
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Aging Neurosci. , 11 October 2023
Sec. Neurocognitive Aging and Behavior
Volume 15 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2023.1297736
This article is a correction to:
The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with mild cognitive impairment in community-dwelling older women aged over 70 years: a population-based cross-sectional study
 Shengjie Li1,2†
Shengjie Li1,2† Xiaoyu Chen1†
Xiaoyu Chen1† Mengze Gao1,2
Mengze Gao1,2 Xingyu Zhang1,2
Xingyu Zhang1,2 Peipei Han1
Peipei Han1 Liou Cao3
Liou Cao3 Jing Gao4
Jing Gao4 Qiongying Tao5
Qiongying Tao5 Jiayi Zhai5
Jiayi Zhai5 Dongyu Liang6
Dongyu Liang6 Qi Guo1*
Qi Guo1*by Li, S., Chen, X., Gao, M., Zhang, X., Han, P., Cao, L., Gao, J., Tao, Q., Zhai, J., Liang, D., and Guo, Q. (2023). Front. Aging Neurosci. 15:1261026. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1261026
In the published article, there was an error in the legend for Figure 2 Logistic regression of MCI and NLR after adjusted model in four subgroups by sex and age (A–D). as published. Because we are not familiar with the submitted page, we revised Figure 2 as suggested by the reviewers, figure 2 has made changes in word and PDF but has not been submitted to the system. The corrected legend appears below.
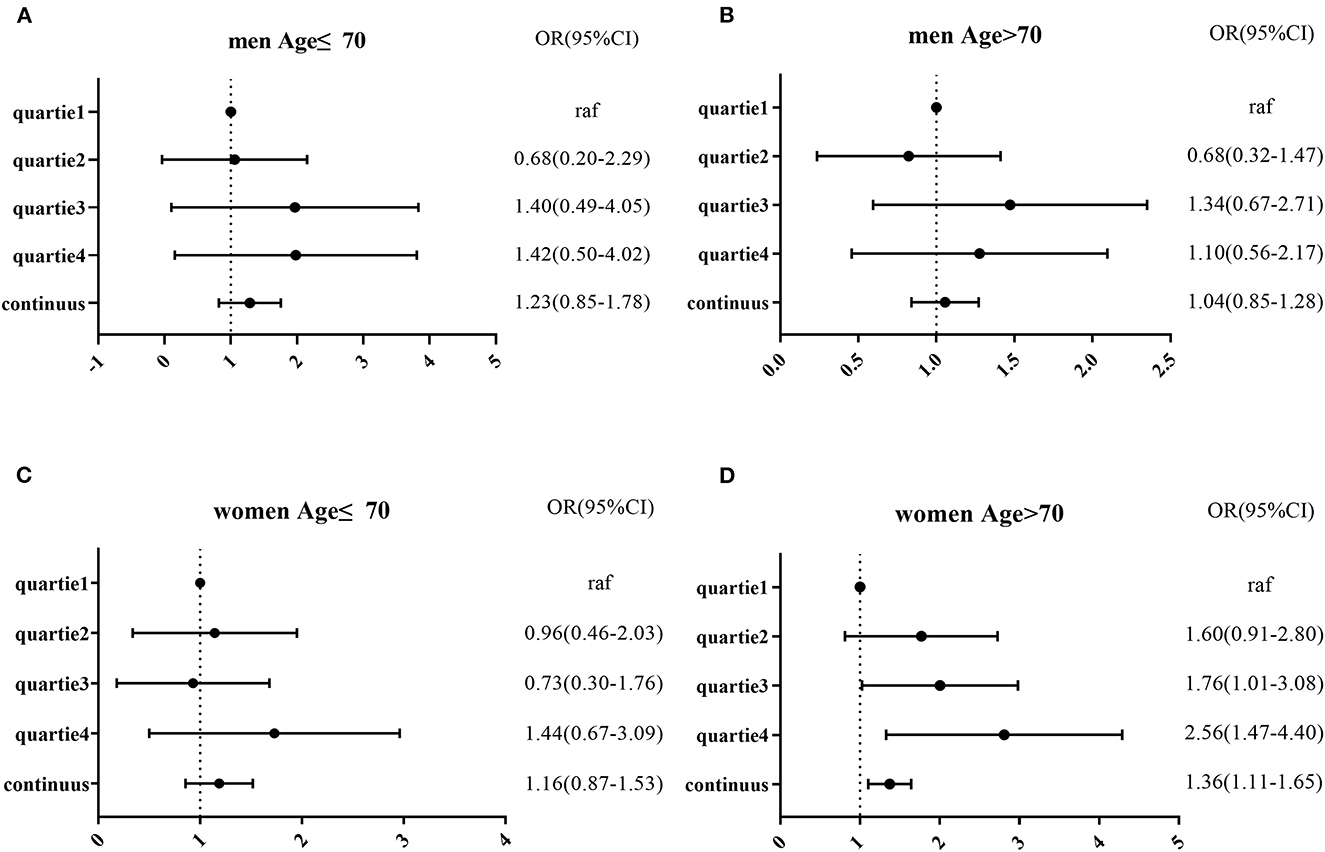
Figure 2. Logistic regression of MCI and NLR after adjusted model in four subgroups by sex and age (A–D).
In the published article, there was an error. We revised the tables as suggested by the reviewers, but forgot to modify the content of the abstract and results.
A correction has been made to Abstract, “Methods”, 1. This sentence previously stated:
“A total of 3,126 individuals aged over 60 years in Shanghai were recruited for face-to-face interviews, and blood samples were collected.”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“A total of 3,169 individuals aged over 60 years in Shanghai were recruited for face-to-face interviews, and blood samples were collected.”
A correction has been made to Abstract, “Results”, 1. This sentence previously stated:
“MCI in women [odds ratio (OR) = 1.33; 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.14–1.55]. In addition, the elevated NLR quartile was associated with an increased risk of MCI, especially in women older than 70 years (p-value for trend = 0.012).”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“MCI in women [odds ratio (OR) = 1.28; 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.09–1.49]. In addition, the elevated NLR quartile was associated with an increased risk of MCI, especially in women older than 70 years (p-value for trend = 0.011).”
A correction has been made to Results, 3.
The sentence previously stated:
“Table 1 presents the characteristics of the study participants (n = 3,168) stratified by sex.”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“Table 1 presents the characteristics of the study participants (n = 3,169) stratified by sex.”
The sentence previously stated:
“The prevalence of MCI was highest in the fourth quartile of the NLR [odds ratio (OR) = 2.10; 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.35–2.35].”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“The prevalence of MCI was highest in the fourth quartile of the NLR [odds ratio (OR) = 2.10; 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.35–3.25].”
The sentence previously stated:
“Table 3 shows that the prevalence of MCI was higher in the third (OR = 1.76; 95% CI = 1.01–3.05),”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“Table 3 shows that the prevalence of MCI was higher in the third (OR = 1.76; 95% CI = 1.01–3.08),”
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: inflammations, mild cognitive impairment, sex difference, population-based study, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR)
Citation: Li S, Chen X, Gao M, Zhang X, Han P, Cao L, Gao J, Tao Q, Zhai J, Liang D and Guo Q (2023) Corrigendum: The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with mild cognitive impairment in community-dwelling older women aged over 70 years: a population-based cross-sectional study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 15:1297736. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1297736
Received: 20 September 2023; Accepted: 29 September 2023;
Published: 11 October 2023.
Edited and reviewed by: Sonal Agrawal, Rush University, United States
Copyright © 2023 Li, Chen, Gao, Zhang, Han, Cao, Gao, Tao, Zhai, Liang and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qi Guo, Z3VvcWlqcEBnbWFpbC5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.