
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
MINI REVIEW article
Front. Mol. Biosci., 12 August 2022
Sec. Protein Biochemistry for Basic and Applied Sciences
Volume 9 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2022.959425
This article is part of the Research TopicMolecular Determinants of Protein Assemblies in Health and DiseaseView all 9 articles
The major hallmark of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is represented by the formation of pathological protein plaques largely consisting of α-synuclein (αSN) amyloid fibrils. Nevertheless, the implications of αSN oligomers in neuronal impairments and disease progression are more importantly highlighted than mature fibrils, as they provoke more detrimental damages in neuronal cells and thereby exacerbate α-synucleinopathy. Interestingly, although generation of oligomeric species under disease conditions is likely correlated to cytotoxicity and different cellular damages, αSN oligomers manifest varying toxicity profiles dependent on the specific environments as well as the shapes and conformations the oligomers adopt. As such, this minireview discusses polymorphism in αSN oligomers and the association of the underlying heterogeneity in regard to toxicity under pathological conditions.
The pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease (PD), the second most common type of neurodegenerative disease, is multifactorial with various known molecular and transgenic factors. Irrespective of the precise cause, α-synucleinopathy is considered as the major pathological hallmark of PD characterized by the abnormal fibrillation and subsequent aggregation of a presynaptic neuronal protein called α- synuclein (αSN) (Spillantini et al., 1997; Dawson and Dawson, 2003). Although different putative functions of αSN such as the regulation of neurotransmitter release have been suggested, its exact functions under normal conditions remain elusive (Stefanis, 2012). The implications of αSN most prominently manifest in different neurodegenerative diseases including PD, as pathological deposits called Lewy bodies (LBs) are largely formed by αSN amyloid fibrils (Kim et al., 2014). As the disease progresses, these deleterious αSN aggregates undergo neuron-to-neuron propagation along the midbrain, which progressively kill off dopamine producing neurons in the substantia nigra (Desplats et al., 2009). Thus, in the early days of studies, researchers devoted their attention to the exploration of mature fibrils in the hopes of understanding the formation of LBs and their association with the disease progression.
Around the late 1990s, however, attention shifted to soluble oligomers, as growing evidence from cellular toxicity studies suggested that oligomeric species provoke more severe detriments to neurons when compared against fibrillar aggregates (Bemporad and Chiti, 2012; Stefani, 2012). The ensuing findings from established in vitro and in vivo experiments, coupled with the biofluids and tissue samples from human patients, further validate the implications of oligomeric species in triggering and aggravating α-synucleinopathy in PD (Kalia et al., 2013; Cremades et al., 2017). The oligomerization of αSN unavoidably produces a heterogenous population of oligomers varying in size and morphology. Namely, assorted oligomers ranging from small (∼2–5-mers), medium (∼5–15-mers), to large (∼15–150-mers) species can be formed in different shapes (Oliveri, 2019). In addition to the distinctive toxicity profiles these oligomers exhibit, their structural and conformational heterogeneity consequentially gives rise to polymorphism in mature fibrils, which remains crucial for garnering further insight into the formation of LBs (Stefani, 2012). Therefore, beyond their overarching impact in neuronal impairment, understanding polymorphism in αSN oligomers, including drawing a clearer connection between heterogeneity and toxicity, is crucial for a more complete comprehension of disease progression and drug development to yield an effective target selection for PD.
As such, this minireview highlights the importance of polymorphism in αSN oligomers through the correlation with various forms of cellular damages in neurodegenerative diseases, focused on PD. While understanding the in vivo formation and progression of αSN oligomers stands as a critical element in drug development, obtaining granular information around the fibrillation process inevitably demands extensive in vitro studies to investigate key aspects that are comparably infeasible in vivo. Hence, this minireview predominantly focuses on various in vitro studies with suggested relevance and correlation to in vivo environments, as well as further translation of these findings into clinical settings. Foremost, we discuss the reported pathways of oligomer generation, which primarily take place during the formation and disaggregation of amyloid fibrils. Several noticeable features are highlighted and common across these oligomers, such as size, shape, post-translational modifications, as well as relevance in their distinct toxicity profiles. Based on these unique characteristics, the specific types of damages different oligomeric species provoke in neuronal cells are outlined. Finally, we present several notable modulators for varying types of αSN oligomers, which provide important and timely insight into the ongoing and forthcoming drug development efforts to surmount α-synucleinopathy which exhibits a polymorphic fibrillation process.
The formation of diverse non-fibrillar aggregates can be identified with several standardized biophysical methods including electron microscope (EM), atomic force microscope (AFM), and fluorescence spectrometer at the onset of amyloidogenesis. Namely, the early stages of αSN fibrillation generate an array of distinct oligomeric species varying in size, shape, stability, and
Previous findings have also demonstrated that mature αSN amyloid fibrils release soluble polymorphic dimers and oligomers, which may provoke severe toxic outcomes to neurons in the vicinity (Cremades et al., 2012; Cascella et al., 2021). Interestingly, oligomers produced from short fibrils elicit significantly more deleterious effects in neurons when compared to species released from long fibrils. This is partly because the release of toxic oligomers occurs from the fibrillar ends; shorter fibrils facilitate a faster release owing to their higher proportion of ends (Cascella et al., 2021). In addition to immediate functional impairments in the neurons, these oligomeric species can be internalized and contribute to progressive diffusion of α-synucleinopathy through neuron-to-neuron transmission. Studies on denatured mature fibrils under supercooling conditions show annular and spherical oligomeric species, which reportedly exhibit similar toxicity levels to oligomers generated during amyloid formation (Kim et al., 2008).
The interactions between αSN monomers and the cell membrane are particularly critical during the initial stages of amyloid formation (Terakawa et al., 2018a; Terakawa et al., 2018b; Lin et al., 2022). Upon binding to lipid membranes, αSN monomers oligomerize, primarily to dimers and trimers, as the cross-linking between αSN monomers act to stabilize the conformations of membrane-bound αSN (Cole et al., 2002; Ding et al., 2002). Notably, the membrane-induced oligomerization of αSN may result in the formation of nucleation sites for subsequent aggregation and aggravated α-synucleinopathy. Some researchers suggest that a longer incubation of membrane-bound spherical oligomers results in structural conversion into membrane-bound annular oligomers, where such alteration may contribute to increased toxicity and accelerated disease progression (Ding et al., 2002).
Unlike mature amyloid fibrils, αSN oligomers are predominantly localized in the presynaptic terminals, where they exert harmful impacts on synapses and dendrites. Similar to their provocation of distinct fibrillation kinetics to mature amyloids, differently structured and shaped oligomers elicit distinctive toxic outcomes.
The early onset of the fibrillation process typically produces small spherical oligomers, which further assemble into annular protofibrils or even mature fibrils in the presence of excess αSN monomers (Cremades et al., 2017). While the mechanisms underlying the toxicity of αSN oligomers primarily pertain to various forms of cell membrane perturbation, the interactions between spherical oligomers and the membrane are not particularly pronounced (Surguchov et al., 2017). Therefore, compared to annular oligomers, spherical or globular oligomers are considered more stable and thus generally display less deleterious toxicity profiles (Cremades et al., 2012). In support of this notion, studies on brain tissue samples of multiple system atrophy (MSA) patients manifesting α-synucleinopathy revealed that mild detergent treatment breaks apart the inclusions into 30–50 nm-sized annular oligomers. On the other hand, the same treatment on recombinant wild type (WT) αSN results in the release of spherical oligomers (Pountney et al., 2005). The findings suggest that pathological conditions preferentially form annular oligomers with higher toxicity. However, it should be noted that unlike annular oligomers, spherical oligomers can be internalized by neuronal cells and function as a seed for consequential nucleation and elongation (Danzer et al., 2007). Taken together, although the direct toxicity of spherical oligomers is deemed relatively subtle in eliciting destructive outcomes, their spontaneous conversion to annular oligomers and/or the creation of further nucleation sites may contribute to exacerbated α-synucleinopathy.
Annular species have become the focal point for understanding the neuronal impairments induced by αSN oligomers under disease conditions. In addition to the studies with MSA patients’ brain tissue samples showing αSN inclusions are predominantly formed by annular species, several subsequent studies further validate the implications of annular oligomers in toxicity including the specific types of damages they provoke.
In the past, the prevailing hypothesis around the toxicity of αSN oligomers proposed the embedment of annular species into lipid bilayers, which leads to the formation of pore-like protein channels (Kostka et al., 2008). However, further analyses have since corroborated that the intercalation of the oligomers between tightly packed lipid domains induces disintegration of the hydrophobic core where destabilized membrane permeability thus triggers an aberrant transport of molecules across the membrane (Stöckl et al., 2013). Indeed, the updated notion with decreased lipid order is consistent with the observations of elevated lipid flip-flops induced by oligomers. Importantly, membrane destabilization can lead to dysregulation of intracellular calcium homeostasis; several hypotheses consider atypically increased intracellular calcium levels as an important factor contributing to neurodegeneration (Zaichick et al., 2017). In addition to the formation of toxic annular oligomers of 70–90 nm in diameter when bound to the C-terminal of αSN, elevated intracellular calcium levels via unregulated transport of extracellular calcium induce a remarkable increase in the activation of caspase-3 for consequential apoptosis (Danzer et al., 2007). It should also be noted that aberrant ion flux correlates with abnormal patterns in the neuronal excitabilities, which allude to another aspect of neuronal vulnerability in PD.
While growing evidence supports disruption of the plasma membrane integrity via oligomer-membrane interaction, various other forms of cellular damages by αSN oligomers have been reported. Akin to the plasma membrane destabilization, destructive permeabilization into the membranes of mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and various trafficking vesicles can be more readily provoked by annular oligomers. Such damages trigger enhanced oxidative stress, membrane depolarization, and various forms of dysfunction including disruption of the electron transport chain in mitochondria (Stefani, 2012). Impairments in the ER-Golgi membranes are linked to ubiquitin/proteasome system-mediated clearance pathways as well as obstruction of trafficking. In addition, severe lysosomal leakages and/or adverse cytoskeletal changes can manifest (Oliveri, 2019). Finally, membrane-bound forms or internalized soluble species can act as nucleation sites to spread and aggravate α-synucleinopathy (Cascella et al., 2021). Possible toxicity pathways induced by αSN oligomers are outlined in Figure 1A.
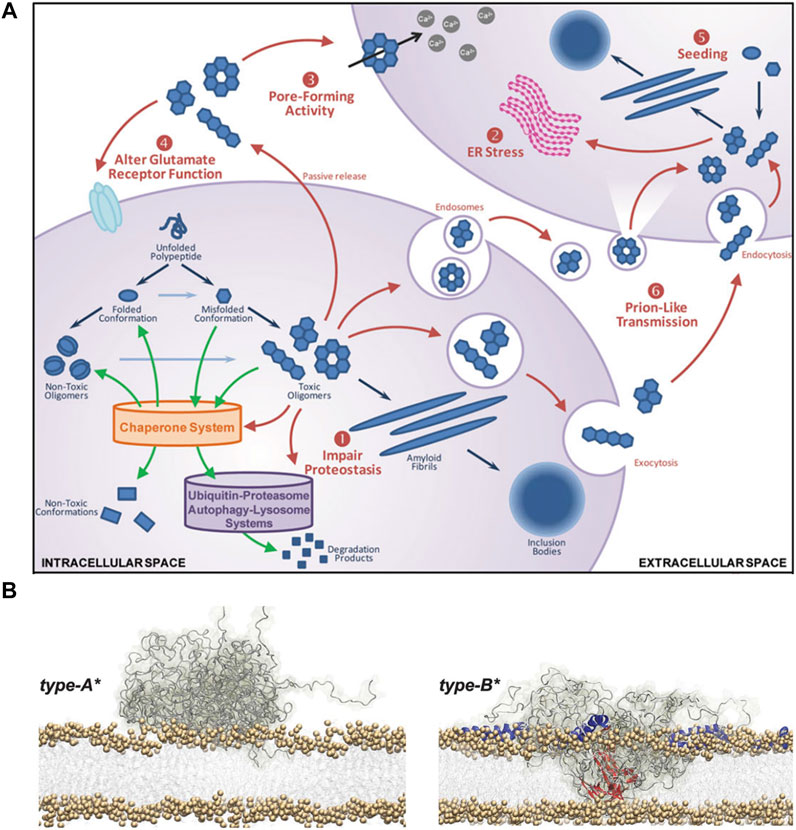
FIGURE 1. Toxic effects of αSN oligomers. (A) Schematic representation of the αSN oligomerization and ensuing toxicity. The outlined process includes: 1) impaired proteostasis, 2) prolonged ER stress, 3) aberrant pore formation, 4) dysfunctional glutamate receptor, and 5) intracellular uptake and seeding followed by 6) neuron-to-neuron transmission of pathological aggregates (Kalia et al., 2013). (B) Schematic representation of the membrane destabilization process by two types of oligomers with distinct secondary structure contents. Type-A* oligomers are predominantly unstructured and can only bind to the surface of biological membranes (left). Type-B* oligomers exhibit both disordered (gray) and β-sheet (red) regions where the β-sheet regions penetrate through the lipid bilayers, provoking destabilization (right). In addition, the folding of the N-terminal regions into α-helices (blue) provide more binding regions to the membrane (Fusco et al., 2017).
In addition to morphological characteristics, distinct secondary structure contents within similarly shaped and sized αSN oligomers can lead to conflicting outcomes in cytotoxicity. Namely, oligomeric species with richer
αSN can undergo several types of post-translational modifications that alter the propensity for aggregation, which thereby affect the toxicity profiles and levels of oligomers (Alam et al., 2019).
Phosphorylation of αSN plays a critical role in modulating the fibrillation process and relevant neurotoxicity (Barrett and Greenamyre, 2015). While αSN can be phosphorylated at different residues including tyrosine 133 and 136 (Y133 & 136), phosphorylation at serine 129 (S129) is one of the most representative hallmarks of the fibrillation process, which increases the levels of toxic αSN oligomers (Fujiwara et al., 2002). On the other hand, phosphorylation at other residues such as S87 and Y125 can decrease the production of αSN oligomers by modulating the interactions between αSN and the cell membrane (Chen et al., 2009; Paleologou et al., 2010).
Various reactive nitrogen species (RNS) including peroxynitrite (ONOO−) can nitrate tyrosine residues in αSN, which can be detected with 3-nitrotyrosine antibodies. Nitration of αSN may render a protective factor against α-synucleinopathy as in vitro nitrated αSN cannot undergo fibrillation while also preventing the fibrillation of non-nitrated αSN in the vicinity (Yamin et al., 2003; Hodara et al., 2004). This can be attributed to the preferential production of stable spherical oligomers that are predominantly octamers with some dimeric and trimeric populations. On the other hand, several contrasting results report that nitrated αSN oligomers’ reduced association with lipid vesicles favors self-aggregation, which promotes the formation of inclusions to exacerbate α-synucleinopathy (Liu et al., 2011). However, it should be noted that the cytotoxicity of nitrated αSN has a deeper connection with the integrin- inducible NO synthase (iNOS)/-focal adhesion kinase (FAK) signaling pathway than with the formation of cytotoxic oligomers.
Under pathological conditions, increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) causes lipid peroxidation of various polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in the brain that alter αSN fibrillation. Foremost, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which localizes at synapses, is known to promote αSN aggregation with the production of heterogeneous oligomers dependent on the molar ratio (De Franceschi et al., 2011; Fecchio et al., 2013). More importantly, peroxidation of DHA is implicated in the generation of reactive aldehydes such as 4-hydroxyl-2-nonenal (4-HNE), when other peroxidation adducts produce acrolein, malondialdehyde (MDA), and 4-oxo-2-nonenal (4-ONE), which all exhibit considerable cytotoxicity by themselves (Esterbauer et al., 1991; Lee and Blair, 2000). Noticeably, covalent modifications of αSN by 4-ONE and 4-HNE are known to trigger the production of highly toxic off-pathway αSN oligomers rich in
While the brain maintains proper metal homeostasis, dysregulated levels of metal ions under pathological conditions lead to increased ROS production and aberrant interactions with αSN that stimulate aggregation. In addition to the aforementioned role of Ca2+ ions in producing annular oligomers, the implications of different metal ions including Cu2+, Fe3+, Al3+, and Cd2+ in promoting the formation of αSN oligomers and fibrils have been highlighted (Uversky et al., 2001). Akin to Ca2+, Cu2+ also accelerates oligomerization by binding to the C-terminal of αSN, where the presence of Cu2+ chelators reposition αSN towards the membrane with decreased aggregation (Wang et al., 2010). It is also important to note that Fe3+ results in the creation of destructive ion-permeable pores by inducing the formation of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-resistant oligomers (Kostka et al., 2008).
The interplay between αSN and nucleic acids has also been investigated under different conditions. Particularly, double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) interacts with αSN to promote fibrillation along with evident association with the mature fibrils (Cherny et al., 2004; Di Domizio et al., 2012). Namely, soluble αSN oligomers display preferential binding with nucleic acids and glycosaminoglycans (GAG) to accelerate the formation of mature fibrils. Interestingly, such binding decreases the cytotoxicity presumably due to the structural conversion of strongly toxic oligomers into less toxic fibrils (Di Domizio et al., 2012). Nevertheless, the in vivo and clinical significance of nucleic acids in αSN fibrillation remains questionable as a recent study demonstrated that amyloid αS binding to dsDNA is weak and nonspecific (Jos et al., 2021).
Current PD medications in the clinic focus on mitigating major motor symptoms by administering levodopa to compensate for the dopamine deficiency-provoked disruption of the nigrostriatal pathway (Salat and Tolosa, 2013). In the hope of fundamentally altering the disease progression for a more efficacious and sustainable intervention, several studies have introduced modulators of toxic αSN oligomers, which can effectively reduce neuronal impairments and impede disease progression by multiple mechanisms (Figure 2).
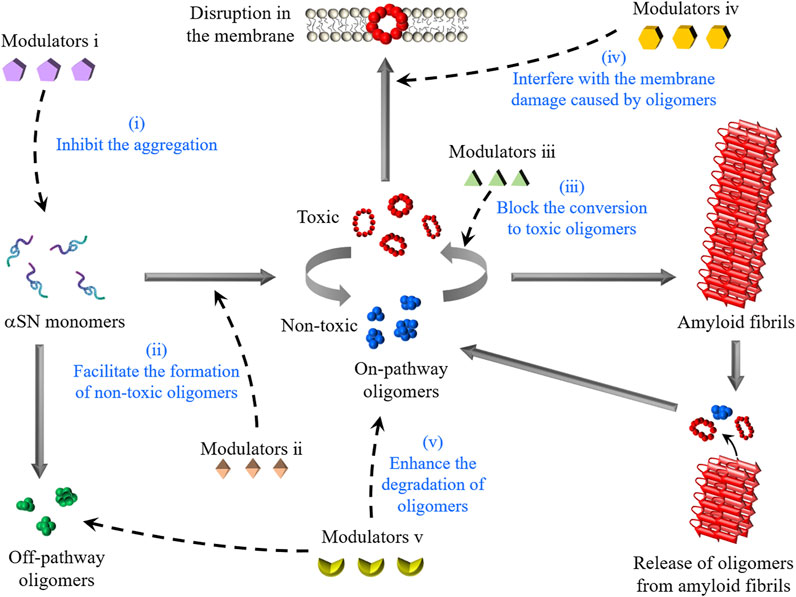
FIGURE 2. Schematic representation of the formation of αSN oligomers and intervention strategies. αSN oligomers are generated through the aggregation of monomers or the disaggregation of amyloid fibrils. The modulators described in this review interfere with the toxicity of αSN oligomers by five molecular mechanisms: (1) the inhibition of αSN amyloid formation, (2) the enhanced formation of non-toxic oligomers, (3) the stabilization of non-toxic oligomers for blocking their conversion to toxic oligomers, (4) the displacement of toxic oligomers from cell membranes, and (5) the enhancement of the degradation of oligomers.
Vast exploration has been made into the inhibitory functions of several polyphenols against the fibrillation of amyloidogenic proteins such as αSN, amyloid beta (A
Different types of non-polyphenolic small molecules also display therapeutic effects by modulating the levels or properties of αSN oligomers. Authorized as a diuretic for several medical purposes including the reduction of intracranial pressure, mannitol plays a notable function in αSN oligomerization (Shaltiel-Karyo et al., 2013). Remarkably, while mannitol does not prevent the generation of oligomers, it blocks the formation of large oligomers and induces conformational changes from α-helices to unidentified structures. The secondary structure change presumably leads to an alternative aggregation pathway that manifests decreased neurotoxicity. Several compounds isolated from natural sources have also shown efficacy in alleviating oligomer-provoked toxicity. Squalamine, obtained from the spiny dogfish shark, is known to displace toxic oligomers from cellular membranes and thereby interfere with the membrane damage caused by oligomers (Limbocker et al., 2021). Active ingredients of Ginseng, particularly Rb1, can act to stabilize non-toxic αSN oligomers with negligible
A selective degradation of αSN oligomers can be achieved by the expression of carboxyl terminus of Hsp70-interacting protein (CHIP), a member of E3 ubiquitin ligase (Tetzlaff et al., 2008). Akin to Anle138b, one the most popular strategies in designing novel drug candidates incorporates the use of modified short peptides with sequence homology to αSN that either leads to an alternative pathway to generate non-toxic species or prevents the fibrillation process. The synthetic peptides predominantly correspond to the non-amyloid-
In this minireview, the implications of polymorphic αSN oligomers with focus on the toxicity and disease progression in PD are outlined. It is important to note that different types of oligomers including Aβ, amylin (IAPP), and transthyretin (TTR) oligomers behave akin to αSN oligomers in vitro and follow analogous molecular pathways of aggregation (Nguyen et al., 2021). As such, understanding the intrinsic heterogeneity of amyloid oligomers provides insight into the pathoprogression of other diseases beyond PD. Particularly, as illustrated in the development of Lecanemab (BAN2401), which is currently in phase 3 clinical trials, preferential targeting of soluble oligomers stands as one of the most popular and promising approaches in the development of drugs for diseases with deleterious fibrillation of amyloidogenic proteins (Tolar et al., 2020). Even for drugs such as Aducanumab, which predominantly address insoluble
Y-HL supervised the project and JY wrote the manuscript. YL and YH reviewed and edited the manuscript.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Korean government [NRF-2019R1A2C1004954 and NRF-2022R1A2C1011793] (to Y-HL), the KBSI funds [C220000, C230130, and C280320] (to Y-HL).
The authors acknowledge J. P. Hostetler for assisting with manuscript completion and revision.
JY is employed by BioGraphene Inc.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Alam, P., Bousset, L., Melki, R., and Otzen, D. E. (2019). α-Synuclein oligomers and fibrils: A spectrum of species, a spectrum of toxicities. J. Neurochem. 150 (5), 522–534. doi:10.1111/jnc.14808
Ardah, M. T., Paleologou, K. E., Lv, G., Menon, S. A., Abul Khair, S. B., Lu, J. H., et al. (2015). Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits fibrillation and toxicity of alpha-synuclein and disaggregates preformed fibrils. Neurobiol. Dis. 74, 89–101. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2014.11.007
Barrett, P. J., and Greenamyre, J. T. (2015). Post-translational modification of α-synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Brain Res. 1628, 247–253. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2015.06.002
Bemporad, F., and Chiti, F. (2012). Protein misfolded oligomers: Experimental approaches, mechanism of formation, and structure-toxicity relationships. Chem. Biol. 19 (3), 315–327. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2012.02.003
Bieschke, J. (2013). Natural compounds may open new routes to treatment of amyloid diseases. Neurotherapeutics 10 (3), 429–439. doi:10.1007/s13311-013-0192-7
Bisaglia, M., Mammi, S., and Bubacco, L. (2007). Kinetic and structural analysis of the early oxidation products of dopamine: Analysis of the interactions with alpha-synuclein. J. Biol. Chem. 282 (21), 15597–15605. doi:10.1074/jbc.M610893200
Brown, J. W. P., Buell, A. K., Michaels, T. C. T., Meisl, G., Carozza, J., Flagmeier, P., et al. (2016). β-Synuclein suppresses both the initiation and amplification steps of α-synuclein aggregation via competitive binding to surfaces. Sci. Rep. 6, 36010. doi:10.1038/srep36010
Cascella, R., Chen, S. W., Bigi, A., Camino, J. D., Xu, C. K., Dobson, C. M., et al. (2021). The release of toxic oligomers from α-synuclein fibrils induces dysfunction in neuronal cells. Nat. Commun. 12 (1), 1814. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-21937-3
Castellani, R. J., Perry, G., Siedlak, S. L., Nunomura, A., Shimohama, S., and Zhang, J. (2002). Hydroxynonenal adducts indicate a role for lipid peroxidation in neocortical and brainstem Lewy bodies in humans. Neurosci. Lett. 319 (1), 25–28. doi:10.1016/s0304-3940(01)02514-9
Chemerovski-Glikman, M., Rozentur-Shkop, E., Richman, M., Grupi, A., Getler, A., Cohen, H. Y., et al. (2016). Self-assembled cyclic d, l-α-Peptides as generic conformational inhibitors of the α-synuclein aggregation and toxicity: In vitro and mechanistic studies. Chemistry 22 (40), 14236–14246. doi:10.1002/chem.201601830
Chen, L., Periquet, M., Wang, X., Negro, A., McLean, P. J., and Hyman, B. T. (2009). Tyrosine and serine phosphorylation of alpha-synuclein have opposing effects on neurotoxicity and soluble oligomer formation. J. Clin. Invest. 119 (11), 3257–3265. doi:10.1172/JCI39088
Cherny, D., Hoyer, W., Subramaniam, V., and Jovin, T. M. (2004). Double-stranded DNA stimulates the fibrillation of alpha-synuclein in vitro and is associated with the mature fibrils: An electron microscopy study. J. Mol. Biol. 344 (4), 929–938. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.09.096
Choi, M. Y., Kim, Y. S., Lim, D., Kang, S. J., Kim, Y. H., Lee, K., et al. (2011). The hexapeptide PGVTAV suppresses neurotoxicity of human α-synuclein aggregates. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 408 (2), 334–338. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.04.034
Cole, N. B., Murphy, D. D., Grider, T., Rueter, S., Brasaemle, D., Nussbaum, R. L., et al. (2002). Lipid droplet binding and oligomerization properties of the Parkinson's disease protein α-synuclein. J. Biol. Chem. 277 (8), 6344–6352. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108414200
Cremades, N., Chen, S. W., and Dobson, C. M. (2017). Structural characteristics of α-synuclein oligomers. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 329, 79–143. doi:10.1016/bs.ircmb.2016.08.010
Cremades, N., Cohen, S. I. A., Deas, E., Abramov, A. Y., Chen, A. Y., Orte, A., et al. (2012). Direct observation of the interconversion of normal and toxic forms of α-synuclein. Cell 149 (5), 1048–1059. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.037
Danzer, K. M., Haasen, D., Karow, A. R., Moussaud, S., Habeck, M., Giese, A., et al. (2007). Different species of alpha-synuclein oligomers induce calcium influx and seeding. J. Neurosci. 27 (34), 9220–9232. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.2617-07.2007
Dawson, T. M., and Dawson, V. L. (2003). Molecular pathways of neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease. Science 302 (5646), 819–822. doi:10.1126/science.1087753
De Franceschi, G., Frare, E., Pivato, M., Relini, A., Penco, A., Greggio, E., et al. (2011). Structural and morphological characterization of aggregated species of α-synuclein induced by docosahexaenoic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 286 (25), 22262–22274. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.202937
Dear, A. J., Meisl, G., Šarić, A., Michaels, T. C. T., Kjaergaard, M., Linse, S., et al. (2020). Identification of on- and off-pathway oligomers in amyloid fibril formation. Chem. Sci. 11 (24), 6236–6247. doi:10.1039/c9sc06501f
Desplats, P., Lee, H.-J., Bae, E.-J., Patrick, C., Rockenstein, E., Crews, L., et al. (2009). Inclusion formation and neuronal cell death through neuron-to-neuron transmission of alpha-synuclein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106 (31), 13010–13015. doi:10.1073/pnas.0903691106
Di Domizio, J., Zhang, R., Stagg, L. J., Gagea, M., Zhuo, M., Ladbury, J. E., et al. (2012). Binding with nucleic acids or glycosaminoglycans converts soluble protein oligomers to amyloid. J. Biol. Chem. 287 (1), 736–747. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.238477
Ding, T. T., Lee, S.-J., Rochet, J.-C., and Lansbury, P. T. (2002). Annular α-synuclein protofibrils are produced when spherical protofibrils are incubated in solution or bound to brain-derived membranes. Biochemistry 41 (32), 10209–10217. doi:10.1021/bi020139h
Ehrnhoefer, D. E., Bieschke, J., Boeddrich, A., Herbst, M., Masino, L., Lurz, R., et al. (2008). EGCG redirects amyloidogenic polypeptides into unstructured, off-pathway oligomers. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 15 (6), 558–566. doi:10.1038/nsmb.1437
Esterbauer, H., Schaur, R. J., and Zollner, H. (1991). Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 11 (1), 81–128. doi:10.1016/0891-5849(91)90192-6
Fecchio, C., De Franceschi, G., Relini, A., Greggio, E., Serra, M. D., Bubacco, L., et al. (2013). α-Synuclein oligomers induced by docosahexaenoic acid affect membrane integrity. PLoS One 8 (11), e82732. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0082732
Freyssin, A., Page, G., Fauconneau, B., and Bilan, A. R. (2018). Natural polyphenols effects on protein aggregates in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's prion-like diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 13 (6), 955–961. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.233432
Fujiwara, M., Hasegawa, M., Dohmae, N., Kawashima, A., Masliah, E., and Goldberg, M. S. (2002). alpha-Synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions. Nat. Cell Biol. 4, 160–164. doi:10.1038/ncb748
Fusco, G., Chen, S. W., Williamson, P. T. F., Cascella, R., Perni, M., Jarvis, J. A., et al. (2017). Structural basis of membrane disruption and cellular toxicity by α-synuclein oligomers. Science 358 (6369), 1440–1443. doi:10.1126/science.aan6160
Hodara, R., Norris, E. H., Giasson, B. I., Mishizen-Eberz, A. J., Lynch, D. R., Lee, V. M. Y., et al. (2004). Functional consequences of α-synuclein tyrosine nitration: Diminished binding to lipid vesicles and increased fibril formation. J. Biol. Chem. 279 (46), 47746–47753. doi:10.1074/jbc.M408906200
Hong, D.-P., Fink, A. L., and Uversky, V. N. (2008). Structural characteristics of alpha-synuclein oligomers stabilized by the flavonoid baicalein. J. Mol. Biol. 383 (1), 214–223. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.08.039
Hornedo-Ortega, R., Álvarez-Fernández, M. A., Cerezo, A. B., Richard, T., Troncoso, A. M. A., Garcia-Parrilla, M. a. C., et al. (2016). Protocatechuic acid: Inhibition of fibril formation, destabilization of preformed fibrils of amyloid-β and α-synuclein, and neuroprotection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 64 (41), 7722–7732. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.6b03217
Jos, S., Gogoi, H., Prasad, T. K., Hurakadli, M. A., Kamariah, N., Padmanabhan, B., et al. (2021). Molecular insights into α-synuclein interaction with individual human core histones, linker histone, and dsDNA. Protein Sci. 30 (10), 2121–2131. doi:10.1002/pro.4167
Kalia, L. V., Kalia, S. K., McLean, P. J., Lozano, A. M., and Lang, A. E. (2013). α-Synuclein oligomers and clinical implications for Parkinson disease. Ann. Neurol. 73 (2), 155–169. doi:10.1002/ana.23746
Karamanos, T. K., Jackson, M. P., Calabrese, A. N., Goodchild, S. C., Cawood, E. E., Thompson, G. S., et al. (2019). Structural mapping of oligomeric intermediates in an amyloid assembly pathway. Elife 8, e46574. doi:10.7554/eLife.46574
Kim, H.-Y., Cho, M.-K., Riedel, D., Fernandez, C. O., and Zweckstetter, M. (2008). Dissociation of amyloid fibrils of α-synuclein in supercooled water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 47 (27), 5046–5048. doi:10.1002/anie.200800342
Kim, W. S., Kågedal, K., and Halliday, G. M. (2014). Alpha-synuclein biology in Lewy body diseases. Alzheimer's Res. Ther. 6 (5), 73. doi:10.1186/s13195-014-0073-2
Kostka, M., Högen, T., Danzer, K. M., Levin, J., Habeck, M., Wirth, A., et al. (2008). Single particle characterization of iron-induced pore-forming alpha-synuclein oligomers. J. Biol. Chem. 283 (16), 10992–11003. doi:10.1074/jbc.M709634200
Lee, S. H., and Blair, A. (2000). Characterization of 4-oxo-2-nonenal as a novel product of lipid peroxidation. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 13 (8), 698–702. doi:10.1021/tx000101a
Limbocker, R., Staats, R., Chia, S., Ruggeri, F. S., Mannini, B., Xu, C. K., et al. (2021). Squalamine and its derivatives modulate the aggregation of amyloid-β and α-synuclein and suppress the toxicity of their oligomers. Front. Neurosci. 15, 680026. doi:10.3389/fnins.2021.680026
Lin, Y., Ito, D., Yoo, J. M., Lim, M. H., Yu, W., Kawata, Y., et al. (2022). Dual effects of presynaptic membrane mimetics on α-synuclein amyloid aggregation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. (in press).
Liu, Y., Qiang, M., Wei, Y., and He, R. (2011). A novel molecular mechanism for nitrated {alpha}-synuclein-induced cell death. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 3 (4), 239–249. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjr011
Mor, D. E., Tsika, E., Mazzulli, J. R., Gould, N. S., Kim, H., Daniels, M. J., et al. (2017). Dopamine induces soluble α-synuclein oligomers and nigrostriatal degeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 20 (11), 1560–1568. doi:10.1038/nn.4641
Näsström, T., Fagerqvist, T., Barbu, M., Karlsson, M., Nikolajeff, F., Kasrayan, A., et al. (2011). The lipid peroxidation products 4-oxo-2-nonenal and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal promote the formation of α-synuclein oligomers with distinct biochemical, morphological, and functional properties. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 50 (3), 428–437. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.11.027
Nguyen, P. H., Ramamoorthy, A., Sahoo, B. R., Zheng, J., Faller, P., Straub, J. E., et al. (2021). Amyloid oligomers: A joint experimental/computational perspective on alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, type II diabetes, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Chem. Rev. 121 (4), 2545–2647. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c01122
Oliveri, V. (2019). Toward the discovery and development of effective modulators of α-synuclein amyloid aggregation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 167, 10–36. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.01.045
Ono, K., Hirohata, M., and Yamada, M. (2007). Anti-fibrillogenic and fibril-destabilizing activity of nicotine in vitro: Implications for the prevention and therapeutics of Lewy body diseases. Exp. Neurol. 205 (2), 414–424. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.03.002
Paleologou, K. E., Oueslati, A., Shakked, G., Rospigliosi, C. C., Kim, H.-Y., and Lamberto, G. R. (2010). Phosphorylation at S87 is enhanced in synucleinopathies, inhibits α-synuclein oligomerization, and influences synuclein-membrane interactions. J. Neurosci. 30 (9), 3184–3198. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5922-09.2010
Pandey, N., Strider, J., Nolan, W. C., Yan, S. X., and Galvin, J. E. (2008). Curcumin inhibits aggregation of α-synuclein. Acta Neuropathol. 115 (4), 479–489. doi:10.1007/s00401-007-0332-4
Pountney, D. L., Voelcker, N. H., and Gai, W. P. (2005). Annular alpha-synuclein oligomers are potentially toxic agents in alpha-synucleinopathy. Hypothesis. Neurotox. Res. 7 (1), 59–67. doi:10.1007/BF03033776
Salat, D., and Tolosa, E. (2013). Levodopa in the treatment of Parkinson's disease: Current status and new developments. J. Park. Dis. 3 (3), 255–269. doi:10.3233/JPD-130186
Shaltiel-Karyo, R., Frenkel-Pinter, M., Rockenstein, E., Patrick, C., Levy-Sakin, M., Schiller, A., et al. (2013). A blood-brain barrier (BBB) disrupter is also a potent α-synuclein (α-syn) aggregation inhibitor: A novel dual mechanism of mannitol for the treatment of Parkinson disease (PD). J. Biol. Chem. 288 (24), 17579–17588. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.434787
Spillantini, M. G., Schmidt, M. L., Lee, V. M., Trojanowski, J. Q., Jakes, R., Goedert, M., et al. (1997). Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388 (6645), 839–840. doi:10.1038/42166
Stefani, M. (2012). Structural features and cytotoxicity of amyloid oligomers: Implications in Alzheimer’s disease and other diseases with amyloid deposits. Prog. Neurobiol. 99 (3), 226–245. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2012.03.002
Stefanis, L. (2012). α-Synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2 (2), a009399. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a009399
Stöckl, M. T., Zijlstra, N., and Subramaniam, V. (2013). α-Synuclein oligomers: An amyloid pore? Insights into mechanisms of α-synuclein oligomer-lipid interactions. Mol. Neurobiol. 47 (2), 613–621. doi:10.1007/s12035-012-8331-4
Surguchov, A., Surgucheva, I., Sharma, M., Sharma, R., and Singh, V. (2017). Pore-forming proteins as mediators of novel epigenetic mechanism of epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 8, 3. doi:10.3389/fneur.2017.00003
Terakawa, M. S., Lee, Y.-H., Kinoshita, M., Lin, Y., Sugiki, T., Fukui, N., et al. (2018a). Membrane-induced initial structure of α-synuclein control its amyloidogenesis on model membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Biomembr. 1860 (3), 757–766. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.12.011
Terakawa, M. S., Lin, Y., Kinoshita, M., Kanemura, S., Itoh, D., Sugiki, T., et al. (2018b). Impact of membrane curvature on amyloid aggregation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Biomembr. 1860 (9), 1741–1764. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2018.04.012
Tetzlaff, J. E., Putcha, P., Outeiro, T. F., Ivanov, A., Berezovska, O., Hyman, B. T., et al. (2008). CHIP targets toxic alpha-Synuclein oligomers for degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 283 (26), 17962–17968. doi:10.1074/jbc.M802283200
Tolar, M., Abushakra, S., Hey, J. A., Porsteinsson, A., and Sabbagh, M. (2020). Aducanumab, gantenerumab, BAN2401, and ALZ-801—The first wave of amyloid-targeting drugs for alzheimer’s disease with potential for near term approval. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 12 (1), 95. doi:10.1186/s13195-020-00663-w
Uversky, V. N., Li, J., and Fink, A. L. (2001). Metal-triggered structural transformations, aggregation, and fibrillation of human alpha-synuclein. A possible molecular NK between Parkinson's disease and heavy metal exposure. J. Biol. Chem. 276 (47), 44284–44296. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105343200
Wagner, J., Ryazanov, S., Leonov, A., Levin, J., Shi, S., and Schmidt, F. (2013). Anle138b: A novel oligomer modulator for disease-modifying therapy of neurodegenerative diseases such as prion and Parkinson's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 125 (6), 795–813. doi:10.1007/s00401-013-1114-9
Wang, X., Moualla, D., Wright, J. A., and Brown, D. R. (2010). Copper binding regulates intracellular alpha-synuclein localisation, aggregation and toxicity. J. Neurochem. 113 (3), 704–714. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06638.x
Xu, C. K., Castellana-Cruz, M., Chen, S. W., Du, Z., Meisl, G., Levin, A., et al. (2022). The pathological G51D mutation in alpha-synuclein oligomers confers distinct structural attributes and cellular toxicity. Molecules 27 (4), 1293. doi:10.3390/molecules27041293
Yamin, G., Uversky, V. N., and Fink, A. L. (2003). Nitration inhibits fibrillation of human α-synuclein in vitro by formation of soluble oligomers. FEBS Lett. 542 (1-3), 147–152. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00367-3
Zaichick, S. V., McGrath, K. M., and Caraveo, G. (2017). The role of Ca2+ signaling in Parkinson's disease. Dis. Model. Mech. 10 (5), 519–535. doi:10.1242/dmm.028738
Zhao, J., Liang, Q., Sun, Q., Chen, C., Xu, L., Ding, Y., et al. (2017). (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) inhibits fibrillation, disaggregates amyloid fibrils of α-synuclein, and protects PC12 cells against α-synuclein-induced toxicity. RSC Adv. 7 (52), 32508–32517. doi:10.1039/C7RA03752J
Zhu, M., Han, S., and Fink, A. L. (2013). Oxidized quercetin inhibits α-synuclein fibrillization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1830 (4), 2872–2881. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.12.027
Keywords: alpha-synuclein, oligomers, polymorphism, fibrillation, toxicity, disease progression, Parkinson’s disease
Citation: Yoo JM, Lin Y, Heo Y and Lee Y-H (2022) Polymorphism in alpha-synuclein oligomers and its implications in toxicity under disease conditions. Front. Mol. Biosci. 9:959425. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.959425
Received: 01 June 2022; Accepted: 11 July 2022;
Published: 12 August 2022.
Edited by:
Anoop Arunagiri, University of Michigan, United StatesReviewed by:
Bikash Ranjan Sahoo, Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI), United StatesCopyright © 2022 Yoo, Lin, Heo and Lee. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Young-Ho Lee, bXIwNTA1QGtic2kucmUua3I=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.