
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Mol. Biosci. , 13 April 2022
Sec. Molecular Diagnostics and Therapeutics
Volume 9 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2022.901322
This article is part of the Research Topic Volume II: Novel Molecular Mechanisms and Innovative Therapeutic Approaches for Age-Associated Diseases View all 10 articles
This article is a correction to:
Sevoflurane Alleviates Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting P2X7-NLRP3 Mediated Pyroptosis
 Jiaxuan Wu1
Jiaxuan Wu1 Wenfeng Cai2
Wenfeng Cai2 Ruiming Du1
Ruiming Du1 Haiyang Li2
Haiyang Li2 Bin Wang2
Bin Wang2 Yanqiong Zhou1
Yanqiong Zhou1 Daifei Shen1
Daifei Shen1 Huimin Shen1
Huimin Shen1 Yang Lan1
Yang Lan1 Lesi Chen1
Lesi Chen1 Xiaoxia Zheng1
Xiaoxia Zheng1 Danmei Huang2
Danmei Huang2 Ganggang Shi2*
Ganggang Shi2*Corrigendum on
Sevoflurane Alleviates Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting P2X7-NLRP3 Mediated Pyroptosis
by Wu, J., Cai, W., Du, R., Li, H., Wang, B., Zhou, Y., Shen, D., Shen, H., Lan, Y., Chen, L., Zheng, X., Huang, D., and Shi, G. (2021). Front. Mol. Biosci. 8:768594. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.768594
There is an error in the Funding statement. The correct number for “the National Natural Science Foundation of China” is “ 81473215 and 81870276”.
Additionally, in the original article, there was a mistake in “Figures 2–4” as published. The problem was caused by the incomplete uploading of some figures in the process of uploading revised manuscripts and figures before publication. We did not carefully check it, which led to the error when publishing the article. The correct figures appear below:
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
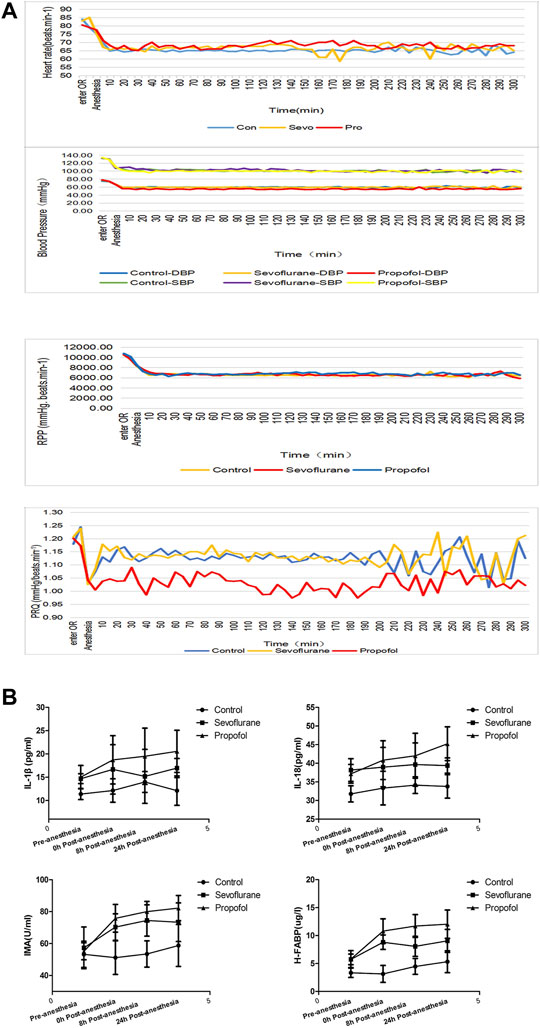
FIGURE 2. Changes in vital signs and inflammatory factors in these three groups of patients. (A) different general anesthetics on the changes of heart rate, blood pressure, RPP and PRQ in peri-anesthesia in the three groups. (B) Changes of IL-18 at different time points at pre- and post-anesthesia.
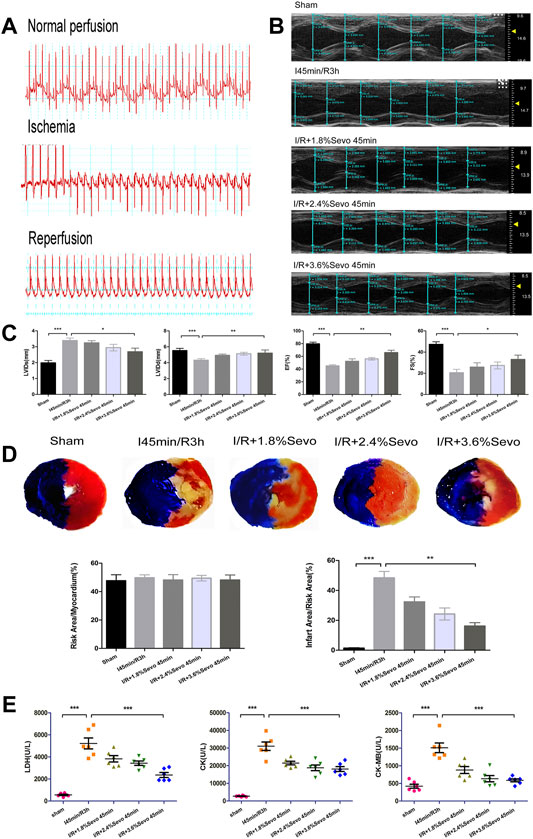
FIGURE 3. Sevoflurane alleviates MIRI in rats. (A) Typical electrocardiogram of normal perfusion, ligation of LAD and reperfusion. (B) Cardiac ultrasonography in rats of normal perfusion, MIRI and treatment with different concentrations of sevoflurane. (C) Histogram of rat cardiac ultrasonography. (D) Myocardial infarction area and histogram of rats treated with different concentrations of sevoflurane. (E) Effects of Sevoflurane at different concentrations on the release of LDH, CK, and CK-MB in myocardial tissue after MIRI. Data are expressed relative to the mean value of sham group and were presented as mean ± SD (n = 6). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. respective controls.
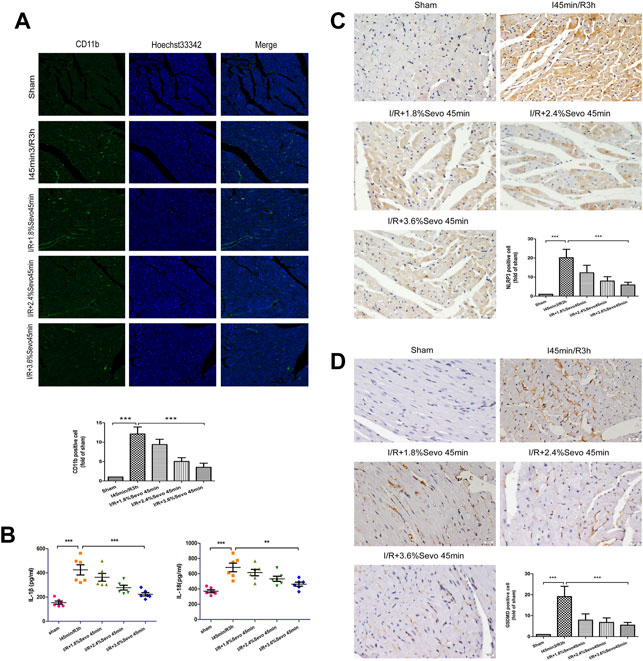
FIGURE 4. Sevoflurane alleviates inflammatory cell infiltration in MIRI rats. (A) The expression of CD11b in rat myocardial tissue determined by immunofluorescence staining (n = 6, Scale bars 20 µm). (B) Effects of Sevoflurane at different concentrations on the release of IL-1β and IL-18 in myocardial tissue after MIRI. All values are expressed as means ± SD (n = 6). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. respective controls. (C) Expression of NLRP3 in rat myocardial tissue by immunohistochemical staining of normal perfusion, MIRI and sevoflurane treatment with different concentrations in rats (n = 6, Scale bars 20 µm). (D) The Expression of GSDMD in rat myocardial tissue by immunohistochemical staining of normal perfusion, MIRI and sevoflurane treatment with different concentrations in rats (n = 6, Scale bars 20 µm). Data are expressed relative to the mean value for sham group and were presented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. respective controls.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: sevoflurane, myocardial ischemia reperfusion, hypoxia and reoxygenation, P2X7, NLRP3, pyroptosis
Citation: Wu J, Cai W, Du R, Li H, Wang B, Zhou Y, Shen D, Shen H, Lan Y, Chen L, Zheng X, Huang D and Shi G (2022) Corrigendum: Sevoflurane Alleviates Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting P2X7-NLRP3 Mediated Pyroptosis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 9:901322. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.901322
Received: 21 March 2022; Accepted: 22 March 2022;
Published: 13 April 2022.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2022 Wu, Cai, Du, Li, Wang, Zhou, Shen, Shen, Lan, Chen, Zheng, Huang and Shi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ganggang Shi, Z2dzaGlAc3R1LmVkdS5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.