- 1Department of Pediatrics, Kaohsiung Municipal Hsiao-Kang Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
- 3Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
- 4Graduate Institute of Clinical Medicine, College of Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
Immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM) is a type of inflammatory myopathy. Most patients with IMNM produce anti-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase or anti-signal-recognition particle autoantibodies. IMNM is much rarer in children than in adults. We conducted this mini review focusing on pediatric IMNM to present current evidence regarding its epidemiology, clinical characteristics, diagnosis, and treatment. Our findings indicate that pediatric IMNM often causes severe muscle weakness and is refractory to corticosteroids alone. Furthermore, delayed diagnosis is common because of the clinicopathological similarity between IMNM and inherited myopathy. Raising awareness regarding pediatric IMNM may facilitate early diagnosis and effective treatment.
1. Introduction
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM) is a group of autoimmune disease causing muscle inflammation with/without other organ involvement. Initially, IIM is categorized into dermatomyositis (DM) and polymyositis (PM) only (1). The patients with IIM presented with limb girdle weakness, often with myalgia and sometimes with dysphagia or respiratory involvement. Disease course typically progresses in weeks or months. The way to differentiate DM from PM is only by the presence of characteristic skin rash and perifascicular atrophy on muscle pathology. In 1995, IBM was established by clinical course with relatively slow onset and characteristic pathological features including inflammation, vacuoles, amyloid deposits, and 15–18 nm tubulofilament inclusions (2). In the past decade, anti-sythetase syndrome (ASS) and immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM) have been determined as new subgroups of IIM by clinical, pathological and serological characters. After the establishment of new disease category, PM seems to become a diagnosis of exclusion and continuous use of this disease name may need further debate (3).
IMNM is characterized by acute onset of proximal muscle weakness, markedly elevated creatine kinase levels, and muscle pathology delineated by necrotic, regenerating fibers and scarce lymphocyte infiltration. On the basis of the seroantibodies involved, IMNM can be divided into the following three subtypes: anti-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMGCR) myopathy, anti-signal recognition particle (SRP) myopathy, and seronegative myopathy. In 2010, anti-HMGCR antibody was first identified as autoantibody in patients with necrotizing myopathy. Notably, most antibody-positive patients had a history of statin exposure (4). Thus, anti-HMGCR myopathy was initially considered to be associated with statin exposure and to mainly affect adults based on the hypothesis of upregulated expression of HMGCR by statin (5). However, as more cases of anti-HMGCR myopathy were reported in statin-naive children, the pathomechanism was speculated to be different in the pediatric population. In general, pediatric patients with IMNM exhibit more insidious onset, treatment resistance, and unfavorable outcomes than adults. Due to a relatively slow onset and a dystrophic pattern of muscle pathology, IMNM is often misdiagnosed as muscular dystrophy (6); the diagnosis of IMNM is therefore challenging to make in pediatric patients. With regard to treatment, corticosteroids alone may exhibit low efficiency in the treatment of pediatric IMNM. Most pediatric patients require combination therapy including intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) and immunosuppressants, such as rituximab, cyclophosphamide, and methotrexate (MTX). Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are necessary for better outcomes and minimal permanent disability. In this review, we would present current understanding and evidence s of the epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment, focusing on pediatric IMNM.
2. Epidemiology
In juvenile IIM, the most common disease is juvenile dermatomyositis which accounts for 75% (7) of patients. Pediatric IMNM is a relatively rare subgroup. In one study with 440 juvenile IIM patients, pediatric IMNM accounts for only 2.9% in juvenile IIM (8). Remarkably, a relatively high IMNM proportion (21%) was reported by an Asian juvenile IIM study (9). Among pediatric IMNM, the proportions of Anti-HMGCR myopathy and anti-SRP myopathy are reported 38.4 and 61.5%, respectively (8). The proportion of seronegative subgroup in pediatric IMNM is difficult to estimate as only two case reports have been published so far (10, 11).
IMNM seems to make up larger proportion of adult IIM, which accounts for 10–38% (12, 13). Previous studies including mainly adult IMNM patients showed that proportion of anti-HMGCR myopathy, anti-SRP myopathy and seronegative IMNM were 21.8–54%, 28.5–44%, and 13–40%, respectively (13–18). The difference of prevalence from pediatric IMNM patients might come from the underdiagnosis of pediatric IMNM and longer investigation time is necessary.
Statin exposure was previously hypothesized to be a trigger for anti-HMGCR myopathy; studies conducted in adult patients reported that 15–65% of adult patients were exposed to statins (5, 19). However, our literature review revealed no reports of statin use in pediatric patients with anti-HMGCR myopathy. In addition to medications, statin is present in mushrooms (20), red yeast rice (21), and Pu-erh tea (22), which are commonly used in Asian dishes. A study reported the exacerbation of adult anti-HMGCR myopathy after mushroom intake (23). Therefore, food-derived statin may be a risk factor for anti-HMGCR myopathy in pediatric patients who usually would not receive statin-based medications.
3. Human leukocyte antigen typing
Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) typing is strongly correlated with several autoimmune diseases; for example, HLA DRB1*11:01 is a risk factor for adult anti-HMGCR myopathy (24–26). By contrast, a study on juvenile anti-HMGCR myopathy revealed that all pediatric patients carried DRB1*07:01 but none carried DRB1*11:01 (8). In another study, DRB1*08:03 was frequently detected in Japanese patients with anti-SRP myopathy compared with the findings in the control group (25). The prevalence of DRB1*08:03 is relatively high in the Japanese population (27). In a Korean study, DRB1*14:03 was associated with anti-SRP myopathy (28). Thus, HLA typing may explain the geographical difference in the prevalence of IMNM.
4. Clinical manifestation
The most common clinical symptoms of IMNM is progressive proximal muscle weakness, especially lower extremities (3). Weakness often started from lower extremities, whereas initial presentation with upper extremities weakness was ever reported in about one-fifth of patients by one Japanese study (29). The severity of muscle involvement is often more than other IIM (3, 5, 16). Marked elevated creatine kinase (often ranging from 4,000 to 8,000 IU/L (30)) is a characteristic finding, and it is also a biomarker of disease activity (31). Only one-third of IMNM patients have insidious-onset (> 6 months) disease course. Most of IMNM patients are with onset less than 6 months (17).
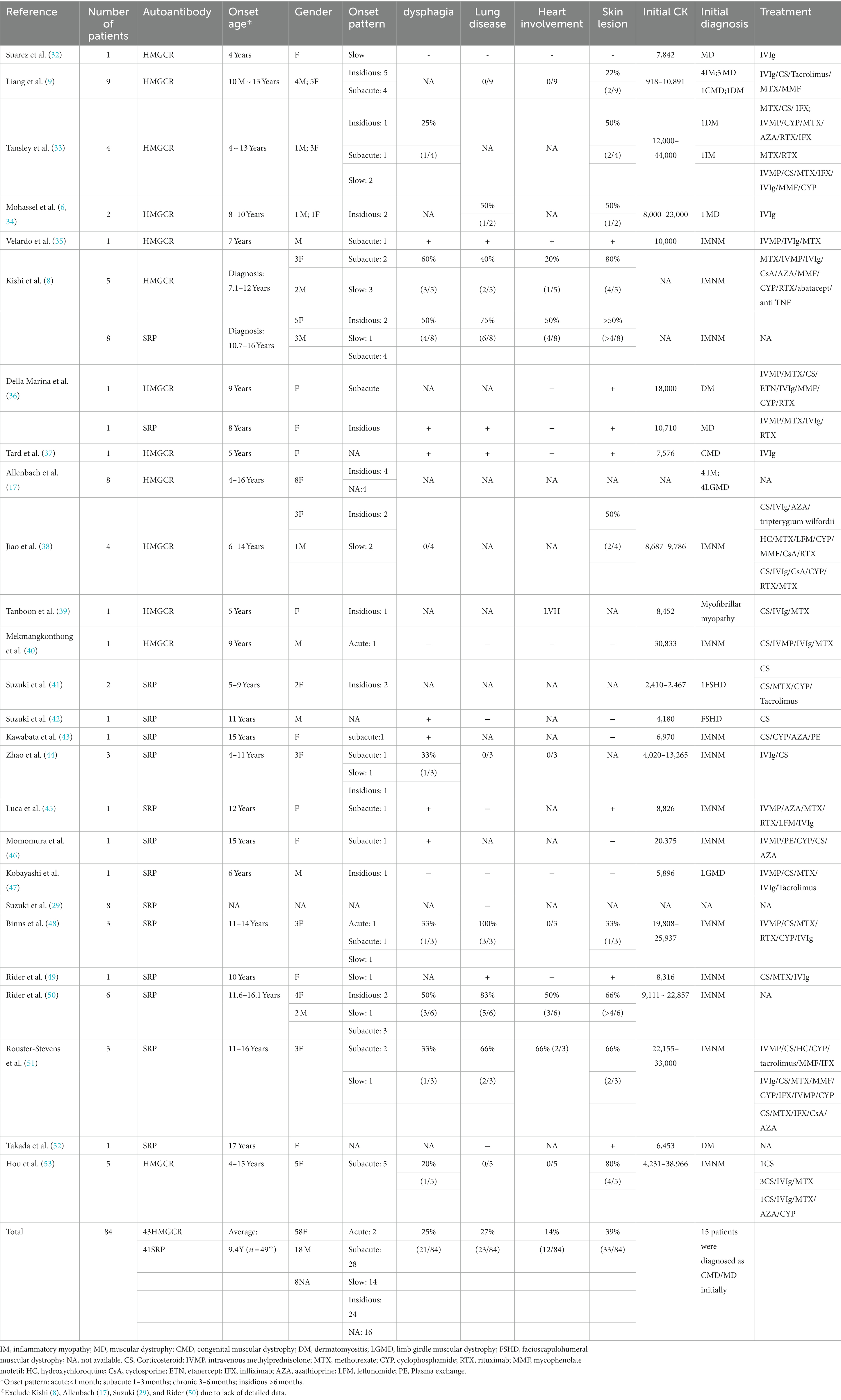
Because of its relatively low prevalence, large-scale case series on pediatric IMNM are rare. We reviewed the literature and summarized the clinical manifestations of pediatric patients (Table 1), excluding those for whom detailed data were unavailable. A total of 84 pediatric patients with IMNM were included; of them, 43 had anti-HMGCR myopathy and 41 had anti-SRP myopathy. Female predominance (female/male = 3.2:1) was noted, and the ratio was slightly higher than that noted in adult patients (1.69–2.75:1) (13, 17). The average onset age was 9.4 years (n = 49), and the youngest patient was 10 months old (9). The most common clinical pattern in pediatric patients is a subacute onset [1–3 months: 41% (28/68)] followed by an insidious course [>6 months: 35% (24/68)]. Because the disease onset and course could be slow, a timely and accurate diagnosis is difficult. In a case series (17), approximately 50% of pediatric IMNM patients were misdiagnosed with limb girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD). Another study revealed that 55% of all patients (6/11, including children and adult patients) had a clinical diagnosis of LGMD but tested negative on genetic examination; notably, anti-HMGCR antibody were detected in their blood samples (6). Other than LGMD, IMNM might also resemble facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy due to a winged scapula and shoulder girdle involvement (41, 42). Therefore, autoantibody assessment is recommended for patients with suspicious muscular dystrophy without any positive genetic test results or family history.
Compared to anti-HMGCR myopathy, anti-SRP myopathy is accompanied by more frequent neck weakness, bulbar dysfunction (e.g., dysphagia), cardiac involvement, and interstitial lung disease (8, 13, 29, 36, 43). Cardiac abnormality has been reported in only three pediatric patients with anti-HMGCR myopathy, including hypokinesia, rigidity over interventricular septum basal segments, and left ventricular hypertrophy (8, 35, 39).
Cancer risk is much higher in cases of seronegative IMNM than anti-SRP myopathy. The association between cancer and anti-HMGCR myopathy is debatable, although some studies have reported a positive relationship (54, 55). However, to the best of our knowledge, no pediatric patient with IMNM has been diagnosed with concurrent malignancy.
Cutaneous involvement is not uncommon in IMNM. Per existing case reports, it is most common among pediatric patients. However, a recent study indicated that 56% of all adult patients with anti-HMGCR have skin lesions (56). Our review revealed that 39% (33/84) of all pediatric patients with IMNM exhibited cutaneous manifestations (Table 1). The manifestations include rash, urticaria, alopecia, cracked fingertip, palm desquamation, mechanic’s hands, linear scleroderma morphea, linear extensor erythema, periungual exanthema, periungual capillary abnormality, malar rash, shawl rash, Gottron’s papules, heliotrope rash, Raynaud phenomenon, hypopigmentation, and interstitial granulomatous dermatitis (8, 9, 33–38, 45, 48, 49, 51–53).
In some patients, IMNM developed or worsened after an infection (36, 43, 46, 48, 51, 57). The most common event preceding IMNM development was respiratory tract infection; in addition, lymphadenitis (43) and dengue fever (40) were ever reported to be preceding events in pediatric patients. The interval between an infection and muscle weakness onset is 1–4 weeks. A case report published during the COVID-19 pandemic reported that an adult patient with anti-HMGCR myopathy experienced disease relapse after SARS-CoV-2 infection (58). Another adult patient developed anti-SRP myopathy after receiving the Pfizer–BioNTech vaccine (59). The association between infection and IMNM remains unknown; therefore, further studies are necessary to elucidate the pathomechanism of IMNM.
Pediatric seronegative IMNM is very rare and there were only two reported cases (10, 11). Their onset age were 10 years old and 11 years old, respectively. Both of them showed bilateral proximal symmetric weakness over extremities. One patient developed myopericarditis and cardiogenic shock after mild clinical improvement toward initial treatment including steroid pulse therapy/IVIg/MTX. Although the case number is too small to compare with seropositive pediatric IMNM patients, it seems that cardiac evaluation is essential in these patients.
5. Diagnosis
5.1. Imaging
Although muscle imaging is not included in IMNM diagnostic criteria, it has emerged to be an important tool for differential diagnosis among IIMs. Recent accumulation of evidence demonstrated that muscle magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is helpful for IMNM evaluation. The muscle MRI for IMNM typically reveals prominent muscle edema, atrophy, and fatty infiltration, primarily over the thigh muscle (60, 61). The most severely fatty infiltrated region are hamstrings and adductor magnus while quadriceps femoris is the least (61). Pelvic and adductor involvement is common and usually severe during the early period of the disease course. By contrast, these regions are often unaffected in patients with dermatomyositis (62). In addition, adductor brevis edema and obturator externus atrophy are unique common findings in IMNM (60). Shoulder involvement with a clinical scapular winging has been observed in some patients with IMNM (6, 63); however, the frequency of this phenomenon is relatively low in other IIMs. Fascial edema in the semitendinosus was very rare in IMNM, in contrary to DM (60). Compared with patients with anti-HMCGR myopathy, those with anti-SRP myopathy exhibit marked atrophy and fatty infiltration on muscle imaging (60), which are consistent with their clinical symptoms. The distribution of muscle involvement seems to be no different between pediatric and adult IMNM patients.
5.2. Muscle pathology
Myo-pathological analysis plays an important role in differential diagnosis of IIM. Sarcoplasmic major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) staining is usually observed in all IIM but the combination use of some other immunohistochemical staining might make the subtypes of IIM distinguishable. In DM, in addition to classical perifascicular atrophy, sarcoplasmic myxovirus resistance protein A (MxA) expression especially in perifascicular areas has been recently identified as a pathological hallmark. Membrane attack complex (MAC; C5b-9 complement complex) is often deposited on endomysial capillaries, not sarcolemma of myofibers. MHC-II is negative. In ASS, perifascicular necrosis with perimyisial connective tissue fragmentation is often observed which might look like perifascicular atrophy, but contrary to DM, MxA is negative and MAC deposition could be present on sarcolemma; MHC-II expression is characteristically observed on the sarcolemma of many myofibers. In IBM, there are fibers with p62-positive coarse aggregates in the sarcoplasm. Endomysial infiltrating lymphocytes are positive for CD8. MHC-II staining on both the sarcolemma and the sarcoplasm of myofibers is present (64, 65).
The typical muscle pathologies associated with IMNM are as follows: necrosis and regeneration of muscle fibers; elevated expression levels of MHC-I, but not MHC-II, on the sarcolemma; frequent deposition of MAC on the sarcolemma (14, 66); infiltration of lymphocytes to the endomysium but rare invasion of healthy myofibers; and fine granular patterns of p62 (autophagy marker) over the sarcolemma (14, 66–69). In some pediatric patients with a prolonged disease duration, increased endomysial fibrosis, increased fiber size variability, and internal nuclei have been observed (34, 35, 37). Because of the pathological similarity between IMNM and muscular dystrophy, initial misdiagnosis is common. Thus, immunohistochemical staining is crucial for IMNM diagnosis. Because MHC-I expression indicates muscle damage, it is a sensitive, but not a specific marker, for IMNM (70). The deposition of MAC on the sarcolemma and a fine granular pattern of p62, a positive autophagy marker in sarcoplasm are regarded as characteristic features but lack of specificity (67, 71).
6. Treatment
In 2022 British Society for Rheumatology guideline for juvenile IIM (72), it recommended that combination of high dose corticosteroids and methotrexate should be used as first-line treatment in most pediatric cases. Although corticosteroid is essential, it should be weaned when disease activity improved (often 6 weeks after treatment initiation). For pediatric with myositis and skin lesion, mycophenolate mofetil is an alternative treatment option. Intravenous immunoglobulin, rituximab or cyclophosphamide may be considered in severe and/or refractory IIM. Clinician should treat juvenile onset IIM aggressively to achieve early, complete recovery of muscle weakness and inflammation to improve outcome.
Among juvenile IIM, juvenile DM have favorable treatment response. Previous literature showed that the probability of corticosteroid discontinuation was 56%, complete clinical response 38% and remission 30% by 5 years after initial treatment for juvenile DM (73). However, pediatric IMNM is often refractory to treatment. Because of the low prevalence of pediatric IMNM, few randomized controlled trials have focused on its treatment options. In adult patients, treatment is prescribed primarily on the basis of the attending physician’s experience or expert consensus. Corticosteroids are often used as the initial therapeutic agent for pediatric IMNM. Initially, prednisolone is administered at a dose of 1 or 2 mg/kg/day; then, intravenous pulse therapy may be added to the treatment regimen considering disease severity. However, corticosteroids alone may not be an effective treatment option because most pediatric patients require additional immunosuppressants for disease management. In a study (8) comprising five pediatric patients with anti-HMGCR myopathy, the patients required the simultaneous administration of an average of 2.4 therapeutic agents and 8 different medication trials during the entire disease course.
Also by the consensus of the European Neuromuscular Center (ENMC) (14) meeting, the initial treatment for IMNM should include corticosteroids combined with additional agents (simultaneous administration or within 1 month). In general, MTX is the first choice of treatment. Rituximab and IVIg may be combined with MTX or used instead of MTX for patients with anti-SRP myopathy and patients with anti-HMGCR myopathy, respectively.
Other immunosuppressants used in some pediatric patients include cyclophosphamide, azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, infliximab, tacrolimus, cyclosporine, leflunomide, etanercept, abatacept, anti-tumor necrosis factor, and hydroxychloroquine. In two female pediatric patients with anti-SRP myopathy, plasma exchange was performed in addition to the simultaneous administration of immunosuppressants. Thus, the exact effects of plasma exchange therapy remain obscure. The most commonly used therapeutic agents other than corticosteroids are discussed as follows.
6.1. MTX
The ENMC guideline recommends the use of MTX with corticosteroids. In pediatric patients with IMNM, the dosage of MTX should be 0.3 mg/kg/week (maximum: 15 mg/week). However, a case series on pediatric anti-SRP myopathy reported that none of their patients (n = 3) responded to a combination therapy comprising a corticosteroid and MTX (48). Thus, aggressive combination therapy is required for anti-SRP myopathy.
6.2. IVIg
The initial dosage of IVIg for patients with IMNM is 2 g/kg/month for 3–6 months. IVIg is effective in treating IMNM, particularly anti-HMGCR myopathy. In some pediatric patients with anti-HMGCR myopathy, their symptoms improved and were successfully managed through IVIg monotherapy (6). A pediatric case series including patients with anti-HMGCR myopathy and those with anti-SRP myopathy reported that IVIg administration ensured a relative long disease remission period compared with the outcomes of a combination of pulse methylprednisolone therapy with MTX or etanercept (36). In addition to IVIg, subcutaneous immunoglobulins were found to be effective in adult patients with anti-HMGCR myopathy (74). Recently, the US Food and Drug Administration approved IVIg for dermatomyositis. Although the pathomechanism underlying IMNM may not be the exact same as that underlying dermatomyositis, IVIg appears to be effective in both diseases.
6.3. Rituximab
The recommended dosage of rituximab for IMNM is 750 mg/m2 (maximum: 1 g). In adult patients, rituximab was effective in only one-third of all patients with refractory anti-HMGCR myopathy and ineffective in the remaining two-thirds of the population (75). It is generally not used as the initial treatment option in pediatric patients with anti-HMGCR myopathy. Only one study reported the successful management of a pediatric patient, who responded poorly to MTX, using rituximab monotherapy (33). Conversely, in another study, rituximab exhibited prominent and sustained effects in most adult patients with anti-SRP myopathy (76). The benefits of rituximab have also been reported in some pediatric patients (45, 48).
6.4. Cyclophosphamide
Although the ENMC guideline does not recommend cyclophosphamide as a preferential treatment option for IMNM, its use is common in pediatric patients with IMNM. Cyclophosphamide is also used to treat severe juvenile dermatomyositis; the recommended dosage is 3 doses of 500 mg/m2 cyclophosphamide every 2 weeks and then 6 or 7 doses of 750 mg/m2 cyclophosphamide every 3 or 4 weeks (77). Unfortunately, its side effects, including cardiac and pulmonary toxicities, may aggravate cardiac and pulmonary problems in patients with anti-SRP myopathy; thus, the cardiac and pulmonary functions of patients receiving cyclophosphamide should be monitored closely. Regarding cyclophosphamide’s side effects associated with reproduction, a cumulative dosage of >7.5 g/m2 is a major risk factor for male infertility.1
7. Conclusion
Without timely diagnosis and aggressive treatment, irreversible muscle damage may be unavoidable in patients with IMNM. Most pediatric patients experience an insidious disease course with cutaneous manifestations and are often misdiagnosed with muscular dystrophy or dermatomyositis. Because of the similarity between IMNM and the aforementioned conditions in terms of clinical features, autoantibody analysis and muscle MRI are essential for accurate diagnosis. In addition, muscle pathology should be investigated for differential diagnosis. Compared with adult patients with IMNM, most pediatric patients often exhibit treatment resistance. On the basis of expert consensus and real-world data, the early administration of a combination of corticosteroids with immunosuppressants or IVIg is recommended for improved clinical outcomes.
Author contributions
W-CL initiated the need for this article, revised it critically for important intellectual content, and gave critical comments. C-HW wrote the manuscript and created the included table. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ichizo Nishino and Yuh-Jyh Jong for valuable suggestion and comments to this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
References
1. Bohan, A, and Peter, JB. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. (1975) 292:344–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197502132920706
2. Griggs, RC, Askanas, V, DiMauro, S, Engel, A, Karpati, G, Mendell, JR, et al. Inclusion body myositis and myopathies. Ann Neurol. (1995) 38:705–13. doi: 10.1002/ana.410380504
3. Mariampillai, K, Granger, B, Amelin, D, Guiguet, M, Hachulla, E, Maurier, F, et al. Development of a new classification system for idiopathic inflammatory myopathies based on clinical manifestations and myositis-specific autoantibodies. JAMA Neurol. (2018) 75:1528–37. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.2598
4. Christopher-Stine, L, Casciola-Rosen, LA, Hong, G, Chung, T, Corse, AM, and Mammen, AL. A novel autoantibody recognizing 200-Kd and 100-Kd proteins is associated with an immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy. Arthritis Rheum. (2010) 62:2757–66. doi: 10.1002/art.27572
5. Mammen, AL, Chung, T, Christopher-Stine, L, Rosen, P, Rosen, A, Doering, KR, et al. Autoantibodies against 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase in patients with statin-associated autoimmune myopathy. Arthritis Rheum. (2011) 63:713–21. doi: 10.1002/art.30156
6. Mohassel, P, Landon-Cardinal, O, Foley, AR, Donkervoort, S, Pak, KS, Wahl, C, et al. Anti-hmgcr myopathy may resemble limb-girdle muscular dystrophy. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. (2019) 6, 6:e523. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000523
7. Pachman, LM, and Khojah, AM. Advances in juvenile dermatomyositis: myositis specific antibodies aid in understanding disease heterogeneity. J Pediatr. (2018) 195:16–27. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2017.12.053
8. Kishi, T, Rider, LG, Pak, K, Barillas-Arias, L, Henrickson, M, McCarthy, PL, et al. Association of anti-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase autoantibodies with Drb1*07:01 and severe myositis in juvenile myositis patients. Arthritis Care Res. (2017) 69:1088–94. doi: 10.1002/acr.23113
9. Liang, WC, Uruha, A, Suzuki, S, Murakami, N, Takeshita, E, Chen, WZ, et al. Pediatric necrotizing myopathy associated with anti-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase antibodies. Rheumatology (Oxford). (2017) 56:287–93. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kew386
10. Karakas, C, Sah, J, Seidman, R, Chari, G, Hisamoto, Y, Cracco, J, et al. A child with antibody-negative immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy. Muscle Nerve. (2019) 59, 59:E10–3. doi: 10.1002/mus.26375
11. Martin Pedraz, L, Galindo Zavala, R, Yun Castilla, C, Ortiz Garrido, A, and Nunez Cuadros, E. Seronegative immune-mediated necrotising myopathy with myocardial involvement. An Pediatr. (2021) 95, 95:470–2. doi: 10.1016/j.anpede.2020.10.009
12. Senecal, JL, Raynauld, JP, and Troyanov, Y. Editorial: a new classification of adult autoimmune myositis. Arthritis Rheum. (2017) 69, 69:878–84. doi: 10.1002/art.40063
13. Watanabe, Y, Uruha, A, Suzuki, S, Nakahara, J, Hamanaka, K, Takayama, K, et al. Clinical features and prognosis in anti-Srp and anti-Hmgcr necrotising myopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2016) 87:1038–44. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2016-313166
14. Allenbach, Y, Mammen, AL, Benveniste, O, and Stenzel, W, Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myopathies Working G. 224th Enmc international workshop: Clinico-Sero-pathological classification of immune-mediated necrotizing myopathies Zandvoort, the Netherlands, 14-16 October 2016. Neuromuscul Disord. (2018) 28:87–99. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2017.09.016
15. Lim, J, Rietveld, A, De Bleecker, JL, Badrising, UA, Saris, CGJ, van der Kooi, AJ, et al. Seronegative patients form a distinctive subgroup of immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. (2019) 6:e513. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000513
16. Pinal-Fernandez, I, Parks, C, Werner, JL, Albayda, J, Paik, J, Danoff, SK, et al. Longitudinal course of disease in a large cohort of myositis patients with autoantibodies recognizing the signal recognition particle. Arthritis Care Res. (2017) 69:263–70. doi: 10.1002/acr.22920
17. Allenbach, Y, Drouot, L, Rigolet, A, Charuel, JL, Jouen, F, Romero, NB, et al. Anti-Hmgcr autoantibodies in European patients with autoimmune necrotizing myopathies: inconstant exposure to statin. Medicine (Baltimore). (2014) 93:150–7. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000028
18. Kurashige, T, Murao, T, Mine, N, Sugiura, T, Inazuka, Y, Kuraoka, K, et al. Anti-Hmgcr antibody-positive myopathy shows Bcl-2-positive inflammation and lymphocytic accumulations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. (2020) 79:448–57. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlaa006
19. Ge, Y, Lu, X, Peng, Q, Shu, X, and Wang, G. Clinical characteristics of anti-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase antibodies in Chinese patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. PLoS One. (2015) 10:e0141616. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141616
20. Lo, YC, Lin, SY, Ulziijargal, E, Chen, SY, Chien, RC, Tzou, YJ, et al. Comparative study of contents of several bioactive components in fruiting bodies and mycelia of culinary-medicinal mushrooms. Int J Med Mushrooms. (2012) 14:357–63. doi: 10.1615/intjmedmushr.v14.i4.30
21. Klimek, M, Wang, S, and Ogunkanmi, A. Safety and efficacy of red yeast rice (Monascus Purpureus) as an alternative therapy for hyperlipidemia. P T. (2009) 34:313–27.
22. Jeng, KC, Chen, CS, Fang, YP, Hou, RC, and Chen, YS. Effect of microbial fermentation on content of statin, gaba, and polyphenols in Pu-erh tea. J Agric Food Chem. (2007) 55:8787–92. doi: 10.1021/jf071629p
23. Adler, B, Christopher-Stine, L, and Tiniakou, E. Mushroom supplements triggering a flare of Hmgcr immune mediated necrotising myopathy. BMJ Case Rep. (2022) 15:e248880. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2022-248880
24. Mammen, AL, Gaudet, D, Brisson, D, Christopher-Stine, L, Lloyd, TE, Leffell, MS, et al. Increased frequency of Drb1*11:01 in anti-hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase-associated autoimmune myopathy. Arthritis Care Res. (2012) 64:1233–7. doi: 10.1002/acr.21671
25. Ohnuki, Y, Suzuki, S, Shiina, T, Uruha, A, Watanabe, Y, Suzuki, S, et al. Hla-Drb1 alleles in immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy. Neurology. (2016) 87:1954–5. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003160
26. Limaye, V, Bundell, C, Hollingsworth, P, Rojana-Udomsart, A, Mastaglia, F, Blumbergs, P, et al. Clinical and genetic associations of autoantibodies to 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme a reductase in patients with immune-mediated myositis and necrotizing myopathy. Muscle Nerve. (2015) 52:196–203. doi: 10.1002/mus.24541
27. Gragert, L, Madbouly, A, Freeman, J, and Maiers, M. Six-locus high resolution Hla haplotype frequencies derived from mixed-resolution DNA typing for the entire us donor registry. Hum Immunol. (2013) 74:1313–20. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2013.06.025
28. Kang, EH, Go, DJ, Mimori, T, Lee, SJ, Kwon, HM, Park, JW, et al. Novel susceptibility alleles in Hla region for myositis and myositis specific autoantibodies in Korean patients. Semin Arthritis Rheum. (2019) 49:283–7. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.03.005
29. Suzuki, S, Nishikawa, A, Kuwana, M, Nishimura, H, Watanabe, Y, Nakahara, J, et al. Inflammatory myopathy with anti-signal recognition particle antibodies: case series of 100 patients. Orphanet J Rare Dis. (2015) 10:61. doi: 10.1186/s13023-015-0277-y
30. Allenbach, Y, Benveniste, O, Stenzel, W, and Boyer, O. Immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy: clinical features and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2020) 16:689–701. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-00515-9
31. Werner, JL, Christopher-Stine, L, Ghazarian, SR, Pak, KS, Kus, JE, Daya, NR, et al. Antibody levels correlate with creatine kinase levels and strength in anti-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase-associated autoimmune myopathy. Arthritis Rheum. (2012) 64:4087–93. doi: 10.1002/art.34673
32. Suarez, B, Jofre, J, Lozano-Arango, A, Ortega, X, Diaz, J, Calcagno, G, et al. Spontaneous symptomatic improvement in a pediatric patient with anti-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutraryl-coenzyme a reductase myopathy. Neuromuscul Disord. (2020) 30:503–9. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2020.03.008
33. Tansley, SL, Betteridge, ZE, Simou, S, Jacques, TS, Pilkington, C, Wood, M, et al. Anti-Hmgcr autoantibodies in juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies identify a rare but clinically important subset of patients. J Rheumatol. (2017) 44:488–92. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.160871
34. Mohassel, P, Foley, AR, Donkervoort, S, Fequiere, PR, Pak, K, Bonnemann, CG, et al. Anti-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase necrotizing myopathy masquerading as a muscular dystrophy in a child. Muscle Nerve. (2017) 56:1177–81. doi: 10.1002/mus.25567
35. Velardo, D, Faravelli, I, Cinnante, C, Moggio, M, and Comi, GP. Pediatric anti-Hmgcr necrotizing myopathy: diagnostic challenges and literature review. Neurol Sci. (2020) 41:3009–13. doi: 10.1007/s10072-020-04491-6
36. Della Marina, A, Pawlitzki, M, Ruck, T, van Baalen, A, Vogt, N, Schweiger, B, et al. Clinical course, myopathology and challenge of therapeutic intervention in pediatric patients with autoimmune-mediated necrotizing myopathy. Children. (2021) 8:721. doi: 10.3390/children8090721
37. Tard, C, Tiffreau, V, Jaillette, E, Jouen, F, Nelson, I, Bonne, G, et al. Anti-Hmgcr antibody-related necrotizing autoimmune myopathy mimicking muscular dystrophy. Neuropediatrics. (2017) 48:473–6. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1604402
38. Jiao, Y, Cai, S, Lin, J, Zhu, W, Xi, J, Li, J, et al. Statin-naive anti-Hmgcr antibody-mediated necrotizing myopathy in China. J Clin Neurosci. (2018) 57:13–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2018.08.010
39. Tanboon, J, Sanmaneechai, O, Charuvanij, S, Sangruchi, T, Galindo-Feria, AS, Lundberg, IE, et al. Concurrent positive anti-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase antibody with reducing body myopathy: possible double trouble. Neuromuscul Disord. (2019) 29:543–8. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2019.05.007
40. Mekmangkonthong, A, Amornvit, J, Numkarunarunrote, N, Veeravigrom, M, and Khaosut, P. Dengue infection triggered immune mediated necrotizing myopathy in children: a case report and literature review. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. (2022) 20:40. doi: 10.1186/s12969-022-00699-2
41. Suzuki, S, Ohta, M, Shimizu, Y, Hayashi, YK, and Nishino, I. Anti-signal recognition particle myopathy in the first decade of life. Pediatr Neurol. (2011) 45:114–6. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2011.04.009
42. Suzuki, S, Satoh, T, Sato, S, Otomo, M, Hirayama, Y, Sato, H, et al. Clinical utility of anti-signal recognition particle antibody in the differential diagnosis of myopathies. Rheumatology (Oxford). (2008) 47:1539–42. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken325
43. Kawabata, T, Komaki, H, Saito, T, Saito, Y, Nakagawa, E, Sugai, K, et al. A pediatric patient with myopathy associated with antibodies to a signal recognition particle. Brain Dev. (2012) 34:877–80. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2012.02.009
44. Zhao, Y, Liu, X, Zhang, W, and Yuan, Y. Childhood autoimmune necrotizing myopathy with anti-signal recognition particle antibodies. Muscle Nerve. (2017) 56:1181–7. doi: 10.1002/mus.25575
45. Luca, NJ, Atkinson, A, Hawkins, C, and Feldman, BM. Anti-signal recognition particle-positive juvenile polymyositis successfully treated with rituximab. J Rheumatol. (2012) 39:1483–5. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.111592
46. Momomura, M, Miyamae, T, Nozawa, T, Kikuchi, M, Kizawa, T, Imagawa, T, et al. Serum levels of anti-Srp54 antibodies reflect disease activity of necrotizing myopathy in a child treated effectively with combinatorial methylprednisolone pulses and plasma exchanges followed by intravenous cyclophosphamide. Mod Rheumatol. (2014) 24:529–31. doi: 10.3109/14397595.2013.852852
47. Kobayashi, I, Tozawa, Y, Ueki, M, Takezaki, S, Watanabe, S, Iwafuchi, H, et al. Tacrolimus in combination with methotrexate and corticosteroid for the treatment of child-onset anti-signal recognition particle antibody-positive necrotizing myopathy. Scand J Rheumatol. (2017) 46:409–10. doi: 10.1080/03009742.2016.1241297
48. Binns, EL, Moraitis, E, Maillard, S, Tansley, S, McHugh, N, Jacques, TS, et al. Effective induction therapy for anti-Srp associated myositis in childhood: a small case series and review of the literature. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. (2017) 15:77. doi: 10.1186/s12969-017-0205-x
49. Rider, LG, Miller, FW, Targoff, IN, Sherry, DD, Samayoa, E, Lindahl, M, et al. A broadened spectrum of juvenile myositis. Myositis-specific autoantibodies in Children. Arthritis Rheum. (1994) 37:1534–8. doi: 10.1002/art.1780371019
50. Rider, LG, Shah, M, Mamyrova, G, Huber, AM, Rice, MM, Targoff, IN, et al. The myositis autoantibody phenotypes of the juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Medicine (Baltimore). (2013) 92:223–43. doi: 10.1097/MD.0b013e31829d08f9
51. Rouster-Stevens, KA, and Pachman, LM. Autoantibody to signal recognition particle in African American girls with juvenile polymyositis. J Rheumatol. (2008) 35:927–9.
52. Takada, T, Hirakata, M, Suwa, A, Kaneko, Y, Kuwana, M, Ishihara, T, et al. Clinical and histopathological features of myopathies in Japanese patients with anti-Srp autoantibodies. Mod Rheumatol. (2009) 19:165. doi: 10.3109/s10165-009-0165-1
53. Hou, Y, Shao, K, Zhao, B, Dai, T, Wang, Q, Zhao, Y, et al. Juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies with anti-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase antibodies in a Chinese cohort. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2021) 27:1041–7. doi: 10.1111/cns.13658
54. Allenbach, Y, Keraen, J, Bouvier, AM, Jooste, V, Champtiaux, N, Hervier, B, et al. High risk of cancer in autoimmune necrotizing myopathies: usefulness of myositis specific antibody. Brain. (2016) 139:2131–5. doi: 10.1093/brain/aww054
55. Kadoya, M, Hida, A, Hashimoto Maeda, M, Taira, K, Ikenaga, C, Uchio, N, et al. Cancer association as a risk factor for anti-Hmgcr antibody-positive myopathy. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. (2016) 3:e290. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000290
56. Williams, B, Horn, MP, Banz, Y, Feldmeyer, L, and Villiger, PM. Cutaneous involvement in anti-Hmgcr positive necrotizing myopathy. J Autoimmun. (2021) 123:102691. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2021.102691
57. Shimizu, T, Kondo, Y, Kanazawa, N, Kaneko, A, Tominaga, N, Nagai, M, et al. Anti-Hmgcr myopathy following acute Epstein-Barr virus infection. Muscle Nerve. (2020) 61:E5–8. doi: 10.1002/mus.26729
58. Barp, A, Velardo, D, Ciscato, P, Sansone, VA, and Lunetta, C. Anti-Hmgcr myopathy misdiagnosed as motor neuron disease and complicated with Covid-19 infection. Neurol Sci. (2021) 42:1679–82. doi: 10.1007/s10072-021-05146-w
59. Dodig, D, Fritzler, MJ, Naraghi, A, Tarnopolsky, MA, and Lu, JQ. Immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy after Bnt162b2 vaccination in a patient with antibodies against receptor-binding domain of Sars-Cov-2 and signal recognition particle. Muscle Nerve. (2022) 65:E11–3. doi: 10.1002/mus.27483
60. Pinal-Fernandez, I, Casal-Dominguez, M, Carrino, JA, Lahouti, AH, Basharat, P, Albayda, J, et al. Thigh muscle Mri in immune-mediated necrotising myopathy: extensive oedema, early muscle damage and role of anti-Srp autoantibodies as a marker of severity. Ann Rheum Dis. (2017) 76:681–7. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210198
61. Zheng, Y, Liu, L, Wang, L, Xiao, J, Wang, Z, Lv, H, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging changes of thigh muscles in myopathy with antibodies to signal recognition particle. Rheumatology (Oxford). (2015) 54:1017–24. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keu422
62. Day, JA, Bajic, N, Gentili, S, Patel, S, and Limaye, V. Radiographic patterns of muscle involvement in the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Muscle Nerve. (2019) 60:549–57. doi: 10.1002/mus.26660
63. Landon-Cardinal, O, Koumako, C, Hardouin, G, Granger, B, Reyngoudt, H, Boisserie, JM, et al. Severe axial and pelvifemoral muscle damage in immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy evaluated by whole-body Mri. Semin Arthritis Rheum. (2020) 50:1437–40. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2020.02.009
64. Uruha, A, Goebel, HH, and Stenzel, W. Updates on the immunopathology in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Curr Rheumatol Rep. (2021) 23 56:1–7. doi: 10.1007/s11926-021-01017-7
65. Tanboon, J, and Nishino, I. Classification of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: pathology perspectives. Curr Opin Neurol. (2019) 32:704–14. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000740
66. Allenbach, Y, Arouche-Delaperche, L, Preusse, C, Radbruch, H, Butler-Browne, G, Champtiaux, N, et al. Necrosis in anti-Srp(+) and anti-Hmgcr(+)myopathies: role of autoantibodies and complement. Neurology. (2018) 90:e507–17. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004923
67. Girolamo, F, Lia, A, Annese, T, Giannini, M, Amati, A, D'Abbicco, D, et al. Autophagy markers Lc3 and P62 accumulate in immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy. Muscle Nerve. (2019) 60:315–27. doi: 10.1002/mus.26608
68. Fischer, N, Preusse, C, Radke, J, Pehl, D, Allenbach, Y, Schneider, U, et al. Sequestosome-1 (P62) expression reveals chaperone-assisted selective autophagy in immune-mediated necrotizing myopathies. Brain Pathol. (2020) 30:261–71. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12772
69. Damoiseaux, J, Mammen, AL, Piette, Y, Benveniste, O, and Allenbach, Y. Group EtWS. 256(Th) Enmc international workshop: myositis specific and associated autoantibodies (Msa-ab): Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 8-10 October 2021. Neuromuscul Disord. (2022) 32, 32:594–608. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2022.05.011
70. Rodriguez Cruz, PM, Luo, YB, Miller, J, Junckerstorff, RC, Mastaglia, FL, and Fabian, V. An analysis of the sensitivity and specificity of Mhc-I and Mhc-ii immunohistochemical staining in muscle biopsies for the diagnosis of inflammatory myopathies. Neuromuscul Disord. (2014) 24:1025–35. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2014.06.436
71. Yin, X, Wang, Q, Chen, T, Niu, J, Ban, R, Liu, J, et al. Cd4+ cells, macrophages, Mhc-I and C5b-9 involve the pathogenesis of dysferlinopathy. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. (2015) 8:3069–75.
72. Oldroyd, AGS, Lilleker, JB, Amin, T, Aragon, O, Bechman, K, Cuthbert, V, et al. British Society for Rheumatology Guideline on Management of Paediatric, adolescent and adult patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. Rheumatology (Oxford). (2022) 61:1760–8. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac115
73. Kishi, T, Warren-Hicks, W, Bayat, N, Targoff, IN, Huber, AM, Ward, MM, et al. Corticosteroid discontinuation, complete clinical response and remission in juvenile dermatomyositis. Rheumatology (Oxford). (2021) 60:2134–45. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa371
74. Zuppa, A, De Michelis, C, Meo, G, Prada, V, Gemelli, C, Infantino, M, et al. Maintenance treatment with subcutaneous immunoglobulins in the long-term management of anti-Hmcgr myopathy. Neuromuscul Disord. (2021) 31:134–8. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2020.12.012
75. Landon-Cardinal, O, Allenbach, Y, Soulages, A, Rigolet, A, Hervier, B, Champtiaux, N, et al. Rituximab in the treatment of refractory anti-Hmgcr immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy. J Rheumatol. (2019) 46:623–7. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.171495
76. Valiyil, R, Casciola-Rosen, L, Hong, G, Mammen, A, and Christopher-Stine, L. Rituximab therapy for myopathy associated with anti-signal recognition particle antibodies: a case series. Arthritis Care Res. (2010) 62:1328–34. doi: 10.1002/acr.20219
Keywords: immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy, HMGCR, SRP, idiopathic inflammatory myopathy, juvenile myositis
Citation: Wang C-H and Liang W-C (2023) Pediatric immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy. Front. Neurol. 14:1123380. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1123380
Edited by:
Merrilee Needham, Fiona Stanley Hospital, AustraliaReviewed by:
Paulo Victor Sgobbi Souza, Federal University of São Paulo, BrazilCopyright © 2023 Wang and Liang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wen-Chen Liang, d2VuLmNoZW4ubGlhbmdAZ21haWwuY29t
 Chen-Hua Wang
Chen-Hua Wang Wen-Chen Liang
Wen-Chen Liang