- 1Neuromodulation Disorders Cluster at Border Biomedical Research Center, Department of Biological Sciences, University of Texas at El Paso, El Paso, TX, United States
- 2The Inositide Laboratory, The Babraham Institute, Cambridge, United Kingdom
Male flies under the influence of ethanol display disinhibited courtship, which is augmented with repeated ethanol exposures. We have previously shown that dopamine is important for this type of ethanol-induced behavioral sensitization but the underlying mechanism is unknown. Here we report that DopEcR, an insect G-protein coupled receptor that binds to dopamine and steroid hormone ecdysone, is a major receptor mediating courtship sensitization. Upon daily ethanol administration, dumb and damb mutant males defective in D1 (dDA1/DopR1) and D5 (DAMB/DopR2) dopamine receptors, respectively, showed normal courtship sensitization; however, the DopEcR-deficient der males exhibited greatly diminished sensitization. der mutant males nevertheless developed normal tolerance to the sedative effect of ethanol, indicating a selective function of DopEcR in chronic ethanol-associated behavioral plasticity. DopEcR plays a physiological role in behavioral sensitization since courtship sensitization in der males was reinstated when DopEcR expression was induced during adulthood but not during development. When examined for the DopEcR’s functional site, the der mutant’s sensitization phenotype was fully rescued by restored DopEcR expression in the mushroom body (MB) αβ and γ neurons. Consistently, we observed DopEcR immunoreactivity in the MB calyx and lobes in the wild-type Canton-S brain, which was barely detectable in the der brain. Behavioral sensitization to the locomotor-stimulant effect has been serving as a model for ethanol abuse and addiction. This is the first report elucidating the mechanism underlying behavioral sensitization to another stimulant effect of ethanol.
Introduction
Fruit flies are routinely exposed to ethanol in fermented fruits and food. In a laboratory setting, ethanol causes many behavioral responses that include hyper-locomotor activity, disinhibition, loss of motor control and sedation. Specifically, low doses of ethanol increase walking speed and turning, low to moderate doses induce disinhibited sexual activity and high doses lead to loss of postural control and sedation (Bainton et al., 2000; Lee et al., 2008). Flies develop tolerance to the sedative effect when repeatedly exposed to ethanol (Scholz et al., 2000; Lee et al., 2008). These observations indicate that ethanol-induced behaviors in flies and intoxicated humans are similar; thus, the knowledge of their neurobiological basis could help not only uncover evolutionarily conserved vs. distinct neural, cellular and molecular pathways but also gain insight into effective intervention of ethanol abuse and addiction. The biogenic amine dopamine is involved in locomotor stimulating and rewarding effects of ethanol in flies, rodents and humans (Devineni and Heberlein, 2013; Abrahao et al., 2014; Jayaram-Lindström et al., 2016). For example, ethanol intake elevates extracellular dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens in rodents (Meyer et al., 2009; Vena et al., 2016). Likewise in flies, blockade of dopamine biosynthesis via 3IY that inhibits tyrosine hydroxylase dampens the ethanol’s locomotor stimulant effect, which is reversed by L-DOPA feeding (Bainton et al., 2000). D1 and D2 dopamine receptors are involved in the locomotor stimulating and rewarding effects of ethanol in rodents (Lê et al., 1997; Matsuzawa et al., 1999; Arias et al., 2010) while D1 receptor is involved in both effects in flies (Kong et al., 2010; Kaun et al., 2011).
Behavioral sensitization is an escalated response to repeated drug use and underlies drug abuse and addiction (Berridge and Robinson, 2016). Dopamine is also important for behavioral sensitization to the ethanol’s locomotor stimulant effect in rodents (Camarini and Pautassi, 2016). Repeated local or global ethanol treatments induce sensitized activity of dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area (Brodie, 2002; Ding et al., 2009). Pharmacological and genetic studies show involvement of both D1 and D2 family receptors in sensitization. For example, D1 and D3 knockout mice are defective in sensitization to chronic ethanol exposure (Harrison and Nobrega, 2009). Interestingly, D3 knockout mice develop normal sensitization to amphetamine, indicating the D3’s function in the selective sensitization pathway. Observations on D2 knockout mice are conflicting: one study (Harrison and Nobrega, 2009) shows defective sensitization whereas another study (Palmer et al., 2003) reveals enhanced sensitization when the knockout mice in the same genetic background are compared. Thus, only a particular environmental or treatment condition involves D2-mediated sensitization. Together these observations indicate that the dopamine system mediates multiple yet distinct sensitization processes. Similar to rodents, flies develop sensitization to the locomotor stimulant effect of ethanol (Kong et al., 2010) and the mechanism is yet to be determined.
A prominent effect of ethanol in humans is disinhibition. Disinhibited cognition and motor functions lead to risk taking behaviors and impulsivity, which facilitate ethanol or other substance abuse and addiction (Field et al., 2010; Dalley et al., 2011; Morris et al., 2016). However, the mechanism underlying ethanol-induced disinhibition remains poorly understood. We have previously shown that dopamine mediates ethanol-induced courtship disinhibition and behavioral sensitization to this effect in Drosophila (Lee et al., 2008). Drosophila has three D1 family receptors: dDA1/DopR1 D1; Sugamori et al., 1995), DAMB/DopR2 (D5; Han et al., 1996) and DopEcR (Srivastava et al., 2005). When stimulated by dopamine, DopEcR activates an increase in cAMP and the PI3 kinase pathway whereas ecdysone inhibits the effect of dopamine on cAMP and activates the MAP kinase pathway. Here we report that sensitization to the disinhibition effect of ethanol requires DopEcR function in the mushroom body (MB) neurons. The findings reported here provide a framework to unravel the relevant neural circuits and the cellular mechanisms.
Materials and Methods
Drosophila Strains and Culture
Flies were maintained on standard cornmeal agar medium at 25°C with 50% relative humidity under the 12 h light/12 h dark illumination condition. Canton-S was used as a wild-type strain. The DopEcR mutant used in this study is the insertion mutant DopEcRc02142 (also known as DopEcRPB1; hereafter der) generated by the Gene Disruption Project (FlyBase Consortium, 2003; Thibault et al., 2004) and has been previously described (FlyBase Consortium, 2003; Inagaki et al., 2012; Petruccelli et al., 2016). der was obtained from the Bloomington Stock Center (stock no. 10847) and backcrossed with Cantonized w1118 for six generations, and then the X chromosome was replaced with that of Canton-S to remove the w1118 mutation. elav-GAL4 (stock no. 8765), c739-GAL4 (stock no. 7362), c305a-GAL4 (stock no. 30829), UAS-mCD8-GFP (stock no. 5137) and PTRiP.JF03415 (stock no. 31981; FlyBase Consortium, 2003; Perkins et al., 2015) flies were obtained from the Bloomington Stock Center; NP1131-GAL4 from Dr. Dubnau (Stony Brook University School of Medicine, Stony Brook, NY, USA); fruNP21-GAL4 from Dr. Yamamoto (Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan); NP225-GAL4 from Dr. Thum (University of Konstanz, Konstanz, Germany); tub-GS-GAL4 from Dr. Kitamoto (University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, USA); and MB-GS-GAL4 from Dr. Roman (University of Houston, Houston, TX, USA). We have previously described MB247-GAL4 and MB247-GAL4, GAL80ts (Kim et al., 2007, 2013). DopEcR cDNA containing the open reading frame (Srivastava et al., 2005) was cloned under UAS in the gateway vector pTW (Akbari et al., 2009). The cloned receptor was injected into w1118 embryos, and germ-line transformed lines were outcrossed with Cantonized w1118 for six generations to normalize the genetic background and to remove potential second site mutations. Individual transgenes were placed in the der mutant background for rescue experiments. We previously reported the dDA1 (D1) mutant dumb1 and dumb2 (Kim et al., 2007) and the damb mutant defective in DAMB (D5; Cassar et al., 2015). For conditional rescue experiments involving the gene switch lines MB-GS-GAL4 and tub-GS-GAL4, 10 mM RU486 (Mifepristone, M8046, Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA) was made in 80% ethanol and added to fly food to the final concentration of 500 μM. Flies were reared on the food containing RU486 for 1 day before and between ethanol exposures. All genotypes used for behavioral analyses including the controls (Canton-S and der mutants carrying only GS-GAL4) were fed with RU486 or vehicle for comparison.
Immunohistochemical Analysis
The polyclonal DopEcR antibody was made commercially in a New Zealand white rabbit against the peptide GEPIHDKEYATALAEN that corresponds to the third cytoplasmic loop of the receptor (Pacific Immunology Corp, Ramona, CA, USA). Immunostaining was performed as previously described (Kim et al., 2013; Lim et al., 2014). Briefly, 4–5 day-old male brains were dissected in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) where the trachea around the brain was removed. Dissected brains were individually fixed with 4% PFA (paraformaldehyde and 0.04 M Lysine in PBS) at 4°C for 3 h and then rinsed three times in PBHT containing 0.5% Triton X-100 for 10 min each. Brains were solubilized in 1% Triton X-100 in PBHT for 1 h, incubated in the blocking solution (5% normal goat serum in PBHT) for 2 h and then incubated with the anti-DopEcR antibody (1:100 diluted in the blocking solution) at room temperature overnight. Brains were washed four times in PBHT for 1 h at room temperature and then overnight at 4°C before incubation with the goat Alexa 488-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG (Molecular Probes, Carlsbad, CA, USA) at room temperature for 2 h. After washes in PBHT, PBS and 0.12 M Tris-HCl, pH 7.4 (three times in each solution), brains were mounted in the VECTASHIELD medium (Vector Labs, Burlingame, CA, USA). Images were taken using the Zeiss LSM 700 confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss, Thornwood, NY, USA) and analyzed using the ImageJ software (NIH).
Behavioral Tests
One to two-day-old males were collected under carbon dioxide (CO2) and aged in food vials for 2–3 days before tests. A group of 33 males was used as one data point in all behavioral tests. Ethanol exposure was performed in the Flypub consisting of a plastic chamber (57 mm D × 103 mm H) with the clear ceiling for videotaping behavior and the open bottom for administering ethanol as previously described (Lee et al., 2008). Flies were acclimated to the chamber for 10 min before ethanol exposure. A small petri dish containing a cotton pad applied with 1 ml of 95% ethanol was inserted to the bottom opening and flies were exposed to ethanol vapor till they were sedated. Four to six Flypubs were recorded together using a HD video camera (Q2F-00013 Microsoft LifeCam Studio, Redmond, WA, USA). The recorded movie files were used to score courtship activity. Flies were exposed to ethanol every 24 h for six consecutive days and were kept in food vials between exposures. The sedative effect of ethanol was measured by counting every 2 min the number of flies lying on their back or immobile for over 10 s. To obtain the mean sedation time (MST), the total sedation time, i.e., ∑(the number of sedated flies at each time interval × each time interval after ethanol administration, e.g., 2, 4, 6 and etc.), was divided by the total number of flies (Lee et al., 2008). Courtship activity consisting of singing (unilateral wing vibration), licking or attempted copulation (Baker et al., 2001) was monitored during 30 s (1 block) and the maximum number of flies engaged in courtship at a given time was scored. The average of 10 consecutive blocks (i.e., 5 min) giving the highest value was used to represent the percentage of males engaged in active intermale courtship per Flypub (Lee et al., 2008). Our earlier study (Lee et al., 2008) has shown that the maximal level of ethanol-induced courtship disinhibition is achieved on the exposure 4 or 5 and then maintained steady. Thus, we focus on exposure 1 for the initial level of ethanol-induced disinhibition, exposure 2 for sensitization induction and exposure 6 for maintenance in this study. The genotypes were blinded to the experimenters conducting ethanol exposure and scoring courtship or sedation.
Data Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using Minitab 16 (Minitab, State College, PA, USA) and JMP 13 (SAS, Cary, NC, USA). All data are reported as mean + or ± standard error of means (SEM). Normality was determined by the Anderson Darling goodness-of-fit test. Normally distributed data were analyzed by a two-tailed Student’s t-test or analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post hoc Tukey-Kramer HSD or Dunnett’s tests. Non-normally distributed data were analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis and post hoc Mann-Whitney tests.
Results
Tolerance to the Sedative Effect of Ethanol
To investigate the roles of D1 family receptors in chronic ethanol effects, we employed the Flypub for mild ethanol delivery (Lee et al., 2008). We first measured the sedative effect of ethanol. Compared to the control Canton-S males, it took longer for der mutant males to get sedated (p < 0.0001; Figure 1A), demonstrating that der males defective in DopEcR have decreased sensitivity to the sedative effect of ethanol. This corroborates the finding by Petruccelli et al. (2016). In contrast, dumb and damb males defective in dDA1 (D1) and DAMB (D5) receptors, respectively, exhibited normal sensitivity (p > 0.05, Figure 1B). When MSTs of dumb, damb and der males were examined during daily ethanol exposures, all mutants developed tolerance similar to Canton-S (Canton-S: F(3,101) = 35.9762, p < 0.0001; der: F(3,90) = 7.4871, p = 0.0002; dumb1, p < 0.001; dumb2, p < 0.0001; p < 0.0001, damb; Figures 1C,D). This indicates that D1 family receptors are not important for tolerance to the sedative effect of ethanol.
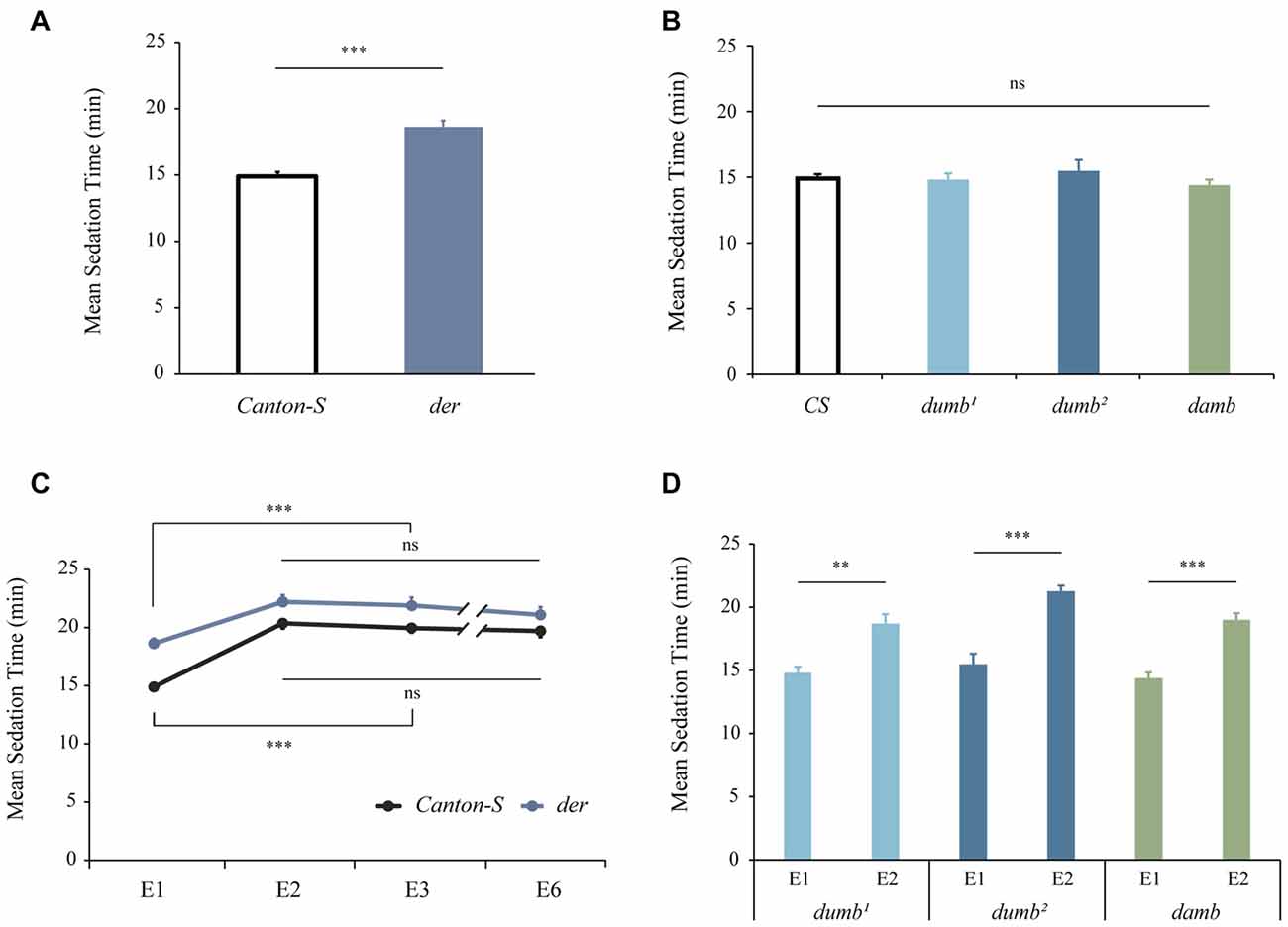
Figure 1. D1 family receptors are dispensable for ethanol tolerance. The wild-type Canton-S and D1 receptor mutants were exposed to ethanol and mean sedation time (MST) was measured. (A) der mutant males defective in DopEcR showed decreased sensitivity to the sedative effect of ethanol (***p < 0.0001 by two-tailed Student’s t-test; Canton-S, n = 26; der, n = 22). (B) dumb1and dumb2 mutant males defective in dDA1 (D1) and damb defective in DAMB (D5) exhibited normal sensitivity. Analysis of variance (ANOVA): p > 0.05, n = 8; ns, not significant. (C) der males showed normal tolerance development and maintenance to the sedative effect of ethanol. (***p < 0.0001 by ANOVA and post hoc Tukey-Kramer HSD tests; Canton-S, n = 26; der, n = 22). (D) dumb and damb males displayed normal tolerance. Student t-test; **p < 0.001; ***p < 0.0001; n = 8.
Behavioral Sensitization to the Disinhibition Effect of Ethanol
Drosophila males typically court females and rarely court males. Under daily ethanol exposure, however, Canton-S males display the escalated levels of intermale courtship (R2 = 0.7289, F(2,48) = 64.5414, p < 0.0001; Figure 2A), which require dopamine neuronal activity (Lee et al., 2008). To explore the mechanism by which dopamine regulates behavioral disinhibition and sensitization, we examined the D1 family receptor mutants’ courtship behavior under the influence of ethanol. Both dumb and damb males developed behavioral sensitization to the disinhibition effect of ethanol (dumb1: R2 = 0.8966, F(3,24) = 69.3456, p < 0.0001; dumb2: R2 = 0.7936, F(3,24) = 30.7652, p < 0.0001; damb: R2 = 0.9316, F(3,20) = 90.8291, p < 0.0001; Figure 2B). der males, on the other hand, exhibited the substantially reduced levels of intermale courtship on all exposures compared to Canton-S males (p < 0.0001; Figure 2A). This suggests that DopEcR is required for behavioral sensitization to the disinhibition effect of ethanol.
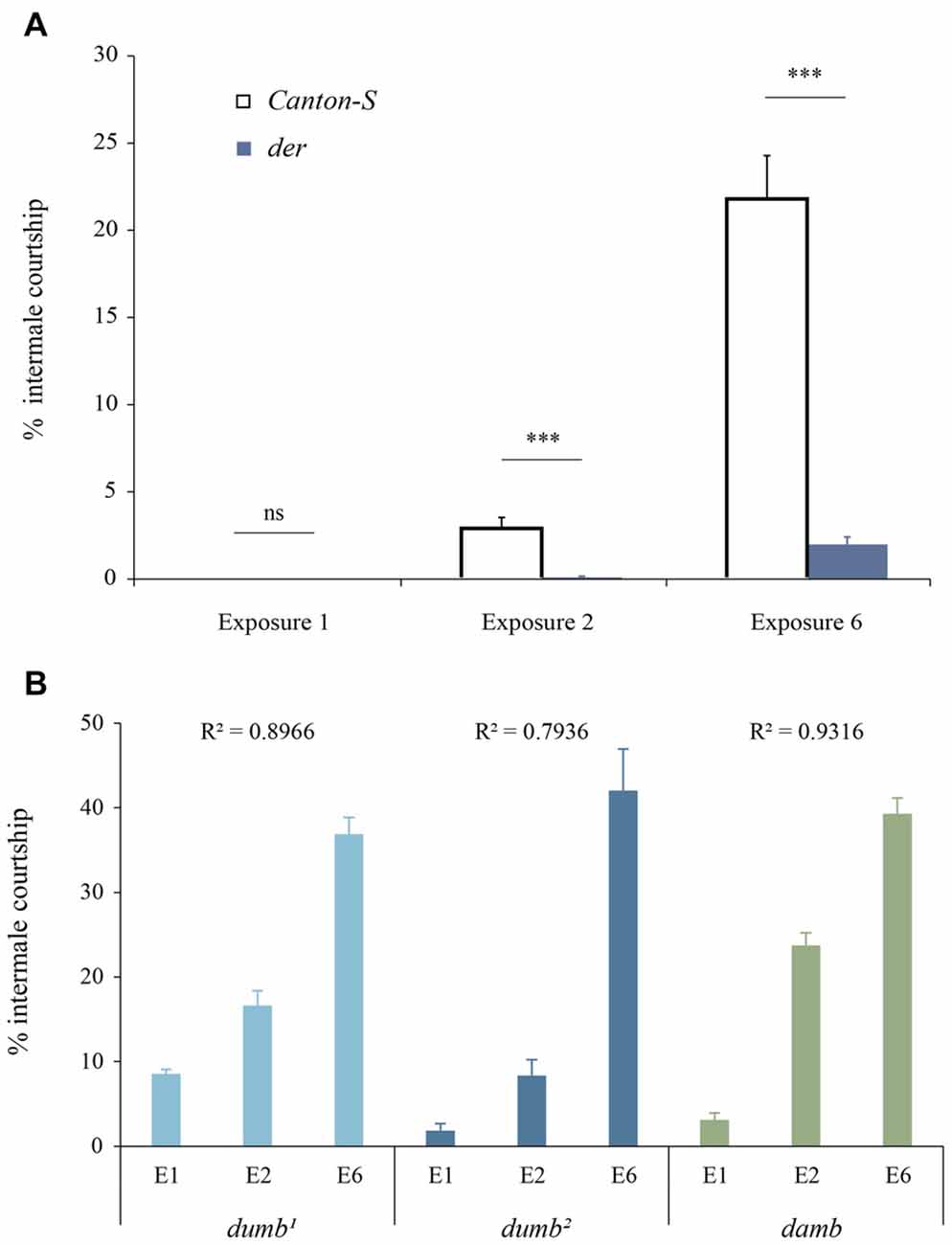
Figure 2. der mutant males exhibit impaired sensitization to the disinhibition effect of ethanol. (A) der mutant males showed significantly reduced disinhibited courtship compared to the control Canton-S on the 2nd (exposure 2) and 6th (exposure 6) day of daily ethanol exposure (***p < 0.0001 by ANOVA and post hoc Tukey-Kramer HSD tests; Canton-S, n = 17; der, n = 19). ns, not significant. (B) dDA1 receptor mutants dumb1 and dumb2 as well as DAMB receptor mutant damb developed normal behavioral sensitization to the ethanol-induced disinhibition. (dumb1, p < 0.0001, n = 7; dumb2, p < 0.0001, n = 7; damb, p < 0.0001, n = 6). E, exposure.
Neural Substrate for Behavioral Sensitization
To identify the neural structure where DopEcR regulates behavioral sensitization, we employed the GAL4/UAS binary system and RNA interference (RNAi) for cell type-specific knockdown of DopEcR expression. In this study we used an additional control line carrying UAS-GFP and UAS-DopEcR RNAi since courtship behavior could be sensitive to the mw in a transgenic construct (Lee et al., 2008). To establish effectiveness of DopEcR RNAi, we used the pan-neuronal driver elav-GAL4 to express double-stranded DopEcR RNA for RNAi in all neurons. Like der mutants, the flies with pan neuronal DopEcR knockdown showed severe impairment in behavioral sensitization (p < 0.0001; Figure 3A). We reasoned that the neural substrate for the DopEcR’s function in behavioral sensitization could be the neurons regulating courtship behavior or high order brain structures mediating learning and memory. Fruitless-expressing neurons control male courtship behavior (Manoli et al., 2005; Stockinger et al., 2005) thus represent a potential neural site for the DopEcR’s function. The projection neurons are another candidate for the DopEcR’s function because they have dendrites in the antennal lobes and axons at the lateral horn and the MB calyx that are high order brain centers for pheromone information processing, learning and memory (Thum et al., 2007; Grosjean et al., 2011). When DopEcR was knocked down in Fruitless neurons, we did not observe a significant change in behavioral sensitization (p > 0.05; fru-GAL4 in Figure 3A) while DopEcR knockdown in the projection neurons resulted in slightly increased sensitization (p = 0.0186; NP225-GAL4). Above all, we observed markedly reduced sensitization in the flies with DopEcR knockdown in the MB neurons (p < 0.0001; MB247-GAL4 in Figure 3B). The MB consists of αβ, α’β’ and γ neurons where MB247-GAL4 is expressed in αβ and γ neurons. We next asked whether DopEcR in each MB substructure is sufficient for behavioral sensitization. When DopEcR RNAi was induced only in αβ, α’β’ or γ neurons via the c739-, c305a- or NP1131-GAL4 driver, respectively, the flies developed normal behavioral sensitization (p > 0.05). This suggests that DopEcR in the αβ and γ, but not αβ or γ alone, is needed for behavioral sensitization to the disinhibition effect of ethanol.
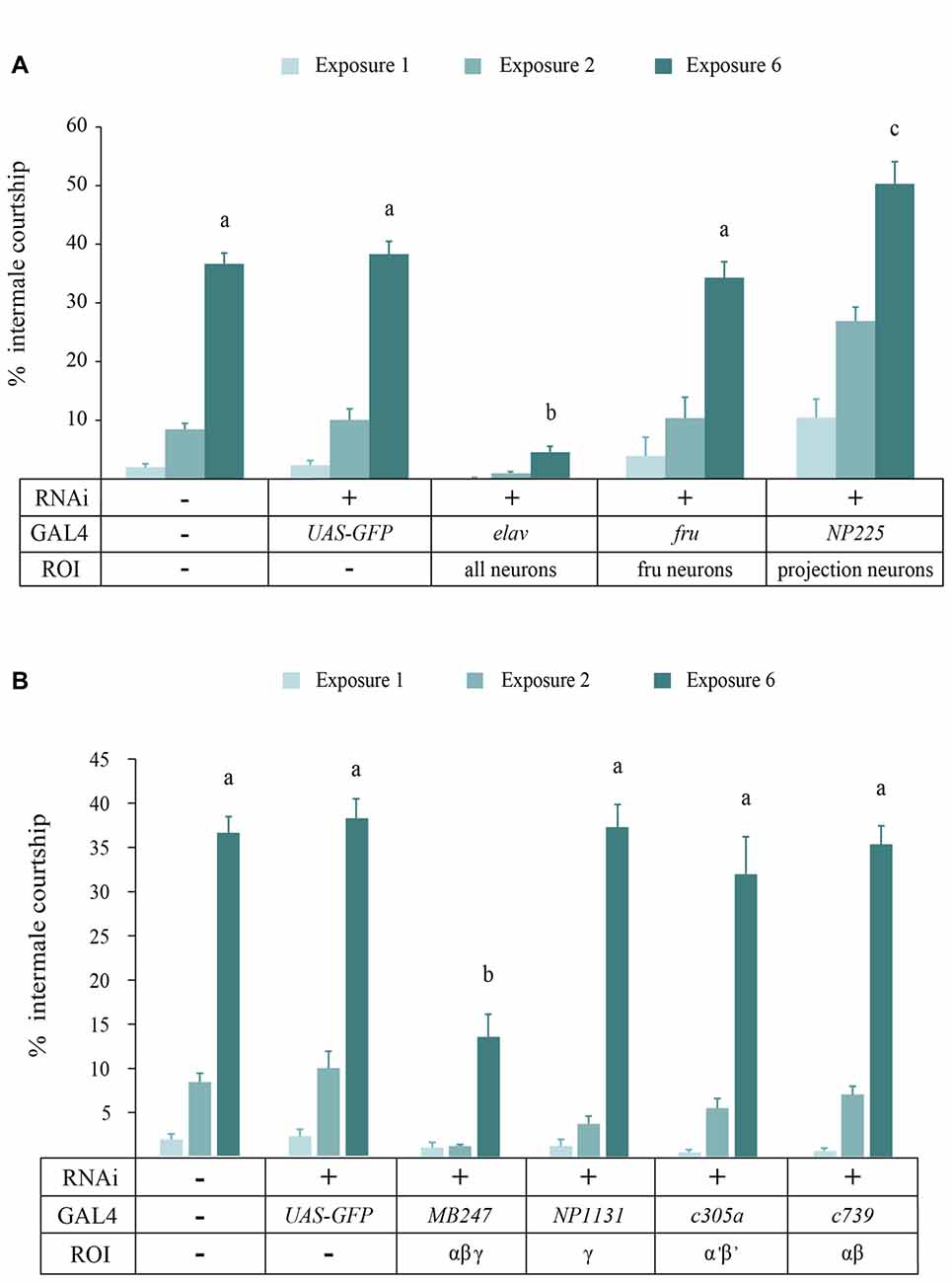
Figure 3. DopEcR knockdown in the mushroom body (MB) αβ and γ neurons suppresses sensitization. (A) Pan-neuronal DopEcR knockdown (elav-GAL4/+;UAS-DopEcR-RNAi/+, R2 = 0.50, n = 6) led to substantially reduced sensitization compared to Canton-S or the transgenic control (UAS-GFP/+;UAS-DopEcR-RNAi/+, R2 = 0.91, n = 6). Different letters on the bars (i.e., a, b and c) denote significant difference when all genotypes on exposure 6 were compared (ANOVA, p < 0.0001). Normal behavioral sensitization was observed when DopEcR was knocked down in the fruitless (fru) neurons (fru-GAL4/+;UAS-DopEcR-RNAi/+, R2 = 0.70, n = 5). DopEcR knockdown in the projection neurons resulted in slightly increased sensitization (NP225-GAL4/+;UAS-DopEcR-RNAi/+, R2 = 0.75, n = 7) (c, p = 0.0186 compared to the transgenic control by post hoc Dunnett’s test). (B) DopEcR knockdown in the MB α, β and γ neurons (MB247-GAL4/+;UAS-DopEcR-RNAi/+, R2 = 0.61, n = 7) led to significant reduction in behavioral sensitization (p < 0.0001). DopEcR knockdown in individual MB subsets (αβ, c739/+;UAS-DopEcR-RNAi/+, R2 = 0.95, n = 6; α’β’, c305a/+;UAS-DopEcR-RNAi/+, R2 = 0.81, n = 6; γ, NP1131/+;UAS-DopEcR-RNAi/+, R2 = 0.93, n = 6) resulted in normal sensitization.
Temporal Requirement for DopEcR Function
DopEcR is expressed throughout development and adulthood (FlyBase Consortium, 2003; Inagaki et al., 2012; Ishimoto et al., 2013; Petruccelli et al., 2016). To test whether the sensitization phenotype is caused by developmental or physiological DopEcR deficiency, we adopted two approaches, TARGET and Gene Switch (GS) for temporally restricted reinstatement of DopEcR expression in the MB neurons of der mutants. TARGET (McGuire et al., 2004) is the GAL4/UAS combined with GAL80ts that confers temporally restricted expression of a transgene downstream of UAS, which we used successfully in the study of dDA1 in olfactory memory formation (Kim et al., 2007). Briefly, GAL80ts is active as a GAL4 repressor at 20°C but inactive at 30°C, allowing GAL4 activity thereby UAS activation. The der mutants carrying tub-GAL80ts, MB247-GAL4 and UAS-DopEcR cDNA were reared at 30°C throughout development but maintained at 20°C right after eclosion to induce DopEcR expression only during development (Figure 4A). To induce DopEcR only during adulthood, possibly at the time of ethanol exposure, the der mutants carrying tub-GAL80ts, MB247-GAL4 and UAS-DopEcR cDNA were reared at 20°C throughout development but maintained at 30°C 2 days after eclosion. Canton-S and der mutant carrying tub-GAL80ts and MB247-GAL4 but not UAS-DopEcR cDNA were treated with the same temperature manipulation to serve as controls. As shown in Figure 4A, the der males with DopEcR expression only during development exhibited impaired behavioral sensitization thus there was no rescue (F(2,16) = 23.2, p < 0.0001). In contrast, the der males with DopEcR expression only during adulthood fully reinstated behavioral sensitization (p > 0.05 compared to Canton-S; Figure 4B). This indicates the role of DopEcR during adulthood for disinhibition sensitization.
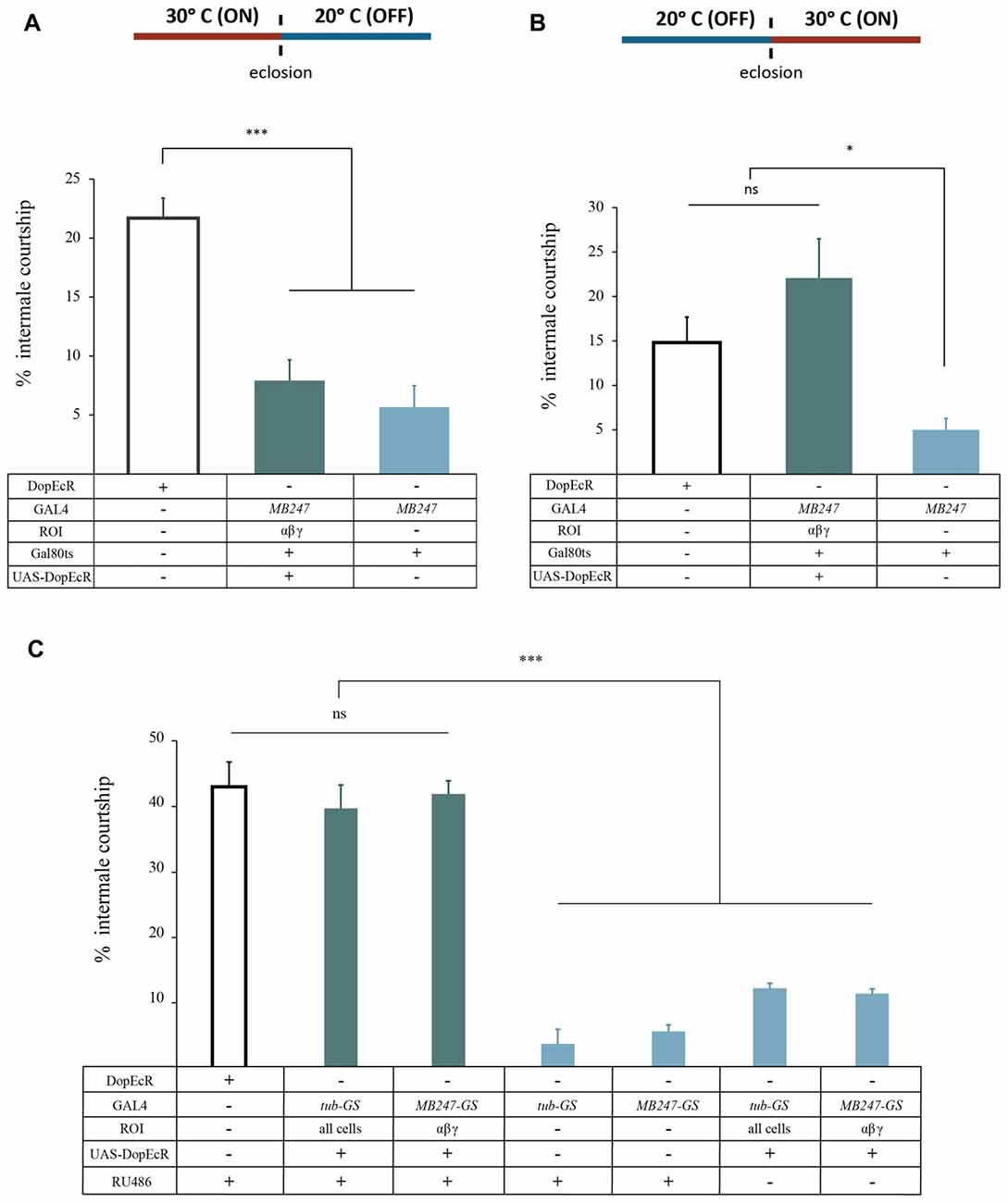
Figure 4. DopEcR is needed during adulthood to mediate sensitization. The der mutant males carrying tub-GAL80ts, MB247-GAL4 and UAS-DopEcR cDNA were reared at 30°C before eclosion to induce DopEcR expression during development (A) or after eclosion to induce DopEcR expression during adulthood (B). (A) The der males with reinstated DopEcR expression only during development (MB247, GAL80ts/UAS-DopEcR cDNA;der, n = 7) exhibited behavioral sensitization at the level comparable to that of the der transgenic mutant (MB247, GAL80ts/+;der; p > 0.05, n = 6) but lower than that of the Canton-S control (***p < 0.0001, n = 6). (B) The der males with reinstated DopEcR expression only during adulthood (MB247, GAL80 ts/UAS-DopEcR cDNA;der; n = 7) showed behavioral sensitization comparable to the control (ns, p > 0.05, n = 7) but higher than the der mutant (MB247, GAL80ts/+;der; *p < 0.05, n = 4). (C) The der males carrying UAS-DopEcR-cDNA and either tub-GS-GAL4 (UAS-DopEcR cDNA/+;tub-GS-GAL4, der/der, R2 = 0.8486, n = 7) or MB247-GS-GAL4 (UAS-DopEcR cDNA /+;MB247-GS-GAL4, der/der, R2 = 0.9834, n = 4) displayed sensitization similar to the control (R2 = 0.9113, n = 5) when treated with RU486 (ns, p > 0.05), but significantly higher than the der mutant controls (tub-GS-GAL4, der/der, n = 4; MB247-GS-GAL4, der/der, n = 4) treated with RU486 or the der mutants carrying the rescue transgenes without RU486 treatment (***p < 0.0001). The percent intermale courtship on the exposure 6 are shown. ns, not significant.
We observed that the flies with the temperature manipulation displayed highly variable ethanol sensitivity and sensitization. Thus as a complementary approach, we used the GS system in which GAL4 is fused to the progesterone receptor. Only in the presence of the steroid RU486, GAL4 can activate UAS for downstream gene expression (Roman et al., 2001). We tested the der mutants carrying UAS-DopEcR cDNA and tub-GS-GAL4 or MB-GS-GAL4 for ubiquitous or MB expression of DopEcR, respectively, at the time of ethanol exposure. When treated with RU486, the der males with DopEcR expression in all cells or MB neurons displayed the level of sensitization substantially higher than that of the der males carrying only tub-GS-GAL4 or MB-GS-GAL4, but comparable to the Canton-S level (F(6,24) = 43.2375, p < 0.0001; Figure 4C). The der males carrying the same transgenes (i.e., UAS-DopEcR-cDNA and tub-GS-GAL4 or MB-GS-GAL4) that were not fed with RU486 exhibited impaired sensitization similar to the der mutants carrying tub-GS-GAL4 or MB-GS-GAL4 (p > 0.05 by post hoc Tukey-Kramer HSD test; Figure 4C). These observations together demonstrate that DopEcR expression during adulthood is sufficient for sensitization, supporting the physiological role of DopEcR at the time of ethanol exposure for this behavioral plasticity.
Expression Patterns of DopEcR
The study of DopEcR enhancer-GAL4 shows that DopEcR is expressed in the MB αβ and γ neurons (Ishimoto et al., 2013). It is however unclear where DopEcR is localized in the MB. To address this, we used immunohistochemical analysis. We made the fusion construct of Glutathione S-transferase and the third cytoplasmic loop of DopEcR as we have previously characterized the dDA1 and DAMB expression patterns (Han et al., 1996, 1998). We also made the antibody against the peptide corresponding to part of the third cytoplasmic loop. The antibodies made against the fusion protein in rabbits and mice did not provide reliable staining; however, the antibody made against the peptide revealed consistent staining in the MB neuropil. It is worth mentioning that the antibody did not penetrate inside the brain under numerous conditions that we tried and also strongly stained the cell membrane of nearly all neurons and glia in both Canton-S and der (Figure 5; Supplementary Movie Files). Nonetheless, DopEcR immunoreactivity was clearly visible in the MB calyx (dendritic structure; Figure 5A, Supplementary Figure S1), α lobe core and β lobe (axonal structure) in the Canton-S brain (Figure 5C, Supplementary Movie 1). DopEcR immunoreactivity in the γ lobe was also detectable but at a very low level (Figure 5C and Supplementary Movie 1). On the contrary, DopEcR immunoreactivity in all MB neuropil was barely detectable in the der brain (Figures 5B,D, Supplementary Figure S1 and Supplementary Movie 2). These observations suggest that the site of DopEcR’s function for sensitization is the MB dendrites in the calyx or axons in the α, β or γ lobe, or both locations.
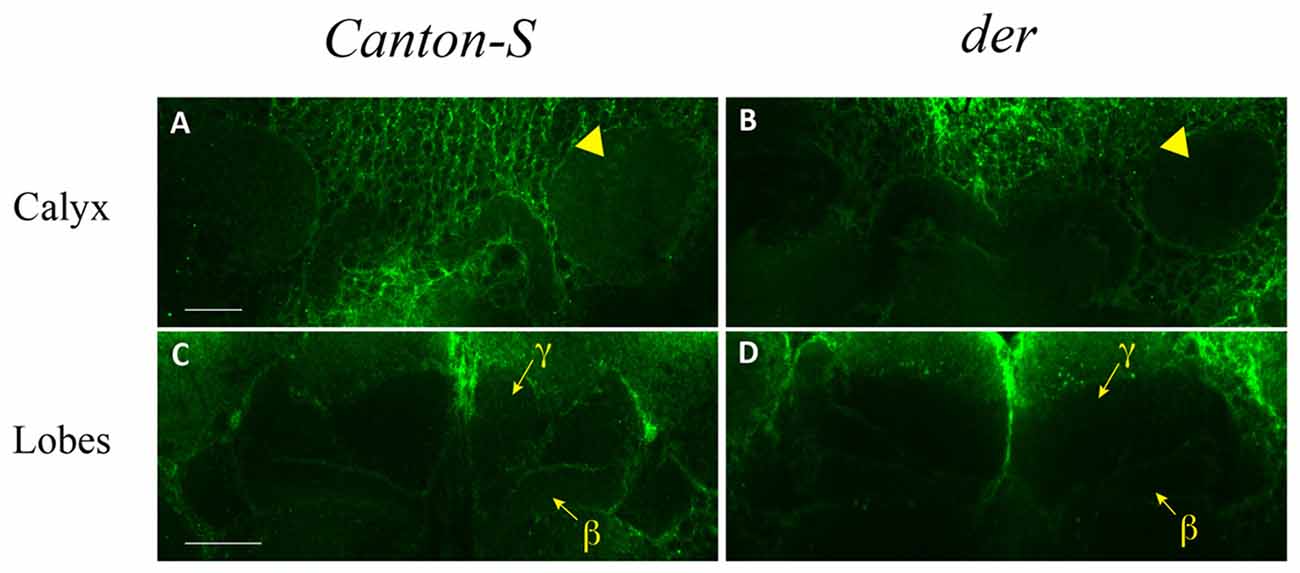
Figure 5. DopEcR expression in the MB neuropil. DopEcR immunoreactivity is evident in the calyx (A, arrowhead) and medial lobes β and γ (C, arrows) in the Canton-S brain but barely detectable in the der brain (B, arrowhead for calyx; D, arrows for medial lobes). One micron optical sections were made using a 40x (A,B) or 63x (C,D) objective in the confocal microscope and three sections were stacked in all images. Scale bar, 25 micron.
Discussion
In this report, we show that DopEcR in the MB αβ and γ neurons mediates behavioral sensitization to the disinhibition effect of ethanol. Further, we demonstrate that the DopEcR’s function is physiological rather than developmental. As in mammals, dopamine is important for the locomotor activating and rewarding effects of ethanol in flies (Bainton et al., 2000; Kong et al., 2010; Kaun et al., 2011). The D1 receptor dDA1/DopR in the ellipsoid body is involved in the locomotor stimulant effect (Kong et al., 2010) while the dopamine receptor mediating the rewarding effect is unknown. We have noted that the flies deficient in dDA1 or DAMB display augmented disinhibition on all ethanol exposures tested, and we are currently following up on this finding. These observations together indicate that dDA1 is involved in diverse effects of ethanol possibly through distinct neural circuits.
Kaun et al. (2011) examined the rewarding property of ethanol using a conditioned preference assay. They have found that all MB subsets are important for conditioned preference to the cue associated with ethanol. It has been postulated that the dopamine signal to the MB αβ lobe is crucial for preference expression (Kaun et al., 2011). Behavioral sensitization represents a form of learning and memory (Camarini and Pautassi, 2016). The neural substrate that we identified for DopEcR’s function in sensitization is consistent with the MB’s role in learning and memory as opposed to simple sensory information processing. We have previously shown that the dDA1 receptor in the MB αβ and γ neurons mediates reward memory of sucrose (Kim et al., 2007) but it is not needed for behavioral sensitization (this study). Thus, the MB αβ and γ neurons process the reinforcing effects of the natural substance sucrose and the addictive drug ethanol via distinct dopamine receptors dDA1 and DopEcR, respectively.
DopEcR responds to dopamine as well as the steroid hormone ecdysone (Srivastava et al., 2005). For short-term memory in courtship conditioning and the sedative effect of ethanol, ecdysone is as a major ligand for DopEcR (Ishimoto et al., 2013; Petruccelli et al., 2016). Dopamine, on the other hand, activates DopEcR in the gustatory receptor neurons to enhance sensitivity to sugar in hungry flies (Inagaki et al., 2012). In male moths, DopEcR in the antennal lobe regulates behavioral responses to pheromones, which require both dopamine and ecdysone as ligands (Abrieux et al., 2013, 2014). We show that both dopamine neurotransmission blockade (Lee et al., 2008) and DopEcR deficiency (this study) cause severely impaired behavioral sensitization, implicating dopamine as a major ligand for the DopEcR function. This notion is supported by the recent study (Chen et al., 2017) demonstrating that the increased level of dopamine in the PPL2ab neurons enhances intermale courtship. The PPL2ab neurons innervate the MB calyx (Mao and Davis, 2009) where DopEcR is localized (Figure 5A). It remains to be clarified, nevertheless, whether dopamine or both dopamine and ecdysone together act on DopEcR for behavioral sensitization to the ethanol’s effect on courtship disinhibition.
Dopamine is a key neuromodulator mediating not only reward and pleasure associated with natural stimuli and addictive substances but also neuroadaptations underlying abuse and addiction (Clarke and Adermark, 2015; Volkow and Morales, 2015; Camarini and Pautassi, 2016). Behavioral sensitization is widely studied as a model for drug addiction and typically measured to the locomotor-stimulant effect of alcohol and other drugs (Berridge and Robinson, 2016). Enhanced disinhibition and impulsivity induced by ethanol contribute to risky behaviors such as sexual assaults, aggression and drug seeking or abuse (Field et al., 2010; Dalley et al., 2011; Morris et al., 2016), all of which negatively impact our society. However, the underlying mechanism still remains poorly understood. The study reported here may help narrow the knowledge gap. On this line of thought, GPR30/GPER1 represents the membrane G-protein coupled receptor that mediates non-genomic actions of the steroid hormone estrogen in mammals (Maggiolini and Picard, 2010). When tested in vitro, GPR30 responds to dopamine in a dose-dependent manner to increase cAMP similar to DopEcR (Evans et al., 2014, 2016). GPR30’s function in ethanol-induced behaviors is unknown but it plays a crucial role in sexual motivation of male rats (Hawley et al., 2017). It would be of interest to learn whether GPR30 mediates ethanol-induced disinhibition and sensitization similar to DopEcR.
Author Contributions
K-AH conceived and designed the experiments. GPA, SJH, PRS and PDE performed the experiments. K-AH, GPA, SJH, and PRS analyzed the data. GPA and K-AH wrote the article.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciate Drs. Dubnau, Yamamoto, Thum, Kitamoto and Roman and the Bloomington Stock Center for providing fly lines; Dr. Varela and the Cytometry, Screening and Imaging Core at Border Biomedical Research Center for confocal microscopy. We are also very grateful for Hyun-Gwan Lee, Maryam Kherad Pezhouh, Ivan Mercado, Idaly Olivas and Jose Barragan for their contributions on the study of dumb and damb mutants, and Erick Saldes for his help on brain dissection and immunostaining. This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH)-funded RISE program (R25GM069621; to SJH), National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA; 1R15AA020996) and National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities (NIMHD; 2G12MD007592) grants to K-AH.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fnsys.2017.00056/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Movie 1 (CS) and 2 (der) 1 | The Canton-S (CS; Movie 1) and der (Movie 2) brains stained with the DopEcR antibody were scanned using the confocal microscope with a 20× objective, and the optical sections made every micron were stacked to create the movie files. Available online at: http://datarepo.bioinformatics.utep.edu/getdata?acc=SHF53E1DZOVXOB1.
FIGURE S1 | Shown are the posterior areas of the Canton-S (top) and der (bottom) brains immunostained with the anti-DopEcR antibody. The optical sections were made every micron with a 20X objective and two sections were stacked. The calyx area on the right hemisphere in each brain is marked by arrowheads. Scale bar, 25 micron.
References
Abrahao, K. P., Goeldner, F. O., and Souza-Formigoni, M. L. O. (2014). Individual differences in ethanol locomotor sensitization are associated with dopamine D1 receptor intra-cellular signaling of DARPP-32 in the nucleus accumbens. PLoS One 9:e98296. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098296
Abrieux, A., Debernard, S., Maria, A., Gaertner, C., Anton, S., Gadenne, C., et al. (2013). Involvement of the G-protein-coupled dopamine/ecdysteroid receptor DopEcR in the behavioral response to sex pheromone in an insect. PLoS One 8:e72785. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072785
Abrieux, A., Duportets, L., Debernard, S., Gadenne, C., and Anton, S. (2014). The GPCR membrane receptor, DopEcR, mediates the actions of both dopamine and ecdysone to control sex pheromone perception in an insect. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 8:312. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00312
Akbari, O. S., Oliver, D., Eyer, K., and Pai, C. Y. (2009). An Entry/Gateway cloning system for general expression of genes with molecular tags in Drosophila melanogaster. BMC Cell Biol. 10:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-10-8
Arias, C., Mlewski, E. C., Hansen, C., Molina, J. C., Paglini, M. G., and Spear, N. E. (2010). Dopamine receptors modulate ethanol’s locomotor-activating effects in preweanling rats. Dev. Psychobiol. 52, 13–23. doi: 10.1002/dev.20407
Bainton, R. J., Tsai, L. T., Singh, C. M., Moore, M. S., Neckameyer, W. S., and Heberlein, U. (2000). Dopamine modulates acute responses to cocaine, nicotine and ethanol in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 10, 187–194. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00336-5
Baker, B. S., Taylor, B. J., and Hall, J. C. (2001). Are complex behaviors specified by dedicated regulatory genes? Reasoning from Drosophila. Cell 105, 13–24. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00293-8
Berridge, K. C., and Robinson, T. E. (2016). Liking, wanting, and the incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Am. Psychol. 71, 670–679. doi: 10.1037/amp0000059
Brodie, M. S. (2002). Increased ethanol excitation of dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area after chronic ethanol treatment. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 26, 1024–1030. doi: 10.1097/00000374-200207000-00013
Camarini, R., and Pautassi, R. M. (2016). Behavioral sensitization to ethanol: neural basis and factors that influence its acquisition and expression. Brain Res. Bull. 125, 53–78. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.04.006
Cassar, M., Issa, A.-R., Riemensperger, T., Petitgas, C., Rival, T., Coulom, H., et al. (2015). A dopamine receptor contributes to paraquat-induced neurotoxicity in Drosophila. Hum. Mol. Genet. 24, 197–212. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu430
Chen, S.-L., Chen, Y.-H., Wang, C.-C., Yu, Y.-W., Tsai, Y.-C., Hsu, H.-W., et al. (2017). Active and passive sexual roles that arise in Drosophila male-male courtship are modulated by dopamine levels in PPL2ab neurons. Sci. Rep. 7:44595. doi: 10.1038/srep44595
Clarke, R., and Adermark, L. (2015). Dopaminergic regulation of striatal interneurons in reward and addiction: focus on alcohol. Neural Plast. 2015:814567. doi: 10.1155/2015/814567
Dalley, J. W., Everitt, B. J., and Robbins, T. W. (2011). Impulsivity, compulsivity, and top-down cognitive control. Neuron 69, 680–694. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.01.020
Devineni, A. V., and Heberlein, U. (2013). The evolution of Drosophila melanogaster as a model for alcohol research. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 36, 121–138. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-062012-170256
Ding, Z. M., Rodd, Z. A., Engleman, E. A., and McBride, W. J. (2009). Sensitization of ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons to the stimulating effects of ethanol. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 33, 1571–1581. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2009.00985.x
Evans, P. D., Bayliss, A., and Reale, V. (2014). GPCR-mediated rapid, non-genomic actions of steroids: comparisons between DmDopEcR and GPER1 (GPR30). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 195, 157–163. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2013.10.015
Evans, N. J., Bayliss, A. L., Reale, V., and Evans, P. D. (2016). Characterisation of signalling by the endogenous GPER1 (GPR30) receptor in an embryonic mouse hippocampal cell line (mHippoE-18). PLoS One 11:e0152138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152138
Field, M., Wiers, R. W., Christiansen, P., Fillmore, M. T., and Verster, J. C. (2010). Acute alcohol effects on inhibitory control and implicit cognition: implications for loss of control over drinking. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 34, 1346–1352. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01218.x
FlyBase Consortium. (2003). The FlyBase database of the Drosophila genome projects and community literature. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 172–175. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg094
Grosjean, Y., Rytz, R., Farine, J. P., Abuin, L., Cortot, J., Jefferis, G. S., et al. (2011). An olfactory receptor for food-derived odours promotes male courtship in Drosophila. Nature 478, 236–240. doi: 10.1038/nature10428
Han, K.-A., Millar, N. S., and Davis, R. L. (1998). A novel octopamine receptor with preferential expression in Drosophila mushroom bodies. J. Neurosci. 18, 3650–3658.
Han, K.-A., Millar, N. S., Grotewiel, M. S., and Davis, R. L. (1996). DAMB, a novel dopamine receptor expressed specifically in Drosophila mushroom bodies. Neuron 16, 1127–1135. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80139-7
Harrison, S. J., and Nobrega, J. N. (2009). Differential susceptibility to ethanol and amphetamine sensitization in dopamine D3 receptor-deficient mice. Psychopharmacology 204, 49–59. doi: 10.1007/s00213-008-1435-x
Hawley, W. R., Battista, C., Divack, S. R., and Morales Nunez, N. B. (2017). The role of estrogen G-protein coupled receptor 30 (GPR30) and sexual experience in sexual incentive motivation in male rats. Physiol. Behav. 177, 176–181. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2017.05.001
Inagaki, H. K., Ben-Tabou de-Leon, S., Wong, A. M., Jagadish, S., Ishimoto, H., Barnea, G., et al. (2012). Visualizing neuromodulation in vivo: TANGO-mapping of dopamine signaling reveals appetite control of sugar sensing. Cell 148, 583–595. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.12.022
Ishimoto, H., Wang, Z., Rao, Y., Wu, C.-F., and Kitamoto, T. (2013). A novel role for ecdysone in Drosophila conditioned behavior: linking GPCR-mediated non-canonical steroid action to cAMP signaling in the adult brain. PLoS Genet. 9:e1003843. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003843
Jayaram-Lindström, N., Ericson, M., Steensland, P., and Jerlhag, E. (2016). “Dopamine and alcohol dependence: from bench to clinic,” in Recent Advances in Drug Addiction Research and Clinical Applications, eds M. M. William and L. R. Christina, (East Province, RI: InTech), 81–114. doi: 10.5772/61445
Kaun, K. R., Azanchi, R., Maung, Z., Hirsh, J., and Heberlein, U. (2011). A Drosophila model for alcohol reward. Nat. Neurosci. 14, 612–619. doi: 10.1038/nn.2805
Kim, Y.-C., Lee, H.-G., and Han, K.-A. (2007). D1 dopamine receptor dDA1 is required in the mushroom body neurons for aversive and appetitive learning in Drosophila. J. Neurosci. 27, 7640–7647. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1167-07.2007
Kim, Y.-C., Lee, H.-G., Lim, J., and Han, K.-A. (2013). Appetitive learning requires the α1-like octopamine receptor OAMB in the Drosophila mushroom body neurons. J. Neurosci. 33, 1672–1677. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3042-12.2013
Kong, E. C., Woo, K., Li, H., Lebestky, T., Mayer, N., Sniffen, M. R., et al. (2010). A pair of dopamine neurons target the D1-like dopamine receptor DopR in the central complex to promote ethanol-stimulated locomotion in Drosophila. PLoS One 5:e9954. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009954
Lê, A., Tomkins, D., Higgins, G., Quan, B., and Sellers, E. (1997). Effects of 5-HT 3, D 1 and D 2 receptor antagonists on ethanol-and cocaine-induced locomotion. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 57, 325–332. doi: 10.1016/s0091-3057(96)00333-4
Lee, H.-G., Kim, Y.-C., Dunning, J. S., and Han, K.-A. (2008). Recurring ethanol exposure induces disinhibited courtship in Drosophila. PLoS One 3:e1391. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001391
Lim, J., Sabandal, P. R., Fernandez, A., Sabandal, J. M., Lee, H.-G., Evans, P., et al. (2014). The octopamine receptor Octβ2R regulates ovulation in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS One 9:e104441. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104441
Maggiolini, M., and Picard, D. (2010). The unfolding stories of GPR30, a new membrane-bound estrogen receptor. J. Endocrinol. 204, 105–114. doi: 10.1677/JOE-09-0242
Manoli, D. S., Foss, M., Villella, A., Taylor, B. J., Hall, J. C., and Baker, B. S. (2005). Male-specific fruitless specifies the neural substrates of Drosophila courtship behaviour. Nature 436, 395–400. doi: 10.1038/nature03859
Mao, Z., and Davis, R. L. (2009). Eight different types of dopaminergic neurons innervate the Drosophila mushroom body neuropil: anatomical and physiological heterogeneity. Front. Neural Circuits 3:5. doi: 10.3389/neuro.04.005.2009
Matsuzawa, S., Suzuki, T., Misawa, M., and Nagase, H. (1999). Involvement of dopamine D 1 and D 2 receptors in the ethanol-associated place preference in rats exposed to conditioned fear stress. Brain Res. 835, 298–305. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(99)01606-6
McGuire, S. E., Mao, Z., and Davis, R. L. (2004). Spatiotemporal gene expression targeting with the TARGET and gene-switch systems in Drosophila. Sci. STKE 2004:pl6. doi: 10.1126/stke.2202004pl6
Meyer, P. J., Meshul, C. K., and Phillips, T. J. (2009). Ethanol- and cocaine-induced locomotion are genetically related to increases in accumbal dopamine. Genes Brain Behav. 8, 346–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2009.00481.x
Morris, L. S., Kundu, P., Baek, K., Irvine, M. A., Mechelmans, D. J., Wood, J., et al. (2016). Jumping the gun: mapping neural correlates of waiting impulsivity andrelevance across alcohol misuse. Biol. Psychiatry 79, 499–507. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.06.009
Palmer, A. A., Low, M. J., Grandy, D. K., and Phillips, T. J. (2003). Effects of a Drd2 deletion mutation on ethanol-induced locomotor stimulation and sensitization suggest a role for epistasis. Behav. Genet. 33, 311–324. doi: 10.1023/A:1023450625826
Perkins, L. A., Holderbaum, L., Tao, R., Hu, Y., Sopko, R., McCall, K., et al. (2015). The transgenic RNAi project at harvard medical school: resources and validation. Genetics 201, 843–852. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.180208
Petruccelli, E., Li, Q., Rao, Y., and Kitamoto, T. (2016). The unique dopamine/ecdysteroid receptor modulates ethanol-induced sedation in Drosophila. J. Neurosci. 36, 4647–4657. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3774-15.2016
Roman, G., Endo, K., Zong, L., and Davis, R. L. (2001). P Switch, a system for spatial and temporal control of gene expression in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 98, 12602–12607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.221303998
Scholz, H., Ramond, J., Singh, C. M., and Heberlein, U. (2000). Functional ethanol tolerance in Drosophila. Neuron 28, 261–271. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)00101-x
Srivastava, D. P., Yu, E. Y., Kennedy, K., Chatwin, H., Reale, V., Hamon, M., et al. (2005). Rapid, nongenomic responses to ecdysteroids and catecholamines mediated by a novel Drosophila G-protein-coupled receptor. J. Neurosci. 25, 6145–6155. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1005-05.2005
Stockinger, P., Kvitsiani, D., Rotkopf, S., Tirián, L., and Dickson, B. J. (2005). Neural circuitry that governs Drosophila male courtship behavior. Cell 121, 795–807. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.04.026
Sugamori, K. S., Demchyshyn, L. L., McConkey, F., Forte, M. A., and Niznik, H. B. (1995). A primordial dopamine D1-like adenylyl cyclase-linked receptor from Drosophila melanogaster displaying poor affinity for benzazepines. FEBS Lett. 362, 131–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00224-w
Thibault, S. T., Singer, M. A., Miyazaki, W. Y., Milash, B., Dompe, N. A., Singh, C. M., et al. (2004). A complementary transposon tool kit for Drosophila melanogaster using P and piggyBac. Nat. Genet. 36, 283–287. doi: 10.1038/ng1314
Thum, A. S., Jenett, A., Ito, K., Heisenberg, M., and Tanimoto, H. (2007). Multiple memory traces for olfactory reward learning in Drosophila. J. Neurosci. 27, 11132–11138. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2712-07.2007
Vena, A. A., Mangieri, R., and Gonzales, R. A. (2016). Regional analysis of the pharmacological effects of acute ethanol on extracellular striatal Dopamine activity. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 40, 2528–2536. doi: 10.1111/acer.13246
Keywords: dopamine, behavioral sensitization, courtship disinhibition, mushroom body, ethanol, tolerance, D1 receptors, DopEcR
Citation: Aranda GP, Hinojos SJ, Sabandal PR, Evans PD and Han K-A (2017) Behavioral Sensitization to the Disinhibition Effect of Ethanol Requires the Dopamine/Ecdysone Receptor in Drosophila. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 11:56. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2017.00056
Received: 15 April 2017; Accepted: 17 July 2017;
Published: 02 August 2017.
Edited by:
Irina T. Sinakevitch, Arizona State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Troy Zars, University of Missouri, United StatesPreeti Sareen, Yale University, United States
Copyright © 2017 Aranda, Hinojos, Sabandal, Evans and Han. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kyung-An Han, a2hhbkB1dGVwLmVkdQ==
 Gissel P. Aranda
Gissel P. Aranda Samantha J. Hinojos
Samantha J. Hinojos Paul R. Sabandal
Paul R. Sabandal Peter D. Evans
Peter D. Evans Kyung-An Han
Kyung-An Han