
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Cell. Neurosci. , 22 November 2021
Sec. Cellular Neuropathology
Volume 15 - 2021 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.782716
This article is a correction to:
IRSp53 Deletion in Glutamatergic and GABAergic Neurons and in Male and Female Mice Leads to Distinct Electrophysiological and Behavioral Phenotypes
A Corrigendum on
IRSp53 Deletion in Glutamatergic and GABAergic Neurons and in Male and Female Mice Leads to Distinct Electrophysiological and Behavioral Phenotypes
by Kim, Y., Noh, Y. W., Kim, K., Yang, E., Kim, H., and Kim, E. (2020). Front. Cell Neurosci. 14:23. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00023
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 3 as published. It was due to an inadvertent mistake in the quantification process. The new quantification indicates that there is no statistical difference in the NMDA/AMPA ratio between WT and IRSp53-KO mice; previous Figure 3C indicated a decrease in the mutant mice. The correct Figure 3 and legend appears below.
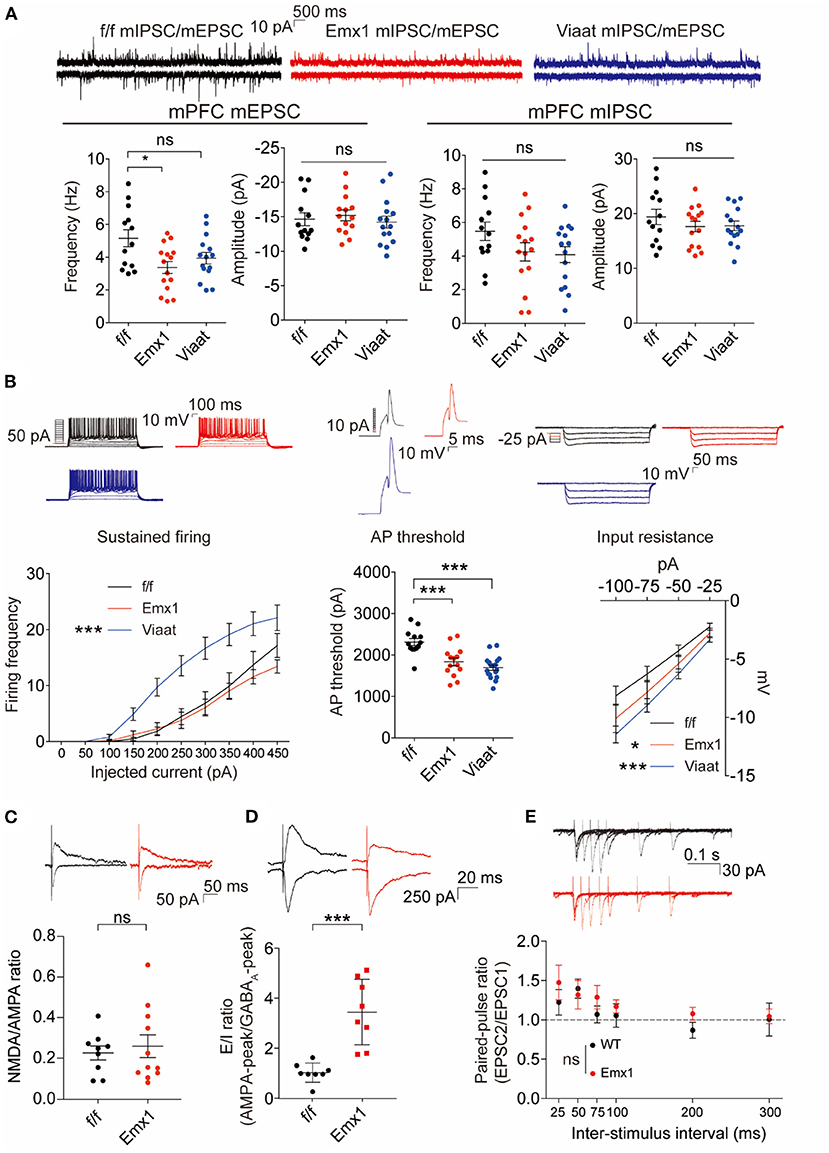
Figure 3. Emx1-Cre;Irsp53fl/fl and Viaat-Cre;Irsp53fl/fl mice show distinct changes in synaptic transmission and intrinsic excitability in medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) pyramidal neurons. (A) Miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs) and miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents (mIPSCs) in layer V pyramidal neurons in the prelimbic region of the mPFC in Emx1-Cre;Irsp53fl/fl and Viaat-Cre;Irsp53fl/fl mice (3 months; male). Note that the frequency of mEPSCs is significantly decreased in Emx1-Cre;Irsp53fl/fl mice. n = 13 neurons from three mice for f/f-mEPSC, 14, 3 for Emx1-mEPSC, 15, 3 for Viaat-mEPSC, 13, 3 for f/f-mIPSC, 15, 3 for Emx1-mIPSC, and 15, 3 for Viaat-mIPSC, *P < 0.05, ns, not significant, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's test. mEPSC frequency, F(2, 39) = 4.119; mEPSC amplitude, F(2, 39) = 0.342; mIPSC frequency, F(2, 40) = 2.012; mIPSC amplitude, F(2, 40) = 0.7806. (B) Intrinsic excitability in layer V pyramidal neurons in the prelimbic region of the mPFC in Emx1-Cre;Irsp53fl/fl and Viaat-Cre;Irsp53fl/fl mice (3 weeks; male). Note that intrinsic excitability is increased both in Emx1-Cre;Irsp53fl/fl and Viaat-Cre;Irsp53fl/fl mice. n = 13, 3 for f/f-firing frequency, 14, 3 for Emx1-firing frequency, 18, 3 for Viaat-firing frequency, 13, 3 for f/f-AP threshold, 14, 3 for Emx1-AP threshold, 18, 3 for Viaat-AP threshold, 13, 3 for f/f-input resistance, 14,3 for Emx1-input resistance, 18, 3 for Viaat-input resistance, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's test for AP threshold, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's test for firing frequency and input resistance. Sustained firing, interaction F(18, 420) = 3.165, current F(9, 420) = 61.89, genotype F(2, 420) = 56.73; action potential threshold, F(2, 42) = 16.14; input resistance, interaction F(6, 168) = 0.5088, current F(3, 168) = 60.88, genotype F(2, 168) = 11.33. (C) Normal ratio of evoked N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDAR)-EPSCs and AMPA receptor (AMPAR)-EPSCs in Emx1-Cre;Irsp53fl/fl layer V pyramidal neurons in the prelimbic region of the mPFC (2 months; male). n = 9 neurons for three mice for f/f, 11, 3 for Emx1, ns, not significant, Student's t-test, t = 0.2447, df = 18. (D) Increased ratio of evoked EPSCs and IPSCs in Emx1-Cre;Irsp53fl/fl layer V pyramidal neurons in the prelimbic region of the mPFC (2 months; male). n = 8 neurons for three mice for f/f, 8, 3 for Emx1, ***P < 0.001, Student's t-test, t = 5.019, df = 14. (E) Normal paired-pulse ratio in Emx1-Cre;Irsp53fl/fl layer V pyramidal neurons in the prelimbic region of the mPFC (2 months; male). n = 10 neurons for three mice for f/f, 9, 3 for Emx1, ns, not significant, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's test, interaction F(5, 85) = 0.6379, time F(5, 85) = 4.100, genotype F(1, 17) = 0.7348.
To reflect this change a correction has also been made to the Results, Emx1-Cre; Irsp53fl/fl and Viaat-Cre; Irsp53fl/fl Mice Show Distinct Changes in Synaptic Transmission and Intrinsic Excitability in mPFC Pyramidal Neurons, Second paragraph:
“When evoked synaptic transmission was measured, the ratio of NMDAR-mediated EPSCs and AMPA receptor (AMPAR)-mediated EPSCs was not altered in Emx1-Cre; Irsp53fl/fl layer V pyramidal neurons (Figure 3C). These results collectively suggest that Irsp53 deletion in glutamatergic neurons leads to reduced spontaneous excitatory but not inhibitory synaptic transmission, increased ratio of evoked EPSCs/IPSCs, and increased neuronal excitability without affecting evoked NMDAR-EPSC/AMPAR-EPSC ratio in layer V mPFC neurons.”
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: autism, synapse, IRSp53, mPFC, social interaction, hyperactivity
Citation: Kim Y, Noh YW, Kim K, Yang E, Kim H and Kim E (2021) Corrigendum: IRSp53 Deletion in Glutamatergic and GABAergic Neurons and in Male and Female Mice Leads to Distinct Electrophysiological and Behavioral Phenotypes. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 15:782716. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.782716
Received: 24 September 2021; Accepted: 15 October 2021;
Published: 22 November 2021.
Edited and reviewed by: Lei Shi, Jinan University, China
Copyright © 2021 Kim, Noh, Kim, Yang, Kim and Kim. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Eunjoon Kim, a2ltZUBrYWlzdC5hYy5rcg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.