- 1State Key Laboratory of Advanced Technology for Materials Synthesis and Processing, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, China
- 2School of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 3Laboratory of Solar Fuel, Faculty of Materials Science and Chemistry, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China
Photocatalytic CO2 reduction is a promising method to mitigate the greenhouse effect and energy shortage problem. Development of effective photocatalysts is vital in achieving high photocatalytic activity. Herein, the S-scheme heterojunctions composed by BiOBr and g-C3N4 with or without S doping are thoroughly investigated for CO2 reduction by density functional theory (DFT) calculation. Work function and charge density difference demonstrate the existence of a built-in electric field in the system, which contributes to the separation of photogenerated electron-hole pairs. Enhanced strength of a built-in electric field is revealed by analysis of Bader charge and electric field intensity. The results indicate that S doping can tailor the electronic structures and thus improve the photocatalytic activity. According to the change in absorption coefficient, system doping can also endow the heterojunction with increased visible light absorption. The in-depth investigation indicates that the superior CO2 reduction activity is ascribed to low rate-determining energy. And both of the heterojunctions are inclined to generate CH3OH rather than CH4. Furthermore, S doping can further reduce the energy from 1.23 to 0.44 eV, indicating S doping is predicted to be an efficient photocatalyst for reducing CO2 into CH3OH. Therefore, this paper provides a theoretical basis for designing appropriate catalysts through element doping and heterojunction construction.
Introduction
With the development of society, the greenhouse effect has posed a great threat to human life due to excessive CO2 emission. Numerous solutions have been explored, including electrochemical Liu et al. (2016), Albo et al. (2017), thermochemical Erb and Zarzycki (2016), Gong et al. (2016), and photochemical methods (Deng et al., 2020; Deng et al., 2021; Gogoi et al., 2021; Meng et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2021b). Among them, photocatalytic methods are promising due to the sustainability of solar light (Chen et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2020b; Zhen et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2021a; Wei et al., 2021a; Zhang et al., 2021c). Specifically, photocatalytic CO2 reduction can convert CO2 into usable hydrocarbon fuels (Huo et al., 2021; Kang et al., 2021; Ke et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2021b; Zhang et al., 2021d). Even though photocatalysis shows great advantages, its application in CO2 reduction is still greatly limited because of the chemical inertness of CO2 and low visible-light utilization. Therefore, exploration of effective photocatalysts is necessary. In the past few years, various photocatalysts have been explored for photocatalytic CO2 reduction such as metals (Dong et al., 2020), metal sulfides (Suzuki et al., 2018; Ge et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2020a), metal oxides (Wang et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2021), and nonmetals (He et al., 2020; Fei et al., 2021). Despite the great progress, low visible-light absorption and poor catalytic activity are still common problems faced by these photocatalysts. Therefore, modification, especially element doping and heterojunction construction, have been widely implemented to improve the photocatalytic activity (Truc et al., 2019; Ren et al., 2020; Lian et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2021b). Through element doping and heterojunction construction, the electronic structure and recombination of photogenerated electron-hole pairs can be effectively regulated and inhibited.
As a promising metal-free polymeric photocatalyst, graphitic carbon nitride has features of good physicochemical stability, a narrow bandgap, and appropriate band potential (Wang et al., 2009; Li et al., 2020a; Xia et al., 2020; Xie et al., 2020; Li et al., 2021b; Zhang et al., 2021a). In addition, the CO2 molecule exhibits a strong affinity to pyridine nitrogen in g-C3N4, which is beneficial for CO2 reduction (Zhu et al., 2017). Construction of hybrids has also proven to be effective for g-C3N4 (Li et al., 2020b; Li et al., 2020c; Li et al., 2021a; Li et al., 2021c; Li et al., 2020d; Mei et al., 2021; Tao et al., 2021). For instance, Fu et al. designed a 2D/2D WO3/g-C3N4 composite, in which atomic-level thickness of each is realized (Fu et al., 2019). The ultrathin 2D/2D WO3/g-C3N4 is proven to be S-scheme heterojunction, exhibiting high redox capacity and improved photocatalytic activity. In addition, element doping can also have a great influence on the properties of g-C3N4 through tailoring the electronic structures (Chen et al., 2021). Tian et al. fabricated P-doped g-C3N4 by mixing melamine and diammonium hydrogenphosphate (Tian et al., 2020). It was found that the light absorption is redshifted with the increase of doping concentration which is due to the electronic redistribution by P ion doping. It can be deduced that appropriate element doping and heterojunction building is fruitful in regulating the electronic structures and improving the photocatalytic performance.
Among available photocatalysts, BiOBr is deemed to be a prominent candidate for constructing a heterojunction with g-C3N4. It has appropriate bandgap and layered structure where one (Bi2O2) slab is surrounded by the upper and lower chlorine atoms. More importantly, its unique layered structure allows the formation of 2D/2D Van der Waals heterojunction with g-C3N4. In addition, the BiOBr/g-C3N4 hybrid has already been investigated by theoretical and experimental research as photocatalysts (Jiang et al., 2018; Qu et al., 2020). It has been proven that the BiOBr/g-C3N4 hybrids show superior photocatalytic activities in degradation of dyes and organic pollutants. Even though theoretical and numerous experimental studies have been done on the BiOBr/g-C3N4, reports on CO2 reduction are lacking, and further investigation is still needed to figure out the intrinsic photocatalytic mechanism of CO2 reduction on BiOBr/g-C3N4. In addition, previous studies indicate that element doping such as S doping can promote the performance of photocatalytic CO2 reduction (Raziq et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2018; Ojha et al., 2019). It can be inferred that the introduction of S atom into BiOBr/g-C3N4 (BiOBr/S-g-C3N4) can improve the photocatalytic CO2 reduction performance.
Herein, the effect of sulfur doping on the BiOBr/g-C3N4 heterojunction is investigated by exploring electronic, optical properties, and CO2 reduction reaction. Through the theoretical calculation, comprehensive understanding of the CO2 reduction over BiOBr/g-C3N4 systems will be acquired. Furthermore, electron distribution, visible light adsorption, and CO2 reduction will also be investigated comprehensively. It is expected that this research can provide a basis for the design of novel CO2 reduction materials.
Calculation Details
Vienna ab initio simulation package (VASP) was employed for calculations (Hafner, 2008). The geometry structures were optimized utilizing the generalized gradient approximation (GGA) Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof (PBE) as exchange–correlation function (Grimme, 2006; Wu and Cohen, 2006). The DFT-D method of Grimme was selected to treat van der Waals interaction (Le et al., 2012). A 500 eV cutoff energy was adopted for the plane-wave expansion. For Brillouin-zone, a 4 × 2 × 1 Monkhorst–Pack k-point mesh was used in the geometry optimization and other properties calculation. A vacuum distance of 15 Å was used to eliminate periodic interactions between adjacent images. The convergence criteria of the geometry optimization for the energy change and maximum force were set to be 10−5 eV and 0.01 eV/Å, respectively.
In the process of constructing heterojunction, the lattice match is the key point. It is necessary to choose two components with similar cell parameters. Herein, a 1 × √3 single layered g-C3N4 is placed at the top of a 2 × 3 single-layered BiOBr for constructing 2D/2D BiOBr/g-C3N4 heterojunction. The 2D/2D BiOBr/S-g-C3N4 heterojunction is built by stacking a 1 × √3 S-g-C3N4 monolayer above a 2 × 3 BiOBr monolayer.
For CO2 reduction, the reaction processes of each step were evaluated by calculating their Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) (Han and Sohn, 2005; Yan et al., 2016), which is expressed by the following equation:
In this formula, ΔH denotes the energy difference of each reaction step gained from DFT calculation. T represents the temperature at 298.15 K ΔS and ZPE are the change of entropy and zero-point energy, respectively.
Results and Discussion
Geometric Structures
Prior to the investigation of heterojunctions, the geometric structures of monolayered g-C3N4, S-doped g-C3N4 (S-g-C3N4) and BiOBr along the (001) facet were first studied. As shown in Figure 1, the optimized lattice parameters are a = b = 7.13 Å for monolayered g-C3N4; the parameters are a = b = 3.95 Å for monolayered BiOBr. These results agree well with the experimental and theoretical results (Zhao and Dai, 2014; Bai et al., 2016; Zhu et al., 2018). According to previous research, S atom is more inclined to substitute pyridine nitrogen on g-C3N4 (Wang et al., 2018; Ghashghaee et al., 2020). Therefore, the doped g-C3N4 is constructed by replacing the 2-fold coordinated N atom with S atom (Figure 1B). The calculated lattice constants are a = b = 7.15 Å. Compared with the pristine g-C3N4, the S−C bonds in S-doped g-C3N4 are slightly longer than the corresponding N−C bonds because of the larger atomic radius of S atom than that of N atom. Figures 2A,B are the top and side view of optimized BiOBr/g-C3N4 heterojunction; Figures 2C,D depict the top and side view of optimized BiOBr/S-g-C3N4 heterojunction. The equilibrium distance between g-C3N4 and BiOBr in BiOBr/g-C3N4 is 2.66 Å, while it is 2.64 Å in BiOBr/S-g-C3N4. The equilibrium distance of these two heterojunctions exhibits the feature of van der Waals (vdW) heterojunction, indicating that a vdW interaction is established between (S-doped) g-C3N4 and BiOBr. Moreover, it can be seen clearly that the g-C3N4 in both heterojunctions changes from a planar structure to a curved structure, indicating there is an interaction between g-C3N4 and BiOBr.
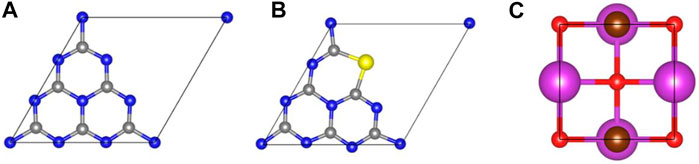
FIGURE 1. Optimized geometric structures of monolayered g-C3N4, S-g-C3N4, and BiOBr. The C, N, S, Bi, O, and Br atoms are represented by the grey, blue, yellow, purple, orange, and brown balls, respectively.
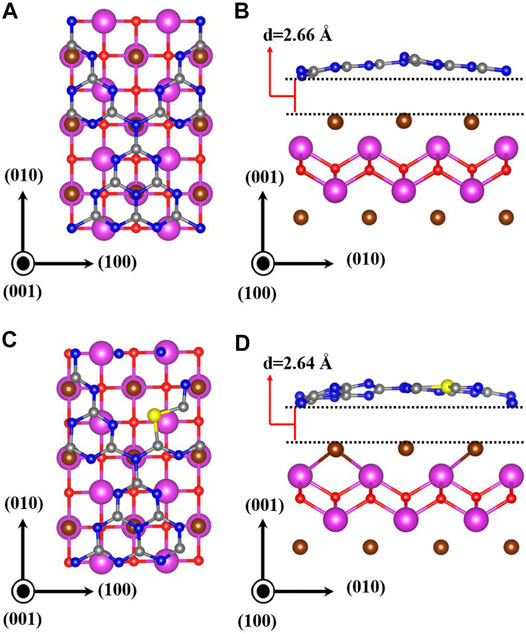
FIGURE 2. Optimized geometric structures of BiOBr/g-C3N4 and BiOBr/S-g-C3N4 heterojunctions. (A) and (C) are the top view; (B) and (D) are the side view.
In addition, the thermodynamic stability of BiOBr/(S-doped)g-C3N4 heterojunctions is evaluated by calculating the formation energy based on the following equations:
where EH is the total energy of BiOBr/g-C3N4 or BiOBr/S-g-C3N4 heterojunction, EA represents total energy of pure or S-doped g-C3N4, and EB represents the total energy of BiOBr. A more negative value of binding energy suggests a more stable structure. The calculated formation energies of BiOBr/g-C3N4 and BiOBr/S-g-C3N4 are −0.52 and −0.63 eV, respectively, demonstrating that both the constructed heterojunctions are stable.
Work Function
As an important criterion to judge charge transfer, the work function is equivalent to the gap between Fermi level and vacuum level. It is expressed by the following formula:
where Evac and EF represent vacuum level and Fermi level, respectively. The work functions of g-C3N4, S-doped g-C3N4, and BiOBr are obtained and shown in Figure 3. The calculated Φ of g-C3N4 is 4.62 eV, consistent with the previous results (Mahmood et al., 2020). After the introduction of S atom, the work function is reduced to 3.96 eV. This is mainly due to the fact that S atoms own more valence electrons than N atoms, which can raise the Fermi level. In addition, it is found that the Fermi level of BiOBr (6.40 eV) is lower than those of g-C3N4 and S-g-C3N4. Therefore, it can be deduced that the electrons will flow from the pure and S-doped g-C3N4 to the BiOBr until reaching the uniform Fermi level.
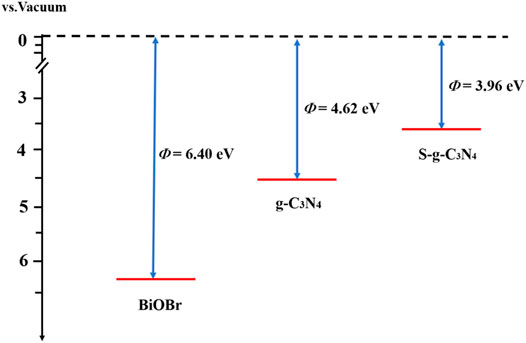
FIGURE 3. The calculated work functions of BiOBr, g-C3N4, and S-g-C3N4. The red and black dotted lines signify the Fermi level and vacuum energy level, respectively.
Charge Density Difference
To intuitively reflect the charge transfer and separation between different constituents, the charge density difference is calculated by:
where ρ[BiOBr/(S-doped)-g-C3N4], ρ[(S-doped)-g-C3N4], and ρ(BiOBr) are the charge densities of S-doped or pure BiOBr/g-C3N4 hybrids, S-doped or pure g-C3N4, and BiOBr, respectively. Figure 4 depicts the charge density difference of hybrid systems along Z axis. The charge depiction and accumulation are marked by blue and yellow regions, respectively. It is obvious that the surface of S-doped and pure g-C3N4 are mainly covered by the blue region, while the BiOBr surface is dominant by the yellow region. Therefore, the electrons transfer from S-doped and pure g-C3N4 to BiOBr in the heterojunctions, which agrees well with the analysis of aforementioned work function. Particularly, the blue and yellow coverage areas in the S-doped hybrids are broader than those in the pure hybrids, indicating that S doping brings about a stronger interface interaction. In addition, the Bader charge is calculated to quantitatively investigate the charge transfer. It is found that there are 0.08 electrons transferring from g-C3N4 to BiOBr. As for the S doping counterpart, the number of charge transfers from S-doped g-C3N4 to BiOBr increases to 0.15 e. This further confirms that the introduction of S atom to the hybrid can have a great effect on increasing interfacial electron transfer.
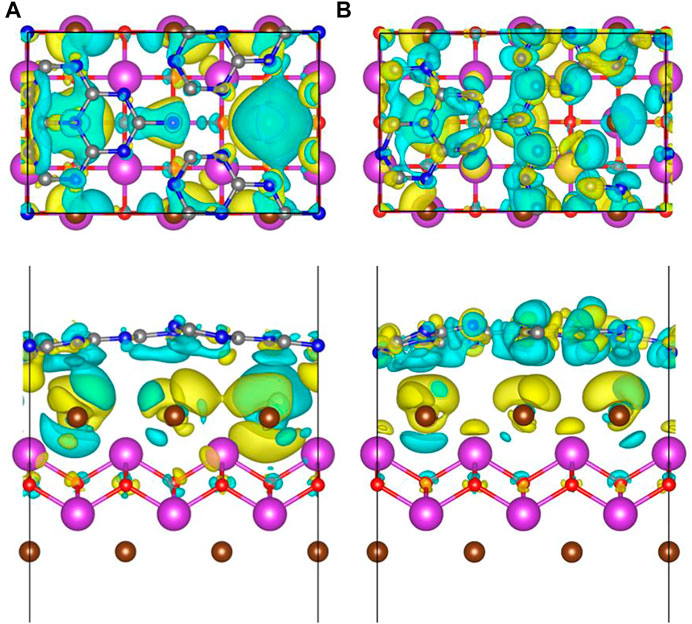
FIGURE 4. The top and side view of charge density difference in (A) BiOBr/g-C3N4 and (B) BiOBr/S-g-C3N4. The blue and yellow areas represent charge consumption and accumulation, respectively. The isosurface value was 0.3 e⋅nm−3.
Strength of Built-in Electric Field
Electron transfer results in uneven charge distribution at the interface, thus forming a polarized electric field at the hybrid’s interface. As an important physical quality, the electric field has a great correlation with band bending and separation of photogenic electrons and holes. The strength of the built-in field can be evaluated by the following equation:
Herein, P is the dipole moment; ε is the dielectric constant which is equal to 8.85 × 10−12 Fm−1; S represents the surface area of heterojunctions; and d represents the interfacial distance of heterojunctions. The calculated E value for doped and non-doped hybrid is 2.56 × 109 and 0.64 × 109 Vm−1, respectively. Obviously, the electric field intensity of S-doped heterogeneous junction is greatly improved. This improvement is mainly attributed to the magnitude of p value, which is related to the number of electron transfers at the interface. Following the above analysis of charge transfer, the BiOBr/S-g-C3N4 exhibits more electron transfer at the interface, thus leading to a larger dipole moment and stronger electric field intensity.
Optical Absorption
To explore the influence of doping and heterojunction construction on light absorption, the absorption coefficient α(ω) is calculated according to equation:
where ε1 and ε2 denote the real and imaginary parts of dielectric function, respectively. ω is the optical frequency which determines the dielectric functions. Figure 5 describes the calculated absorption spectra of g-C3N4, S-g-C3N4, BiOBr/g-C3N4, and BiOBr/S-g-C3N4. In the visible light range (1.5–3.1 eV), the light absorption intensity is ordered by BiOBr/S-g-C3N4 > BiOBr/g-C3N4 > S-g-C3N4 > g-C3N4. There are obvious red shift and enhanced light absorption intensity for S-g-C3N4, BiOBr/g-C3N4 relative to pure g-C3N4. Moreover, the strongest visible light absorption occurs in BiOBr/S-g-C3N4 heterojunction which further verifies the positive effect of element doping and heterojunction constructing on optical property. Therefore, both the S doping and heterojunction construction of g-C3N4 with BiOBr can improve the visible light absorption.
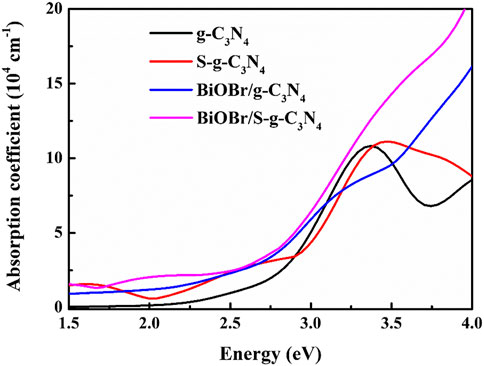
FIGURE 5. Optical absorption coefficients of single layered g-C3N4, single layered S-g-C3N4, BiOBr/g-C3N4, and BiOBr/S-g-C3N4 heterojunction.
Photocatalytic Mechanism
Based on the aforesaid results, it is found that the S atom can elevate the Fermi level of g-C3N4, thus enhancing the strength of the built-in electric field of BiOBr/g-C3N4 heterojunction. To further explore the reasons for photocatalytic activity enhancement, the photocatalytic mechanism is interpreted comprehensively (Figure 6). According to the analysis of work function, before contact, the g-C3N4 possesses a higher Fermi level than the BiOBr. Upon contact, the electrons will transfer from g-C3N4 to the BiOBr until Fermi level is equalized. The electron flow leads to a built-in electric field pointing to BiOBr and band bending of each component. Upon light illumination, the electrons on the valance band (VB) are excited to the conduction band (CB), leaving the photogenerated holes in the VB. Under the effect of internal electric field and band bending, the holes in the g-C3N4 VB will combine with the electrons in the BiOBr CB at the interface. The electrons with strong reduction ability are reserved in the g-C3N4 CB for CO2 reduction; holes with superior oxidation capacity in the BiOBr VB survive for oxidation reactions such as pollutant degradation. Therefore, BiOBr/g-C3N4 heterojunction follows the S-scheme photocatalytic mechanism. After the introduction of S atom, the doped heterojunction still follows the S-scheme photocatalytic mechanism. And the main difference between the S-doped and undoped one is their interface interaction.
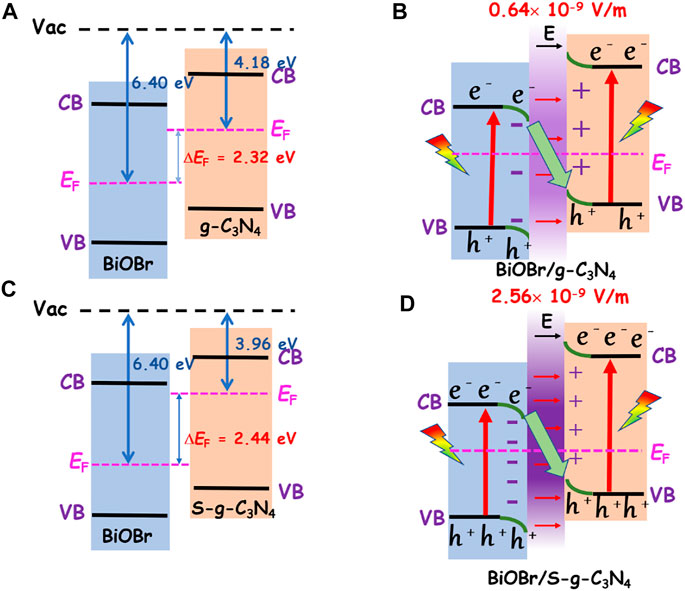
FIGURE 6. (A) and (B) are the charge transfer mechanism in BiOBr/g-C3N4 before and after contact, while (C) and (D) are the charge transfer mechanism in BiOBr/S-g-C3N4 before and after contact.
Specifically, the S atom enlarges the Fermi level difference between BiOBr and g-C3N4 by 0.12 eV, which induces more interfacial electron transfer. Consequently, an increased interfacial field (2.56 × 10−9 V/m) is established. In general, the elevated Fermi level of S-doped heterojunction generates a stronger interfacial field, which provides a stronger force for the recombination of electrons and holes than the non-doped counterpart. Additionally, it also leads to more effective separation of electrons and holes. To sum up, the introduction of S atom can promote the photocatalytic activity by facilitating charge separation.
CO2 Reduction
The above analysis indicates that the S atom doping can regulate electric fields and increase light absorption. In this regard, the heterojunction with S doping is expected to be a preferable photocatalyst for CO2 reduction. Through the investigation of the reaction mechanisms, as well as identification of active sites and reduction products of BiOBr/g-C3N4 with or without S doping for CO2 reduction, we will have a profound understanding of CO2 reduction reaction.
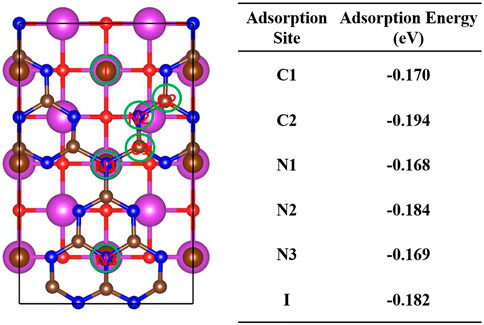
As the initial step for CO2 reduction, the absorption of CO2 attaches importance to the further reduction processes. It is critical to find the active sites for CO2 molecules. According to the photocatalytic mechanism of the BiOBr/(S-doped)g-C3N4 heterojunction, the photogenerated electrons for CO2 reduction are mainly on the surface of g-C3N4. Thus, the CO2 reaction process proceeds on the (S-doped) g-C3N4 side of BiOBr/g-C3N4. As shown in Figure 7, various possible adsorption sites on the g-C3N4 side of BiOBr/g-C3N4 are considered by comparing their adsorption energy. For convenience, different kinds of C and N atoms are labeled as C1, C2, C3, N1, and N2, respectively. It is found that the C2 and N2 atoms exhibit more negative adsorption energy than the rest, indicating higher affinity to CO2. In addition, after the structure optimization, the CO2 molecule adsorbed on the C2 site inclines to move over the N2 atom, indicating that the N2 position is the most favorable site for CO2 adsorption. Thus, the two coordination N atoms are selected to be the active sites for the initial CO2 adsorption, in agreement with the previous studies (Zhu et al., 2017). For the BiOBr/S-g-C3N4, the C2, N2, and S positions are selected as potential active sites. The calculated absorption energy for C2, N2, and S are −0.10, −0.17, and −0.14 eV, respectively. After S doping, judging from absorption energy, the two coordination N atoms still preserve the strongest affinity for CO2 molecules. Thus, the N2 atom in the BiOBr/S-g-C3N4 is also treated as the initial active site. In general, both the pure and S-doped BiOBr/g-C3N4 exhibit strong CO2 adsorption capacity, which is beneficial for the subsequent reduction reaction.
After the CO2 adsorption, the following reduction processes can proceed by a hydrogenation step on the C or O atom. All the possible intermediates and reaction paths are listed in Figure 8. The most favorable reaction pathways of CO2 reduction to CH3OH or CH4 are obtained by comparing their free energy of each step. For the pure BiOBr/g-C3N4, the scheme and the most stable structure of the optimal path for CO2 reduction are depicted in Figure 9. The first step of the reaction is the hydrogenation of CO2 into COOH* with a free energy of 1.23 eV. In terms of the whole barrier diagram, this step is deemed to be the rate-limiting step with the highest energy barrier, which is due to the inertness of CO2 molecules, and similar results have been found in other studies (Zhi et al., 2019). After the generation of COOH*, the following step is related to the acquisition of CO and HCOOH by a dehydroxylation or hydrogenation step of COOH*, respectively. The respective free energy for CO and HCOOH formation is calculated to be −0.51 and −1.12 eV, indicating that both processes are exothermic and spontaneous. Moreover, the more negative ΔG of HCOOH generation manifests that the formation of HCCOH is more competitive relative to that of CO. The desorption ability of the two intermediates is further investigated to evaluate whether they are intermediates or final products. The calculated adsorption energy for HCOOH and CO are −0.78 and −0.14 eV, respectively. The interaction between HCOOH and catalyst is strong due to the more negative adsorption energy, indicating that the HCOOH is more likely to be intermediate for the next reduction. By contrast, the CO inclines to desorb from the catalyst surface. Therefore, we focus the subsequent reaction on the hydrogenation and dehydration of HCOOH. The calculated ΔG from HCOOH to HCO* is 0.64 eV, suggesting an endothermic process. During the process of HCO* protonation, the reaction free energy of H2CO and CHOH* differs considerably. The energy barrier for H2CO formation is −0.22 eV, while that for CHOH* is 1.93 eV, which is apparently a non-spontaneous process. Thus, the H2CO intermediate is more favorable for the next reaction. After comparing the free energy in generating H3CO* (1.23 eV) and CH2OH* (0.05 eV), the CH2OH* is selected for the latter reaction. It is worth noting that the two products, CH3OH and CH4, share the same reaction path before the formation of CH2OH*. After that, the product of CH3OH is obtained through a hydrogenation at the C of CH2OH*; while the CH4 is generated by experiencing the CH2OH*, CH2*, CH3*, and CH4 reaction path. Moreover, the rate-determining step for CH4 and CH3OH generation on the pure and S-doped heterojuncions is the same, to explore the reaction selectivity, the free energy of each reaction step is further compared. It is obvious that the protonation of CH2OH to CH3OH is a spontaneous exothermic process with a free energy of −0.51 eV, while the highest energy barrier of CH2OH to CH4 is 0.98 eV. Thus, compared with CH4, CH3OH is more liable to be the final product. On the whole, among the three reduction products, i.e. CO, CH3OH, and CH4, the BiOBr/g-C3N4 heterojunction showed stronger selectivity to CO and CH3OH than CH4.
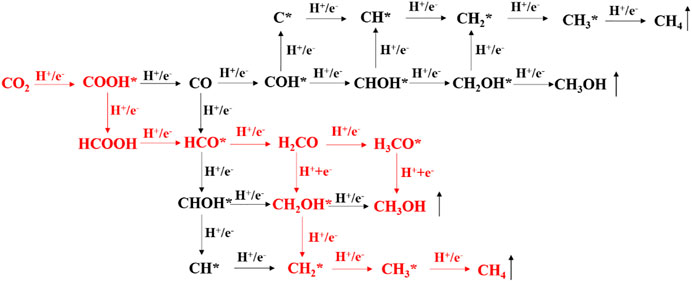
FIGURE 8. The possible reaction paths and intermediates of CO2 reduction by hydrogenation of C and O. The red part is the optimal reaction path on the BiOBr/g-C3N4 and BiOBr/S-g-C3N4.
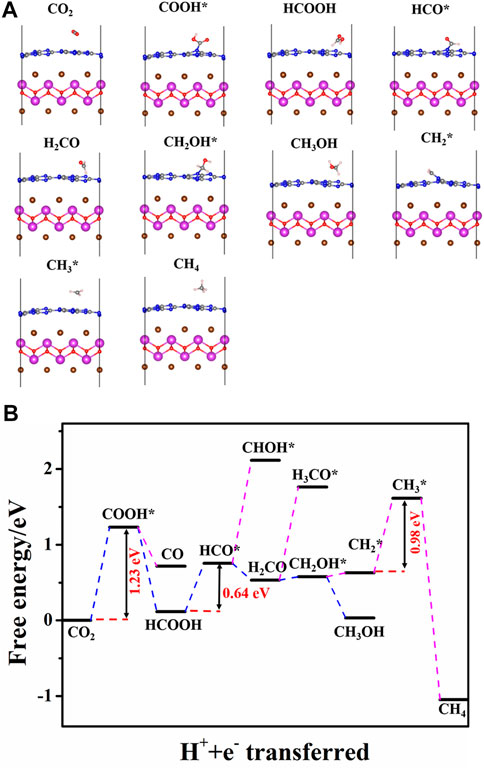
FIGURE 9. (A) Optimized structure of reaction intermediates and (B) free energy diagram on the optimal path of CO2 reduction on BiOBr/g-C3N4. The blue and red dotted lines indicate optimal and infeasible reaction paths, respectively. The white spheres represent H atoms.
Figure 10 shows the favorable free energy scheme and the most favorable adsorption geometries of the optimal path for CO2 reduction on BiOBr/S-g-C3N4. It is found that the reaction pathways for CO2 reduction to CO, CH3OH, and CH4 on S-doped hybrid are the same as those on the undoped counterpart but the reaction energy of each step is quite different. The respective optimal reaction path for the CO and CH3OH formation on the doped system still proceeds sequentially in the following order: CO2, COOH*, CO; CO2, COOH*, HCOOH, HCO*, H2CO, CH2OH*, and CH3OH. However, the formation of CH4 is obtained according to CO2, COOH*, HCOOH, HCO*, H2CO, CH2OH*, CH2*, CH3*, and CH4. For CO generation, each step of the reaction is endothermic with a rate-determining energy of 0.46 eV. It is clear that the rate-determining step for CH3OH formation on doped hybrid is the last step, namely, conversion of CH2OH* into CH3OH. Unlike it, the highest energy barrier for CH3OH on pure hybrid occurs at the first step. And the BiOBr/S-g-C3N4 possesses lower rate-determining energy (0.44 eV) than the undoped hybrid (1.24 eV). Thus, S-doped hybrid is more conductive to the CH3OH formation. Moreover, in the process of CO, CH3OH, and CH4 generation, the energy barrier of the rate-determining step of CO and CH4 is larger than that of CH3OH. Therefore, the BiOBr/S-g-C3N4 also inclines to reduce CO2 into CH3OH rather than CO and CH4.
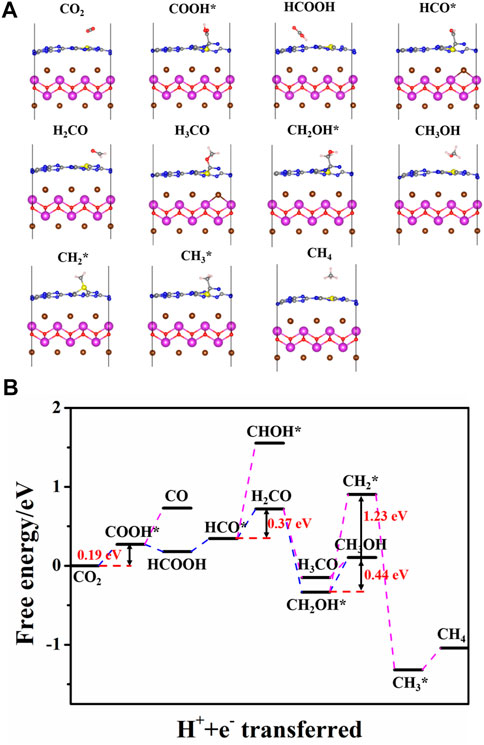
FIGURE 10. (A) Optimized structure of reaction intermediates and (B) free energy diagram on the optimal path of CO2 reduction on BiOBr/S-g-C3N4.
Conclusion
In this work, DFT calculations are adopted to investigate the geometric structure, electronic properties, and CO2 reduction mechanism of pristine and S-dopedBiOBr/g-C3N4. The charge density difference demonstrates the existence of a built-in electric field pointing to BiOBr, and the formation of S-schemeheterojunction is validated. Bader charge analysis indicates that more electrons transfer in the doped hybrids compared with the pristine one. Integrated with the calculation of the strength of thebuilt-infield, it can be inferred that S doping can enhance the interfacial electric field intensity. The improved electronic interaction is on account of the elevation of the Fermi level by S doping. Also, the computed optical absorption coefficient indicates improved visible-light absorption after S doping and construction of heterojunction. Through the investigation of CO2 reduction, it is found that both the pure and S-doped hybrids prefer to reduce CO2 to CH3OH rather than CH4. Moreover, compared with the pure heterojunction, the BiOBr/S-g-C3N4 exhibits a more superior CO2 reduction activity towards CH3OH due to the lower limiting energy. Therefore, the heterojunctions construction and nonmetal doping can lower CO2 reduction energy barrier, which will ultimately improve the photocatalytic activity. This work will provide a theoretical basis for the design of g-C3N4-based photocatalysts.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author Contributions
LZ: Conceptualization, Writing-Reviewing and Editing, Supervision. JY: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision. BZ: Software, Validation.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFB1502001), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51872220, 21905219, 51932007, U1905215, 21871217, and U1705251), the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (2021IVA137), National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents (BX20180231), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M672432), and the Hubei Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Research Post.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
Albo, J., Vallejo, D., Beobide, G., Castillo, O., Castaño, P., and Irabien, A. (2017). Copper-Based Metal-Organic Porous Materials for CO2 Electrocatalytic Reduction to Alcohols. ChemSusChem, 10, 1100–1109. doi:10.1002/cssc.201600693
Bai, Y., Chen, T., Wang, P., Wang, L., Ye, L., Shi, X., et al. (2016). Size-dependent Role of Gold in G-C3N4/BiOBr/Au System for Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction and Dye Degradation. Solar Energ. Mater. Solar Cell. 157, 406–414. doi:10.1016/j.solmat.2016.07.001
Chen, C., Jin, J., Chen, S., Wang, T., Xiao, J., and Peng, T. (2021). In-situ Growth of Ultrafine ZnO on G-C3N4 Layer for Highly Active and Selective CO2 Photoreduction to CH4 under Visible Light. Mater. Res. Bull. 137, 111177. doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2020.111177
Chen, Y., Su, F., Xie, H., Wang, R., Ding, C., Huang, J., et al. (2021). One-step Construction of S-Scheme Heterojunctions of N-Doped MoS2 and S-Doped G-C3N4 for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. Chem. Eng. J. 404, 126498. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2020.126498
Chen, Y., Wang, F., Cao, Y., Zhang, F., Zou, Y., Huang, Z., et al. (2020). Interfacial Oxygen Vacancy Engineered Two-Dimensional G-C3N4/BiOCl Heterostructures with Boosted Photocatalytic Conversion of CO2. ACS Appl. Energ. Mater. 3, 4610–4618. doi:10.1021/acsaem.0c00273
Deng, H., Fei, X., Yang, Y., Fan, J., Yu, J., Cheng, B., et al. (2021). S-scheme Heterojunction Based on P-type ZnMn2O4 and N-type ZnO with Improved Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction Activity. Chem. Eng. J. 409, 127377. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2020.127377
Deng, H., Xu, F., Cheng, B., Yu, J., and Ho, W. (2020a). Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction of C/ZnO Nanofibers Enhanced by an Ni-NiS Cocatalyst. Nanoscale. 12, 7206–7213. doi:10.1039/c9nr10451h
Dong, H., Zhang, X., Lu, Y., Yang, Y., Zhang, Y.-P., Tang, H.-L., et al. (2020b). Regulation of Metal Ions in Smart Metal-Cluster Nodes of Metal-Organic Frameworks with Open Metal Sites for Improved Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction Reaction. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 276, 119173. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119173
Erb, T. J., and Zarzycki, J. (2016). Biochemical and Synthetic Biology Approaches to Improve Photosynthetic CO2-fixation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 34, 72–79. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2016.06.026
Fei, X., Tan, H., Cheng, B., Zhu, B., and Zhang, L. (2020). 2D/2D Black Phosphorus/g-C3N4 S-Scheme Heterojunction Photocatalysts for CO2 Reduction Investigated Using DFT Calculations. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 37, 2010027. doi:10.3866/pku.Whxb202010027
Fu, J., Xu, Q., Low, J., Jiang, C., and Yu, J. (2019). Ultrathin 2D/2D WO3/g-C3N4 Step-Scheme H2-Production Photocatalyst. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 243, 556–565. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.11.011
Ge, H., Xu, F., Cheng, B., Yu, J., and Ho, W. (2019). S‐Scheme Heterojunction TiO 2/CdS Nanocomposite Nanofiber as H2 ‐Production Photocatalyst. ChemCatChem. 11, 6301–6309. doi:10.1002/cctc.201901486
Ghashghaee, M., Azizi, Z., and Ghambarian, M. (2020). Conductivity Tuning of Charged Triazine and Heptazine Graphitic Carbon Nitride (G-C3N4) Quantum Dots via Nonmetal (B, O, S, P) Doping: DFT Calculations. J. Phys. Chem. Sol. 141, 109422. doi:10.1016/j.jpcs.2020.109422
Gogoi, D., Makkar, P., and Ghosh, N. N. (2021). Solar Light-Irradiated Photocatalytic Degradation of Model Dyes and Industrial Dyes by a Magnetic CoFe2O4/g-C3N4 S-Scheme Heterojunction Photocatalyst. Acs Omega. 6, 4831–4841. doi:10.1021/acsomega.0c05809
Gong, F., Cai, Z., and Li, Y. (2016). Synthetic Biology for CO2 Fixation. Sci. China Life Sci. 59, 1106–1114. doi:10.1007/s11427-016-0304-2
Grimme, S. (2006). Semiempirical GGA-type Density Functional Constructed with a Long-Range Dispersion Correction. J. Comput. Chem. 27, 1787–1799. doi:10.1002/jcc.20495
Hafner, J. (2008). Ab-initiosimulations of Materials Using VASP: Density-Functional Theory and beyond. J. Comput. Chem. 29, 2044–2078. doi:10.1002/jcc.21057
Han, G., and Sohn, H. Y. (2005). Kinetics of the Hydrogen Reduction of Silica Incorporating the Effect of Gas-Volume Change upon Reaction. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 88, 882–888. doi:10.1111/j.1551-2916.2005.00144.x
He, F., Wang, Z., Li, Y., Peng, S., and Liu, B. (2020). The Nonmetal Modulation of Composition and Morphology of g-C3N4-Based Photocatalysts. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 269, 118828. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118828
Huo, Y., Zhang, J., Dai, K., and Liang, C. (2021). Amine-Modified S-Scheme Porous G-C3N4/CdSe-Diethylenetriamine Composite with Enhanced Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction Activity. ACS Appl. Energ. Mater. 4, 956–968. doi:10.1021/acsaem.0c02896
Jiang, M., Shi, Y., Huang, J., Wang, L., She, H., Tong, J., et al. (2018). Synthesis of Flowerlike G-C3N4/BiOBr with Enhanced Visible Light Photocatalytic Activity for Dye Degradation. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 1834–1841. doi:10.1002/ejic.201800110
Kang, S., Khan, H., and Lee, C. S. (2021). CO2 Selectivity of Flower-like MoS2 Grown on TiO2 Nanofibers Coated with Acetic Acid-Treated Graphitic Carbon Nitride. Solar Energ. Mater. Solar Cell. 221, 110890. doi:10.1016/j.solmat.2020.110890
Ke, X., Zhang, J., Dai, K., Fan, K., and Liang, C. (2021). Integrated S‐Scheme Heterojunction of Amine‐Functionalized 1D CdSe Nanorods Anchoring on Ultrathin 2D SnNb2O6 Nanosheets for Robust Solar‐Driven CO2 Conversion. Sol. RRL. 5, 2000805. doi:10.1002/solr.202000805
Le, D., Kara, A., Schröder, E., Hyldgaard, P., and Rahman, T. S. (2012). Physisorption of nucleobases on graphene: a comparative van der Waals study. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 24, 424210. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/24/42/424210
Li, Q., Zhao, W., Zhai, Z., Ren, K., Wang, T., Guan, H., et al. (2020a). 2D/2D Bi2MoO6/g-C3N4 S-Scheme Heterojunction Photocatalyst with Enhanced Visible-Light Activity by Au Loading. J. Mater. Sci. Technology 56, 216–226. doi:10.1016/j.jmst.2020.03.038
Li, Y., Li, X., Zhang, H., Fan, J., and Xiang, Q. (2020b). Design and Application of Active Sites in G-C3N4-Based Photocatalysts. J. Mater. Sci. Technology 56, 69–88. doi:10.1016/j.jmst.2020.03.033
Li, Y., Zhou, M., Cheng, B., and Shao, Y. (2020c). Recent Advances in G-C3N4-Based Heterojunction Photocatalysts. J. Mater. Sci. Technology 56, 1–17. doi:10.1016/j.jmst.2020.04.028
Li, H., Li, F., Yu, J., and Cao, S. (2021a). 2D/2D FeNi-LDH/g-C3N4 Hybrid Photocatalyst for Enhanced CO2 Photoreduction. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 37, 2010073. doi:10.3866/pku.Whxb202010073
Li, X., Liu, J., Huang, J., He, C., Feng, Z., Chen, Z., et al. (2021b). All Organic S-Scheme Heterojunction PDI-Ala/S-C3N4 Photocatalyst with Enhanced Photocatalytic Performance. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 37, 2010030. doi:10.3866/pku.Whxb202010030
Li, Y., Zhang, M., Zhou, L., Yang, S., Wu, Z., and Ma, Y. (2021c). Recent Advances in Surface-Modified G-C3N4-Based Photocatalysts for H2 Production and CO2 Reduction. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 37, 2009030. doi:10.3866/pku.Whxb202009030
Lian, X., Xue, W., Dong, S., Liu, E., Li, H., and Xu, K. (2021). Construction of S-Scheme Bi2WO6/g-C3N4 Heterostructure Nanosheets with Enhanced Visible-Light Photocatalytic Degradation for Ammonium Dinitramide. J. Hazard. Mater. 412, 125217. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125217
Liu, J., Wei, X., Sun, W., Guan, X., Zheng, X., and Li, J. (2021a). Fabrication of S-Scheme CdS-G-C3N4-Graphene Aerogel Heterojunction for Enhanced Visible Light Driven Photocatalysis. Environ. Res. 197, 111136. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2021.111136
Liu, L., Hu, T., Dai, K., Zhang, J., and Liang, C. (2021b). A Novel Step-Scheme BiVO4/Ag3VO4 Photocatalyst for Enhanced Photocatalytic Degradation Activity under Visible Light Irradiation. Chin. J. Catal. 42, 46–55. doi:10.1016/s1872-2067(20)63560-4
Liu, M., Pang, Y., Zhang, B., De Luna, P., Voznyy, O., Xu, J., et al. (2016). Enhanced Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction via Field-Induced Reagent Concentration. Nature. 537, 382–386. doi:10.1038/nature19060
Liu, X., Gu, S., Zhao, Y., Zhou, G., and Li, W. (2020). BiVO4, Bi2WO6 and Bi2MoO6 Photocatalysis: A Brief Review. J. Mater. Sci. Technology 56, 45–68. doi:10.1016/j.jmst.2020.04.023
Mahmood, A., Shi, G., Wang, X., Xie, X., and Sun, J. (2020). Photocatalytic properties of novel two-dimensional B4C3/g-C3N4 van der Waals heterojunction with moderate bandgap and high carrier mobility: A theoretical study. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 278, 119310. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119310
Mei, F., Zhang, J., Liang, C., and Dai, K. (2021). Fabrication of Novel CoO/porous Graphitic Carbon Nitride S-Scheme Heterojunction for Efficient CO2 Photoreduction. Mater. Lett. 282, 128722. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128722
Meng, A., Cheng, B., Tan, H., Fan, J., Su, C., and Yu, J. (2021). TiO2/polydopamine S-Scheme Heterojunction Photocatalyst with Enhanced CO2-reduction Selectivity. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 289, 120039. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120039
Ojha, N., Bajpai, A., and Kumar, S. (2019). Visible Light-Driven Enhanced CO2 Reduction by Water over Cu Modified S-Doped G-C3N4. Catal. Sci. Technol. 9, 4598–4613. doi:10.1039/c9cy01185d
Raziq, F., Humayun, M., Ali, A., Wang, T., Khan, A., Fu, Q., et al. (2018). Synthesis of S-Doped Porous G-C3N4 by Using Ionic Liquids and Subsequently Coupled with Au-TiO2 for Exceptional Cocatalyst-free Visible-Light Catalytic Activities. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 237, 1082–1090. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.06.009
Ren, D., Zhang, W., Ding, Y., Shen, R., Jiang, Z., Lu, X., et al. (2020). In Situ Fabrication of Robust Cocatalyst‐Free CdS/g‐C3N4 2D-2D Step‐Scheme Heterojunctions for Highly Active H2 Evolution. Sol. RRL. 4, 1900423. doi:10.1002/solr.201900423
Suzuki, T. M., Takayama, T., Sato, S., Iwase, A., Kudo, A., and Morikawa, T. (2018). Enhancement of CO2 Reduction Activity under Visible Light Irradiation over Zn-Based Metal Sulfides by Combination with Ru-Complex Catalysts. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 224, 572–578. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.10.053
Tao, J., Yu, X., Liu, Q., Liu, G., and Tang, H. (2021). Internal Electric Field Induced S-Scheme Heterojunction MoS2/CoAl LDH for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 585, 470–479. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2020.10.028
Tian, Y., Tang, W., Xiong, H., Chen, T., Li, B., Jing, X., et al. (2020). Luminescence and Structure Regulation of Graphitic Carbon Nitride by Electron Rich P Ions Doping. J. Lumin. 228, 117616. doi:10.1016/j.jlumin.2020.117616
Truc, N., Bach, L., Hanh, N., Pham, T., Chi, N., Tran, D., et al. (2019). The superior Photocatalytic Activity of Nb Doped TiO2/g-C3N4 Direct Z-Scheme System for Efficient Conversion of CO2 into Valuable Fuels. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 540, 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2019.01.005
Wang, J., Wang, G., Cheng, B., Yu, J., and Fan, J. (2021). Sulfur-doped g-C3n4/TiO2 S-Scheme Heterojunction Photocatalyst for Congo Red Photodegradation. Chin. J. Catal. 42, 56–68. doi:10.1016/S1872-2067(20)63634-8
Wang, X., Maeda, K., Thomas, A., Takanabe, K., Xin, G., Carlsson, J. M., et al. (2009). A Metal-free Polymeric Photocatalyst for Hydrogen Production from Water under Visible Light. Nat. Mater. 8, 76–80. doi:10.1038/nmat2317
Wang, Y., Tian, Y., Yan, L., and Su, Z. (2018). DFT Study on Sulfur-Doped G-C3N4 Nanosheets as a Photocatalyst for CO2 Reduction Reaction. J. Phys. Chem. C. 122, 7712–7719. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b00098
Wang, Z., Chen, Y., Zhang, L., Cheng, B., Yu, J., and Fan, J. (2020). Step-scheme CdS/TiO2 Nanocomposite Hollow Microsphere with Enhanced Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction Activity. J. Mater. Sci. Technology 56, 143–150. doi:10.1016/j.jmst.2020.02.062
Wei, J., Chen, Y., Zhang, H., Zhuang, Z., and Yu, Y. (2021). Hierarchically Porous S-Scheme CdS/UiO-66 Photocatalyst for Efficient 4-nitroaniline Reduction. Chin. J. Catal. 42, 78–86. doi:10.1016/s1872-2067(20)63661-0
Wu, Z., and Cohen, R. E. (2006). More Accurate Generalized Gradient Approximation for Solids. Phys. Rev. B. 73, 235116. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.73.235116
Xia, P., Cao, S., Zhu, B., Liu, M., Shi, M., Yu, J., et al. (2020). Designing a 0D/2D S‐Scheme Heterojunction over Polymeric Carbon Nitride for Visible‐Light Photocatalytic Inactivation of Bacteria. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 5218–5225. doi:10.1002/anie.201916012
Xie, Q., He, W., Liu, S., Li, C., Zhang, J., and Wong, P. K. (2020). Bifunctional S-Scheme G-C3N4/Bi/BiVO4 Hybrid Photocatalysts toward Artificial Carbon Cycling. Chin. J. Catal. 41, 140–153. doi:10.1016/S1872-2067(19)63481-9
Xu, F., Meng, K., Cheng, B., Wang, S., Xu, J., and Yu, J. (2020a). Unique S-Scheme Heterojunctions in Self-Assembled TiO2/CsPbBr3 Hybrids for CO2 Photoreduction. Nat. Commun. 11, 4613. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-18350-7
Xu, Q., Zhang, L., Cheng, B., Fan, J., and Yu, J. (2020b). S-scheme Heterojunction Photocatalyst. Chem. 6, 1543–1559. doi:10.1016/j.chempr.2020.06.010
Yan, L., Lu, Y., and Li, X. (2016). A Density Functional Theory Protocol for the Calculation of Redox Potentials of Copper Complexes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18, 5529–5536. doi:10.1039/c5cp06638g
Yang, Y., Zhang, D., Fan, J., Liao, Y., and Xiang, Q. (2021). Construction of an Ultrathin S‐Scheme Heterojunction Based on Few‐Layer g‐C3N4 and Monolayer Ti3C2TX MXene for Photocatalytic CO 2 Reduction. Sol. RRL. 5, 2000351. doi:10.1002/solr.202000351
Zhang, B., Shi, H., Yan, Y., Liu, C., Hu, X., Liu, E., et al. (2021a). A Novel S-Scheme 1D/2D Bi2S3/g-C3N4 Heterojunctions with Enhanced H2 Evolution Activity. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochemical Eng. Aspects. 608, 125598. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125598
Zhang, X., Kim, D., Yan, J., and Lee, L. Y. S. (2021b). Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction Enabled by Interfacial S-Scheme Heterojunction between Ultrasmall Copper Phosphosulfide and G-C3N4. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 13, 9762–9770. doi:10.1021/acsami.0c17926
Zhang, X., Yang, P., and Jiang, S. P. (2021c). Pt Nanoparticles Embedded Spine-like G-C3N4 Nanostructures with superior Photocatalytic Activity for H2 Generation and CO2 Reduction. Nanotechnology 32, 175401. doi:10.1088/1361-6528/abdcee
Zhang, X., Yan, J., Zheng, F., Zhao, J., and Lee, L. Y. S. (2021d). Designing Charge Transfer Route at the Interface between WP Nanoparticle and G-C3N4 for Highly Enhanced Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction Reaction. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 286, 119879. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.119879
Zhao, Z.-Y., and Dai, W.-W. (2014). Structural, Electronic, and Optical Properties of Eu-Doped BiOX (X = F, Cl, Br, I): A DFT+U Study. Inorg. Chem. 53, 13001–13011. doi:10.1021/ic5021059
Zhen, Y., Yang, C., Shen, H., Xue, W., Gu, C., Feng, J., et al. (2020). Photocatalytic Performance and Mechanism Insights of a S-Scheme G-C3N4/Bi2MoO6 Heterostructure in Phenol Degradation and Hydrogen Evolution Reactions under Visible Light. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 22, 26278–26288. doi:10.1039/D0CP02199G
Zhi, X., Jiao, Y., Zheng, Y., and Qiao, S. Z. (2019). Impact of Interfacial Electron Transfer on Electrochemical CO2 Reduction on Graphitic Carbon Nitride/Doped Graphene. Small. 15, 1804224. doi:10.1002/smll.201804224
Zhu, B., Zhang, L., Cheng, B., and Yu, J. (2018). First-principle Calculation Study of Tri-s-triazine-based G-C3N4: A Review. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 224, 983–999. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.11.025
Keywords: graphitic carbon nitride, density functional theory, CO2 reduction, photocatalytic, nonmetal doping, heterojunctions
Citation: Fei X, Zhang L, Yu J and Zhu B (2021) DFT Study on Regulating the Electronic Structure and CO2 Reduction Reaction in BiOBr/Sulphur-Doped G-C3N4 S-Scheme Heterojunctions. Front. Nanotechnol. 3:698351. doi: 10.3389/fnano.2021.698351
Received: 21 April 2021; Accepted: 11 May 2021;
Published: 22 June 2021.
Edited by:
Wee-Jun Ong, Xiamen University, MalaysiaReviewed by:
Quanjun Xiang, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, ChinaKai Dai, Huaibei Normal University, China
Copyright © 2021 Fei, Zhang, Yu and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Liuyang Zhang, emx5MjAxN0B3aHV0LmVkdS5jbg==; Jiaguo Yu, eXVqaWFndW85M0B3aHV0LmVkdS5jbg==
 Xingang Fei
Xingang Fei Liuyang Zhang1*
Liuyang Zhang1* Jiaguo Yu
Jiaguo Yu