Ribosomal Protein L40e Fused With a Ubiquitin Moiety Is Essential for the Vegetative Growth, Morphological Homeostasis, Cell Cycle Progression, and Pathogenicity of Cryptococcus neoformans
- 1Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Medical Mycology, Department of Dermatology, Changzheng Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Dermatology, Shanghai Eastern Hepatobiliary Surgery Hospital, Shanghai, China
- 3Department of Dermatology, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
- 4Department of Dermatology, Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital, People's Hospital of Hangzhou Medical College, Hangzhou, China
- 5The Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
by Zhao, J., Yang, Y., Fan, Y., Yi, J., Zhang, C., Gu, Z., Pan, W., Gu, J., Liao, W., and Fang, W. (2020). Front. Microbiol. 11:570269. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.570269
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 3B as published. Upon recent review of our experimental data, we discovered that Figure 3B in this manuscript incorrectly used the same data as Figure 3B in our previous paper, “Pd@Ag Nanosheets in Combination with Amphotericin B Exert a Potent Anti-Cryptococcal Fungicidal Effect” (PMID: 27271376). The corrected Figure 3 and its caption appear below.
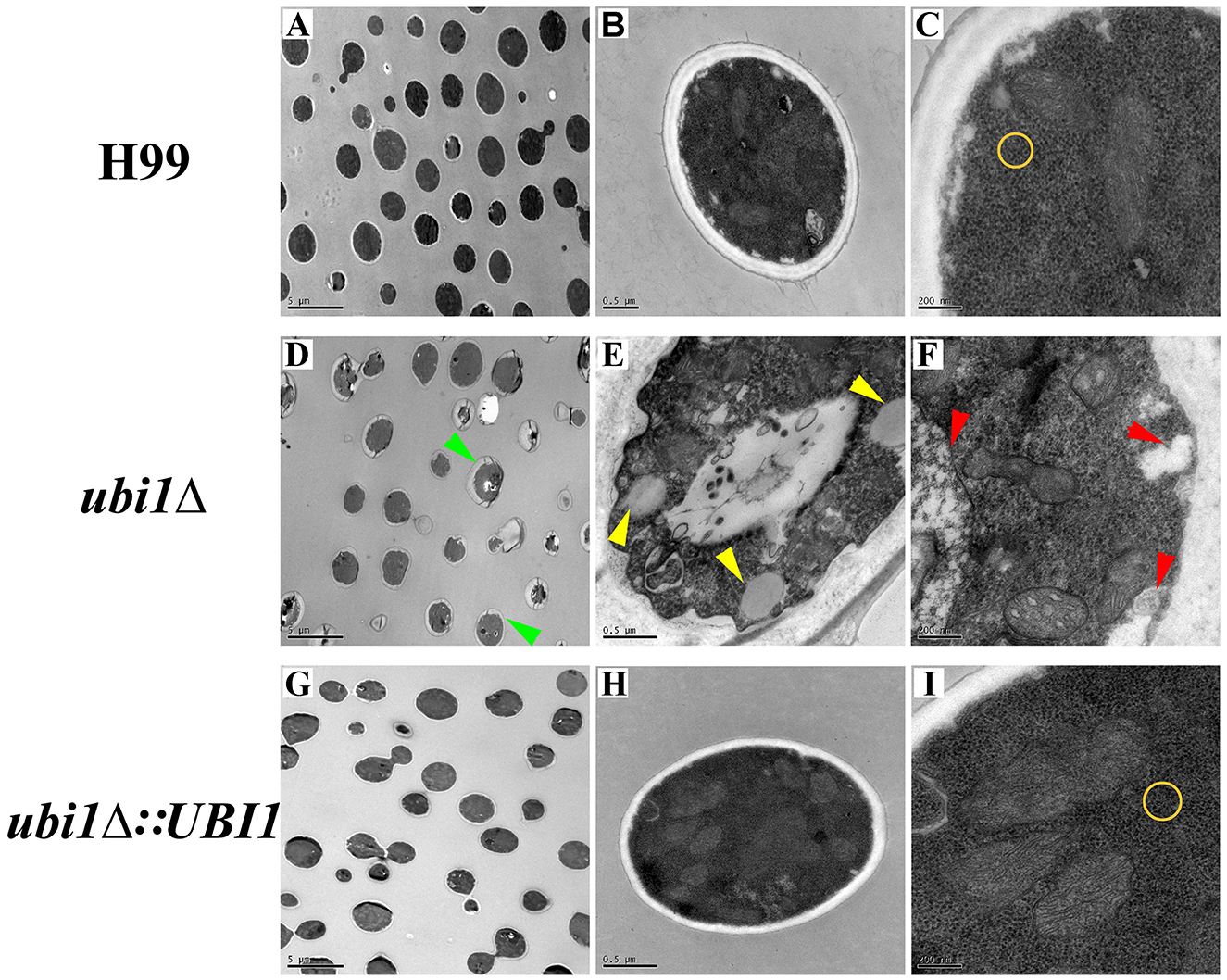
Figure 3. Impact of UBI1 deletion on the cell morphology and intracellular structure of C. neoformans. The TEM images represent different strains as follows, H99 (A–C), ubi1Δ (D–F), and ubi1Δ:UBI1 (G, H). Sizes of the scale bar: 5 μm for (A, D, G); 0.5 μm for (B, E, H); and 200 nm for (C, F, I). Green arrow, irregular cell shape and uneven cell wall thickness; red arrow, swelling mitochondria with dissoluted ridge; yellow arrow, intracellular vacuoles; yellow circle, comparison of ribosomal density.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: Cryptococcus neoformans, ubiquitin, growth restriction, cellular morphology, virulence, immune evasion
Citation: Zhao J, Yang Y, Fan Y, Yi J, Zhang C, Gu Z, Pan W, Gu J, Liao W and Fang W (2025) Corrigendum: Ribosomal protein L40e fused with a ubiquitin moiety is essential for the vegetative growth, morphological homeostasis, cell cycle progression, and pathogenicity of Cryptococcus neoformans. Front. Microbiol. 15:1545744. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1545744
Received: 15 December 2024; Accepted: 30 December 2024;
Published: 09 January 2025.
Edited and reviewed by: Axel Cloeckaert, Institut National de recherche pour l'agriculture, l'alimentation et l'environnement (INRAE), France
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Yang, Fan, Yi, Zhang, Gu, Pan, Gu, Liao and Fang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Julin Gu, d3VqZ2psQDEyNi5jb20=; Wanqing Liao, bGlhb3dhbnFpbmdAc29odS5jb20=; Wei Fang, d2VpZmFuZzA4MTc4MkAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jingyu Zhao
Jingyu Zhao Yali Yang
Yali Yang Yibin Fan
Yibin Fan Jiu Yi
Jiu Yi Chao Zhang
Chao Zhang Zhongkai Gu
Zhongkai Gu Weihua Pan
Weihua Pan Julin Gu
Julin Gu Wanqing Liao
Wanqing Liao Wei Fang
Wei Fang