
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Aging Neurosci. , 30 January 2019
Sec. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Brain-aging
Volume 11 - 2019 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2019.00004
This article is a correction to:
Detection of Microbial 16S rRNA Gene in the Blood of Patients With Parkinson’s Disease
A Corrigendum on
Detection of Microbial 16S rRNA Gene in the Blood of Patients With Parkinson's Disease
by Qian, Y., Yang, X., Xu, S., Wu, C., Qin, N., Chen, S.-D., et al. Front. Neurosci. (2018). 10:156. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00156
Due to a flaw in analysis, there was a technical error used in the following classical formula to calculate copy numbers.
“Number of copies = (amount of DNA (ng) * 6.022 x 1023) / (length * 1 x 109 * 650) (650 = Molecular weight/bp, 6.022 *1023 = Avogadro' s number).”
The length of 16S rRNA gene of Escherichia coli BL21 strain, which is “1,542 bp,” instead of the length of its genome, which is “4,558,947 bp,” was used to match the amount of DNA of this strain. This led to the errors regarding the 16S gene (copies/ng) of the PD and healthy group in the Table 2, Supplementary Figure S1 and a statement in the Results in the original article.
The corrected Table 2 and Supplementary Figure S1 appear below.
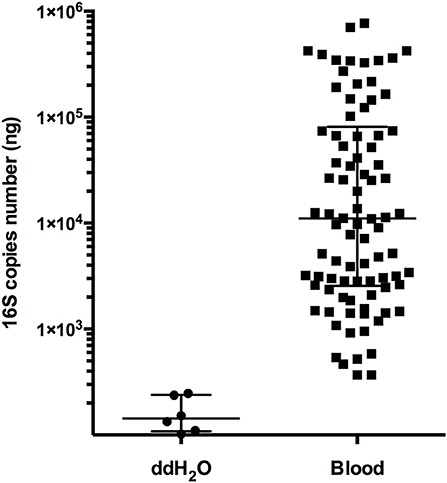
Figure S1. Comparison the 16S gene copies from the no template control and blood samples from 90 individuals by real-time PCR analysis.
A correction has also been made to the Results, Characteristics of the Studied Groups:
“There was no significant difference in the 16S rRNA gene copies between PD and healthy groups by real-time PCR (1.22E+04 ± 1.21E+05 copies/ng of PD vs. 7.78E+03 ± 6.86E+04 copies/ng of controls, P = 0.316, Wilcoxon rank-sum test analysis).”
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Keywords: neurodegeneration disease, blood, microbiota, 16S rRNA gene, inflammation
Citation: Qian Y, Yang X, Xu S, Wu C, Qin N, Chen S-D and Xiao Q (2019) Corrigendum: Detection of Microbial 16S rRNA Gene in the Blood of Patients With Parkinson's Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 11:4. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00004
Received: 01 January 2019; Accepted: 09 January 2019;
Published: 30 January 2019.
Edited and reviewed by: Jiawei Zhou, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences (CAS), China
Copyright © 2019 Qian, Yang, Xu, Wu, Qin, Chen and Xiao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Nan Qin, cWlubmFuQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
Sheng-Di Chen, cnVpamluY3NkQDEyNi5jb20=
Qin Xiao, eHExMDUzN0ByamguY29tLmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.