
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CASE REPORT article
Front. Med. , 22 June 2023
Sec. Gastroenterology
Volume 10 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2023.1198378
Visceral artery pseudoaneurysm is a rare disease that most commonly occurs in male patients in their 50s, with gastroduodenal artery (GDA) pseudoaneurysm accounting for only 1.5% of these. The treatment options generally include open surgery and endovascular treatment. In 40 cases of GDA pseudoaneurysm from 2001 to 2022, endovascular therapy was the mainstay of treatment in 30 cases, and most of them (77%) were treated by coil embolization. Our case report describes a 76-year-old female patient with a GDA pseudoaneurysm, which was treated by endovascular embolization using liquid embolic agent N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate (NBCA) alone. This is the first time this treatment strategy has been used for GDA pseudoaneurysm. We demonstrate a successful outcome with this unique treatment. The successful experience of our case may provide a new treatment strategy for this rare disease.
Visceral artery aneurysm, including true aneurysm and pseudoaneurysm, is a rare disease, with an incidence of 0.01–0.2% (1). A true aneurysm is the dilation of all three layers of the vessel wall and is often caused by atherosclerosis as well as hypertension (2). A pseudoaneurysm is blood accumulation surrounded by fibrous tissue, whose etiologies are inflammation, vasculitis, iatrogenic trauma, or infection resulting in blood extravasation via this damage into the space between the tunica media and tunica adventitia (3). There is usually a periarterial hematoma surrounding the pseudoaneurysm (4).
The most frequent sites of visceral artery aneurysm, in the order of the most to least common, are the splenic (60%), hepatic (20%), and superior mesenteric arteries (5.5%), with the gastroduodenal artery accounting for only 1.5% of cases (3). Traditionally, the treatment of visceral artery aneurysm is via open surgery. However, in the last two decades, endovascular treatment has become the mainstay therapy in hemodynamically stable patients, with coil embolization being the most commonly used endovascular therapy. In this case report, we present a special case of duodenal obstruction caused by GDA pseudoaneurysm and an associated intramural hematoma. We used the liquid embolic agent NBCA, a unique treatment strategy, as our means of endovascular therapy and achieved a successful outcome. A review of relevant medical literature about GDA pseudoaneurysm in the last two decades is also presented in this case report.
A 76-year-old female with past histories of a gastric ulcer, chronic superficial gastritis, and morbid obesity came to the emergency department due to fever with abdominal pain for 1 day. The abdominal pain was dull, localized, and persistent in character. Associated symptoms included nausea and vomiting with food content. The patient did not have diarrhea, tarry stool, or bloody stool. The physical examination showed that the abdomen was mildly distended and that there was upper abdominal tenderness. The laboratory findings revealed leukocytosis of 21,700/μL, elevated C-reactive protein level of 123 mg/L, anemia with hemoglobin level of 8.4 g/dL, and electrolyte disturbance with hypokalemia of 3.1 mEq/L. Due to the above findings, intra-abdominal infection was initially suspected. Therefore, contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) of the lower chest, abdomen, and pelvis was performed. The CT incidentally demonstrated a pseudoaneurysm with a large intramural hematoma up to 8.8 cm at the second portion of the duodenal wall, the large hematoma compress the duodenal lumen and therefore cause the distention of stomach and esophagus (Figures 1A–C). After discussion with gastroenterologists and general surgeons, transarterial embolization (TAE) for pseudoaneurysm was indicated. The angiography revealed that the pseudoaneurysm originated from the side branch of the proximal gastroduodenal artery (GDA) (Figure 2A), and embolization of both the pseudoaneurysm (Figure 2B) and feeding artery was performed using N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate (NBCA), one kind of liquid embolic agent.
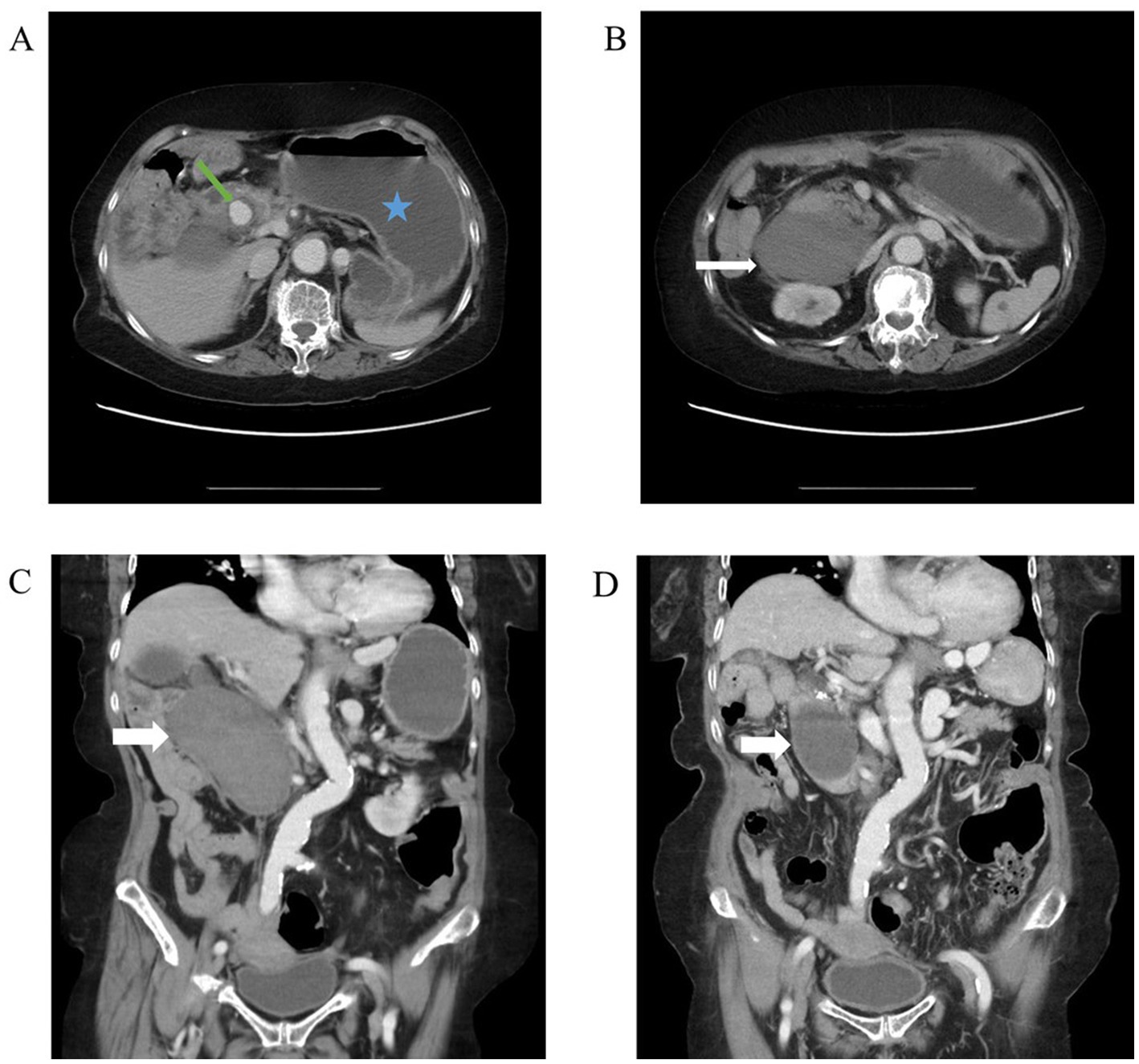
Figure 1. Abdominal CT. (A) Axial view of abdominal CT revealed a distended abdomen (blue star) and an enhanced circular lesion around duodenal second portion (green arrow). Due to its location corresponding to gastroduodenal artery, it was more likely to be a pseudoaneurysm than a true aneurysm. (B) Axial view of abdominal CT revealed large, non-enhanced mass (white arrow). Given the patient’s hemodynamic stability and absence of signs for gastrointestinal bleeding, it was likely to be an intramural hematoma. (C) Coronal view of abdominal CT showed large intramural hematoma (white arrow). (D) Coronal view of abdominal CT 3 months after transarterial embolization (TAE) revealed shrinkage of the hematoma (white arrow).
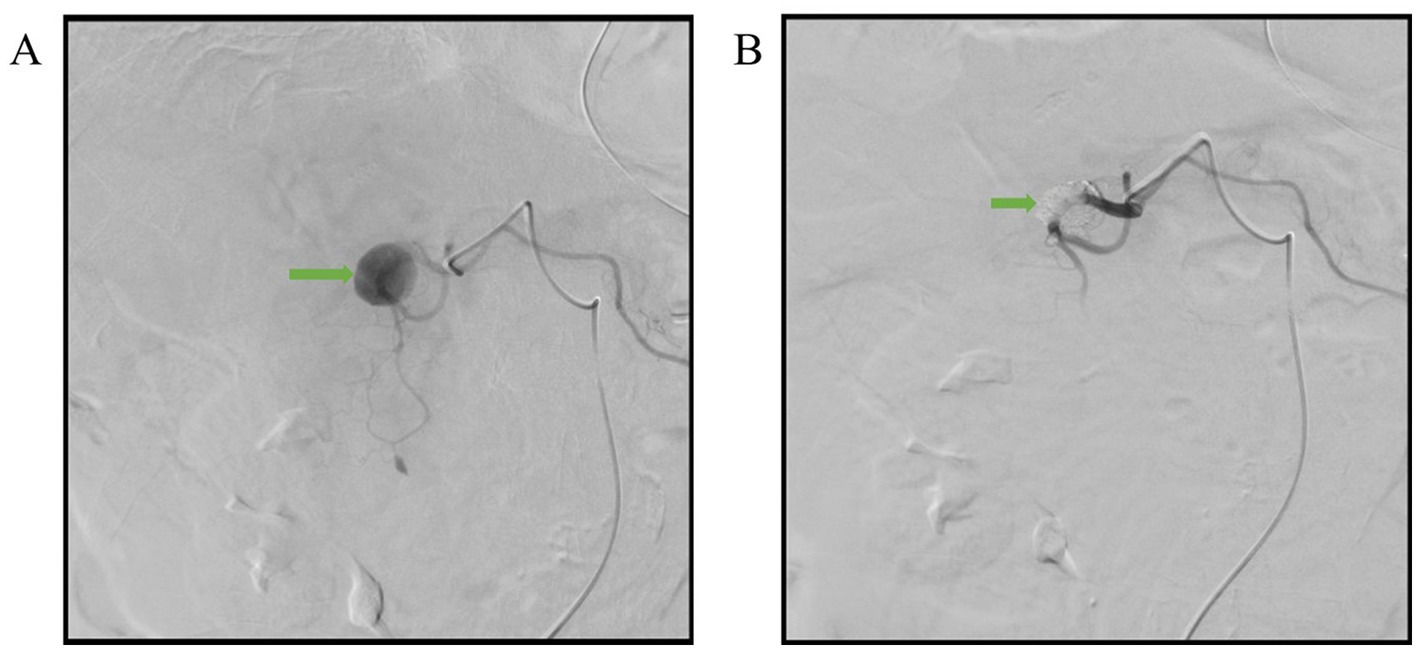
Figure 2. Angiographic images. (A) The pseudoanuerysm (arrow) originated from the side branch of proximal gastroduodenal artery. (B) Complete embolization of the pseudoaneurysm (arrow) with NBCA.
After TAE, the patient’s condition was stable. The patient was initially fasted except for water and underwent nasogastric tube decompression. Intravenous fluid resuscitation, an antibiotic for infection control, and lansoprazole for long-term gastric ulcer were also given. On day 5 of admission, we placed a nasoduodenal (ND) tube under endoscopic guidance for feeding of nutritional supplements (Figure 3). On day 14 of admission, the patient started to try oral ingestion in addition to ND tube feeding, which was completed smoothly. Hence, she was discharged on day 15. One month after discharge, the patient recovered well when followed-up in the outpatient clinic. Three months after TAE, the follow-up CT image revealed shrinkage of the hematoma to 5.7 cm (Figure 1D).
Visceral artery pseudoaneurysm is a rare disease which most often occur in middle-aged people between 50 and 58 years old, with a male predominance of a male:female ratio of 4.5:1 (5). The age of our patient (76 years old) is older than the usual age of onset, and the female gender of our case is also unique in this male predominant disease. In visceral arteries, generally true aneurysm is more common than pseudoaneurysm. However, in gastroduodenal, pancreaticoduodenal, and superior mesenteric arteries, it is the pseudoaneurysm more frequent (6).
In gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm, the most common causes are pancreatitis (47%), followed by ethanol abuse (25%), and peptic ulcer disease (17%) (5). There are also several cases of GDA pseudoaneurysm appearing several days, weeks, months, or even 1–3 years after surgery or other invasive procedures (7–19). Due to past histories of gastric ulcer, it is likely that peptic ulcer disease is the cause of GDA pseudoaneurysm in our patient.
When a GDA pseudoaneurysm is unruptured, common presentations are abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting resulting from compression of gastrointestinal tract, as in our case. Moreover, due to the proximity between GDA and the bile duct, a GDA pseudoaneurysm or its associated hematoma can also compress the bile duct and result in obstructive jaundice (20–22). There is even a case of duodenal necrosis from compression by a GDA pseudoaneurysm (23). Also, rare presentations of hyperamylasemia (24) and midline back soreness (25) are reported. When a GDA pseudoaneurysm ruptures, it has a mortality of 40% (5). If a GDA pseudoaneurysm ruptures into the duodenum, the clinical presentations are signs of upper gastrointestinal bleeding such as hematemesis and melena (5). There are also cases the pseudoaneurysm rupture into pancreatic duct and bile duct, leading to hemosuccus pancreaticus (26–28) and hemobilia (16), respectively.
The most frequent imaging modality to detect pseudoaneurysms is CT angiography (CTA), which revealed a contrast filled sac (4). However, the gold standard for diagnosing pseudoaneurysms is digital subtraction angiography (DSA), which is mainly used in conditions when a pseudoaneurysm is highly suspected clinically but is not seen in CTA (4). The pseudoaneurysm appear to be more irregular than true aneurysm, and it also has features of eccentric thrombosis, eccentric location, and saccular in shape (4). Sometimes, it may be difficult to distinguish between a pseudoaneurysm and true aneurysm in imaging (4).
In true aneurysms of visceral arteries, the indications of treatment are symptomatic, size greater than 2 cm, growth rate exceeding 0.5 cm per year, or in women of childbearing age. In pseudoaneurysms, however, regardless of size, all should be managed as soon as possible once detected (29). The reason is that pseudoaneurysms can rupture more easily than true aneurysms (76.3% vs. 3.1%) (6). GDA pseudoaneurysm has a 75% incidence of rupture (30).
Generally, the treatment options for visceral artery aneurysm include open surgery and minimally invasive endovascular treatment. Open surgery is indicated when the patient’s vital signs are unstable or when endovascular treatment has failed (5). It typically involves ligation of arteries proximal and distal to the aneurysm, aneurysmectomy, and reestablishment of vascular network or end organ resection depending on the collateral circulation of the organ as well as the aneurysm location (31). When the patient is hemodynamically stable, with multiple comorbidities, or previous abdominal surgery with possible intraperitoneal adhesion, endovascular treatment is the treatment of choice. Endovascular treatment has advantages of minimal invasiveness, lower morbidity, and better quality of life (32). The endovascular treatments exclude the aneurysm from the circulation and include coil embolization, liquid embolic agents (e.g., NBCA), and stent placement (33). Which endovascular techniques are being performed depends on anatomical factors. Coil embolization is the most commonly used endovascular treatment. It involves embolization of aneurysm as well as proximal and distal arteries, with a potential complication of coil migration when used in large saccular aneurysm or when there is infection, inflammation, or malignancy around the pseudoaneurysm (31, 32, 34). Embolization with liquid embolic agents carries the risk of distal embolization and is therefore more technically challenging. It can be used when the aneurysm is in the terminal branch of arteries or when the vessels are too small and tortuous for coil embolization (31, 35). Stent placement requires adequate vessel length and minimal vessel tortuosity, carrying a risk of stent thrombosis, and is only considered when flow through the artery is essential (32). Our patient was hemodynamically stable in the emergency department. Also, the pseudoaneurysm was in the terminal branch of the gastroduodenal artery. Hence, endovascular therapy using liquid embolic agent NBCA is a reasonable treatment option.
In addition to open surgery and endovascular treatment, there are other treatment options including percutaneous and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) approaches. Percutaneous thrombin injection is used when the pseudoaneurysm cannot be accessed by endovascular means (4). It involves direct injection of thrombin into the pseudoaneurysm under ultrasound, CT, or fluoroscopy guidance, resulting in thrombosis of the pseudoaneurysm (29). The drawback of this technique is that thrombin is not radiopaque and hence may cause undetectable distal embolization. An endoscopic ultrasound approach is only used when the pseudoaneurysm can be detected on EUS, and thrombin or other embolic agents are injected into the pseudoaneurysm under EUS guidance (4). Also, using over-the-scope-clip to treat active bleeding from GDA pseudoaneurysm has also been reported (36).
The society for vascular surgery published a clinical practice guideline on the management of visceral artery aneurysms in 2020. For the gastroduodenal artery, there is a strong recommendation for using coli embolization whether the aneurysm is ruptured or unruptured (35). As for the liquid embolic agent used in our case, it is weakly recommended in the guideline (35). This is consistent with the literature in the last two decades. In the medical literature regarding GDA pseudoaneurysms from 2001 to 2022, there are 30 cases that have been treated with endovascular embolization, 5 cases treated with open surgery, 2 cases treated with percutaneous embolization, 1 case treated with EUS-guided embolization, and 2 cases without any treatment (Table 1). These treatment strategies were all successful except for 2 failed cases in endovascular embolization (case 11 and case 23). Both initially presented with hypovolemic shock and subsequently managed successfully with open surgery. The success rate of endovascular therapy is comparable to open surgery (93.3% vs. 100%). Among the 30 cases of endovascular embolization, 23 cases are managed with coil embolization, 2 cases with stent placement, 3 cases with liquid embolic agent NBCA combined with coil embolization, 1 case with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) particles, and 1 case with an unknown endovascular method. To the best of our knowledge, there was no patient of GDA pseudoaneurysm treated with liquid embolic agent NBCA alone. However, we demonstrated such a successful case using NBCA alone in the elder female patient with GDA pseudoaneurysm.
In general, GDA pseudoaneurysm is an uncommon disease that should be managed as soon as possible given the high risk of rupture. Endovascular therapy with coil embolization is the most recommended treatment in the hemodynamic stable patient with such a condition. However, we present a case of GDA pseudoaneurym managed with endovascular embolization using liquid embolic agent NBCA alone, a treatment strategy that has not been used in such a condition. The successful experience of our case may provide a new treatment strategy in patients with GDA pseudoaneurysm.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Written informed consent was obtained from the participant/patient(s) for the publication of this case report.
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work and approved it for publication.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. George, J, Besant, S, Cleveland, T, and Al-Mukhtar, A. Pseudoaneurysm of the inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery due to cholecystitis. Reports. (2019) 2:11. doi: 10.3390/reports2010011
2. Sant’Anna, CV, Kuhl, FG, Leite, AM, De Oliveira Raymundo, SR, Miquelin, AR, Acar, V, et al. Ruptured ileocolic artery pseudoaneurysm: case report. J Vasc Bras. (2021) 20:e20210163. doi: 10.1590/1677-5449.210163
3. Chapman, BM, Bolton, JS, Gioe, SM, and Conway, WC. Gastroduodenal artery Pseudoaneurysm causing obstructive jaundice. Ochsner J. (2021) 21:104–7. doi: 10.31486/toj.19.0110
4. Madhusudhan, KS, Venkatesh, HA, Gamanagatti, S, Garg, P, and Srivastava, DN. Interventional radiology in the Management of Visceral Artery Pseudoaneurysms: a review of techniques and embolic materials. Korean J Radiol. (2016) 17:351–63. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2016.17.3.351
5. Habib, N, Hassan, S, Abdou, R, Torbey, E, Alkaied, H, Maniatis, T, et al. Gastroduodenal artery aneurysm, diagnosis, clinical presentation and management: a concise review. Ann Surg Innov Res. (2013) 7:4. doi: 10.1186/1750-1164-7-4
6. Saran, M, and Biswas, S. A rare case of Jejunal Pseudoaneurysm presenting as acute small bowel obstruction after blunt trauma: discussion, management dilemmas, and a review of relevant literature. Cureus. (2019) 11:e5655. doi: 10.7759/cureus.5655
7. Santos-Rancano, R, Antona, EM, and Montero, JV. A challenging case of a large gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm after surgery of a peptic ulcer. Case Rep Surg. (2015) 2015:370937. doi: 10.1155/2015/370937
8. João, M, Alves, S, Carvalheiro, V, and Areia, M. An astounding percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy complication: a pseudoaneurysm of gastroduodenal artery. GE Port J Gastroenterol. (2021) 28:294–6. doi: 10.1159/000511463
9. Stravodimos, G, Komporozos, V, and Papazoglou, A. Case report of a successful non-operative management of postoperative bleeding from pseudoaneurysm of the gastroduodenal artery, following gastric surgery. Int J Surg Case Rep. (2021) 78:54–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2020.11.157
10. Miyazawa, R, Kamo, M, Nishiyama, T, Ohigashi, S, and Yagihashi, K. Covered stent placement using "pull-through" technique for a gastroduodenal artery stump Pseudoaneurysm after pancreaticoduodenectomy. J Vasc Interv Radiol. (2016) 27:1743–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2016.06.033
11. Zarin, M, Ali, S, Majid, A, and Jan, ZU. Gastroduodenal artery aneurysm–post traumatic pancreatic pseudocyst drainage–an interesting case. Int J Surg Case Rep. (2018) 42:82–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2017.11.049
12. Kunitomo, A, Misawa, K, Sato, Y, Ito, Y, Ito, S, Hosoi, T, et al. Gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm hemorrhage 1 year after laparoscopic distal gastrectomy: a case report. Surg Case Rep. (2020) 6:38. doi: 10.1186/s40792-020-00802-3
13. Awada, Z, Al Moussawi, H, and Alsheikh, M. Gastroduodenal artery Pseudoaneurysm rupture post-Billroth II surgery: case report. Cureus. (2019) 11:e3833. doi: 10.7759/cureus.3833
14. Young, R, Gagandeep, S, Grant, E, Palmer, S, Mateo, R, Selby, R, et al. Gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm secondary to pancreatic head biopsy. J Ultrasound Med. (2004) 23:997–1001. doi: 10.7863/jum.2004.23.7.997
15. Phelps, TN, Maloney, TG, and Cura, M. Hemorrhagic gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm coil embolization. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). (2019) 32:552–3. doi: 10.1080/08998280.2019.1646596
16. Kurniawan, K, Wibawa, IDN, Somayana, G, Mariadi, IK, and Mulyawan, IM. Massive hemobilia caused by rupture of gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm, a delayed complication of laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a case report. J Med Case Rep. (2021) 15:331. doi: 10.1186/s13256-021-02915-1
17. Kim, DY, Joo, JK, Ryu, SY, Kim, YJ, Kim, SK, and Jung, YY. Pseudoaneurysm of gastroduodenal artery following radical gastrectomy for gastric carcinoma patients. World J Gastroenterol. (2003) 9:2878–9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i12.2878
18. Loveček, M, Havlík, R, Köcher, M, Vomáčková, K, and Neoral, C. Pseudoaneurysm of the gastroduodenal artery following pancreatoduodenectomy. Stenting for hemorrhage. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. (2014) 9:297–301. doi: 10.5114/wiitm.2011.38178
19. Macedo, C, Gravito-Soares, E, and Gravito-Soares, M. Pseudoaneurysm of the gastroduodenal artery with arterio-duodenal fistulization secondary to acute pancreatitis: an unusual endoscopic diagnosis. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. (2021) 113:72–3. doi: 10.17235/reed.2020.7070/2020
20. Casas Deza, D, Gotor Delso, J, Gascón Ruiz, M, Bernal Monterde, V, Jimeno Ayllón, C, Gracia Ruiz, M, et al. Bile duct obstruction secondary to a pseudoaneurysm of the gastroduodenal artery. An unusual presentation. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. (2019) 42:384–6. doi: 10.1016/j.gastrohep.2018.07.002
21. Kossak, J, Janik, J, Debski, J, Rytlewski, R, and Sałaciński, A. Pseudoaneurysm of the gastroduodenal artery as a cause of obstructive jaundice. Med Sci Monit. (2001) 7:759–61.
22. Shell, M, Reinhart, E, Smith, S, DeMarris, D, and Naumann, C. Successful minimally invasive management of a gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm causing extrinsic bile duct compression. ACG Case Rep J. (2021) 8:e00663. doi: 10.14309/crj.0000000000000663
23. Chen, X, Ge, J, Zhao, J, Yuan, D, Yang, Y, and Huang, B. Duodenal necrosis associated with a threatened ruptured gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm complicated by chronic pancreatitis: case report. Ann Vasc Surg. (2020) 68:571.e9–571.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2020.04.050
24. Galanakis, V. Pseudoaneurysm of the gastroduodenal artery: an unusual cause for hyperamylasaemia. BMJ Case Rep. (2018) 2018:223882. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-223882
25. Huang, CF, Liu, YT, Wu, YC, Bai, YM, Yeh, YH, and Hung, TY. Spontaneous pseudoaneurysm rupture of gastroduodenal artery: a rare and life-threatening condition of back pain. J Formos Med Assoc. (2014) 113:756–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2012.08.019
26. Saqib, NU, Ray, HM, al Rstum, Z, DuBose, JJ, Azizzadeh, A, and Safi, HJ. Coil embolization of a ruptured gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm presenting with hemosuccus pancreaticus. J Vasc Surg Cases Innov Tech. (2020) 6:67–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jvscit.2019.11.014
27. Cui, HY, Jiang, CH, Dong, J, Wen, Y, and Chen, YW. Hemosuccus pancreaticus caused by gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm associated with chronic pancreatitis: a case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases. (2021) 9:236–44. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i1.236
28. Lacey, SR, and Chak, A. Hemosuccus pancreaticus: dorsal pancreatic duct stone and gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm. Gastrointest Endosc. (2001) 54:363. doi: 10.1067/mge.2001.116901
29. Hemp, JH, and Sabri, SS. Endovascular management of visceral arterial aneurysms. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. (2015) 18:14–23. doi: 10.1053/j.tvir.2014.12.003
30. Chang, D, Patel, P, Persky, S, Ng, J, and Kaell, A. Management of gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm rupture with duodenal ulcer complicated by coil migration. ACG Case Rep J. (2020) 7:e00347. doi: 10.14309/crj.0000000000000347
31. Obara, H, Kentaro, M, Inoue, M, and Kitagawa, Y. Current management strategies for visceral artery aneurysms: an overview. Surg Today. (2020) 50:38–49. doi: 10.1007/s00595-019-01898-3
32. Cordova, AC, and Sumpio, BE. Visceral artery aneurysms and Pseudoaneurysms-should they all be managed by endovascular techniques? Ann Vasc Dis. (2013) 6:687–93. doi: 10.3400/avd.ra.13-00045
33. Barbiero, G, Battistel, M, Susac, A, and Miotto, D. Percutaneous thrombin embolization of a pancreatico-duodenal artery pseudoaneurysm after failing of the endovascular treatment. World J Radiol. (2014) 6:629–35. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i8.629
34. Choi, J, and Kim, YM. A rare case of coil migration into the duodenum after embolization of a right colic artery Pseudoaneurysm. Clin Endosc. (2021) 54:920–3. doi: 10.5946/ce.2020.228
35. Chaer, RA, Abularrage, CJ, Coleman, DM, Eslami, MH, Kashyap, VS, Rockman, C, et al. The society for vascular surgery clinical practice guidelines on the management of visceral aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. (2020) 72:3S–39S. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2020.01.039
36. el Douaihy, Y, Kesavan, M, Deeb, L, Abergel, J, and Andrawes, S. Over-the-scope clip to the rescue of a bleeding gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm. Gastrointest Endosc. (2016) 84:854–5. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2016.05.043
37. Sharma, M, Somani, P, Sunkara, T, Prajapati, R, and Talele, R. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided coil embolization and thrombin injection of a bleeding gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm. Endoscopy. (2019) 51:E36–7. doi: 10.1055/a-0790-8134
38. Budzynski, J, Meder, G, and Suppan, K. Giant gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm as a pancreatic tumor and cause of acute bleeding into the digestive tract. Prz Gastroenterol. (2016) 4:299–301. doi: 10.5114/pg.2016.61478
39. Suzuki, T, Ishida, H, Komatsuda, T, Oyaké, J, Miyauchi, T, Heianna, J, et al. Pseudoaneurysm of the gastroduodenal artery ruptured into the superior mesenteric vein in a patient with chronic pancreatitis. J Clin Ultrasound. (2003) 31:278–82. doi: 10.1002/jcu.10170
40. Sinduja, R, Vijayakumar, C, Sudharshan, M, Kumbhar, US, Naik, BM, and Naik, D. Pseudoaneurysm of the gastroduodenal artery secondary to diverticulitis of the first part of duodenum: a rare presentation of upper gastrointestinal bleed. BMJ Case Rep. (2021) 14:e238232. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-238232
41. Volpi, MA, Voliovici, E, Pinato, F, Sciuto, F, Figoli, L, Diamant, M, et al. Pseudoaneurysm of the gastroduodenal artery secondary to chronic pancreatitis. Ann Vasc Surg. (2010) 24:1136.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2010.03.034
42. Nouira, K, Nouira, Y, Yahmed, AB, Bedioui, H, Abid, HB, and Menif, E. Spontaneous false aneurysm of the gastroduodenal artery in a hemophilic patient ruptured into the duodenum: case report. Abdom Imaging. (2006) 31:43–4. doi: 10.1007/s00261-005-0352-2
43. Kohama, K, Ito, Y, Kai, T, Kotani, J, and Nakao, A. Successfully treated life-threatening upper gastrointestinal bleeding from fistula between gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm and duodenum. Acute Med Surg. (2016) 3:192–4. doi: 10.1002/ams2.157
44. Elazary, R, Abu-Gazala, M, Schlager, A, Shussman, N, Rivkind, AI, and Bloom, AI. Therapeutic angiography for giant bleeding gastro-duodenal artery pseudoaneurysm. World J Gastroenterol. (2010) 16:1670–2. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i13.1670
45. Ahmed, G, Abid, M, Hosmane, S, and Mathew, S. Unusual case of upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage secondary to a ruptured gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm: case presentation and literature review. BMJ Case Rep. (2020) 13:e236463. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-236463
46. Singh, O, Gupta, SS, Raikwar, RS, Shukla, S, and Mathur, RK. A rare case of 'spontaneous rupture of partially thrombosed pseudoaneurysm of gastroduodenal artery associated with chronic pancreatitis'. Indian J Surg. (2009) 71:282–3. doi: 10.1007/s12262-009-0070-z
47. Shrestha, A, Shrestha, A, and Ghimire, B. A ruptured pseudoaneurysm of an anomalous gastroduodenal artery: a rare presentation. Cureus. (2021) 13:e14899. doi: 10.7759/cureus.14899
48. Smith, ZT, Johnston, G, and Morris, CS. Gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm and chronic superior mesenteric vein thrombosis treated with transcatheter embolization and stent dilatation, respectively: 7 year clinical and imaging follow-up. Radiol Case Rep. (2022) 17:1013–20. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2022.01.013
49. Lim, SG, Park, SE, Nam, IC, Choi, HC, Won, JH, Jo, SH, et al. Large gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm, arterioportal fistula and portal vein stenosis in chronic pancreatitis treated using combined transarterial embolization and transportal stenting: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). (2022) 101:e32593. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032593
50. Leow, VM, Siam, F, Saravanan, K, Murbita, SB, Krishnan, R, and Harjit, S. Management of bleeding pseudoaneurysm of gastroduodenal artery secondary to chronic pancreatitis. Med J Malaysia. (2013) 68:271–2.
51. Geoghegan, T, Tuite, D, McAuley, G, O’Keeffe, S, and Torreggiani, WC. Percutaneous thrombin injection for the treatment of a post-pancreatitis pseudoaneurysm of the gastroduodenal artery. Eur Radiol. (2004) 14:2144–5. doi: 10.1007/s00330-004-2399-9
52. Sgantzou, IK, Samara, AA, Diamantis, A, Karagiorgas, GP, Zacharoulis, D, and Rountas, C. Pseudoaneurysm of gastroduodenal artery and pulmonary embolism: rare co-incidence of two complications of pancreatitis. J Surg Case Rep. (2020) 2020:rjz407. doi: 10.1093/jscr/rjz407
Keywords: duodenal obstruction, gastroduodenal artery, pseudoaneurysm, transarterial embolization, liquid embolic agent, case report
Citation: Zhou Y-Y, Wang S-C, Seak C-J, Huang S-W and Cheng H-T (2023) Case report: Duodenal obstruction caused by gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm with hematoma: an unusual case and literature review. Front. Med. 10:1198378. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1198378
Received: 01 April 2023; Accepted: 30 May 2023;
Published: 22 June 2023.
Edited by:
Antonietta G. Gravina, University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, ItalyReviewed by:
Akira Umemura, Iwate Medical University, JapanCopyright © 2023 Zhou, Wang, Seak, Huang and Cheng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hao-Tsai Cheng, aGF1dGFpQGFkbS5jZ21oLm9yZy50dw==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.