
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Microbiol. , 02 August 2021
Sec. Systems Microbiology
Volume 12 - 2021 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.687259
This article is part of the Research Topic Computational Predictions, Dynamic Tracking, and Evolutionary Analysis of Antibiotic Resistance Through the Mining of Microbial Genomes and Metagenomic Data View all 12 articles
Helicobacter pylori exhibit specific geographic distributions that are related to clinical outcomes. Despite the high infection rate of H. pylori throughout the world, the genetic epidemiology surveillance of H. pylori still needs to be improved. This study used the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) profiling approach based on whole genome sequencing (WGS) to facilitate genomic population analyses of H. pylori and encourage the dissemination of microbial genotyping strategies worldwide. A total number of 1,211 public H. pylori genomes were downloaded and used to construct the typing tool, named HpTT (H. pylori Typing Tool). Combined with the metadata, we developed two levels of genomic typing, including a continent-scale and a country scale that nested in the continent scale. Results showed that Asia was the largest isolate source in our dataset, while isolates from Europe and Oceania were comparatively more widespread. More specifically, Switzerland and Australia are the main sources of widespread isolates in their corresponding continents. To integrate all the typing information and enable researchers to compare their dataset against the existing global database easily and rapidly, a user-friendly website (https://db.cngb.org/HPTT/) was developed with both genomic typing tools and visualization tools. To further confirm the validity of the website, ten newly assembled genomes were downloaded and tested precisely located on the branch as we expected. In summary, the H. pylori typing tool (HpTT) is a novel genomic epidemiological tool that can achieve high-resolution analysis of genomic typing and visualizing simultaneously, providing insights into the genetic population structure, evolution analysis, and epidemiological surveillance of H. pylori.
Helicobacter pylori are one of the most sophisticated colonizers in the world that infects more than half of the world’s population, ranging from infants to the elderly (Suerbaum and Michetti, 2002). It is a Gram-negative bacterium that normally colonizes the gastric mucosa of humans with about 10–20% infection result in diseases (Pohl et al., 2019; Attila et al., 2020). The typical diseases that have been reported include gastritis, peptic ulcer, mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma, and gastric cancer (Ernst and Gold, 2000). Globally speaking, the risks of disease and the incidence and mortality of gastric cancer were geographically different (Kodaman et al., 2014).
H. pylori display a distinguished mutation rate among bacterial pathogens due to the lack of genes that initiate classical methyl-directed mismatch repair (MMR) (Alm et al., 1999). The high mutation and recombination rate made H. pylori genomes have enormous plasticity, facilitating this pathogen and enabling it to perfectly adapt to its host (Kang and Blaser, 2006; Didelot et al., 2013). It has been reported that H. pylori in chronic infection could take place through vertical and familial transmission (Schwarz et al., 2008; Ailloud et al., 2019). In within-host evolution, the mutation rate could reach ∼30 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) per genome per year (Kennemann et al., 2011), compared to Escherichia coli at ∼1 SNP per genome per year (Reeves et al., 2011). Taking into account this occurrence and large recombination events, a simple and efficient way to define the geographical pattern and epidemiological surveillance of H. pylori is needed (Yamaoka, 2009; Jolley et al., 2018).
The transmission of H. pylori transmission is slow, taking place mostly within a household it does not tend to spread like a rapid epidemic (Didelot et al., 2013). Their phylogeny was based on MLST genes and later whole genomes revealed a population structure primarily reflecting early human migration events especially out of Africa 60,000 years ago but not recent spreading (Falush et al., 2003). The global population was split into hp groups, each of which is split into hsp subgroups in the agreed convention. The hpEastAsia includes hspEastAsia, hspMaori, and hspAmerind (Kawai et al., 2011; Montano et al., 2015; Thorell et al., 2017).
To describe the population structure of H. pylori, genetic typing methods such as single gene typing (e.g., cagA, vacA) were recorded in previous studies (Salama et al., 2007; Yamaoka, 2009), while seven-gene multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) became the dominant tool in the later stage due to its simple and rapid typing strategy, which covers genes including atpA, efp, mutY, ppa, trpC, urel, yphC that categorize H. pylori into different sequence types (STs) (Achtman et al., 1999). However, the resolution of seven-gene MLST was still low, which limited us to tracing the epidemiological origins of H. pylori strains (Banerji et al., 2020). Comparatively, SNP typing covers comprehensive core genes that can generate a matrix comprising concatenated SNPs and location information in the genome, which facilitated the newly sequenced genomes to be comparable by mapping and increase the typing resolution.
It has been found that 7-gene MLST are also linked to regional epidemics across the world. The 7-gene MLST typing method enables the regional specific recognition based on the defined STs, in which geographical pattern is linked with the different risks of clinical disease. For example, non-African and African lineage could be associated with different risks of gastric disease (Campbell et al., 2001). Thus, geographic patterns can somehow link to the possibility of clinical disease. However, the seven-gene genotypes of H. pylori are diverse due to the high variability of H. pylori genomes, which hinders the recognition of patterns directly from the sequence types (STs) in 7-gene MLST. In addition, there is no information on geographical patterns or visualization tools for seven-gene MLST, thus such related geographic patterns were hard to find when a new ST was found.
This study describes a H. pylori genomic typing tool, HpTT (H. pylori Typing Tool) that uses the SNP profiling based on whole-genome sequencing data. In addition to genomic typing, HpTT also provides a phylogenetic and geographic visualization tool based on the Nextstrain framework (Hadfield et al., 2018). This tool allows users to upload H. pylori WGS data for genomic typing and uncover possible transmission events of H. pylori. It is believed that this tool can not only improve genome typing resolutions but may also predict the possible origin of the epidemic H. pylori isolates, enabling the global surveillance of H. pylori.
A total number of 1,654 assembled H. pylori genomes were downloaded from the NCBI RefSeq database (genomes available as of May 4, 2020) using the ncbi-genome-download tool (version 0.2.12). The corresponding metadata of assembled genomes was searched by function using Entrez Direct (version 10.9) (Kans, 2020). By metadata filtering, 1,211 genomes were selected with sample collection location available (Table 1). All genomes were scanned by mlst (version 2.11) with the library of MLST updated on December 31, 2020 (Jolley and Maiden, 2010).
The 1,211 assembled genomes were mapped to the reference genome H. pylori 26695 (GenBank: AE000511.1) (Tomb et al., 1997) using MUMmer (version 3.23) (Kurtz et al., 2004). SNPs were filtered with a minimum mapping quality cutoff at 0.90 across 1,211 assembled H. pylori genomes. 6,129 SNPs were found, and an SNP profile of H. pylori is established for the corresponding isolates.
The maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree was constructed by iqtree (version 2.0.3) (Nguyen et al., 2015) based on 6,129 SNPs alignments of all 1,211 isolates. The reference genome H. pylori 26695 was used as an outgroup. The tree was generalized by the Gamma distribution to model site-specific rate variation (the GTR model). Bootstrap pseudo-analyses of the alignment were set at > = 1000. All ML trees were visualized and annotated using Figtree (version 1.4.4). The minimum spanning tree was constructed by the GrapeTree (v1.5.0) (Zhou et al., 2018). The mutation rate of the cagA gene was calculated by BEAST v1.8.4 (Suchard et al., 2018).
Based on the phylogenetic tree, two levels of the geographic group were defined, including the first level defined at the continent scale and the second level defined as a country-specific scale. In the first level of genotyping, lineages carrying more than seven isolates and >75% isolates sourced from one major continent were defined as a continent-specific group or clade. A mixed continent group was defined when there was no major continent identified with isolates at >75%. In the second level, lineages carrying more than one isolate and >75% isolates sourced from one major country were defined as a country-specific group or subclade. In addition, a mixed group was also defined at level two when there were more than two isolates and not a major country identified with isolates at >75%. The association of the genomic lineage of H. pylori with the geographic information of isolates provided a map that allows us to trace both the possible transmission and evolution of a detected or sequenced H. pylori genome.
The HpTT website was established based on two modules: (1) The genomic-geographical typing tool of H. pylori isolates and (2) a visualization tool of both the genomic and geographic typing results. The online typing tool was written in PHP, Javascript, css, and HTML. The online visualization service was performed based on the CodeIgniter framework1, tree visualization was analyzed by the augur2 bioinformatics tool and the auspice3 visualization tool imbedded in the Nextstrain (Hadfield et al., 2018) open source project. The H. pylori database was stored in a Mysql database.
A total of 1,211 assembled genomes with available geographic information from the NCBI RefSeq database were downloaded and analyzed for establishing the H. pylori genotyping database (Supplementary Table 1). All assembly genomes were mapped to the reference genome H. pylori 26695. Based on the maximum likelihood tree, 6,129 SNPs extracted from 1,135 genes on the reference genome were defined for further genomic typing. In terms of geographic information, 1,112 isolates were grouped at two levels, including 37 continent-level groups (Figures 1A,B) and/or 236 country-level groups (Figures 1C,D). The median pairwise distances (the median number of SNPs shared by the branches) between isolates were found as follows: 319 SNPs within continent clades and 1,493 SNPs within country subclades. We labeled these continent clades and country subclades using a structured hierarchical nomenclature system similar to that used for M. tuberculosis (Coll et al., 2014). For instance, region 1 clade (G1) is subdivided into country subclades G1.C1 and G1.C2. The mutation rate of cagA was 2.413 × 10–2 (95% CI: 1.600 × 10–2–3.900 × 10–2), which was 1.739 × 10–2/site/year (95% CI: 1.153 × 10–2–2.811 × 10–2).
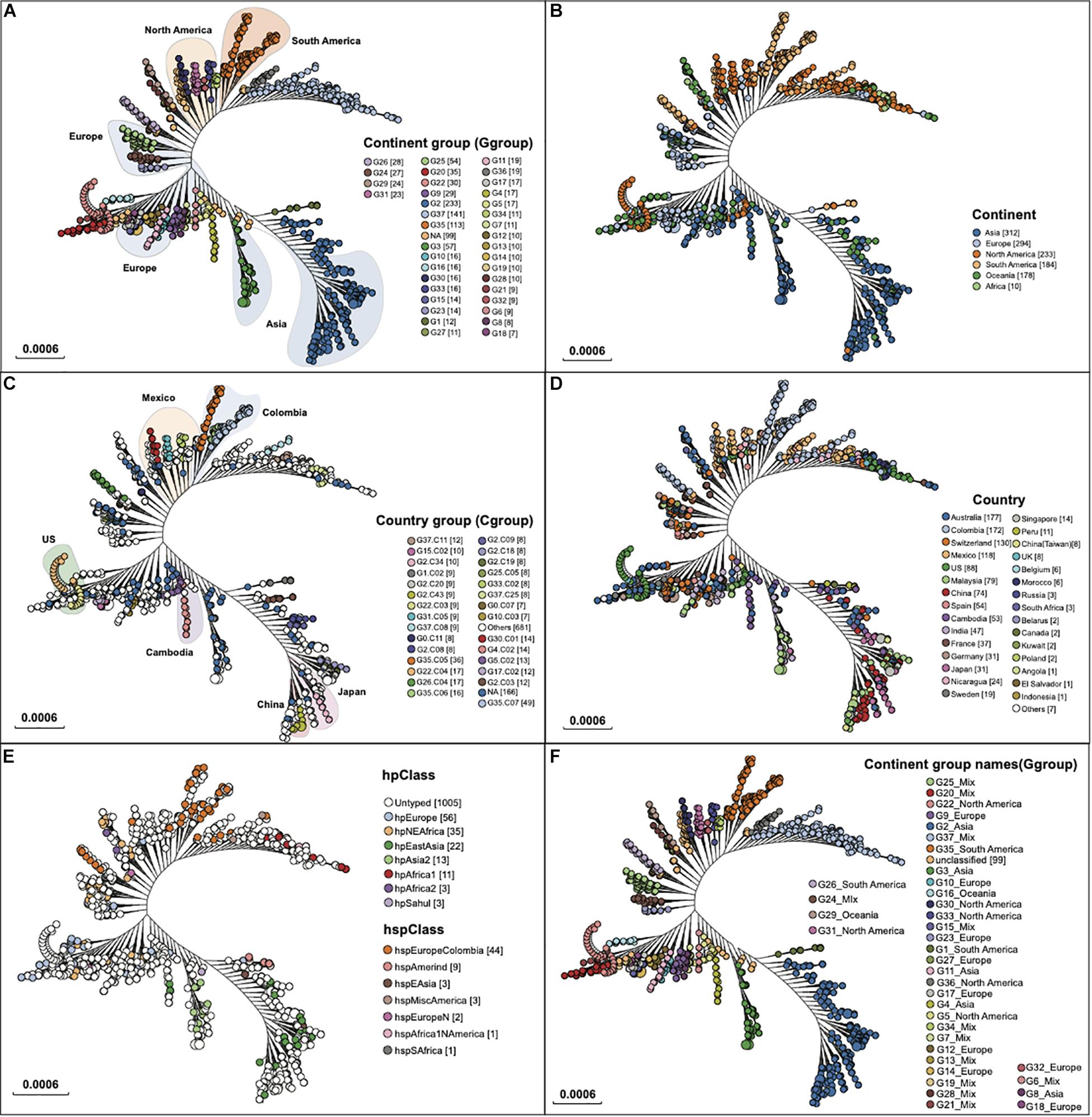
Figure 1. Two clades of geographic typing based on the WGS. The HpTT enrolled 1,211 H. pylori genomes downloaded from NCBI. The clade nodes in each figure correspond to (A) G groups for continent level of typing, (B) the continent that isolates collected from, (C) C groups for country-level typing, (D) the country that isolates were collected from. (E) the hp Class and hsp Class, (F) G groups for continent level of typing with group names. Numbers in parenthesis refer to the number of isolates in each genogroup.
A total number of 37 continent level groups (n = 1,112) were defined, including 25 continent-specific groups and 12 mixed-continent groups (Figures 1A,B). Isolates across the tree did not fall into the continent group but can be defined as a country group that was named G0 (n = 74). Isolates across the tree that fell into neither fall into the country group nor the continent group were defined as non-grouped (n = 25). Because the genome data of H. pylori were downloaded from the NCBI database, and these genomes came from various regions of the world. Compared with their ancestors, these strains have different genomes, which has led to the formation of independent evolutionary branches. After they formed independent evolutionary branches, (1) they may not have spread. (2) After the spread, it was not collected. These two reasons could account for an insufficient number of strains in the branch, which cannot form a group with regional characteristics under our typing method.
Five continent-specific groups contain more than 75% Asian isolates, supporting Asia to be the continent with the largest isolate source (n = 319, 26.34%) (Figure 2). North America was found to be the second-largest group of isolate pool which consisted of six continent-specific groups (n = 132, 10.90%). Although fewer isolates were found to be sourced from Europe (n = 109, 9.00%), these isolates were distributed in nine continent-specific groups. Two groups (G16 & G29) of isolates were found to be part of the Oceania specific group (n = 39, 3.22%) and three groups (G1 & G26 & G35) were found to be from the South America specific groups (n = 109, 9.00%). In addition, the 12 mixed groups of isolates contained 226 isolates (18.66%). Among all G level groups, G2 was the largest continent specific group (n = 223) that mainly contained isolates from Asia (193/223, 82.83%), while G35 was the second largest continent specific group (n = 109) that mainly contained isolates from South America (99/109, 87.61%). Apart from all the continent groups above, there was no Africa-specific group found, but only with isolates collected from Africa defined in G28 (n = 2), G37 (n = 7), and G29 (n = 1) (Figure 2).
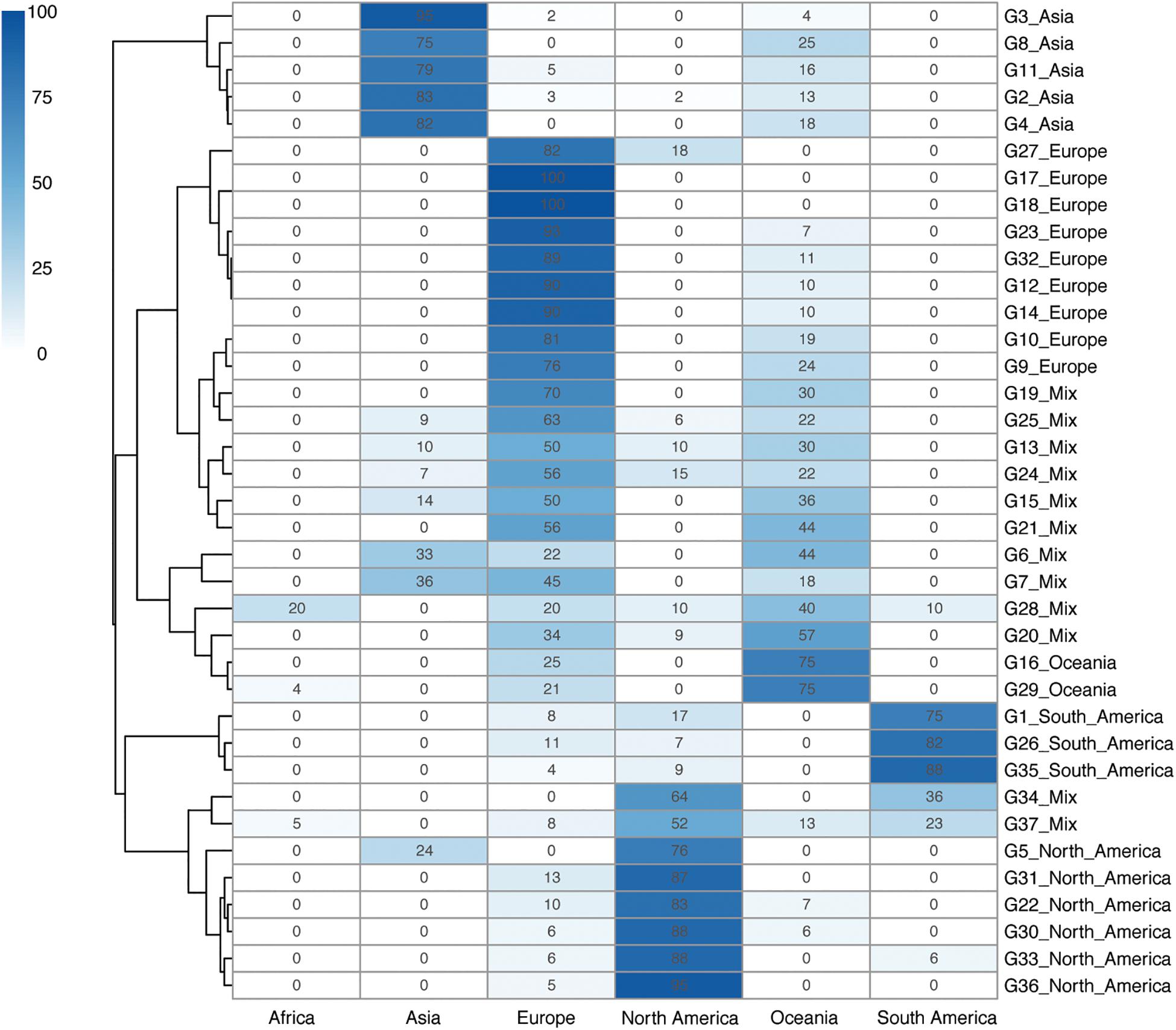
Figure 2. Geographical clustering of H. pylori continent clades. The number in each cube represents the percentage of unique isolates sourced from each of the continents. A total number of 37 continent-level groups were defined. The deeper the color, the higher the percentage of the isolates in that continent level of clade groups. A phylogenetic tree is also shown on the left side of the table. Background information on the isolates is provided in Supplementary Table 1.
Although the continent-specific groups did not 100% stick to one continent in our typing system, the transmission events were still possible to predict. While most of the Asian isolates fell into the Asia groups, a small proportion of the Asian isolates belonged to the mixed groups. Similarly, most of the isolates sourced from North America and South America fell in their own region groups, while a minority of the isolates were in the mixed groups. Interestingly, isolates from Oceania and Europe could be found across all 12 mixed continent groups, reflecting the fact that H. pylori isolates from these two continents were relatively widespread across the globe.
A total number of 859 isolates were grouped into 216 geographic patterns at a country level, which were predominant in 29 countries across six continents (Figure 3). Among these 29 countries encompassing 216 groups, 20 countries found in 168 groups were defined as country-specific groups, while the remaining 9 countries were scattered over the 48 country-level mixed groups that were left.
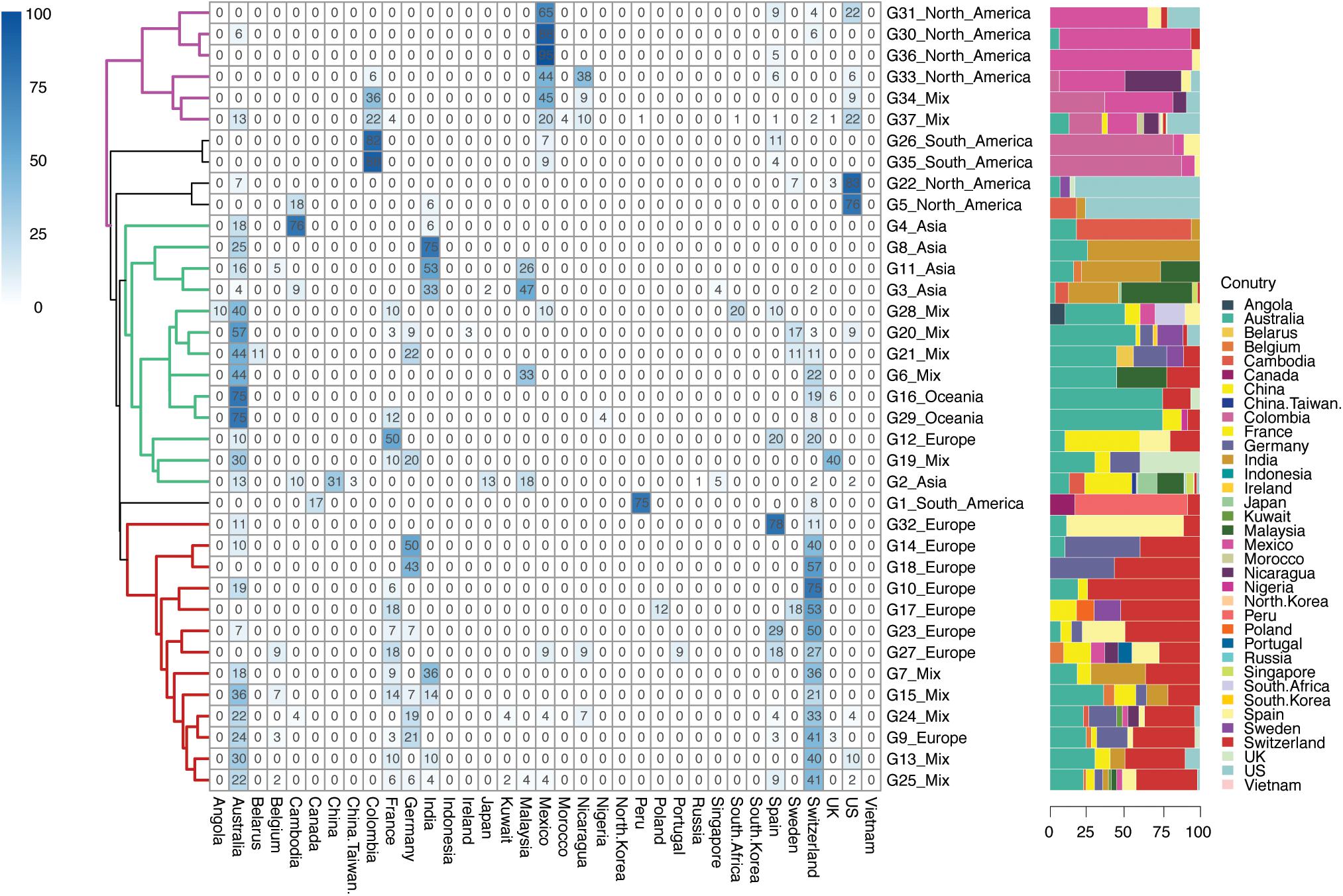
Figure 3. Geographical clustering of H. pylori country subclades. The number in each cube represents the percentage of unique isolates sourced from each of the countries in that continent group. A total number of 216 country-level groups were defined. The deeper the color, the higher the percentage of the isolates sourced from that country in continent-level groups. Background information on isolates is provided in Supplementary Table 1.
G35.C07 was the largest country-specific group that contained 49 isolates from Colombia, followed by the G35.C05 (n = 35) dominated in Colombia as well. These isolates from Colombia were mainly collected from the NCBI Bioproject PRJNA352848, which study contained the population structure of H. pylori in regional evolution in South America (Muñoz-Ramírez et al., 2017). The isolates from groups G35.C07 and G35.C05 were mainly found in Colombia, Mexico, and Spain (Figure 3). This result provided evidence that the H. pylori isolates were possibly transmitted from Spain and spread locally in South America and North America. In comparison, Australia and Switzerland were the largest countries of isolate sources with isolates scattered across more than half of the country-specific groups.
When comparing the percentage of isolates from different countries, those isolates from France, Germany, Malaysia, Nicaragua, Sweden, and the United Kingdom were found to be scattered in more than one continent group, while isolates from Cambodia, Colombia, India, Peru, Spain, and the United States were focused in one continent group when they were also found in other continent groups. More importantly, Australia and Switzerland were two countries that were mostly found to have scattered isolates in different regional specific groups.
Three clusters were observed in the percentage of different isolate sources at continent scale (G32 to G25 with red branches in Figure 3), consisting of groups from Europe and mixed continents. Specifically, those isolates from mixed groups were mainly sourced from European and Oceania countries, making this cluster dominated by Europe-Oceania. The second cluster was the mixed by Asian, Oceanian, European, and mixed groups (G4 to G2 with green branches in Figure 3) but dominated by isolates from Australia and Asian countries. Therefore, cluster two was specified as the Asian-Pacific cluster. The third cluster was formed by North American groups (G31 to G37 with purple branches in Figure 3), while South American branches were next to the North American cluster.
hp and hsp class were designed for the geographic-genetic typing of H. pylori (Kawai et al., 2011; Montano et al., 2015; Thorell et al., 2017; Lamichhane et al., 2020). Of 1,211 H. pylori genomes, 231 were found to have been typed by hp and hsp class, which were well fit to our typing groups. Specifically, hpEastAsia, hpAsia2, and hspEAsia were included in the three Asia continent groups G2, G3, and G4 (Figures 1E,F), while hspEuropeColombia fell in two south America groups, G26 and G35. Similarly, hpAfrica1, hspMiscAmerica, and hspAfrica1NAmerica were mapped to a mixed group G37. The comparison with hp and hsp clusters enhanced the validity of our typing method.
Seven-gene MLST was implied to get the sequence types (STs) for all 1,211 isolates. Unfortunately, due to the high mutation rate of the H. pylori strains, most of the seven-gene allele were only found to have high similarity instead of an accurate type, as a result, a large number of isolates (n = 876, 72.3%) were untyped in our dataset (Supplementary Table 1 and Figure 1). Among all the countries, Australia and Switzerland were the two countries with a higher number of untyped isolates, which is probably due to the isolates being collected by those two countries having not been submitted to the pubMLST website to be typed.
To support our H. pylori geographic typing tool, a user-friendly typing website was established and made available at https://db.cngb.org/HPTT/. Our HpTT approach is compatible with any whole-genome sequencing (WGS) data with metadata (Figure 4). For the sequencing data from pure-cultured isolates, the assembled genomes can be directly submitted to our website. However, it is worth noting that sequences or assembled genomes needed to be extracted from metagenome samples before submission (Parks et al., 2017; Olekhnovich et al., 2019). Except for the sequenced genome data, the available assembled contigs from NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) or assembly database (RefSeq), or other genome databases (e.g., European Nucleotide Achieve) can also be directly uploaded to our website. By using MUMmer alignment and blast process, the uploaded genome can be located to the closest matching genomes, further facilitating the possible transmission route analysis across the globe. In addition, our database can be also linked to the NCBI genome database, helping the user easily locate the metadata information from the available database (see Supplementary Material).
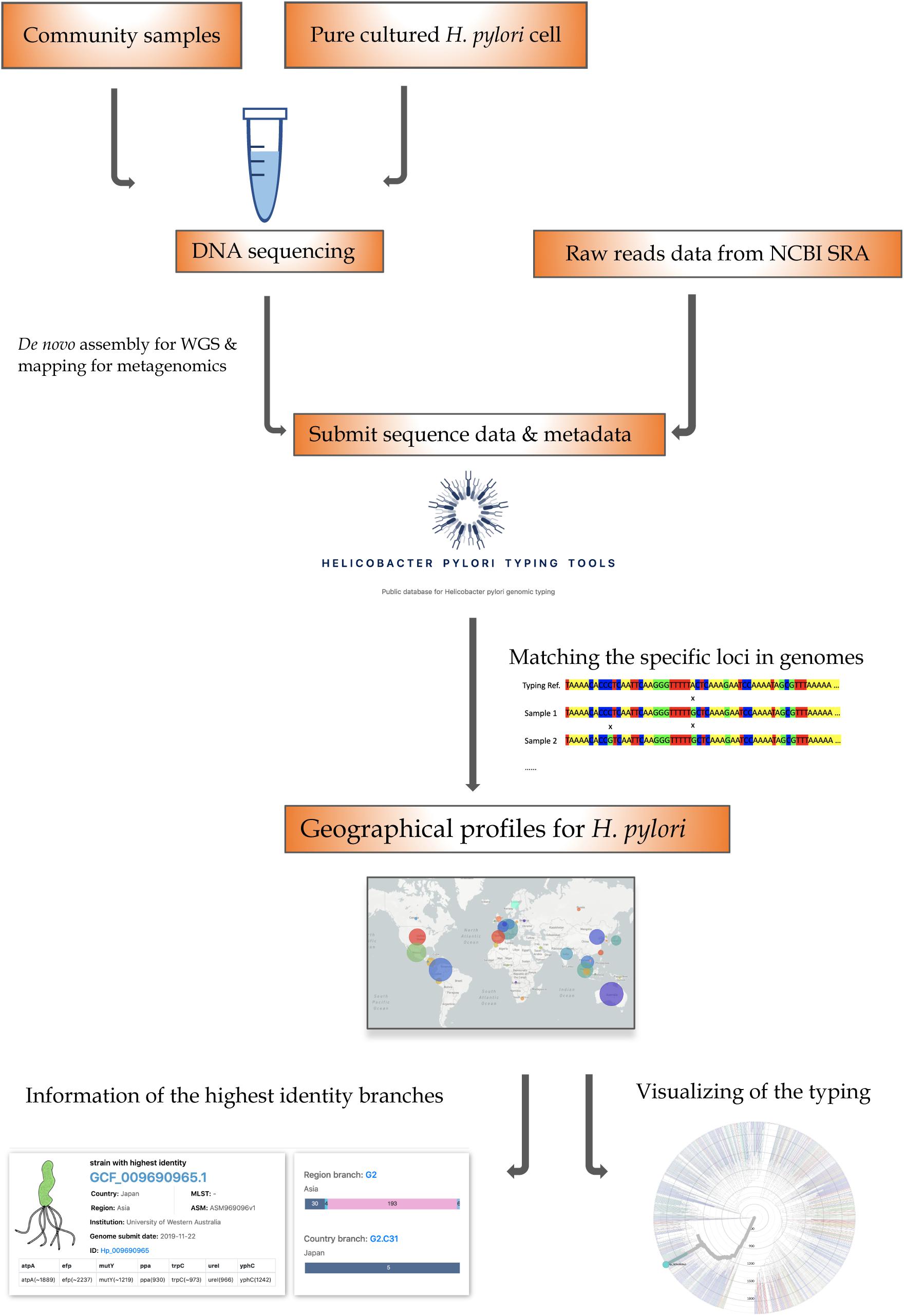
Figure 4. The HpTT workflow. The SNP-based genotyping approach can be used with the Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) data, which can be acquired in the following ways: DNA can be extracted from a pure cultured bacterial cell with WGS data or a community sample with metagenomic sequencing data. After being sequenced by an appropriate platform, the assembled genomes can be directly submitted to our database. In addition, the public assembled data can also be directly submitted to our database. The downstream analyses of the aligned sequence data can be linked to the phylogenetic and geographic page.
Except for the typing tool, the Nextstrain framework was also embedded in our website. By clicking the uploaded genome number, information can be linked to the phylogenetic tree with the corresponding continent and country. Possible evolution relationships and interactive located functions have made our typing tools easy to be applied and understood.
For validating the accuracy of the genomic typing method and the efficiency of the web tool, ten new genomes from NCBI were downloaded and tested (Supplementary Table 2). Except for one genome (GCF_002206465.1), which failed due to being sequenced by Pacbio, the remaining nine genomes were typed successfully [Our typing tool was established based on the MPS (Massive Parallel Sequencing) data, Pacbio sequencing may generate many SNPs in the gap region in MPS sequencing].
The epidemiological patterns of H. pylori isolates have been reported with specific geographic characteristics. In this study, the new typing webtool HpTT not only illustrated the population structure of H. pylori but also made genomic typing easy to approach. In the continent level of typing, 1,112 isolates were grouped into 37 continent-specific patterns. Except for 12 continent mixed groups, the rest could be defined as continent-specific groups across the five continents. Isolates from Europe and Oceania were universally found in most of the continent-level groups (Europe 33/37, 89.19% and Oceania 26/37, 70.27%), illustrating that isolates from these two continents were widely spread across the world.
In the country level of typing, 1,045 isolates were grouped into 216 country-level groups. Most of the isolates were defined as country-specific groups (168/216, 77.77%), while the rest of the isolates were grouped as country mixed groups (48/216, 22.22%). Australian and Swiss isolates were found to be widespread around the world, while isolates from Columbia were more regionally specific. It has been reported that H. pylori in South America were originally transmitted from Spain (Muñoz-Ramírez et al., 2017), this data perfectly aligned with our results in G35.C05 and G35.C07, giving support to the accuracy of our genomic typing method.
The phylogenetic tree in this study was built by the collection of H. pylori genomes downloaded from the NCBI Refseq database. Ideally, all the isolates would be able to be grouped into different geographic groups, but there are still a few isolates that cannot be grouped by our typing tool due to the following reasons: (1) They have not spread after forming independent evolutionary branches, (2) After spreading, their offspring have not been collected and sequenced.
H. pylori show high and fine (∼40 bp patch) intergenic recombination (Bubendorfer et al., 2016), which leads to sharing patches of genome sequences and makes the phylogenetic relationship obscure. Special methods have been developed to infer a population structure based on this sharing (Yahara et al., 2013). Although such typing methods are built based on core SNPs that cannot accurately trace the origin of the isolates comparing to a recent comprehensive study of H. pylori (Muñoz-Ramírez et al., 2021), we established a simple, rapid, and user-friendly genetic-geographic typing tool in the population structure description. The core SNPs of 1,211 H. pylori genomes were filtered with a minimum mapping quality cut off at 0.90, which means the individual indels for isolates were not kept. Our typing method has been further validated by testing genomes, suggesting that the typing tool was successfully established.
The addition of 7-gene MLST to our database intended to offer an easy way for users to visualize both results from our typing method and 7-gene MLST with comparisons. The large set of untyped isolates in 7-gene MLST might be related to the insufficient submission of genomes to pubMLST. In our typing database, isolates collected from Australia and Switzerland were scattered across different regional groups, which might be due to the frequent transmission event that occurred between Australia/Switzerland and other countries.
In this study, except for the novel typing tool, a user-friendly website was also established. By using this typing tool, users can achieve fast and precise genomic typing, easily locating the possible origins and transmission events across the world. When located in the actual geographic group, it is easy for users to check the details of the corresponding components of the branches in our database. The genome with the highest identity can be easily linked to the NCBI database as well as the visualization tool where the dynamic evolution of H. pylori was shown. At the same time, seven-gene MLST results were displayed for each genome in the database, as well as the hp groups and hsp subgroup results studied previously (Kawai et al., 2011; Yahara et al., 2013).
The most interesting part of the HpTT tool and methodology allows us to perform genome typing with assembled genomes from the metagenomics samples, as illustrated in Figure 4. Due to the rapid mutation of H. pylori, it is most likely that the sample from one’s gut is heterogeneous. Whole-genome sequencing by combining sequencing libraries labeled with different barcodes on a meta sample, and a cultured pure isolate could yield enough data from one single run to perform the epidemiological surveillance of H. pylori on a global level to find the possible transmission event in evolution profile. An open-source assay protocol will be developed and shared in the future to combine with this HpTT tool to enable the epidemiological surveillance of H. pylori.
Although our typing tool filled a gap in the genetic epidemiological surveillance of H. pylori, some functions still need to be improved. For example, cytotoxin-associated gene A (cagA) and vacA were two crucial genes that were reported to be correlated with geographic patterns of H. pylori (Yamaoka, 2009; Breurec et al., 2011). The cagA gene is one of the most important virulence genes in H. pylori, located at the end of a cag pathogenicity island (cag PAI) that encodes 120–145 kDa CagA protein (Šterbenc et al., 2019). Another virulence factor was vacuolating cytotoxin encoded by the gene vacA (Šterbenc et al., 2019). The variation of these two genes was widely reported by the H. pylori groups that can reflect the genomic difference for different geographic patterns. However, such a rapid typing method on a website for these two genes is still lacking, which could be considered in the further HpTT version 2.
H. pylori are normally treated by antibiotics without antimicrobial susceptibility testing (Pohl et al., 2019). Antibiotics-resistant H. pylori has been reported related to several mutations within the genes pbp1A, 23S rRNA, gyrA, rdxA, frxA, and rpoB (Domanovich-Asor et al., 2021). These antibiotics-resistant genes will be included in the second version despite there already being an antibiotics-specific resource available (Yusibova et al., 2020). As more strains or isolates are being deposited into our database along with geographic information, HpTT could be more powerfully associate genomic typing with geographic information and phenotypes.
In summary, this work illustrates efforts in a global epidemiological study of H. pylori isolates. Two functions were designed for the web typing tool, one for genomic typing and the other for phylogenetic and geographic visualization. The accuracy of our genomic typing system was proved by ten unused genomes as well as in another published study (Muñoz-Ramírez et al., 2017). Together with the visualization tool, the genomic population structure of H. pylori with geographic documents were described. Future studies will be expanded by the crucial virulence gene and antibiotic-related genes. This tool is beneficial for the surveillance of H. pylori for public health and the monitoring of its epidemic development.
All assembled H. pylori genomes used in this study were downloaded from NCBI assembly database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/assembly/) under the accession numbers in Supplementary Tables 1, 2.
ZX and HT conceived the study. XJ performed the analysis. TZ, YL and WL revised the manuscript. HT provided critical analysis and discussions. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the revision of the final manuscript.
This study was supported by the Science, Technology, and Innovation Commission of Shenzhen Municipality under a grant (No. JCYJ20170412153155228).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
We thank China National GeneBank at Shenzhen for supporting this study. We wish to thank Daoming Wang by the timely help of genome downloading and analysis.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2021.687259/full#supplementary-material
Achtman, M., Azuma, T., Berg, D. E., Ito, Y., Morelli, G., Pan, Z. J., et al. (1999). Recombination and clonal groupings within Helicobacter pylori from different geographical regions. Mole. Microb. 32, 459–470. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01382.x
Ailloud, F., Didelot, X., Woltemate, S., Pfaffinger, G., Overmann, J., Bader, R. C., et al. (2019). Within-host evolution of Helicobacter pylori shaped by niche-specific adaptation, intragastric migrations and selective sweeps. Nat. Comm. 10, 1–13.
Alm, R. A., Ling, L.-S. L., Moir, D. T., King, B. L., Brown, E. D., Doig, P. C., et al. (1999). Genomic-sequence comparison of two unrelated isolates of the human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 397, 176–180. doi: 10.1038/16495
Attila, T., Zeybel, M., Yigit, Y. E., Baran, B., Ahishali, E., Alper, E., et al. (2020). Upper socioeconomic status is associated with lower Helicobacter pylori infection rate among patients undergoing gastroscopy. J. Infect. Dev. Count. 14, 298–303. doi: 10.3855/jidc.11877
Banerji, S., Simon, S., Tille, A., Fruth, A., and Flieger, A. (2020). Genome-based Salmonella serotyping as the new gold standard. Sci. Rep. 10, 1–10.
Breurec, S., Guillard, B., Hem, S., Papadakos, K. S., Brisse, S., Huerre, M., et al. (2011). Expansion of European vacA and cagA alleles to East-Asian Helicobacter pylori strains in Cambodia. Infect. Genet. Evol. 11, 1899–1905. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2011.08.007
Bubendorfer, S., Krebes, J., Yang, I., Hage, E., Schulz, T. F., Bahlawane, C., et al. (2016). Genome-wide analysis of chromosomal import patterns after natural transformation of Helicobacter pylori. Nat. Comm. 7, 1–12.
Campbell, D. I., Warren, B. F., Thomas, J. E., Figura, N., Telford, J. L., and Sullivan, P. B. (2001). The African enigma: low prevalence of gastric atrophy, high prevalence of chronic inflammation in West African adults and children. Helicobacter 6, 263–267. doi: 10.1046/j.1083-4389.2001.00047.x
Coll, F., McNerney, R., Guerra-Assunção, J. A., Glynn, J. R., Perdigao, J., Viveiros, M., et al. (2014). A robust SNP barcode for typing Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains. Nat. Comm. 5, 1–5.
Didelot, X., Nell, S., Yang, I., Woltemate, S., Van der Merwe, S., and Suerbaum, S. (2013). Genomic evolution and transmission of Helicobacter pylori in two South African families. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 110, 13880–13885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1304681110
Domanovich-Asor, T., Craddock, H. A., Motro, Y., Khalfin, B., Peretz, A., and Moran-Gilad, J. (2021). Unraveling antimicrobial resistance in Helicobacter pylori: Global resistome meets global phylogeny. Helicobacter 2021:e12782.
Ernst, P. B., and Gold, B. D. (2000). The disease spectrum of Helicobacter pylori: the immunopathogenesis of gastroduodenal ulcer and gastric cancer. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 54, 615–640. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.54.1.615
Falush, D., Wirth, T., Linz, B., Pritchard, J. K., Stephens, M., Kidd, M., et al. (2003). Traces of human migrations in Helicobacter pylori populations. Science 299, 1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.1080857
Hadfield, J., Megill, C., Bell, S. M., Huddleston, J., Potter, B., Callender, C., et al. (2018). Nextstrain: real-time tracking of pathogen evolution. Bioinformatics 34, 4121–4123. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty407
Jolley, K. A., Bray, J. E., and Maiden, M. C. (2018). Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST. org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018:3.
Jolley, K. A., and Maiden, M. C. (2010). BIGSdb: scalable analysis of bacterial genome variation at the population level. BMC Bioinform. 11, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-595
Kang, J., and Blaser, M. J. (2006). Bacterial populations as perfect gases: genomic integrity and diversification tensions in Helicobacter pylori. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 4, 826–836. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1528
Kans, J. (2020). Entrez direct: E-utilities on the UNIX command line in Entrez Programming Utilities Help [Internet]. Bethesda: National Center for Biotechnology Information.
Kawai, M., Furuta, Y., Yahara, K., Tsuru, T., Oshima, K., Handa, N., et al. (2011). Evolution in an oncogenic bacterial species with extreme genome plasticity: Helicobacter pylori East Asian genomes. BMC Microbiol. 11, 1–28.
Kennemann, L., Didelot, X., Aebischer, T., Kuhn, S., Drescher, B., Droege, M., et al. (2011). Helicobacter pylori genome evolution during human infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 108, 5033–5038.
Kodaman, N., Pazos, A., Schneider, B. G., Piazuelo, M. B., Mera, R., Sobota, R. S., et al. (2014). Human and Helicobacter pylori coevolution shapes the risk of gastric disease. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 111, 1455–1460.
Kurtz, S., Phillippy, A., Delcher, A. L., Smoot, M., Shumway, M., Antonescu, C., et al. (2004). Versatile and open software for comparing large genomes. Genome Biol. 5:R12.
Lamichhane, B., Wise, M. J., Chua, E. G., Marshall, B. J., and Tay, C. Y. (2020). A novel taxon selection method, aimed at minimizing recombination, clarifies the discovery of a new sub-population of Helicobacter pylori from Australia. Evol. Appl. 13, 278–289. doi: 10.1111/eva.12864
Montano, V., Didelot, X., Foll, M., Linz, B., Reinhardt, R., Suerbaum, S., et al. (2015). Worldwide population structure, long-term demography, and local adaptation of Helicobacter pylori. Genetics 200, 947–963. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.176404
Muñoz-Ramírez, Z. Y., Mendez-Tenorio, A., Kato, I., Bravo, M. M., Rizzato, C., Thorell, K., et al. (2017). Whole genome sequence and phylogenetic analysis show Helicobacter pylori strains from Latin America have followed a unique evolution pathway. Front. Cell. Infect. Microb. 7:50. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00050
Muñoz-Ramírez, Z. Y., Pascoe, B., Mendez-Tenorio, A., Mourkas, E., Sandoval-Motta, S., Perez-Perez, G., et al. (2021). A 500-year tale of co-evolution, adaptation, and virulence: Helicobacter pylori in the Americas. ISME J. 15, 78–92. doi: 10.1038/s41396-020-00758-0
Nguyen, L.-T., Schmidt, H. A., Von Haeseler, A., and Minh, B. Q. (2015). IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mole. Biol. Evol. 32, 268–274. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu300
Olekhnovich, E. I., Manolov, A. I., Samoilov, A. E., Prianichnikov, N. A., Malakhova, M. V., Tyakht, A. V., et al. (2019). Shifts in the human gut microbiota structure caused by quadruple Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy. Front. Microb. 10:1902. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01902
Parks, D. H., Rinke, C., Chuvochina, M., Chaumeil, P.-A., Woodcroft, B. J., Evans, P. N., et al. (2017). Recovery of nearly 8,000 metagenome-assembled genomes substantially expands the tree of life. Nat. Microb. 2, 1533–1542. doi: 10.1038/s41564-017-0012-7
Pohl, D., Keller, P. M., Bordier, V., and Wagner, K. (2019). Review of current diagnostic methods and advances in Helicobacter pylori diagnostics in the era of next generation sequencing. World J. Gastroent. 25:4629. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i32.4629
Reeves, P. R., Liu, B., Zhou, Z., Li, D., Guo, D., Ren, Y., et al. (2011). Rates of mutation and host transmission for an Escherichia coli clone over 3 years. PLoS One 6:e26907. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026907
Salama, N. R., Gonzalez-Valencia, G., Deatherage, B., Aviles-Jimenez, F., Atherton, J. C., Graham, D. Y., et al. (2007). Genetic analysis of Helicobacter pylori strain populations colonizing the stomach at different times postinfection. J. Bacteriol. 189, 3834–3845. doi: 10.1128/jb.01696-06
Schwarz, S., Morelli, G., Kusecek, B., Manica, A., Balloux, F., Owen, R. J., et al. (2008). Horizontal versus familial transmission of Helicobacter pylori. PLoS Pathog. 4:e1000180. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000180
Šterbenc, A., Jarc, E., Poljak, M., and Homan, M. (2019). Helicobacter pylori virulence genes. World J Gastroenterol. 25:4870. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i33.4870
Suchard, M. A., Lemey, P., Baele, G., Ayres, D. L., Drummond, A. J., and Rambaut, A. (2018). Bayesian phylogenetic and phylodynamic data integration using BEAST 1.10. Virus Evol. 4:vey016.
Suerbaum, S., and Michetti, P. (2002). Helicobacter pylori infection. New Engl. J. Med. 347, 1175–1186.
Thorell, K., Yahara, K., Berthenet, E., Lawson, D. J., Mikhail, J., Kato, I., et al. (2017). Rapid evolution of distinct Helicobacter pylori subpopulations in the Americas. PLoS Genet. 13:e1006546. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006546
Tomb, J.-F., White, O., Kerlavage, A. R., Clayton, R. A., Sutton, G. G., Fleischmann, R. D., et al. (1997). The complete genome sequence of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 388, 539–547.
Yahara, K., Furuta, Y., Oshima, K., Yoshida, M., Azuma, T., Hattori, M., et al. (2013). Chromosome painting in silico in a bacterial species reveals fine population structure. Mole. Biol. Evol. 30, 1454–1464. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst055
Yamaoka, Y. (2009). Helicobacter pylori typing as a tool for tracking human migration. Clinical Microbiol. Infect. 15, 829–834. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02967.x
Yusibova, M., Hasman, H., Clausen, P. T. L. C., Imkamp, F., Wagner, K., and Andersen, L. P. (2020). CRHP Finder, a webtool for the detection of clarithromycin resistance in Helicobacter pylori from whole-genome sequencing data. Helicobacter 25:e12752.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori, genomic, antibiotic-resistant, phylogenetic, webtool, whole-genome sequencing, genotyping
Citation: Jiang X, Xu Z, Zhang T, Li Y, Li W and Tan H (2021) Whole-Genome-Based Helicobacter pylori Geographic Surveillance: A Visualized and Expandable Webtool. Front. Microbiol. 12:687259. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.687259
Received: 29 March 2021; Accepted: 07 June 2021;
Published: 02 August 2021.
Edited by:
Liang (Leon) Wang, Xuzhou Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Yuehua Gong, The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, ChinaCopyright © 2021 Jiang, Xu, Zhang, Li, Li and Tan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hongdong Tan, cnRhbkBtZ2ktdGVjaC5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.