
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
MINI REVIEW article
Front. Mol. Biosci. , 13 June 2022
Sec. Structural Biology
Volume 9 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2022.900547
This article is part of the Research Topic Small molecules Targeting Transmembrane Receptors and Ion Channels in Drug Discovery View all 6 articles
Opioid agonists produce their analgesic effects primarily by acting at the µ-opioid receptor (µOR). µOR agonists with different efficacies exert diverse molecular changes in the µOR which dictate the faith of the receptor’s signaling pathway and possibly it’s the degree of desensitization. Since the development of the active conformations of the µOR, growing data have been published in relation to ligand-specific changes in µOR activation. In this regard, this review summarizes recent data regarding the most studied opioid agonists in in silico µOR activation, including how these ligands are recognized by the µOR, how their binding signal is transmitted toward the intracellular parts of the µOR, and finally, what type of large-scale movements do these changes trigger in the µOR’s domains.
Growing data support that the rate of opioid side-effects including analgesic tolerance development strongly correlates with the pharmacodynamic properties of opioid ligands. Opioids with different efficacies distinctly induce molecular mechanisms related to tolerance, namely receptor phosphorylation and endocytosis, as the basis of G-protein coupled µ-opioid receptor (µOR) desensitization (Williams et al., 2013; Allouche et al., 2014; Lemel et al., 2020). It has been proposed that the selective and sequential phosphorylation of the C-terminus is due to the possible different conformational states of the receptor-triggered agonist specifically (Lemel et al., 2020). In recent years, we have gained more information regarding the nature of opioid agonists binding to the active conformation of the µOR (Huang et al., 2015; Koehl et al., 2018). This review will focus on the current knowledge of agonist specific residue contacts (Figure 1B), how the different agonists transmit the ligand-binding signal toward the intracellular receptor parts (Figure 1C), and finally, how these affect the orientation of certain receptor domains (e.g., transmembrane regions (TM) or intracellular loops (IL)) (Table 1), which eventually decide the faith of the receptor’s downstream signaling and the rate of desensitization. In addition, only data with the active conformation of the µOR will be reviewed here, namely the BU72 co-crystallized form and µOR-Gi complex co-crystallized with D-Ala2, N-MePhe4, and Gly-ol-enkephalin (DAMGO; PDB: 5C1M and PDB: 6DDF, respectively). Data on prototypic µOR-specific agonist ligands (Figure 1A), namely morphine, DAMGO, and fentanyl, will be reviewed alongside BU72, the first compound to be crystallized with the active conformational state of the µOR (Huang et al., 2015). TRV-130 and PZM21, newly developed G-protein-biased agonists, will be also reviewed (Figure 1A). In general, in the highlighted studies CHARMM (Brooks et al., 2009) and/or AMBER (Maier et al., 2015) force field was used, with 0.1–3.5 µs simulation time (in some cases, 24 µs; see Vo et al. (2020) in POPC (palmitoyl-oleoyl-phosphatidylcholine) lipid membrane model at ∼1 bar pressure and 310 K temperature in a ∼75–85 x 75–85 x 90–140 Å size simulation box. Some studies also used NMR spectroscopy to obtain dynamic structural information (Okude et al., 2015; Sounier et al., 2015). Such a pool of data will help us to better understand the basic molecular factors of ligand-specific receptor activation and tolerance, and allow us to purposefully develop opioids with delayed analgesic tolerance profiles and ameliorated side effects.
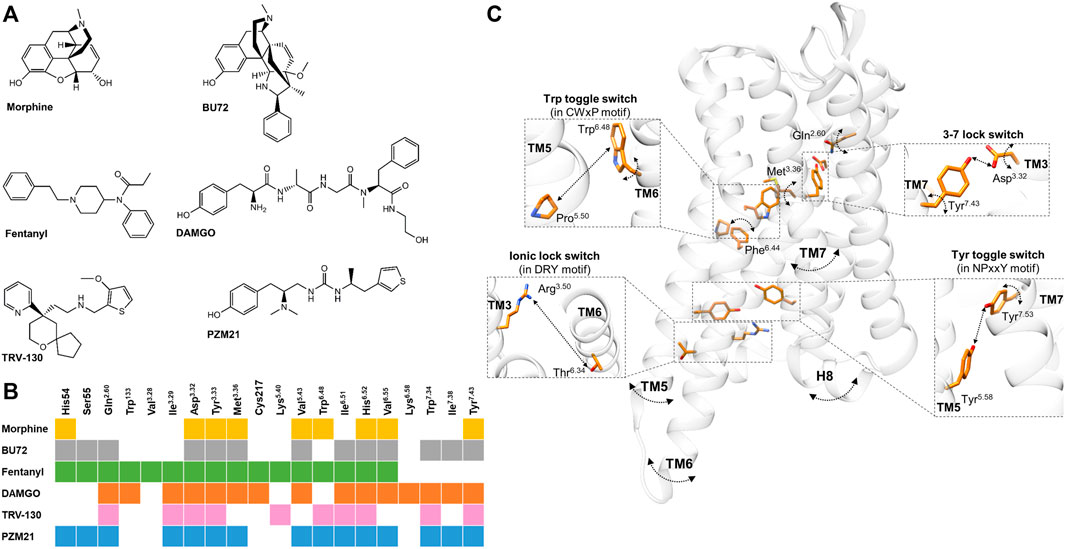
FIGURE 1. (A) Chemical structures of µOR-selective agonists discussed in the review. (B) The known µOR residual contacts of the indicated agonists. The original concept of the figure was based on Figure 4 of Podlewska and co-workers’ study (Podlewska et al., 2020) and extended by other data (Huang et al., 2015; Cheng et al., 2018; Koehl et al., 2018; Mafi et al., 2020; Ricarte et al., 2021). (C) Individual movements of the highlighted residues, molecular switches, and TM domains based on the data reviewed in the 3rd and 4th sections.. Participating residues are indicated in orange, arched arrows indicate the presence of spatial movements (but not the direction itself), while straight arrows depict the presence of altered distance between two residues. The corresponding agonists inducing these movements and alterations are not indicated for clarity; for details see in the 3rd and 4th sections. µOR is transparent for better visibility. The figure was constructed with UCSF Chimera 1.13.1 (Pettersen et al., 2004) based on Huang and co-workers using the BU72 co-crystallized active µOR structure (PDB: 5C1M) (Huang et al., 2015).
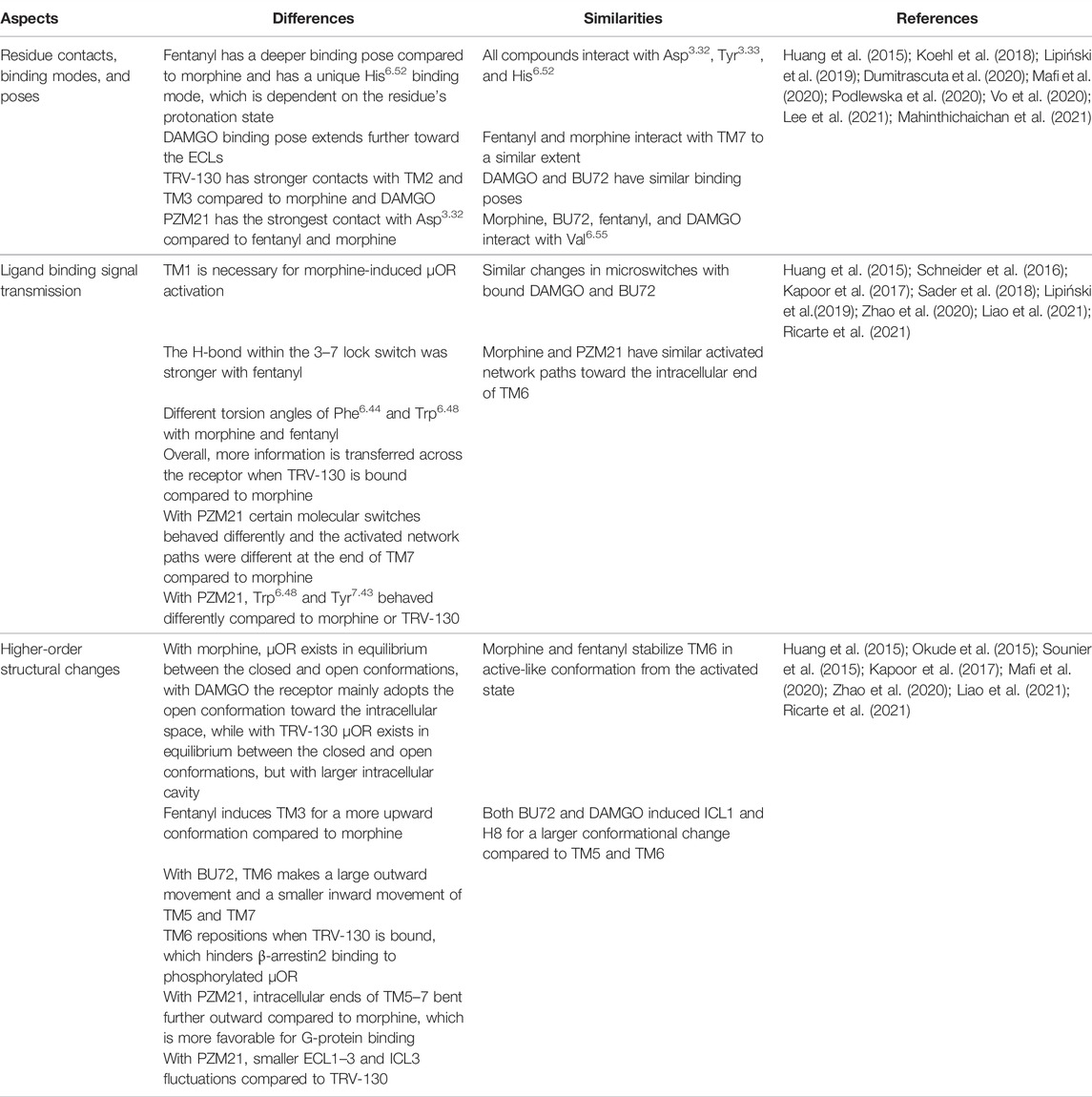
TABLE 1. Main differences and similarities within the highlighted ligands once bound to the µOR in terms of ligand recognition, binding signal transmission, and global movements.
Based on site-directed mutagenesis and in silico studies, multiple conserved residues have been identified in the µOR binding pocket, which have significant roles in ligand orientation and receptor activation (Mansour et al., 1997; Manglik et al., 2012, 2015, 2016; Katritch et al., 2013; Kaserer et al., 2016; Koehl et al., 2018; Marino et al., 2018; Manglik, 2020; Ricarte et al., 2021). Hitherto, data on the agonist-specific residue contacts and binding modes will be reviewed in this section.
Despite morphine and fentanyl interacting with the same contact residues (Figure 1B), their binding poses were less overlapped (Lipiński et al., 2019). Accordingly, fentanyl is in close proximity to seven TM3 residues and three TM6 residues, while in the case of morphine these numbers are four and five with respect to the same transmembrane domains. They also interact with TM7 to a similar extent but with different positions. Fentanyl is also able to reach the ECL1, ECL2, and the N-terminus. These findings were later confirmed by another group (Ricarte et al., 2021).
Analyzing the dissociation of morphine from the µOR, it showed that morphine directly dissociated from the orthosteric site region and also transitioned to the vestibule region after the Asp3.32 salt bridge was disrupted (Ribeiro et al., 2020) (superscript numbering refers to the Ballesteros and Weinstein’s generic numbering scheme (Ballesteros and Weinstein, 1995)).
Fentanyl binds deeper compared to morphinan structures (for fentanyl it is indicated by a lower ΔZ value, the distance between the centers of mass (COM) of fentanyl and µOR z direction) and it can form a salt-bridge interaction between the piperidine amine and the conserved Asp3.32 (Vo et al., 2020) similar to DAMGO or BU72 (Huang et al., 2015; Weis and Kobilka, 2018). Vo and co-workers described a His6.52 binding mode unique to fentanyl, which was also dependent on the protonation state of this residue (Vo et al., 2020). Another study found that the dissociation pathways, time, the depth of insertion, and the strength of TM6 interaction of fentanyl are dependent on the protonation state of His6.52 (Mahinthichaichan et al., 2021).
In the case of BU72, most of its interactions with the active µOR are hydrophobic or aromatic. The phenolic hydroxyl group of BU72 interacts with His6.52 in a water-mediated fashion (Huang et al., 2015). There is also an ionic interaction between Asp3.32 and the morphinan tertiary amine structure of BU72. BU72 stabilizes the rearrangement of a triad of conserved residues upon receptor activation (Huang et al., 2015). BU72 also forms a hydrophobic surface with Ile6.51 and Val6.55 in TM6 and Ile7.39 in TM7, similarly to other morphinan structures (Figure 1B) (Huang et al., 2015). Another study demonstrated that BU72 binding poses distinct from the active µOR crystal structures and presumed that the high affinity and agonist character of BU72 is in part presented by its configurational entropy (Feinberg et al., 2017).
Koehl et al. found that the conformation of the active-state binding pocket and the orientation of the residues that interact with the agonist are highly similar between BU72 and DAMGO, despite the structural differences (Figure 1B) (Koehl et al., 2018). On the other hand, compared to BU72, the C-terminus of DAMGO extends further toward the ECLs. Another study with DAMGO has shown that the tyrosine of the peptide forms lipophilic contacts with Met3.36, Ile6.51, and Val6.55 residues and forms a charge interaction with Asp3.32 (Figure 1B) (Dumitrascuta et al., 2020).
It has been proved that TRV-130 has stronger interactions (a greater number of hydrophobic contacts) with TM2 and TM3 compared to morphine or DAMGO in β-arrestin2 stabilized with phosphorylated µOR (Mafi et al., 2020). Based on docking simulations, the protonated nitrogen ion of TRV130 formed electrostatic interactions with Asp3.32 and through its ring structure formed interactions with His6.52 (Figure 1B) (Cheng et al., 2018).
PZM21 interacts with the active µOR binding pocket by hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and an ionic bond (Manglik et al., 2016). Podlewska and co-workers have compared PZM21 with fentanyl or morphine in docking and MD simulations in BU72 and DAMGO co-crystallized active structures (Podlewska et al., 2020). Interestingly, all compounds showed less stability in their orientations in the DAMGO co-crystallized conformation, especially morphine, meaning that their initial and final binding orientations were significantly different during the simulation. They also found that during simulation time, PZM21 had more contacts with Asp3.32 in both crystal structures compared to fentanyl or morphine (Podlewska et al., 2020). Another recent study compared PZM21 to morphine in MD simulations and found that besides PZM21 interacting with key residues Asp3.32 and Tyr3.33 of TM3 (Figure 1B), similar to morphine, yet it strongly interacts with Tyr7.43 of TM7 (Figure 1B), as indicated by a higher percentage of interaction fractions in H-bonds (Liao et al., 2021). Finally, Lee and co-workers have performed molecular docking with new potential biased µOR agonists, where they also compared these novel compounds to TRV-130 and PZM21 for control. Here, they found that TRV-130 and PZM21 failed to accomplish contact with Val6.55 in contrast to the novel compounds, which is heavily involved with hydrophobic interactions (Lee et al., 2021).
The subtle changes in the ligand-binding pocket induced by the bound ligand trigger further delicate changes through a channel of residues within certain TM domains. These changes transmit the ligand-binding signal from the ligand-binding site to the cytoplasmic region of the receptor (Weng et al., 2017; Liao et al., 2021). Some of these groups of residues are generally termed as molecular switches and they are conserved across the GPCR family. Among these, the 3–7 lock switch, the NPxxY motif (Asn-Pro-Xaa-Xaa-Tyr), the tyrosine (Tyr7.53) toggle switch, the Trp6.48 rotamer toggle switch, ionic lock (or DRY motif, Asp-Arg-Tyr), or the transmission switch (or CWxP motif, Cys-Trp-Xaa-Pro) have been described to be altered in an agonist specific manner in the µOR and will be discussed in this section, among other related data. The role of these molecular switches has been described in detail in other studies (Lagerström and Schiöth, 2008; Nygaard et al., 2009; Chabbert et al., 2012; Trzaskowski et al., 2012; Marino et al., 2018; Filipek, 2019) and due to length limitations will not be discussed here.
A study demonstrated that the conformations of certain residues (Met3.36 and Gln2.60) were different compared to morphine and fentanyl bound states (Figure 1C) (Ricarte et al., 2021). These differences affected the Asp3.32−Tyr7.43 H-bonding (3–7 lock switch) (Figure 1C), which was stronger when fentanyl was present (indicated by higher H-bond occupancy values) (Ricarte et al., 2021). They also found that the conformational changes in the NPxxY motif were consistently induced in the more stable active-like state by fentanyl (Ricarte et al., 2021). These specific changes might explain the higher efficacy of fentanyl. Another study proposed that the N-aniline ring of fentanyl mediates µOR β-arrestin coupling through the Met3.36 residue (de Waal et al., 2020). Additionally, a clear difference was shown in torsion angles of Trp6.48 between morphine and fentanyl (Figure 1C) (Lipiński et al., 2019). Also, the frequency changes of the torsion angles of Phe6.44 were considered the main difference between morphine and fentanyl. The same study revealed differences between morphine and fentanyl in the 3–7 lock switch and being tighter in the presence of morphine (Figure 1C) (Lipiński et al., 2019).
Sena et al. showed that morphine tends to drive the receptor toward increasing the distance in the 3–7 lock switch (Figure 1C) and found an important conformational change in TM5 when morphine was present (Sena et al., 2021). It is worth noting that MD simulations have been performed with morphine and a µOR splice variant lacking the complete TM1 (Majumdar et al., 2011,2012; Lu et al., 2015) where TM1 truncation results in the loss of key interactions that are necessary for morphine-induced µOR activation (Sader et al., 2018).
Huang and co-workers revealed an extensive network of polar interactions between the orthosteric binding pocket and the G-protein coupling interface, which rearranges upon receptor activation with BU72 (Huang et al., 2015). The NPxxY motif is also involved in this polar network and moves inward toward the TM5 upon activation (Figure 1C) (Huang et al., 2015). Later on, they found similar changes in the microswitches when DAMGO was bound to the µOR–Gi protein complex structure (Koehl et al., 2018).
Cheng and co-workers compared BU72 and TRV130, where the stability of Asp3.32 was lower with TRV-130 compared to BU72 (Figure 1C) since the dominant torsion angle was ∼ -12° and occupied ∼23% of the simulation time in the presence of TRV-130 (BU72: ∼28°, ∼45%) (Cheng et al., 2018). A study analyzed the allosteric communication between the orthosteric binding pocket and the intracellular region of the µOR with TRV-130 compared to morphine (Schneider et al., 2016). According to contact probability calculations, TRV-130 only communicated with residues of the intracellular end of TM3 and there was no strong contact with residues at the end of TM6. Morphine allosterically regulated significant interactions with the intracellular ends of both TM3 and TM6. Additionally, the network of side-chain interactions adjacent to TRV-130 was significantly smaller compared to morphine (Schneider et al., 2016). Also, when TRV-130 was bound, the residues in the EC2 and EC3 loops of the µOR formed a substantially extensive network of polar interactions when compared to morphine (Schneider et al., 2016). Kapoor and co-workers had found that more information is transferred across the receptor in TRV-130-bound µOR than in morphine-bound µOR based on transfer entropy analysis; for instance, the three extracellular loop regions are not involved entirely in any information transfer in the case of morphine (Kapoor et al., 2017).
Another study has found that morphine- and PZM21-activated network paths toward the intracellular end of TM6 were mostly identical, but the paths to the end of TM7 were evidently different (Liao et al., 2021). The same study also compared three key molecular switches, the ionic lock (DRY), transmission (CWxP), and Tyr toggle switches. Here, they found distance and rotational changes between morphine- and PMZ21-bound µOR, which affect the positions of TM5-7 (see later) (Figure 1C) (Liao et al., 2021). In another MD simulation, they compared TRV-130 and PZM21 with morphine, and one of the main differences was that the side chain of Trp6.48 (Figure 1C) was reversed with a delay with PZM21 compared to morphine (300 vs. 50 ns) and that Tyr7.43 side chain (Figure 1C) rotated with less fluctuation range compared to TRV-130-bound µOR (PZM21: 100°–175° vs. TRV-130: 100°–150°) (Zhao et al., 2020). These results also point to the low potency and lower bias effect of PZM21.
With GPCRs, the subtle changes in the ligand-binding pocket and ligand binding signal transmission throughout the TM domains add up to large, global toggle switch movements of the TM domains (Nygaard et al., 2009; Venkatakrishnan et al., 2013). These movements are crucial in the receptor inactive–active conformation transition (Huang et al., 2015; Zhou et al., 2019). However, regarding the µOR, there are multiple data pointing out that agonists with different efficacies or functional selectivities trigger these large movements differently or to a different degree. Such data will be reviewed in this section.
A study comparing fentanyl and morphine showed that fentanyl selects for more upward conformations of TM3 than morphine (+0.6 Å vs +0.2 Å) (Ricarte et al., 2021). Additionally, both compounds are able to stabilize an active-like conformation of TM6 in simulations initiated from the activated state; however, only fentanyl can achieve the same when starting from the inactive state of the receptor. This difference may contribute to the greater efficacy of fentanyl relative to morphine.
In the case of BU72, upon activation, TM6 makes a large 10 Å outward movement and smaller inward movement of TM5 and TM7 (Figure 1C) (Huang et al., 2015). Complementing these data in the presence of a G-protein mimetic nanobody in solution-state NMR, a weak allosteric coupling was revealed between the agonist-binding pocket and the G-protein-coupling interface (TM5 and TM6) (Sounier et al., 2015), similar to that observed for the β2-adrenergic receptor (Manglik et al., 2015). Most interestingly, in the presence of BU72 or DAMGO alone, ICL1 and H8 showed larger conformational changes (Figure 1C) (indicated by larger spectral signals) compared to TM5 and TM6, suggesting that these domains might play a role in the initial interaction with the G-protein (Sounier et al., 2015).
Okude et al. studied the NMR signals from methionine residues of the µOR in the morphine-, DAMGO-, and TRV-130-bound states. They found that when morphine was bound, µOR exists in equilibrium between the closed and open conformations; in the DAMGO-bound state, the receptor mainly adopts the open conformation. Upon TRV-130 binding, µOR exists in equilibrium between the closed and open conformations; however, in such cases, the open conformation adopts a larger intracellular cavity (Okude et al., 2015). The study also demonstrated that the population of each open conformation defines the G-protein- and arrestin-mediated signaling levels in each ligand-bound state.
Kapoor et al. found that morphine-bound μOR motions involved the cytoplasmic ends of only TM6, TM3, and TM5 (Figure 1C). On the other hand, the TRV-130-bound μOR motions involved residues in TM1, TM2, TM3, TM5, TM7, and helix 8 (Kapoor et al., 2017). Also, TM6 bending and intra-helical backbone hydrogen bond rearrangement were only observed with morphine- but not with TRV-130-bound µOR (Kapoor et al., 2017).
Mafi and co-workers compared morphine, DAMGO, and TRV-130 in MD simulations with the β-arrestin2-stabilized active phosphorylated µOR (Mafi et al., 2020). Accordingly, in the presence of non-biased agonists, β-arrestin2 coupled to the phosphorylated µOR by forming more polar connections with ICL2 and either the ICL3 or the cytoplasmic region of TM6. In contrast, TRV-130 induced a reposition of TM6 in the cytoplasmic region of the µOR by forming more polar interactions with TM2 and TM3. This repositioning hinders β-arrestin2 from properly binding to the phosphorylated µOR.
PZM21 was bound to µOR, TM5-6 and TM7 showed a larger outward and less inward movement, respectively (Figure 1C) (Liao et al., 2021). Also, the further outward movement of TM5–7 of the PZM21-bound µOR created a larger cavity potentially favorable for G protein binding. Zhao et al. analyzed and compared the flexibility of the loop region of PZM21 with morphine and TRV-130, and they found that the protein root mean square fluctuation (RMSF) values of morphine- and PZM21-bound µOR in the ECL1-3 and ICL3 regions were significantly smaller than those of TRV130-bound µOR (Zhao et al., 2020).
The introduction of the two active conformational structures of the µOR now allows a more precise analysis of ligand-specific changes in the receptor. Reviewing the increasing amount of the data regarding ligand-specific structural changes in µOR activation, certain tendencies can be observed (Table 1; Figure 1C). The current data proved that ligand recognition largely depends on the structural properties of the ligand. The highlighted ligands in this review differ in terms of flexibility, H-bond capabilities, and energy landscapes (Podlewska et al., 2020; Vo et al., 2020; Giannos et al., 2021). For instance, morphine and fentanyl despite being in contact with similar residues (Figure 1B), the binding pose itself is significantly different since morphine is more rigid and compact, while fentanyl is more flexible with an elongated shape. On the other hand, BU72 and DAMGO structurally differ significantly and there is also a difference regarding the depth of their binding pose. However, the conformation of the active binding pocket is highly similar. In the case of biased agonists TRV-130 and PZM21, it seems that they accomplish stronger and/or more contact with the receptor compared to unbiased ligands.
There are significantly more differences than similarities when it comes to forwarding the ligand-binding signal to the intracellular regions of the receptor. There are subtle, but important ligand-specific changes within the molecular switches; for instance, the different torsion angles or distances between the involved residues (Figure 1C). As mentioned above, such minor changes might also explain the higher efficacy of fentanyl (Ricarte et al., 2021) or β-arrestin coupling (de Waal et al., 2020). Another interesting finding is that with PZM21 the difference in rotations of certain residues can be associated with its lower bias effect (Zhao et al., 2020). Such delicate changes induce larger-scale movements for the µOR, which eventually dictate the faith of the receptor’s signaling pathway and possibly it’s degree of desensitization. These larger movements in essence allow a physical barrier or a favorable position for either the G-protein or β-arrestins, depending on the bound ligand.
In conclusion, ligand-specific µOR activation is defined by the following: 1) distinct number and/or degree of residue contacts within the ligand-binding pocket; 2) ligand-specific subtle changes within the residues (with respect to torsion angles and distances) of the TM regions, and as a consequence 3) triggers large-scale movements, toggles in certain domains of the receptor defining the type of downstream signaling of the µOR, as well as the degree of receptor desensitization. Further mapping these steps might open new strategies to develop opioid agonists with reduced analgesic tolerance and other side effects.
FZ and MA-K performed the conceptualization. FZ constructed the figures and tables and performed the writing of the original draft. FZ, NE, KK, and MA-K performed the reviewing and editing of the manuscript.
This work was supported by the Hungarian Academy of Sciences “Bolyai János” Research Fellowship (BO/00476/20/5). Project no. FK_138389 and TKP2021-EGA-25 have been implemented with the support provided by the Ministry of Innovation and Technology of Hungary from the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund, financed under the FK_21 and TKP2021-EGA funding scheme.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Allouche, S., Noble, F., and Marie, N. (2014). Opioid Receptor Desensitization: Mechanisms and its Link to Tolerance. Front. Pharmacol. 5, 280. doi:10.3389/fphar.2014.00280
Ballesteros, J. A., and Weinstein, H. (1995). “Integrated Methods for the Construction of Three-Dimensional Models and Computational Probing of Structure-Function Relations in G Protein-Coupled Receptors,” in Methods in Neurosciences. Editor S.C. Sealfon (Cambridge, MA: Academic Press), 366–428. doi:10.1016/s1043-9471(05)80049-7
Brooks, B. R., Brooks, C. L., Mackerell, A. D., Nilsson, L., Petrella, R. J., Roux, B., et al. (2009). CHARMM: The Biomolecular Simulation Program. J. Comput. Chem. 30, 1545–1614. doi:10.1002/jcc.21287
Chabbert, M., Castel, H., Pele, J., Deville, J., Legendre, R., and Rodien, P. (2012). Evolution of Class A G-Protein-Coupled Receptors: Implications for Molecular Modeling. Cmc 19, 1110–1118. doi:10.2174/092986712799320600
Cheng, J.-x., Cheng, T., Li, W.-h., Liu, G.-x., Zhu, W.-l., and Tang, Y. (2018). Computational Insights into the G-Protein-Biased Activation and Inactivation Mechanisms of the μ Opioid Receptor. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 39, 154–164. doi:10.1038/aps.2017.158
de Waal, P. W., Shi, J., You, E., Wang, X., Melcher, K., Jiang, Y., et al. (2020). Molecular Mechanisms of Fentanyl Mediated β-arrestin Biased Signaling. PLoS Comput. Biol. 16, e1007394. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007394
Dumitrascuta, M., Bermudez, M., Ballet, S., Wolber, G., and Spetea, M. (2020). Mechanistic Understanding of Peptide Analogues, DALDA, [Dmt1]DALDA, and KGOP01, Binding to the Mu Opioid Receptor. Molecules 25, 2087. doi:10.3390/molecules25092087
Feinberg, E. N., Farimani, A. B., Hernandez, C. X., and Pande, V. S. (2017). Kinetic Machine Learning Unravels Ligand-Directed Conformational Change of μ Opioid Receptor. bioRxiv 114, 170886. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2017.11.359
Filipek, S. (2019). Molecular Switches in GPCRs. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 55, 114–120. doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2019.03.017
Giannos, T., Lešnik, S., Bren, U., Hodošček, M., Domratcheva, T., and Bondar, A.-N. (2021). CHARMM Force-Field Parameters for Morphine, Heroin, and Oliceridine, and Conformational Dynamics of Opioid Drugs. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 61, 3964–3977. doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.1c00667
Huang, W., Manglik, A., Venkatakrishnan, A. J., Laeremans, T., Feinberg, E. N., Sanborn, A. L., et al. (2015). Structural Insights into Μ-Opioid Receptor Activation. Nature 524, 315–321. doi:10.1038/nature14886
Kapoor, A., Martinez-Rosell, G., Provasi, D., de Fabritiis, G., and Filizola, M. (2017). Dynamic and Kinetic Elements of Μ-Opioid Receptor Functional Selectivity. Sci. Rep. 7, 11255. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-11483-8
Kaserer, T., Lantero, A., Schmidhammer, H., Spetea, M., and Schuster, D. (2016). μ Opioid Receptor: Novel Antagonists and Structural Modeling. Sci. Rep. 6, 21548. doi:10.1038/srep21548
Katritch, V., Cherezov, V., and Stevens, R. C. (2013). Structure-Function of the G Protein-Coupled Receptor Superfamily. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 53, 531–556. doi:10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-032112-135923
Koehl, A., Hu, H., Maeda, S., Zhang, Y., Qu, Q., Paggi, J. M., et al. (2018). Structure of the Μ-Opioid Receptor-Gi Protein Complex. Nature 558, 547–552. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0219-7
Lagerström, M. C., and Schiöth, H. B. (2008). Structural Diversity of G Protein-Coupled Receptors and Significance for Drug Discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 7, 339–357. doi:10.1038/nrd2518
Lamim Ribeiro, J. M., Provasi, D., and Filizola, M. (2020). A Combination of Machine Learning and Infrequent Metadynamics to Efficiently Predict Kinetic Rates, Transition States, and Molecular Determinants of Drug Dissociation from G Protein-Coupled Receptors. J. Chem. Phys. 153, 124105. doi:10.1063/5.0019100
Lee, J. H., Shon, S.-Y., Jeon, W., Hong, S.-J., Ban, J., and Lee, D. S. (2021). Discovery of μ,δ-Opioid Receptor Dual-Biased Agonists that Overcome the Limitation of Prior Biased Agonists. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 4, 1149–1160. doi:10.1021/acsptsci.1c00044
Lemel, L., Lane, J. R., and Canals, M. (2020). GRKs as Key Modulators of Opioid Receptor Function. Cells 9, 2400. doi:10.3390/cells9112400
Liao, S., Tan, K., Floyd, C., Bong, D., Pino, M. J., and Wu, C. (2021). Probing Biased Activation of Mu-Opioid Receptor by the Biased Agonist PZM21 Using All Atom Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Life Sci. 269, 119026. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119026
Lipiński, P. F. J., Jarończyk, M., Dobrowolski, J. C., and Sadlej, J. (2019). Molecular Dynamics of Fentanyl Bound to μ-opioid Receptor. J. Mol. Model. 25, 144. doi:10.1007/s00894-019-3999-2
Lu, Z., Xu, J., Rossi, G. C., Majumdar, S., Pasternak, G. W., and Pan, Y.-X. (2015). Mediation of Opioid Analgesia by a Truncated 6-transmembrane GPCR. J. Clin. Investig. 125, 2626–2630. doi:10.1172/jci81070
Mafi, A., Kim, S.-K., and Goddard, W. A. (2020). Mechanism of β-arrestin Recruitment by the μ-opioid G Protein-Coupled Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 117, 16346–16355. doi:10.1073/pnas.1918264117
Mahinthichaichan, P., Vo, Q. N., Ellis, C. R., and Shen, J. (2021). Kinetics and Mechanism of Fentanyl Dissociation from the μ-Opioid Receptor. JACS Au 1, 2208–2215. doi:10.1021/jacsau.1c00341
Maier, J. A., Martinez, C., Kasavajhala, K., Wickstrom, L., Hauser, K. E., and Simmerling, C. (2015). ff14SB: Improving the Accuracy of Protein S ide Chain and Backbone Parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 11, 3696–3713. doi:10.1021/acs.jctc.5b00255
Majumdar, S., Grinnell, S., Le Rouzic, V., Burgman, M., Polikar, L., Ansonoff, M., et al. (2011). Truncated G Protein-Coupled Mu Opioid Receptor MOR-1 Splice Variants Are Targets for Highly Potent Opioid Analgesics Lacking Side Effects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 19778–19783. doi:10.1073/pnas.1115231108
Majumdar, S., Subrath, J., Le Rouzic, V., Polikar, L., Burgman, M., Nagakura, K., et al. (2012). Synthesis and Evaluation of Aryl-Naloxamide Opiate Analgesics Targeting Truncated Exon 11-Associated μ Opioid Receptor (MOR-1) Splice Variants. J. Med. Chem. 55, 6352–6362. doi:10.1021/jm300305c
Manglik, A., Kim, T. H., Masureel, M., Altenbach, C., Yang, Z., Hilger, D., et al. (2015). Structural Insights into the Dynamic Process of β 2 -Adrenergic Receptor Signaling. Cell. 161, 1101–1111. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.04.043
Manglik, A., Kruse, A. C., Kobilka, T. S., Thian, F. S., Mathiesen, J. M., Sunahara, R. K., et al. (2012). Crystal Structure of the Μ-Opioid Receptor Bound to a Morphinan Antagonist. Nature 485, 321–326. doi:10.1038/nature10954
Manglik, A., Lin, H., Aryal, D. K., McCorvy, J. D., Dengler, D., Corder, G., et al. (2016). Structure-based Discovery of Opioid Analgesics with Reduced Side Effects. Nature 537, 185–190. doi:10.1038/nature19112
Manglik, A. (2020). Molecular Basis of Opioid Action: From Structures to New Leads. Biol. Psychiatry 87, 6–14. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.08.028
Mansour, A., Taylor, L. P., Fine, J. L., Thompson, R. C., Hoversten, M. T., Mosberg, H. I., et al. (1997). Key Residues Defining the Mu-Opioid Receptor Binding Pocket: a Site-Directed Mutagenesis Study. J. Neurochem. 68, 344–353. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.1997.68010344.x
Marino, K. A., Shang, Y., and Filizola, M. (2018). Insights into the Function of Opioid Receptors from Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Available Crystal Structures. Br. J. Pharmacol. 175, 2834–2845. doi:10.1111/bph.13774
Nygaard, R., Frimurer, T. M., Holst, B., Rosenkilde, M. M., and Schwartz, T. W. (2009). Ligand Binding and Micro-switches in 7TM Receptor Structures. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 30, 249–259. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2009.02.006
Okude, J., Ueda, T., Kofuku, Y., Sato, M., Nobuyama, N., Kondo, K., et al. (2015). Identification of a Conformational Equilibrium that Determines the Efficacy and Functional Selectivity of the μ‐Opioid Receptor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 15771–15776. doi:10.1002/anie.201508794
Pettersen, E. F., Goddard, T. D., Huang, C. C., Couch, G. S., Greenblatt, D. M., Meng, E. C., et al. (2004). UCSF Chimera?A Visualization System for Exploratory Research and Analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 25, 1605–1612. doi:10.1002/jcc.20084
Podlewska, S., Bugno, R., Kudla, L., Bojarski, A. J., and Przewlocki, R. (2020). Molecular Modeling of Μ Opioid Receptor Ligands with Various Functional Properties: PZM21, SR-17018, Morphine, and Fentanyl-Simulated Interaction Patterns Confronted with Experimental Data. Molecules 25, 4636. doi:10.3390/molecules25204636
Ricarte, A., Dalton, J. A. R., and Giraldo, J. (2021). Structural Assessment of Agonist Efficacy in the μ-Opioid Receptor: Morphine and Fentanyl Elicit Different Activation Patterns. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 61, 1251–1274. doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.0c00890
Sader, S., Anant, K., and Wu, C. (2018). To Probe Interaction of Morphine and IBNtxA with 7TM and 6TM Variants of the Human μ-opioid Receptor Using All-Atom Molecular Dynamics Simulations with an Explicit Membrane. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20, 1724–1741. doi:10.1039/c7cp06745c
Schneider, S., Provasi, D., and Filizola, M. (2016). How Oliceridine (TRV-130) Binds and Stabilizes a μ-Opioid Receptor Conformational State that Selectively Triggers G Protein Signaling Pathways. Biochemistry 55, 6456–6466. doi:10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00948
Sena, D. M., Cong, X., and Giorgetti, A. (2021). Ligand Based Conformational Space Studies of the μ-opioid Receptor. Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subj. 1865, 129838. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2020.129838
Sounier, R., Mas, C., Steyaert, J., Laeremans, T., Manglik, A., Huang, W., et al. (2015). Propagation of Conformational Changes during μ-opioid Receptor Activation. Nature 524, 375–378. doi:10.1038/nature14680
Trzaskowski, B., Latek, D., Yuan, S., Ghoshdastider, U., Debinski, A., and Filipek, S. (2012). Action of Molecular Switches in GPCRs - Theoretical and Experimental Studies. Cmc 19, 1090–1109. doi:10.2174/092986712799320556
Venkatakrishnan, A. J., Deupi, X., Lebon, G., Tate, C. G., Schertler, G. F., and Babu, M. M. (2013). Molecular Signatures of G-Protein-Coupled Receptors. Nature 494, 185–194. doi:10.1038/nature11896
Vo, Q., Mahinthichaichan, P., Shen, J., and Ellis, C. (2021). How Mu-Opioid Receptor Recognizes Fentanyl. Nat. Commun. 12(1), 984. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-21262-9
Weis, W. I., and Kobilka, B. K. (2018). The Molecular Basis of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Activation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 87, 897–919. doi:10.1146/annurev-biochem-060614-033910
Weng, W.-H., Li, Y.-T., and Hsu, H.-J. (2017). Activation-Induced Conformational Changes of Dopamine D3 Receptor Promote the Formation of the Internal Water Channel. Sci. Rep. 7, 12792. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-13155-z
Williams, J. T., Ingram, S. L., Henderson, G., Chavkin, C., von Zastrow, M., Schulz, S., et al. (2013). Regulation Ofµ-Opioid Receptors: Desensitization, Phosphorylation, Internalization, and Tolerance. Pharmacol. Rev. 65, 223–254. doi:10.1124/pr.112.005942
Zhao, Z., Huang, T., and Li, J. (2020). Molecular Dynamics Simulations to Investigate How PZM21 Affects the Conformational State of the μ-Opioid Receptor upon Activation. Ijms 21, 4699. doi:10.3390/ijms21134699
Keywords: μ-opioid receptor, agonist-specific receptor activation, prototypic μ-opioid receptor agonist, TRV-130, PZM21
Citation: Zádor F, Király K, Essmat N and Al-Khrasani M (2022) Recent Molecular Insights into Agonist-specific Binding to the Mu-Opioid Receptor. Front. Mol. Biosci. 9:900547. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.900547
Received: 20 March 2022; Accepted: 21 April 2022;
Published: 13 June 2022.
Edited by:
Fabio Arturo Iannotti, Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (CNR), ItalyReviewed by:
Haiguang Liu, Beijing Computational Science Research Center (CSRC), ChinaCopyright © 2022 Zádor, Király, Essmat and Al-Khrasani. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ferenc Zádor, emFkb3IuZmVyZW5jQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
†Present address: Pharmacological and Drug Safety Research, Gedeon Richter Plc, Budapest, Hungary
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.