
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Microbiol. , 30 November 2021
Sec. Antimicrobials, Resistance and Chemotherapy
Volume 12 - 2021 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.815909
This article is a correction to:
Fine-Tuning of Alkaline Residues on the Hydrophilic Face Provides a Non-toxic Cationic α-Helical Antimicrobial Peptide Against Antibiotic-Resistant ESKAPE Pathogens
 Xudong Luo1,2
Xudong Luo1,2 Xiangdong Ye1,2
Xiangdong Ye1,2 Li Ding1,3
Li Ding1,3 Wen Zhu1
Wen Zhu1 Pengcheng Yi1
Pengcheng Yi1 Zhiwen Zhao1
Zhiwen Zhao1 Huanhuan Gao1
Huanhuan Gao1 Zhan Shu1
Zhan Shu1 Shan Li1
Shan Li1 Ming Sang4
Ming Sang4 Jue Wang1
Jue Wang1 Weihua Zhong5
Weihua Zhong5 Zongyun Chen1,2*
Zongyun Chen1,2*by Luo, X., Ye, X., Ding, L., Zhu, W., Yi, P., Zhao, Z., Gao, H., Shu, Z., Li, S., Sang, M., Wang, J., Zhong, W., and Chen, Z. (2021). Front. Microbiol. 12:684591. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.684591
In the original article, the Figure 6A, which shows the survival curves of infected mice after treatment with BmKn2-7K, was placed mistakenly using the same image as Figure 5C, due to a mistake made inadvertently in the preparation of the revised manuscript. The corrected Figure 6 appears below.
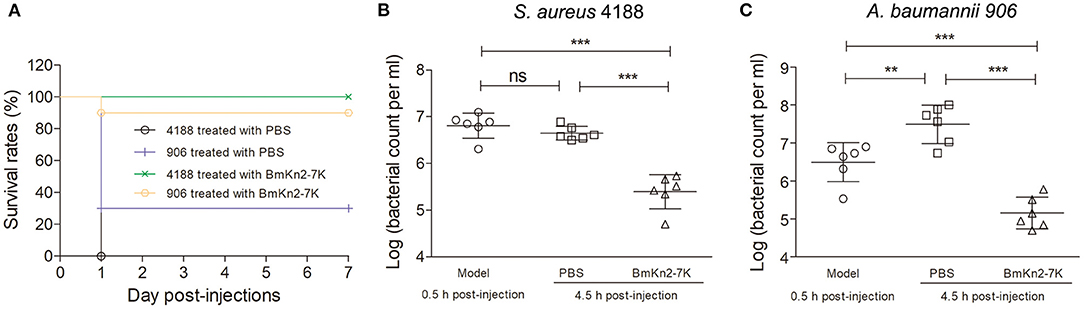
Figure 6. In vivo antimicrobial efficacy of BmKn2-7K. (A) Survival curves of infected mice after treatment with BmKn2-7K. Each cohort of ICR mice (n = 10) was infected with 5 × 107 cfu of S. aureus 4188 (or 6.25 × 107 cfu of A. baumannii 906) and cultured for 0.5 h to establish the lethal peritoneal infection model. Drug treatments were performed with a single dose of 20 (or 25) mg kg−1 body weight BmKn2-7K for the S. aureus 4188 (or A. baumannii 906) infected model, respectively. (B) Quantitative determination of bacterial loads in the peritoneal fluid of S. aureus infected ICR mice (n = 6). (C) Quantitative determination of bacterial loads in the peritoneal fluid of A. baumannii infected ICR mice (n = 6). The logarithm value of the number of viable bacteria from each mouse was plotted as individual dots, error bars represent the standard deviation from the mean within each cohort, **P < 0.01; and ***P < 0.001; ns represents “no significance.” The statistical significance between the groups was analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test to correct for multiple comparisons.
The authors apologize for the error and state that the correction has not changed the description, interpretation, or the original conclusion of the manuscript. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: ESKAPE pathogens, antibiotic resistance, cationic α-helical antimicrobial peptide, hydrophilic face, lysine vs arginine, hemolytic activity, in vivo efficacy
Citation: Luo X, Ye X, Ding L, Zhu W, Yi P, Zhao Z, Gao H, Shu Z, Li S, Sang M, Wang J, Zhong W and Chen Z (2021) Corrigendum: Fine-Tuning of Alkaline Residues on the Hydrophilic Face Provides a Non-toxic Cationic α-Helical Antimicrobial Peptide Against Antibiotic-Resistant ESKAPE Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 12:815909. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.815909
Received: 16 November 2021; Accepted: 17 November 2021;
Published: 30 November 2021.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2021 Luo, Ye, Ding, Zhu, Yi, Zhao, Gao, Shu, Li, Sang, Wang, Zhong and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zongyun Chen, Y2hlbnp5MjAwNUAxMjYuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.