- 1College of Food Science and Engineering, Hainan University, Haikou, China
- 2Engineering Research Center of Utilization of Tropical Polysaccharide Resources, Ministry of Education, Haikou, China
- 3Hainan Key Laboratory of Food Nutrition and Functional Food, Haikou, China
Glucose repression is a key regulatory system controlling the metabolism of non-glucose carbon source in yeast. Glucose represses the utilization of maltose, the most abundant fermentable sugar in lean dough and wort, thereby negatively affecting the fermentation efficiency and product quality of pasta products and beer. In this study, the focus was on the role of three kinases, Elm1, Tos3, and Sak1, in the maltose metabolism of baker’s yeast in lean dough. The results suggested that the three kinases played different roles in the regulation of the maltose metabolism of baker’s yeast with differential regulations on MAL genes. Elm1 was necessary for the maltose metabolism of baker’s yeast in maltose and maltose-glucose, and the overexpression of ELM1 could enhance the maltose metabolism and lean dough fermentation ability by upregulating the transcription of MALx1 (x is the locus) in maltose and maltose-glucose and MALx2 in maltose. The native level of TOS3 and SAK1 was essential for yeast cells to adapt glucose repression, but the overexpression of TOS3 and SAK1 alone repressed the expression of MALx1 in maltose-glucose and MALx2 in maltose. Moreover, the three kinases might regulate the maltose metabolism via the Snf1-parallel pathways with a carbon source-dependent manner. These results, for the first time, suggested that Elm1, rather than Tos3 and Sak1, might be the dominant regulator in the maltose metabolism of baker’s yeast. These findings provided knowledge about the glucose repression of maltose and gave a new perspective for breeding industrial yeasts with rapid maltose metabolism.
Introduction
Glucose repression is a key regulatory system controlling the synthesis of a series of enzymes involved in the carbohydrate metabolism in yeast (Trumbly, 1992; Klein et al., 1998; Carlson, 1999; Kim et al., 2019). In the presence of glucose, the expression of genes involved in the metabolism of alternate fermentable carbon sources (such as maltose, galactose, and sucrose), non-fermentable ones (such as glycerol, ethanol, and acetate), and respiratory metabolism is repressed (Srđan et al., 2004; Martinez-Ortiz et al., 2019; Lin, 2021). This disadvantage could be substantial in biotechnological production processes, in which glucose is sometimes not the primary carbon source or respiratory metabolism is demanded (Verstrepen et al., 2004). For example, maltose is the most abundant fermentable sugar in lean dough (Hazell and Attfield, 1999; Bell et al., 2001; Jiang et al., 2008). The ability to utilize the maltose in baker’s yeast determines the fermentation efficiency and quality of pasta products (Bell et al., 2001; Jiang et al., 2008). However, glucose represses the expression of genes encoding for maltose permease and maltase, and inhibits the activity of these enzymes in baker’s yeast, thereby, negatively affecting the maltose metabolism and lean dough fermentation of baker’s yeast (Srđan et al., 2004; Hatanaka et al., 2009; Sun et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2015b,c). Thus, alleviating glucose repression is essential to improve the utilization efficiency of non-glucose carbon sources.
The Snf1 protein kinase is a member of the remarkably conserved AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) family in eukaryotes (Meng et al., 2021). The Snf1 kinase is crucial to the glucose derepression of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, ensuring the availability of non-preferred carbon sources (Coccetti et al., 2018; Persson et al., 2020). Snf1 regulates the expression of glucose-repressed genes by regulating the phosphorylation status and nuclear localization of the repressor Mig1 (Östling and Ronne, 1998). In glucose limitation, Snf1 is activated, and phosphorylates repressor Mig1, thereby preventing the interaction of Mig1 with the corepressors Ssn6-Tup1 and promoting the transcription of downstream glucose-repressed genes (Östling and Ronne, 1998; Papamichos-Chronakis et al., 2004). Unphosphorylated Mig1 is retained in the nucleus, and interacts with Ssn6-Tup1 when Snf1 is inactive in high glucose (Östling and Ronne, 1998; Papamichos-Chronakis et al., 2004).
The Snf1 protein kinase is a complex that consists of an alpha catalytic subunit Snf1, a gamma regulatory subunit Snf4, and one of the three alternative beta regulatory subunits, namely, Sip1, Sip2, and Gal83 (Daniel and Carling, 2002; García-Salcedo et al., 2014; Meng et al., 2020). Snf1 activation requires at least two steps: First, Snf4 binds to the C-terminal regulatory domain of the catalytic subunit Snf1 to counteract the autoinhibition of Snf1, in which β regulatory subunits participate in the linkage of Snf1 and Snf4, and direct the subcellular localization of Snf1 (McCartney and Schmidt, 2001). Second, the phosphorylation of the Thr210 site of the catalytic subunit Snf1 is initiated by three upstream protein kinases, namely, Elm1, Tos3, and Sak1 (Hong et al., 2003; García-Salcedo et al., 2014). The three kinases exhibit a stress-dependent demand for the activation of different isoforms of Snf1, and contribute differently to cellular regulation in various carbon sources (McCartney et al., 2005). Although Sak1 appears to be the major one in the Snf1-dependent regulation of the metabolism of non-preferred carbon sources such as raffinose, ethanol, and glycerol, any of the three kinases is sufficient to activate Snf1 (Hedbacker et al., 2004; Liu et al., 2011). The sak1Δ mutants of Candida albicans fail to grow on many alternative carbon sources (Ramírez-Zavala et al., 2017). Tos3 is more important in the activation of Snf1 in non-fermentable carbon sources than in an abrupt glucose stress (Kim et al., 2005). The single mutation of ELM1 does not display an Snf1 phenotype in raffinose, but SAK1, TOS3, and ELM1 triple deletions do (Sutherland et al., 2003). However, the role of the three upstream kinases in maltose metabolism is unclear.
In the current study, the genes ELM1, TOS3, and SAK1 were overexpressed and deleted in baker’s yeast ABY3α alone to explore the role of the kinases Elm1, Tos3, and Sak1 in the maltose metabolism of baker’s yeast. The growth characteristic, maltose utilization, lean dough leavening ability, and mRNA level of genes related to the maltose metabolism of the strains were analyzed.
Materials and Methods
Strains and Plasmids
The strains and plasmids used in the current work were listed in Table 1.
Media and Culture Conditions
The E. coli strains were cultured in the Luria-Bertani medium (10 g/L of tryptone, 10 g/L of NaCl, and 5 g/L of yeast extract) at 37°C, and 100 mg/L of ampicillin was used for selecting the positive E. coli transformants. The yeast strains were cultured in the yeast extract peptone dextrose (YEPD) medium that contains 20 g/L of glucose, 20 g/L of peptone, and 10 g/L of yeast extract. Maltose fermentation was conducted in the low sugar model liquid dough (LSMLD) medium, in which 33.25 g/L of maltose mixed with 5 g/L of glucose or 38 g/L of maltose was used as the carbon source, according to the previous study (Lin et al., 2018).
The yeast strains, which were preserved on slopes at the exponential phase, were inoculated into the YEPD medium by an inoculating loop to the stationary stage at 30°C. Then, 10% of the cultures were inoculated to the YEPD medium at 30°C with 180 rpm rotary shaking for 24 h. The second-cultures were centrifugated at 4°C with 1,500 × g for 5 min. The cells were collected after washing with distilled water twice.
Construction of Plasmids and Transformants
Yeast genomic DNA was obtained using the yeast DNA kit (D1900, Solarbio, Beijing, China). Plasmids were obtained using the Plasmid Mini Kit II (DC201-01, Vazyme, Jiangsu, China). The gene fragments were cloned to the plasmids using the ClonExpressIIOne Step Cloning Kit (C112, Vazyme, Jiangsu, China). Primers used in this work were listed in Table 2.
To construct the episomal plasmid Yep-PEK, firstly, the gene ELM1 was amplified using the primers ELM1-F/ELM1-R with the genome of ABY3α as a template. Secondly, the fragment of ELM1 was inserted into the XhoI site of the promoter and terminator of PGK1 in the plasmid Yep-P, yielding the plasmid Yep-PE. Finally, the selectable marker fragment KanMX, which was amplified using the primers Kan-F/Kan-R with the vector pUG6 as a template, was inserted into the SphI site of the plasmid Yep-PE. The episomal plasmids Yep-PTK and Yep-PSK were constructed using the abovementioned strategy with the primers TOS3-F/TOS3-R and SAK1-F/SAK1-R, respectively.
To obtain the ELM1-deleted mutant, the method ‘DNA assembler’ was used to rapidly assemble the fragments on the chromosome (Shao et al., 2008; Li et al., 2018). The upstream and downstream sequences of ELM1 were amplified using the primers ELM1-BA-F/ELM1-BA-R, and ELM1-BB-F/ELM1-BB-R, respectively, with the genome of ABY3α as a template. The selectable marker gene KanMX was amplified using the primers ELM1-Kan-F/ELM1-Kan-R with the vector pUG6 as a template. The three fragments were transformed into the strain ABY3α, and KanMX was integrated to the ELM1 site of ABY3α by homologous recombination. The TOS3-deleted and SAK1-deleted mutants were constructed using the same strategy with the primers TOS3-BA-F/TOS3-BA-R, TOS3-BB-F/TOS3-BB-R, and TOS3-Kan-F/TOS3-Kan-R and SAK1-BA-F/SAK1-BA-R, SAK1-BB-F/SAK1-BB-R, and SAK1-Kan-F/SAK1-Kan-R, respectively.
To obtain the SNF1-deleted mutant, firstly, the selectable marker gene KanMX was amplified using the primers SNF1-Kan-F/SNF1-Kan-R with the vector pUG6 as a template. Secondly, the fragment SNF1F-Kan-SNF1R was integrated to the SNF1 fragment site of ABY3α. Finally, the gene KanMX was knocked out by the Cre/Lox system. The REG1-deleted mutant was constructed using the same strategy with the primers REG1-Kan-F/REG1-Kan-R.
Yeast transformations were obtained using the lithium acetate/PEG method (Gietz, 2015). A total of 800 mg/L of G418 (Promega, Madison, WI, United States) was used to select the positive S. cerevisiae transformants. The YEPG medium (20 g/L of galactose, 20 g/L of peptone, and 10 g/L of yeast extract) was used for the Cre expression in the yeast transformants. A total of 500 mg/L of Zeocin (R25001, Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States) was used to select the yeast strains carrying the plasmid pSH-Zeocin. The plasmids Yep-PK, Yep-PEK, Yep-PTK, and Yep-PSK were transformed into the parental strain to obtain the transformants A+YP, A+E, A+T, and A+S, respectively. The plasmid Yep-PEK was transformed into the SNF1-deleted mutant to get the transformant A+E-SNF1. The plasmids Yep-PEK, Yep-PTK, and Yep-PSK were transformed into the REG1-deleted mutant to get the transformants A+E-REG1, A+T-REG1, and A+S-REG1, respectively. The primers used in the verification of the strains were listed in Table 2. The fragment containing PGK1 and the overexpressed gene was verified by PCR to confirm the transformation of an episomal plasmid. The fixed-point verification method, which used the primers that were intercepted from the outside of the upstream/downstream homologous of the target gene and from the inside of the KanMX gene, was used to verify the gene-deleted mutants. The amplification of Zeocin was used to verify the transformation of the plasmid pSH-Zeocin.
Measurement of Growth Curve
Yeast cells were inoculated in the 2% glucose and 2% maltose conditions at 30°C. Then, the 3% (vol/vol) inoculations (equivalent to 3 × 108 cells) were transferred to the same condition, and the cell density OD600 was monitored at 30°C using a UV spectrophotometer (T6, Persee, Beijing, China). The specific growth rate was calculated by the change in the OD600 Napierian logarithm versus time during exponential growth. A total of 10 mL of the cell culture was filtered in the stationary phase, washed twice with 10 mL of distilled water, and then dried at 105°C for 24 h to measure the cell dry weight. The biomass yield was expressed as the gram (dry weight) of yeast cells per liter of medium. Experiments were conducted thrice.
Measurement of Extracellular Sugar
A total of 2 g of fresh yeast was cultured in the LSMLD media at 30°C. The cultures were sampled at different fermentation time points. The measurement of extracellular sugars and the calculation of maltose utilization efficiency and time span value were conducted using the previous method (Lin et al., 2018). The samples were filtered through 0.45 μm pore size cellulose acetate filters (Millipore Corp, Danvers, MA, United States) and analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography with a refractive index detector and a SilGreen R GH0830078H column (300∗7.8 mm∗8 um, SilGreen, Beijing, China) at 65°C. 5 mM H2SO4 was used as the mobile phase at a flow rate of 0.6 mL/min.
The maltose utilization efficiency in the maltose LSMLD medium was determined by the ratio of the consumed maltose in the whole process to the total maltose. The maltose utilization efficiency in the maltose-glucose LSMLD medium was determined by the ratio of the consumed maltose when glucose was exhausted to the total maltose. The time span refers to the difference between the time points at which half of the maltose and half of the glucose was consumed in the maltose-glucose LSMLD medium. Three independent experiments were performed.
Test of CO2 Production
The leavening ability of yeast cells in lean dough was tested according to the previous study (Zhang et al., 2015b), based on the Chinese National Standards for yeast used in food processing with the following modification. First, 140 g of standard flour, 72.5 mL of water, 4.5 g of fresh yeast, and 2 g of salt were evenly and quickly mixed at 30 ± 0.2°C of the dough center temperature in 5 min. Then, 50 g of mixed lean dough was transferred to a 250 mL graduated cylinder and fermented at 30°C. CO2 amounts were measured by the change of dough height in 120 min. Three independent experiments were carried out.
Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
Two grams (2 g) of fresh yeast was cultured in the LSMLD media, and 1 mL cultures (equivalent to 5 × 106 cells) were sampled at 30 min. The expression levels of the genes MAL61/MAL31 encoding maltose permease and MAL62/MAL32 encoding maltase were tested according to the previous study (Lin et al., 2018). The total cellular RNA was extracted using an RNA-eazy isolation reagent (R701, Vazyme, Jiangsu, China). Using mRNA as a template, cDNA was synthesized using a HIScript III RT SuperMix for qPCR (+gDNA wiper) (R323-01, Vazyme, Jiangsu, China). Changes in the expression levels of MAL genes were assessed through qRT-PCR with a ChamQ Universal SYBR qPCR Master Mix (Q711-02, Vazyme, Jiangsu, China). Actin was used as the loading control. The primers used for amplifying the target genes and the reference gene ACT1 were shown in Table 2. The expression level of the target genes in the parental strain ABY3α was normalized to the reference gene. Experiments were conducted thrice.
Statistical Analysis
Student’s t-test was performed to analyze the differences of the transformants and the parental strain. Differences at P < 0.05 were considered as statistically significant differences.
Results
Growth Property
Under the control of the constitutive yeast phosphoglycerate kinase gene (PGK1) promoter (PGK1P) and terminator (PGK1T), the mRNA expression level of ELM1, TOS3, and SAK1 were upregulated by 68-, 77-, and 64-fold in the transformants A+E, A+T, and A+S, respectively, compared with the parental strain (Figure 1). To test the influence of ELM1/TOS3/SAK1 overexpression on the growth characteristic of baker’s yeast, the growth curves of the strains were monitored in 2% glucose and maltose (Figure 2). Moreover, the specific growth rate and biomass yield of the strains were calculated (Table 3). Transformant A+YP, a blank control to reflect any possible influence of an empty vector, displayed growth similar to that of the parental strain. ELM1-overexpressed transformant A+E, TOS3-overexpressed transformant A+T, and SAK1-overexpressed transformant A+S improved cell proliferation to varying degrees in glucose. In maltose, compared with parental strain ABY3α, the specific growth rate of the transformant A+E decreased from 0.460 to 0.423 h–1 in maltose, but the final biomass yield showed a slight change. Only the transformant A+S exhibited an enhanced specific growth rate and biomass yield in maltose. Compared with the parental strain, although obvious changes of the specific growth rate were observed in the gene-deleted mutants (Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Figure 1), the deletion of any of the three genes did not influence the final biomass yield in glucose; the deletions of ELM1 and SAK1 inhibited the biomass yield in maltose instead.
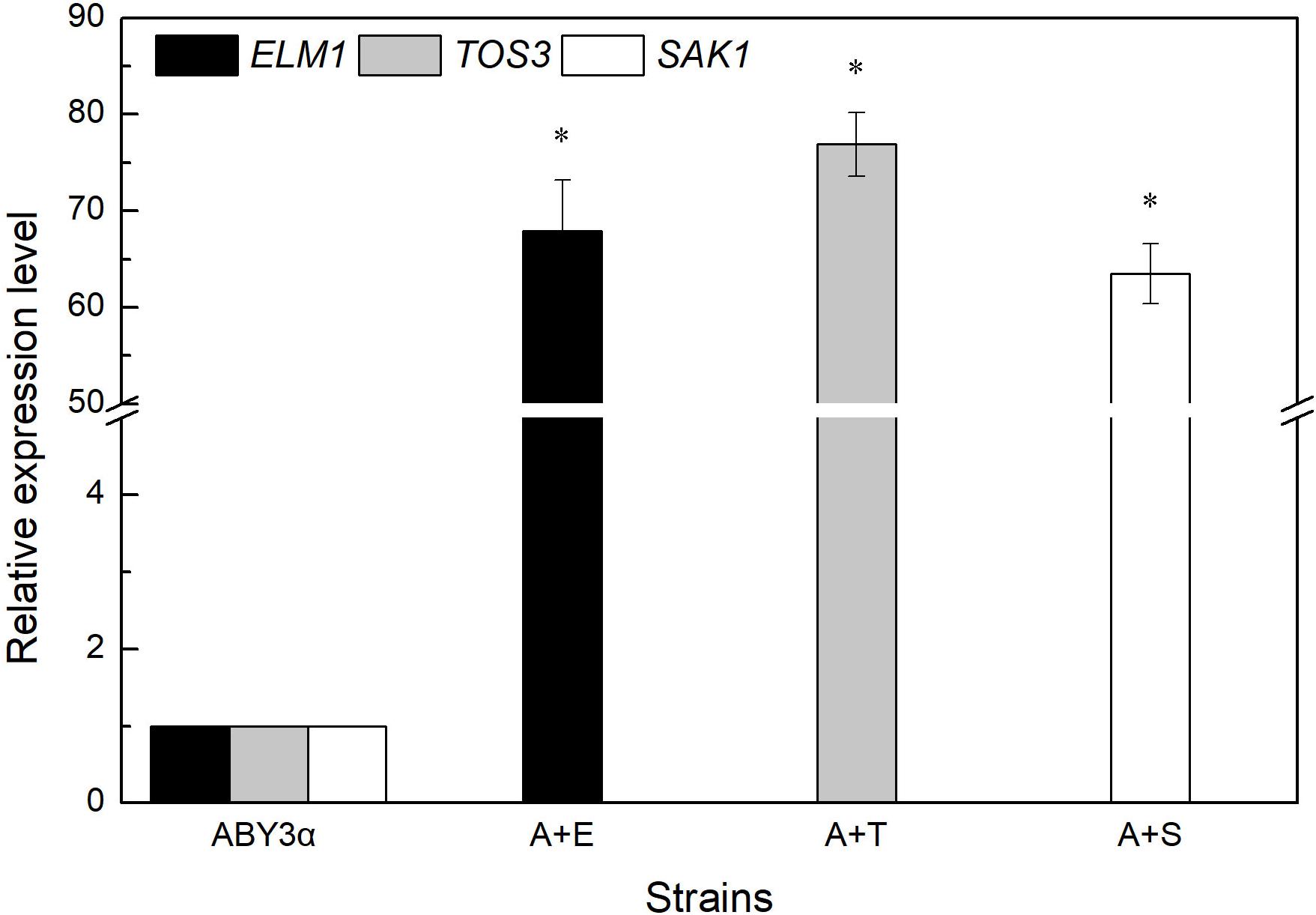
Figure 1. mRNA level of the overexpressed genes. The expression level of ELM1 in the strain A+E, TOS3 in the strain A+T, and SAK1 in the strain A+S was tested using qRT-PCR. The cells were sampled from YEPD medium at 16 h. ABY3α: the parental strain; A+E: the transformant carrying ELM1 overexpression; A+T: the transformant carrying TOS3 overexpression; A+S: the transformant carrying SAK1 overexpression. Significant differences of the transformants to the parental strain were confirmed at *p < 0.05.
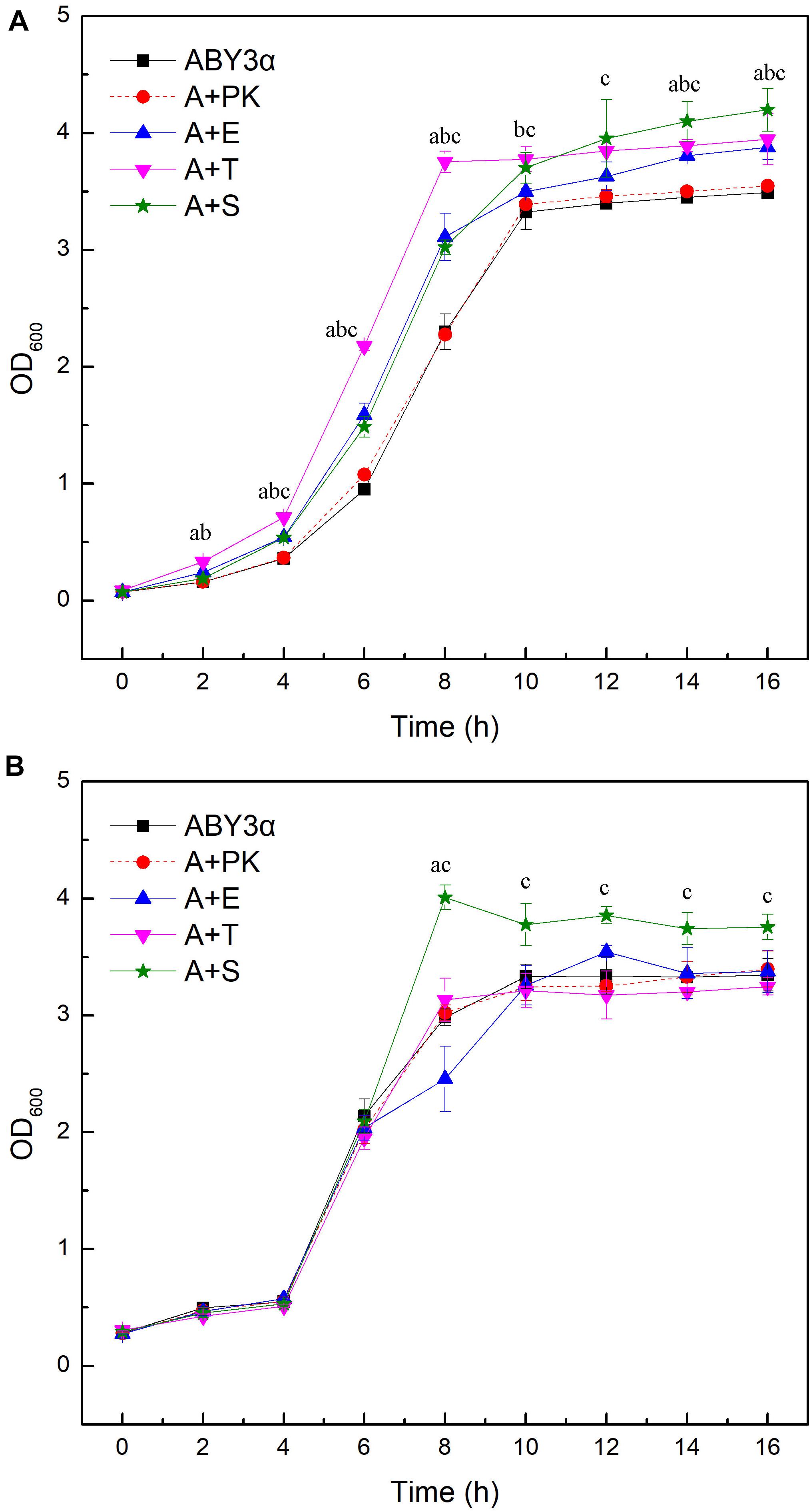
Figure 2. Growth curves of the strains carrying genes overexpression. Growth curves were monitored in (A) 2% glucose (YEPD medium) and (B) 2% maltose (YEPM medium consisted of 20 g/L maltose, 20 g/L peptone, and 10 g/L yeast extract) conditions at appropriate time intervals at 30°C. ABY3α, the parental strain; A+PK, the strain carrying the vector Yep-PK used as a blank control to demonstrate any possible effect of the empty vector; A+E, the transformant carrying ELM1 overexpression; A+T, the transformant carrying TOS3 overexpression; A+S, the transformant carrying SAK1 overexpression. Significant differences of the transformants A+E, A+T, and A+S to the parental strain were confirmed at ap < 0.05, bp < 0.05, and cp < 0.05, respectively.
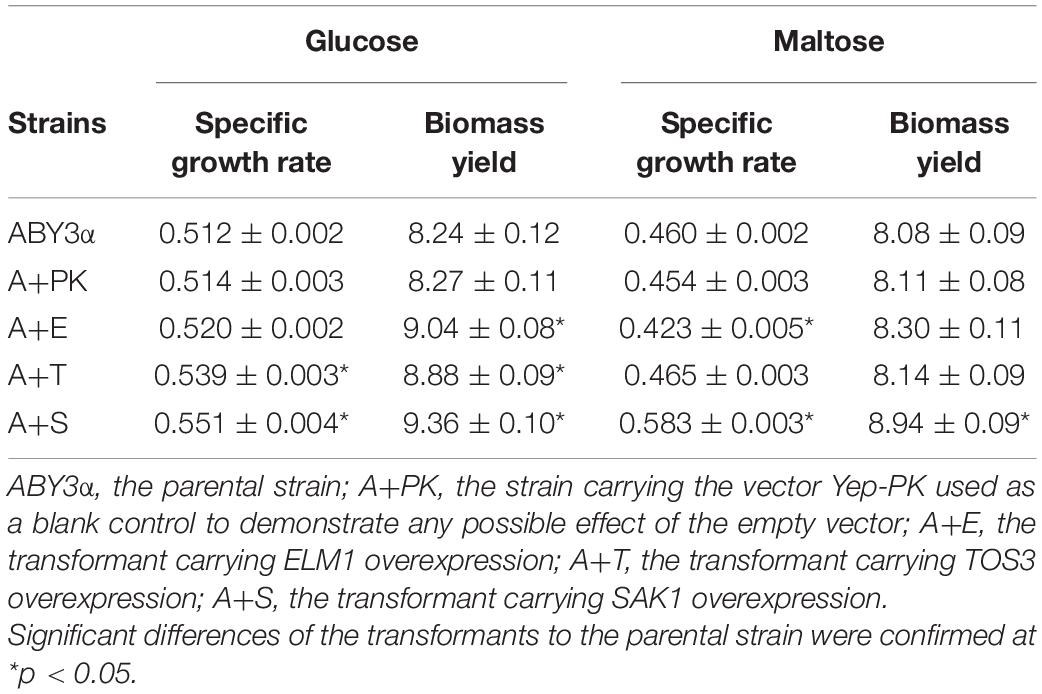
Table 3. Specific growth rate (h–1) and biomass yield (g/L) of the strains carrying genes overexpression.
These results demonstrated that the three kinases had a redundancy function in the cell growth of baker’s yeast in glucose. However, increasing each gene dosage was sufficient to enhance cell growth in glucose, and only an increased SAK1 level could promote cell growth in maltose. Therefore, the three kinases, Elm1, Tos3, and Sak1, performed a different regulation of the baker’s yeast growth via a carbon source-dependent pathway.
Sugar Consumption in the LSMLD Media
To investigate the influence of ELM1/TOS3/SAK1 overexpression on the maltose metabolism of baker’s yeast, the utilization of maltose and glucose was tested in the LSMLD media (Figure 3). Blank control strain A+YP exhibited sugar consumption similar to that of the parental strain ABY3α. Compared with the parental strain ABY3α, ELM1 overexpression strain A+E increased the maltose utilization efficiency by 15 and 11% in the maltose-glucose and maltose LSMLD media, respectively, and no evident changes of glucose utilization were observed in the maltose-glucose condition. Simultaneously, the deletion of ELM1 repressed the maltose consumption in maltose-glucose and maltose (Supplementary Figure 2). Time span value, a parameter that judges the degree of glucose repression, was calculated from Figure 3B. An 18% decrease (1.65 h in the parental strain and 1.35 h in the strain A+E) of the time span was obtained in the transformant A+E compared with the parental strain. Unexpectedly, TOS3 overexpression strain A+T and SAK1 overexpression strain A+S showed a much lower maltose utilization than the parental strain in the maltose-glucose and maltose conditions, with no noticeable difference in glucose consumption. The single deletion of TOS3 and SAK1 did not affect maltose consumption in maltose, whereas, a negative effect was observed in maltose-glucose (Supplementary Figure 2).
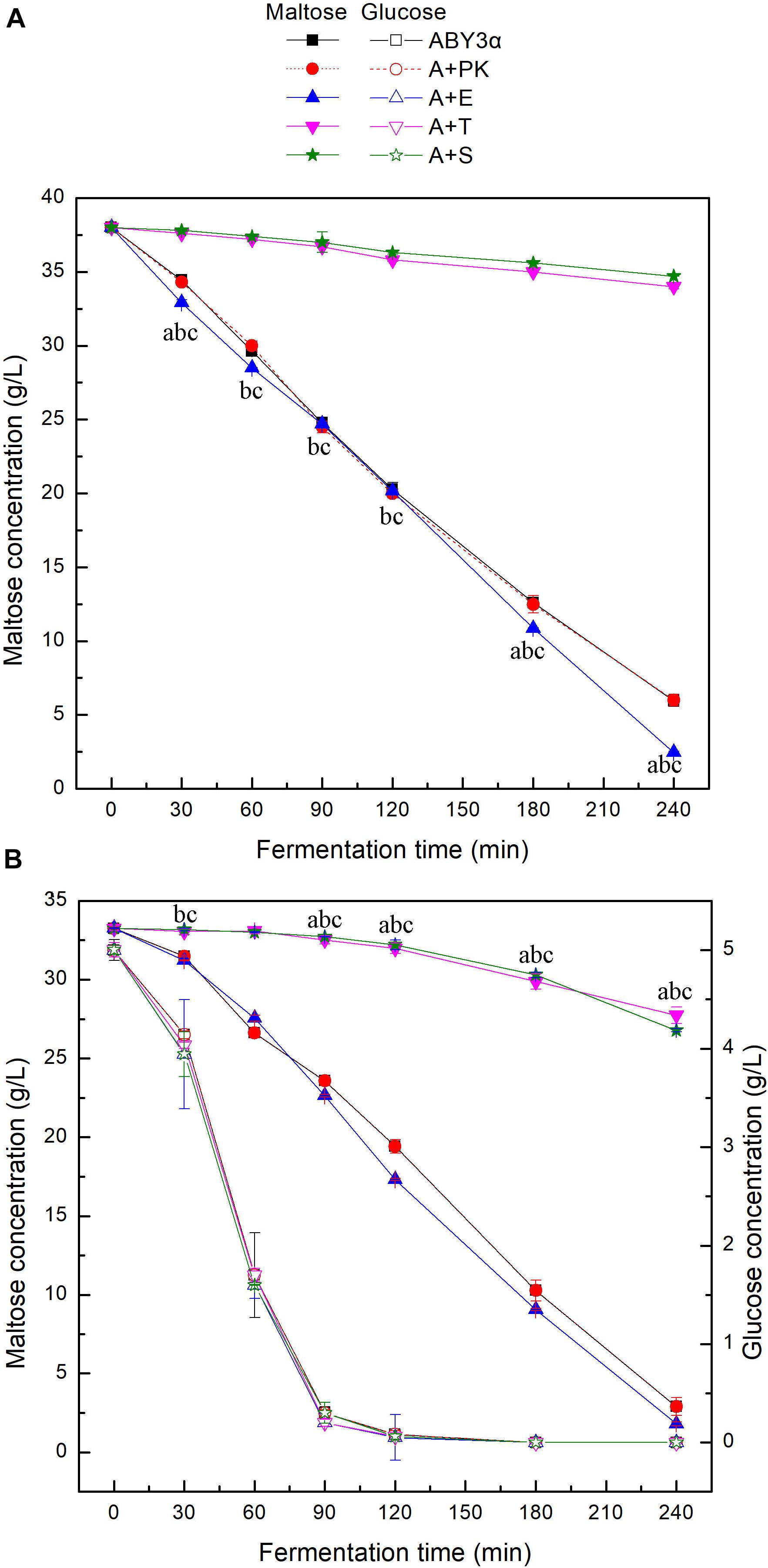
Figure 3. Sugar consumption of the strains carrying genes overexpression in LSMLD media. 2 g fresh yeast was cultured in the (A) maltose and (B) maltose-glucose LSMLD media at 30°C and 1 mL cultures were sampled at a certain interval. ABY3α, the parental strain; A+PK, the strain carrying the vector Yep-PK used as a blank control to demonstrate any possible effect of the empty vector; A+E, the transformant carrying ELM1 overexpression; A+T, the transformant carrying TOS3 overexpression; A+S, the transformant carrying SAK1 overexpression. Significant differences of the transformants A+E, A+T, and A+S to the parental strain were confirmed at ap < 0.05, bp < 0.05, and cp < 0.05, respectively.
These findings reflected that Elm1 might be the positive regulator of the maltose metabolism in baker’s yeast used in this work in the analyzed conditions. Tos3 and Sak1 were not necessary for maltose metabolism in maltose, and even negatively regulated the maltose metabolism at a high expression level. Nevertheless, native expression levels of TOS3 and SAK1 were essential for the baker’s yeast cell to resist glucose repression to utilize maltose in the maltose-glucose condition.
Fermentation Property in Lean Dough
The fermentation capacity of the transformants and the parental strain was measured in lean dough to further test the influence of ELM1/TOS3/SAK1 overexpression on the maltose metabolism of baker’s yeast (Figure 4). Blank control strain A+YP exhibited a fermentation performance similar to that of the parental strain ABY3α. ELM1 overexpression strain A+E exhibited a stronger CO2-releasing ability than the parental strain. Compared with the parental strain ABY3α, the transformant A+E increased the total amounts of CO2 within 120 min and leavening ability by 12 and 15%, respectively; decreases of 21 and 26% were observed in the ELM1 deletion (Supplementary Figure 3). On the contrary, the total amounts of CO2 within 120 min and the leavening power of TOS3 overexpression strain A+T were 12 and 23% lower than those of the parental strain, respectively; those for SAK1 overexpression strain A+S were 30 and 21% lower, respectively.
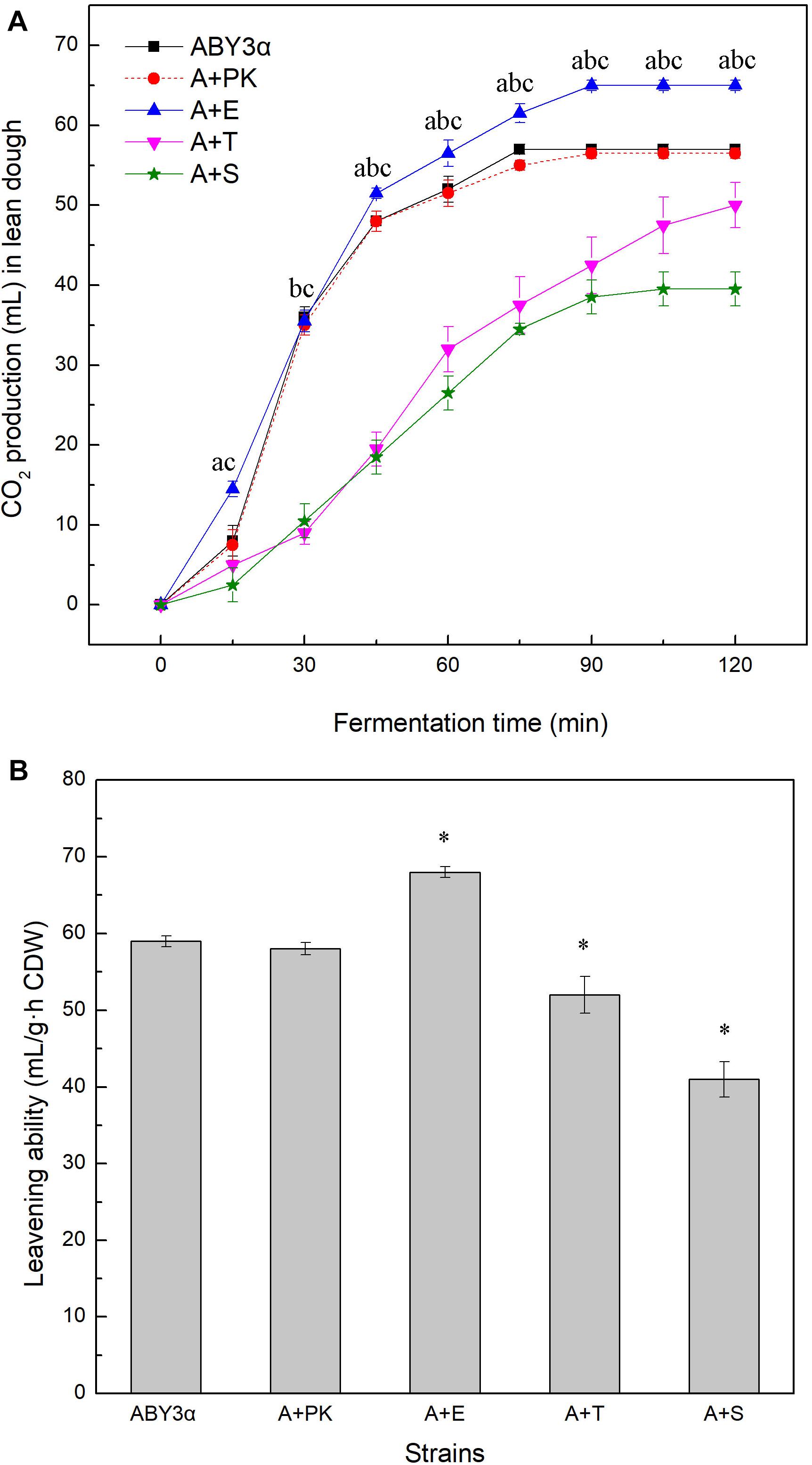
Figure 4. CO2 production of the strains carrying genes overexpression in lean dough. (A) Mixed dough was placed into a graduated cylinder, and CO2 amounts were recorded at 30°C for 120 min. Significant differences of the transformants A+E, A+T, and A+S to the parental strain were confirmed at ap < 0.05, bp < 0.05, and cp < 0.05, respectively. (B) Leavening ability was determined by CO2 production per hour per gram (dry weight) of yeast cells. Significant differences of the transformants to the parental strain were confirmed at ∗P < 0.05. ABY3α, the parental strain; A+PK, the strain carrying the vector Yep-PK used as a blank control to demonstrate any possible effect of the empty vector; A+E, the transformant carrying ELM1 overexpression; A+T, the transformant carrying TOS3 overexpression; A+S, the transformant carrying SAK1 overexpression.
The single deletion of TOS3 and SAK1 delayed the release of CO2 in the early stage of fermentation, but this inhibition effect might be relieved with the release of glucose repression in lean dough.
These results confirmed the positive effect of ELM1 overexpression on maltose metabolism of baker’s yeast and suggested the importance of the normal transcription of TOS3 and SAK1 in the lean dough fermentation.
Expression Level of MAL Genes
The transcription of genes MAL61/MAL31 and MAL62/MAL32 was analyzed in the maltose-glucose and maltose conditions (Figure 5, Supplementary Figure 4). In general, Elm1 positively regulated the transcription of MAL61 and MAL31 in maltose and maltose-glucose and the transcription of MAL62 and MAL32 in maltose. By contrast, Tos3 and Sak1 negatively regulated the expression of MAL61/MAL31 in maltose-glucose and the expression of MAL32 in maltose.
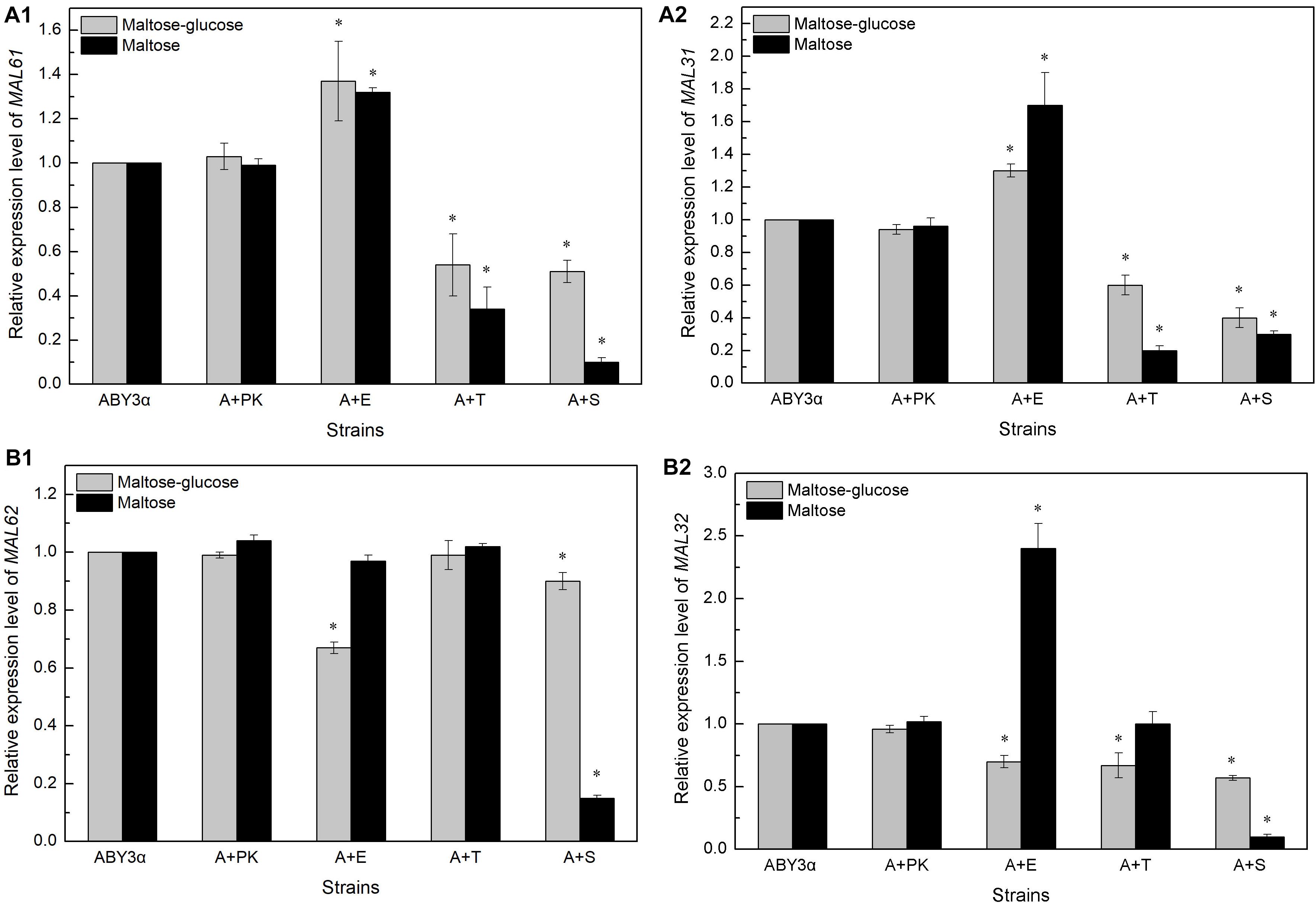
Figure 5. Expression levels of (A) MALx1 and (B) MALx2 in the single-kinase gene overexpression. 2 g fresh yeast was cultured in the LSMLD media and cultures were sampled at 30 min. The expression levels of genes (A1) MAL61, (A2) MAL31 and (B1) MAL62, (B2) MAL32 were tested using qRT-PCR. ABY3α, the parental strain; A+PK, the strain carrying the vector Yep-PK used as a blank control to demonstrate any possible effect of the empty vector; A+E, the transformant carrying ELM1 overexpression; A+T, the transformant carrying TOS3 overexpression; A+S, the transformant carrying SAK1 overexpression. Significant differences of the transformants to the parental strain were confirmed at ∗ P < 0.05.
The MAL61 mRNA level was tested in the overexpression of ELM1 combined with the deleted SNF1 to investigate whether Elm1 regulated the expression of MALx1 via the Snf1 pathway. Compared with the parental strain, the expression of MAL61 considerably decreased in strain A+E-SNF1 (Figure 6A), suggesting the possibility of the Elm1-Snf1-Malx1 pathway in the maltose metabolism of baker’s yeast. The downregulated transcription of MAL in the overexpression strains suggested the Snf1-independent regulatory pathways by the kinases. Liu et al. (2011) showed that Sak1 interacted with the other protein (mainly referred to Reg1) without relying on Snf1 in glucose. Reg1 is one of the regulatory subunits of the type 1 protein phosphatase of baker’s yeast and regulates glucose repression by targeting the catalytic subunit Glc7 to the corresponding substrates (Tabba et al., 2010). The deletion of REG1 can increase the expression of MAL61 and MAL62, and enhance the activities of maltose permease and maltase of industrial baker’s yeast (Lin et al., 2015, 2018). Therefore, the expression levels of MAL61 and MAL62 were tested in the REG1-deleted genetic background. The expression levels of MAL61 and MAL62 in strain A+S-REG1 were lower than those of the parental strain in maltose-glucose and maltose (Figure 6). These results suggested the possibility of a Reg1-independent form in the regulation of genes involved in maltose metabolism by Sak1. Similarly, Tos3 regulated the expression of MAL61 via pathways unrelated to Reg1 under the maltose-glucose and maltose conditions as well as the regulation of MAL62 by Elm1 (Figure 6). These results indicated that the three kinases differentially regulated the transcription of MAL genes via unknown, complex pathways but in a carbon source- and MAL-dependent manner.
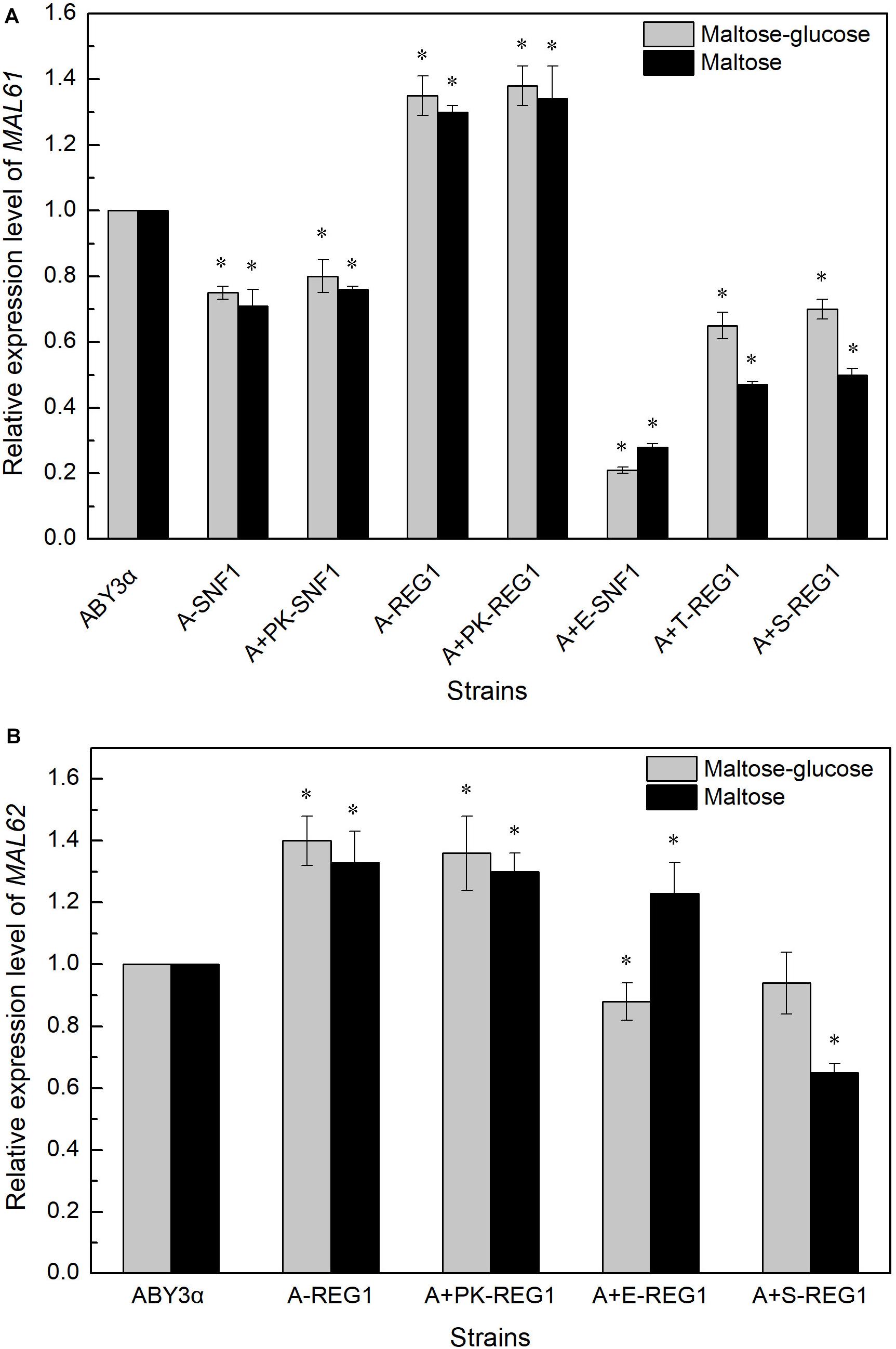
Figure 6. Expression levels of (A) MALx1 and (B) MALx2 in the gene-combination mutants. 2 g fresh yeast was cultured in the LSMLD media and cultures were sampled at 30 min. The expression levels of genes (A) MAL61 and (B) MAL62 were tested using qRT-PCR. ABY3α, the parental strain; A-SNF1, the SNF1-deleted mutant; A+PK-SNF1, the SNF1-deleted mutant carrying the vector Yep-PK; A-REG1, the REG1-deleted mutant; A+PK-REG1, the REG1-deleted mutant carrying the vector Yep-PK; A+E-SNF1, the SNF1-deleted mutant carrying ELM1 overexpression; A+E-REG1, the REG1-deleted mutant carrying ELM1 overexpression; A+T-REG1, the REG1-deleted mutant carrying TOS3 overexpression; A+S-REG1, the REG1-deleted mutant carrying SAK1 overexpression. Significant differences of the transformants to the parental strain were confirmed at ∗P < 0.05.
Discussion
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Elm1, Tos3, and Sak1 kinases are known as the upstream regulators of the Snf1-Mig1 pathway in glucose repression (Hedbacker and Carlson, 2008). In this study, the focus was on the role of the three upstream kinases in the maltose metabolism of baker’s yeast. The results suggested that Elm1, Tos3, and Sak1 played different roles in the regulation of the maltose metabolism of baker’s yeast. Elm1 was necessary for the maltose metabolism of baker’s yeast in maltose and maltose-glucose, and the overexpression of ELM1 could promote the utilization of maltose. Native Tos3 and Sak1 were essential for yeast cells to adapt glucose inhibition, but high levels of TOS3 and SAK1 negatively affected the maltose metabolism.
In this study, the overexpression of ELM1 alleviated glucose repression and upregulated the expression of MAL61 and MAL31 in glucose repression and maltose induction. The increase in maltose uptake by MAL61 overexpression could facilitate the maltose metabolism and fermentation ability of baker’s yeast in lean dough (Zhang et al., 2015b). The existence of the Elm1-Snf1-Mal61 pathway demonstrated that Elm1 might be one of the dominant upstream regulators in the glucose repression of maltose. The inferior transcription of MAL62 and MAL32 could affect maltose hydrolysis and delay the release of CO2 in the initial lean dough fermentation in ELM1 overexpression, and then, high CO2 was produced with an upregulated MAL32 in a glucose derepression condition. These findings demonstrated the differential regulation on MAL genes by Elm1. Snf1 is a positive regulator of maltose metabolism in baker’s yeast. Elm1 functions in many cellular activities of yeast in addition to glucose repression, and multiple pathways intersect in response to signals (Souid et al., 2006; Ye et al., 2008; Casamayor et al., 2012). Therefore, Elm1 might regulate the expression of MALx2, even MALx1, via other unknown pathways rather than relying on Snf1.
The overexpression of TOS3 and SAK1 repressed the uptake of maltose with a downregulated transcription of MAL61/MAL31 in maltose-glucose, thereby inhibiting maltose metabolism and lean dough fermentation. However, native Tos3 and Sak1 were necessary to adapt the glucose repression because the deletion of TOS3 and SAK1 decreased maltose metabolism in maltose-glucose and the initial lean dough fermentation. The increased expression of MAL32 without glucose repression could contribute to the release of CO2 in the late lean dough fermentation in TOS3 and SAK1 deletions. These findings did not contradict the view that Sak1 is the central upstream kinase involved in the regulation of Snf1 in glucose repression (Hedbacker et al., 2004) and suggested Snf1-independent pathways other than the Reg1-dependent form by the kinases. The regulation of the kinases on maltose metabolism differed from that of invertase in glucose limitation (McCartney et al., 2005). Therefore, the three protein kinases regulated carbon sources metabolism in a signal-dependent manner, and different responses were produced in the same signal (Hong et al., 2003). The specific regulation pathway of Elm1, Tos3, and Sak1 in the maltose metabolism of baker’s yeast needs to be studied further.
The function of the three protein kinases in the regulation of cell growth differed from that in the regulation of maltose metabolism. The overexpression of ELM1 improved the growth of baker’s yeast in glucose, confirming the role of Elm1 in the coordination of cell growth in budding yeast (Bouquin et al., 2000; Sreenivasan et al., 2003). A similar effect was caused by TOS3 overexpression in the same condition. This result showed a discrepancy to the findings of Kim et al. (2005), who reported that the mutation of TOS3 negatively affects the growth of a laboratory S. cerevisiae strain in a non-fermentable carbon source with no effect on glucose and raffinose. This finding may be attributed to the discrepancy of yeast strains and the test method used. The overexpression of SAK1 enhanced the growth of baker’s yeast in glucose and maltose. This finding was consistent with the results of Raab et al. (2011), who analyzed in glucose and non-fermentable carbon source conditions, and suggested the dominant role of Sak1 in the regulation of cell growth in maltose. The increase in growth cannot compensate for the reduction in maltose metabolism caused by downregulated MAL in TOS3 and SAK1 mutants.
Overall, Elm1, Tos3, and Sak1 played different roles in the regulation of maltose metabolism of baker’s yeast with differential regulations on MAL genes (Figure 7). Elm1 was necessary for the maltose metabolism of baker’s yeast in maltose and maltose-glucose, and the overexpression of ELM1 could enhance the maltose metabolism and lean dough fermentation ability of baker’s yeast by upregulating the transcription of MAL61 and MAL31 in maltose and maltose-glucose and the transcription of MAL62 and MAL32 in maltose. The native level of TOS3 and SAK1 was essential for yeast cells to adapt glucose repression, but the overexpression of TOS3 and SAK1 alone negatively affected maltose metabolism largely by repressing the expression of MAL61/MAL31 in maltose-glucose and the expression of MAL32 in maltose. Moreover, the three upstream kinases might regulate maltose metabolism via the Snf1-parallel pathways with a carbon source-dependent manner. These findings provided a new perspective for breeding industrial yeasts with rapid maltose metabolism and insights into the study of glucose repression in other carbon sources.
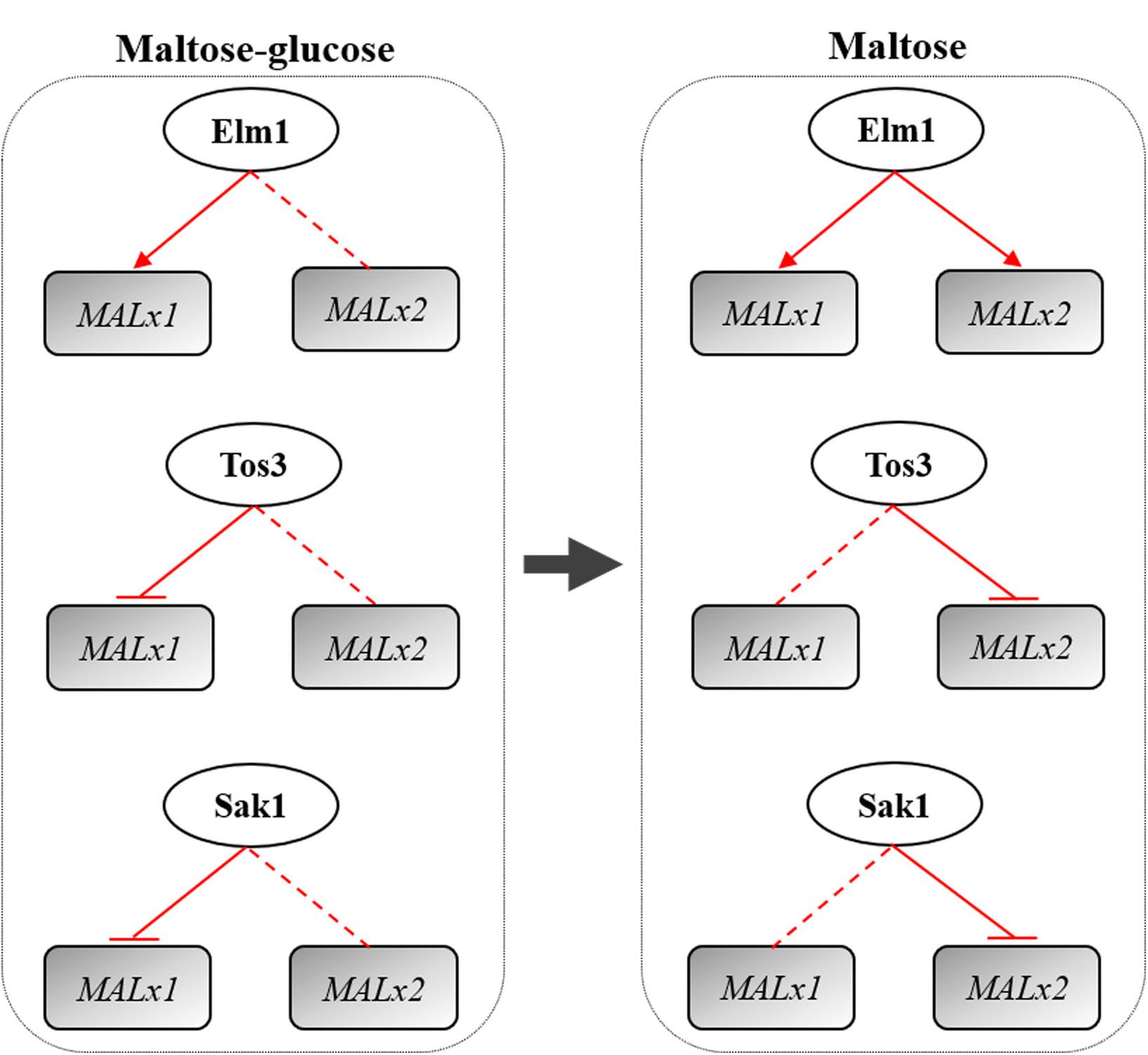
Figure 7. Regulation of the kinases Elm1, Tos3, and Sak1 on MALx1 and MALx2 in maltose-glucose and maltose. x was the locus and MAL3 and MAL6 were analyzed in this study. Red arrow line: positive regulation. Red straight line: native level of the kinase needed. Red flat end line: negative regulation. MALx2 in the regulation of Tos3 in maltose mainly was MAL32. MALx1 in the regulation of Sak1 in maltose-glucose mainly was MAL31. MALx2 in the regulation of Sak1 in maltose mainly was MAL32.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author Contributions
XL conceived and designed the research, and drafted the manuscript. XY and LM preformed the experiments. H-YJ participated in the data analysis. X-PH and C-FL revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 2019RC083), the Scientific Research Foundation of Hainan University (grant number KYQD1660), and the Foundation (No. 2018KF001) of Key Laboratory of Industrial Fermentation Microbiology of Ministry of Education and Tianjin Key Lab of Industrial Microbiology (Tianjin University of Science & Technology).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2021.665261/full#supplementary-material
References
Bell, P., Higgins, V. J., and Attfield, P. V. (2001). Comparison of fermentative capacities of industrial baking and wild-type yeasts of the species Saccharomyces cerevisiae in different sugar media. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 32, 224–229. doi: 10.1046/j.1472-765X.2001.00894.x
Bouquin, N., Barral, Y., Courbeyrette, R., Blondel, M., Snyder, M., and Mann, C. (2000). Regulation of cytokinesis by the Elm1 protein kinase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Cell Sci. 113, 1435–1445. doi: 10.1023/A:1005568132027
Carlson, M. (1999). Glucose repression in yeast. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2, 202–207. doi: 10.1016/S1369-5274(99)80035-6
Casamayor, A., Serrano, R., Platara, M., Casado, C., Ruiz, A., and Ariño, J. (2012). The role of the Snf1 kinase in the adaptive response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to alkaline pH stress. Biochem. J. 444, 39–49. doi: 10.1042/BJ20112099
Coccetti, P., Nicastro, R., and Tripodi, F. (2018). Conventional and emerging roles of the energy sensor Snf1/AMPK in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb. Cell 5, 482–494. doi: 10.15698/mic2018.11.655
Daniel, T., and Carling, D. (2002). Expression and regulation of the AMP-activated protein kinase-SNF1 (sucrose non-fermenting 1) kinase complexes in yeast and mammalian cells: studies using chimaeric catalytic subunits. Biochem. J. 365, 629–638. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020124
García-Salcedo, R., Lubitz, T., Beltran, G., Elbing, K., Tian, Y., Frey, S., et al. (2014). Glucose de-repression by yeast AMP-activated protein kinase SNF1 is controlled via at least two independent steps. FEBS. J. 281, 1901–1917. doi: 10.1111/febs.12753
Gietz, R. D. (2015). “High efficiency DNA transformation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with the LiAc/SS-DNA/PEG method,” in Genetic Transformation Systems in Fungi. Fungal Biology, Vol. 1, eds M. Van den Berg and K. Maruthachalam (Cham: Springer), 177–186. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10142-2_17
Hatanaka, H., Omura, F., Kodama, Y., and Ashikari, T. (2009). Gly-46 and His-50 of yeast maltose transporter Mal21p are essential for its resistance against glucose-induced degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 15448–15457. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808151200
Hazell, B., and Attfield, P. (1999). Enhancement of maltose utilisation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae in medium containing fermentable hexoses. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biot. 22, 627–632. doi: 10.1038/sj.jim.2900672
Hedbacker, K., and Carlson, M. (2008). SNF1/AMPK pathways in yeast. Front. Biosci. 13:2408–2420. doi: 10.2741/2854
Hedbacker, K., Hong, S. P., and Carlson, M. (2004). Pak1 protein kinase regulates activation and nuclear localization of Snf1-Gal83 protein kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24, 8255–8263. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.18.8255-8263.2004
Hong, S. P., Leiper, F. C., Woods, A., Carling, D., and Carlson, M. (2003). Activation of yeast Snf1 and mammalian AMP-activated protein kinase by upstream kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 8839–8843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1533136100
Jiang, T. X., Xiao, D. G., and Gao, Q. (2008). Characterisation of maltose metabolism in lean dough by lagging and non-lagging baker’s yeast strains. Ann. Microbiol. 58, 655–660. doi: 10.1007/BF03175571
Kim, M. D., Hong, S. P., and Carlson, M. (2005). Role of Tos3, a Snf1 protein kinase, during growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on nonfermentable carbon sources. Eukaryot. Cell 4, 861–866. doi: 10.1128/EC.4.5.861-866.2005
Kim, S. B., Kwon, D. H., Park, J. B., and Ha, S. J. (2019). Alleviation of catabolite repression in Kluyveromyces marxianus: the thermotolerant SBK1 mutant simultaneously coferments glucose and xylose. Biotechnol. Biofuels 12:90. doi: 10.1186/s13068-019-1431-x
Klein, C. J., Olsson, L., and Nielsen, J. (1998). Glucose control in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: the role of Mig1 in metabolic functions. Microbiology 144, 13–24. doi: 10.1099/00221287-144-1-13
Li, P., Gao, Y. Y., Wang, C. L., Zhang, C. Y., Guo, X. W., and Xiao, D. G. (2018). Effect of ILV6 deletion and expression of aldB from Lactobacillus plantarum in Saccharomyces uvarum on diacetyl production and wine flavor. J. Agr. Food Chem. 66, 8556–8565. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b02356
Lin, X. (2021). The regulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Snf1 protein kinase on glucose utilization is in a glucose-dependent manner. Curr. Genet. 67, 245–248. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01137-0
Lin, X., Zhang, C. Y., Bai, X. W., and Xiao, D. G. (2015). Effects of GLC7 and REG1 deletion on maltose metabolism and leavening ability of baker’s yeast in lean dough. J. Biotechnol. 209, 1–6.
Lin, X., Zhang, C. Y., Meng, L., Bai, X. W., and Xiao, D. G. (2018). Overexpression of SNF4 and deletions of REG1- and REG2-enhanced maltose metabolism and leavening ability of baker’s yeast in lean dough. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 45, 827–838. doi: 10.1007/s10295-018-2058-9
Liu, Y., Xu, X., and Carlson, M. (2011). Interaction of SNF1 protein kinase with its activating kinase Sak1. Eukaryot. Cell 10, 313–319. doi: 10.1128/EC.00291-10
Martinez-Ortiz, C., Carrillo-Garmendia, A., Correa-Romero, B. F., Canizal-García, M., González-Hernández, J. C., Regalado-Gonzalez, C., et al. (2019). SNF1 controls the glycolytic flux and mitochondrial respiration. Yeast 36, 487–494. doi: 10.1002/yea.3399
McCartney, R. R., and Schmidt, M. C. (2001). Regulation of Snf1 kinase Activation requires phosphorylation of threonine 210 by an upstream kinase as well as a distinct step mediated by the Snf4 subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 36460–36466. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M104418200
McCartney, R. R., Rubenstein, E. M., and Schmidt, M. C. (2005). Snf1 kinase complexes with different beta subunits display stress-dependent preferences for the three Snf1-activating kinases. Curr. Genet. 47, 335–344. doi: 10.1007/s00294-005-0576-2
Meng, L., Liu, H. L., Lin, X., Hu, X. P., and Liu, S. X. (2020). Enhanced multi-stress tolerance and glucose utilization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by overexpression of the SNF1 gene and varied beta isoform of Snf1 dominates in stresses. Microb. Cell Fact. 19:134. doi: 10.1186/s12934-020-01391-4
Meng, L., Yang, X., Lin, X., Jiang, H. Y., and Liu, S. X. (2021). Effect of overexpression of SNF1 on the transcriptional and metabolic landscape of baker’s yeast under freezing stress. Microb. Cell Fact. 20:10. doi: 10.1186/s12934-020-01503-0
Östling, J., and Ronne, H. (1998). Negative control of the MIG1p repressor by Snf1p-dependant phosphorylation in the absence of glucose. Eur. J. Biochem. 252, 162–168. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2520162.x
Papamichos-Chronakis, M., Gligoris, T., and Tzamarias, D. (2004). The Snf1 kinase controls glucose repression in yeast by modulating interactions between the Mig1 repressor and the Cyc8-Tup1 co-repressor. EMBO Rep. 5, 368–372. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400120
Persson, S., Welkenhuysen, N., Shashkova, S., and Cvijovic, M. (2020). Fine-tuning of energy levels regulates SUC2 via a SNF1-dependent feedback loop. Front. Physiol. 11:954. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00954
Raab, A. M., Hlavacek, V., Bolotina, N., and Lang, C. (2011). Shifting the fermentative/oxidative balance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by transcriptional deregulation of Snf1 via overexpression of the upstream activating kinase Sak1p. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 1981–1989. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02219-10
Ramírez-Zavala, B., Mottola, A., Haubenreißer, J., Schneider, S., Allert, S., Brunke, S., et al. (2017). The Snf1-activating kinase Sak1 is a key regulator of metabolic adaptation and in vivo fitness of Candida albicans. Mol. Microbiol. 104, 989–1007. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13674
Shao, Z. Y., Zhao, H., and Zhao, H. M. (2008). DNA assembler, an in vivo genetic method for rapid construction of biochemical pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:e16. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn991
Souid, A. K., Gao, C., Wang, L. M., Milgrom, E., and Shen, W.-C. W. (2006). ELM1 is required for multidrug resistance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 173, 1919–1937. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.057596
Srđan, N., Vesna, Z. K., and Vladimir, M. (2004). Regulation of maltose transport and metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Food Technol. Biotech. 42, 213–218. doi: 10.1016/S0950-3293(03)00100-9
Sreenivasan, A., Bishop, A. C., Shokat, K. M., and Kellogg, D. R. (2003). Specific inhibition of Elm1 kinase activity reveals functions required for early G1 events. Mol. Cell Biol. 23, 6327–6337. doi: 10.1128/mcb.23.17.6327-6337.2003
Sun, X., Zhang, C., Dong, J., Wu, M., Zhang, Y., and Xiao, D. (2012). Enhanced leavening properties of baker’s yeast overexpressing MAL62 with deletion of MIG1 in lean dough. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 39, 1533–1539. doi: 10.1007/s10295-012-1144-7
Sutherland, C. M., Hawley, S. A., Mccartney, R. R., Leech, A., Stark, M. J. R., Schmidt, M. C., et al. (2003). Elm1p is one of three upstream kinases for the Saccharomyces cerevisiae SNF1 complex. Curr. Biol. 13, 1299–1305. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00459-7
Tabba, S., Mangat, S., McCartney, R., and Schmidt, M. C. (2010). PP1 phosphatase-binding motif in Reg1 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is required for interaction with both the PP1 phosphatase Glc7 and the Snf1 protein kinase. Cell Signal. 22, 1013–1021. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.02.003
Trumbly, R. J. (1992). Glucose repression in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Microbiol. 6, 15–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00832.x
Verstrepen, K. J., Iserentant, D., Malcorps, P., Derdelinckx, G., Van Dijck, P., Winderickx, J., et al. (2004). Glucose and sucrose: hazardous fast-food for industrial yeast? Trends Biotechnol. 22, 531–537. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2004.08.001
Ye, T., Elbing, K., and Hohmann, S. (2008). The pathway by which the yeast protein kinase Snf1p controls acquisition of sodium tolerance is different from that mediating glucose regulation. Microbiology 154, 2814–2826. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2008/020149-0
Zhang, C. Y., Bai, X. W., Lin, X., Liu, X. E., and Xiao, D. G. (2015a). Effects of SNF1 on maltose metabolism and leavening ability of baker’s yeast in lean dough. J. Food Sci. 80, M2879–M2885. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13137
Zhang, C. Y., Lin, X., Song, H. Y., and Xiao, D. G. (2015b). Effects of MAL61 and MAL62 overexpression on maltose fermentation of baker’s yeast in lean dough. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 31, 1241–1249. doi: 10.1007/s11274-015-1874-6
Zhang, C. Y., Song, H. Y., Lin, X., Bai, X. W., and Xiao, D. G. (2015c). “Expression, purification and characterization of maltase from “Quick” baker’s yeast,” in Advances in Applied Biotechnology. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, Vol. 333, eds T. C. Zhang and M. Nakajima (Berlin: Springer), doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-46318-5_29
Keywords: Elm1, Tos3, Sak1, maltose metabolism, glucose repression, Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Citation: Yang X, Meng L, Lin X, Jiang H-Y, Hu X-P and Li C-F (2021) Role of Elm1, Tos3, and Sak1 Protein Kinases in the Maltose Metabolism of Baker’s Yeast. Front. Microbiol. 12:665261. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.665261
Received: 07 February 2021; Accepted: 23 April 2021;
Published: 01 June 2021.
Edited by:
Wanping Chen, Georg August University of Göttingen, GermanyReviewed by:
Jun Dai, Hubei University of Technology, ChinaChoowong Auesukaree, Mahidol University, Thailand
Estéfani García Ríos, Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISCIII), Spain
Copyright © 2021 Yang, Meng, Lin, Jiang, Hu and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xue Lin, bGlueGlhb3h1ZWx4QDE2My5jb20=; Cong-Fa Li, bGljb25nZmFsY2ZAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Y29uZ2ZhQHZpcC4xNjMuY29t
 Xu Yang1
Xu Yang1 Xue Lin
Xue Lin