Top-Down Proteomics of Human Saliva Highlights Anti-inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Antimicrobial Defense Responses in Alzheimer Disease
- 1Dipartimento di Scienze della Vita e dell'Ambiente, Università di Cagliari, Cagliari, Italy
- 2Dipartimento di Scienze Biotecnologiche di Base, Cliniche Intensivologiche e Perioperatorie, Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Rome, Italy
- 3Fondazione Policlinico Universitario “A. Gemelli” – IRCCS, Rome, Italy
- 4Laboratorio di Proteomica, Centro Europeo di Ricerca sul Cervello, IRCCS Fondazione Santa Lucia, Rome, Italy
- 5UOC Continuità Assistenziale, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario “A. Gemelli” – IRCCS, Rome, Italy
- 6Dipartimento di Scienze Mediche e Sanità Pubblica, University of Cagliari, Cagliari, Italy
- 7Istituto di Scienze e Tecnologie Chimiche “Giulio Natta”, Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche, Rome, Italy
- 8Dipartimento di Neuroscienze, Sez. Neurologia, Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Rome, Italy
A Corrigendum on
Top-Down Proteomics of Human Saliva Highlights Anti-inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Antimicrobial Defense Responses in Alzheimer Disease
by Contini, C., Olianas, A., Serrao, S., Deriu, C., Iavarone, F., Boroumand, M., et al. (2021). Front. Neurosci. 15:668852. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.668852
In the original article, the Supplementary Table 4 and the Supplementary Figure 6, cited on page 6 in the original article, are missing from the Supplementary Materials. The corrected Supplementary Table 4 and Supplementary Figure 6 are shown below. The Supplementary Material of the original article has been updated.
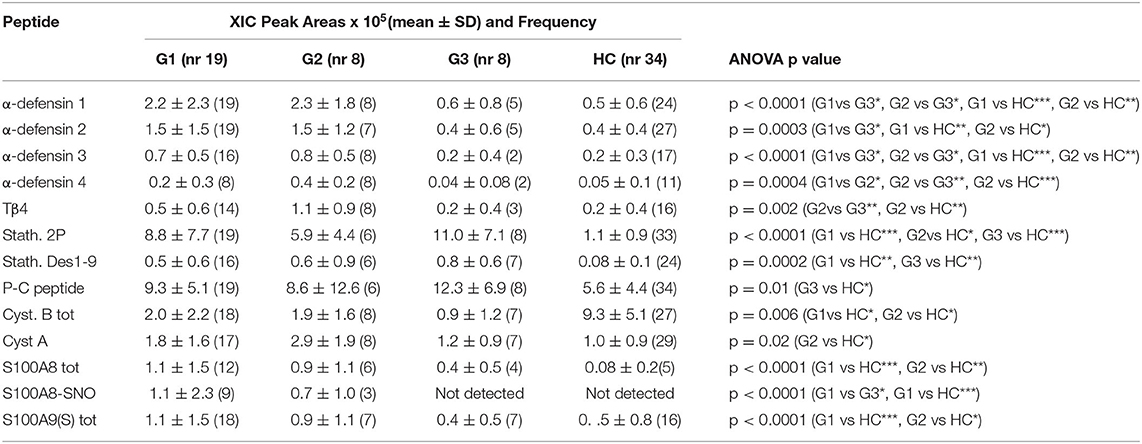
Table S4. XIC peak areas values (mean ± SD) normalized on TPC, frequencies and p-values obtained by statistical analysis by comparing the three patients' groups treated with different therapies by non-parametric ANOVA with the Krustal-Wallis test and Dunn's post test. p-values > 0.05 are not statistically significant (∙).
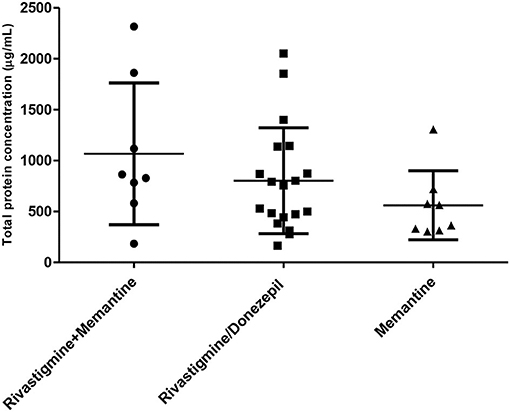
Supplementary Figure 6. Total protein concentration measured in the subgroups of patients with different pharmacological treatment.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease, salivary proteomics, S100A, cystatins, α-defensins, thymosin β4, antimicrobial peptides, oxidative stress
Citation: Contini C, Olianas A, Serrao S, Deriu C, Iavarone F, Boroumand M, Bizzarro A, Lauria A, Faa G, Castagnola M, Messana I, Manconi B, Masullo C and Cabras T (2021) Corrigendum: Top-Down Proteomics of Human Saliva Highlights Anti-inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Antimicrobial Defense Responses in Alzheimer Disease. Front. Neurosci. 15:743596. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.743596
Received: 18 July 2021; Accepted: 22 July 2021;
Published: 13 August 2021.
Edited and reviewed by: Rossen Donev, MicroPharm Ltd, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2021 Contini, Olianas, Serrao, Deriu, Iavarone, Boroumand, Bizzarro, Lauria, Faa, Castagnola, Messana, Manconi, Masullo and Cabras. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Barbara Manconi, bmanconi@unica.it
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
‡These authors have contributed equally to this work and share last authorship
 Cristina Contini1†
Cristina Contini1† Alessandra Olianas
Alessandra Olianas Carla Deriu
Carla Deriu Federica Iavarone
Federica Iavarone Mozhgan Boroumand
Mozhgan Boroumand Gavino Faa
Gavino Faa Massimo Castagnola
Massimo Castagnola Irene Messana
Irene Messana Barbara Manconi
Barbara Manconi Carlo Masullo
Carlo Masullo Tiziana Cabras
Tiziana Cabras