- 1Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 2Chengdu Second People's Hospital, Chengdu, China
- 3Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Jiaotong University & The Third People’s Hospital of Chengdu, Chengdu, China
Although the risk of recurrent stroke is very high in patients with ischemic stroke (IS), the implementation of secondary prevention of IS has not received enough attention. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the cognition and compliance status of secondary prevention in patients with IS in southwest China and explore the factors affecting compliance with secondary prevention 1 year after discharge. We conducted a cross-sectional survey of patients with IS 1 year after discharge in southwest China through convenience sampling. Factors affecting the compliance of secondary prevention in patients with IS after discharge were analysed. A total of 1,041 patients were included in our study. Nearly one-third of patients did not follow secondary prevention measures according to the guidelines, and an improvement in lifestyle was even less likely. Living with or without children did not significantly affect patient compliance (odds ratio 1.11; 95% confidence interval 0.83–1.49; p = 0.47). Furthermore, no significant differences were observed in the probability of treatment acceptance between patients experiencing one or two of the following conditions: hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia, and those with all three conditions. Thus, patients with IS have insufficient compliance with secondary prevention and there is a particular lack of emphasis on lifestyle improvement. Further interventions are needed to improve compliance with secondary prevention in patients with IS, especially patients with all three conditions of hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia.
1 Introduction
Stroke is the second leading cause of death worldwide and the leading cause of death in China, where one-fifth of the world’s population resides (1, 2). The overall stroke recurrence rate for patients at 3, 6, and 12 months and within 5 years after onset is 12.3, 15.5, and 17.7%, > 40%, respectively (3, 4). Ischemic stroke (IS) and transient ischemic attack (TIA) are the most common types of strokes. Approximately 10–17% patients with IS or TIA have a risk of recurrent stroke in the first year after the onset of symptoms (1–4).
Effective secondary prevention measures, including lifestyle improvements and prevention of risk factors, can reduce IS recurrence and mortality (5–8). According to recent studies, it is possible to prevent up to 90% of strokes by addressing and treating 10 modifiable stroke risk factors, half of which are related to making lifestyle modifications (9, 10). A study conducted by China’s third National Stroke Registry (CNSR-III) found that only 34.9% of patients adhered to guideline-based secondary prevention. Patients who followed the guidelines for secondary prevention had a lower rate of stroke recurrence compared to those who did not (11). Moreover, studies from other countries have indicated that more than one-third to one-half of patients fail to follow long-term strategies for secondary prevention (12, 13).
The incidence of IS varies regionally, with different regions within a country having different incidence and recurrence rates of stroke owing to differences in race, geographical location, and living habits (13–16). China’s southwest region, home to a population of 249 million, contributes 13.3% to China’s GDP. Previous epidemiological investigations on stroke have reported the incidence and mortality rates of IS in southwest China to be 154.6/100,000 and 103.8/100,000, respectively (17). However, despite the high prevalence of stroke in this region, there is a dearth of studies focusing on the investigation and intervention of secondary prevention for patients with IS in southwest China. This study aimed to investigate the cognition and compliance status of secondary prevention in patients with IS in southwest China and explore the factors affecting compliance with secondary prevention 1 year after discharge.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study population
This study was approved by the Hospital Ethics Committee of Chengdu Second People’s Hospital (Ethics approval number: 2024352). Informed consent was obtained from all participants.
We selected patients admitted for IS before June 2022 in Grade III and Class A public general hospitals in Chongqing and Chengdu, which have the highest population density and most developed economy in southwest China, using convenience sampling. The patients met the following diagnostic criteria for IS: age > 18 years, hospitalization for the diagnosis of IS based on the diagnostic criteria of the Chinese Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute ischemic Stroke 2018 and confirmed through head computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (13), patients with a high risk of recurrence, complete medical records and contact information, and patients or their families were willing to participate in the study and signed the informed consent form.
Exclusion criteria were patient death during hospitalization; voluntary discharge; incomplete medical records, such as previous medical history and imaging results of stroke; inability to communicate with investigators and family members owing to critical illness; and refusal to participate in the survey.
2.2 Survey content
We classified traditional risk factors such as smoking, hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and lifestyle as preventable and controllable factors in line with the Chinese Guidelines for the Secondary Prevention of ischemic Stroke and Transient ischemic Attack 2022 (18). The guidelines cover lifestyle recommendations in four main areas: diet and nutrition, physical activity, alcohol consumption, and obesity.
2.3 Survey methods
A hospitalization data survey was used to collect demographic information, such as age, sex, marital status, education level, and cardiovascular risk factors (smoking, drinking, hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia) through the patients’ hospitalization records.
Patient visits and information survey: Based on patient electronic records, patients or family members were contacted via telephone interviews by four experienced neurologists with unified training. We collected the following patient information: (1) general information (marital status, whether they live with their children, and type of medical insurance); (2) control of risk factors: smoking status, awareness of their disease (including hypertension, diabetes, atrial fibrillation or hyperlipidemia history), or adherence to drug treatment (hypoglycemic, antihypertensive, hypolipidemic, antiplatelet, and anticoagulant therapies); (3) lifestyle improvement (variety of dietary types, low-salt diet, increased activity, alcohol abstinence, and weight loss); and (4) regular hospital visits(make regular visit to the neurology outpatient department of the hospital where you were last treated or a convenient nearby hospital). The follow-up period was between June and September 2023.
2.4 Statistical analysis
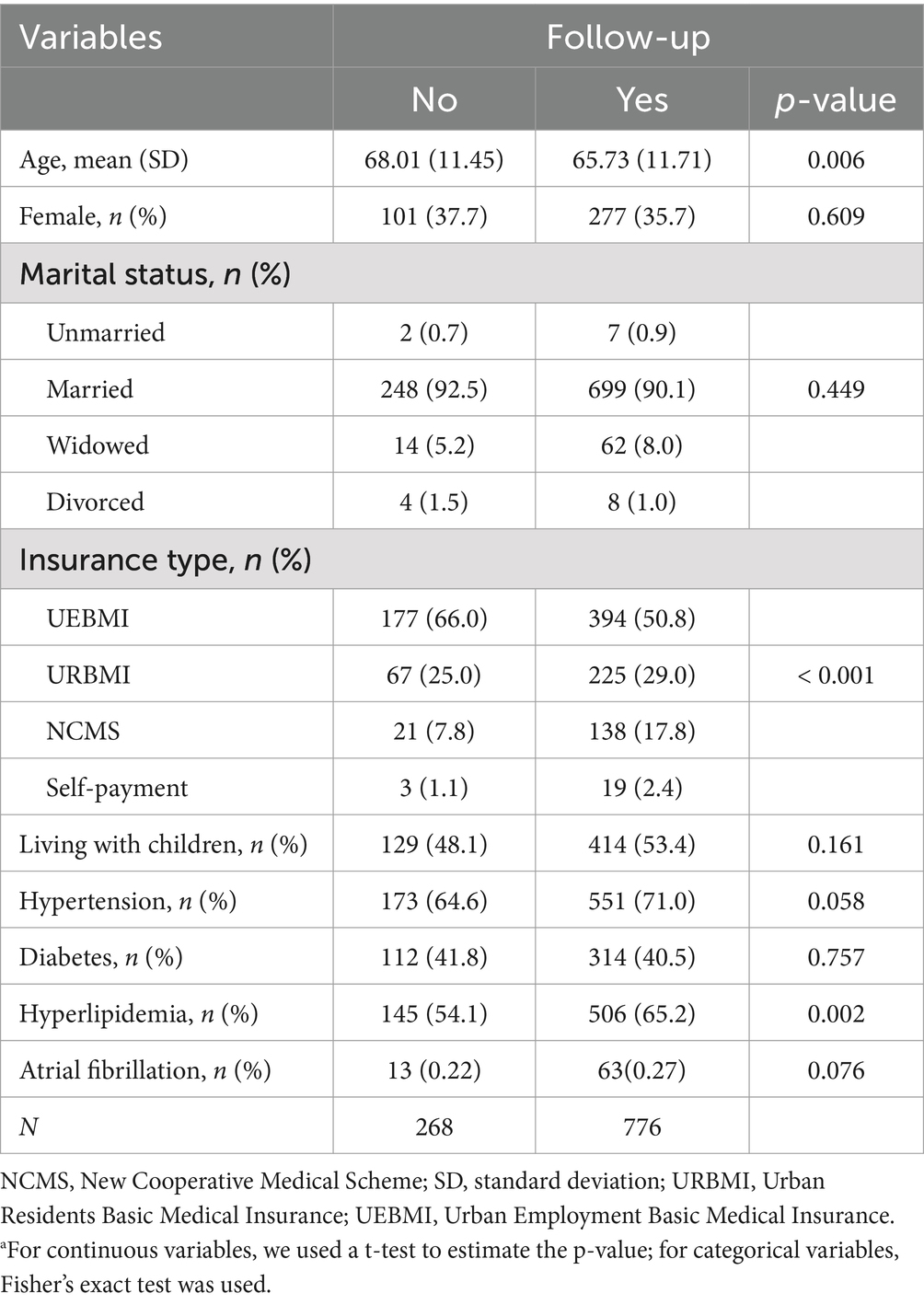
Continuous variables are presented as means and standard deviations, whereas categorical variables are presented as counts and proportions. We divided the participants into two groups based on their compliance with the doctor’s advice for regular follow-up. We used a t-test to detect statistical differences in continuous variables between the two groups. We employed Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables to identify statistical differences between the groups.
Logistic regression was used to determine the factors that influenced patients with IS who did not have regular follow-up after discharge. Adherence to follow-up procedures was represented as a binary variable (1 = Yes, 0 = No). The above model was used to analyze the data for the two dependent variables. Patienti represents a vector of patient-level independent variables, including sex, age, marital status, type of medical insurance, and whether the patient lives with a child. β is a vector of the parameters of interest, and exp. (β) represents the odds ratio (OR).
Subsequently, we included indicators for hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia, along with their interaction terms in Model 1. This study aimed to evaluate whether patients diagnosed with multiple cardiovascular diseases (all three conditions) exhibit higher treatment compliance rates than those with one or two of these conditions. Patients with all three cardiovascular diseases were included in the reference group. Statistical analyses were performed using R version 4.1.2 (R Foundation, Vienna, Austria).
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics
A total of 1,041 patients were followed up in our study. The median age of the patients with regular follow-up at 1 year after discharge was 65.73 years, and the proportion of females was 35.7%. The median age of patients with irregular follow-up was 68.01, and the proportion of females was 37.7%. Additional general information is presented in Table 1.
3.2 Patients’ knowledge of their illness
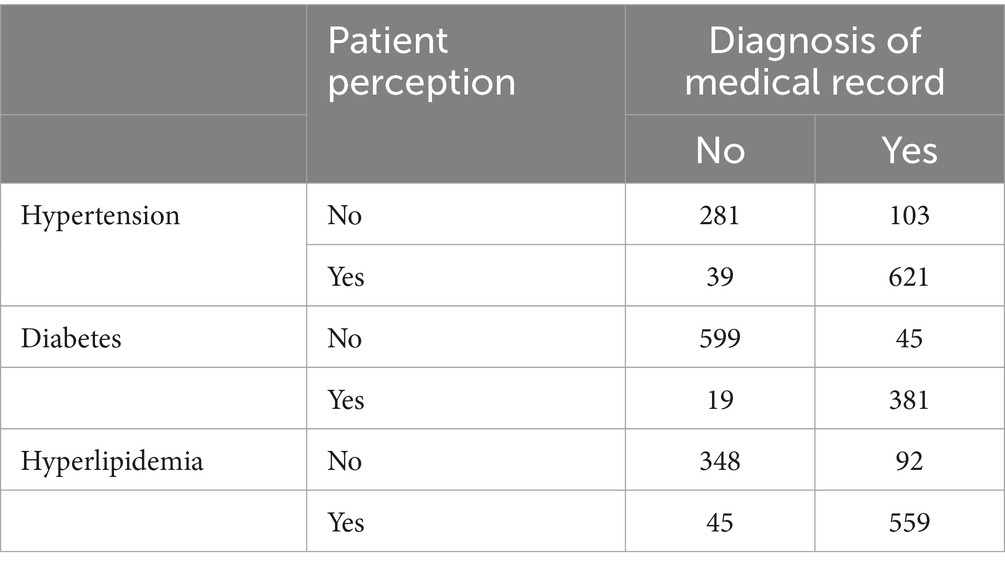
Overall, 103, 19, and 45 patients diagnosed with diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia, respectively, were unaware of their illness (Table 2).
3.3 Secondary prevention in patients with IS 1 year after discharge
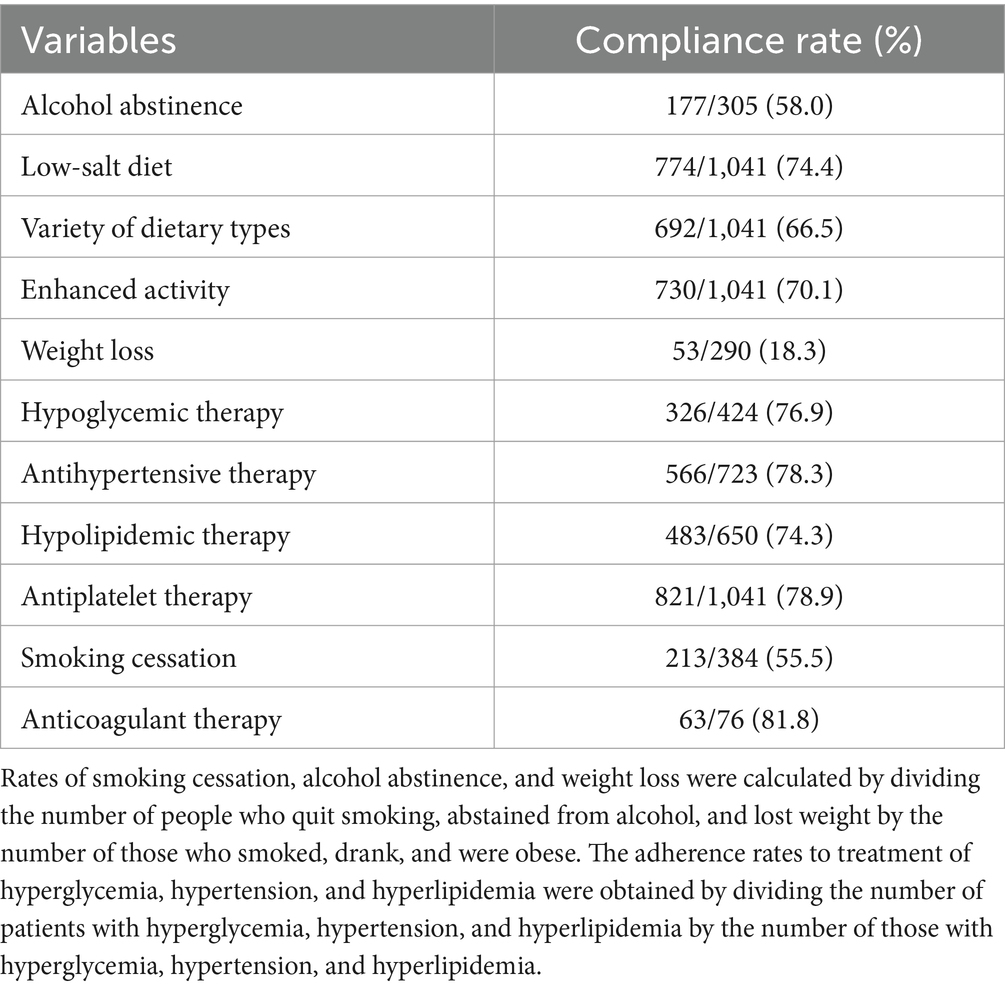
Only 18.3% of patients with IS combined with obesity lost weight. Whereas 58% patients abstained from alcohol, 55.5% quit smoking, and less than 80% patients adhered to the three high levels of treatment and antithrombotic therapy (Table 3).
3.4 Analysis of factors influencing regular follow-up in patients with IS 1 year after discharge
The results of the logistic regression with follow-up as the dependent variable are presented in Table 4. The older the patient, the less likely they were to accept treatment (odds ratio [OR] 0.99, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.97–0.99). Furthermore, patients under the New Cooperative Medical Scheme (NCMS) were more likely to accept treatment than those with Urban Employment Basic Medical Insurance (UEBMI) (OR 2.19, 95% CI 1.34–3.74). Patients with hypertension (OR 1.51, 95% CI 1.11–2.06), atrial fibrillation (OR 2.17, 95% CI 1.19–4.26) or hyperlipidemia (OR 1.49, 95% CI 1.10–2.01) were more likely to accept treatment.
3.5 Correlation analysis of secondary prevention in patients with IS complicated with hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia
Figure 1 displays the ORs between patients with one or two of the three cardiovascular diseases (hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia) and those with all three. No significant differences were observed in the probability of treatment acceptance between patients experiencing one or two of the three cardiovascular diseases and those with all three, with treatment as the dependent variable (Figure 1A). No significant differences were noted in the probability of treatment acceptance between patients experiencing one or two of the three cardiovascular diseases and those with all three (Figure 1B), with follow-up as the dependent variable. The results align with those of Figure 1A.

Figure 1. Correlation analysis of secondary prevention in patients with ischemic stroke complicated with hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia. OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
4 Discussion
According to the investigation of several of Grade III and A general hospitals in Chengdu and Chongqing, we found that the awareness and adherence to secondary prevention measures among patients with IS are not high. Additionally, whether or not patients have children did not significantly impact their compliance. Furthermore, no difference was observed in the prevalence of risk factors between patients with one or two of the three cardiovascular diseases (hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia) and those with all three.
Although these patients had already experienced an IS, their adherence to secondary prevention was low. A previous study from the Chinese National Stroke Registry-II (CNSR-II) found that the compliance rates with antiplatelet, hypoglycemic, and antihypertensive drugs were 57.58, 63.68, and 61.90%, respectively, 1 year after discharge (1, 7). The results of the Adherence eValuation After ischemic stroke–Longitudinal (AVAIL) study showed that the regimen persistence for secondary prevention medications at 12 months was 65.6% (19). The patients surveyed in our study in 2023 had relatively high medication compliance compared with the CNSR-II study in 2018, which may be owing to the recent health education related to IS. Nonetheless, adherence in western China is lower than that in developed countries. In the AVAIL study, the 12-month persistence was the highest for antihypertensive medications (87.9%), followed by those of antiplatelet (87.1%), diabetes (82.3%), and lipid-lowering (77.6%) medications (19). Other studies, such as Preventing Recurrence of Thromboembolic Events through Coordinated Treatment reported that antithrombotic and statin use was maintained at 98 and 99%, respectively at 1-year follow-up (20). Another study conducted in eastern Canada showed that patients with stroke had a self-reported persistence of 90% for all categories of stroke-prevention medications (21). Our 1-year follow-up results were similar to that of the Riks-Stroke Register (22) in Sweden, which found that persistence by medication category at 2 years post-discharge (56% for statins and 74% for antihypertensive drugs). Taking strong measures for the health education of secondary prevention of AIS is essential.
Age and type of medical insurance affect outpatient follow-up. Similarly, previous studies have found that age and type of medical insurance are factors that affect the medication compliance of patients with IS after discharge (23–25). Our study also found that the proportion of follow-up visits by patients with the NCMS insurance type was higher than that of other insurance types. Chronic disease management in community hospitals has ensured that patients with hypertension, diabetes, and IS are treated with special medical insurance, and the reimbursement ratio is high. However, this may be related to the insurance type of Urban Residents’ Basic Medical Insurance (URBMI) and UEBMI, in which people can visit a pharmacy to buy drugs without registering at a hospital. However, living with children did not promote regular follow-up. This could be attributed to the high work pressure and lack of time among young people to care for patients. Previous studies have shown the significance of caregivers in patient compliance after discharge (26, 27). Therefore, it is crucial to prioritize health education for patients’ families in the future. Furthermore, we observed a lesser focus on lifestyle improvements to prevent recurrent IS compared to regular outpatient follow-up. The cost of improving one’s lifestyle is much lower than healthcare costs. Thus, greater emphasis should be placed on high-value lifestyle interventions, which are consistently reasonable and effective for patients with IS (28–32). Alongside enhancing patients’ medication compliance, it is important to strengthen lifestyle and health education.
Consistent with previous studies, most patients with a history of hypertension and hyperlipidemia in this study had regular follow-up (19, 33). Patients with one or two of the three risk factors had a lower risk of IS recurrence than those with IS having the above three risk factors; however, these patients did not closely monitor their risk factors in our study. Hypertension, hyperglycemia, and dyslipidemia have an evident tendency to aggregate and usually occur in pairs or triplets in the same patient, forming a “two-high” or “three-high” coexistence (34–36). Patients with “three-high” coexistence have an exponentially increased risk of IS recurrence, however, the implementation of “three-high” co-management can produce good health and economic benefits (37, 38). Strengthening secondary prevention interventions for patients with IS at three high levels is essential.
Our findings were based on a real-world study of the cognition and compliance status of secondary prevention measures in patients with IS in southwest China. However, it is important to note that our study had certain limitations. First, we could not analyze the education level of the patients. Second, we did not categorize the type of ischemic stroke in the patients. Third, data collection needs to be more comprehensive, including indicators such as whether the patient is experiencing a first-time stroke, severity of the IS, and functional prognosis of the patients in future research. Fourth, our analyses primarily focused on correlations rather than causal inference; hence, our findings may be susceptible to confounding bias. Fifth, owing to our large sample size, we can explain the secondary prevention of some patients with IS in China. However, there is indeed a lack of generalizability. In the future, an even larger sample size is needed to better investigate the secondary prevention of ischemic stroke in China.
5 Conclusion
The recurrence rate of ischemic stroke is high; however, nearly one-third of patients do not perform secondary prevention per the guidelines, particularly for lifestyle improvement. In the future, strengthening the secondary prevention of health publicity for patients with ischemic stroke and their families is essential.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Chengdu Second People’s Hospital (Approval number: 2024352). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Informed consent to participate in this study was provided by the patients/participants or patients/participants’ legal guardian/next of kin.
Author contributions
XZ: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LL: Writing – original draft. QY: Writing – review & editing. JW: Writing – original draft. LH: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. CL: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Chengdu Science and Technology Bureau (Grant/Award Number: 2022-YF05-01776-SN).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Chengdu Science and Technology Bureau, Second People’s Hospital of Chengdu, all the patients with IS who cooperated with the investigation, and the experts who helped in the design of this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Wu, S, Wu, B, Liu, M, Chen, Z, Wang, W, Anderson, CS, et al. Stroke in China: advances and challenges in epidemiology, prevention, and management. Lancet Neurol. (2019) 18:394–405. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30500-3
2. Li, Z, Jiang, Y, Li, H, Xian, Y, and Wang, Y. China’s response to the rising stroke burden. BMJ. (2019) 364:l879. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l879
3. Du, W, Zhao, X, Wang, Y, Pan, Y, Liu, G, Wang, A, et al. Gastrointestinal bleeding during acute ischaemic stroke hospitalisation increases the risk of stroke recurrence. Stroke Vasc Neurol. (2020) 5:116–20. doi: 10.1136/svn-2019-000314
4. Amarenco, P, Lavallée, PC, Monteiro Tavares, L, Labreuche, J, Albers, GW, Abboud, H, et al. Five-year risk of stroke after TIA or minor ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:2182–90. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1802712
5. Ford, ES, Ajani, UA, Croft, JB, Critchley, JA, Labarthe, DR, Kottke, TE, et al. Explaining the decrease in U.S. deaths from coronary disease, 1980–2000. N Engl J Med. (2007) 356:2388–98. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa053935
6. Asberg, S, Henriksson, KM, Farahmand, B, Asplund, K, Norrving, B, Appelros, P, et al. Ischemic stroke and secondary prevention in clinical practice: a cohort study of 14,529 patients in the Swedish stroke register. Stroke. (2010) 41:1338–42. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.580209
7. Yan-Xue, C, Yue, J, Li, Z-X, Pan, Y, Wang, Y, Wang, Y, et al. Status of drug compliance for secondary prevention of acute ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack in China. Chin J Stroke. (2018) 13:6.
8. Zeinhom, MG, Khalil, MFE, Kamel, IFM, Kohail, AM, Ahmed, SR, Elbassiouny, A, et al. Predictors of the unfavorable outcomes in acute ischemic stroke patients treated with alteplase, a multi-center randomized trial. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:5960. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56067-5
9. Govori, V, Budinčević, H, Morović, S, Đerke, F, and Demarin, V. Updated perspectives on lifestyle interventions as secondary stroke prevention measures: a narrative review. Medicina (Kaunas). (2024) 60:504. doi: 10.3390/medicina60030504
10. Bailey, RR. Lifestyle modification for secondary stroke prevention. Am J Lifestyle Med. (2018) 12:140–7. doi: 10.1177/1559827616633683
11. Pan, Y, Li, Z, Li, J, Jin, A, Lin, J, Jing, J, et al. Residual risk and its risk factors for ischemic stroke with adherence to guideline-based secondary stroke prevention. J Stroke. (2021) 23:51–60. doi: 10.5853/jos.2020.03391
12. Chinese Society of Neurology, cerebrovascular group, Chinese Society of Neurology. Chinese guidelines for secondary prevention of ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack. Chin J Neurol. (2015) 48:258–73.
13. Liu, L, Wang, D, Wong, KSL, and Wang, Y. Stroke and stroke care in China: huge burden, significant workload, and a national priority. Stroke. (2011) 42:3651–4. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.635755
14. Yue, J, Chen, W, Yong, J, Yuesong, P, and Zixiao, L. Study on the sociological factors of drug compliance for secondary prevention of acute ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack. Chin J Clin Health Care. (2019) 22:5.
15. Jia, Q, Liu, L, and Wang, Y. Risk factors and prevention of stroke in the Chinese population. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (2011) 20:395–400. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2010.02.008
16. Chinese Society of Neurology, Cerebrovascular Disease Group, Chinese Society of NeurologyBin, P, et al. Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of acute ischemic stroke 2018. Chin J Neurol. (2018) 51:666–82. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2018.09.004
17. Wang, W, Jiang, B, Sun, H, Ru, X, Sun, D, Wang, L, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and mortality of stroke in China: results from a nationwide population-based survey of 480 687 adults. Circulation. (2017) 135:759–71. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.025250
18. Chinese Society of Neurology, Cerebrovascular Group, Chinese Society of Neurology. Chinese guidelines for secondary prevention of ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack 2022. Chin J Neurol. (2022) 55:40.
19. Bushnell, CD, Olson, DM, Zhao, X, Pan, W, Zimmer, LO, Goldstein, LB, et al. Secondary preventive medication persistence and adherence 1 year after stroke. Neurology. (2011) 77:1182–90. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31822f0423
20. Ovbiagele, B, Kidwell, CS, Selco, S, Razinia, T, and Saver, JL. Treatment adherence rates one year after initiation of a systematic hospital-based stroke prevention program. Cerebrovasc Dis. (2005) 20:280–2. doi: 10.1159/000087711
21. Lummis, HL, Sketris, IS, Gubitz, GJ, Joffres, MR, and Flowerdew, GJ. Medication persistence rates and factors associated with persistence in patients following stroke: a cohort study. BMC Neurol. (2008) 8:25. doi: 10.1186/1471-2377-8-25
22. Glader, EL, Sjölander, M, Eriksson, M, and Lundberg, M. Persistent use of secondary preventive drugs declines rapidly during the first 2 years after stroke. Stroke. (2010) 41:397–401. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.566950
23. Ullberg, T, Glader, EL, Zia, E, Petersson, J, Eriksson, M, and Norrving, B. Associations between ischemic stroke follow-up, socioeconomic status, and adherence to secondary preventive drugs in southern Sweden: observations from the Swedish Stroke Register (Riksstroke). Neuroepidemiology. (2017) 48:32–8. doi: 10.1159/000456618
24. Esenwa, C, and Gutierrez, J. Secondary stroke prevention: challenges and solutions. Vasc Health Risk Manag. (2015) 11:437–50. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S63791
25. Han, SW, and Bushnell, CD. Stroke secondary medication persistence and risk for hospital readmission within 90 days after discharge. J Neurol Nen. (2016) 7:87–96. doi: 10.21767/2171-6625.100087
26. Wei, JW, Wang, J-G, Huang, Y, Liu, M, Wu, Y, Wong, LKS, et al. Secondary prevention of ischemic stroke in urban China. Stroke. (2010) 41:967–74. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.571463
27. Jamison, J, Sutton, S, Mant, J, and De Simoni, A. Barriers and facilitators to adherence to secondary stroke prevention medications after stroke: analysis of survivors and caregivers views from an online stroke forum. BMJ Open. (2017) 7:e016814. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016814
28. Wang, Y, Feng, L, Zeng, G, Zhu, H, Sun, J, Gao, P, et al. Effects of cuisine-based Chinese heart-healthy diet in lowering blood pressure among adults in China: multicenter, single-blinded, randomized, parallel controlled feeding trial. Circulation. (2022) 146:303–15. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.059045
29. Lloyd-Jones, DM, Allen, NB, Anderson, CAM, Black, T, Brewer, LC, Foraker, RE, et al. Life’s essential 8: updating and enhancing the American Heart Association’s construct of cardiovascular health: a presidential advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2022) 146:e18–43. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001078
30. Wan, EYF, Fung, CSC, Yu, EYT, Chin, WY, Fong, DYT, Chan, AKC, et al. Effect of multifactorial treatment targets and relative importance of hemoglobin A1C, blood pressure, and low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol on cardiovascular diseases in Chinese primary care patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a population-based retrospective cohort study. J Am Heart Assoc. (2017) 6:e006400. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.006400
31. China Cholesterol Education Program (CCEP) Working Committee, Atherosclerosis Thrombosis Prevention and Control Subcommittee of Chinese International Exchange and Promotion Association for Medical and Healthcare, Cardiovascular Disease Subcommittee of China Association of Gerontology and Geriatrics, Atherosclerosis Professional Committee of Chinese College of Cardiovascular Physicians. China cholesterol education program (CCEP) expert advice for the management of dyslipidaemias to reduce cardiovascular risk (2019). Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. (2020) 59:18–22. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2020.01.003
32. Hilkens, NA, Casolla, B, Leung, TW, de, FE, et al. Stroke. Lancet. (2024) 403:2820–36. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00642-1
33. Wawruch, M, Zatko, D, Wimmer, G Jr, Luha, J, Kuzelova, L, Kukumberg, P, et al. Factors influencing non-persistence with antiplatelet medications in elderly patients after ischaemic stroke. Drugs Aging. (2016) 33:365–73. doi: 10.1007/s40266-016-0365-2
34. Grundy, SM. Does a diagnosis of metabolic syndrome have value in clinical practice? Am J Clin Nutr. (2006) 83:1248–51. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/83.6.1248
35. Chen, SC, and Tseng, C-H. Dyslipidemia, kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease in diabetic patients. Rev Diabet Stud. (2013) 10:88–100. doi: 10.1900/RDS.2013.10.88
36. Weycker, D, Nichols, GA, O’Keeffe-Rosetti, M, Edelsberg, J, Khan, ZM, Kaura, S, et al. Risk-factor clustering and cardiovascular disease risk in hypertensive patients. Am J Hypertens. (2007) 20:599–607. doi: 10.1016/j.amjhyper.2006.10.013
37. Wong, ND, Zhao, Y, Patel, R, Patao, C, Malik, S, Bertoni, AG, et al. Cardiovascular risk factor targets and cardiovascular disease event risk in diabetes: a pooling project of the atherosclerosis risk in communities study, multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis, and Jackson Heart Study. Diabetes Care. (2016) 39:668–76. doi: 10.2337/dc15-2439
38. Sever, PS, Dahlöf, B, Poulter, NR, Wedel, H, Beevers, G, Caulfield, M, et al. Prevention of coronary and stroke events with atorvastatin in hypertensive patients who have average or lower-than-average cholesterol concentrations, in the Anglo-Scandinavian cardiac outcomes trial–lipid lowering arm (ASCOT-LLA): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. (2003) 361:1149–58. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12948-0
Keywords: ischemic stroke, recurrence rate, secondary prevention, patient compliance, lifestyle
Citation: Zhong X, Li L, Ye Q, Wang J, He L and Li C (2025) Cognition and influencing factors of secondary prevention in patients with ischemic stroke 1 year after discharge in Southwest China: a cross-sectional survey. Front. Neurol. 15:1488180. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1488180
Edited by:
Patricia Pia Wadowski, Medical University of Vienna, AustriaReviewed by:
Xian-Le Bu, Third Military Medical University, ChinaMohamed G. Zeinhom, Kafrelsheikh University, Egypt
Copyright © 2025 Zhong, Li, Ye, Wang, He and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Changqing Li, bGljcUBjcW11LmVkdS5jbg==
 Xuemin Zhong
Xuemin Zhong Li Li
Li Li Qing Ye3
Qing Ye3 Jian Wang
Jian Wang Lanying He
Lanying He Changqing Li
Changqing Li