Bactericidal Property of Oregano Oil Against Multidrug-Resistant Clinical Isolates
- 1Wellman Center for Photomedicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States
- 2First Area Medical Laboratory, JBSA-Fort Sam Houston, Houston, TX, United States
A Corrigendum on
Bactericidal Property of Oregano Oil Against Multidrug-Resistant Clinical Isolates
by Lu, M., Dai, T., Murray, C. K., and Wu, M. X. (2018). Front. Microbiol. 9:2329. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02329
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 4, panels C and D as published. The images from days 5 and 7 in Figures 4C and 4D are too similar and are not from two days apart (day 5 and day 7). The corrected Figure 4 appears below.
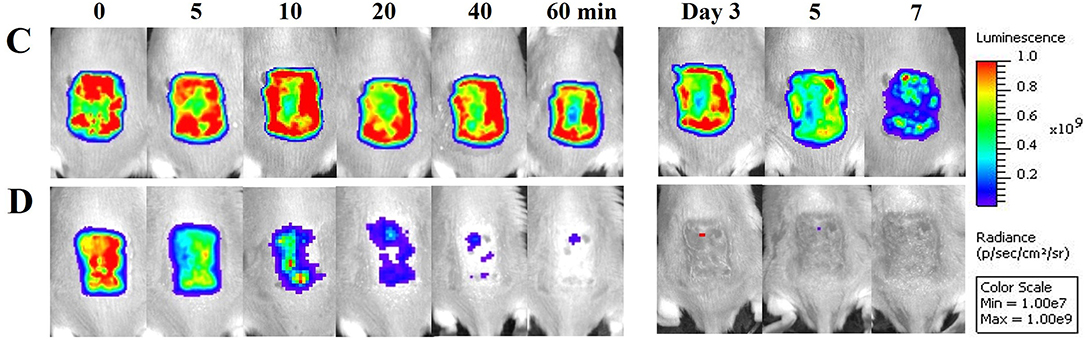
Figure 4. Oregano oil treatment of PA01 infections in the burn wounds. (A,B) Gram-stained longitudinal section (A) and crossing section (B) of a representative wound showing the presence of PA01 biofilms outlined in red. The skin sample was harvested 24 h after bacterial inoculation. (C,D) Successive bacterial luminescence images of representative wounds infected with 5 × 106 CFU of luminescent PA01 with (D) and without (C) oregano oil at 10 mg/ml. The oregano oil was topically applied onto the wounds at 24 h after bacterial inoculation. (E) A dose response of mean bacterial luminescence of the wounds infected with 5 × 106 CFU of PA01 in the presence or absence of oregano oil treatment at 5 or 10 mg/ml. (F) Time courses of mean bacterial luminescence of the infected wounds in the presence or absence of oregano oil treatment at 5 or 10 mg/ml from days 2 to 7. (G) Mean areas under the bacterial luminescence curves (F), representing the overall bacterial burden of infected wounds. (H). The wounds were treated with grape seed oil (control) or oregano oil 24 h after infection and bacterial CFU were quantified on day 7 after bacterial inoculation. RLU, relative luminescence units; A.U., arbitrary units. The data represent means ± SDs (n = 8). **p < 0.01, ### or ***p < 0.001 and #### or ****p < 0.0001 in the presence vs. absence of oregano oil. ns, no significance.
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 6, panels C and D as published. Figure 6C was mistakenly duplicated from Figure 6D. The matched images of Figures 6E and F from the same level of tissue slices as Figures 6C and 6D are updated accordingly. The corrected Figure 6 appears below.
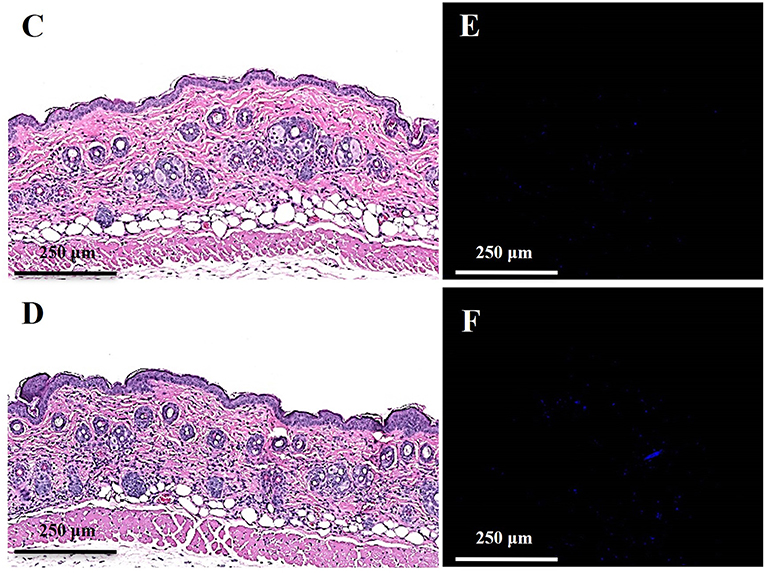
Figure 6. Toxicity evaluation of oregano oil to normal mouse skins. The dorsal skin of mice was topically treated with (A,C,E) or without 10 mg/ml oregano oil (B,D,F) once a day for three consecutive days. On day 4, the skins were photographed (A,B), followed by histological examination (C,D). The skin sections were also TUNEL stained (E,F). DNase I treated skin samples (G) were TUNEL stained in parallel as positive-staining controls.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: oregano oil, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, MRSA, biofilms, burn wound, mouse model, bioluminescence imaging
Citation: Lu M, Dai T, Murray CK and Wu MX (2021) Corrigendum: Bactericidal Property of Oregano Oil Against Multidrug-Resistant Clinical Isolates. Front. Microbiol. 12:713573. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.713573
Received: 23 May 2021; Accepted: 14 June 2021;
Published: 12 July 2021.
Edited and reviewed by: Santi M. Mandal, Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, India
Copyright © 2021 Lu, Dai, Murray and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tianhong Dai, VERBSSYjeDAwMDQwO21naC5oYXJ2YXJkLmVkdQ==; Mei X. Wu, TVdVNSYjeDAwMDQwO21naC5oYXJ2YXJkLmVkdQ==
 Min Lu
Min Lu Tianhong Dai
Tianhong Dai Clinton K. Murray2
Clinton K. Murray2 Mei X. Wu
Mei X. Wu