Evidence for the Cytoplasmic Localization of the L-α-Glycerophosphate Oxidase in Members of the “Mycoplasma mycoides Cluster”
- 1Institute of Veterinary Bacteriology, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
- 2Division of Veterinary Anatomy, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
- 3J. Craig Venter Institute, Rockville, MD, United States
- 4Institute for Genome Sciences, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, United States
A corrigendum on
Evidence for the cytoplasmic localization of the L-α-Glycerophosphate oxidase in members of the “Mycoplasma mycoides cluster”
by Schumacher, M., Nicholson, P., Stoffel, M. H., Chandran, S., D'Mello, A., Ma, L., Vashee, S., Jores, J., and Labroussaa, F. (2019). Front. Microbiol. 10:1344. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01344
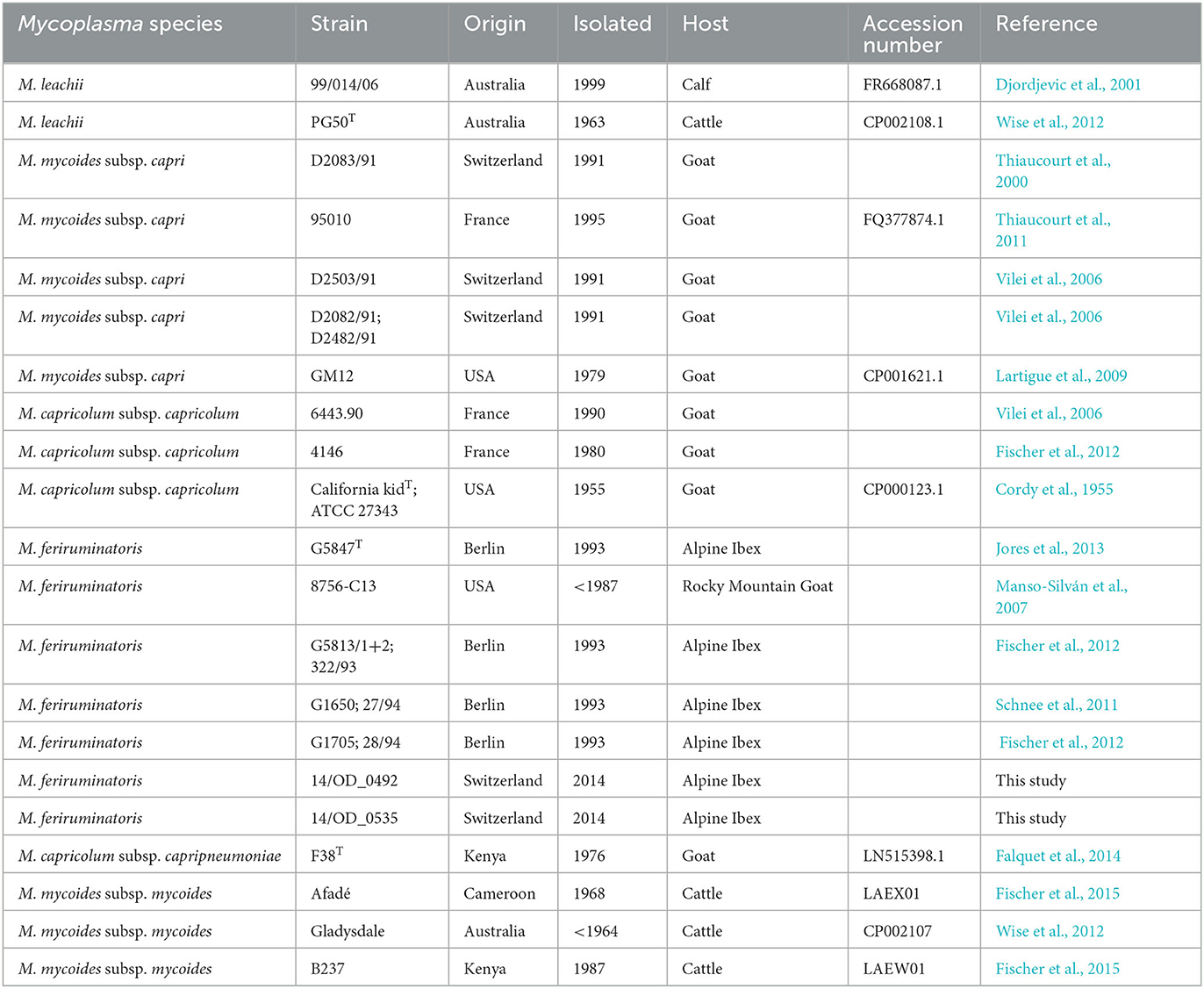
In the published article, there were several errors in Table 1 as published. The host species from several Mycoplasma feriruminatoris was wrongly indicated as “Goat”. M. feriruminatoris strain G5813/1+2 was isolated from a Rocky Mountain Goat, whereas the six other M. feriruminatoris strains were isolated from Alpine Ibex. In addition, the Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. capri strain D2082/91 is also referred as strain D2482/91 elsewhere and both names are now indicated. The year of isolation of the two M. feriruminatoris strains 14/OD_0492 and 14/OD_0535 was wrongly indicated as “1994” and is now updated to “2014”. Finally, several references appearing in Table 1 were wrongly stated as “This study”. The reference for the two Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. capri strain D2503/91 and D2082/91 is now indicated as Vilei et al. (2006). The reference for the two Mycoplasma feriruminatoris strain G5813/1+2 and G1705 is now indicated as Fischer et al. (2012). The references for the Mycoplasma feriruminatoris strains 8756-C13 and G1650 are now indicated as Manso-Silván et al. (2007) and Schnee et al. (2011), respectively.
The corrected Table 1 and its caption appear below.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that these do not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Cordy, D., Adler, H., and Yamamoto, R. (1955). A pathogenic pleuropneumonia-like organism from goats. Cornell. Vet. 45, 50–68.
Djordjevic, S. R., Forbes, W. A., Forbes-Faulkner, J., Kuhnert, P., Hum, S., Hornitzky, M. A., et al. (2001). Genetic diversity among Mycoplasma species bovine group 7: clonal isolates from an outbreak of polyarthritis, mastitis, and abortion in dairy cattle. Electrophoresis 22, 3551–3561. doi: 10.1002/1522-2683(200109)22:16<3551::AID-ELPS3551>3.0.CO;2-#
Falquet, L., Liljander, A., Schieck, E., Gluecks, I., Frey, J., and Jores, J. (2014). Complete genome sequences of virulent Mycoplasma capricolum subsp. capripneumoniae strains F38 and ILRI181. Genome Announc. 2, e01041–e01014. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01041-14
Fischer, A., Santana-Cruz, I., Hegerman, J., Gourlé, H., Schieck, E., Lambert, M., et al. (2015). High quality draft genomes of the Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides challenge strains Afadé and B237. Stand. Genomic Sci. 10, 89. doi: 10.1186/s40793-015-0067-0
Fischer, A., Shapiro, B., Muriuki, C., Heller, M., Schnee, C., Bongcam-Rudloff, E., et al. (2012). The origin of the “Mycoplasma mycoides Cluster” coincides with domestication of ruminants. PLoS ONE 7, e36150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036150
Jores, J., Fischer, A., Sirand-Pugnet, P., Thomann, A., Liebler-Tenorio, E. M., Schnee, C., et al. (2013). Mycoplasma feriruminatoris sp. nov., a fast growing Mycoplasma species isolated from wild Caprinae. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 36, 533–538. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2013.07.005
Lartigue, C., Vashee, S., Algire, M. A., Chuang, R.-Y., Benders, G. A., Ma, L., et al. (2009). Creating bacterial strains from genomes that have been cloned and engineered in yeast. Science 325, 1693–1696. doi: 10.1126/science.1173759
Manso-Silván, L., Perrier, X., and Thiaucourt, F. (2007). Phylogeny of the Mycoplasma mycoides cluster based on analysis of five conserved protein-coding sequences and possible implications for the taxonomy of the group. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 2247–2258. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.64918-0
Schnee, C., Heller, M., Jores, J., Tomaso, H., and Neubauer, H. (2011). Assessment of a novel multiplex real-time PCR assay for the detection of the CBPP agent Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides SC through experimental infection in cattle. BMC Vet. Res. 7, 47. doi: 10.1186/1746-6148-7-47
Thiaucourt, F., Lorenzon, S., David, A., and Breard, A. (2000). Phylogeny of the Mycoplasma mycoides cluster as shown by sequencing of a putative membrane protein gene. Vet. Microbiol. 72, 251–268. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1135(99)00204-7
Thiaucourt, F., Manso-Silvan, L., Salah, W., Barbe, V., Vacherie, B., Jacob, D., et al. (2011). Mycoplasma mycoides, from “mycoides Small Colony” to “capri”. A microevolutionary perspective. BMC Genom. 12, 114. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-114
Vilei, E. M., Korczak, B. M., and Frey, J. (2006). Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. capri and Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides LC can be grouped into a single subspecies. Vet. Res. 37, 779–790. doi: 10.1051/vetres:2006037
Wise, K. S., Calcutt, M. J., Foecking, M. F., Madupu, R., DeBoy, R. T., Röske, K., et al. (2012). Complete genome sequences of Mycoplasma leachii strain PG50T and the pathogenic Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides small colony biotype strain Gladysdale. J. Bacteriol. 194, 4448–4449. doi: 10.1128/JB.00761-12
Keywords: “Mycoplasma mycoides cluster”, synthetic genomics, mycoplasma virulence traits, L-α-glycerophosphate oxidase, Triton X-114, scanning electron microscopy
Citation: Schumacher M, Nicholson P, Stoffel MH, Chandran S, D'Mello A, Ma L, Vashee S, Jores J and Labroussaa F (2023) Corrigendum: Evidence for the cytoplasmic localization of the L-α-Glycerophosphate oxidase in members of the “Mycoplasma mycoides cluster”. Front. Microbiol. 14:1293129. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1293129
Received: 12 September 2023; Accepted: 13 September 2023;
Published: 27 September 2023.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2023 Schumacher, Nicholson, Stoffel, Chandran, D'Mello, Ma, Vashee, Jores and Labroussaa. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fabien Labroussaa, ZmFiaWVuLmxhYnJvdXNzYWFAdmV0c3Vpc3NlLnVuaWJlLmNo
†These authors have contributed equally as first authors
‡These authors have contributed equally as last authors
 Melanie Schumacher1†
Melanie Schumacher1† Michael H. Stoffel
Michael H. Stoffel Suchismita Chandran
Suchismita Chandran Adonis D'Mello
Adonis D'Mello Sanjay Vashee
Sanjay Vashee Joerg Jores
Joerg Jores Fabien Labroussaa
Fabien Labroussaa