
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Microbiol. , 12 July 2023
Sec. Evolutionary and Genomic Microbiology
Volume 14 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1236756
This article is part of the Research Topic Genetics, Genomics, and Breeding of Edible Mushrooms in Asia View all 10 articles
This article is a correction to:
milR20 negatively regulates the development of fruit bodies in Pleurotus cornucopiae
 Yuhui Qi1,2,3
Yuhui Qi1,2,3 Chenyang Huang1,2,3
Chenyang Huang1,2,3 Mengran Zhao1,2,3
Mengran Zhao1,2,3 Xiangli Wu1,2,3
Xiangli Wu1,2,3 Guangyu Li1,2,3
Guangyu Li1,2,3 Yingjie Zhang1,2,3,4
Yingjie Zhang1,2,3,4 Lijiao Zhang1,2,3*
Lijiao Zhang1,2,3*A corrigendum on
milR20 negatively regulates the development of fruit bodies in Pleurotus cornucopiae
by Qi, Y., Huang, C., Zhao, M., Wu, X., Li, G., Zhang, Y., and Zhang, L. (2023). Front. Microbiol. 14:1177820. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1177820
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 5 as published. The gene in Figure 5E was displayed as “g3400”. The correct statement is “g10683”. The gene in Figure 5F was displayed as “g3400”. The correct statement is “g7031”. The corrected Figure 5 and its caption appear below.
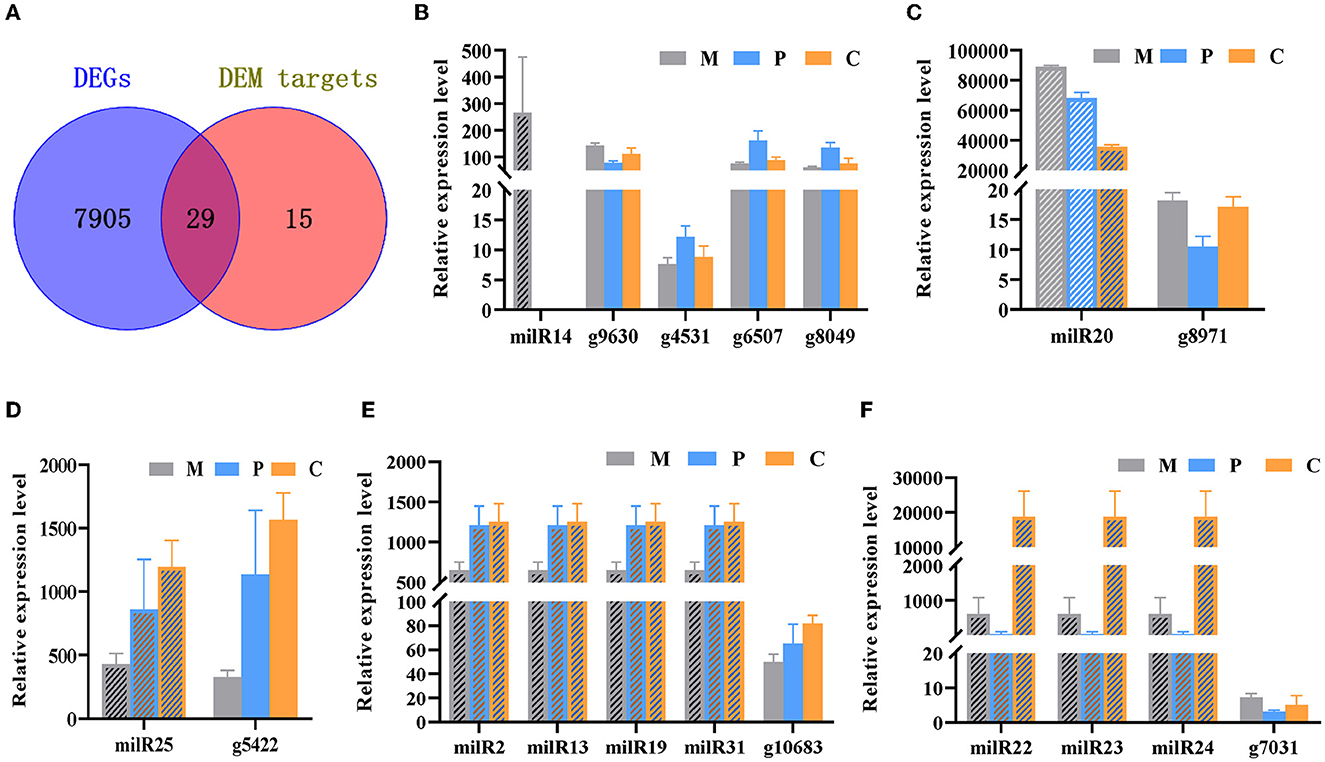
Figure 5. Integrated analyses of mRNA and milRNA data. (A) Venn diagram depicting the DEGs in the different stages of development and DEM targets. (B–F) Analysis of the expression levels of the DEMs and their targets DEGs.
In the published article, there was an error in the Funding statement. The names of the first two funding bodies were incorrectly presented as “Fundamental Research Funds for China Agriculture Research System” and “Central Nonprofit Scientific Institution”. The correct Funding statement appears below.
This study was financially supported by the China Agriculture Research System (CARS20), Fundamental Research Funds for Central Nonprofit Scientific Institution (No. 1610132020004), National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFD1200600), and the Beijing Agriculture Innovation Consortium (BAIC03).
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: milR20, fruit body development, Pleurotus cornucopiae, comparative transcriptome, MAPK signaling pathway
Citation: Qi Y, Huang C, Zhao M, Wu X, Li G, Zhang Y and Zhang L (2023) Corrigendum: milR20 negatively regulates the development of fruit bodies in Pleurotus cornucopiae. Front. Microbiol. 14:1236756. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1236756
Received: 08 June 2023; Accepted: 30 June 2023;
Published: 12 July 2023.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2023 Qi, Huang, Zhao, Wu, Li, Zhang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lijiao Zhang, emhhbmdsaWppYW9AY2Fhcy5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.