
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Mol. Biosci. , 23 July 2024
Sec. Molecular Diagnostics and Therapeutics
Volume 11 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2024.1452740
This article is a correction to:
CMTM6 as a candidate risk gene for cervical cancer: Comprehensive bioinformatics study
 Xiaoting Huang1,2†
Xiaoting Huang1,2† Wei Liu1,2†
Wei Liu1,2† Chunshan Liu1,2†
Chunshan Liu1,2† Jijie Hu3
Jijie Hu3 Baiyao Wang1,2
Baiyao Wang1,2 Anbang Ren1,2
Anbang Ren1,2 Xiaona Huang4
Xiaona Huang4 Yawei Yuan1,2*
Yawei Yuan1,2* Jinquan Liu1,2*
Jinquan Liu1,2* Mingyi Li1,2*
Mingyi Li1,2*A Corrigendum on
CMTM6 as a candidate risk gene for cervical cancer: Comprehensive bioinformatics study
by Huang X, Liu W, Liu C, Hu J, Wang B, Ren A, Huang X, Yuan Y, Liu J and Li M (2022). Front. Mol. Biosci. 9:983410. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.983410
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 6 as published. In Figure 6A, in the Western blot bands labeled “ERK” and “JNK,” the use of ERK was incorrect and caused an overlap. The corrected Figure 6 and its caption appear below.
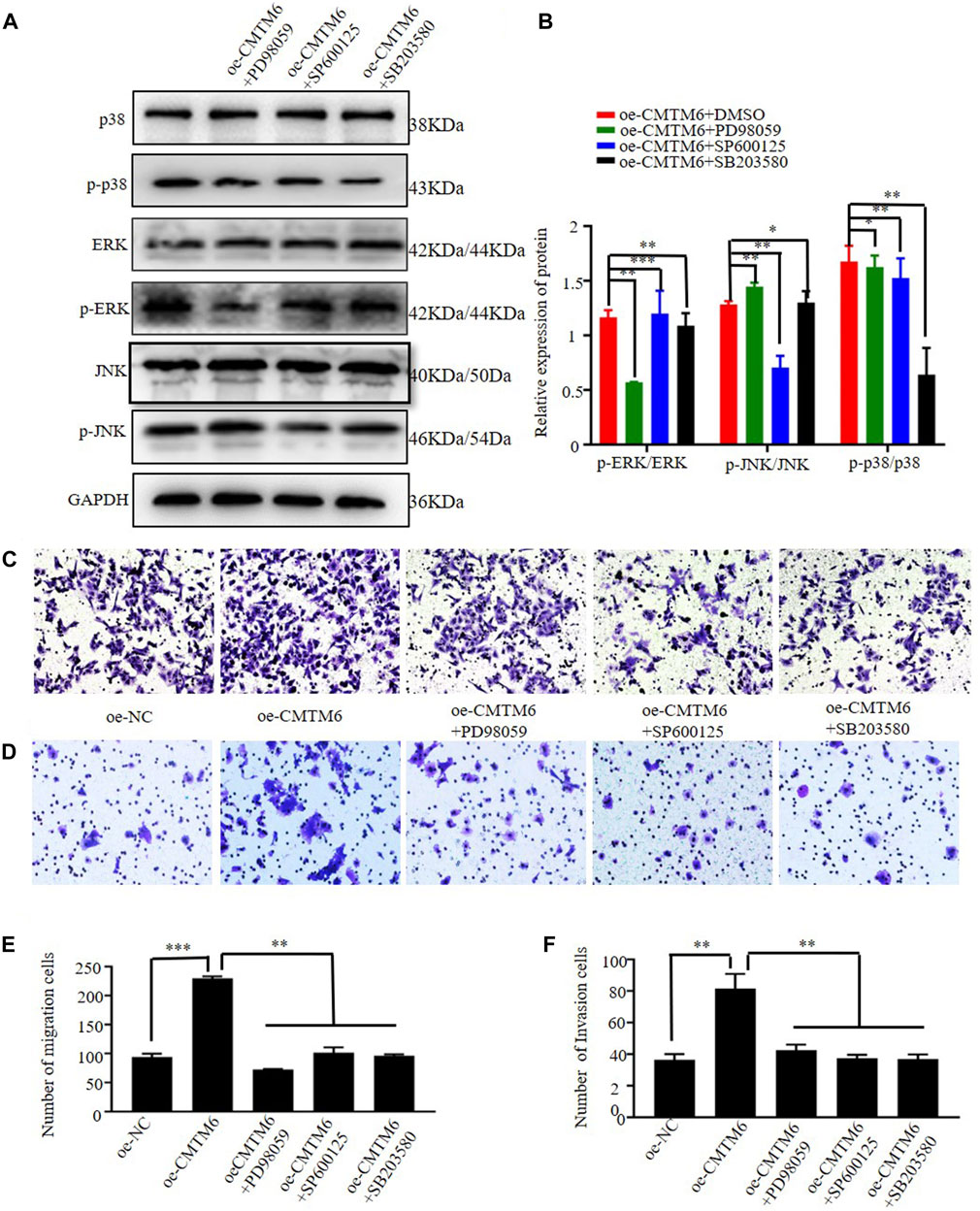
Figure 6. Effect of inhibited MAPK signaling on CMTM6-regulated cell invasion and migration. (A, B) Western blotting showing the levels of MAPK-related proteins in each group. Data were normalized to the level of GAPDH. (C–F) Cell metastasis and migration were assessed using Transwell assays in which CMTM6 acted as an inhibitor of the MAPK signaling pathway. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: CMTM6, cervical cancer, proliferation, migration, MAPK signaling
Citation: Huang X, Liu W, Liu C, Hu J, Wang B, Ren A, Huang X, Yuan Y, Liu J and Li M (2024) Corrigendum: CMTM6 as a candidate risk gene for cervical cancer: comprehensive bioinformatics study. Front. Mol. Biosci. 11:1452740. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1452740
Received: 21 June 2024; Accepted: 04 July 2024;
Published: 23 July 2024.
Edited and reviewed by:
Matteo Becatti, University of Firenze, ItalyCopyright © 2024 Huang, Liu, Liu, Hu, Wang, Ren, Huang, Yuan, Liu and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yawei Yuan, eXVhbnlhd2VpQGd6aG11LmVkdS5jbg==; Jinquan Liu, Y2NnbXVsaXVqaW5xdWFuQDE2My5jb20=; Mingyi Li, aHVhbmd4aWFvdGluZzU5NjBAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.