- 1Emergency Department, State Key Laboratory of Complex Severe and Rare Diseases, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Peking Union Medical College, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Critical Care Medicine, Chifeng Municipal Hospital, Chifeng Clinical Medical College of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Chifeng, China
- 3Department of Anesthesiology, Chifeng Municipal Hospital, Chifeng Clinical Medical College of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Chifeng, China
- 4Department of Neurology, Yidu Central Hospital Affiliated to Weifang Medical University, Weifang, China
by Zhao, L., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Gao, Q., Ge, Z., Sun, X., and Li, Y. (2021). Front. Microbiol. 12:737066. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.737066
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 1 as published. Patients with sepsis without encephalopathy should be 1480. We wrote this as 1408 by error. Therefore 3279 patients for the final analysis should be modified to 3207. In the excluded patients, all excluded patients add up to 2152, not 3560. Therefore, there are three numbers in Figure 1 that need to be changed. (1) “sepsis without encephalopathy (n=1408)” changed to “sepsis without encephalopathy (n=1480).” (2) “3279 patients for the final analysis” changed to “3207 patients for the final analysis.” (3) “Exclude the following patients (n=3560)” changed to “Exclude the following patients (n=2152).” The corrected Figure 1 appears below.
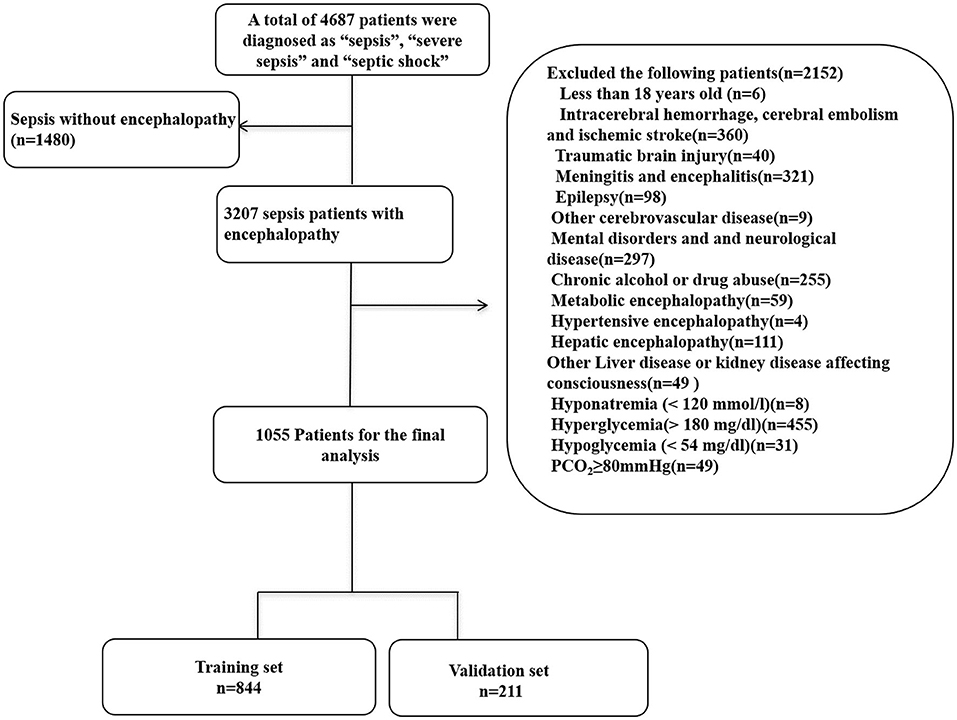
Figure 1. Flow chart of the enrolled patients. MIMIC-III, Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care III.
We apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: sepsis associated encephalopathy, prognosis, hospital mortality, nomogram, microbial infection
Citation: Zhao L, Li Y, Wang Y, Gao Q, Ge Z, Sun X and Li Y (2021) Corrigendum: Development and Validation of a Nomogram for the Prediction of Hospital Mortality of Patients With Encephalopathy Caused by Microbial Infection: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Front. Microbiol. 12:773499. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.773499
Received: 10 September 2021; Accepted: 11 October 2021;
Published: 03 November 2021.
Edited and reviewed by: George Tsiamis, University of Patras, Greece
Copyright © 2021 Zhao, Li, Wang, Gao, Ge, Sun and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yi Li, YmlsbGxpeWlAMTI2LmNvbQ==; orcid.org/0000-0002-7158-3624; Xibo Sun, c3VueGlibzkyQHNpbmEuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Lina Zhao
Lina Zhao Yun Li3†
Yun Li3† Yi Li
Yi Li