
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Microbiol. , 11 August 2023
Sec. Antimicrobials, Resistance and Chemotherapy
Volume 14 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1266723
This article is a correction to:
Laser speckle imaging for visualization of hidden effects for early detection of antibacterial susceptibility in disc diffusion tests
 Ilya Balmages1,2*
Ilya Balmages1,2* Aigars Reinis3,4
Aigars Reinis3,4 Svjatoslavs Kistkins1,3
Svjatoslavs Kistkins1,3 Dmitrijs Bliznuks2
Dmitrijs Bliznuks2 Emilija Vija Plorina1
Emilija Vija Plorina1 Alexey Lihachev1
Alexey Lihachev1 Ilze Lihacova1
Ilze Lihacova1A corrigendum on
Laser speckle imaging for visualization of hidden effects for early detection of antibacterial susceptibility in disc diffusion tests
by Balmages, I., Reinis, A., Kistkins, S., Bliznuks, D., Plorina, E. V., Lihachev, A., and Lihacova, I. (2023). Front. Microbiol.14:1221134. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1221134
In the published article, the order of the image files for Figures 6, 7, 8, and 9 was incorrect. The corrected Figures 6, 7, 8, and 9, and their captions appear below.
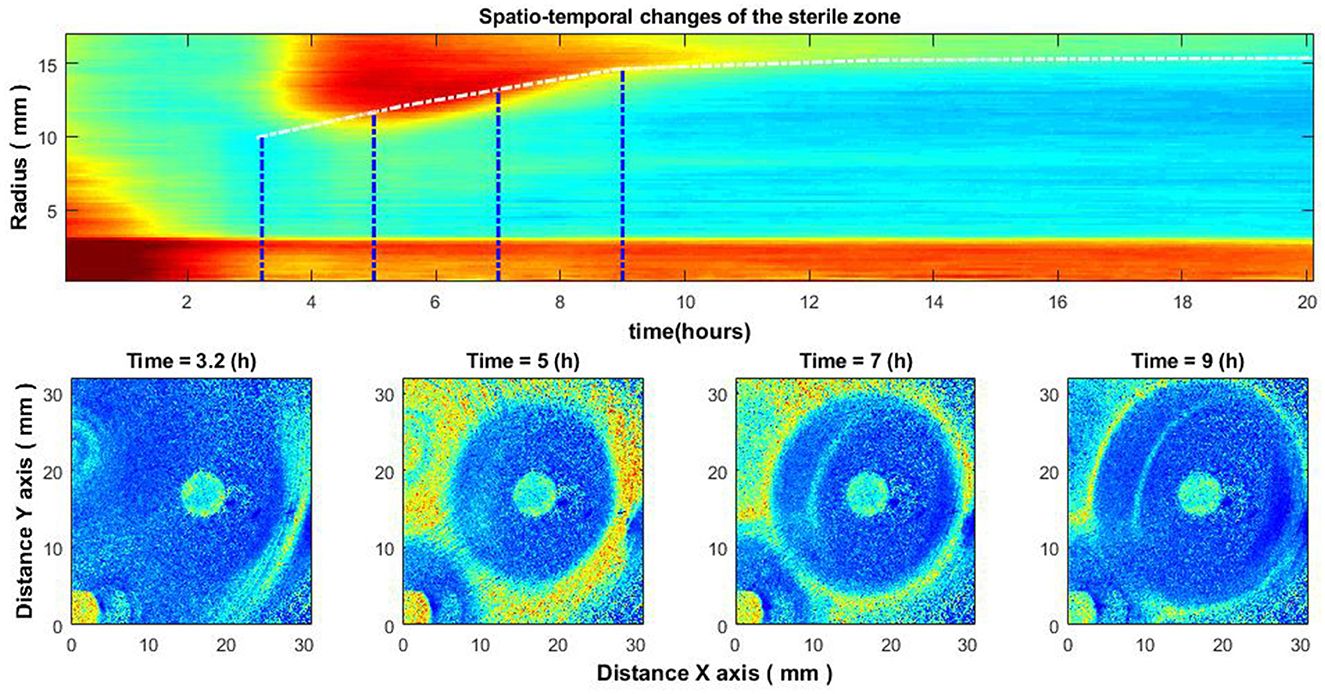
Figure 6. Spatio-temporal changes of the zone of inhibition (top), and zone of inhibition formation in the growth of bacteria around the antibiotic disc (bottom). Bacteria: E. coli, antibiotic CIP 5 μg. Antibiotics were placed on the Petri dish immediately after bacteria inoculation.
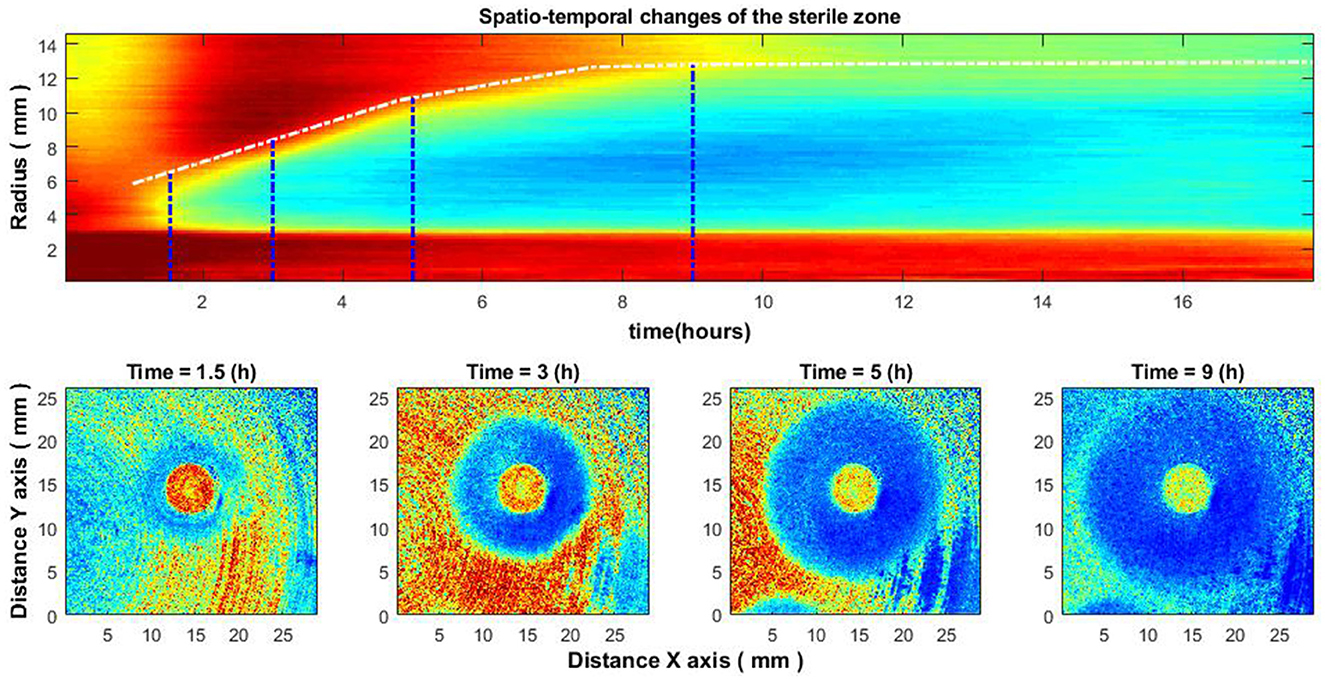
Figure 7. Spatio-temporal changes of the zone of inhibition (top), and zone of inhibition formation in the growth of bacteria around the antibiotic disc (bottom). Bacteria: E. coli, antibiotic CIP 5 μg. Antibiotics were placed on the Petri dish 4–4.5 h after the bacteria inoculation.
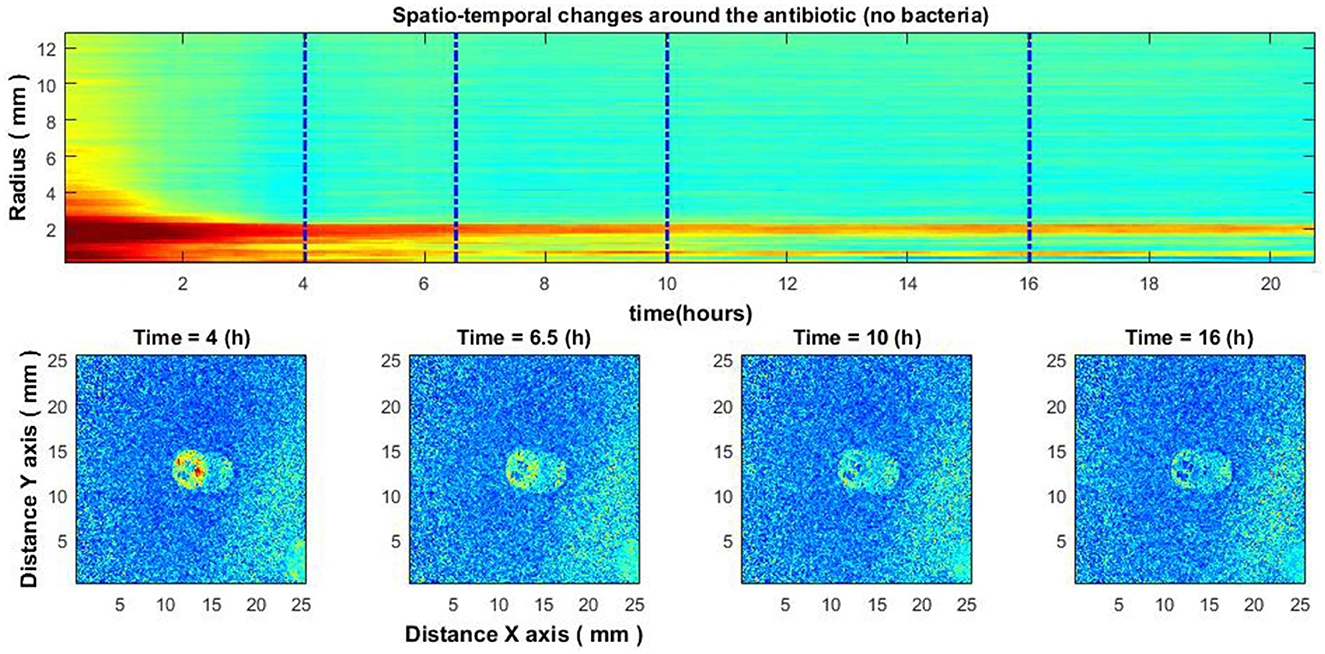
Figure 8. Experiment without bacteria. Spatio-temporal image of the area around the antibiotic AK 30 μg (top) and the spatial zone around the antibiotic at different times (bottom).
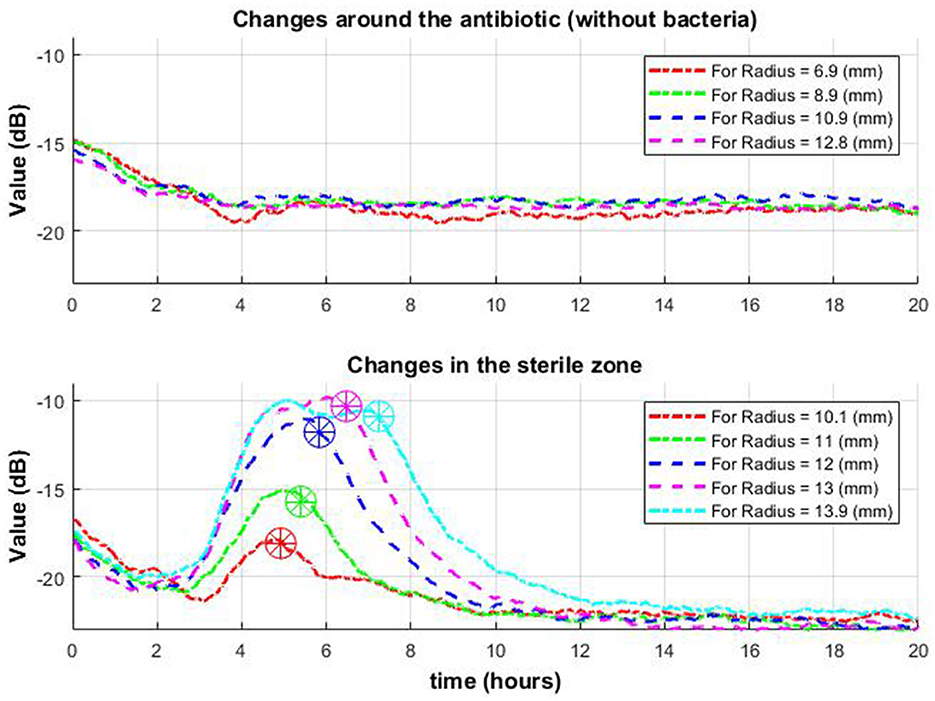
Figure 9. Change of signal envelope over time for several different radii around the antibiotic: without bacteria (top row) and with bacteria (bottom row). On the bottom graph, it is observed that as it moves away from the center, the drop (which means the appearance of a zone of inhibition in this place) occurs later (stars in a circle).
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: phenotypic antibacterial resistance, antibacterial resistance estimation, laser speckle imaging, sub-pixel correlation analysis, image processing, disc diffusion method
Citation: Balmages I, Reinis A, Kistkins S, Bliznuks D, Plorina EV, Lihachev A and Lihacova I (2023) Corrigendum: Laser speckle imaging for visualization of hidden effects for early detection of antibacterial susceptibility in disc diffusion tests. Front. Microbiol. 14:1266723. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1266723
Received: 25 July 2023; Accepted: 27 July 2023;
Published: 11 August 2023.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2023 Balmages, Reinis, Kistkins, Bliznuks, Plorina, Lihachev and Lihacova. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ilya Balmages, aWx5YS5iYWxtYWdlc0BydHUubHY=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.