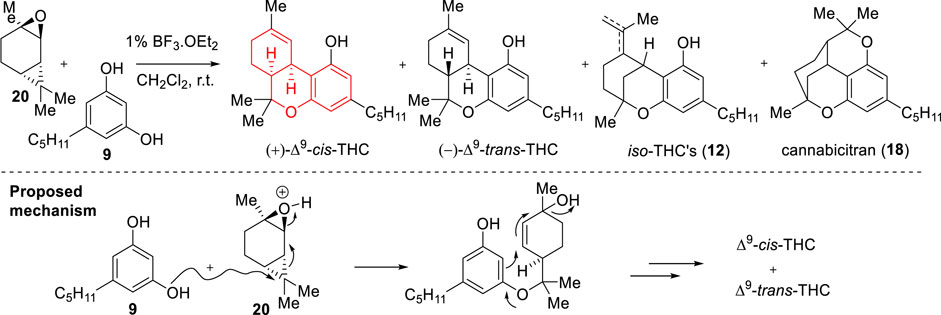
SCHEME 6. Asymmetric synthesis of (+)-Δ9-cis-THC reported by Razdan and Handrick (1970).
Taylor’s direct condensation between olivetol (9) and citral (10) was reinvestigated by Razdan and co-workers in 1975 using HCl (0.5 N) in EtOH/benzene for structure-activity relationship studies during their program on THC analogues (Uliss et al., 1975b). The reaction led to the formation of Δ9-cis-THC in 10% yield and regioisomer Δ9-cis-21 in 20% yield (Scheme 7). The same year the group reported a synthetic strategy to prepare Δ8-cis-THC, an isomer that had not been previously prepared in the THC series (Uliss et al., 1975a). The asymmetric version of this strategy was then realized accomplishing the preparation of (+)-Δ9-cis-THC and (+)-Δ8-cis-THC in 0.7% and 0.06% yields, respectively (Uliss et al., 1977).
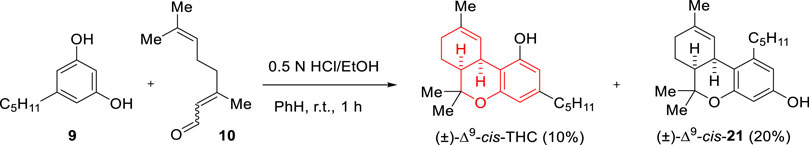
SCHEME 7. Reinvestigation of Taylor’s condensation approach by the group of Uliss et al. (1975a).
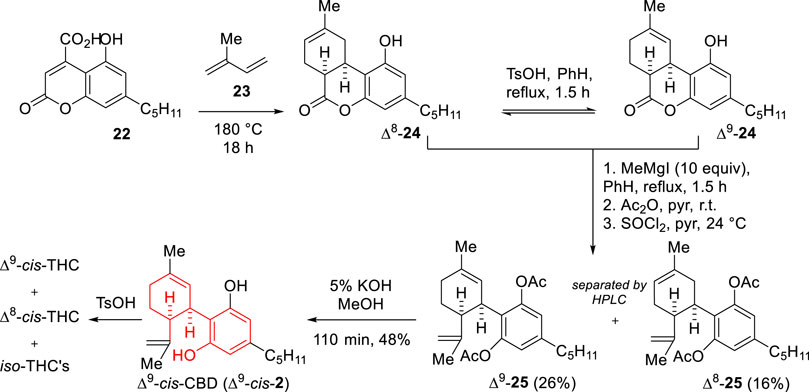
Based on a Diels–Alder approach previously developed by Taylor and Strojny (1960), the group of Razdan reported in 1977 an entry to Δ9-cis-THC via prior preparation of cis-CBD (Scheme 8) (Handrick et al., 1977). Tandem Diels–Alder reaction/decarboxylation between isoprene (23) and 3-carboxy-5-hydroxy-7-pentylcoumarin (22) led to lactone 24, bearing a cis-ring fusion, which under acid treatment becomes an equilibrated 1:1 mixture of Δ8- and Δ9-olefins. To this mixture, addition of MeMgI leads to a mixture of triols, which upon bis-acetylation and dehydration using thionyl chloride affords Δ8- and Δ9-cis-CBD diacetates (25), separable by HPLC. Basic hydrolysis of Δ9-25 provided an entry to Δ9-cis-CBD which upon acid treatment (TsOH) underwent cyclization toward a mixture of Δ9-cis-THC, Δ8-cis-THC and iso-THC’s in ratio 40:17:43. Remarkably, a recent patent described the use of triisobutylaluminium as efficient Lewis acid for this same cyclization, actually performed on each enantiomer of Δ9-cis-CBD, towards the corresponding Δ9-cis-THC cyclized product (85% yield) (Abdur-Rashid et al., 2020).
In 1979 Luteijn and Spronck reported an alternative synthesis of (±)-Δ9-cis-THC based on the reaction between olivetol bis(tetrahydropyranyl ether)homocuprate (26) and dehydrolinalool acetate (27) (Scheme 9, overall yield 20%) (Luteijn and Spronck, 1979). The reaction would work via initial SN2’ reaction leading to an allene intermediate (28) which upon acid treatment undergoes hydrolysis of the tetrahydropyranyl groups (THP) followed by bicyclization.
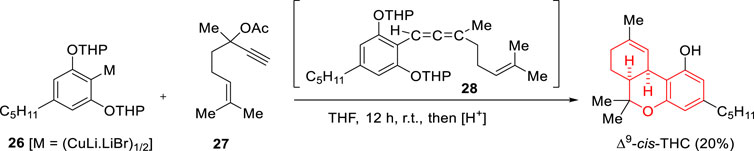
SCHEME 9. Synthesis of (±)-Δ9-cis-THC reported by Luteijn and Spronck (1979).
In 1984, Rickards’ group showed that the use of olivetol di (methoxymethyl)ether as coupling partner of citral (10) enables an efficient route to (±)-Δ9-cis-THC (Scheme 10) (Moore et al., 1984). The reaction begins with the alkylation of citral (10) with a protected olivetol substrate lithiated at C-2 which yielded the corresponding alcohol product 29 in 79% yield. Reaction of this intermediate with TMSCl in the presence of tetraethylammonium bromide at 0°C, followed by aqueous work-up, led to the formation of (±)-Δ9-cis-THC in 65% yield. The mild conditions are believed to favor the formation of an ortho-quinone methyde-type intermediate that undergoes the required intramolecular hetero-Diels Alder reaction towards the product avoiding cationic intermediates. Later, in 2001, Malkov and Kočovský reported that the condensation between olivetol (9) and citral (10) catalyzed by a Mo(IV) catalyst [(acac)2MoCl2] affords a mixture of (±)-Δ9-cis-THC and (±)-Δ9-trans-THC in 20% yield and 1:2.2 cis-trans ratio (Malkov and Kočovský, 2001).
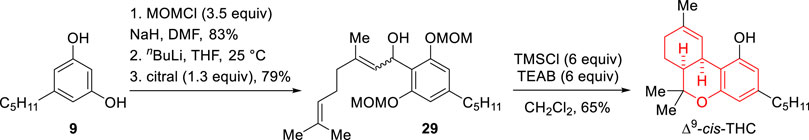
SCHEME 10. Synthesis of Δ9-cis-THC reported by the group of Moore et al. (1984).
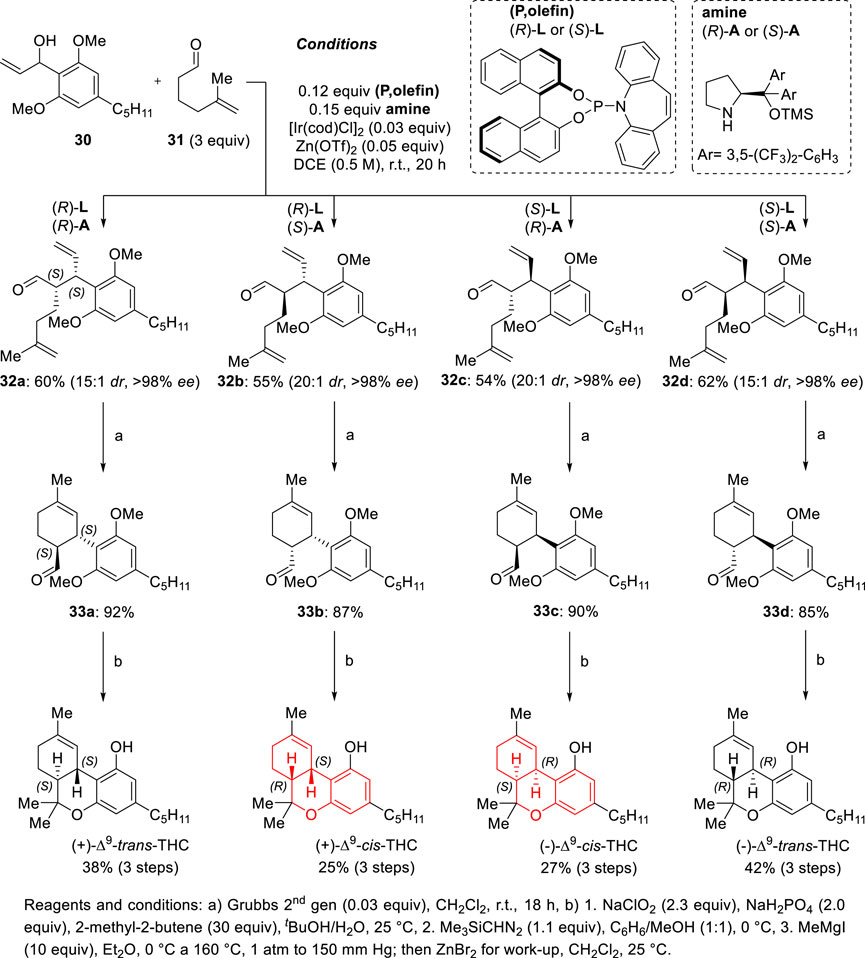
A major breakthrough in the total synthesis of THC natural products was achieved in 2014, when the group of Carreira established an efficient catalytic asymmetric synthetic strategy to access any stereoisomer of Δ9-THC (Scheme 11) (Schafroth et al., 2014). This uniform stereodivergent assembly of all stereoisomers of Δ9-THC was achieved via dual stereodivergent catalysis, applying identical synthetic sequences, under identical reaction conditions and using the same set of substrates though five synthetic steps. The asymmetric approach involves simultaneously using two chiral catalysts, each of which exerts full and independent control over the configuration of one of the stereocenters and the concept was implemented in the α-allylation of 5-methylhex-5-enal (31) catalyzed by a chiral Ir/(P,olefin) complex and a chiral amine. In the presence of 3 mol% of [{Ir(cod)Cl)}2], 12 mol% of (R)-L or (S)-L, and 15 mol% of Jørgensen amine (R)-A or (S)-A, all possible stereoisomers of γ,δ-unsaturated aldehyde product 32 were obtained in good yields (55%–62%) and excellent selectivity (dr 15:1, er > 99:1) via activation of both allylic alcohol (30) and aldehyde (31). Reactions could be performed in Gram scale with similar selectivity and yields. From the aldehyde 32 intermediates, ring-closing metathesis using Grubbs second-generation catalyst first secured cyclohexenecarbaldehydes 33 in 85%–92% yield. Pinnick oxidation of the aldehydes to the corresponding carboxylic acids, followed by treatment with trimethylsilyldiazomethane gave the corresponding methyl esters (60%–66% yield over two steps). The formation of a tertiary alcohol and double methyl ether deprotection was achieved with excess MeMgI at 0°C–160°C at reduced pressure (150 mm Hg). After aqueous work-up and extraction, the organic phase was treated with Lewis acid ZnBr2, which promoted aryl ether formation and thus the formation of each stereoisomer of Δ9-THC.
More recently, another asymmetric and straightforward approach towards (−)-Δ9-cis-THC, also applicable to many analogues, was reported by Dorsch and Schneider. The group reinvestigated the bicyclization reaction studied by Rickards and found that chiral imidodiphosphorimidates (IDPis, e.g., 34), as sterically confined Brønsted acid catalysts, allow the cyclization to proceed with high yield and selectivities (Scheme 12) (Dorsch and Schneider, 2023). In particular, cyclization of 29 led to derivative 35 which after MOM-removal using AcCl afforded (−)-Δ9-cis-THC (71% yield from 29). Some control experiments supported a cationic stepwise mechanism for the organocatalyzed cyclization involving initial carbocycle formation via a Prins-type reaction.
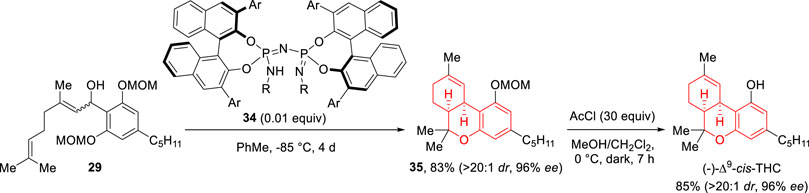
SCHEME 12. Asymmetric synthesis of (−)-Δ9-cis-THC by Dorsch and Schneider (2023).
It should be noted that some of the presented strategies, such as Rickards’ synthetic sequence, have also been used for the preparation of other natural products bearing the cis-fused tetrahydro-6H-benzo[c]chromene system of Δ9-cis-THC. These natural products can be found in species other than Cannabis sativa and include, for instance, perrottetinene from different Radula liverwort species (Toyota et al., 1994; Cullmann and Becker, 1999; Park and Lee, 2010), which medicinal potential has attracted considerable attention (Chicca et al., 2018); and epiconicol found in many marine ascidians, which displays considerable antiproliferative activity against different cancer cell lines (Carroll et al., 1993; Garrido et al., 2002; Simon-Levert et al., 2005; Ren et al., 2020). Also, other synthetic strategies have been explored and developed to gain access to this same cis-fused structural motif but have not been yet applied to cis-THC in particular. A radical cyclization approach was explored by Parker and co-workers to gain access to natural product bisabosqual A (am Ende et al., 2013; am Ende and Parker, 2019). Substituted 1-aryl-1,3-butadienes have been evaluated in Diels–Alder strategies toward cis-fused tetrahydrobenzo[c]chromenes including epiconicol and some members of palodesangrens family of natural products (Minuti et al., 2015; Tangdenpaisal et al., 2019; Tangdenpaisal et al., 2022). A domino electrocyclic ring-opening/hetero Diels–Alder reaction of 2-prenylated 2H-pyrans, originally developed by Chizhova and Anufriev (Chizhova and Anufriev, 2000), has been employed for the synthesis of reduced versions of cannabinoids (Garcia et al., 2009), natural products benzosimuline (Riveira et al., 2016), 7-demethylnaphterpin (Murray et al., 2018), as well as others (Coleman et al., 2019; Murray et al., 2019). Interestingly, a related strategy was developed by Appendino and co-workers using iodine as promoter but to afford aromatized versions of the corresponding tetrahydro-6H-benzo[c]chromene derivatives (Caprioglio et al., 2019). Based on all the available data, a direct oxidative cyclization method (resembling THCA synthase activity) that converts geranylresorcinols (such as CBG) into cis-THC derivatives selectively is also lacking. The only examples involve oxidative cyclization toward chromenes promoted by oxidants such as DDQ, MnO2 or through Pd-catalyzed procedures (Miyase et al., 1980; Lok et al., 1983; Verotta et al., 2004; Ma et al., 2020). Studies on all the established synthetic strategies in the future will prove whether they can efficiently provide access to cis-THC and analogues in order to advance biological studies on these precious molecules.
Natural occurrence and biological activity of cis-THC isomers
In 1977, Smith and Kempfert reported for the first time the isolation of Δ9-cis-THC from a natural source (Smith and Kempfert, 1977). Natural Δ9-cis-THC was found as a contaminant during routine analysis of samples of marijuana. An amount of 460 g of dried plant material afforded ca 1 mg of the compound which absolute stereochemistry was assigned as (6aS,10aR) based on circular dichroism studies. The researchers found that this natural product was prominent in samples that had high content of CBD. In general, samples that had CBD:THC ratios of ca 16:1 were found to exhibit trans:cis ratios of THC of about 1:1 to 2:1 (phenotype considered as non-narcotic hemp). Phenotypes having ratios less than 1 showed trans-THC:cis-THC ratios greater than 10:1. The total concentration of Δ9-cis-THC in plants having a phenotype ratio greater than ca 2 was relatively constant at ca 0.04% of the dry plant weight. On the other hand, plants having low amounts or lacking CBD did not exhibit detectable amounts of Δ9-cis-THC. Remarkably, this natural product as well as other cis-homologues (different alkyl branched chains) and carboxylated versions were identified more recently in C. sativa L. varieties (Basas-Jaumandreu and de las Heras, 2020). In particular, Δ9-cis-THCA (Δ9-cis-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, Δ9-cis-8), found in samples that had not been heated before analysis, would be the biosynthetic precursor of Δ9-cis-THC which would then be formed via non-enzymatic decarboxylation (Tolomeo et al., 2022). As for Δ9-cis-THC, the corresponding carboxylated cannabinoid Δ9-cis-THCA was present in concentrations comparable to or slightly lower than those of the well-known trans isomer in CBD-rich or CBG-rich varieties of the plant.
Mechoulam and co-workers were the first to report in1971 on the biological activity of Δ9-cis-THC. The group found that (±)-Δ9-cis-THC was inactive in behavioral tests in adult Rhesus monkeys at doses of 1.5 mg/kg (Edery et al., 1971). Later, in 1975, Razdan’s group described racemic Δ9-cis-THC as a mild depressor and reported that it was 20-fold less potent than natural (−)-Δ9-trans-THC in the “popcorn assay”, a rarely used mouse model of cannabinoid activity based on the association of ataxia and hyperexcitability to touch (Uliss et al., 1975a). Additionally, in 1984 Razdan and Martin showed that (+)-Δ9-cis-THC, together with (+)-Δ9-trans-THC, were quite less active in behavioral tests in dogs compared to (−)-Δ9-trans-THC (Martin et al., 1981).
In 2021, the groups of Appendino, Carreira and Gertsch published a thorough study on Δ9-cis-THC addressing its natural occurrence, chirality and pharmacological activity (Schafroth et al., 2021). Consistent with the report by Smith and Kempfert, the authors found that in hemp non-narcotic varieties of the plant featuring low content of (−)-Δ9-trans-THC the concentration of Δ9-cis-THC was in the same order of the psychoactive component whereas the concentration of Δ9-cis-THC was below the limits of detection in a sample of medicinal Cannabis chemotype with high content of (−)-Δ9-trans-THC. In this same medicinal Cannabis sample Δ9-THC was found with very high enantiomeric purity (ee > 99%) and exclusively as the trans diastereoisomer. On the contrary, in 34 samples of Cannabis varieties in which CBD or CBG was the most prominent phytocannabinoid, Δ9-THC was found with lower diastereomeric purity. The authors showed that natural Δ9-cis-THC is scalemic (approx. 80–90% enantiomeric purity), the major enantiomer being 6aS, 10aR [(−)]. Regarding binding affinity to cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2, (−)-Δ9-cis-THC exhibited binding affinities ten times lower than the ones found for the natural trans isomer, whereas (+)-Δ9-cis-THC was found to be inactive. The researchers found that (−)-Δ9-cis-THC mildly inhibits endocannabinoid hydrolytic enzymes similarly to (−)-Δ9-trans-THC. In general, IC50 values of these natural tetrahydrocannabinols on endocannabinoid degrading enzymes were higher than the in vivo achieved concentrations after Cannabis consumption. Possible effects of isomer (−)-Δ9-cis-THC were evaluated in vivo and compared with the effects of (−)-Δ9-trans-THC on a series of four tests typically associated with the activation of receptor CB1 in mice (hypothermia, catalepsy, hypomobility and analgesia). The experiments showed that (−)-Δ9-cis-THC could provoke the complete tetrad in mice with a dose of 50 mg/kg, whereas Δ9-trans-THC exhibited similar potency at lower doses between 6 and 10 mg/kg, according to the different potencies measured in vitro for the activation of receptor CB1. The group proposed that if lower doses of Δ9-trans-THC cause therapeutic beneficial effects with little secondary effects, then less potent (−)-Δ9-cis-THC could retain the therapeutic potential of Δ9-trans-THC without undesired effects. The group also raised the debate on the legal status of all isomers of THC which are currently not distinguished nor discriminated to determine the classification of marijuana samples as narcotics and non-narcotic variants (La Maida et al., 2022).
On the other hand, the same year, first patents appeared on the potential therapeutic use of each enantiomer of Δ9-cis-THC based on animal models of disease (Guy et al., 2021; Guy et al., 2021). Taking into account the natural products featuring the cis-fused system that have been shown to display antiproliferative properties against a diverse set of cancer cell lines, future studies should address whether Δ9-cis-THC enantiomers exhibit anticancer potential.
Concluding remarks
Cis-THC, as well as other natural products bearing the cis-fused tetrahydrobenzo[c]chromene motif, demonstrated an interesting biological activity profile. A review such as this is hoped to enhance both synthetic chemists and medicinal chemists in their pursuit of discovering the biological potential of natural products including Δ9-cis-THC and related systems, leading to more simple, straightforward, and selective synthetic processes as well as greater application possibilities.
Author contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work and approved it for publication.
Funding
Support from Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET, PUE-2016, PIP 2021-2023-1045), Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (ANPCyT, PICT-2021-353, PICT-2018-4150), and Universidad Nacional de Rosario (BIO 580, UNR-80020180300024UR, 80020210200028UR) is acknowledged. Work in Novara (DC) was supported by MIUR (PRIN 2017, Project 2017WN73 PL, Bioactivity-directed exploration of the phytocannabinoid chemical space).
Acknowledgments
LG thanks CONICET for fellowship.
Conflict of interest
The authors MR and DC declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdur-Rashid, K., Jia, W., and Adbur-Rashid, K. (2020). Catalytic cannabinoid processes and precursors. International publication No WO2020/232545 A1.
am Ende, C. W., and Parker, K. A. (2019). Development of a 5-exo, 6-exo tandem radical cyclization to access bisabosqual A. Tetrahedron 75, 4255–4260. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2019.05.001
am Ende, C. W., Zhou, Z., and Parker, K. A. (2013). Total synthesis of (±)-bisabosqual A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 582–585. doi:10.1021/ja3108577
Appendino, G. (2020). The early history of cannabinoid research. Rend. Lincei Sci. Fis. Nat. 31, 919–929. doi:10.1007/s12210-020-00956-0
Basas-Jaumandreu, J., and de las Heras, F. X. C. (2020). GC-MS Metabolite profile and identification of unusual homologous cannabinoids in high potency Cannabis sativa. Planta Med. 86, 338–347. doi:10.1055/a-1110-1045
Caprioglio, D., Amin, H. I. M., Taglialatela-Scafati, O., Muñoz, E., and Appendino, G. (2022). Minor phytocannabinoids: A misleading name but a promising opportunity for biomedical research. Biomolecules 12, 1084. doi:10.3390/biom12081084
Caprioglio, D., Mattoteia, D., Minassi, A., Pollastro, F., Lopatriello, A., Munoz, E., et al. (2019). One-pot total synthesis of cannabinol via iodine-mediated deconstructive annulation. Org. Lett. 21, 6122–6125. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.9b02258
Carroll, A. R., Bowden, B. F., and Coll, J. C. (1993). Studies of Australian ascidians. III. A new tetrahydrocannabinol derivative from the ascidian Synoicum castellatum. Aust. J. Chem. 46, 1079–1083. doi:10.1071/CH9931079
Chicca, A., Schafroth, M. A., Reynoso-Moreno, I., Erni, R., Petrucci, V., Carreira, E. M., et al. (2018). Uncovering the psychoactivity of a cannabinoid from liverworts associated with a legal high. Sci. Adv. 4, eaat2166. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aat2166
Chizhova, A. Y., and Anufriev, V. F. (2000). Isomerization of 6,9-dihydroxy-2-methyl-2-(4-methyl-3-pentenyl)-2h-benzo[g]chromene-5,10-dione into naphthoherniarin A derivatives. Russ. J. Org. Chem. 36, 1007–1010. doi:10.1002/chin.200121168
Coleman, M. A., Burchill, L., Sumby, C. J., and George, J. H. (2019). Biomimetic synthesis enables the structure revision of furoerioaustralasine. Org. Lett. 21, 8776–8778. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.9b03392
Crombie, L., and Ponsford, R. (1971). Synthesis of cannabinoids by pyridine-catalysed citral–olivetol condensation: Synthesis and structure of cannabicyclol, cannabichromen, (hashish extractives), citrylidene-cannabis, and related compounds. J. Chem. Soc. C 0, 796–804. doi:10.1039/J39710000796
Cullmann, F., and Becker, H. (1999). Prenylated bibenzyls from the liverwort Radula laxiramea. Z. Naturforsch. 54c, 147–150. doi:10.1515/znc-1999-3-401
Degenhardt, F., Stehle, F., and Kayser, O. (2017). “The biosynthesis of cannabinoids,” in Handbook of Cannabis and related pathologies Editor V. R. Preedy (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 13–23.
Dorsch, C., and Schneider, C. (2023). Brønsted acid catalyzed asymmetric synthesis of cis-tetrahydrocannabinoids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202302475. doi:10.1002/anie.202302475
Edery, H., Grunfeld, Y., Ben-Zvi, Z., and Mechoulam, R. (1971). Structural requirements for cannabinoid activity. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 191, 40–53. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb13985.x
Fahrenholtz, K. E., Lurie, M., and Kierstead, R. W. (1967). Total synthesis of (±)-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol and four of its isomers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 89, 5934–5941. doi:10.1021/ja00999a034
Gaoni, Y., and Mechoulam, R. (1966). Concerning the isomerization of Δ1-to Δ1(6)-tetrahydrocannabinol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 88, 5673–5675. doi:10.1021/ja00975a071
Gaoni, Y., and Mechoulam, R. (1964). Isolation, structure, and partial synthesis of an active constituent of hashish. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 86, 1646–1647. doi:10.1021/ja01062a046
Garcia, A., Borchardt, D., Chang, C. - E. A., and Marsella, M. J. (2009). Thermal isomerization of cannabinoid analogues. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 16640–16641. doi:10.1021/ja907062v
Garrido, L., Zubía, E., Ortega, M. J., and Salvá, J. (2002). New meroterpenoids from the ascidian Aplidium conicum. J. Nat. Prod. 65, 1328–1331. doi:10.1021/np020176+
Guy, G., Knappertz, V., Whalley, B., and Wool-Ley-Roberts, M. (2021). (+)-cis-tetrahidrocannabinol ((+)-cis-THC) for use as a medicament. International publication No WO 2021/079136 A1.
Guy, G., Knappertz, V., Whalley, B., and Wool-Ley-Roberts, M. (2021). (−)-cis-Tetrahidrocannabinol ((−)-cis-THC) for use as a medicament. International publication No WO 2021/079135 A1.
Handrick, G. R., Razdan, R. K., Uliss, D. B., Dalzell, H. C., and Boger, E. (1977). Hashish. Synthesis of (±)-Δ1- and (±)-Δ6-3,4-cis-cannabidiols and their isomerization by acid catalysis. J. Org. Chem. 42, 2563–2568. doi:10.1021/jo00435a007
Hanuš, L. O., Meyer, S. M., Muñoz, E., Taglialatela-Scafati, O., and Appendino, G. (2016). Phytocannabinoids: A unified critical inventory. Nat. Prod. Rep. 33, 1357–1392. doi:10.1039/C6NP00074F
Jamieson, C. S., Misa, J., Tang, Y., and Billingsley, J. M. (2021). Biosynthesis and synthetic biology of psychoactive natural products. Chem. Soc. Rev. 50, 6950–7008. doi:10.1039/D1CS00065A
Khalsa, J. H., Bunt, G., Blum, K., Maggirwar, S. B., Galanter, M., and Potenza, M. N. (2022). Review: Cannabinoids as medicinals. Curr. Addict. Rep. 9, 630–646. doi:10.1007/s40429-022-00438-3
La Maida, N., Di Giorgi, A., Pichini, S., Busardò, F. P., and Huestis, M. A. (2022). Recent challenges and trends in forensic analysis: Δ9-THC isomers pharmacology, toxicology and analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 220, 114987. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2022.114987
Lok, C. M., Groenewegen, A., Stroink, J. B. A., and Ward, J. P. (1983). Kombic acid, a hydroquinone polyisoprenoic carboxylic acid from Pycnanthus kombo seed fat. Phytochemistry 22, 1973–1976. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(83)80026-0
Luteijn, J. M., and Spronck, H. J. W. (1979). Condensation reactions of olivetol bis(tetrahydropyranyl ether) homocuprate with propargylic substrates. A convenient synthesis of (±)-3,4-cis-Δ1,2-tetrahydrocannabinol and (±)-3,4-trans-Δ1,2-cannabidiol. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1979, 201–203. doi:10.1039/P19790000201
Ma, T.-K., Parsons, P. J., and Barrett, A. G. M. (2020). Synthesis, aromatization and derivatization reactions of 2-[9-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-4-oxo-1,5-dioxa-9-azaspiro[5.5]undec-2-en-2-yl]acetic acid. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 28–34. doi:10.1002/ejoc.201901451
Maioli, C., Mattoteia, D., Amin, H. I. M., Minassi, A., and Caprioglio, D. (2022). Cannabinol: History, syntheses, and biological profile of the greatest “minor” cannabinoid”. Plants 11, 2896. doi:10.3390/plants11212896
Malkov, A. V., and Kočovský, P. (2001). Tetrahydrocannabinol revisited: Synthetic approaches utilizing molybdenum catalysts. Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. 66, 1257–1268. doi:10.1135/cccc20011257
Martin, B. R., Balster, R. L., Razdan, R. K., Harris, L. S., and Dewey, W. L. (1981). Behavioral comparisons of the stereoisomers of tetrahydrocannabinols. Life Sci. 29, 565–574. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(81)90434-3
Mechoulam, R., Braun, P., and Gaoni, Y. (1972). Syntheses of Δ1-tetrahydrocannabinol and related cannabinoids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 94, 6159–6165. doi:10.1021/ja00772a038
Mechoulam, R., and Hanuš, L. O. (2000). A historical overview of chemical research on cannabinoids. Chem. Phys. Lipids 108, 1–13. doi:10.1016/S0009-3084(00)00184-5
Mechoulam, R., Hanuš, L. O., Pertwee, R., and Howlett, A. C. (2014). Early phytocannabinoid chemistry to endocannabinoids and beyond. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 15, 757–764. doi:10.1038/nrn3811
Mechoulam, R., Yagnitinsky, B., and Gaoni, Y. (1968). Stereoelectronic factor in the chloranil dehydrogenation of cannabinoids. Total Synthesis of dl-cannabichromene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 90, 2418–2420. doi:10.1021/ja01011a037
Minuti, L., Ballerini, E., Barattucci, A., Bonaccorsi, P. M., Di Gioia, M. L., Leggio, A., et al. (2015). A unified strategy for the synthesis of three conicol marine natural products. Tetrahedron 71, 3253–3262. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2015.03.118
Miyase, T., Ueno, A., Noro, T., and Fukushima, S. (1980). Studies on the constituents of Lespedeza cyrtobotrya Miq. I. The structures of a new chalcone and two new isoflav-3-ens. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 28, 1172–1177. doi:10.1248/cpb.28.1172
Moore, M., Rickards, R. W., and Rønneberg, H. (1984). Cannabinoid studies. IV. Stereoselective and regiospecific syntheses of (±)-Δ9-trans- and (±)-Δ9-cis-6a, 10a-tetrahydrocannabinol. Aust. J. Chem. 37, 2339–2348. doi:10.1071/CH9842339
Murray, L. A. M., Fallon, T., Sumby, C. J., and George, J. H. (2019). Total synthesis of naphterpin and marinone natural products. Org. Lett. 21, 8312–8315. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.9b03095
Murray, L. A. M., McKinnie, S. M. K., Pepper, H. P., Erni, R., Miles, Z. D., Cruickshank, M. C., et al. (2018). Total synthesis establishes the biosynthetic pathway to the naphterpin and marinone natural products. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 11009–11014. doi:10.1002/anie.201804351
Nguyen, G.-N., Jordan, E. N., and Kayser, O. (2022). Synthetic strategies for rare cannabinoids derived from Cannabis sativa. J. Nat. Prod. 85, 1555–1568. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.2c00155
Park, B. H., and Lee, Y. R. (2010). Concise synthesis of (±)-perrottetinene with bibenzyl cannabinoid. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 31, 2712–2714. doi:10.5012/bkcs.2010.31.9.2712
Purdy, T. N., Moore, B. S., and Lukowski, A. L. (2022). Harnessing ortho-quinone methides in natural product biosynthesis and biocatalysis. J. Nat. Prod. 85, 688–701. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.1c01026
Razdan, R. K., and Handrick, G. R. (1970). Hashish. V. A stereospecific synthesis of (−)-Δ1 and (−)-Δ1(6)-tetrahydrocannabinols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 92, 6061–6062. doi:10.1021/ja00723a044
Razdan, R. K., and Zitko, B. A. (1969). Hashish IV: Some acid catalyzed transformations in cannabinoids. Tetrahedron Lett. 10, 4947–4950. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)88854-7
Ren, P., Miao, X., Tang, T., Wu, Y., Wang, J., Zeng, Y., et al. (2020). Construction of a meroterpenoid-like compound collection by precursor-assisted biosynthesis. Org. Biomol. Chem. 18, 5850–5856. doi:10.1039/D0OB01235A
Riveira, M. J., La-Venia, A., and Mischne, M. P. (2016). Pericyclic cascade toward isochromenes: Application to the synthesis of alkaloid benzosimuline. J. Org. Chem. 81, 7977–7983. doi:10.1021/acs.joc.6b01278
Russo, E. B. (2014). “The pharmacological history of Cannabis,” in Handbook of Cannabis Editor R. G. Pertwee (Oxford: Oxford University Pres).
Sampson, P. B. (2021). Phytocannabinoid pharmacology: Medicinal properties of Cannabis sativa constituents aside from the “big two”. J. Nat. Prod. 84, 142–160. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c00965
Schafroth, M. A., Mazzoccanti, G., Reynoso-Moreno, I., Erni, R., Pollastro, F., Caprioglio, D., et al. (2021). Δ9-cis-tetrahydrocannabinol: Natural occurrence, chirality, and pharmacology. J. Nat. Prod. 84, 2502–2510. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.1c00513
Schafroth, M. A., Zuccarello, G., Krautwald, S., Sarlah, D., and Carreira, E. M. (2014). Stereodivergent total synthesis of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 13898–13901. doi:10.1002/anie.201408380
Simon-Levert, A., Arrault, A., Bontemps-Subielos, N., Canal, C., and Banaigs, B. (2005). Meroterpenes from the ascidian Aplidium aff. densum. Aplidium Aff. Densum. J. Nat. Prod. 68, 1412–1415. doi:10.1021/np050110p
Smith, R. M., and Kempfert, K. D. (1977). Δ1-3,4-cis-tetrahydrocannabinol in Cannabis sativa. Phytochemistry 16, 1088–1089. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)86745-X
Tahir, M. N., Shahbazi, F., Rondeau-Gagné, S., and Trant, J. F. (2021). The biosynthesis of the cannabinoids. J. Cannabis Res. 3, 7. doi:10.1186/s42238-021-00062-4
Tangdenpaisal, K., Songthammawat, P., Akkarasereenon, K., Chuayboonsong, K., Ruchirawat, S., and Ploypradith, P. (2019). Total synthesis of palodesangren B trimethyl ether and D dimethyl ether via a late-stage formation of 2H-pyran-2-one of the tetrahydrobenzo[c]pyranochromenone core. J. Org. Chem. 84, 13410–13429. doi:10.1021/acs.joc.9b01596
Tangdenpaisal, K., Songthammawat, P., Ruchirawat, S., and Ploypradith, P. (2022). Total synthesis of palodesangrens A and C. J. Org. Chem. 87, 386–398. doi:10.1021/acs.joc.1c02417
Taylor, E. C., Lenard, K., and Shvo, Y. (1966). Active constituents of hashish. Synthesis of dl-Δ6-3,4-trans-tetrahydrocannabinol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 88, 367–369. doi:10.1021/ja00954a039
Taylor, E. C., and Strojny, E. J. (1960). The synthesis of some model compounds related to tetrahydrocannabinol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 82, 5198–5202. doi:10.1021/ja01504a042
Tolomeo, F., Russo, F., Kaczorova, D., Vandelli, M. A., Biagini, G., Laganà, A., et al. (2022). cis-Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid occurrence in Cannabis sativa L. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 219, 114958. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2022.114958
Toyota, M., Kinugawa, T., and Asakawa, Y. (1994). Bibenzyl cannabinoid and bisbibenzyl derivative from the liverwort Radula perrottetii. Phytochemistry 37, 859–862. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)90371-6
Uliss, D. B., Dalzell, H. C., Handrick, G. R., Howes, J. F., and Razdan, R. K. (1975a). Hashish. Importance of the phenolic hydroxyl group in tetrahydrocannabinols. J. Med. Chem. 18, 213–215. doi:10.1021/jm00236a025
Uliss, D. B., Razdan, R. K., Dalzell, H. C., and Handrick, G. R. (1975b). Hashish: Synthesis of dl-Δ1,6-cis-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). Tetrahedron Lett. 16, 4369–4372. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)91126-2
Uliss, D. B., Handrick, G. R., Dalzell, H. C., and Razdan, R. K. (1978). The conversion of 3,4-cis- to 3,4-trans-cannabinoids. Tetrahedron 34, 1885–1888. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(78)80092-1
Uliss, D. B., Razdan, R. K., Dalzell, H. C., and Handrick, G. R. (1977). Synthesis of racemic and optically active Δ1-and Δ6-3,4-cis-tetrahydrocannabinols. Tetrahedron 33, 2055–2059. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(77)80313-X
Vemuri, V. K., and Makriyannis, A. (2015). Medicinal chemistry of cannabinoids. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 97, 553–558. doi:10.1002/cpt.115
Verotta, L., Lovaglio, E., Vidari, G., Finzi, P. V., Neri, M. G., Raimondi, A., et al. (2004). 4-Alkyl- and 4-phenylcoumarins from Mesua ferrea as promising multidrug resistant antibacterials. Phytochemistry 65, 2867–2879. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2004.07.001
Walsh, K. B., McKinney, A. E., and Holmes, A. E. (2021). Minor cannabinoids: Biosynthesis, molecular pharmacology and potential therapeutic uses. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 777804. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.777804
Keywords: stereoselective synthesis, cannabinoids, THC, isochromenes, hetero-Diels-Alder, bioactive natural products
Citation: Gurgone L, La-Venia A, Caprioglio D and Riveira MJ (2023) Synthetic approaches to cis-THC, a promising scaffold in medicinal chemistry. Front. Nat. Produc. 2:1225627. doi: 10.3389/fntpr.2023.1225627
Received: 19 May 2023; Accepted: 20 July 2023;
Published: 02 August 2023.
Edited by:
Olumayokun Olajide, University of Huddersfield, United KingdomReviewed by:
Daniele Passarella, University of Milan, ItalyYang Qu, University of New Brunswick Fredericton, Canada
Copyright © 2023 Gurgone, La-Venia, Caprioglio and Riveira. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Martín J. Riveira, cml2ZWlyYUBpcXVpci1jb25pY2V0Lmdvdi5hcg==
 Lucía Gurgone1
Lucía Gurgone1 Diego Caprioglio
Diego Caprioglio Martín J. Riveira
Martín J. Riveira