A machine learning model for visualization and dynamic clinical prediction of stroke recurrence in acute ischemic stroke patients: A real-world retrospective study
- 1Department of Neurology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, Jiangsu, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Neurological Diseases, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, Jiangsu, China
- 3State Key Laboratory of Molecular Vaccinology and Molecular Diagnostics & Center for Molecular Imaging and Translational Medicine, School of Public Health, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, China
- 5Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, China
- 6Division of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, NY, United States
- 7Department of Dermatology, Xianyang Central Hospital, Xianyang, China
- 8Faculty of Medicine, Macau University of Science and Technology, Macau, China
by Wang, K., Shi, Q., Sun, C., Liu, W., Yau, V., Xu, C., Liu, H., Sun, C., Yin, C., Wei, X., Li, W., and Rong, L. (2023). Front. Neurosci. 17:1130831. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1130831
In the published article, there was an error in the legend for Figures 2–6 as published. Due to the unfamiliarity of some graduate students in our team with the submission system and the operation process of the writing software, the final version of the image was incorrectly uploaded as the image in the middle of the iteration of our machine learning algorithm model, not the final result of the model. The corrected legend appears below.
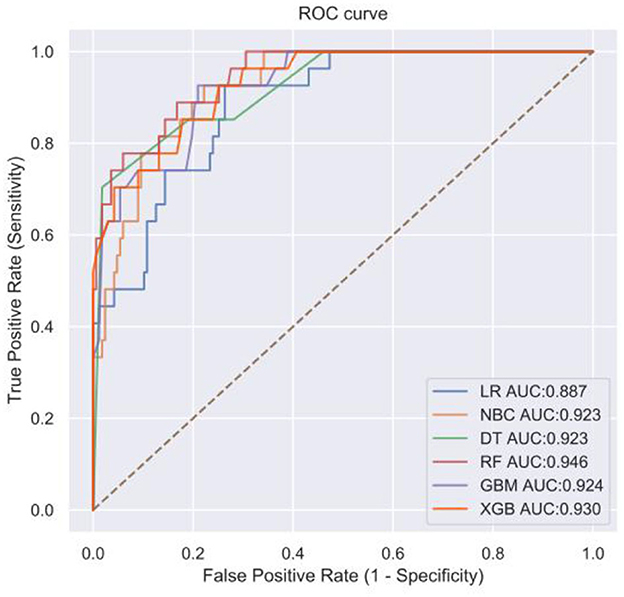
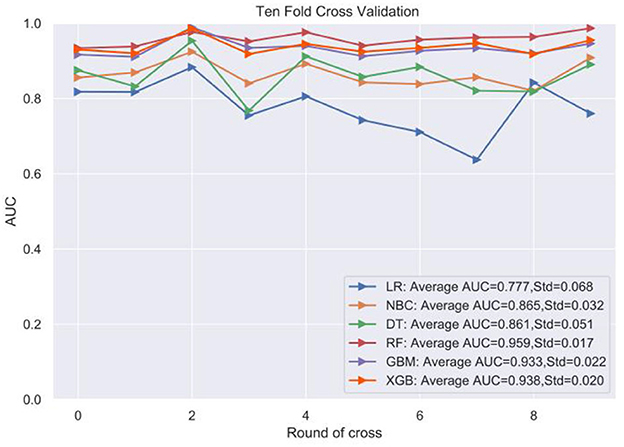
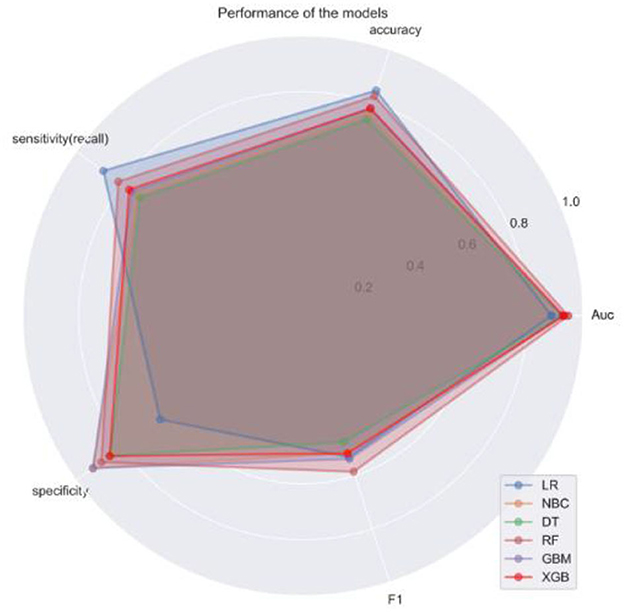
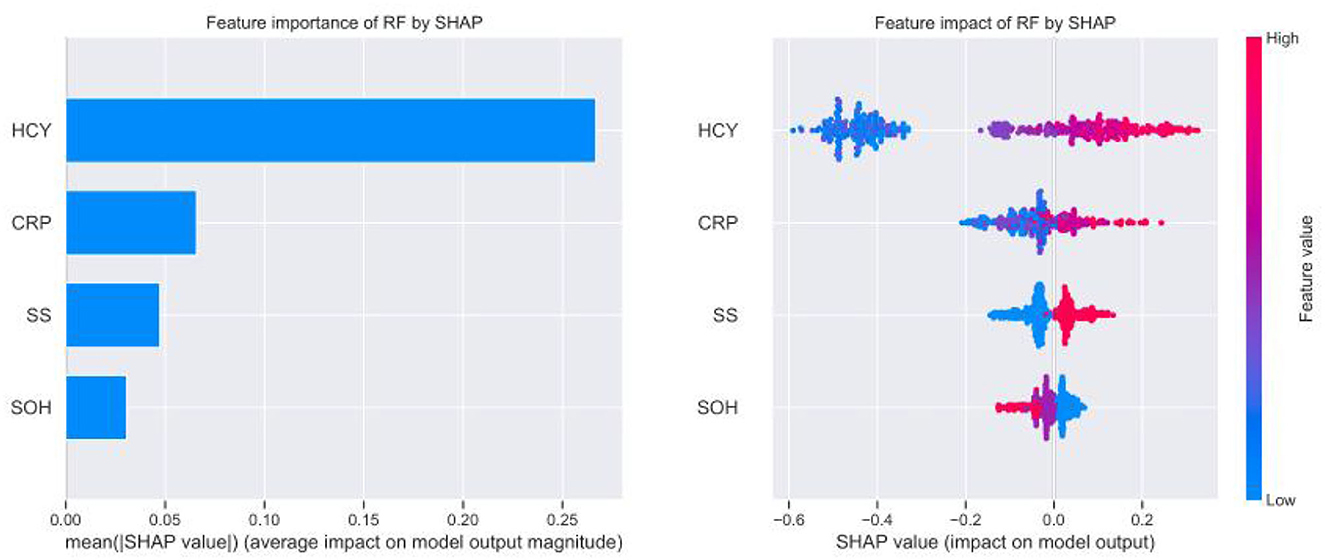
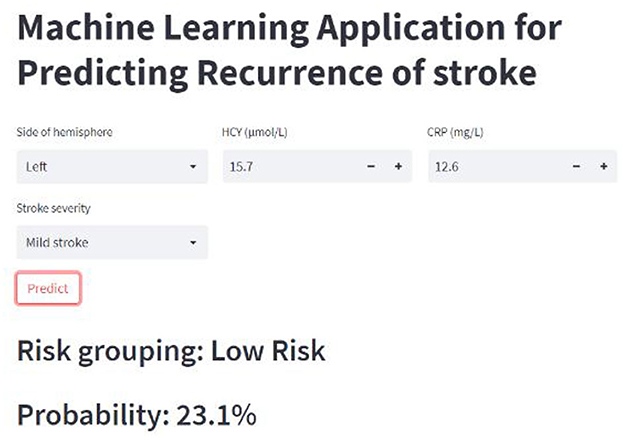
Figure 3. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of machine algorithm model under the test set.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: stroke, recurrence, machine learning, SHAP, web calculator
Citation: Wang K, Shi Q, Sun C, Liu W, Yau V, Xu C, Liu H, Sun C, Yin C, Wei X, Li W and Rong L (2023) Corrigendum: A machine learning model for visualization and dynamic clinical prediction of stroke recurrence in acute ischemic stroke patients: a real-world retrospective study. Front. Neurosci. 17:1235340. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1235340
Received: 06 June 2023; Accepted: 21 June 2023;
Published: 10 July 2023.
Edited and reviewed by: Ming Li, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong SAR, China
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Shi, Sun, Liu, Yau, Xu, Liu, Sun, Yin, Wei, Li and Rong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenle Li, ZHJsZWUwOTEwJiN4MDAwNDA7MTYzLmNvbQ==; Liangqun Rong, cm9uZ2xpYW5ncXVuJiN4MDAwNDA7MTYzLmNvbQ==; Xiu'e Wei, d3hlcXEmI3gwMDA0MDsxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
‡ORCID: Wenle Li orcid.org/0000-0002-2933-646X
 Kai Wang1,2†
Kai Wang1,2† Wenle Li
Wenle Li