- 1Jiangxi Province Key Laboratory of Immunology and Inflammation, Jiangxi Provincial Clinical Research Center for Laboratory Medicine, Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Jiangxi Medical College, Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
- 2Department of Clinical Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, Sichuan, China
- 3Department of Orthopedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Jiangxi Medical College, Nanchang University, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China
Background: This study aimed to investigate the association between serum heat shock protein 27 (HSP27) levels and 28-day mortality in patients with sepsis.
Methods: This retrospective study analyzed the clinical data of 76 septic patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU). Fifty non-septic ICU patients and 50 healthy individuals served as control groups. Serum HSP27 levels were measured on the day of ICU admission and compared to sepsis severity and survival outcomes.
Results: Median serum HSP27 levels in septic patients (4.70 ng/mL, IQR: 2.10–13.48 ng/mL) were significantly higher than those in both non-septic ICU controls and healthy controls (all p < 0.05). Moreover, non-survivors exhibited significantly higher median HSP27 levels (9.30 ng/mL, IQR: 3.62–25.91 ng/mL) compared to survivors (3.03 ng/mL, IQR: 1.48–7.39 ng/mL, p < 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis confirmed the association between HSP27 levels and 28-day mortality in sepsis patients. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis revealed an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.720 (95% CI: 0.605–0.817, p < 0.001) for HSP27 in predicting sepsis prognosis. Survival analysis demonstrated that patients with high serum HSP27 levels (≥2.61 ng/mL) had a worse prognosis than those with low levels (<2.61 ng/mL).
Conclusion: HSP27 shows potential as a biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of sepsis, however, further research is necessary to solidify its clinical utility.
1 Introduction
As a systemic inflammatory response syndrome triggered by infection, the definition and diagnostic criteria of sepsis have undergone several revisions in recent years (1). The latest definition, proposed by Sepsis-3 in 2016, describes sepsis as a “life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection” (2). A global cohort study estimated that approximately 49 million cases of sepsis occurred worldwide in 2017, resulting in 11 million deaths related to sepsis, which accounted for 19.7% of all global deaths (3). The high incidence and mortality rate of sepsis pose a significant burden on society, necessitating further measures to improve sepsis prevention and treatment. Existing diagnostic indicators have significant limitations in the early detection of sepsis (4). Traditional biomarkers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and procalcitonin (PCT) are widely used, but their limited sensitivity and specificity hinder their clinical utility (5). Consequently, there is an urgent need to identify novel biomarkers to improve the accuracy of sepsis diagnosis and facilitate early detection.
HSP27, also known as heat shock protein family B (small) member 1 (HSPB1) (6), is a critical stress protein that protects cells from damage (7). It is now understood that the molecular structure of HSP27 exists in both phosphorylated and polymerized states (8). During cellular stress responses, HSP27 plays a key protective role. When cells are exposed to heat, oxidative stress, or inflammatory factors, HSP27 levels are rapidly upregulated, inhibiting protein aggregation and misfolding, thus protecting cells from damage (9).
As a crucial stress protein, HSP27 has demonstrated significant diagnostic and prognostic utility in various diseases (10–13). While studies have shown correlations between other heat shock proteins, such as HSP70, HSP60, and HSP90α, and sepsis severity (14–18), the relationship between HSP27 and sepsis mortality remains uncertain. Therefore, this study aims to assess the prognostic value of HSP27 as a biomarker for sepsis-related mortality.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Ethics statement
Ethical approval for this study was obtained from the Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University. All patients provided written informed consent.
2.2 Study design
This retrospective case–control study enrolled septic patients admitted to the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University between September 2022 and September 2023 who met the Sepsis 3.0 diagnostic criteria (19). Patients were categorized into survival and death groups based on their 28-day survival outcomes. Exclusion criteria included HIV infection, immune system disorders, immunosuppressive or cytotoxic drug use, pregnancy, breastfeeding, refusal of informed consent, age under 18 or over 80 years, acute cerebrovascular or cardiovascular incidents, malignant tumors, severe hematological disorders, and ambiguous medical histories affecting SOFA score assessment. Fifty healthy individuals and 50 non-septic intensive care unit (ICU) patients, matched for age and gender with the septic ICU patients, served as the health control and ICU control groups, respectively. The primary reasons for ICU admission among the 76 septic patients were shock, respiratory failure, high-risk surgery, renal failure, acute pancreatitis, and other critical conditions. The 50 non-septic ICU patients were admitted primarily due to respiratory failure (n = 27), disturbance of consciousness (n = 12), shock (n = 7), and other critical conditions (n = 4).
2.3 Data collection
A retrospective case–control study was conducted using the Hospital Information System (HIS) to retrieve clinical data from patients fulfilling predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Access to this data was granted for research purposes. While the authors had access to personally identifiable information during or post-data collection, all data were handled confidentially. General patient demographics, such as age, gender, infection source, comorbidities, length of hospital stay, and vital signs were recorded. Laboratory investigations included peripheral venous blood samples drawn within 48 h of admission to measure complete blood count, liver and kidney function tests, CRP, PCT, and SOFA score. Additionally, venous blood specimens were collected within 2 days of admission to assess complete blood count, liver and kidney function tests, CRP, interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), PCT, and SOFA score.
2.4 Measurement of HSP27 levels
From all participants, a 5 mL fasting blood sample was drawn within 48 h of admission to the ICU. The serum was isolated and stored at −80°C until analysis. Serum HSP27 concentrations were quantified using a human HSP-27/HSPB1 ELISA Kit (Sangon Biotech). Standards, controls, and serum samples were diluted with sample buffer and added to a 96-well microplate. A horseradish peroxidase-conjugated antibody was subsequently added and incubated at 37°C for 60 min. Color development was induced with tetramethylbenzidine (TMB), and the optical density (OD) at 450 nm was measured using a microplate reader. The concentration of HSP27 in each sample was determined by interpolation from a standard curve generated from the OD values of the standard samples.
2.5 Statistical analysis
Data entry and statistical analysis were conducted utilizing SPSS software version 25.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, United States). Categorical variables were assessed with the χ2 or Fisher’s exact test, depending on sample size considerations. Continuous data were evaluated for normality using appropriate tests. Non-normally distributed data were presented as median and interquartile range (IQR), while normally distributed data were presented as mean and standard deviation. Group comparisons for continuous data were performed using either the Mann–Whitney U test for two independent groups or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with post hoc tests for multiple comparisons, depending on the presence of equal variances among groups. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were generated to assess the sensitivity and specificity of HSP27 in diagnosing sepsis. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) with its corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI) was used to evaluate the prognostic value of HSP27. Survival curves were constructed using the Kaplan–Meier method to compare survival times between patient groups. Data visualizations were created using the online tool Hiplot Pro.1 A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Characteristics of the study population
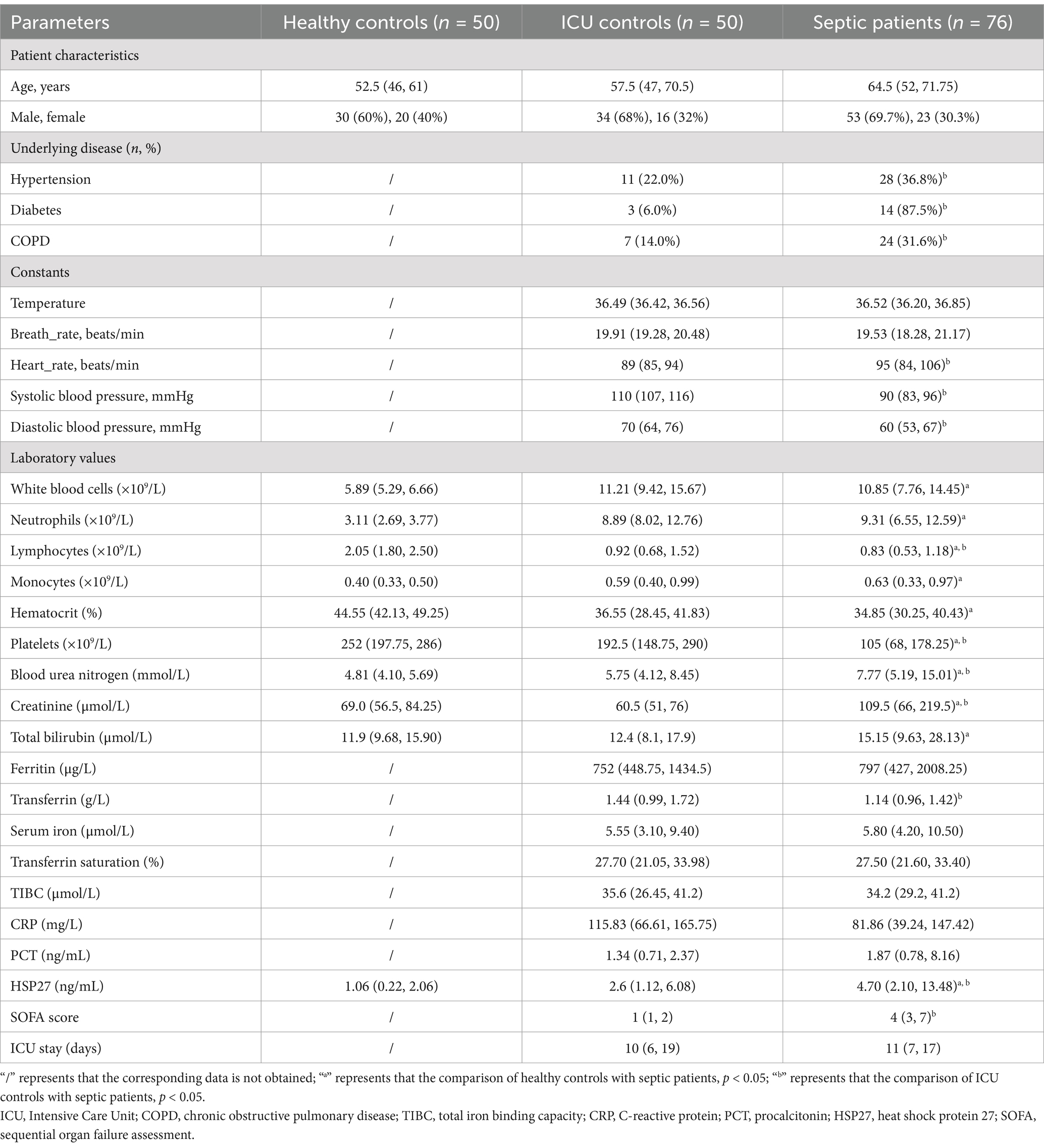
This study enrolled a total of 176 participants, comprising 76 sepsis patients, 50 ICU controls, and 50 healthy controls. Table 1 provides a detailed overview of the demographic and clinical characteristics of the study. Upon admission to the ICU, sepsis patients exhibited significantly elevated heart rate and blood pressure compared to the ICU control group (p < 0.05). The median HSP27 level in sepsis patients at admission was 4.70 ng/mL (IQR: 2.10, 13.48), which was significantly higher than that observed in healthy controls (1.06 ng/mL [IQR: 0.22, 2.06]) and non-septic ICU patients (2.6 ng/mL [IQR: 1.12, 6.08]) (all p < 0.05). Additionally, compared to the healthy control group, sepsis patients displayed significant alterations in various hematological parameters, including elevated levels of creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, monocytes, and neutrophils, as well as decreased levels of platelets, hematocrit, and lymphocytes (all p < 0.05). Compared to the ICU control group, sepsis patients exhibited significantly higher levels of lymphocytes, platelets, and transferrin (all p < 0.05). Furthermore, the SOFA score was significantly higher in sepsis patients compared to ICU controls (p < 0.05), indicating a greater degree of organ dysfunction in the sepsis group.
3.2 Serum HSP27 levels as a potential diagnostic biomarker for sepsis patients
To assess the diagnostic performance of HSP27, SOFA score, and PCT in differentiating ICU sepsis patients from ICU controls, we employed ROC curve analysis. HSP27 exhibited an AUC of 0.706 (95% CI: 0.616–0.795, p < 0.001), with a sensitivity of 72.0% and a specificity of 61.8%. While this performance was inferior to the SOFA score (AUC: 0.962, 95% CI: 0.940–0.984, sensitivity: 76.3%, specificity: 100%, p < 0.001), it surpassed that of PCT (AUC: 0.578, 95% CI: 0.477–0.679, sensitivity: 40.5%, specificity: 86.0%, p = 0.088) (Figure 1). These findings suggest that HSP27 may have potential as a diagnostic biomarker for sepsis.
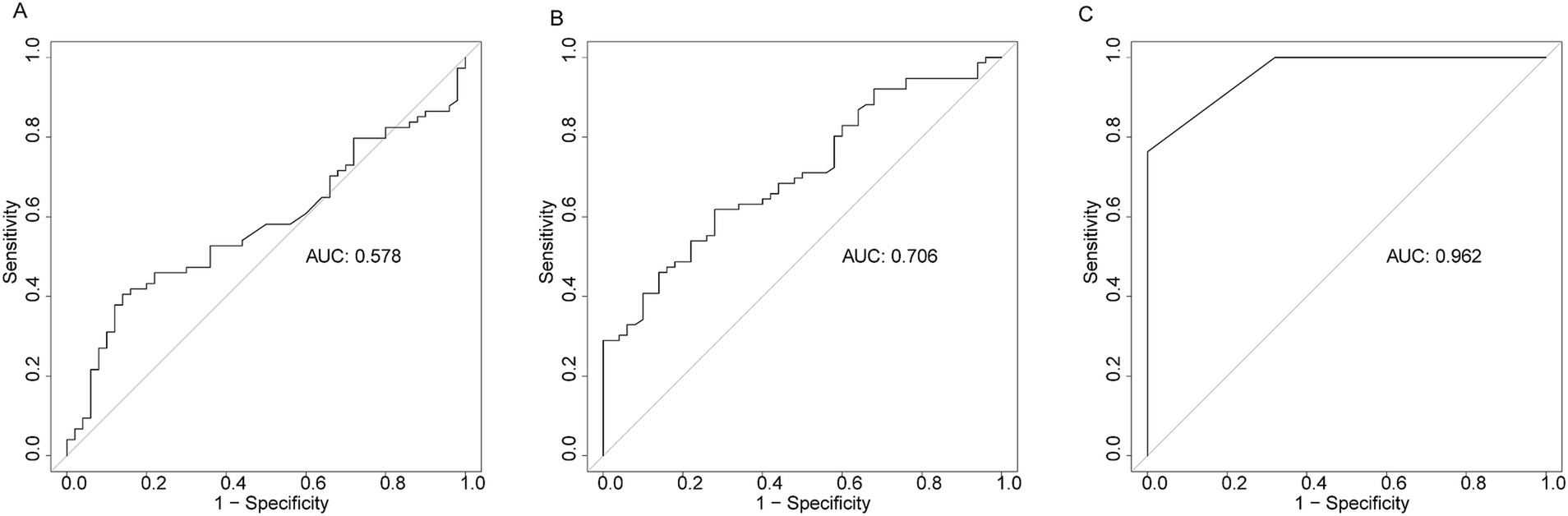
Figure 1. Receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) of PCT (A), HSP27 (B), and SOFA score (C) for diagnosis of sepsis.
3.3 Elevated serum HSP 27 levels are associated with poorer survival outcomes in ICU sepsis patients
Of the 76 sepsis patients, 39.47% (n = 30) succumbed to sepsis within 28 days of ICU admission. Table 2 presents a comparative analysis of the baseline characteristics and laboratory parameters between the surviving and non-surviving patient groups. Notably, non-survivors exhibited significantly elevated levels of creatinine, PCT, and IL-1β compared to survivors (all p < 0.05). Furthermore, the median HSP27 level was significantly higher in non-survivors [9.30 ng/mL (IQR: 3.62, 25.91)] compared to survivors [3.03 ng/mL (IQR: 1.48, 7.39)] (p < 0.001). Besides, non-survivors had significantly higher SOFA scores, indicating a greater degree of organ dysfunction.
3.4 HSP27 levels related to the severity of ICU sepsis patients
To investigate the association between HSP27 levels and sepsis severity, we performed a risk factor analysis. The results indicated that higher HSP27 levels were associated with elevated levels of PCT and SOFA scores (Figure 2). Univariate and multivariate logistic regression models were employed to identify independent predictors of 28-day mortality among septic patients. Univariate analysis revealed a significant positive correlation between higher HSP27 levels and increased 28-day mortality (odds ratio [OR] = 1.035, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.005–1.067, p = 0.022). Similarly, PCT and SOFA scores were significantly associated with increased mortality (OR = 1.160, 95% CI: 1.046–1.265, p = 0.001; and OR = 1.348, 95% CI: 1.130–1.608, p = 0.001, respectively). In contrast, creatinine levels were not significantly associated with 28-day mortality (OR = 1.002, 95% CI: 0.999–1.005, p = 0.122).

Figure 2. Serum PCT, HSP27, IL-1β, and creatinine levels at admission correlated with disease severity (SOFA score) in septic patients.
To further elucidate the independent prognostic value of HSP27, multiple logistic regression models were constructed (Table 3). After adjusting for potential confounders such as creatinine, PCT, and IL-1β, HSP27 remained significantly associated with 28-day mortality in sepsis (Model 2: OR = 1.038, 95% CI: 1.007–1.071, p = 0.017; Model 3: OR = 1.039, 95% CI: 1.006–1.073, p = 0.021; Model 4: OR = 1.036, 95% CI: 1.003–1.071, p = 0.035). However, upon further adjustment for the SOFA score (Model 5: OR = 1.034, 95% CI: 0.998–1.072, p = 0.064), the association between HSP27 and mortality lost statistical significance. These findings suggest that HSP27 levels are related to the 28-day mortality of ICU sepsis, but the SOFA score remains the established gold standard in clinical practice.
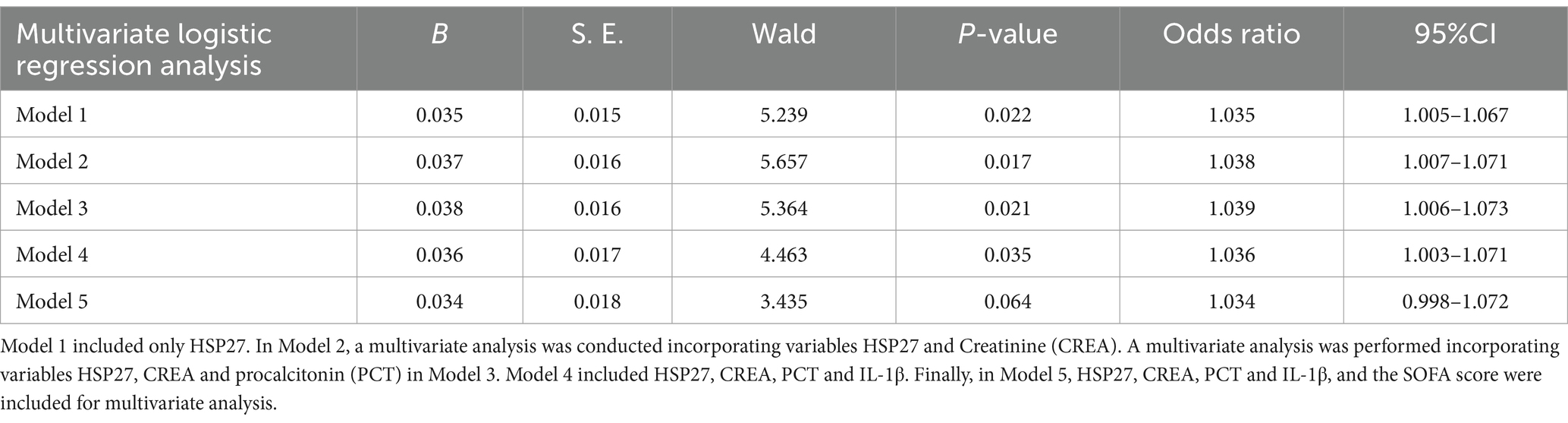
Table 3. Multivariate logistic regression analysis for sepsis after adjusting effects of confounders.
3.5 The ability of HSP27 to predict 28-day mortality in sepsis patients
To evaluate the prognostic significance of HSP27 in predicting 28-day survival, ROC curve analysis was performed. The AUC for HSP27 was 0.720 (95% CI: 0.605–0.817, p < 0.001), indicating good predictive accuracy. The optimal cutoff value for HSP27 was 2.61 ng/mL, yielding a sensitivity of 90.0% and a specificity of 50.0% in predicting 28-day mortality (Table 4). A combination of HSP27 and the SOFA score further improved prognostic accuracy, with an AUC of 0.767 (95% CI: 0.656–0.856, p < 0.001) and a specificity of 91.3%. This combined approach outperformed the use of either SOFA score (AUC: 0.702, 95% CI: 0.607–0.819, specificity: 86.6%) or HSP27 alone. Kaplan–Meier survival curves were constructed to compare the 28-day mortality rates between patients with high and low HSP27 levels based on the established cutoff value. The 28-day survival rate was significantly lower for patients with HSP27 levels above the cutoff than those with lower levels (log-rank test, p = 0.013) (Figure 3).
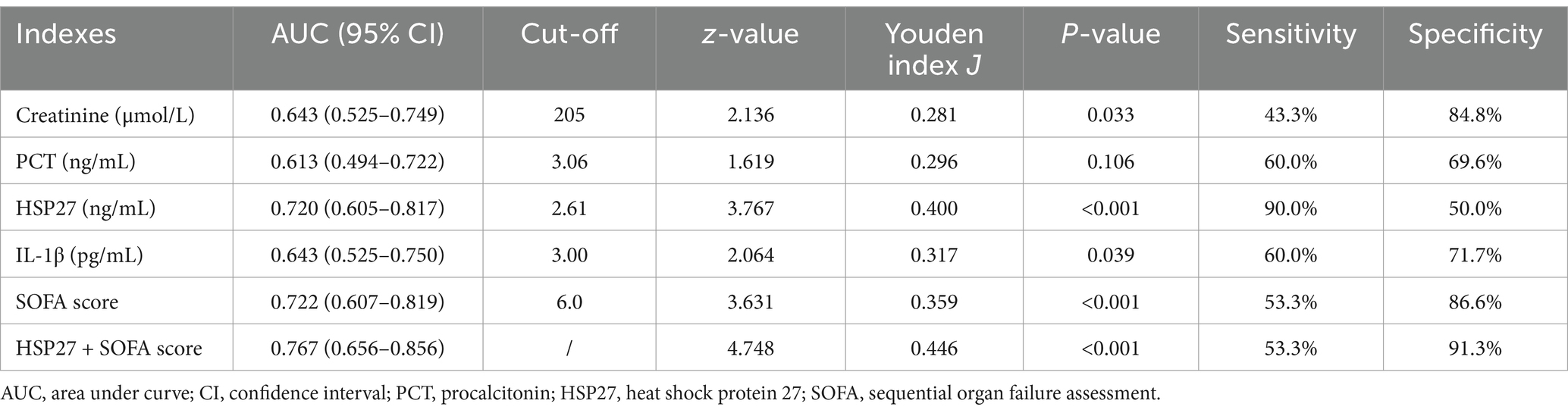
Table 4. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis for laboratory indexes on sepsis prognosis.
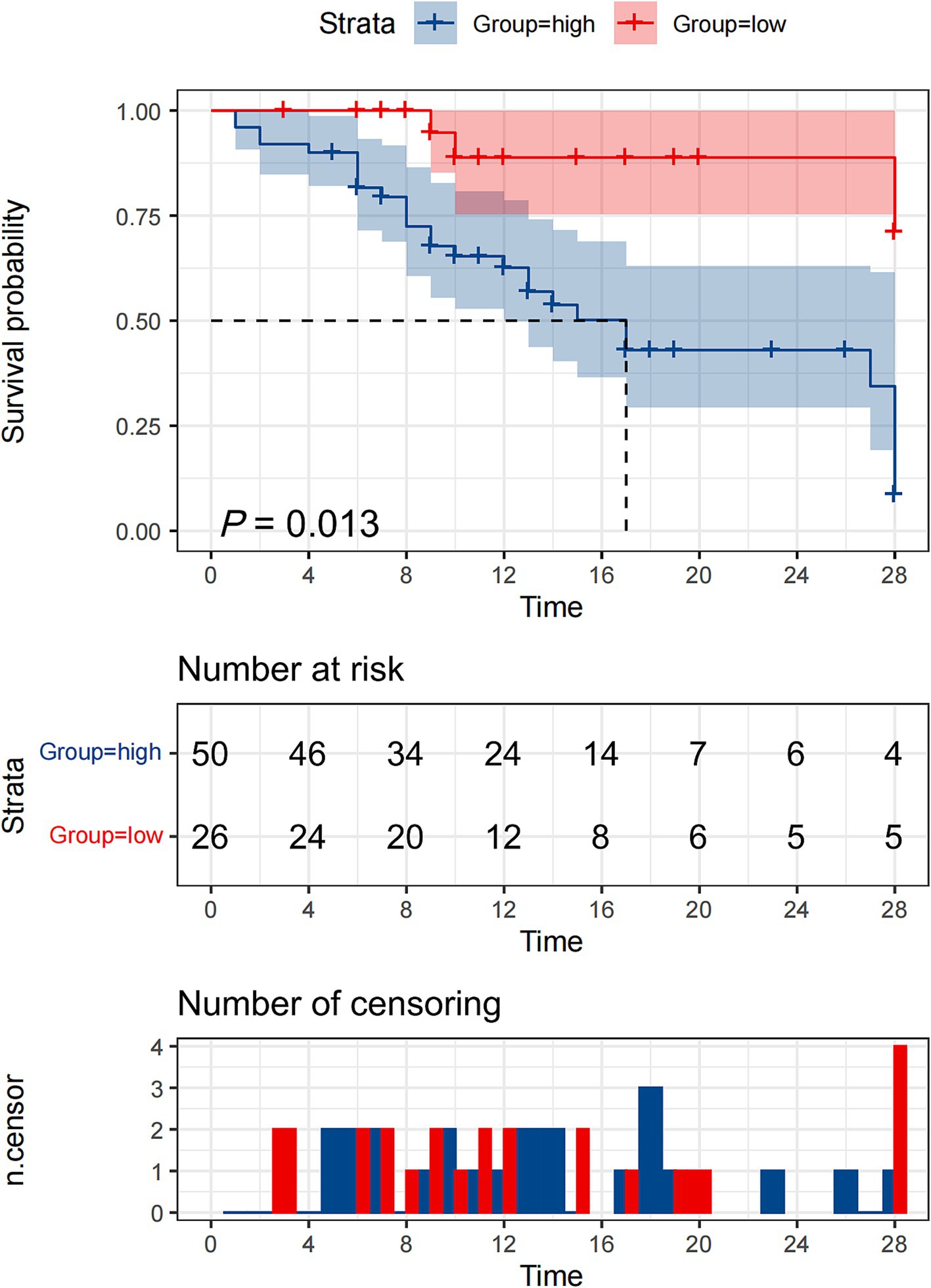
Figure 3. Kaplan–Meier survival curves of 76 adult patients with sepsis based on the HSP27 cutoff value (2.61 ng/mL) on day of ICU admission.
4 Discussion
As a systemic inflammatory response syndrome, sepsis often presents with non-specific symptoms in its early stages, leading to delayed diagnosis (20). However, the underlying pathological processes of sepsis initiate early, gradually causing systemic damage (21, 22). In its advanced stages, sepsis rapidly progresses, characterized by systemic immune dysregulation, uncontrolled inflammation, and tissue injury. Patients with advanced sepsis may develop multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), a life-threatening condition that is difficult to manage and associated with poor outcomes (23). Early intervention is critical to implement timely and effective therapeutic strategies before the condition becomes irreversible (24). Therefore, there is an urgent need for a biomarker that can facilitate early diagnosis and prognostication of sepsis.
The SOFA score, a widely recognized standard for assessing organ dysfunction, is a crucial tool in the diagnosis and prognostication of sepsis. Despite its complexity, which involves multiple variables, the SOFA score remains the primary method used in clinical practice to evaluate the severity and predict the outcome of sepsis (25). In recent years, an increasing number of biomarkers, including CRP, PCT, and IL-1β, are being utilized in clinical settings to enhance, have been explored for their potential to improve the predictive accuracy of sepsis prognosis (26–28). However, their limitations in terms of sensitivity and specificity hinder their widespread clinical application in the diagnosis and prognostication of sepsis.
Our study revealed that ICU sepsis patients exhibited significantly elevated serum HSP27 levels within 48 h of ICU admission compared to a control group. As an anti-inflammatory molecule (29), elevated HSP27 plays a crucial protective role in mitigating organ dysfunction induced by sepsis (30–32). To further assess the diagnostic utility of HSP27 in ICU sepsis, ROC curve analysis demonstrated a significantly higher AUC for HSP27 compared to PCT. Consequently, HSP27 emerges as a promising biomarker for ICU sepsis. Moreover, sepsis patients within the mortality group exhibited significantly higher serum HSP27 levels compared to the survival group. Additionally, sepsis patients with elevated serum HSP27 levels at admission exhibited a higher 28-day mortality rate. By combining HSP27 levels with SOFA scores, the specificity of ROC-based diagnosis increased from 86.6 to 91.3% (p < 0.001, Table 4). Finally, Kaplan–Meier survival analysis indicated a correlation between elevated serum HSP27 levels and reduced patient survival rates. These findings collectively demonstrate the prognostic value of HSP27 levels in ICU patients with sepsis.
More importantly, while the AUC for HSP27 was slightly lower than that for the SOFA score, the early changes in HSP27 expression levels during the onset of sepsis could facilitate earlier diagnosis and prognostic assessment. Early identification of sepsis patients is crucial for improving patient outcomes, and the early diagnostic potential of HSP27 may contribute to more timely clinical interventions. Moreover, the level of HSP27 correlates with sepsis severity, with higher levels associated with more severe disease and poorer prognosis. This suggests that HSP27 may serve as a valuable prognostic biomarker. Additionally, the quantification of serum HSP27 levels using ELISA technology is a convenient and highly accurate method, making it suitable for widespread implementation in hospital laboratories. By closely monitoring changes in HSP27 levels, clinicians can assess the therapeutic response of sepsis patients and make timely adjustments to their treatment plans.
In conclusion, our findings suggest that HSP27 may serve as a valuable biomarker for both the diagnosis and prognosis of sepsis.
4.1 Limitations
Although this retrospective, single-center study offers valuable insights into the role of HSP27 in sepsis, several limitations inherent to its design and scope must be acknowledged. Firstly, the retrospective nature of the study and its single-center design may introduce selection bias, potentially overestimating the diagnostic and prognostic utility of HSP27. To address this, future large-scale, multicenter, prospective studies are imperative. Secondly, the relatively small sample size and the inclusion of predominantly critically ill patients limit the generalizability of the findings to other patient populations, such as those with postoperative or non-critical sepsis. Expanding the sample size and incorporating a broader spectrum of patient conditions would enhance the reliability and applicability of the results. Thirdly, despite efforts to account for known confounders, the possibility of unmeasured or unrecognized confounding factors that may influence the observed associations cannot be entirely excluded. Finally, the lack of serial monitoring of serum HSP27 levels at multiple time points during the course of sepsis precludes a comprehensive understanding of the temporal relationship between HSP27 fluctuations and disease progression. Addressing these limitations through future studies will provide a more comprehensive understanding of the potential clinical utility of HSP27 in sepsis management.
5 Conclusion
In summary, this study demonstrates that serum HSP27 levels are significantly elevated in patients with sepsis, particularly in those who do not survive the 28-day period. These findings suggest a strong association between elevated HSP27 levels and increased mortality risk in sepsis patients. Our results highlight the potential utility of HSP27 as a valuable biomarker for the diagnosis, prognosis, and potentially the therapeutic management of sepsis.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University Medical Research Ethics Committee. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The human samples used in this study were acquired from a by-product of routine care or industry. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
LY: Writing – original draft, Methodology. ZF: Data curation, Writing – original draft. FY: Writing – review & editing. XW: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 82160405) and Science and Technology Plan of Jiangxi Province (grant nos. 20213BCJ22013 and 20212ACB206016).
Acknowledgments
We thank Shanghai Tengyun Biotechnology Co., Ltd. for developing Hiplot Pro platform (https://hiplot.com.cn/) and providing technical assistance and valuable tools for data analysis and visualization.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
References
1. Duncan, CF, Youngstein, T, Kirrane, MD, and Lonsdale, DO. Diagnostic challenges in Sepsis. Curr Infect Dis Rep. (2021) 23:22. doi: 10.1007/s11908-021-00765-y
2. Rhee, C, and Klompas, M. New Sepsis and septic shock definitions: clinical implications and controversies. Infect Dis Clin N Am. (2017) 31:397–413. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2017.05.001
3. Rudd, KE, Johnson, SC, Agesa, KM, Shackelford, KA, Tsoi, D, Kievlan, DR, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990-2017: analysis for the global burden of disease study. Lancet. (2020) 395:200–11. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7
4. Llitjos, JF, Carrol, ED, Osuchowski, MF, Bonneville, M, Scicluna, BP, Payen, D, et al. Enhancing sepsis biomarker development: key considerations from public and private perspectives. Crit Care. (2024) 28:238. doi: 10.1186/s13054-024-05032-9
5. Papafilippou, L, Claxton, A, Dark, P, Kostarelos, K, and Hadjidemetriou, M. Nanotools for Sepsis diagnosis and treatment. Adv Healthc Mater. (2021) 10:e2001378. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202001378
6. Sanchez-Nino, MD, Sanz, AB, Sanchez-Lopez, E, Ruiz-Ortega, M, Benito-Martin, A, Saleem, MA, et al. HSP27/HSPB1 as an adaptive podocyte antiapoptotic protein activated by high glucose and angiotensin II. Lab Investig. (2012) 92:32–45. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2011.138
7. Wang, B, Moon, SP, Cutolo, G, Javed, A, Ahn, BS, Ryu, AH, et al. HSP27 inhibitory activity against Caspase-3 cleavage and activation by Caspase-9 is enhanced by chaperone O-GlcNAc modification in vitro. ACS Chem Biol. (2023) 18:1698–704. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.3c00270
8. Nappi, L, Aguda, AH, Nakouzi, NA, Lelj-Garolla, B, Beraldi, E, Lallous, N, et al. Ivermectin inhibits HSP27 and potentiates efficacy of oncogene targeting in tumor models. J Clin Invest. (2020) 130:699–714. doi: 10.1172/JCI130819
9. Lanneau, D, Wettstein, G, Bonniaud, P, and Garrido, C. Heat shock proteins: cell protection through protein triage. ScientificWorldJOURNAL. (2010) 10:1543–52. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2010.152
10. Bourefis, A, Berredjem, H, Djeffal, O, Le, TK, Giusiano, S, and Rocchi, P. HSP27/Menin expression as new prognostic serum biomarkers of prostate Cancer aggressiveness independent of PSA. Cancers. (2022) 14:4773. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194773
11. Jaroszyński, A, Zaborowski, T, Głuszek, S, Zapolski, T, Sadowski, M, Załuska, W, et al. Heat shock protein 27 is an emerging predictor of contrast-induced acute kidney injury on patients subjected to percutaneous coronary interventions. Cells. (2021) 10:684. doi: 10.3390/cells10030684
12. Lallier, M, Marchandet, L, Moukengue, B, Charrier, C, Baud'huin, M, Verrecchia, F, et al. Molecular chaperones in osteosarcoma: diagnosis and therapeutic issues. Cells. (2021) 10:754. doi: 10.3390/cells10040754
13. Mao, Q, Yang, T, Peng, A, and Wang, Q. HSP 90β (HSP90AB1) as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for Ménière's disease. Asian J Surg. (2024) 47:2222–4. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2024.01.115
14. Miliaraki, M, Briassoulis, P, Ilia, S, Michalakakou, K, Karakonstantakis, T, Polonifi, A, et al. Oxidant/antioxidant status is impaired in Sepsis and is related to anti-apoptotic, inflammatory, and innate immunity alterations. Antioxidants. (2022) 11:231. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020231
15. Delogu, G, Lo Bosco, L, Marandola, M, Famularo, G, Lenti, L, Ippoliti, F, et al. Heat shock protein (HSP70) expression in septic patients. J Crit Care. (1997) 12:188–92. doi: 10.1016/S0883-9441(97)90031-9
16. Wheeler, DS, Fisher, LE, Catravas, JD, Jacobs, BR, Carcillo, JA, and Wong, HR. Extracellular hsp70 levels in children with septic shock. Pediatr Crit Care Med. (2005) 6:308–11. doi: 10.1097/01.PCC.0000161075.97355.2E
17. Wheeler, DS, Lahni, P, Odoms, K, Jacobs, BR, Carcillo, JA, Doughty, LA, et al. Extracellular heat shock protein 60 (Hsp60) levels in children with septic shock. Inflamm Res. (2007) 56:216–9. doi: 10.1007/s00011-007-6108-4
18. Li, F, Zhang, Y, Yu, B, Zhang, Z, Fan, Y, Wang, L, et al. Evaluation of the diagnostic and prognostic values of serum HSP90alpha in sepsis patients: a retrospective study. PeerJ. (2022) 10:e12997. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12997
19. Singer, M, Deutschman, CS, Seymour, CW, Shankar-Hari, M, Annane, D, Bauer, M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for Sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. (2016) 315:801–10. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287
20. Cohen, J, Vincent, JL, Adhikari, NK, Machado, FR, Angus, DC, Calandra, T, et al. Sepsis: a roadmap for future research. Lancet Infect Dis. (2015) 15:581–614. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(15)70112-X
21. Unar, A, Bertolino, L, Patauner, F, Gallo, R, and Durante-Mangoni, E. Pathophysiology of disseminated intravascular coagulation in Sepsis: a clinically focused overview. Cells. (2023) 12:2120. doi: 10.3390/cells12172120
22. Pais, T, Jorge, S, and Lopes, JA. Acute kidney injury in Sepsis. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:5924. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115924
23. Wang, W, and Liu, CF. Sepsis heterogeneity. World J Pediatr. (2023) 19:919–27. doi: 10.1007/s12519-023-00689-8
24. Kim, HJ, Ko, RE, Lim, SY, Park, S, Suh, GY, and Lee, YJ. Sepsis alert systems, mortality, and adherence in emergency departments: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. (2024) 7:e2422823. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.22823
25. Gaini, S, Relster, MM, Pedersen, C, and Johansen, IS. Prediction of 28-days mortality with sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA), quick SOFA (qSOFA) and systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) – a retrospective study of medical patients with acute infectious disease. Int J Infect Dis. (2019) 78:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2018.09.020
26. Gopal, N, Chauhan, N, Jain, U, Dass, SK, Sharma, HS, and Chandra, R. Advancement in biomarker based effective diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. (2023) 51:476–90. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2023.2252016
27. Cao, J, Liu, W, Li, Y, Chen, B, Yu, T, He, Z, et al. Value of IL-1beta and IL-23 in predicting 28-day mortality due to Sepsis: a retrospective study. Med Sci Monit. (2023) 29:e940163. doi: 10.12659/MSM.940163
28. Pierrakos, C, Velissaris, D, Bisdorff, M, Marshall, JC, and Vincent, JL. Biomarkers of sepsis: time for a reappraisal. Crit Care. (2020) 24:287. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02993-5
29. De, AK, Kodys, KM, Yeh, BS, and Miller-Graziano, C. Exaggerated human monocyte IL-10 concomitant to minimal TNF-alpha induction by heat-shock protein 27 (Hsp27) suggests Hsp27 is primarily an anti-inflammatory stimulus. J Immunol. (2000) 165:3951–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.7.3951
30. Shi, P, Wu, J, Li, M, Cao, Y, Wu, J, Ren, P, et al. Upregulation of Hsp27 via further inhibition of histone H2A ubiquitination confers protection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by promoting glycolysis and enhancing mitochondrial function. Cell Death Discov. (2023) 9:466. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01762-x
31. You, W, Min, X, Zhang, X, Qian, B, Pang, S, Ding, Z, et al. Cardiac-specific expression of heat shock protein 27 attenuated endotoxin-induced cardiac dysfunction and mortality in mice through a PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism. Shock. (2009) 32:108–17. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e318199165d
Keywords: HSP27, sepsis, prognosis, infection, inflammatory
Citation: Yao L, Fan Z, Yao F and Wang X (2025) Prognostic value of HSP27 in 28-day mortality in septic ICU patients: a retrospective cohort study. Front. Med. 11:1513788. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1513788
Edited by:
Alessandro Perrella, Hospital of the Hills, ItalyReviewed by:
Pauline Yeung Ng, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaHéctor Flores-Herrera, Instituto Nacional de Perinatología (INPER), Mexico
Copyright © 2025 Yao, Fan, Yao and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaozhong Wang, d2FuZ3hpYW96aG9uZ0BuY3UuZWR1LmNu; Fangyi Yao, NTExMTY3MTIwQHFxLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Lihua Yao
Lihua Yao Zaiwei Fan3†
Zaiwei Fan3†