- 1Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, The City College of New York, New York, NY, United States
- 2PhD Program in Biochemistry, The Graduate Center of CUNY, New York, NY, United States
- 3PhD Program in Chemistry, The Graduate Center of CUNY, New York, NY, United States
- 4PhD Program in Physics, The Graduate Center of CUNY, New York, NY, United States
Bacterial tyrosine kinases (BY-kinases) and shikimate kinases (SKs) comprise two structurally divergent P-loop containing enzyme families that share similar catalytic site geometries, most notably with respect to their Walker-A, Walker-B, and DxD motifs. We had previously demonstrated that in BY-kinases, a specific interaction between the Walker-A and Walker-B motifs, driven by the conserved “catalytic” lysine housed on the former, leads to a conformation that is unable to efficiently coordinate Mg2+•ATP and is therefore incapable of chemistry. Here, using enhanced sampling molecular dynamics simulations, we demonstrate that structurally similar interactions between the Walker-A and Walker-B motifs, also mediated by the catalytic lysine, stabilize a state in SKs that deviates significantly from one that is necessary for the optimal coordination of Mg2+•ATP. This structural role of the Walker-A lysine is a general feature in SKs and is found to be present in members that encode a Walker-B sequence characteristic of the family (Coxiella burnetii SK), and in those that do not (Mycobacterium tuberculosis SK). Thus, the structural role of the Walker-A lysine in stabilizing an inactive state, distinct from its catalytic function, is conserved between two distantly related P-loop containing kinase families, the SKs and the BY-kinases. The universal conservation of this element, and of the key characteristics of its associated interaction partners within the Walker motifs of P-loop containing enzymes, suggests that this structural role of the Walker-A lysine is perhaps a widely deployed regulatory mechanism within this ancient family.
Introduction
P-loop containing proteins are widespread in all three branches of the tree of life suggesting that they emerged prior to the last universal common ancestor (LUCA) (Aravind et al., 2002; Edwards et al., 2013; Longo et al., 2020). Nucleotide triphosphatases (NTPases) (Leipe et al., 2002) and P-loop kinases constitute two of several divergent families of P-loop containing enzymes that encode sequences known as Walker-A (GxxxGK[S/T], x is any residue) and Walker-B (ϕϕϕϕ[D/E]xxG, ϕ is a hydrophobic residue) motifs, or variations thereon (Walker et al., 1982). The BY-kinases (for Bacterial tYrosine kinases), that are widely conserved within the prokaryotic kingdom, but are without archaeal or eukaryotic counterparts (Shi et al., 2014), constitute a unique family of protein tyrosine kinases within the SIMIBI (named for the signal-recognition GTPases, MinD and BioD superfamilies) class of NTPases (Leipe et al., 2002). Instead of the dual-lobed fold characteristic of the eukaryotic protein kinases (Taylor and Radzio-Andzelm, 1994; Scheeff and Bourne, 2005), the catalytic domains (CDs) of BY-kinases (Lee and Jia, 2009; Grangeasse et al., 2012) utilize a fold that closely resembles ATPases of the MinD family. While BY-kinase CDs may be classified as P-loop kinases based on their function, they deviate significantly from the P-loop kinase superfamily (comprising kinases that phosphorylate small molecules e.g., nucleosides, shikimate, 6-phosphofructose etc.) as defined by Leipe et al. (Leipe et al., 2003) (we will adhere to that definition here), notably through the absence of a “LID” domain present in the latter (Supplementary Figure S1A). In addition to modified Walker-A and Walker-B motifs, BY-kinase CDs also encode a sequence, ϕϕϕϕDxDxR, that has been termed the Walker-A′ motif (Grangeasse et al., 2012). The DxD sequence present in the Walker-A’ motif is also found in many members of the SIMIBI class of P-loop enzymes including MinD (Supplementary Figure S1B). Interestingly, the DxD motif, is characteristic of many P-loop kinases including those that utilize shikimate, gluconate or adenosine 5’-phosphosulfate (APS) as substrates (Leipe et al., 2003). A key feature of these “DxD-group” P-loop kinases is a Walker-B motif that is degraded at its C-terminal end and marked by the conspicuous absence of the acidic Asp (or Glu) residue (Supplementary Figure S1C) (Leipe et al., 2003). While the BY-kinase CD and P-loop kinases deviate significantly in their three-dimensional structures, they display similar catalytic site geometries formed by closely related structural motifs (Supplementary Figure S1C). Given the close similarities in the catalytic site architecture despite being embedded in divergent structural scaffolds, and the fact that both families perform similar phospho-transfer chemistry, we wondered whether these two distantly related families retain common structural/dynamic features that characterize their functional states.
We have previously demonstrated the unique conformational dynamics of the catalytic core of the archetypal BY-kinase, Escherichia coli (K12) Wzc (WzcCDΔC); these dynamics appear to have significant functional consequences. Our studies revealed the presence of two major conformations with distinct long- and short-range structural features (Hajredini et al., 2020) in WzcCDΔC. We designated these conformations as open (open state, OS) and closed (closed state, CS) based on their global compactness. The OS has high affinity for ADP but is unable to efficiently engage ATP•Mg2+. The CS, that can optimally engage ATP•Mg2+, is stabilized upon formation of a closed octameric ring seen both in the structure of the isolated CD (Bechet et al., 2010) as well as in the membrane-anchored full-length protein (Yang et al., 2021). Oligomer formation is necessary to enable intermolecular autophosphorylation. Thus, the differential nucleotide preferences of the OS and CS together with the coupling of their relative stabilities to oligomerization appear to play a critical role in maintaining optimal Wzc function through modulation of the substrate affinity and the prevention of futile ATP hydrolysis (Hajredini et al., 2020). A key structural feature that was found to distinguish the OS from the CS involved an alteration in the mode of interaction between conserved Walker-A and Walker-B residues (Hajredini et al., 2020; Hajredini and Ghose, 2021). In the OS, the conserved Walker-A Lys (the so-called “catalytic lysine”, K540) establishes a salt bridge with the conserved Walker-B Asp (D642) generating a conformation that cannot effectively coordinate Mg2+ (and consequently, ATP•Mg2+). In the CS, the Walker-A Lys disengages from the Walker-B Asp and the latter then contacts the conserved Walker-A Thr (T541) generating a conformation required to optimally coordinate Mg2+. To assess whether similar conformational states stabilized by interactions between key conserved residues also populate the landscape of the P-loop kinases, we performed enhanced sampling molecular dynamics simulations (REST2) (Wang et al., 2011) using Mycobacterium tuberculosis SK (SKMtu from hereon) in its unliganded, and its ATP•Mg2+-bound states. Our results suggest that SKMtu samples distinct global conformations that, as in the case of the WzcCDΔC, are distinguished by local interactions of the Walker-A and Walker-B motifs, most notably those involving the catalytic Lys (K15). This structural feature of the Walker-A Lys in SKs is also preserved despite sequence variations in the Walker-B motif (as in Coxiella burnetii SK, SKCbu) suggesting that this particular role of this residue in parsing functional conformations may be a general feature in P-loop containing enzymes.
Materials and Methods
Preparation of Starting Structures
The starting conformation of the SKMtu•ATP•Mg2+ complex was generated using the coordinates of SKMtu from the structure of the SKMtu•ADP•Mg2+•shikimate complex (PDB: 1WE2) (Pereira et al., 2004) after removal of the bound ADP and shikimate. The Mg2+ ion and all solvent molecules were retained. The coordinates of ATP were derived from the structure of the SKMtu•AMPPCP•shikimate complex (PDB: 1ZYU) (Gan et al., 2006) by aligning the 1WE2 and 1ZYU structures using the Cα atoms of their respective protein components and converting the bound AMPPCP to ATP through the replacement of the relevant carbon atom by oxygen. Subsequently, the protein and shikimate coordinates of the 1ZYU structure were removed to generate the SKMtu•ATP•Mg2+ complex. For consistency, the corresponding apo simulations utilized the same starting structure after removal of ATP•Mg2+. For unliganded SKCbu, the starting structure was obtained directly from the coordinates found in PDB: 3TRF (Franklin et al., 2015) after removal of all ligands except solvent.
Molecular Dynamics Simulations
The starting structures, generated as discussed above, were equilibrated using previously described protocols (Hajredini et al., 2020). Briefly, the systems were parameterized within the CHARMM36m force-field (Huang et al., 2017), solvated with TIP3P water molecules, energy minimized and then equilibrated, first in an NVT ensemble, and then in an NPT ensemble to generate starting structures for the enhanced sampling, REST2, (Wang et al., 2011) simulations. Subsequently, REST2 production runs were carried out for 200 ns using 14 replicas spanning a 300–400 K temperature range. The final exchange probabilities for the SKMtu•ATP•Mg2+, SKMtu, and SKCbu simulations were 23.3 ± 8.2, 24.2 ± 8.4, and 29.0 ± 0.6%, respectively. The first 40 ns in each of the simulations were used as “burn-in” periods and discarded, and all subsequent analyses were carried out utilizing the remaining 160 ns. As shown in Supplementary Figure S2, 40 ns was more than sufficient to ensure equilibration of the key observables (θ and |h|, see below) probed in the simulations.
Definition of the Cylindrical Coordinate Frame
To describe the global conformational landscape of SKMtu, a cylindrical coordinate frame, comprising of an angle θ and a rise |h| (Figure 1A), was defined as in the case of WzcCDΔC, described previously (Supplementary Figure S3A) (Hajredini et al., 2020). The centers of mass of the Cα atoms of two segments on helix α1 (that contains the Walker-A motif), comprising residues 15–19 (P1, brown) and 21–25 (P2, yellow), were used to define a vector that was aligned to the z-axis of the molecular frame. Each structure within the REST2-generated ensembles was rotated and translated such that point P3 (cyan), defined by the center of mass of the Cα atoms of the first turn of helix α2 (33–37), was placed on the x-axis along the positive direction. θ is then defined as the angle between the xy-projection of a vector extending from point P1 to P4 (blue; defined by the center of mass of the Cα atoms of residues 155–159 that form the first turn of helix α8). The rise |h| is defined as the absolute value of the distance between points P1 and P3 along the z-axis. Thus, the angle θ and the rise |h| provide measures of the outward rotation and the up/down movement, respectively, of the Walker-A motif relative to the Walker-B and DxD motifs. The crystal structures of SKMtu (listed in Supplementary Table S1) were projected onto the cylindrical coordinate frame using the same protocol. For the structures of the SK enzymes from other organisms (listed in Supplementary Table S1), a similar procedure was utilized to define the points P1-P4 (described in Supplementary Table S2) and subsequently, θ and |h|.
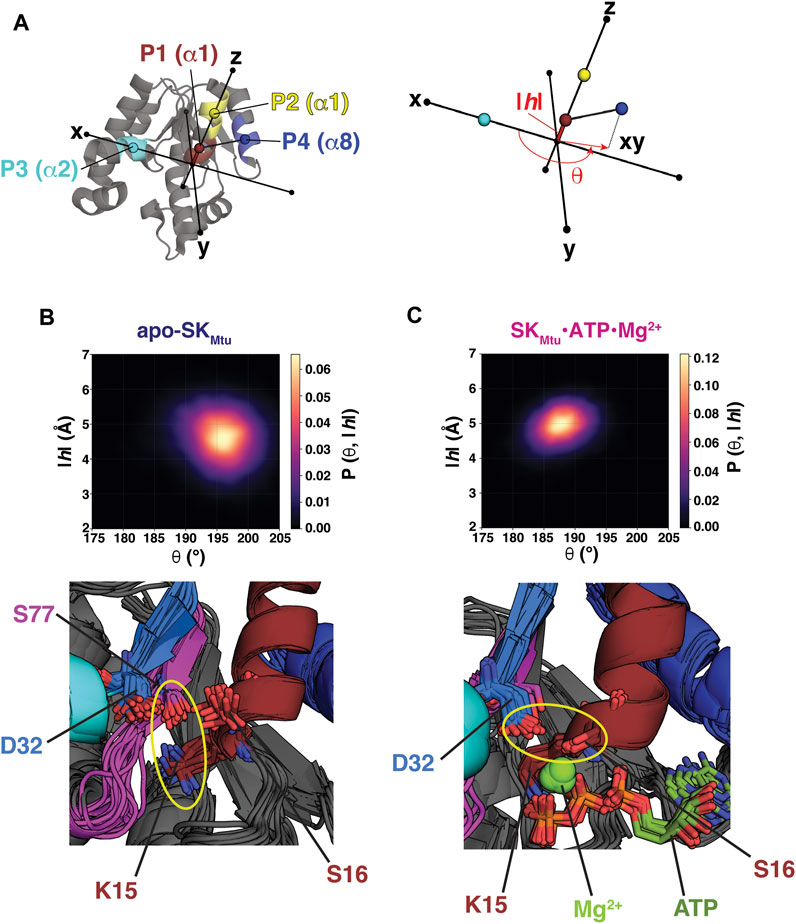
FIGURE 1. (A) Points P1 (brown), P2 (yellow), P3 (cyan) and P4 (dark blue) used to define the cylindrical coordinate frame for analyses of the REST2-generated ensembles of SKMtu are indicated on its structure. The definitions of the angle θ and the rise |h| are shown on the right panel. The REST2-generated structural ensembles of unliganded SKMtu(B) and the SKMtu•ATP•Mg2+ complex (C) are shown projected onto θ-|h| space and plotted using kernel density estimation. The bottom panels show key interactions that stabilize each state using 20 representative structures drawn from the corresponding regions of highest probability density (194–200° and 4–5 Å in the |h| and θ dimensions, respectively for apo-SKMtu and 185–190° and 4.5–5.5 Å for the corresponding dimensions of the SKMtu•ATP•Mg2+ complex). A key feature that distinguishes the Walker Open State (WOS) from the Walker Closed State (WCS) is the orientation of the Walker-A Lys (K15 in SKMtu). For the WOS seen for apo-SKMtu K15 hydrogen bonds with S77 of the Walker-B motif in the bulk of the structures (K15 and S77 are proximal in all of them). This interaction is broken in the SKMtu•ATP•Mg2+ complex. The yellow ellipses highlight the altered interactions of D32 in the two states.
Results and Discussion
Unliganded and Liganded Conformational Ensembles of SKMtu Populate Distinct Structural States
We performed two sets of enhanced sampling simulations utilizing the replica exchange with solute scaling (REST2) approach. REST2 represents a modification of the Hamiltonian scaling protocol of the replica exchange with solute tempering (REST) scheme (Liu et al., 2005) that greatly enhances its efficiency by decoupling the acceptance rate from the solvent. For the REST2 simulations, protocols similar to those described before (Hajredini et al., 2020) were utilized with either unliganded (apo) or ATP•Mg2+-bound SKMtu. To analyze the global conformational states populated by these two ensembles we utilized the cylindrical coordinate frame defined in Figure 1A. Note that this frame is similar, but not identical, to that previously defined for WzcCDΔC (Hajredini et al., 2020) (compare Supplementary Figure S3A) given the significant structural differences between the two proteins. The orientations of the α8 helix (carrying P4) and α1 (carrying P1 and P2) in SKMtu are similar to the α2-α3 pair in WzcCDΔC (the latter carries the Walker-A sequence) (Hajredini et al., 2020). In lieu of a missing WzcCDΔC α4 equivalent in SKMtu, the α2 helix (that hosts the second Asp, D34, of the DxD motif) was utilized to define P3. Thus, while this definition allows for a qualitative comparison of the global conformational states sampled by SKMtu and WzcCDΔC with respect to their key catalytic elements, a quantitative equivalence should not be expected.
Projection of the conformational ensembles of apo-SKMtu (Figure 1B, top panel) and the SKMtu•ATP•Mg2+ complex (Figure 1C, top panel) onto the 2-dimensional θ-|h| space suggests differences in global conformations between the two cases. The presence of ATP•Mg2+ induces a more closed conformation, characterized by smaller θ values, compared to a more open conformation (larger θ values) seen for apo-SKMtu. We designate these global states as a Walker Closed State (WCS, seen in the SKMtu•ATP•Mg2+ complex), and a Walker Open State (WOS, seen in apo-SKMtu) to distinguish them from the closed and open classifications of the relative conformation of the SB and the LID domains traditionally used in the SK literature (Hartmann et al., 2006). Contrasts between the θ-|h| projections of SKMtu and WzcCDΔC are evident upon comparing Figures 1B,C with Supplementary Figures S3B,C. In the case of WzcCDΔC, the OS is characterized by high values of both θ and |h|, while the CS exhibits low values for both variables (Supplementary Figures S3B,C), suggesting that these variables are positively correlated (Hajredini et al., 2020). In contrast, the regions of maximal density for the WOS (Figure 1B, top panel) and the WCS (Figure 1C, top panel) suggest a weak anti-correlation between the θ (WOS: 196 ± 4°, WCS: 188 ± 3°) and |h| dimensions (WOS: 4.6 ± 0.7 Å, WCS: 4.9 ± 0.4 Å), with lower θ and higher |h| for the WCS, and the opposite for the WOS. Further, the apparent separation between the WOS and the WCS seems less prominent than that between the OS and CS of WzcCDΔC (compare Figures 1B,C with Supplementary Figures S3B,C; also see Supplementary Figure S4A). As an independent validation of our simulations, we note that the regions in θ-|h| space spanned by the WOS and the WCS in our REST2 ensembles are well represented (Supplementary Figure S4A) in the several available crystal structures of SKs (and their complexes) from a variety of organisms (listed in Supplementary Table S1).
Representative structures of apo- (Figure 1B, bottom panel) and ATP•Mg2+-bound (Figure 1C, bottom panel) SKMtu extracted from the regions of maximal density in θ−|h| space of the corresponding ensembles show altered conformations of key catalytic site elements. In the presence of ATP•Mg2+ i.e., in the WCS, the Walker-A Lys (K15) assumes a downwards orientation and contacts the β− and γ−phosphates of ATP; the first Asp (D32) of the DxD motif forms a hydrogen bond with the Walker-A S16, thus functionally mimicking the absent Walker-B Asp (Leipe et al., 2003). The D32-S16 interaction is necessary for the optimal coordination of Mg2+ (Figure 1C, bottom panel). Indeed, as shown in Supplementary Figure S4B, the D32,Cγ−S16,Oγ distance is well defined and shows a narrow distribution (3.7 ± 0.2 Å) within the ensemble. In the absence of ligands, i.e., in the WOS, K15 rotates outwards to establish a hydrogen-bond with S77 of the Walker-B motif (Figure 1B, bottom panel) in a significant fraction of the structures. In this configuration, the D32-S16 distance shows a broad distribution (6.0 ± 1.2 Å), suggestive of increased disorder, with a maximum reflective of significantly increased separation (Supplementary Figure S4B) suggesting a conformation that is not conducive for Mg2+ coordination. Conformations displaying the K15-S77 hydrogen bond have been observed in several crystal structures of SKMtu, that are, not surprisingly, free of Mg2+. The structures (representative examples shown in Supplementary Figure S4C) (Hartmann et al., 2006) that display the K15-S77 interaction have the highest values of θ, and correspondingly, the lowest values of |h|, and exist at the outer edges of the WOS. Taken together, these results suggest that the global conformations of SKMtu are coupled to the conformational state of the Walker-A Lys as was observed for WzcCDΔC (Hajredini et al., 2020; Hajredini and Ghose, 2021).
As mentioned above, in a significant fraction of the structures that comprise the WOS of SKMtu, the Walker-A K15 forms a hydrogen bond with the Walker-B S77 (Figure 1B), generating a conformation that mirrors that seen in the WzcCDΔC OS. In the latter case, the equivalent Walker-A Lys (K540) forms a salt bridge with the Walker-B D642. The β-strand housing the Walker-B motif in SKMtu is displaced relative to that in WzcCDΔC, this enables S77 from the degraded Walker-B in the former to assume a spatial position that is approximately equivalent to the Walker-B D642 in the latter to facilitate an interaction with K15 (Figure 2A). It would therefore appear from our current results, that small local structural rearrangements allow the polar Ser to substitute for the now missing Walker-B Asp in preserving the interaction with the Walker-A K15 to maintain the open conformation (WOS) in SKMtu. However, despite these similarities, there are differences in stability between the open conformations involving the Walker-A Lys of SKs and BY-kinases. In WzcCDΔC, this interaction mode, as assessed through the K540,Nξ−D642,Cγ distance distribution, is well defined over the entire OS ensemble, showing a single peak with a maximum at ∼3.3 Å (green trace in Figure 2B). The corresponding distance, K15,Nξ–S77,Oγ in SKMtu, shows a broad distribution with the dominant peak centered at ∼2.8 Å but containing only approximately 50% of the population in the WOS (pink trace in Figure 2B; this disorder is also evident from the bottom panel of Figure 1B). This suggests that while the orientation of the Walker-A Lys is well-defined in WzcCDΔC, it is somewhat more dynamic in SKMtu. The reasons for this difference are analyzed in detail below.
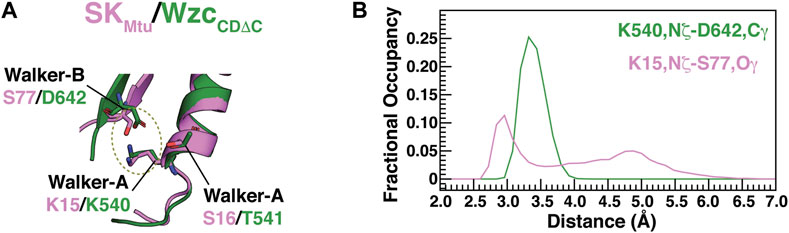
FIGURE 2. (A) Interactions that are characteristic of the open states of BY-kinases (OS) and SKs (WOS). S77 from the degraded Walker-B motif from SKMtu (pink) occupies approximately the same spatial position as the Walker-B D642 from WzcCDΔC (green) allowing the formation of a S77-K15 hydrogen bond reminiscent of the D642-K540 interaction in WzcCDΔC. (B) Distribution of the K540,Nξ-D642,Cγ (green) and K15,Nξ-S77,Oγ (pink) distances from the REST2-generated ensembles of unliganded WzcCDΔC and SKMtu, respectively.
As mentioned earlier, the conformational dynamics of the LID and SB domains have been suggested to be critical for function in the SKs in serving to stabilize the reaction-compatible state, and in facilitating product release (Blanco et al., 2013). The dynamics of these entities have been suggested as suitable targets for drug discovery (Prado et al., 2016). For the sake of completeness, we also analyzed the local conformational variability in the REST2-generated ensembles of SKMtu. There is, not unexpectedly, a slight decrease in overall flexibility upon binding ATP•Mg2+ (Supplementary Figure S5A), and transition from the WOS to the WCS. The LID domain that is the most dynamic region of the protein in the unliganded state remains so in the presence of ATP•Mg2+, though there is some decrease in its overall flexibility. The SB domain is also dynamic in both states of SKMtu, albeit less so than the LID. To probe the presence of opening/closing motions of the SB domain with respect to the protein core, we defined a distance (d47-109, Supplementary Figure S5B, top left panel) between the Cα atoms of D47 (one of the more dynamic parts of the SB domain and therefore likely to sense these motions, if any) and R109 (near start of the LID domain; one of the more rigid parts of the protein in its ATP•Mg2+-bound state). In the absence of ATP•Mg2+ a somewhat bimodal distribution of distances is seen (Supplementary Figure S5B top right panel). Analyses of structures corresponding to the two maxima indicate an open conformation with greater separation between the LID and SB domains (Supplementary Figure S5B bottom right panel), and a more closed conformation where this distance is reduced (Supplementary Figure S5B bottom middle panel). Only the latter conformation is seen in the ATP•Mg2+-bound state (Supplementary Figure S4B bottom left panel).
Conserved Features Define the Global Conformational States of P-Loop Enzymes
While S77 of SKMtu appears to substitute for the Asp/Glu residue of a canonical Walker-B motif in maintaining the WOS through its interaction with the Walker-A Lys, this position is poorly conserved in SKs. In contrast to the ϕϕSLGGG sequence in SKMtu, the consensus sequence for Walker-B motifs of SKs is ϕϕϕTGGG (Leipe et al., 2003); the corresponding consensus in BY-kinases is ϕϕϕϕDT (Leipe et al., 2002). Notably, in WzcCDΔC, the conserved Walker-B Thr (T643) participates in multiple interactions that also serve to stabilize the OS (Figure 3A, top panel). T643 forms a hydrogen bond through its backbone carbonyl with the K540 sidechain (supplementing the interaction of the latter with D642), and an additional hydrogen bond through its sidechain hydroxyl with the backbone carbonyl of M531 on the adjacent β-sheet. Projection of the unliganded WzcCDΔC ensemble (Hajredini et al., 2020) onto the 2-dimensional space spanned by the K540-T643 (D1: K540,Nξ−T643,O) and T643-M531 (D2: T643,Oγ1−M531,O) distances, indicates a single major state (white arrow, Figure 3A, bottom panel). This robust network of interactions (K540-D642, K540-T643 and T643-M531) is the likely reason for the well-defined orientation of K540 in the OS (as is evident from the green trace in Figure 2B). This set of interactions is drastically altered in the CS (T643 now interacts T532, D642 interacts with T541, the latter interaction is necessary to optimally engage Mg2+) and this is the likely cause of the well-defined separation between in the OS and the CS upon comparing the apo- and ATP•Mg2+ complexes of WzcCDΔC (Supplementary Figures S3B,C).
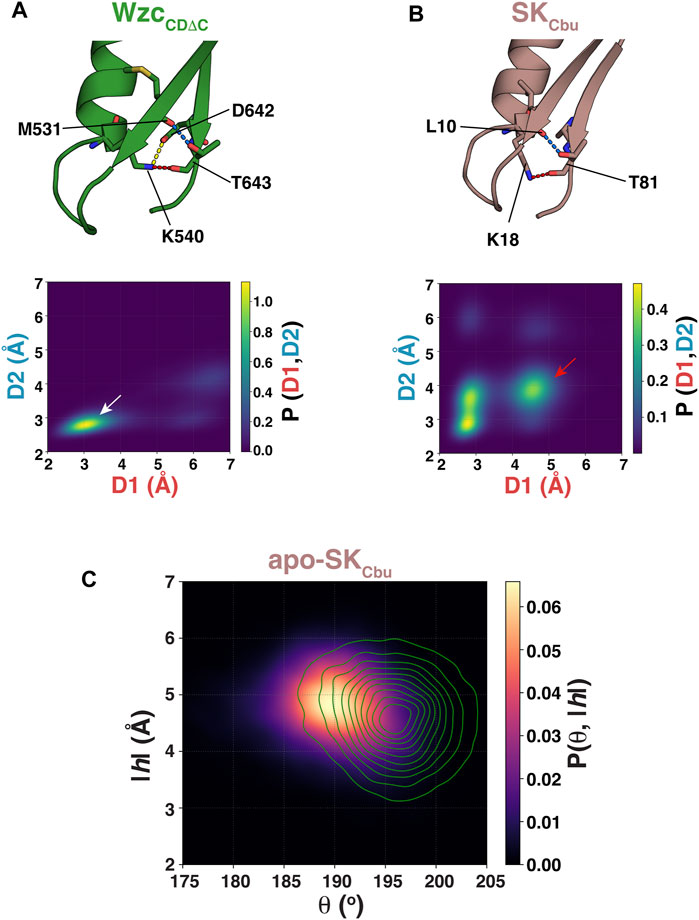
FIGURE 3. (A) Interactions of the Walker-A K540 with the Walker-B D642 (yellow dashed line), of K540 with T643 (red dashed line), and of T643 with M531 (blue dashed line) for WzcCDΔC in the OS are shown. (B) Interactions of the Walker-A K18 with Walker-B T81 (red dashed line) and of T81 with L10 (blue dashed line) for SKCbu in the WOS are shown. The lower panels, in each case, show the structural ensembles of unliganded WzcCDΔC and SKCbu projected onto the 2-dimensional space spanned by the {K540-T643 (D1: K540,Nξ−T643,O), T643-M531 (D2: T643,Oγ1−M531,O)} and {K18-T81 (D1: K18,Nξ−T81,O), T81-L10 (D2: T81,Oγ1−L10,O)} distances, respectively. (C) The structural ensemble of unliganded SKCbu is projected onto θ-|h| space and plotted using kernel density estimation. Also shown as green contours in the corresponding projection of the unliganded SKMtu ensemble.
To test whether a similar interaction mode involving the Walker-B Thr also stabilizes the WOS in SKs that carry the more conventional ϕϕϕTGGG sequence, we performed an additional set of REST2 simulations on the unliganded state of Coxiella burnetii SK (SKCbu). Inspection of the structural ensemble of apo-SKCbu reveals the presence of hydrogen bonds between the backbone carbonyl and sidechain hydroxyl of the Walker-B Thr (T81) with the sidechain of the Walker-A K18 and the backbone carbonyl of L10 (that lies on the adjacent β-sheet), respectively (Figure 3B, top panel), mirroring the interaction mode seen in WzcCDΔC. However, unlike in WzcCDΔC, projection of the resultant ensemble onto the 2-dimensional space spanned by the K18-T81 (D1: K18,Nξ−T81,O) and T81-L10 (D2: T81,Oγ1−L10,Ο) distances reveals a more diffuse set of states (Figure 3B, bottom panel). Nevertheless, a disruption in the T81-K18 interaction leads to a corresponding disruption of the T81-L10 interaction (red arrow in Figure 3B, bottom panel) suggesting that these two sets of interactions are coupled as in WzcCDΔC. It is of note that the canonical Walker-B Thr in SKCbu forms two sets of the hydrogen bonds involving both its backbone and its sidechain to stabilize the WOS. This contrasts a single hydrogen bond involving the sidechain of the unique Walker-B Ser (S77) in SKMtu. One can therefore expect the WOS in SKCbu to be somewhat more closed than in SKMtu. Inspection of Figure 3C shows that this is indeed the case with reduced θ values (SKCbu: 190 ± 5°, SKMtu: 196 ± 4°) and a corresponding increase in the |h| values (SKCbu: 4.8 ± 0.6 Å, SKMtu: 4.6 ± 0.7 Å).
Based on the discussion above, an SK Walker-B motif may be generalized by the following sequence: ϕϕαβGGG; the α- and β-positions represent structural equivalents of the BY-kinase Walker-B Asp and Thr, respectively (Figure 4A). In unliganded WzcCDΔC, both the α- and β-positions are optimal in that they contain polar residues. Thus, the Walker-A Lys (K540) can form hydrogen bonds with both the Walker-B Asp (D642 at the α−position) and with the Walker-B Thr (T643); the latter being a polar residue at the β−position is then able to utilize its sidechain to hydrogen bond with M531. This generates a mesh of interactions (shown schematically in Figure 4B) leading to a well-defined orientation of the Walker-A Lys (K540) in a stabilized OS. In contrast, the fact that only one of these two positions contains a polar residue for the two SKs analyzed here, with T81 (β) in SKCbu (Figure 4C) or S77 (α) in SKMtu (Figure 4D). Thus, only a subset of these interactions is possible in the SKs resulting in less well-defined orientation for the Walker-A Lys and a more diffuse WOS.
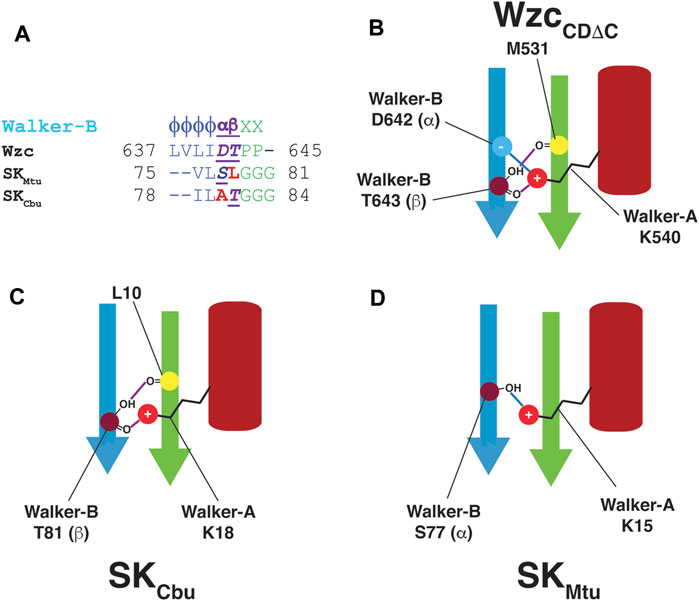
FIGURE 4. (A) Comparison of the Walker-B sequences in Wzc, SKMtu and SKCbu. Wzc contains polar residues at both the α− and β−positions while only one of these positions is polar in SKCbu (β) and SKMtu (α) (B) The presence of polar residues at both the α− (D642) and β−positions (T643) in the Walker-B motif of WzcCDΔC allows the intricate network of interactions to appropriately align the Walker-A Lys (K540) leading to its well-defined orientation in the OS. These interactions are depicted schematically; hydrogen-bonds are indicated using purple and blue lines. Since only one of the α− or β−positions contain a polar residue in (C) SKCbu (β:T81) and (D) SKMtu (α:S77), only one of these sets of interactions (blue or purple) is preserved allowing a greater degree of orientational freedom in the WOS for the corresponding Walker-A Lys (K18 in SKCbu, K15 in SKMtu).
Conclusion
Through enhanced sampling MD simulations on unliganded SKMtu and its ATP•Mg2+ complex, we have shown that as in the case of BY-kinases, the conformational landscapes of SKs contain open (WOS) and closed (WCS) states. The former is found in the unliganded state, while the latter is induced by the presence of nucleotide and Mg2+. In the WOS, the Walker-A K15 of SKMtu populates an extended conformation allowing the formation of a hydrogen bond with S77 of the degraded Walker-B motif that mimics the conserved Asp of the intact Walker-B motif in BY-kinases. In SKCbu, that contains a Walker-B sequence that is more characteristic of P-loop kinases of the DxD group (Leipe et al., 2003), the conserved T81 forms a hydrogen-bond with the Walker-A K18 through its backbone while simultaneously using its polar sidechain to interact with the neighboring L10 backbone to stabilize the WOS. Thus, it appears that specific contacts between the Walker-A and Walker-B motifs, more specifically those involving the so-called catalytic Lys on the former, are necessary in P-loop-containing kinases to maintain the open conformation that cannot efficiently co-ordinate Mg2+ (and therefore, ATP•Mg2+) and is not conducive for chemistry. The importance of the hydrogen-bond involving the Walker-A Lys is evident from the fact that the absence of a Walker-B Asp as in the SKs, is compensated by the presence of a polar residue at a similar position. While the functional role the OS and CS and the interactions encoded within each state for the catalytic domain of Wzc has been extensively tested experimentally (Hajredini et al., 2020; Hajredini and Ghose, 2021), we expect that the computational analyses presented here will provide guidelines for similar experimental validation of key functional features in SKs in particular, and in P-loop kinases, in general.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author Contributions
RG conceived the project; FH performed and analyzed all simulations. FH prepared a first draft of the paper and figures that were refined by RG with input from FH.
Funding
Support from NSF grants MCB1937937 and PHY1811770 is acknowledged. FH is partially supported by United States Department of Education GAANN award P200A150068.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmolb.2021.747206/full#supplementary-material
References
Aravind, L., Mazumder, R., Vasudevan, S., and Koonin, E. V. (2002). Trends in Protein Evolution Inferred from Sequence and Structure Analysis. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 12, 392–399. doi:10.1016/s0959-440x(02)00334-2
Bechet, E., Gruszczyk, J., Terreux, R., Gueguen-Chaignon, V., Vigouroux, A., Obadia, B., et al. (2010). Identification of Structural and Molecular Determinants of the Tyrosine-Kinase Wzc and Implications in Capsular Polysaccharide export. Mol. Microbiol. 77, 1315–1325. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07291.x
Blanco, B., Prado, V., Lence, E., Otero, J. M., Garcia-Doval, C., Van Raaij, M. J., et al. (2013). Mycobacterium tuberculosis Shikimate Kinase Inhibitors: Design and Simulation Studies of the Catalytic Turnover. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 12366–12376. doi:10.1021/ja405853p
Edwards, H., Abeln, S., and Deane, C. M. (2013). Exploring Fold Space Preferences of New-Born and Ancient Protein Superfamilies. Plos Comput. Biol. 9, e1003325. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003325
Franklin, M. C., Cheung, J., Rudolph, M. J., Burshteyn, F., Cassidy, M., Gary, E., et al. (2015). Structural Genomics for Drug Design against the Pathogen Coxiella Burnetii. Proteins 83, 2124–2136. doi:10.1002/prot.24841
Gan, J., Gu, Y., Li, Y., Yan, H., and Ji, X. (2006). Crystal Structure ofMycobacterium tuberculosisShikimate Kinase in Complex with Shikimic Acid and an ATP Analogue†,‡. Biochemistry 45, 8539–8545. doi:10.1021/bi0606290
Grangeasse, C., Nessler, S., and Mijakovic, I. (2012). Bacterial Tyrosine Kinases: Evolution, Biological Function and Structural Insights. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 367, 2640–2655. doi:10.1098/rstb.2011.0424
Hajredini, F., Piserchio, A., and Ghose, R. (2020). Long-range Dynamic Correlations Regulate the Catalytic Activity of the Bacterial Tyrosine Kinase Wzc. Sci. Adv. 6, eabd3718. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abd3718
Hajredini, F., and Ghose, R. (2021). An ATPase with a Twist: a Unique Mechanism Underlies the Activity of the Bacterial Tyrosine Kinase. Wzc. Sci. Adv. 7, eabj5836. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abj5836
Hartmann, M. D., Bourenkov, G. P., Oberschall, A., Strizhov, N., and Bartunik, H. D. (2006). Mechanism of Phosphoryl Transfer Catalyzed by Shikimate Kinase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Mol. Biol. 364, 411–423. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.09.001
Huang, J., Rauscher, S., Nawrocki, G., Ran, T., Feig, M., De Groot, B. L., et al. (2017). CHARMM36m: an Improved Force Field for Folded and Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Nat. Methods 14, 71–73. doi:10.1038/nmeth.4067
Lee, D. C., and Jia, Z. (2009). Emerging Structural Insights into Bacterial Tyrosine Kinases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 34, 351–357. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2009.03.003
Leipe, D. D., Koonin, E. V., and Aravind, L. (2003). Evolution and Classification of P-Loop Kinases and Related Proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 333, 781–815. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2003.08.040
Leipe, D. D., Wolf, Y. I., Koonin, E. V., and Aravind, L. (2002). Classification and Evolution of P-Loop GTPases and Related ATPases. J. Mol. Biol. 317, 41–72. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5378
Liu, P., Kim, B., Friesner, R. A., and Berne, B. J. (2005). Replica Exchange with Solute Tempering: a Method for Sampling Biological Systems in Explicit Water. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 102, 13749–13754. doi:10.1073/pnas.0506346102
Longo, L. M., Jabłońska, J., Vyas, P., Kanade, M., Kolodny, R., Ben-Tal, N., et al. (2020). On the Emergence of P-Loop NTPase and Rossmann Enzymes from a Beta-Alpha-Beta Ancestral Fragment. Elife 9, e64415. doi:10.7554/eLife.64415
Pereira, J. H., De Oliveira, J. S., Canduri, F., Dias, M. V. B., Palma, M. S., Basso, L. A., et al. (2004). Structure of Shikimate Kinase fromMycobacterium Tuberculosisreveals the Binding of Shikimic Acid. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Cryst. 60, 2310–2319. doi:10.1107/s090744490402517x
Prado, V., Lence, E., Maneiro, M., Vázquez-Ucha, J. C., Beceiro, A., Thompson, P., et al. (2016). Targeting the Motion of Shikimate Kinase: Development of Competitive Inhibitors that Stabilize an Inactive Open Conformation of the Enzyme. J. Med. Chem. 59, 5471–5487. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00483
Scheeff, E. D., and Bourne, P. E. (2005). Structural Evolution of the Protein Kinase-like Superfamily. Plos Comput. Biol. 1, e49. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.0010049
Shi, L., Ji, B., Kolar-Znika, L., Boskovic, A., Jadeau, F., Combet, C., et al. (2014). Evolution of Bacterial Protein-Tyrosine Kinases and Their Relaxed Specificity toward Substrates. Genome Biol. Evol. 6, 800–817. doi:10.1093/gbe/evu056
Taylor, S. S., and Radzio-Andzelm, E. (1994). Three Protein Kinase Structures Define a Common Motif. Structure 2, 345–355. doi:10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00036-8
Walker, J. E., Saraste, M., Runswick, M. J., and Gay, N. J. (1982). Distantly Related Sequences in the Alpha- and Beta-Subunits of ATP Synthase, Myosin, Kinases and Other ATP-Requiring Enzymes and a Common Nucleotide Binding Fold. EMBO J. 1, 945–951. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x
Wang, L., Friesner, R. A., and Berne, B. J. (2011). Replica Exchange with Solute Scaling: a More Efficient Version of Replica Exchange with Solute Tempering (REST2). J. Phys. Chem. B 115, 9431–9438. doi:10.1021/jp204407d
Keywords: P-loop, protein kinases, shikimate kinase, molecular dynamics (MD), bacterial tyrosine kinase
Citation: Hajredini F and Ghose R (2021) A Conserved Structural Role for the Walker-A Lysine in P-Loop Containing Kinases. Front. Mol. Biosci. 8:747206. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.747206
Received: 25 July 2021; Accepted: 20 September 2021;
Published: 01 October 2021.
Edited by:
George Lisi, Brown University, United StatesReviewed by:
Xiakun Chu, Stony Brook University, United StatesJulien Roche, Iowa State University, United States
Copyright © 2021 Hajredini and Ghose. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ranajeet Ghose, cmdob3NlQGNjbnkuY3VueS5lZHU=
 Fatlum Hajredini
Fatlum Hajredini Ranajeet Ghose
Ranajeet Ghose