
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Microbiol., 08 July 2021
Sec. Food Microbiology
Volume 12 - 2021 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.704636
This article is part of the Research TopicAntimicrobial Resistance Along the Food Chain: Are We What We Eat?View all 14 articles
The pig industry is the principal source of meat products in China, and the presence of pathogens in pig-borne meat is a crucial threat to public health. Salmonella is the major pathogen associated with pig-borne diseases. However, route surveillance by genomic platforms along the food chain is still limited in China. Here, we conducted a study to evaluate the dynamic prevalence of Salmonella in a pig slaughtering process in Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province, China. Fifty-five of 226 (24.37%) samples were positive for Salmonella; from them, 78 different isolates were selected and subjected to whole genome sequencing followed by bioinformatics analyses to determine serovar distribution, MLST patterns, antimicrobial resistance genes, plasmid replicons, and virulence factors. Moreover, phenotypic antimicrobial resistance was performed using the broth dilution method against 14 antimicrobial agents belonging to 10 antimicrobial classes. Our results showed that samples collected from the dehairing area (66.66%) and the splitting area (57.14%) were the most contaminated. Phenotypic antimicrobial resistance classified 67 of 78 isolates (85.90%) as having multidrug resistance (MDR), while the highest resistance was observed in tetracycline (85.90%; 67/78) followed by ampicillin (84.62%; 66/78), chloramphenicol (71.80%; 56/78), and nalidixic acid (61.54%; 48/78). Additionally, serovar prediction showed the dominance of Salmonella Typhimurium ST19 (51.28%; 40/78) among the 78 studied isolates, while plasmid prediction reported the dominance of IncHI2A_1 (20.51%; 16/78), followed by IncX1_1 (17.95%; 14/78) and IncHI2_1 (11.54%; 9/78). Virulence factor prediction showed the detection of cdtB gene encoding typhoid toxins in two Salmonella Goldcoast ST358 and one Salmonella Typhimurium ST19, while one isolate of Salmonella London ST155 was positive for genes encoding for the siderophore “yersiniabactin” and the gene senB encoding for enterotoxin production. From this study, we conclude that pig slaughterhouses are critical points for the dissemination of virulent and multidrug-resistant Salmonella isolates along the food chain which require the implementation of management systems to control the critical points. Moreover, there is an urgent need for the implementation of the whole genome sequencing platform to monitor the emergence of virulent and multidrug-resistant clones along the food chain.
Salmonellosis is a global zoonotic disease, caused by Salmonella and characterized by self-limited gastroenteritis in immunocompetent adults, in which typical symptoms like diarrhea, fever, abdominal cramps, and vomiting occur between 6 and 72 h (usually 12–36 h) after ingestion of bacteria and the illness lasts from 2 to 7 days [World Health Organisation (WHO), 2018]. It might also cause severe invasive infection, particularly in immunocompromised patients (Deen et al., 2012; Xu X. et al., 2020). Recently, it was estimated that Salmonella was responsible for about 180 million (9%) of the diarrheal illnesses that occur globally each year, causing about 298,000 deaths (41%) of all diarrheal disease-associated deaths (Besser, 2018). In China, a study based on the literature review estimated that the incidence of nontyphoidal salmonellosis was 626.5 cases per 100,000 persons (Mao et al., 2011; Xu Y. et al., 2020). Moreover, it has been reported that Salmonella was responsible for approximately 70∼80% of foodborne pathogenic outbreaks in China (Jun et al., 2007).
Salmonella spp. are Gram-negative rod-shaped bacteria, facultatively anaerobic, and belong to the family Enterobacteriaceae. To date, more than 2,600 serovars have been described among Salmonella species; among them, only a few serovars were mostly linked to human and/or animal infections, including Typhimurium and Enteritidis (so-called majority serovars) for human infections (Xu X. et al., 2020), Gallinarum and Pullorum for poultry infections (Xu Y. et al., 2020), Dublin for cattle infections (Paudyal et al., 2019), and Choleraesuis and Typhisuis for pig infections (Boyen et al., 2008; Asai et al., 2010). Generally, animal farms are considered natural reservoirs of Salmonella, especially poultry and pigs (Li et al., 2013; Zhou et al., 2017; Xu Y. et al., 2020). Salmonella could colonize the digestive tract of animals and are excreted in feces and spread into the environment (Kagambèga et al., 2013; Bonardi, 2017; Jiang et al., 2019), then transmitted to humans via the food chain (Ed-Dra et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2019; Wilson et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2021). Therefore, several studies have reported the presence of Salmonella in foods of animal origin, especially meat products (Ed-Dra et al., 2017; Jiang et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2021).
Pork meat is considered the most frequently contaminated food and the major source of Salmonella infections in humans (Bonardi, 2017; Wilson et al., 2020). In fact, pig farms seem to be a suitable environment for the replication and the persistence of Salmonella (Lettini et al., 2016; Bonardi, 2017; Vico et al., 2020). However, the slaughtering process which is located downstream of the pig-breeding process and upstream of pork sales is a critical step in determining the contamination/decontamination of animal carcasses and thus the meat products (Zhou et al., 2018). Moreover, the application of good hygienic practices in slaughterhouses has great importance and could participate in reducing the prevalence of Salmonella in the final meat products (Rahkio and Korkeala, 1996; Biasino et al., 2018). During the slaughtering process, animals pass through different processing stages with complicated manipulations (Zhou et al., 2018). However, since pigs are considered reservoirs of pathogens, they could contaminate/cross-contaminate the carcasses or muscle tissues during the slaughtering process. In fact, it has been demonstrated that slaughter practices, such as splitting the head and incising tonsils, were associated with higher levels of hygiene indicator bacteria and Salmonella in pig carcasses (Biasino et al., 2018). Therefore, the surveillance of Salmonella along the slaughtering process and its environment is with a high priority to determine the key points that are responsible for the contamination of carcasses and the final meats.
Recently, whole genome sequencing followed by bioinformatics analysis was considered as a cost-effective method for the diagnosis and characterization of foodborne pathogens (Biswas et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2020, 2021; Yu et al., 2020). As proof-of-concept, we conduct a study in a pig slaughterhouse in Hangzhou (Zhejiang Province, China), to obtain Salmonella isolates from different sources. The recovered strains were subjected to whole genome sequencing followed by in silico analysis to determine serovar distribution, multilocus sequence types, plasmid replicons, antimicrobial resistance, and virulence genes. Moreover, phenotypical antimicrobial resistance was investigated by the broth dilution method and compared with genotypical resistance.
The present study was conducted in Linpu Pig Slaughterhouse in Xiaoshan, Hangzhou (China). The capacity of the studied slaughterhouse was approximately 1,000 pigs per day. A sampling visit was organized during December 2018 allowing the collection of 226 samples from different origins (pig carcasses, swab samples, environmental samples, equipment samples, operator samples, intestinal content samples, hepatobiliary samples, and sewer samples) along the slaughtering process of pigs (Table 1). The sampling method was in accordance with those described in previous studies (Cai et al., 2016; Zhou et al., 2017). The isolation of Salmonella was performed from different samples according to the protocols described previously (Jiang et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2021). Then, molecular confirmation of presumptive isolates was carried out by the amplification of invA gene according to the protocol previously described (Zhu et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2021).
Among the 226 collected samples, 55 were positive for the presence of Salmonella. However, since some samples present more than one presumptive isolate, we decided to select 78 different Salmonella isolates that show differences in morphological and biochemical criteria for genome sequencing and analysis (Table 2). Serotyping of the PCR confirmed Salmonella isolates were performed according to White–Kauffmann–Le Minor scheme by slide agglutination method to define O and H antigens using commercial antisera (SSI Diagnostica, Hillerød, Denmark).
All the obtained Salmonella isolates (n = 78) were selected for genomic DNA extraction according to the protocol described previously (Liu et al., 2021). Briefly, a broth culture of each Salmonella isolate was prepared by inoculation of a pure colony in Luria–Bertani broth followed by incubation at 37°C under 180 rpm shaking conditions. Then, DNA extraction was conducted by using TIANamp bacteria DNA kit (Tiangen Biotech, Beijing, China) according to the instructions of the manufacturer. The quantification of the extracted DNA was performed by the Qubit 2.0 Fluorometer (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States), as per the instructions of the manufacturer.
The genomic DNA library was constructed using NovaSeq XT DNA library construction kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, United States, No: FC-131-1024), followed by genomic sequencing using Illumina NovaSeq Platform with NovaSeq 6000 SP Reagent Kit (300 cycles). The raw sequence reads were checked for quality and assembled using SPAdes v3.12.0 (Bankevich et al., 2012). Virulence gene prediction was conducted based on the virulence factors database (VFDB) (Chen et al., 2005). Moreover, in silico serotyping of Salmonella strains was performed by the SISTR web tool, whereas sequence types, antimicrobial resistance genes (ARG), and plasmid replicons were detected using the assemblies of the samples on the in-house Galaxy platform (Afgan et al., 2016), in combination with mlst v2.16.11 and abricate v0.8 (Zankari et al., 2012), including the CGE ResFinder database (updated on February 19, 2021) with a similarity cutoff of 90% for ARG and PlasmidFinder database (updated on February 19, 2021) with a similarity cutoff of 95% (Carattoli et al., 2014).
The antimicrobial resistance of the isolated Salmonella strains was evaluated phenotypically by the broth dilution method to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of a panel of 14 antimicrobial agents belonging to 10 antimicrobial classes according to the protocol described previously (Jiang et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2021). The obtained results were interpreted according to the recommendation of the Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute guidelines (CLSI, 2017). The tested antimicrobial agents were as follows: penicillins (ampicillin: AMP, 0.25–128 μg/ml), β-lactamase inhibitors (amoxicillin/clavulanic acid: AMC, 0.125/0.062–128/64 μg/ml), cephems (ceftiofur: CF, 0.125–128 μg/ml; cefoxitin: CX, 0.125–128 μg/ml), aminoglycosides (gentamicin: GEN, 0.031–64 μg/ml; kanamycin: KAN, 0.25–128 μg/ml; streptomycin: STR, 1–128 μg/ml), tetracyclines (tetracycline: TET, 0.062–128 μg/ml), fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin: CIP, 0.015–16 μg/ml; nalidixic acid: NAL, 0.5–128 μg/ml), folate pathway inhibitors (trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole: TST, 0.25/4.75–32/608 μg/ml), polypeptides (colistin: COL, 0.031–64 μg/ml), macrolides (azithromycin: AZI, 0.25–128 μg/ml), and phenicols (chloramphenicol: CHL, 0.5–128 μg/ml). Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 were used as the quality control strains to validate the antimicrobial susceptibility testing. However, strains showing a decrease in susceptibility (intermediate) were merged with resistant strains for ease of analysis, and the multidrug-resistant (MDR) strains were defined by resistance to at least three antimicrobial classes.
GraphPad Prism 8 software (San Diego, CA, United States) was used for data analysis and generation of the figures. For antimicrobial susceptibility testing, the results of intermediate susceptibility were merged with resistance. Then, each phenotypically antimicrobial susceptibility test result (resistant or susceptible) was compared with the detection (presence or absence) of the corresponding resistance gene by in silico analysis. The isolates that are positive for at least one antimicrobial resistance gene among an antimicrobial class were considered as resistant to the corresponding antimicrobial class. The coherent results group together the isolates that are resistant or susceptible for both phenotypical and genotypical results. However, the incoherent results correspond to the isolates that are phenotypically resistant and genotypically susceptible or phenotypically susceptible and genotypically resistant for an antimicrobial agent. The percentage of incoherence corresponds to the difference between the results obtained by phenotypical and genotypical tests for each antimicrobial agent.
The results obtained in this study showed that 55 of 226 (24.37%) samples were contaminated by Salmonella (Table 1). According to the sampling points along the pig slaughtering process, our results showed that the samples collected from the dehairing area were the most contaminated (66.66%), followed by those collected from the splitting area (57.14%). However, samples collected from the washing area and scalding area were not contaminated (Table 1). Additionally, from the 55 samples, 78 different Salmonella isolates were obtained, purified, and subjected to whole genome sequencing. The genomic prediction of serovars and MLST patterns showed the distribution of five different serovars and six MLST patterns, namely, Typhimurium ST19 (n = 40), Typhimurium ST34 (n = 14), London ST155 (n = 14), Rissen ST469 (n = 7), Goldcoast ST358 (n = 2), and Derby ST40 (n = 1) (Table 3). Additionally, serotyping performed by in silico analysis and slide agglutination methods provided the same results.
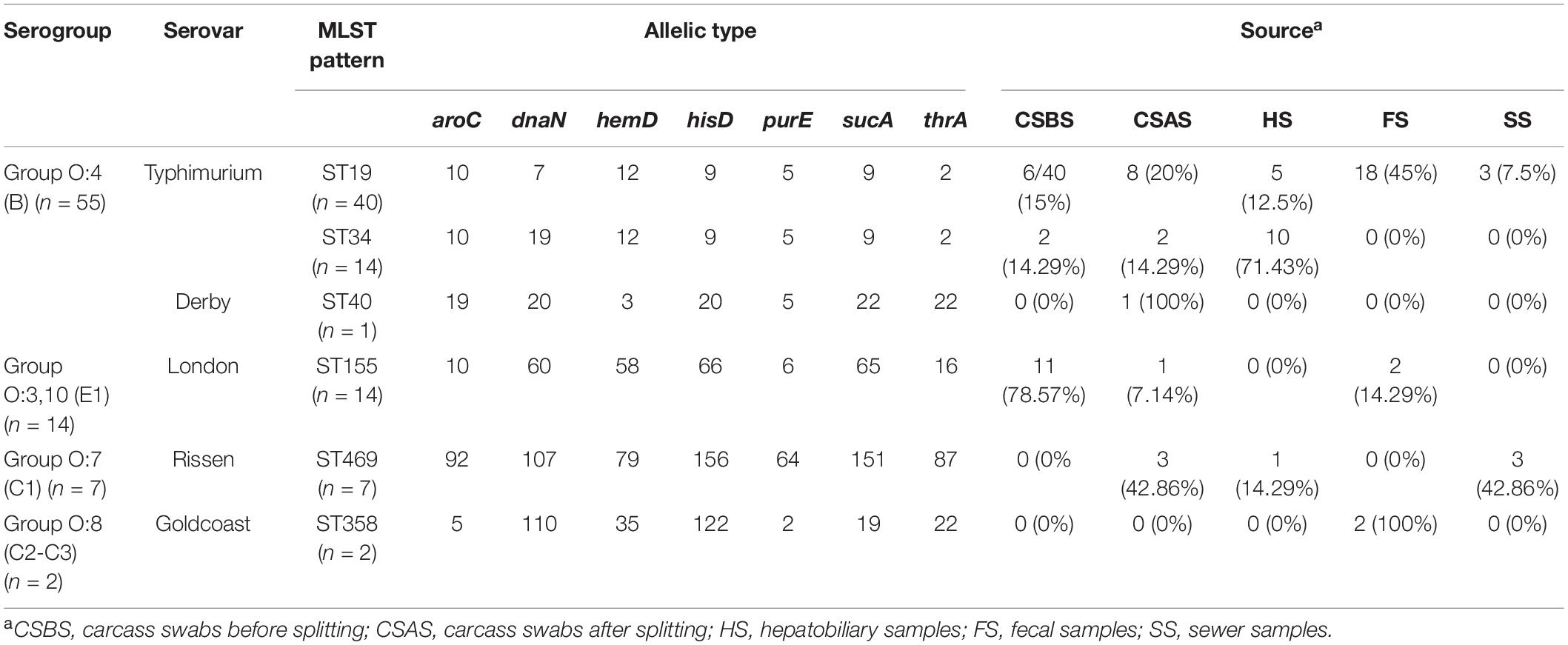
Table 3. Allelic profiles, serogroups, serovars, and MLST patterns of Salmonella isolated from different sources.
The antimicrobial resistance of the isolated Salmonella strains was evaluated against 14 antimicrobial agents belonging to 10 classes or categories. The phenotypic antimicrobial profiles were classified as resistant, susceptible, and intermediate according to the criteria of the Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute guidelines and the results are presented in Table 4 and Supplementary Material 1. Our findings showed that tetracycline (85.90%; 67/78) and ampicillin (84.62%; 66/78) were the most resistant antimicrobial agent, followed by chloramphenicol (71.80%; 56/78) and nalidixic acid (61.54%; 48/78). Additionally, after considering the results of intermediate resistance as resistant strains, our findings showed that 89.74% (70/78) of isolates were resistant at least to one antimicrobial class, 87.18% (68/78) were resistant to at least two antimicrobial classes, and 85.90% (67/78) were resistant to at least three antimicrobial classes and were considered as MDR (Figure 1A).
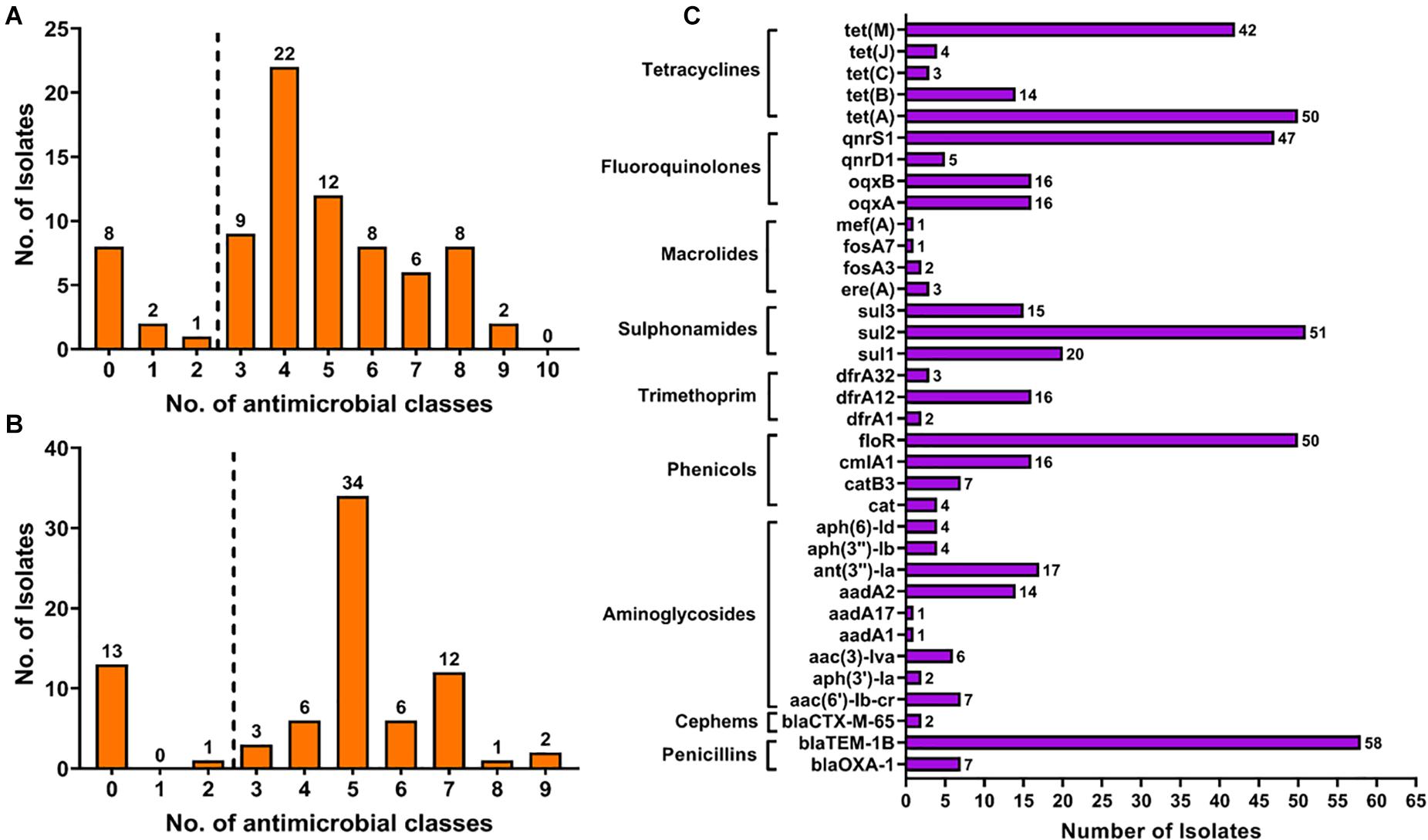
Figure 1. The distribution of multiple drug resistance isolates according to the results obtained by phenotypical (A) and genotypical (B) tests. The detection of antimicrobial resistance genes (C) showed the high prevalence of resistance gene encoding resistance to penicillins, phenicols, sulfonamides, fluoroquinolones, and tetracyclines.
According to the sources, it appears that Salmonella isolates recovered from sewer samples (SS) and hepatobiliary samples (HS) were more resistant to the tested antimicrobial agents compared with those collected from other sources (Figure 2B). Moreover, among different serovars identified in this study, Salmonella serovars Derby and Goldcoast appear to be the most resistant to the tested antimicrobial agents (Figure 2A). However, it should be noted that this conclusion cannot be generalized since only one strain of Salmonella Derby and two strains of Salmonella Goldcoast have been identified in this study. Additionally, Salmonella Typhimurium isolates from ST34 appear to be more resistant than isolates from ST19 (Figure 2A).
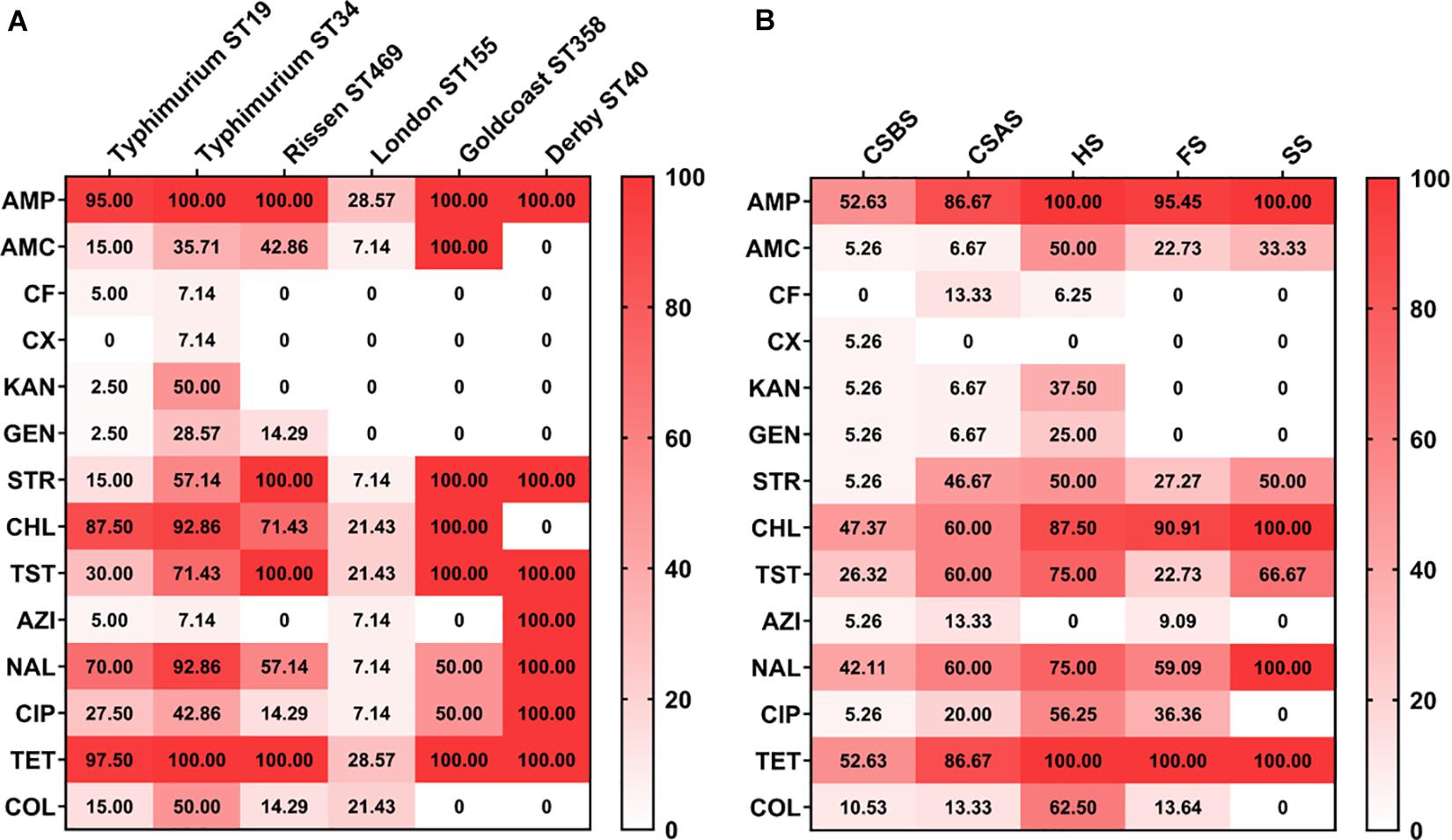
Figure 2. Heatmap of antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella isolated from pig slaughtering process according to serovars and sampling sources. The isolates of Salmonella Typhimurium ST34 were resistant to all the tested antimicrobial agents (A), while Salmonella isolated from HS were the most resistant to the tested antimicrobial agents (B). The numbers in cells correspond to the percentage (%) of antimicrobial resistance isolates. CSBS, carcass swabs before splitting; CSAS, carcass swabs after splitting; HS, hepatobiliary samples; FS, fecal samples; SS, sewer samples.
The whole genome sequences of the 78 isolated Salmonella strains were subjected to in silico detection of antimicrobial resistance genes. The results obtained showed the detection of 35 different genes encoding resistance to nine antimicrobial classes (Figure 3 and Supplementary Material 2). The most detected genes were blaTEM–1B encoding resistance to penicillins (74.36%; 58/78), sul2 encoding resistance to sulfonamides (87.93%; 51/58), tet(A) encoding resistance to tetracyclines (64.10%; 50/78), floR encoding resistance to phenicols (64.10%; 50/78), and qnrS1 encoding resistance to fluoroquinolones (60.26%; 47/78) (Figure 1C). Moreover, 64 of 78 isolates (82.05%) harbor the resistance genes of more than two classes (Figure 1B). However, regarding the serovar distribution, it appears that Salmonella Typhimurium ST34 harbors more diversified antimicrobial resistance genes while Salmonella London ST155 appears to be poor in resistance genes (only one strain that harbors the genes cat and tet(J) encoding resistance to phenicols and tetracyclines classes, respectively) (Figure 4A). Moreover, our results showed that Salmonella isolates obtained from carcass swabs after splitting (CSAS) and HS harbor more resistance genes compared with those isolated from other sources (Figure 4B).
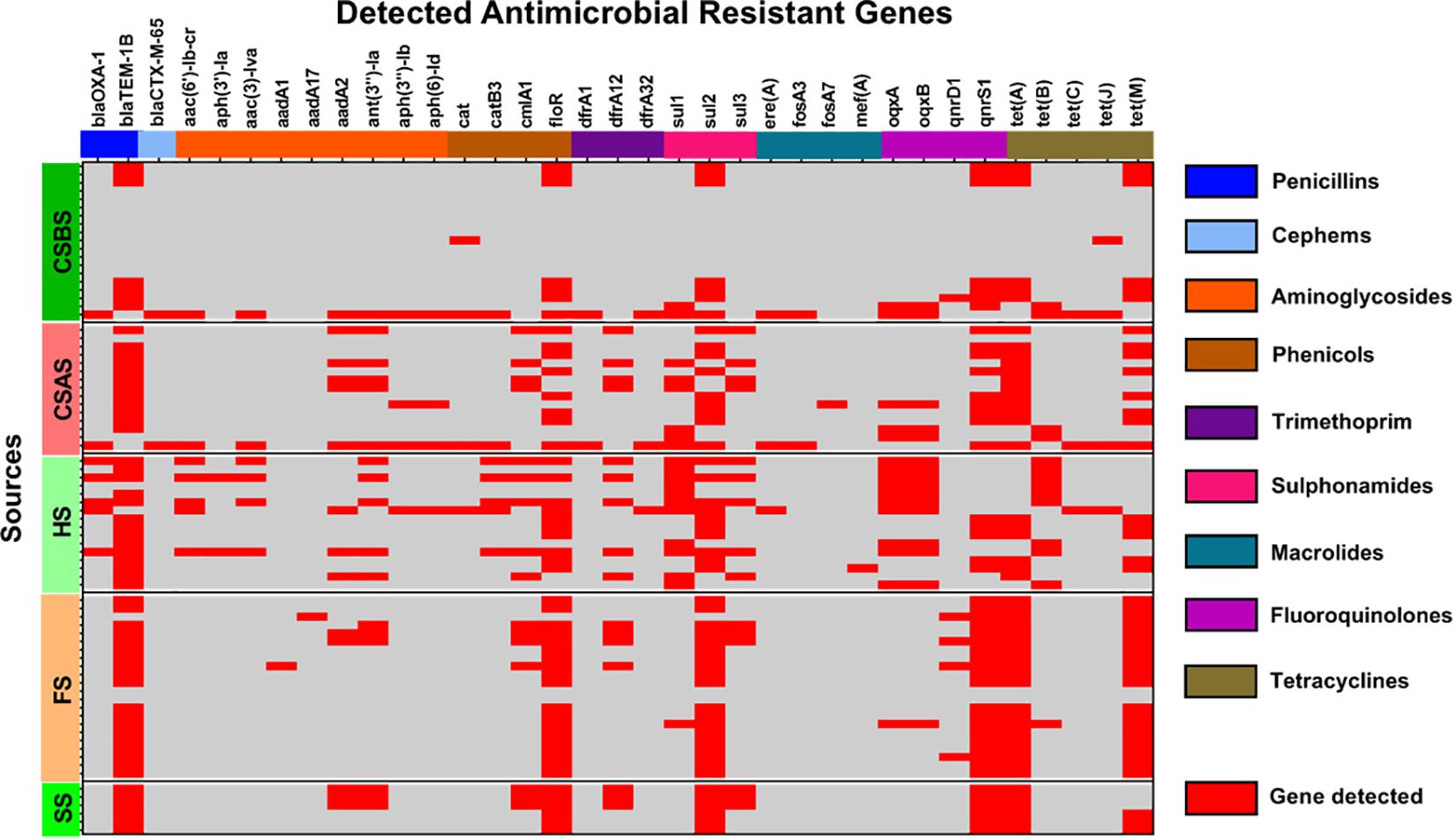
Figure 3. Heatmap of the detection of antimicrobial resistance genes among the studied Salmonella isolates (n = 78).
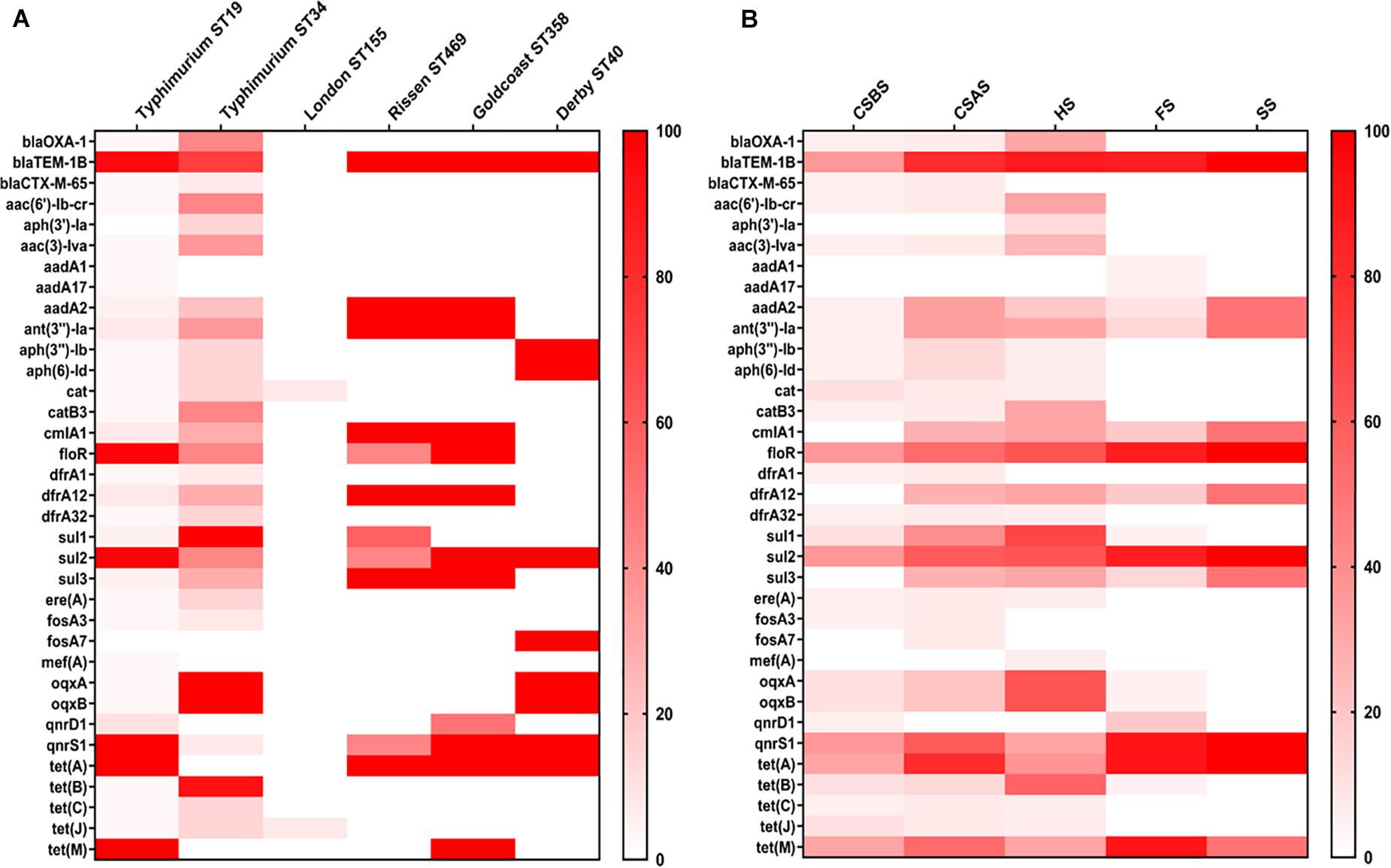
Figure 4. Heatmap of antimicrobial resistance genes according to serovars (A) and sampling sources (B). The isolates of Salmonella Typhimurium ST34 harbor the most diversified antimicrobial resistance genes. However, Salmonella isolates recovered from HS and CSAS contain more resistance genes compared with those isolated from other sources. CSBS, carcass swabs before splitting; CSAS, carcass swabs after splitting; HS, hepatobiliary samples; FS, fecal samples; SS, sewer samples.
The relation between phenotypical antimicrobial resistance and the presence/absence of corresponding resistance gene obtained by in silico analysis was evaluated and the results are presented in Table 5. Our results showed that ciprofloxacin has the higher incoherence percentage (55.13%; 43/78) for which several isolates were genotypically positive but phenotypically negative, while cefoxitin presents the lower incoherence percentage (1.28%; 1/78).
In this study, the presence of 117 genes that are implicated in virulence and pathogenicity mechanisms of Salmonella was evaluated among the genomes of the 78 Salmonella isolates. The results are summarized in Supplementary Material 3. Our results showed that the number of detected genes ranged from 88 to 113 per isolate. Among the 78 isolates, three isolates (two Salmonella Goldcoast ST358 and one Salmonella Typhimurium ST19) were positive for the gene cdtB encoding typhoid toxin production, and these isolates were all isolated from fecal samples (FS). Additionally, only one Salmonella isolate (Salmonella London ST155) isolated from CSBS sample was positive for the genes encoding for the siderophore “yersiniabactin” (fyuA, ybtA, ybtE, ybtP, ybtQ, ybtS, ybtT, ybtU, ybtX, irp1, and irp2) and for the gene senB encoding for enterotoxin production. However, the typical virulence factors carried on Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 and 2 (SPI-1 and SPI-2) were detected in all the studied isolates.
The results of the prediction of plasmid replicons in the 78 Salmonella isolates are presented in Figure 5 and Supplementary Material 4. Our results showed that the most abundant plasmid replicon was IncHI2A_1 (20.51%; 16/78), followed by IncX1_1 (17.95%; 14/78) and IncHI2_1 (11.54%; 9/78). The number of plasmid replicons ranged from 1 to 4 per isolate, while 42 of 78 (53.85%) Salmonella isolates do not harbor any plasmid. Regarding serovars, our results showed that Salmonella Typhimurium ST19 had a large number of different plasmids replicons (five plasmids), followed by Salmonella Goldcoast ST358 and Salmonella Derby ST40 (four plasmids). However, regarding the sampling sources, our results showed that the isolates recovered from FS harbor a large number of plasmid replicons (seven types of plasmids), followed by those recovered from CSAS (five types of plasmids), while Salmonella isolates recovered from SS do not harbor any plasmid.
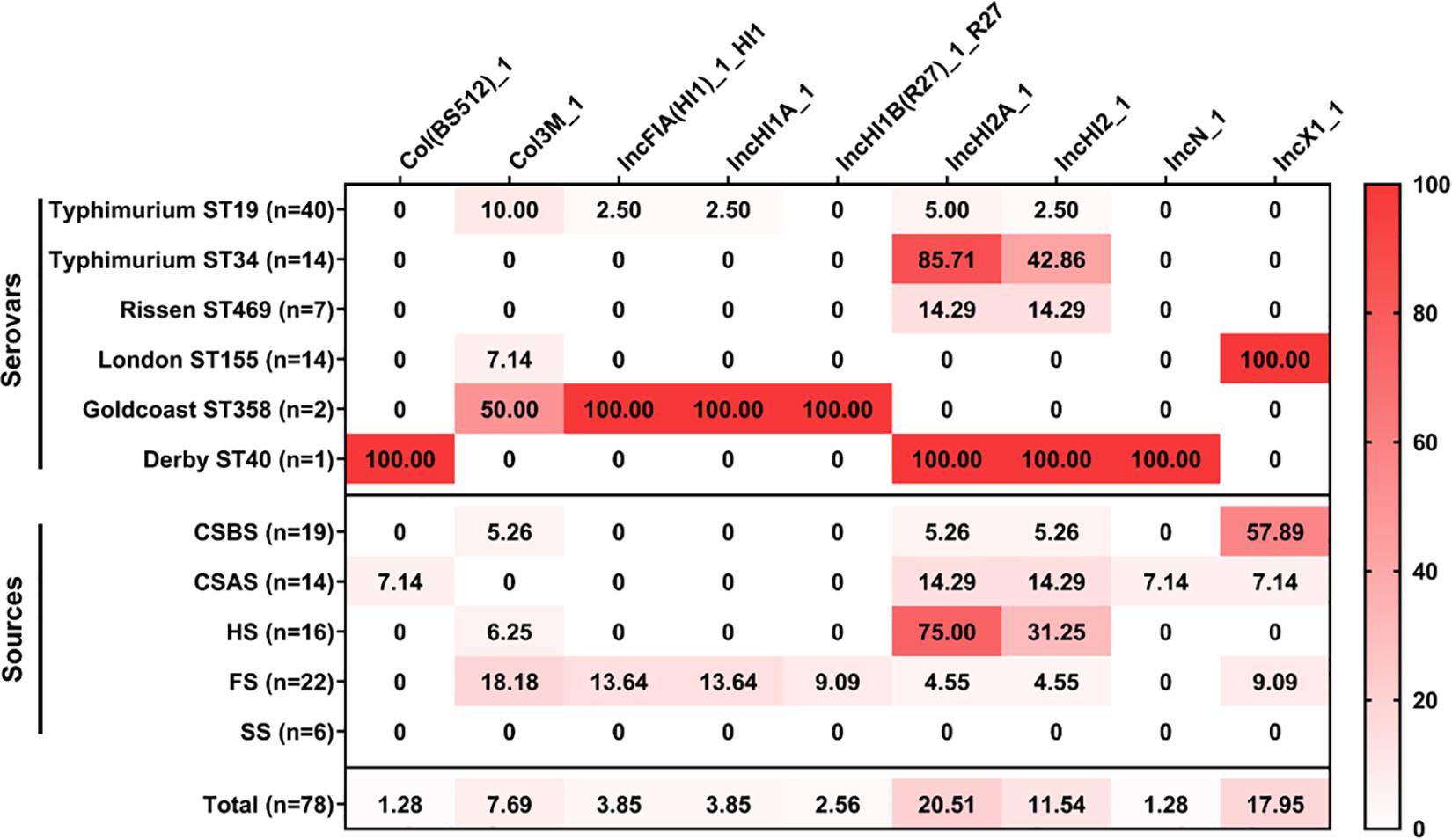
Figure 5. Heatmap of plasmid replicon distribution in the studied Salmonella isolates (n = 78). The numbers in cells correspond to the prevalence (%) of plasmid replicons in Salmonella isolates according to serovar distribution and sampling sources.
Pig slaughterhouses are critical points of the meat processing chain; they are situated downstream of the pig-breeding process and upstream of pork sales. Since reception, animals undergo different complicated manipulations and are in contact with slaughterhouse facilities, workers, etc., which favors the contamination/cross-contamination of animal carcasses and, thus, the meat products (Arguello et al., 2013; Zhou et al., 2018). However, comparison between the contamination rate of Salmonella in pigs in the preslaughter stage and in the postslaughter stage revealed that the prevalence in the preslaughter stage often seems to be lower (Jiang et al., 2019). In this regard, Colello and his group conducted a study along the production chain of pig farms and showed that the prevalence of Salmonella in farms (2.6%) and slaughterhouses (2.0%) was lower than that observed in boning rooms (8.8%) and retail markets (8.0%) (Colello et al., 2018). Additionally, Jiang et al. reported that the prevalence of Salmonella in pigs at the farm stage was 11.77%, lower than that observed in the slaughtered pigs (45.23%) (Jiang et al., 2019), demonstrating the criticality of the slaughtering process in determining the quality and safety of derived pig food products.
In this regard, we conducted a study to evaluate the prevalence of Salmonella during the pig slaughtering process. Our results showed that 55 of the 226 samples (24.37%) were contaminated by Salmonella. These results were lower than those reported previously in pig slaughterhouses in other Chinese regions (ranged between 29.2 and 46.6%) (Bai et al., 2015; Li et al., 2016; Zhou et al., 2017) and in Spain (39.7%) (Arguello et al., 2012), while they were higher than those reported in the slaughtered pigs in Sardinia, Italy (12.9%) (Fois et al., 2017); pig carcasses and intestines from five slaughterhouses in Belgium (14.1%) (De Busser et al., 2011); a pig slaughterhouse in Yangzhou, China (17.43%) (Li et al., 2019); pork and slaughterhouse environment in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India (13.7%) (Chaudhary et al., 2015); and pig slaughterhouses in two different regions of southwestern Spain (12.93%) (Morales-Partera et al., 2018). According to the slaughtering process, samples recovered from the dehairing area and splitting area were the most contaminated samples. In the dehairing area, the frequently used knife for carcass modification was considered as the risk factor for the observed carcass cross-contamination. However, the splitting step located at the next step after evisceration has been confirmed as the other step with a higher risk of Salmonella contamination (Cai et al., 2016; Zhou et al., 2017). After evisceration, the intestinal content can contaminate a part of animal carcasses; however, during splitting, the splitter could be contaminated and then cross-contaminate other carcasses, resulting in the increase of Salmonella prevalence in the splitting area (Cai et al., 2016; Li et al., 2016). Therefore, the implementation of good hygienic practices and management systems to control critical points during the slaughtering process is of high priority to reduce the prevalence of Salmonella.
Among the 55 positive samples, 78 different Salmonella isolates were identified in this study. These isolates belong to five different serovars and six MLST patterns, namely, with importance degree, Salmonella Typhimurium ST19, Salmonella Typhimurium ST34, Salmonella London ST155, Salmonella Rissen ST469, Salmonella Goldcoast ST358, and Salmonella Derby ST40. In China, Salmonella Derby was identified as the most isolated serovar from pig slaughterhouse samples (Li et al., 2016, 2019; Zhou et al., 2017, 2018; Liu et al., 2020). However, Salmonella Typhimurium has been reported previously as the dominant serovar in Salmonella isolates recovered from pig slaughterhouses in Henan Province (Bai et al., 2015). In fact, it is well known that Salmonella Typhimurium was classified among the major serovars causing human salmonellosis worldwide (CDC, 2018; EFSA and ECDC, 2018), especially those with multilocus sequence types ST19 and ST34, which were reported in several cases of human infections (Wong et al., 2013; Carden et al., 2015; Panzenhagen et al., 2018; Luo et al., 2020; Monte et al., 2020). Therefore, the transmission of these isolates to the final meat products along the food chain is of high risk for consumers and may cause severe cases of foodborne diseases.
The infections caused by Salmonella are treated with different antimicrobial drugs. However, in the last decades, development of Salmonella resistance to many antimicrobials has been observed worldwide, either for the isolates provided from clinical, food, and environmental samples. In this study, the phenotypical and genotypical antimicrobial resistance profiles of the 78 isolated Salmonella strains were evaluated. Phenotypical results classified tetracycline and ampicillin as the less effective antimicrobial agents. In fact, the high resistance of Salmonella isolates to tetracycline and ampicillin has been reported over the world in samples collected along the animal food chain (Ed-Dra et al., 2017; Jiang et al., 2019, 2021; Wang et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2020, 2021), since they were frequently used in animal farms (Lekagul et al., 2019). In fact, the abuse and the misuse of antimicrobial drugs in animal livestock for therapeutic, prophylaxis, and growth promotions have led to the development of antimicrobial resistance. Moreover, our results showed that 85.90% of isolates/strains were resistant to more than two antimicrobial classes (MDR), which is considered a serious threat to public health that leads to therapeutic failure after a simple infection by MDR isolates.
Genotypical antimicrobial resistance prediction showed the detection of 35 resistance genes encoding resistance to nine antimicrobial classes, with a high prevalence of blaTEM–1B gene encoding resistance to penicillins, sul2 gene encoding resistance to sulfonamides, tet(A) gene encoding resistance to tetracyclines, floR gene encoding resistance to phenicols, and qnrS1 gene encoding resistance to fluoroquinolone. The presence of these genes in bacterial genomes could be responsible for the acquisition of resistance to the corresponding antimicrobial classes. However, the analysis of coherence between genotypic and phenotypic antimicrobial resistance showed that phenotypic resistance cannot always be linked to the presence of resistance genes. Our results are in agreement with those reported previously in Salmonella isolates, showing a difference between phenotypic and genotypic resistance profiles (Liu et al., 2020, 2021). Hence, the phenotypic test remains the gold method for the assessment of bacterial behavior toward antimicrobial agents.
The prediction of virulence genes implicated in virulence and pathogenicity mechanisms reveals the detection of 117 different genes, particularly the detection of cdtB gene encoding typhoid toxins in two isolates of Salmonella Goldcoast ST358 and one isolate of Salmonella Typhimurium ST19 and the detection of genes encoding for the siderophore “yersiniabactin” in one isolate of Salmonella London ST155, and this isolate also harbors the gene encoding for the enterotoxin TieB (senB). In fact, it has been reported that the presence of cdtB in the Salmonella genome was linked to isolates implicated in human bloodstream and invasive infections (Miller et al., 2018; Xu X. et al., 2020). Additionally, yersiniabactin siderophore that was initially described in Yersinia spp. is required for iron uptake and growth of the bacteria in an iron-restricted environment (Perry and Fetherston, 2011; Khan et al., 2018). However, the enterotoxin TieB was initially described in enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC) (Nataro et al., 1995) and has been suggested to play a key role in bacteria virulence in humans (Meza-Segura et al., 2020). Indeed, the presence of these virulence genes in the genome of Salmonella isolated from the pig slaughtering process may lead to severe disease outcomes in humans.
In this study, nine different plasmid replicons were detected among the 78 Salmonella isolates. The most abundant plasmids were IncHI2A_1, IncX1_1, and IncHI2_1. IncHI2A_1 and IncHI2_1 were predominant in Salmonella Typhimurium ST34, while IncX1_1 was detected only in Salmonella London ST155. These plasmids were identified previously in Salmonella isolates recovered from the animal food chain, especially pork production chains (Liu et al., 2020, 2021; Viana et al., 2020). Interestingly, it has been demonstrated that these plasmids were associated with resistance to different antimicrobial classes, including β-lactams, aminoglycosides, sulfonamides, tetracyclines, and polymyxins (Elbediwi et al., 2020b,a; Gu et al., 2020; McMillan et al., 2020). Consequently, these plasmids may mediate the horizontal transmission of antimicrobial resistance genes during this slaughtering process.
In this study, we provided the dynamic prevalence of Salmonella during the pig slaughtering process. Additionally, we demonstrated the use of whole genome sequencing as a cost-effective approach for routine surveillance of foodborne pathogens, especially Salmonella. The prediction of serovar distribution, MLST patterns, antimicrobial resistance genes, plasmid replicons, and virulence factors in Salmonella isolates recovered from the pig slaughtering process showed the isolation of MDR isolates harboring different antimicrobial resistant determinants and virulence factors like cdtB gene encoding typhoid toxins, senB gene encoding for the enterotoxin production, and several genes encoding for the siderophore “yersiniabactin.” Therefore, it is time to prevent the use of antimicrobials in animal livestock in order to avoid the dissemination of antimicrobial resistance determinants along the food chain and to implement management systems to control critical points in order to avoid the transmission of foodborne pathogens to humans.
The datasets generated for this study can be found in the NCBI Bioproject with the accession number no. PRJNA686895.
BW, AE-D, and HP contributed equally to this work. AE-D and HP analyzed the data and finalized the figures. AE-D and MY were wrote the manuscript. BW, HP, CD, and CJ did the experiment and data collection. MY conceived the idea and assisted with data analysis and writing. All authors read, revised, and approved the final manuscript.
This study was supported by the National Program on Key Research Project of China (2019YFE0103900 and 2017YFC1600103) as well as the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme under Grant Agreement No. 861917 – SAFFI, Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LR19C180001), and Zhejiang Provincial Key R&D Program of China (2021C02008 and 2020C02032).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2021.704636/full#supplementary-material
Afgan, E., Baker, D., van den Beek, M., Blankenberg, D., Bouvier, D., Čech, M., et al. (2016). The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, W3–W10. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw343
Arguello, H., Álvarez-Ordoñez, A., Carvajal, A., Rubio, P., and Prieto, M. (2013). Role of slaughtering in Salmonella spreading and control in pork production. J. Food Prot. 76, 899–911. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-12-404
Arguello, H., Carvajal, A., Collazos, J. A., García-Feliz, C., and Rubio, P. (2012). Prevalence and serovars of Salmonella enterica on pig carcasses, slaughtered pigs and the environment of four Spanish slaughterhouses. Food Res. Int. 45, 905–912. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2011.04.017
Asai, T., Namimatsu, T., Osumi, T., Kojima, A., Harada, K., Aoki, H., et al. (2010). Molecular typing and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serovar Choleraesuis isolates from diseased pigs in Japan. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 33, 109–119. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2008.08.004
Bai, L., Lan, R., Zhang, X., Cui, S., Xu, J., Guo, Y., et al. (2015). Prevalence of Salmonella isolates from chicken and pig slaughterhouses and emergence of ciprofloxacin and cefotaxime co-resistant S. enterica serovar Indiana in Henan, China. PLoS One 10:144532. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144532
Bankevich, A., Nurk, S., Antipov, D., Gurevich, A. A., Dvorkin, M., Kulikov, A. S., et al. (2012). SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 19, 455–477. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Besser, J. M. (2018). Salmonella epidemiology: a whirlwind of change. Food Microbiol. 71, 55–59. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2017.08.018
Biasino, W., De Zutter, L., Mattheus, W., Bertrand, S., Uyttendaele, M., and Van Damme, I. (2018). Correlation between slaughter practices and the distribution of Salmonella and hygiene indicator bacteria on pig carcasses during slaughter. Food Microbiol. 70, 192–199. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2017.10.003
Biswas, S., Elbediwi, M., Gu, G., and Yue, M. (2020). Genomic characterization of new variant of hydrogen sulfide (H2S)-producing escherichia coli with multidrug resistance properties carrying the mcr-1 gene in China. Antibiotics 9:80. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9020080
Bonardi, S. (2017). Salmonella in the pork production chain and its impact on human health in the European Union. Epidemiol. Infect. 145, 1513–1526. doi: 10.1017/S095026881700036X
Boyen, F., Haesebrouck, F., Maes, D., Van Immerseel, F., Ducatelle, R., and Pasmans, F. (2008). Non-typhoidal Salmonella infections in pigs: a closer look at epidemiology, pathogenesis and control. Vet. Microbiol. 130, 1–19. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2007.12.017
Cai, Y., Tao, J., Jiao, Y., Fei, X., Zhou, L., Wang, Y., et al. (2016). Phenotypic characteristics and genotypic correlation between Salmonella isolates from a slaughterhouse and retail markets in Yangzhou, China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 222, 56–64. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2016.01.020
Carattoli, A., Zankari, E., Garciá-Fernández, A., Larsen, M. V., Lund, O., Villa, L., et al. (2014). In Silico detection and typing of plasmids using plasmidfinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58, 3895–3903. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02412-14
Carden, S., Okoro, C., Dougan, G., and Monack, D. (2015). Non-typhoidal Salmonella Typhimurium ST313 isolates that cause bacteremia in humans stimulate less inflammasome activation than ST19 isolates associated with gastroenteritis. Pathog. Dis. 73:ftu023. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftu023
CDC (2018). National Enteric Disease Surveillance: Salmonella Annual Report, 2016. Available online at: https://www.census.gov/geo/pdfs/maps-data/maps/ (Accessed April 24, 2021)
Chaudhary, J. H., Nayak, J. B., Brahmbhatt, M. N., and Makwana, P. P. (2015). Virulence genes detection of Salmonella serovars isolated from pork and slaughterhouse environment in Ahmedabad, Gujarat. Vet. World 8, 121–124. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2015.121-124
Chen, L., Yang, J., Yu, J., Yao, Z., Sun, L., Shen, Y., et al. (2005). VFDB: a reference database for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, D325–D328. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki008
CLSI (2017). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 27th Edn. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.
Colello, R., Ruiz, M. J., Padín, V. M., Rogé, A. D., Leotta, G., Padola, N. L., et al. (2018). Detection and characterization of Salmonella Serotypes in the production chain of two pig farms in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. Front. Microbiol. 9:1370. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01370
De Busser, E. V., Maes, D., Houf, K., Dewulf, J., Imberechts, H., Bertrand, S., et al. (2011). Detection and characterization of Salmonella in lairage, on pig carcasses and intestines in five slaughterhouses. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 145, 279–286. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.01.009
Deen, J., von Seidlein, L., Andersen, F., Elle, N., White, N. J., and Lubell, Y. (2012). Community-acquired bacterial bloodstream infections in developing countries in south and southeast Asia: a systematic review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 12, 480–487. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70028-2
Ed-Dra, A., Filali, F. R., Karraouan, B., El Allaoui, A., Aboulkacem, A., and Bouchrif, B. (2017). Prevalence, molecular and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella isolated from sausages in Meknes, Morocco. Microb. Pathog. 105, 340–345. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.02.042
Ed-Dra, A., Karraouan, B., El Allaoui, A., Khayatti, M., El Ossmani, H., Rhazi Filali, F., et al. (2018). Antimicrobial resistance and genetic diversity of Salmonella Infantis isolated from foods and human samples in Morocco. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 14, 297–301. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2018.05.019
EFSA, and ECDC (2018). The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2017. EFSA J. 16:e05500. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2018.5500
Elbediwi, M., Pan, H., Biswas, S., Li, Y., and Yue, M. (2020a). Emerging colistin resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar Newport isolates from human infections. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 9, 535–538. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1733439
Elbediwi, M., Pan, H., Jiang, Z., Biswas, S., Li, Y., and Yue, M. (2020b). Genomic characterization of mcr-1-carrying Salmonella enterica Serovar 4,[5],12:i:- ST 34 clone isolated from pigs in China. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8:663. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00663
Fois, F., Piras, F., Torpdahl, M., Mazza, R., Consolati, S. G., Spanu, C., et al. (2017). Occurrence, characterization, and antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella enterica in slaughtered pigs in Sardinia. J. Food Sci. 82, 969–976. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13657
Gu, D., Wang, Z., Tian, Y., Kang, X., Meng, C., Chen, X., et al. (2020). Prevalence of Salmonella isolates and their distribution based on whole-genome sequence in a chicken slaughterhouse in Jiangsu, China. Front. Vet. Sci. 7:29. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00029
Jiang, Z., Anwar, T. M., Peng, X., Biswas, S., Elbediwi, M., Li, Y., et al. (2021). Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella recovered from pig-borne food products in Henan, China. Food Control 121:107535. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107535
Jiang, Z., Paudyal, N., Xu, Y., Deng, T., Li, F., Pan, H., et al. (2019). Antibiotic resistance profiles of Salmonella recovered from finishing pigs and slaughter facilities in Henan, China. Front. Microbiol. 10:1513. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01513
Jun, W., ZengRen, Z., and JingYu, W. (2007). Risk assessment of Salmonella in animal derived food. Chin. J. Anim. Quar. 24, 23–25.
Kagambèga, A., Lienemann, T., Aulu, L., Traoré, A. S., Barro, N., Siitonen, A., et al. (2013). Prevalence and characterization of Salmonella enterica from the feces of cattle, poultry, swine and hedgehogs in Burkina Faso and their comparison to human Salmonella isolates. BMC Microbiol. 13:253. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-253
Khan, A., Singh, P., and Srivastava, A. (2018). Synthesis, nature and utility of universal iron chelator–Siderophore: a review. Microbiol. Res. 212–213, 103–111. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2017.10.012
Lekagul, A., Tangcharoensathien, V., and Yeung, S. (2019). Patterns of antibiotic use in global pig production: a systematic review. Vet. Anim. Sci. 7:100058. doi: 10.1016/j.vas.2019.100058
Lettini, A. A., Vo Than, T., Marafin, E., Longo, A., Antonello, K., Zavagnin, P., et al. (2016). Distribution of Salmonella serovars and antimicrobial susceptibility from poultry and swine farms in central Vietnam. Zoonoses Public Health 63, 569–576. doi: 10.1111/zph.12265
Li, Q., Yin, J., Li, Z., Li, Z., Du, Y., Guo, W., et al. (2019). Serotype distribution, antimicrobial susceptibility, antimicrobial resistance genes and virulence genes of Salmonella isolated from a pig slaughterhouse in Yangzhou, China. AMB Express 9:210. doi: 10.1186/s13568-019-0936-9
Li, R., Lai, J., Wang, Y., Liu, S., Li, Y., Liu, K., et al. (2013). Prevalence and characterization of Salmonella species isolated from pigs, ducks and chickens in Sichuan Province, China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 163, 14–18. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.01.020
Li, Y., Cai, Y., Tao, J., Kang, X., Jiao, Y., Guo, R., et al. (2016). Salmonella isolated from the slaughterhouses and correlation with pork contamination in free market. Food Control 59, 591–600. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.06.040
Liu, Q., Chen, W., Elbediwi, M., Pan, H., Wang, L., Zhou, C., et al. (2020). Characterization of Salmonella resistome and plasmidome in pork production system in Jiangsu, China. Front. Vet. Sci. 7:617. doi: 10.3389/FVETS.2020.00617
Liu, Y., Jiang, J., Ed-Dra, A., Li, X., Peng, X., Xia, L. (eds)., et al. (2021). Prevalence and genomic investigation of Salmonella isolates recovered from animal food-chain in Xinjiang, China. Food Res. Int. 142:110198. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110198
Luo, Q., Wan, F., Yu, X., Zheng, B., Chen, Y., Gong, C., et al. (2020). MDR Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ST34 carrying mcr-1 isolated from cases of bloodstream and intestinal infection in children in China. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 75, 92–95. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkz415
Mao, X., Hu, J., and Liu, X. (2011). Estimation on disease burden of foodborne non-typhoid salmonellosis in China using literature review method. Chin. J. Dis. Control Prev. 15, 622–625.
McMillan, E. A., Jackson, C. R., and Frye, J. G. (2020). Transferable plasmids of Salmonella enterica associated with antibiotic resistance genes. Front. Microbiol. 11:562181. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.562181
Meza-Segura, M., Zaidi, M. B., Vera-Ponce de León, A., Moran-Garcia, N., Martinez-Romero, E., Nataro, J. P., et al. (2020). New insights into DAEC and EAEC pathogenesis and phylogeny. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 10:572951. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.572951
Miller, R. A., Betteken, M. I., Guo, X., Altier, C., Duhamel, G. E., and Wiedmann, M. (2018). The typhoid toxin produced by the Nontyphoidal Salmonella enterica serotype javiana is required for induction of a DNA damage response in Vitro and systemic spread in Vivo. MBio 9:e00467-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00467-18
Monte, D. F. M., Sellera, F. P., Lopes, R., Keelara, S., Landgraf, M., Greene, S., et al. (2020). Class 1 integron-borne cassettes harboring blaCARB–2 gene in multidrug-resistant and virulent Salmonella Typhimurium ST19 strains recovered from clinical human stool samples, United States. PLoS One 15:e0240978. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240978
Morales-Partera, A. M., Cardoso-Toset, F., Luque, I., Astorga, R. J., Maldonado, A., Herrera-León, S., et al. (2018). Prevalence and diversity of Salmonella spp., Campylobacter spp., and Listeria monocytogenes in two free-range pig slaughterhouses. Food Control 92, 208–215. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.04.053
Nataro, J. P., Seriwatana, J., Fasano, A., Maneval, D. R., Guers, L. D., Noriega, F., et al. (1995). Identification and cloning of a novel plasmid-encoded enterotoxin of enteroinvasive Escherichia coli and Shigella strains. Infect. Immun. 63, 4721–4728. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.12.4721-4728.1995
Panzenhagen, P. H. N., Paul, N. C., Conte, C. A., Costa, R. G., Rodrigues, D. P., and Shah, D. H. (2018). Genetically distinct lineages of Salmonella Typhimurium ST313 and ST19 are present in Brazil. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 308, 306–316. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2018.01.005
Paudyal, N., Pan, H., Elbediwi, M., Zhou, X., Peng, X., Li, X., et al. (2019). Characterization of Salmonella Dublin isolated from bovine and human hosts. BMC Microbiol. 19:226. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1598-0
Perry, R. D., and Fetherston, J. D. (2011). Yersiniabactin iron uptake: mechanisms and role in Yersinia pestis pathogenesis. Microbes Infect. 13, 808–817. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2011.04.008
Rahkio, M., and Korkeala, H. (1996). Microbiological contamination of carcasses related to hygiene practice and facilities on slaughtering lines. Acta Vet. Scand. 37, 219–228. doi: 10.1186/BF03548089
Viana, C., Grossi, J. L., Sereno, M. J., Yamatogi, R. S., dos Santos Bersot, L., Call, D. R., et al. (2020). Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of non-typhoidal Salmonella isolated from a Brazilian pork production chain. Food Res. Int. 137:109406. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109406
Vico, J. P., Lorenzutti, A. M., Zogbi, A. P., Aleu, G., Sánchez, I. C., Caffer, M. I., et al. (2020). Prevalence, associated risk factors, and antimicrobial resistance profiles of non-typhoidal Salmonella in large scale swine production in Córdoba, Argentina. Res. Vet. Sci. 130, 161–169. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2020.03.003
Wang, X., Biswas, S., Paudyal, N., Pan, H., Li, X., Fang, W., et al. (2019). Antibiotic resistance in Salmonella Typhimurium isolates recovered from the food chain through national antimicrobial resistance monitoring system between 1996 and 2016. Front. Microbiol. 10:985. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00985
World Health Organisation (WHO) (2018). Salmonella (Non-Typhoidal). World Health Organisation. Available online at: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/salmonella-(non-typhoidal) (Accessed March 30, 2021)
Wilson, C. N., Pulford, C. V., Akoko, J., Sepulveda, B. P., Predeus, A. V., Bevington, J., et al. (2020). Salmonella identified in pigs in Kenya and Malawi reveals the potential for zoonotic transmission in emerging pork markets. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 14:e0008796. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008796
Wong, M. H. Y., Yan, M., Chan, E. W. C., Liu, L. Z., Kan, B., and Chen, S. (2013). Expansion of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ST34 clone carrying multiple resistance determinants in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 57, 4599–4601. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01174-13
Xu, X., Chen, Y., Pan, H., Pang, Z., Li, F., Peng, X., et al. (2020). Genomic characterization of Salmonella Uzaramo for human invasive infection. Microb. genom. 6:mgen000401. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000401
Xu, Y., Zhou, X., Jiang, Z., Qi, Y., Ed-Dra, A., and Yue, M. (eds) (2020). Epidemiological investigation and antimicrobial resistance profiles of Salmonella isolated from breeder chicken hatcheries in Henan, China. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 10:497. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00497
Yu, H., Elbediwi, M., Zhou, X., Shuai, H., Lou, X., Wang, H., et al. (2020). Epidemiological and genomic characterization of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from a foodborne outbreak at Hangzhou, China. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21:3001. doi: 10.3390/ijms21083001
Zankari, E., Hasman, H., Cosentino, S., Vestergaard, M., Rasmussen, S., Lund, O., et al. (2012). Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 67, 2640–2644. doi: 10.1093/jac/dks261
Zhou, Z., Jin, X., Zheng, H., Li, J., Meng, C., Yin, K., et al. (2018). The prevalence and load of Salmonella, and key risk points of Salmonella contamination in a swine slaughterhouse in Jiangsu province, China. Food Control 87, 153–160. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.12.026
Zhou, Z., Li, J., Zheng, H., Jin, X., Shen, Y., Lei, T., et al. (2017). Diversity of Salmonella isolates and their distribution in a pig slaughterhouse in Huai’an, China. Food Control 78, 238–246. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.02.064
Keywords: Salmonella, antimicrobial resistance, plasmid replicons, virulence factors, pig slaughterhouse, whole genome sequencing
Citation: Wu B, Ed-Dra A, Pan H, Dong C, Jia C and Yue M (2021) Genomic Investigation of Salmonella Isolates Recovered From a Pig Slaughtering Process in Hangzhou, China. Front. Microbiol. 12:704636. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.704636
Received: 03 May 2021; Accepted: 11 June 2021;
Published: 08 July 2021.
Edited by:
Bojana Bogovic Matijasic, University of Ljubljana, SloveniaReviewed by:
Baowei Yang, Northwest A&F University, ChinaCopyright © 2021 Wu, Ed-Dra, Pan, Dong, Jia and Yue. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Min Yue, bXl1ZUB6anUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.