Comprehensive Evaluation of White Matter Damage and Neuron Death and Whole-Transcriptome Analysis of Rats With Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion
- 1Department of Neurology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China
- 2Department of Neurology, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China
- 3Department of Urology, Xijing Hospital, The Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an, China
- 4Medical Imaging Center, The First Affiliated Hospital, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China
A Corrigendum on
Comprehensive Evaluation of White Matter Damage and Neuron Death and Whole-Transcriptome Analysis of Rats With Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion
by Li, W., Wei, D., Liang, J., Xie, X., Song, K., and Huang, L. (2019). Front. Cell. Neurosci. 13:310. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00310
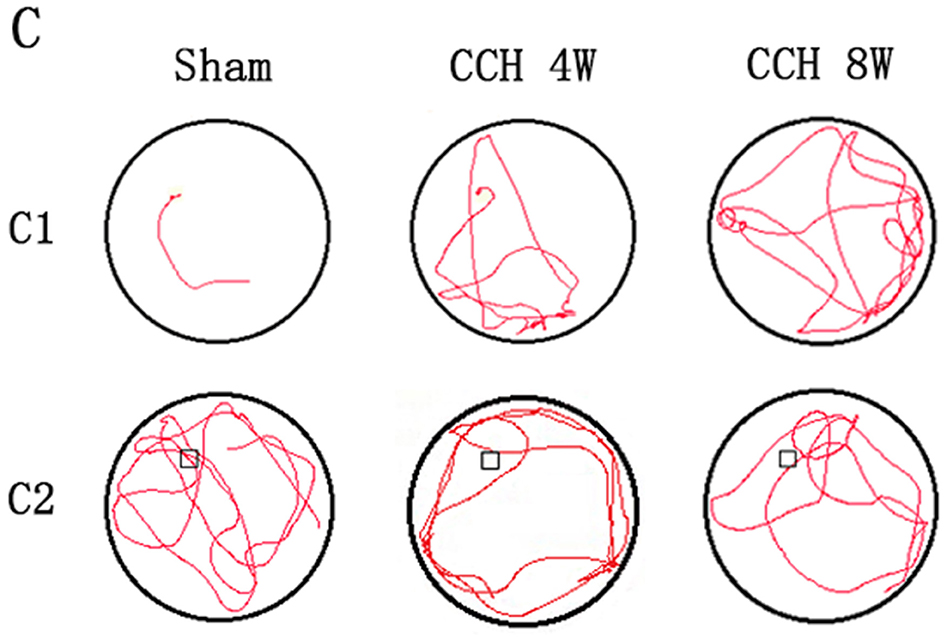
In the original article, there was a mistake in **Figure 2C2** as published. **The third image in original Figure 2C2 was incorrect**. The corrected **Figure 2C2** appears below.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: chronic cerebral hypoperfusion, white matter damage, neuron death, whole-transcriptome, vascular dementia
Citation: Li W, Wei D, Liang J, Xie X, Song K and Huang L (2020) Corrigendum: Comprehensive Evaluation of White Matter Damage and Neuron Death and Whole-Transcriptome Analysis of Rats With Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 14:616236. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.616236
Received: 11 October 2020; Accepted: 27 October 2020;
Published: 11 December 2020.
Edited and reviewed by: Dirk M. Hermann, University of Duisburg-Essen, Germany
Copyright © 2020 Li, Wei, Liang, Xie, Song and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Li'an Huang, aHVhbmdsaWFuMTMwNiYjeDAwMDQwOzEyNi5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Wenxian Li1,2†
Wenxian Li1,2† Jianye Liang
Jianye Liang Kangping Song
Kangping Song Li'an Huang
Li'an Huang