
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
MINI REVIEW article
Front. Med., 26 May 2021
Sec. Nephrology
Volume 8 - 2021 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2021.666973
This article is part of the Research TopicImmune Landscape of Kidney PathologyView all 23 articles
COVID-19 pandemic has been a major global issue, its eventual influences on the population welfare, global markets, public security, and everyday activities remain uncertain. Indeed, the pandemic has arisen a significant global threat. Its psychological impact is predicted to be severe and enduring, but the absolute magnitude is still largely unclear. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a complication markedly contributes to the mortality of COVID-19 cases, meanwhile several studies have demonstrated the high frequency and seriousness of the COVID-19 in CKD patients receiving dialysis. Importantly, the influence of COVID-19 among CKD patients without dialysis is still largely unexplored. Thus, we systemically summarized how mental health affects the spreading of COVID-19 to virtually worldwide, covering perspectives from several countries across a wide range of fields and clinical contexts. This review aims to provide the latest details and reveal potential concerns on the public health including psychological well-being of the older patients with CKD.
Psychological well-being (PWB) is fundamentally equivalent to other phrases that apply to desirable psychological operations, including pleasure or fulfillment. It is not essential or valuable to consider the fundamental differences between all these phrases (1). Psychological well-being means being on good terms with others and leading a purposeful and meaningful life (2). It was found that people with positive psychological well-being are more carefree and enjoy a more vibrant and comfortable life (3). However, nearly 25% of people with chronic conditions experienced psychological problems related to COVID-19, particularly CKD patients (4, 5). Currently, personalized treatment should be the norm in handling CKD patients (6–10). Because of COVID-19, it seems to be far more critical that this approach be pursued to minimize the possibility of excessive or insufficient treatment and reduce the likelihood of developing a prejudice (11). This applies to COVID-19 as people's psychological well-being experienced the most significant impact during the pandemic. The ones with stable psychological well-being were in a better state than those whose well-being was below par (3). As there have been constant interruptions to everyday life owing to social distancing, which has been imposed to minimize the transmission of COVID-19, precedent hazards to public mental health were observed (12). The risk of COVID-19 severe complications and poor prognosis is higher for CKD patients, particularly those who undergo chronic dialysis therapy, including higher rates of hospitalization, intensive-care unit admission, mechanical ventilation, and death (13). The well-being of patients has been a significant issue during the pandemic considering the mental effects on even ordinary healthy people were more critical than expected (14). Hence, the impact on the psychological well-being of older CKD patients will be studied.
The findings of the research conducted by Moreno et al. (15) are diverse (Table 1), possibly due to variations in the methodology adopted, the venues of the analysis, and the fact that the research takes place during the pandemic. Possible consequences of modifications to health resources on accessibility and reliability and performance of psychiatric services throughout the COVID-19 pandemic (16). Phobic anxiety, impulse purchase, and television addiction, all linked to psychological disruptions, insomnia, exhaustion, and consciousness deterioration, have been documented, and digital networking has been linked to heightened anxiety and depression-associated anxiety (17–19).
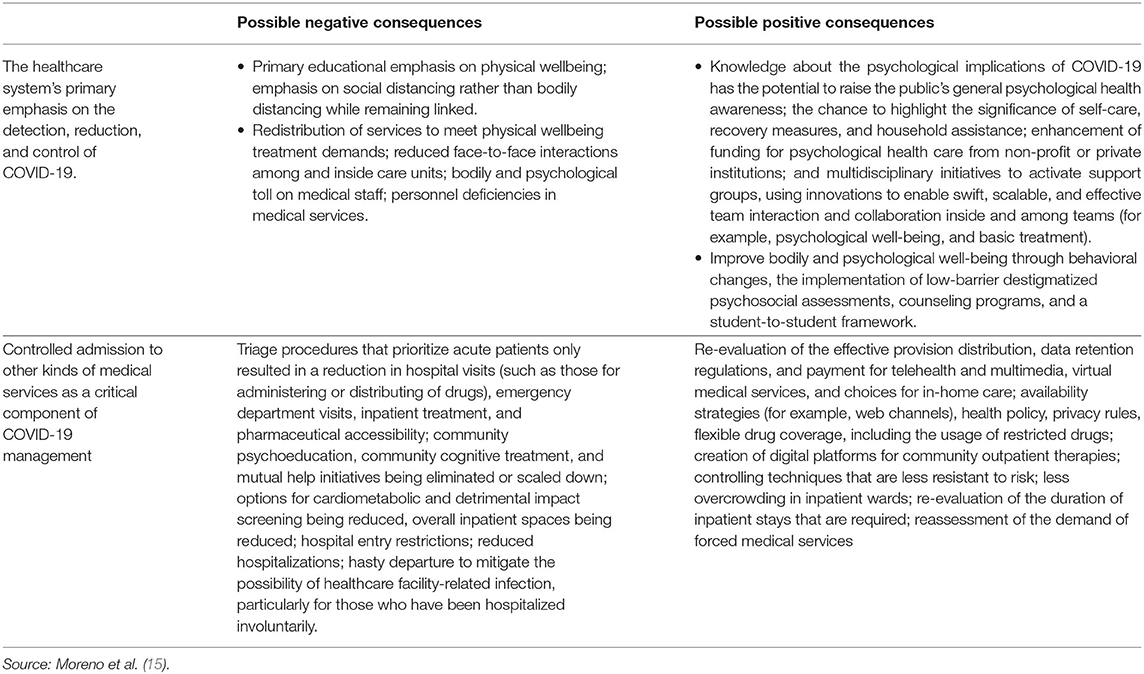
Table 1. Implications for medical resources changes on availability, efficiency, and output of psychological treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The illustration (Table 1) shows the possible effects of modifications to health resources on psychiatric services throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. It further describes the reliability and impact of these adjustments in resources amid the COVID-19 pandemic (13). Numerous people worldwide are now feeling stress and paranoia, particularly the elderly or people with existing health issues and even active and energetic youths. The anxiety is about the novel coronavirus, which the technical term is severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) (20). This hideous virus induces a lethal respiratory condition known COVID-19, which brings fever, severe chest infections, and breathlessness (occasional lack of taste and smell or digestive troubles). COVID-19 is a disease that can escalate quickly; in certain instances, it can be fatal (21). Therefore, the psychological well-being of CKD patients during the period of COVID-19 should be concerned. The current situation is difficult for everyone in public, particularly for the older people who are existing mental health issues; such as anxiety and depression-associated anxiety that are more vulnerable to major medical problems related to coronavirus infection and the emergence of COVID-19 pulmonary disease with possibly catastrophic results (22).
Lockdown may also lead to pressure, resentment, and intensified harmful activities like internet gambling. In earlier outbreaks, the older person affected by lockdown had a higher likelihood of experiencing psychological problems and sorrow (23, 24). It has been observed that the number of elderly resorting to counseling services because of psychological distress has increased (25, 26). Local personal networks and experiences with other inhabitants, relatives, and caregivers due to isolation could also contribute to depression, immobility, and an inactive lifestyle among citizens, adding to their solitude. Solitude as well as social alienation have been associated with worse psychological health (for example, stress, despair, and neurological damage) along with the reduced quality of life (for example, weaker motor control, poorer heart health, sleep disturbance, and loss of strength) and increased death rates. Forced alienation may very well contribute to an inactive lifestyle, yet a person's lifestyle is crucial to reducing physical, mental, and societal medical issues (27, 28).
Based on current evidence from past disease outbreaks and new data from the recent episode, it is anticipated that mental morbidity will eventually increase. Also, such morbidity may escalate afterward and last longer than the external harmful effects of the outbreak (29). Such a pattern is shown in various aspects throughout this edition, which states that the initial stages of the epidemic did not automatically trigger a rise in psychological well-being sessions. Nevertheless, transition to the current constraints introduced by COVID-19 has added burdens to the field of psychological well-being (30). Moreover, the predicted rise in psychiatric illness, which could lead to more suicidal behavior, is more likely to emerge during and after the outbreak, as the financial crisis, local mental health services, human weaknesses, and the harsh truth of radically transformed habits converge (31).
The World Health Organization states that the global transmission of COVID-19 is accelerated bit by bit. As shown by the data updated on 18 February 2020, the total number of confirmed instances had reached over 72,000, with almost 1,900 coming from China (32). The total number of deaths from COVID-19 is estimated to be more significant since the estimates vary from country to country. Although the virus affects everyone, assuming that all factors are identical, evidence has consistently shown that the death rate is higher among older individuals and people with complications (3, 33). The case fatality rate (CFR) of individuals aged 70 was between 0.3 and 3.5%. These figures are lower than the 8% CFR in patients between 70 and 79 and ~15% in patients over 80 in China. As for Italy, empirical studies indicate the average age of patients dying from COVID-19 was 80, with CFR rising above 70 years of age; 12.5% (34–43), 19.7% (44–53), and 22.7% (over 90) (54). A study found that found the subjects to have obtained COVID-19-related information once in a while from the following channels: online (including sites, online news, and internet networks, such as Facebook and Twitter), acquaintances, traditional media (including television, newspapers, and radio), structured activities on COVID-19 (be it online or face-to-face), medical workers in healthcare environments, colleagues, and families. This research concluded that about 80% of the subjects received COVID-19 information online (55).
Psychological symptoms and illnesses can occur as an adjunct to an unavoidable disease incident. These can appear at an active stage or later in time. The outbreak itself is a traumatic event, but it is significantly more disturbing to work as a medical practitioner to cope with such a severe disease (56). In America, the fatality rate in New York City for patients 75 years old or older was over 1,500 per 100,000 people. Advanced age and complications such as coronary disease, diabetes, chronic lung ailments, and persistent kidney dysfunction tend to increase the dangers of COVID-19. In many more existing patients with renal failure, where the health care system may evaluate employees, The CKD patients should consider the risks of death from COVID-19 in assessing the risks and benefits of treatment options (57).
Controversial expectations, coping with significant shortcomings in the resources for screening and therapy and the protection of patients and health care professionals from infection, the pressure of current overall well-being measures that place restrictions on personal autonomy, tremendous and rising financial troubles, and contradictory instructions from professionals are some of the major factors which would inevitably contribute to endless difficulty and heightened threats of Covid-19-related psychological disorder (58, 59). Healthcare practitioners have a major role in resolving these serious consequences as part of the pandemic response (60, 61).
Wide analysis of poor mental health has proven that tremendous problems are widespread in infected communities, an observation that is likely to be replicated in populations affected by the Covid-19 pandemic. Owing to these challenges, numerous people refuse to give in to therapy. Some individuals have developed new attributes. Considering all factors, in “standard” disastrous incidents, technological failures, and deliberate events of massive destruction, a major concern is post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) arising from exposure to trauma. Contagious illnesses, such as dangerous virus infection, may not follow existing trauma frameworks required to study PTSD, but other psychological issues such as stress and anxiety can arise (62). Several communities could be more vulnerable than others in coping with the psychosocial effects of disease outbreaks. Particularly, people who suffer from the disease, those at increased risk for infection (including the elderly, people with lower resistance, and those residing in community surroundings), and people with prior medical, emotional, or drug use problems are at heightened risk for antagonistic psychosocial outcomes (63).
The COVID-19 pandemic revealed the notorious vulnerability of the monetary system and the overwhelming ramifications for our financial structure should new tactics not be adopted to tailor medical services to specific patient subgroups. The massive group of elderly and feeble people over 65 poses a public health concern. According to the latest data from the Istituto Superiore di Sanità of Italy, COVID-19 tends to be more deadly among elderly patients: 96.4% of deaths were over 60 years of age. People aged 70 or above account for 35.5% of instances as statistics were classified by age level, whereas participants aged over 80 accounts for 52.3%. Patients with renal disease are an elderly group that is especially susceptible to infection and carries a higher risk of death than the average person. The massive group of elderly and feeble people over 65 poses a public health concern. The COVID-19 pandemic revealed the notorious vulnerability of the monetary system and the overwhelming ramifications for our financial structure should new tactics not be adopted to tailor medical services to specific patient subgroups (64).
Given that most patients with CKD are seniors, who experience biological deterioration of renal function and are more vulnerable to renal disease, COVID-19 emerges as a pertinent issue because of the heightened risk of comorbidities and fatality in patients with chronic renal disease (65). Moreover, specific antiviral and immunosuppressive approaches to combat COVID-19 infection have been hampered by severe renal damage. The combination of age and chronic renal disease is most likely a possible cause of COVID-19 in immunosuppressive activity. Immunol senescence is a condition that occurs in older adults and is accompanied by weakened responsive and inherent immune function (66). Numerous changes have occurred, including thymic involution, a reduction in naïve T-cells and progenitor B-cells, and a reduction in the production of MHC class II on macrophages. Among chronic renal disease cases, a significant immunosuppressive condition has been observed as well: (i) diminished granulocyte and monocyte/macrophage phagocytic activity; (ii) reduced antigen-presenting potential of antigen-presenting cells; (iii) loss of antigen-presenting dendritic cells; (iv) weakened B lymphocyte numbers and immune generating ability; (v) reduction in naïve and central memory CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes; (vi) disrupted cell-mediated resistance. Because of such considerations, older CKD patients must fully adhere to the guidelines of the Ministry of Health and Nephrological Scientific Societies for COVID-19 reduction(34–53, 67–92).
Under the outbreak, further attention to be paid to public health, both physical and psychological, to help communities during this challenging period (71–73). The COVID-19 outbreak has brought many extra challenges to the study, planning, and management of health (4, 74, 75). The problems of COVID-19 mental health and bureaucratic responses to the outbreak are not exactly unprecedented. Past mental health deficiencies could become more deep-rooted and considerably more difficult to tackle (76, 77). Evidence from all over the world of shifts in individuals' mental health, possibly attributable to the COVID-19 outbreak, has been hindered by the use of residence assessments, distorted or unverifiable mental health metrics, and the lack of other pre-COVID-19 conventional knowledge to measure the transition, be it among individuals or throughout the whole population (78, 79, 93–95).
One study showed elevated rates of mental illness among US adults in 2020 compared with 2018, and the increase was the most significant among young adults aged between 18 and 24 and females (19). Legislators, politicians, and specialized agencies require accurate information on the shifts in mental health associated with the outbreak so that decisions are backed by knowledge on the extent of transitions in individuals' mental health and vulnerability to psychiatric problems (80). In such a crisis, the ability to track and address psychosocial needs during proper consultation in clinical care is severely constrained by the immense complexity of household regulation. Strategies for telemedicine are given to psychosocial institutions and are increasingly distributed in stimulating environments (81). As far as COVID-19 is concerned, psychosocial evaluation and monitoring may include concerns linked to COVID-19 stress factors (e.g., exposures to infected materials, infected family members, loss of loved ones, and segregation) and further mishaps (e.g., economic hardship) (82, 83).
Psychosocial impacts include depression, stress, psychiatric disturbances, insomnia, heightened drug use and aggressive actions at home, and signs of vulnerability (84) (Table 2), such as previous physical or emotional disorders. Some individuals may need guidance regarding structured psychological health evaluation and treatment. Others benefit from ongoing counseling to enhance health and facilitate adjustment (e.g., psychoeducation or cognitive behavior approaches) (85, 86). Given the increasing financial crisis and the multiple threats of this outbreak, self-destructive thoughts may emerge, which entails a timely meeting with professionals or a recommendation for possible crisis psychiatric hospitalization (87, 88). At the gentler end of the psychosocial spectrum, a large amount of interaction between patients, families, and the wider populace could be better structured by presenting evidence on typical reactions to this form of resistance and by drawing attention to what people can do in the middle of severe circumstances (89, 90).
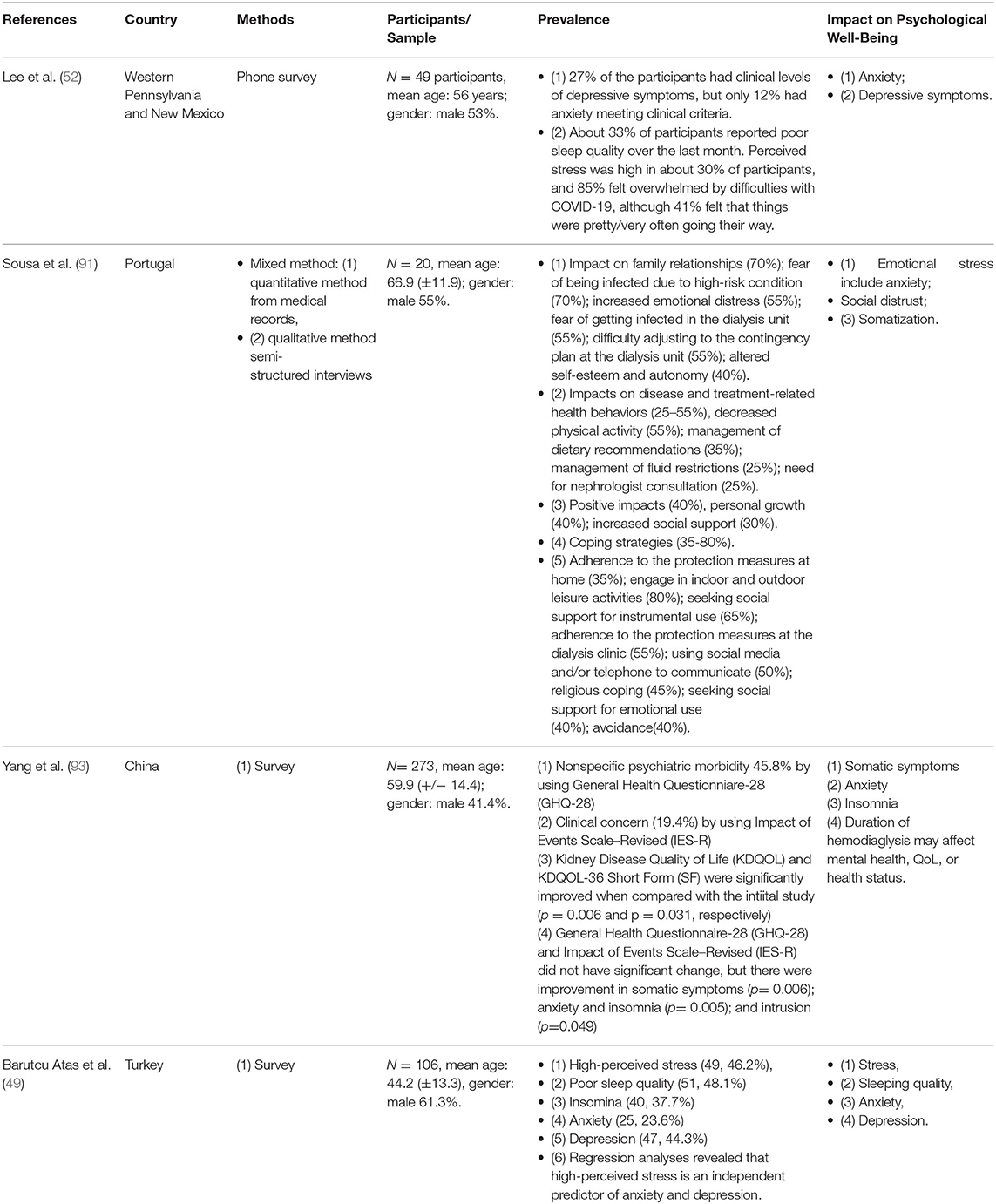
Table 2. Description of studies on older CKD patients negative psychological impact during COVID-19 in the review.
In a multivariable study, Varshney et al. (48) found that advanced age, prolonged illness, the existence of breathing troubles, and absence of community backup have a significant correlation with unusual mental effects of COVID-19 on individuals with chronic disease. Once they need to go outside for provisions, elderly CKD patients and those living on their own become especially susceptible. Throughout the COVID-19 epidemic, numerous CKD patients in the early to later phases of kidney disease might have testing arrangements postponed. Failure to detect significant development of CKD has profound implications for both the patient and the community (Figure 1) (64, 91).

Figure 1. During COVID-19, the phenomenon has a detrimental psychological impact on CKD patients. Source: Coppolino et al. (64) and Varshney et al. (48).
Healthcare practitioners may provide guidelines for mental stress and adjustment (such as planning exercises and timetabling) (92), connect patients with psychosocial health departments, and encourage patients to pursue adequate mental health assistance as needed (34). Nadler et al. (35) noted that because the caregivers typically lessen their children's discomfort, transparent talks should be encouraged to discuss children's reactions and issues. As far as health care providers themselves are concerned, the innovative concept of SARS-CoV-2, preliminary screening, minimal treatment options, insufficient PPE and other medical resources, prolonged unresolved pressures, and other related risks are sources of stress and could potentially overwhelm systems (36, 37). SARS-CoV-2 is spread from humans to humans through direct contact with an infected person via nasal spills or touching contaminated substances. Maturity and chronic illness have been identified as possible causes of severe disease and death (38). Ghinai et al. (39) confirmed that SARS-CoV-2, which resulted in the condition currently known as COVID-19, had been disseminated across China and 26 more countries as of 18 February 2020. Advanced age, being female, extended illness, breathing symptoms, and lack of social support were essentially related to the peculiar mental impact of COVID-19 on patients with renal impairment. Patients aged 34 or older were more likely to suffer from psychiatric disorders due to the recent outbreak (40, 41). This result invalidates an Indian study where young adults encountered more significant psychological problems due to COVID-19. This discrepancy may be attributed to the incorrect assumption that COVID-19 is not as accurate in younger individuals (42, 43).
Self-care offered by providers, like mental healthcare providers, requires training on disease and risks (44), tracking someone's pressure reaction, as well as seeking adequate assistance with personal and occupational responsibilities and issues, such as professional mental health (22, 45, 46). Healthcare systems must handle the burden of subcontractors and comprehensive operations by evaluating reactions and implementation, modifying projects and plans, adjusting expectations, and designing tools to deliver psychosocial assistance based on the circumstances (47).
The health care system must offer coaching and instruction on psychosocial problems to healthcare service administrators, emergency personnel, and health care providers. Mental health and emergency response systems must work together to identify, establish and allocate evidence-based resources such as disaster-related mental health, psychological well-being crisis and referral, special patient needs, and alarm and distress treatment. Risk consultation initiatives should resolve the difficulty of emerging problems, such as legislation, vaccination affordability and sufficiency, and the need for evidence-based arrangements related to disease outbreaks, and tackle various psychosocial considerations. Psychological well-being practitioners may strengthen perceptions that can be expressed through supporting the experts. The COVID-19 episode has a devastating impact on personal and collective welfare and care work. Despite health concerns, ultimately, medical treatment practitioners have a significant role in tracking psychosocial needs and delivering psychosocial assistance to their patients, providers of therapeutic services, and social initiatives that should be integrated into overall pandemic healthcare.
COVID-19 has contributed to increased recognized risk factors for mental health problems. In addition to weirdness and insecurity, quarantine and physical isolation can lead to significant alienation, lack of income, delays, limited access to core domains, increased exposure to alcohol and internet betting, and decreased family and community assistance, especially in more vulnerable people (21). The COVID-19 outbreak also provides a significant barrier to involvement in preliminary testing for older adults with tumors who are currently under-served in oncology and other clinical tests. Testing or possible admission to such therapeutic initial testing has been completed or based on several assessment projects worldwide.
COVID-19 is an evolving and rapidly growing disease that warrants personalized attention and assessment depending on the incidence of the infection. When humanity is dealing with the outbreak and working to find ways to effectively distribute cancer treatment to more mature patients, it is necessary to intervene to protect the vulnerable and counter the prolonged detrimental consequences in this age group. Since this is unlikely the last outbreak in human history, it is crucial to embrace this opportunity to discover facts and formulate strategies for any possible scenarios. It should also be understood that previous studies could contribute to a range of uses depending on the stage of the outbreak. Overall, it is especially critical that older individuals practice social distancing. Nevertheless, the scientific evidence of the experiences of older adults has been minimal so far. To understand the impact of the outbreak on more mature people and to develop viable arrangements, it is vital to examine how older individuals respond to quarantine measures and identify the difficulties and frustrations faced by older people and patients with CKD.
AC and PT carried out the outline of this manuscript. AC wrote the manuscript with support from JH and JL. JH and JL gave valuable comments and suggestion. PT helped to supervise the whole manuscript with his professional advances in Chronic Kidney Disease. AC and PT linked up the situation of nowadays older CKD patients during COVID-19 and their risk factors of psychological well-being. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
The preparation of this manuscript was partially supported by funding's from the Department of Applied Social Sciences, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University and supported by Research Grants Council of Hong Kong (14106518, 14111019, and 14111720), The Chinese University of Hong Kong's Faculty Innovation Award (4620528), and Direct Grant for Research (4054510).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
1. Shanthanna H, Bhatia A, Radhakrishna M, Belley-Cote E, Vanniyasingam T, Thabane L, et al. Interventional pain management for chronic pain: a survey of physicians in Canada. Canad J Anesthesia. (2020) 67:343–52. doi: 10.1007/s12630-019-01547-w
2. Salehinejad MA, Majidinezhad M, Ghanavati E, Kouestanian S, Vicario CM, Nitsche MA, et al. Negative impact of COVID-19 pandemic on sleep quantitative parameters, quality, and circadian alignment: implications for health and psychological well-being. EXCLI J. (2020) 19:1297. doi: 10.1101/2020.07.09.20149138
3. Torales J, O'Higgins M, Castaldelli-Maia JM, Ventriglio A. The outbreak of COVID-19 coronavirus and its impact on global mental health. Int J Soc Psychiatry. (2020) 66:317–20. doi: 10.1177/0020764020915212
4. Heid AR, Cartwright F, Wilson-Genderson M, Pruchno R. Challenges experienced by older people during the initial months of the COVID-19 pandemic. COVID-19 Res. (2021) 61:48–58. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnaa138
5. Singhai K, Swami MK, Nebhinani N, Rastogi A, Jude E. Psychological adaptive difficulties and their management during COVID-19 pandemic in people with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metabolic Syndr Clin Res Rev. (2020) 14:1603–5. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.08.025
6. Tang PMK, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Lan HY. Macrophages: versatile players in renal inflammation and fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2019) 15:144–58. doi: 10.1038/s41581-019-0110-2
7. Tang PMK, Zhang YY, Hung JSC, Chung JYF, Huang XR, To KF, et al. DPP4/CD32b/NF-κB circuit: a novel druggable target for inhibiting CRP-driven diabetic nephropathy. Mol Ther. (2021) 29:365–75. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.08.017
8. Tang PCT, Chan ASW, Zhang CB, Córdoba CAG, Zhang YY, To KF, et al. TGF-β1 signaling: immune dynamics of chronic kidney diseases. Front Med. (2021) 8:628519. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.628519
9. Tang PMK, Zhang YY, Xiao J, Tang PCT, Chung JYF, Li J, et al. Neural transcription factor Pou4f1 promotes renal fibrosis via macrophage–myofibroblast transition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2020) 117:20741–52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1917663117
10. Tang PCT, Zhang YY, Chan MKK, Lam WWY, Chung JYF, Kang W, et al. The emerging role of innate immunity in chronic kidney diseases. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:4018. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114018
11. Martel AL, Abolmaesumi P, Stoyanov D, Mateus D, Zuluaga MA, Zhou SK, et al. Medical image computing and computer assisted intervention – MICCAI 2020: 23rd International Conference, Lima, Peru, October 4–8, 2020. In: Proceedings, Part IV. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 12264. (2020). doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-59713-9
12. Xiong J, Lipsitz O, Nasri F, Lui LM, Gill H, Phan L, et al. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on mental health in the general population: a systematic review. J Affect Disord. (2020) 277:55–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.08.001
13. Yamada T, Mikami T, Chopra N, Miyashita H, Chernyavsky S, Miyashita S. Patients with chronic kidney disease have a poorer prognosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): an experience in New York City. Int Urol Nephrol. (2020) 52:1405–6. doi: 10.1007/s11255-020-02494-y
14. Bostan S, Erdem R, Öztürk YE, Kiliç T, Yilmaz A. The effect of COVID-19 pandemic on the Turkish society. Electronic J General Med. (2020) 17:em237. doi: 10.29333/ejgm/7944
15. Moreno C, Wykes T, Galderisi S, Nordentoft M, Crossley N, Jones N, et al. How mental health care should change as a consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet Psychiatry. (2020) 7:813–24. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30307-2
16. Strang P, Bergstrom J, Martinsson L, Lundstrom S. Dying from COVID-19: loneliness, end-of-life discussions, and support for patients and their families in nursing homes and hospitals. A national register study. J Pain Symptom Manage. (2020) 60:e2–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2020.07.020
17. Simoes e Silva AC, Miranda AS, Rocha NP, Teixeira AL. Neuropsychiatric disorders in chronic kidney disease. Front Pharmacol. (2019) 10:932. doi: 10.1055/b-006-161146
18. Rigoli F. The link between coronavirus, anxiety, and religious beliefs in the United States and United Kingdom. PsyArXiv [Preprint]. (2020). doi: 10.31234/osf.io/wykeq
19. Singu S, Acharya A, Challagundla K, Byrareddy SN. Impact of social determinants of health on the emerging COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. Front Public Health. (2020) 8:406. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00406
20. Elbeddini A, Wen CX, Tayefehchamani Y, To A. Mental health issues impacting pharmacists during COVID-19. J Pharmaceutical Policy Prac. (2020) 13:1–6. doi: 10.1186/s40545-020-00252-0
21. Chew QH, Wei KC, Vasoo S, Chua HC, Sim K. Narrative synthesis of psychological and coping responses towards emerging infectious disease outbreaks in the general population: practical considerations for the COVID-19 pandemic. Singapore Med J. (2020) 61:350–6. doi: 10.11622/smedj.2020046
22. Chudasama YV, Gillies CL, Zaccardi F, Coles B, Davies MJ, Seidu S, et al. Impact of COVID-19 on routine care for chronic diseases: a global survey of views from healthcare professionals. Diabetes Metabolic Syndr Clin Res Rev. (2020) 14:965–7. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.06.042
23. Ballivian J, Alcaide ML, Cecchini D, Jones DL, Abbamonte JM, Cassetti I. Impact of COVID−19-related stress and lockdown on mental health among people living with HIV in Argentina. J Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndr. (2020) 85:475–82. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000002493
24. Dickerson J, Kelly B, Lockyer B, Bridges S, Cartwright C, Willan K, et al. Experiences of lockdown during the Covid-19 pandemic: descriptive findings from a survey of families in the Born in Bradford study. Wellcome Open Res. (2020) 5:228. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.16317.1
25. Goethals L, Barth N, Guyot J, Hupin D, Celarier T, Bongue B. Impact of home quarantine on physical activity among older adults living at home during the COVID-19 pandemic: qualitative interview study. JMIR Aging. (2020) 3:e19007. doi: 10.2196/19007
26. Louvardi M, Pelekasis P, Chrousos GP, Darviri C. Mental health in chronic disease patients during the COVID-19 quarantine in Greece. Palliative Support Care. (2020) 18:394–9. doi: 10.1017/S1478951520000528
27. Vindegaard N, Benros ME. COVID-19 pandemic and mental health consequences: systematic review of the current evidence. Brain Behav Immun. (2020) 89:531–42. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.048
28. Santini ZI, Jose PE, Cornwell EY, Koyanagi A, Nielsen L, Hinrichsen C, et al. Social disconnectedness, perceived isolation, and symptoms of depression and anxiety among older Americans (NSHAP): a longitudinal mediation analysis. Lancet Public Health. (2020) 5:e62–70. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(19)30230-0
29. Holmes EA, O'Connor RC, Perry VH, Tracey I, Wessely S, Arseneault L, et al. Multidisciplinary research priorities for the COVID-19 pandemic: a call for action for mental health science. Lancet Psychiatry. (2020) 7:547. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30168-1
30. Paradise AW, Kernis MH. Self-esteem and psychological well-being: implications of fragile self-esteem. J Soc Clin Psychol. (2002) 21:345–61. doi: 10.1521/jscp.21.4.345.22598
31. Chang AY, Cullen MR, Harrington RA, Barry M. The impact of novel coronavirus COVID-19 on noncommunicable disease patients and health systems: a review. J Internal Med. (2020) 289:450–62. doi: 10.1111/joim.13184
32. Korczyn AD. Dementia in the COVID-19 period. J Alzheimer's Dis. (2020) 75:1071. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200609
33. Velayudhan L, Aarsland D, Ballard C. Mental health of people living with dementia in care homes during COVID-19 pandemic. Int Psychogeriatrics. (2020) 32:1253–4. doi: 10.1017/S1041610220001088
34. Li Y, Mutchler JE. Older adults and the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. J Aging Soc Policy. (2020) 32:477–87. doi: 10.1080/08959420.2020.1773191
35. Nadler MB, Barry A, Murphy T, Prince R, Elliott M. Strategies to support health care providers during the COVID-19 pandemic. CMA192 J. (2020) 192:E522. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.75499
36. McGinty EE, Presskreischer R, Han H, Barry CL. Psychological distress and loneliness reported by US adults in 2018 and April 2020. JAMA. (2020) 324:93–4. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.9740
37. Seyahi E, Poyraz BC, Sut N, Akdogan S, Hamuryudan V. The psychological state and changes in the routine of the patients with rheumatic diseases during the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak in Turkey: a web-based cross-sectional survey. Rheumatol Int. (2020) 40:1229–38. doi: 10.1007/s00296-020-04626-0
38. Keng A, Brown EE, Rostas A, Rajji TK, Pollock BG, Mulsant BH, et al. Effectively caring for individuals with behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia during the COVID-19 pandemic. Front Psychiatry. (2020) 11:573367. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.573367
39. Ghinai I, McPherson TD, Hunter JC, Kirking HL, Christiansen D, Joshi K, et al. First known person-to-person transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in the USA. Lancet. (2020) 395:1137–44. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30607-3
40. Gavin B, Lyne J, McNicholas F. Mental health and the COVID-19 pandemic. Irish J Psychol Med. (2020) 37:156–8. doi: 10.1017/ipm.2020.72
41. Guan WJ, Liang WH, He JX, Zhong NS. Cardiovascular comorbidity and its impact on patients with COVID-19. Euro Respir J. (2020) 55:2001227. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01227-2020
42. Birditt KS, Turkelson A, Fingerman KL, Polenick CA, Oya A. Age differences in stress, life changes, and social ties during the COVID-19 pandemic: implications for psychological well-being. Gerontologist. (2020) 61:205–16. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnaa204
43. Addis SG, Nega AD, Miretu DG. Psychological impact of COVID-19 pandemic on chronic disease patients in Dessie town government and private hospitals, Northeast Ethiopia. Diabetes Metabolic Syndr Clin Res Rev. (2021) 15:129–35. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.12.019
44. Pasay-An E. Exploring the vulnerability of frontline nurses to COVID-19 and its impact on perceived stress. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. (2020) 15:404–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2020.07.003
45. Lodha P, De Sousa. A. Mental health perspectives of COVID-19 and the emerging role of digital mental health and telepsychiatry. Arch Med Health Sci. (2020) 8:133. doi: 10.4103/amhs.amhs_82_20
46. Koenig HG. Maintaining health and well-being by putting faith into action during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Religion Health. (2020) 59:2205–14. doi: 10.1007/s10943-020-01035-2
47. Greenberg N, Docherty M, Gnanapragasam S, Wessely S. Managing mental health challenges faced by healthcare workers during covid-19 pandemic. BMJ. (2020) 368:M1211. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1211
48. Varshney M, Parel JT, Raizada N, Sarin SK. Initial psychological impact of COVID-19 and its correlates in Indian Community: an online (FEEL-COVID) survey. PLoS ONE. (2020) 15:e0233874. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233874
49. Barutcu Atas D, Aydin Sunbul E, Velioglu A, Tuglular S. The association between perceived stress with sleep quality, insomnia, anxiety and depression in kidney transplant recipients during Covid-19 pandemic. PLoS ONE. (2021) 16:e0248117. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248117
50. Hernández-García I, Giménez-Júlvez T. Assessment of health information about COVID-19 prevention on the internet: infodemiological study. JMIR Public Health Surv. (2020) 6:e18717. doi: 10.2196/18717
51. Kobia F, Gitaka J. COVID-19: are Africa's diagnostic challenges blunting response effectiveness? AAS Open Res. (2020) 3:4. doi: 10.12688/aasopenres.13061.1
52. Lee J, Steel J, Roumelioti ME, Erickson S, Myaskovsky L, Yabes JG, et al. Psychosocial impact of COVID-19 pandemic on patients with end-stage kidney disease on hemodialysis. Kidney360. (2020) 1:1390–7. doi: 10.34067/KID.0004662020
53. Levey AS, Atkins R, Coresh J, Cohen EP, Collins AJ, Eckardt KU, et al. Chronic kidney disease as a global public health problem: approaches and initiatives – a position statement from kidney disease improving global outcomes. Kidney Int. (2007) 72:247–59. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5002343
54. World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Weekly Epidemiological (2020). Available online at: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/333905/nCoV-weekly-sitrep1-eng.pdf
55. Ko NY, Lu WH, Chen YL, Li DJ, Wang PW, Hsu ST, et al. COVID-19-related information sources and psychological well-being: an online survey study in Taiwan. Brain Behav Immunity. (2020) 87:153–4. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.019
56. AlAteeq DA, Aljhani S, Althiyabi I, Majzoub S. Mental health among healthcare providers during coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak in Saudi Arabia. J Infection Public Health. (2020) 13:1432–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.08.013
57. Battisti NML, Mislang AR, Cooper L, O'Donovan A, Audisio RA, Cheung KL, et al. Adapting care for older cancer patients during the COVID-19 pandemic: Recommendations from the International Society of Geriatric Oncology (SIOG) COVID-19 Working Group. J Geriatric Oncol. (2020) 11:1190–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jgo.2020.07.008
58. Sanyaolu A, Okorie C, Marinkovic A, Patidar R, Younis K, Desai P, et al. Comorbidity and its impact on patients with COVID-19. SN Comprehens Clin Med. (2020) 2:1069–76. doi: 10.1007/s42399-020-00363-4
59. Vik-Mo AO, Giil LM, Borda MG, Ballard C, Aarsland D. The individual course of neuropsychiatric symptoms in people with Alzheimer's and Lewy body dementia: 12-year longitudinal cohort study. Br J Psychiatry. (2020) 216:43–8. doi: 10.1192/bjp.2019.195
60. Selvin E, Juraschek SP. Diabetes epidemiology in the COVID-19 pandemic. Diabetes Care. (2020) 43:1690–4. doi: 10.2337/dc20-1295
61. Tan BY, Chew NW, Lee GK, Jing M, Goh Y, Yeo LL, et al. Psychological impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on health care workers in Singapore. Ann Internal Med. (2020) 173:317–20. doi: 10.7326/M20-1083
62. Caqueo-Urízar A, Urzúa A, Aragón-Caqueo D, Charles CH, El-Khatib Z, Otu A, et al. Mental health and the COVID-19 pandemic in Chile. Psychol Trauma Theory Res Prac Policy. (2020) 12:521–3. doi: 10.1037/tra0000753
63. Alonso-Lana S, Marquié M, Ruiz A, Boada M. Cognitive and Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of COVID-19 and Effects on Elderly Individuals With Dementia. Front. Aging Neurosci. (2020) 12:588872. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.588872
64. Coppolino G, Presta P, Nicotera R, Placida G, Vita C, Carullo N, et al. COVID-19 and renal disease in elderly patients. Geriatric Care. (2020) 6. doi: 10.4081/gc.2020.9029
65. Coresh J, Astor BC, Greene T, Eknoyan G, Levey AS. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and decreased kidney function in the adult US population. Third National Health Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Kidney Dis. (2003) 41:1–2. doi: 10.1053/ajkd.2003.50007
66. U. S. Renal Data System. Annual Data Report: Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda, MD (2013).
67. Eckardt KU, Berns JS, Rocco MV, Kasiske BL. Definition and classification of CKD: the debate should be about patient prognosis – a position statement from KDOQI and KDIGO. Am J Kidney Dis. (2009) 53:915–20. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.04.001
68. Fehrman-Ekholm I, Skeppholm L. Renal function in the elderly (>70 years old) measured by means of iohexol clearance, serum creatinine, serum urea and estimated clearance. Scand J Urol Nephrol. (2004) 38:73–7. doi: 10.1080/00365590310015750
69. Dowling TC, Wang ES, Ferrucci L, Sorkin JD. Glomerular filtration rate equations overestimate creatinine clearance in older individuals enrolled in the Baltimore longitudinal study on aging: impact on renal drug dosing. Pharmacotherapy. (2013) 33:912–21. doi: 10.1002/phar.1282
70. Koppe L, Klich A, Dubourg L, Ecochard R, Hadj-Aissa A. Performance of creatinine-based equations compared in older patients. J Nephrol. (2013) 26:716–23. doi: 10.5301/jn.5000297
71. Janiri D, Petracca M, Moccia L, Tricoli L, Piano C, Bove F, et al. COVID-19 pandemic and psychiatric symptoms: the impact on Parkinson's disease in the elderly. Front Psychiatry. (2020) 11:1306. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.581144
72. Hartmann-Boyce J, Morris E, Goyder C, Kinton J, Perring J, Nunan D, et al. Diabetes and COVID-19: risks, management, and learnings from other national disasters. Diabetes Care. (2020) 43:1695–703. doi: 10.2337/dc20-1192
73. Li SY, Tang YS, Chan YJ, Tarng DC. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the management of patients with end-stage renal disease. J Chin Med Assoc. (2020) 83:628. doi: 10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000356
74. Pierce M, Hope H, Ford T, Hatch S, Hotopf M, John A, et al. Mental health before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a longitudinal probability sample survey of the UK population. Lancet Psychiatry. (2020) 7:883–92. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30308-4
75. Rapelli G, Lopez G, Donato S, Pagani AF, Parise M, Bertoni A, et al. A postcard from Italy: challenges and psychosocial resources of partners living with and without a chronic disease During COVID-19 epidemic. Front Psychol. (2020) 11:3559. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.567522
76. Huppert FA. Psychological well-being: evidence regarding its causes and consequences. Appl Psychol Health Well Being. (2009) 1:137–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1758-0854.2009.01008.x
77. Helmich RC, Bloem BR. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on Parkinson's disease: hidden sorrows and emerging opportunities. J Parkinson's Dis. (2020) 10:351. doi: 10.3233/JPD-202038
78. Bambra C, Riordan R, Ford J, Matthews F. The COVID-19 pandemic and health inequalities. J Epidemiol Commun Health. (2020) 74:964–8. doi: 10.1136/jech-2020-214401
79. Godinic D, Obrenovic B, Khudaykulov A. Effects of economic uncertainty on mental health in the COVID-19 pandemic context: social identity disturbance, job uncertainty and psychological well-being model. Int J Innov Econ Dev. (2020) 6:61–74. doi: 10.18775/ijied.1849-7551-7020.2015.61.2005
80. Bebbington PE, McManus S. Revisiting the one in four: the prevalence of psychiatric disorder in the population of England 2000–2014. Br J Psychiatry. (2020) 216:55–7. doi: 10.1192/bjp.2019.196
81. Curigliano G, Cardoso MJ, Poortmans P, Gentilini O, Pravettoni G, Mazzocco K, et al. Recommendations for triage, prioritization and treatment of breast cancer patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. Breast. (2020) 52:8–16. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2020.04.006
82. Philip M, Mahakalka CC, Kapl MN, Kshirsagar S, Shukla A. Mental and behavioral changes during COVID 19 pandemic and how to deal with it. J Crit Rev. (2020) 7:1105–12. doi: 10.31838/jcr.07.08.233
83. Nouri S, Khoong EC, Lyles CR, Karliner L. Addressing equity in telemedicine for chronic disease management during the Covid-19 pandemic. NEJM Catalyst Innov Care Deliv. (2020) 1:1–13. doi: 10.1056/CAT.20.0123
84. Cullen W, Gulati G, Kelly BD. Mental health in the Covid-19 pandemic. QJM Int J Med. (2020) 113:311–2. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcaa110
85. Pfefferbaum B, North CS. Mental health and the Covid-19 pandemic. New Engl J Med. (2020) 383:510–2. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2008017
86. Sultana A, Sharma R, Hossain MM, Bhattacharya S, Purohit N. Burnout among healthcare providers during COVID-19 pandemic: challenges and evidence-based interventions. SocArXiv 4hxga, Center for Open Science (2020). doi: 10.31235/osf.io/4hxga
87. Beaglehole R, Epping-Jordan J, Patel V, Chopra M, Ebrahim S, Kidd M, et al. Improving the prevention and management of chronic disease in low-income and middle-income countries: a priority for primary health care. Lancet. (2008) 372:940–9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61404-X
88. Maugeri G, Castrogiovanni P, Battaglia G, Pippi R, D'Agata V, Palma A, et al. The impact of physical activity on psychological health during Covid-19 pandemic in Italy. Heliyon. (2020) 6:e04315. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04315
89. McGlinchey E, Hitch C, Butter S, McCaughey L, Berry E, Armour C. Understanding the lived experiences of healthcare professionals during the COVID-19 pandemic: an interpretative phenomenological analysis. PsyArXiv [Preprint]. (2020). doi: 10.31234/osf.io/7cvzj
90. Mirsky JB, Horn DM. Chronic disease management in the COVID-19 era. Am J Manag Care. (2020) 26:329–30. doi: 10.37765/ajmc.2020.43838
91. Sousa H, Ribeiro O, Costa E, Frontini R, Paúl C, Amado L, et al. Being on hemodialysis during the COVID-19 outbreak: a mixed-methods' study exploring the impacts on dialysis adequacy, analytical data, patients' experiences. Semin Dial. (2021) 34:66–76. doi: 10.1111/sdi.12914
92. Guo Y, Cheng C, Zeng Y, Li Y, Zhu M, Yang W, et al. Mental health disorders and associated risk factors in quarantined adults during the COVID-19 outbreak in China: cross-sectional study. J Med Internet Res. (2020) 22:e20328. doi: 10.2196/20328
93. Yang ZH, Pan XT, Chen Y, Wang L, Chen QX, Zhu Y, et al. Psychological profiles of Chinese patients with hemodialysis during the panic of coronavirus disease 2019. Front Psychiatry. (2021) 12:157. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.616016
94. Spoorthy MS, Pratapa SK, Mahant S. Mental health problems faced by healthcare workers due to the COVID-19 pandemic–a review. Asian J Psychiatry. (2020) 51:102119. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2020.102119
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic, psychological well-being, aging-old age-seniors, immune system, chronic kidney disease
Citation: Chan ASW, Ho JMC, Li JSF, Tam HL and Tang PMK (2021) Impacts of COVID-19 Pandemic on Psychological Well-Being of Older Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Front. Med. 8:666973. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.666973
Received: 11 February 2021; Accepted: 27 April 2021;
Published: 26 May 2021.
Edited by:
Yiming Zhou, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, ChinaReviewed by:
Haiyong Chen, The University of Hong Kong, ChinaCopyright © 2021 Chan, Ho, Li, Tam and Tang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Alex Siu Wing Chan, Y2hhbnN3LmFsZXhAZ21haWwuY29t; Patrick Ming Kuen Tang, cGF0cmljay50YW5nQGN1aGsuZWR1Lmhr
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.