- 1School of Materials and Chemistry, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai, China
- 2Shanghai Key Laboratory of Materials Protection and Advanced Materials in Electric Power, College of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Shanghai University of Electric Power, Shanghai, China
Bimetallic selenides are considered to be the promising high-capacity anode materials for potassium ion batteries (PIBs). However, the dramatic volume fluctuation of K+ ions and pulverization during cycling still limit their practical application in PIBs. Herein, the nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur tri-doped carbon (SPNC)-coated bimetallic NiCo2Se4 needle arrays grown on carbon cloth (NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC) prepared as a binder-free anode for PIBs. The polyphosphazene (PSZ) was used as ingenious heteroatoms doping carbon source. The coated SPNC layer derived from the PSZ on the surfaces of NiCo2Se4 needle arrays not only effectively alleviate the volume expansion of NiCo2Se4 but also provide abundant active sites for the storage of K+ ions. As the PIB anode, the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC could deliver a high reversible capacity of 880.9 mA h g−1 at a current density of 0.1 A g−1. After 500 cycles, the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC anode still maintains a high reversible capacity of 268.1 mA h·g−1 at a current density of 0.5 A g−1.
Introduction
With the rapid development of portable electronic equipment and electric vehicles, the demand for energy storage devices with high energy density and high safety is increasing. Among the large-scale energy storage devices, lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have attracted extensive attention due to their high energy density, environmental friendliness, and high efficiency. Due to insufficient lithium resources, researchers turned their attention to resource-rich potassium-ion batteries (PIBs) (Hu et al., 2017; Ge et al., 2018). Compared to the LIBs, PIBs have similar energy storage mechanisms, moreover, have the advantages of low production cost and low reduction potential (relative to the standard hydrogen electrode ≈2.94 V) (Liu et al., 2020; Rajagopalan et al., 2020). Therefore, PIBs are expected to become an alternative to LIBs(Zhao et al., 2021). Obtaining the high energy density of PIBs mainly depends on technological breakthroughs in electrode materials. However, toward the PIBs, due to the large radius of potassium ions, the kinetics of K+ during the intercalation/delamination process is slow and the volume is prone to expansion, which will cause the battery’s capacity to decay rapidly and the decrease of coulomb efficiency (Zhang et al., 2021). The key to improving the performance of PIBs is to develop an anode material with excellent electrochemical performance (Zheng et al., 2021).
Among the various explored anode materials, transition metal compounds show great potential due to their excellent electrochemical performance. Compared to the transition metal sulfides and oxides, transition metal selenides have a narrower band gap and a higher volumetric capacity (Qiu et al., 2020). Moreover, the metal-Se bond in the metal selenide is weak and easy to break, which is beneficial to the conversion reaction (Zhu et al., 2017; Hou et al., 2018; Xie et al., 2019; Luo et al., 2020). NiCo2Se4 as a kind of bimetallic selenides is widely used as PIB anodes because of its rich electronic reaction processes, high conductivity, and excellent chemical stability. Nevertheless, NiCo2Se4 still has some problems, such as pulverization of the electrode material due to volume expansion during charging and discharging, which causes the battery’s capacity to rapidly decay. In view of these problems, how to solve the volume change during the continuous intercalation and delamination of K+ ions are the main challenge to improve the electrochemical performance and cycle stability of PIBs. In order to solve the above-mentioned problems of NiCo2Se4, Zhou et al. deposited the hierarchical NiCo2Se4 nanoneedles/nanosheets on the skeleton of N-doped three-dimensional porous graphene (NPG) as sodium-ion battery anode and found that the high conductivity and porous NPG improves the transport of electrons of the anode as well as ions (Zhou et al., 2021). Always, incorporating the carbonaceous materials is considered to be the competitive way to improve the cycling performance and rate capability of PIB anode materials. Huang et al. designed the hierarchical carbon-coated MoSe2/MXene hybrid nanosheets (MoSe2/MXene@C) as anode material for PIBs(Huang et al., 2019). The coated carbon layer reinforced the composite structure of MoSe2/MXene, meantime enhancing the overall conductivity of the hybrid MoSe2/MXene@C, which finally promoted the charge-transfer kinetics and improved the durability of PIB.
Herein, the nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur tri-doped carbon-coated NiCo2Se4 needle arrays grown on carbon cloth (NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC) was prepared as a binder-free anode for PIBs. The NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC owns an internally hierarchical stable structure, which is composed of CC as the base, NiCo2Se4 needle arrays as the middle active layer, and an outer layer of nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur tri-doped carbon layers (SPNC) which effectively alleviate the powdering and volume expansion of the anode material of NiCo2Se4 during the charging and discharging process. The coating of SPNC could improve the conductivity of the anode and the doping of S, P, and N provide abundant active sites for the storage of potassium ions. The NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC anode exhibits high reversible capacity, excellent cycle stability, and good rate performance.
Experimental
Chemicals and Materials
Cobalt nitrate hexahydrate (Co.(NO3)2·6H2O, 99.0%) and nickel nitrate hexahydrate (Ni(NO3)2·6H2O, 99.0%) and Urea (CH4N2O, 99.0%) were provided from Shanghai Titan Technology Co., Ltd. Hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene (HCCP, 99%), 4, 4′-dihydroxydiphenylsulfone (BPS, 99%) and triethylamine (TEA, 99.7%) were purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. The carbon cloth (Ce-tech, W0S1002) was purchased from Phychemi Company Limited.
Instruments and Characterization
The morphologies for the CC, NiCo2O4/CC, and NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC were characterized by a field emission scanning electron microscope (SEM) (JEOL JEM-7800F). The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the CC, NiCo2O4/CC, and NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC were recorded on a Bruker AXS D8 Advance diffractometer. The XPS spectrum of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC was performed from the Thermo Scientific ESCALAB 250Xi using Al Kα radiation.
Synthesis of the NiCo2O4/CC
Firstly, the carbon cloth (CC) was pretreated in mixture acid of concentrated nitric acid (HNO3) and concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) (3:1, v/v) at 80°C for 6 h. After that, the CC was rinsed with plenty of water. The NiCo2O4/CC was prepared by a one-step hydrothermal reaction. 0.291 g of Co.(NO3)2·6H2O, 0.145 g of Ni(NO3)2·6H2O, and 0.27 g of urea were weighed and then added into 30 ml of deionized water under magnetic stirring. After stirring for 30 min, the obtained pink precursor mix solution was transferred into a 50 ml Teflon-lined stainless-steel autoclave. Successively, the pretreated CC was immersed into the aforementioned solution and reacted at 120°C for 6 h. After being naturally cooled to room temperature, the NiCo2O4/CC was taken out and washed with deionized water and ethanol several times. Finally, the NiCo2O4/CC was vacuum dried at 60°C for 12 h.
Preparation of the NiCo2O4⊂SPNC/CC
The NiCo2O4⊂SPNC/CC was prepared from the carbonization of polyphosphazenes-coated NiCo2O4/CC. The polyphosphazenes (PSZ)-coated NiCo2O4/CC (NiCo2O4⊂PSZ/CC) were synthesized via in situ polymerization. The dried NiCo2O4/CC was first soaked in 30 ml of anhydrous acetonitrile. Then, 0.025 g of hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene (HCCP) and 55.7 mg of 4, 4′-dihydroxydiphenylsulfone (BPS) were added with stirring. Subsequently, 10 μL of triethylamine was added to the solution. After a polycondensation of 6 h, the NiCo2O4⊂PSZ/CC was then vacuum dried at 60°C for 12 h. Then, the dried NiCo2O4⊂PSZ/CC was carbonized at 600 °C for 2 h under N2 atmosphere with a heating rate of 2°C·min−1. After the carbonization, the NiCo2O4⊂SPNC/CC was successfully obtained.
Fabrication of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC
The NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC were hydrothermally selenizated from the NiCo2O4⊂SPNC/CC. A 120 mg of selenium (Se) powder was slowly added into 5 ml of hydrazine hydrate (N2H4·H2O) under magnetic stirring. Then, the Se solution was slowly dropwise added into 20 ml of deionized water under magnetic stirring. In the next, the NiCo2O4⊂SPNC/CC were immersed into the above solution and transferred into a 50 ml Teflon-lined stainless-steel autoclave and reacted at 200°C for 10 h. After cooling to room temperature, the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC was carefully washed several times with ethanol and deionized water and dried under vacuum at 60°C for 12 h.
Electrochemical Test
Electrochemical measurements were carried out in CR2032 type coin cells at room temperature. The working electrodes were prepared by mixing 80 wt% of active materials, 10 wt% of Super-P carbon black, and 10 wt% of poly (vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF). Cu foil was employed as the current collector, and the electrodes were directly punched into a disc with a diameter of 14 mm. The active substance loading of carbon cloth on the electrode was approximately 2.5 mg cm−2, which was calculated by weighing on a balance. Fresh K foils were used as reference and counter electrodes, and Whatman
Results and Discussion
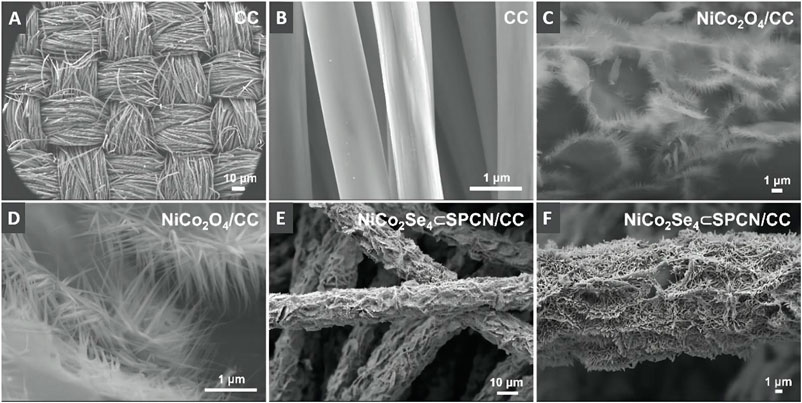
As shown in Figure 1A, the preparation process of NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC was mainly divided into three steps. In the first step, the NiCo2O4/CC was synthesized via hydrothermal reaction. From Figure 2A,B, the surfaces of the carbon fibers of CC are clean and smooth. After the hydrothermal reaction, it is obvious that the NiCo2O4 nanoneedle arrays with the mean root width of ∼85 nm and length of ∼1.5 µm are grown on the carbon fibers of CC (Figure 2C). Secondly, the surfaces of NiCo2O4/CC have coated the polymer layers of the polyphosphazene (PSZ) via in-situ polycondensation of hexachlorotripolyphosphazene (HCCP) and 4,4′-dihydroxydiphenylsulfone (BPS) (Figure 1B), which is demonstrated by the Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra (Supplementary Figure S1). After the following carbonization in an N2 atmosphere at 600 °C for 2 h, the obtained NiCo2O4⊂SPNC/CC were further converted into NiCo2Se4⊂PSZ/CC by using solvothermal selenization at 200°C for 10 h. From Figure 2E,F, after selenization and carbonization, the NiCo2Se4 needles were connected by the layers of SPNC and the surfaces of NiCo2O4 nanoneedle arrays become very rough.
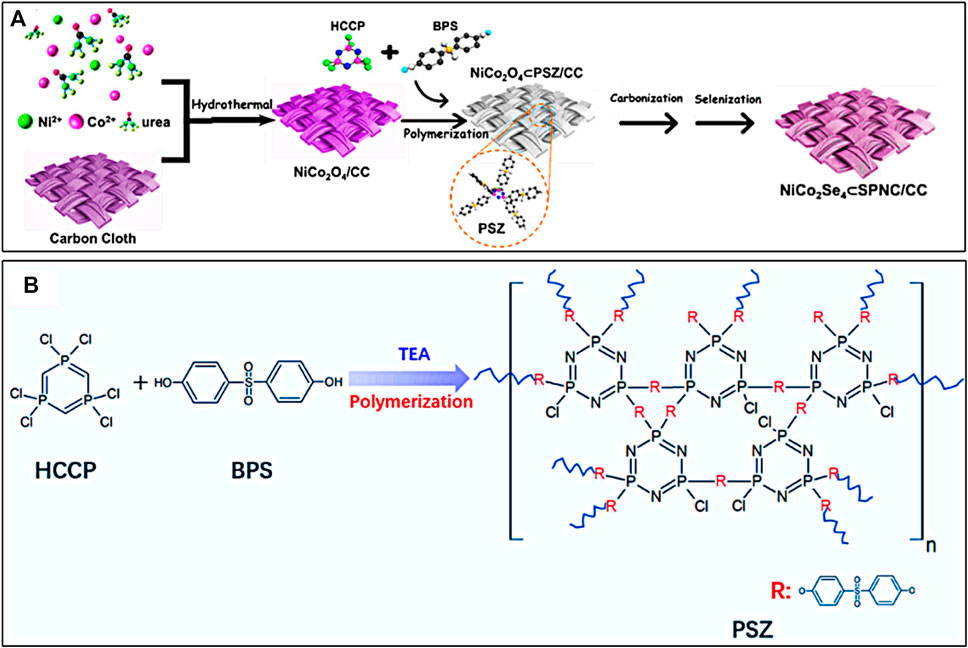
FIGURE 1. (A) Schematic illustration for the preparation of NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC and (B) the poly-condensation process of HCCP and BPS in the presence of TEA.
Figure 3 shows the XRD patterns for the CC, NiCo2O4/CC, and NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC. For the XRD patterns of the pure CC and NiCo2O4/CC, there are evident diffraction peaks at 2θ = 26.2o which are ascribed to the C (002) plane of graphite carbon. For the XRD pattern of NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC, the diffraction peaks at 2θ = 33.7°, 45.3°, and 51.2° are attributed to the (101), (102) and (110) crystal planes of the monoclinic NiCo2Se4 phase standard card (JCPDS No. 08–4821), demonstrating the formation of NiCo2Se4(Zhang et al., 2020). It is worth noting that the diffraction peaks of the C (002) plane of NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC moves to the relatively lower diffraction angles which are attributed to the increase of interplanar spacing after the introduction of nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur heteroatoms (Li et al., 2019). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) spectrum for the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC was further used to characterize the valence states and surface chemical composition. From the XPS survey spectrum, the Ni, Co., Se, N, S, P, C, and O elements exist in the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC (Figure 3B). In the Co. 2p spectrum (Figure 3C,D), there are six cobalt chemical states. The peaks at binding energies of 785.6 and 802.1 eV correspond to the satellite peaks (Yu et al., 2019). The spin-orbit peaks of Co2+ and Co3+ are located at 778.9, 793.8 eV, and 781.4, 797.1 eV, respectively (Guan et al., 2019). Similarly, toward the Ni 2p spectrum, there are also two satellite peaks which are appeared at 861.7 and 882.2 eV (Zeng et al., 2017). The two pair’s peaks at 853.8, 872.7 eV and 856.3, 877.5 eV are ascribed to the spin-orbit peaks of Ni2+ and Ni3+(Xu et al., 2020). In Figure 3E, the peaks at 55.6 and 54.7 eV correspond to the spin-orbit peaks of Se 3d3/2 and Se 3d5/2. A broad peak at 59.4 eV can be related to the SeOx (Chong et al., 2021). The C 1s high-resolution XPS spectrum is depicted in Figure 3F, which can be fitted into four peaks including C-C/C=C (284.4 eV), C–N or C–S (285.9 eV), C-P (287.1 eV), and O=C-O (290.1 eV). As illustrated in Figure 3G, the peak at 161.2 eV is assigned to the C-S-C bonding in the PSZ-derived carbon framework (Shen et al., 2017). The peak at 166.7 eV is mainly attributed to the oxidation state of sulfur (C–SOx). By fitting, the P 2p spectrum could split into the P-C and P-O peaks which are located at 133.5 and 137.7 eV (Qian et al., 2019). Besides the S and P elements, the N dopant in the PSZ-derived carbon framework was also confirmed by the N 1s of the XPS spectrum, as shown in Figure 3I, the peaks for the pyridinic N, pyrrolic N, and graphitic N are clearly observed at 398.6 400.4 and 402.1 eV (Xu et al., 2021). In addition, the peak of the oxidation state N is located at 403.23 eV (Cui et al., 2020). Based on the above analysis, the N, S, and P elements were successfully doped in the carbon framework, which could be acted as active sites for the storage of potassium ions. The atom percentages of N, S, and P elements are 2.66, 4.23, and 2.3%, respectively.
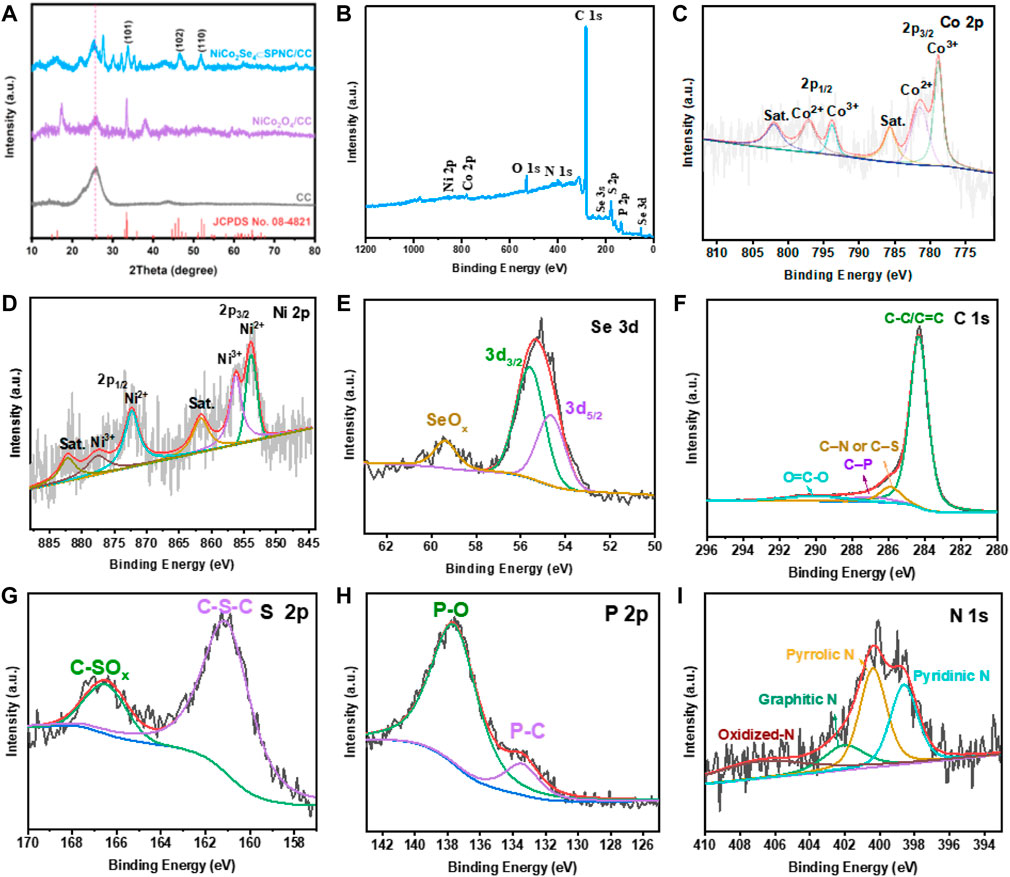
FIGURE 3. (A) XRD patterns for the CC, NiCo2O4/CC and NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC, (B) XPS survey spectrum of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC, the high-resolution XPS spectra for (C) Co. 2p, (D) Ni 2p, (E) Se 3days, (F) C 1s, (g) S 2p, (H) P 2p, and (I) N 1s.
The K-ion storage behavior of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC anode was first studied by cyclic voltammetry (CV). The CV curves for the first three circles are shown in Figure 4A at the scan rate of 0.1 mV·s-1 within the voltage window of 0.01–3 V. In the first cycle, the reduction peak around 0.31 V should be related to the formation of the solid electrolyte interface (SEI) film, and the large reduction band at 1.2 V should be related to the K+ ion insertion in the structure of NiCo2Se4 and the formation of NiCo2Se4(NiCo2Se4+xK++xe− = KxNiCo2Se4) (Li et al., 2020). During the first cycle process, the oxidation peaks at 0.54, 1.73, 1.94 and 2.19 V are attributed to the reaction from KxNiCo2Se4 to Co., Ni, and K2Se(Chen et al., 2021). The peak around 0.01–0.03 V in the cathodic scan may be due to the intercalation of K+ ions in the SPNC layer of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC. In the subsequent cycles, the large reduction band was shifted to 1.44 V which is related to the potassiumization process. The difference between the first and second cycles indicates that the reaction paths of the two cycles are inconsistent, which is the reason for the irreversible capacity in the first cycle. The CV curves almost overlap after the second cycle, indicating the excellent cycle performance of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC electrode.
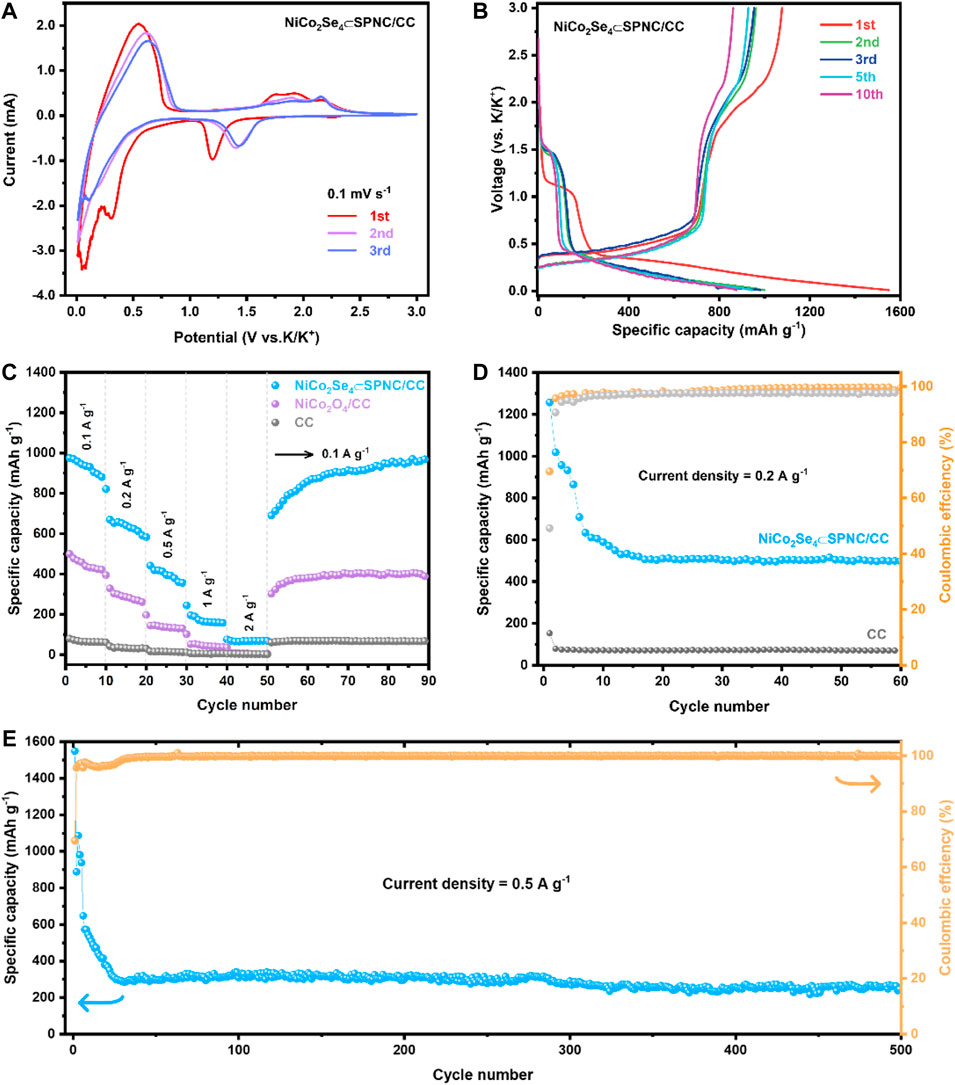
FIGURE 4. (A) CV curves of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC anode at different scan rates, electrode for the first three circles at 0.1 mV s−1, (B) GCD curves for the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC electrode in the different circles at a current density of 0.1 A g−1, (C) Rate performances of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC electrode, (D) Cycle performance and Coulombic efficiency of CC and NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC at a current density of 0.2 A g−1, and (E) Long-term cycling performances of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC anode at a current density of 0.5 A g−1.
Figure 4B shows the galvanostatic charge-discharge (GCD) curves for the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC electrode in the first, second, third, fifth, and 10th circles at a current density of 0.1 A g−1 and applied voltage window of 0.01–3 V. During the initial cycle, a high discharge specific capacity of 1549.2 mA h·g−1 was obtained. The first charge specific capacity is 1076.9 mA h·g−1, and the initial Coulombic efficiency is about 69.5%, which is related to the formation of the SEI film on the electrode surface. In addition, the discharge plateaus of 1.0–1.2 V and 0.2–0.4 V in the first circle are mainly attributed to the formation of KxNiCo2Se4 and the conversion reaction from KxNiCo2Se4 to Co., Ni, and K2Se, which is consistent with the CV analysis. The NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC electrode shows the reversible capacity of ∼890.6 mA h·g−1 after the end of 10 cycles with a Coulombic efficiency of nearly 100%. Moreover, from the second to the 10th cycle, the GCD curves basically coincide, which also shows the excellent cycle stability of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC electrode. The rate performances test of CC, NiCo2O4/CC, and NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC are shown in Figure 4C. When the current densities are 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1, and 2 A g−1, the reversible discharge capacities of NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC are 880.9, 591.4, 356.5, 157.4, and 68.5 mA h·g−1, respectively, indicating that the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC has good rate performance. Afterward, as the current density recovers to 0.1 A g−1 after 50 cycles, the specific capacity recovers to 689.8 mA h g−1, and after 90 cycles it recovers to 968.6 mA h·g−1, which means that potassium ions at high current density the storage performance has not declined. For pure NiCo2O4/CC, when the current density is restored, the specific capacity cannot be restored to the capacity under the initial current density. The excellent rate of performance of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC is due to the increase in selenization capacity and the heteroatoms doping of S, P, and N in the carbon layer originated from the polyphosphazene, which increases the active sites for K+ ions storage. More importantly, the coating of the SPNC layer on the surfaces of NiCo2Se4 improved the structure stability, largely alleviated the volume expansion of anode in the charge-discharge process, and finally improved the cycle performances of KIB. In addition, from the EIS spectra of the NiCo2O4/CC and NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC, the radius of the semicircle in the EIS spectrum of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC is significantly smaller than that of NiCo2O4/CC, implying the selenization and SPNC coating improved the conductivity and interfacial charge transport (Supplementary Figure S2). Figure 4D illustrates the cycle performance and Coulombic efficiency of CC and NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC at the current density of 0.2 A g−1. As a pure carbon material anode, although the CC has a relatively low specific capacity, it has a very good cycling stability electrode. For demonstrating good cycling stability, the cycle performances of CC and NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC were compared. As shown in Figure 4E, the initial specific capacity of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC is ∼1256.7 mA h·g−1, and the Coulombic efficiency stabilizes at about 99.7% in the subsequent cycles. After 60 cycles, the specific capacity of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC can still keep at 497.3 mA h·g−1. Further, the long-cycle performance of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC was also tested at a current density of 0.5 A g−1. After 500 cycles, the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC anode still maintains a high reversible capacity of 268.1 mA h·g−1, and the Coulombic efficiency is close to 100%.
In order to further understand the diffusion dynamics and charge storage of NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC, the electrochemical kinetics of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC was further studied by CV curves at different scan rates (Figure 5A). Increasing with the scan rate, the cathode peak moves to a high potential, and the anode peak moves to a low potential due to the polarization of the electrode at a high current density. The relationship between current and scan rate follows the following formula (Huang et al., 2020):
where a is a constant, and b reflects an adjustable parameter that reflects the mechanism of the charge-storage process. When b = 0.5 or b = 1.0, the charging and discharging process is considered to be controlled by the diffusion control behavior or pseudocapacitance behavior. The value of b calculated from the selected two redox peak potentials is 0.68 and 0.73, respectively (Figure 5B), indicating that the electrochemical process of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC anode has the evident diffusion behavior. Toward the structure and morphology of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC anode, the needle-like NiCo2Se4 array with sufficient void spaces could facilitate the electrolyte penetration and alleviate the effect of the volume change of NiCo2Se4. And, the coating of the SPNC layer not only formed a conductive network which improves the conductivity and interfacial charge transport, but also provides the heteroatomic active sites for K+ ions storage. The contribution ratio of pseudocapacitance can be calculated by the following equation (Zhu et al., 2022):
where k1v and k2v1/2 refer to the currents of the capacitance and diffusion process, respectively. As shown in Figure 5C, the blue shaded part is corresponding to the capacitance current response, and the scan rate is 0.1 mV s−1, where the capacitance contribution is calculated to be ≈41.2%. Figure 5D shows the contribution rate of pseudocapacitance and diffusion control at different scan rates. When the scan speed is increased from 0.1 to 1.2 mV s−1, the contribution rate of pseudocapacitance gradually increases from 41.2 to 88.3%, demonstrating that the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC anode has a good potassium ion storage capacity during the charge and discharge process.
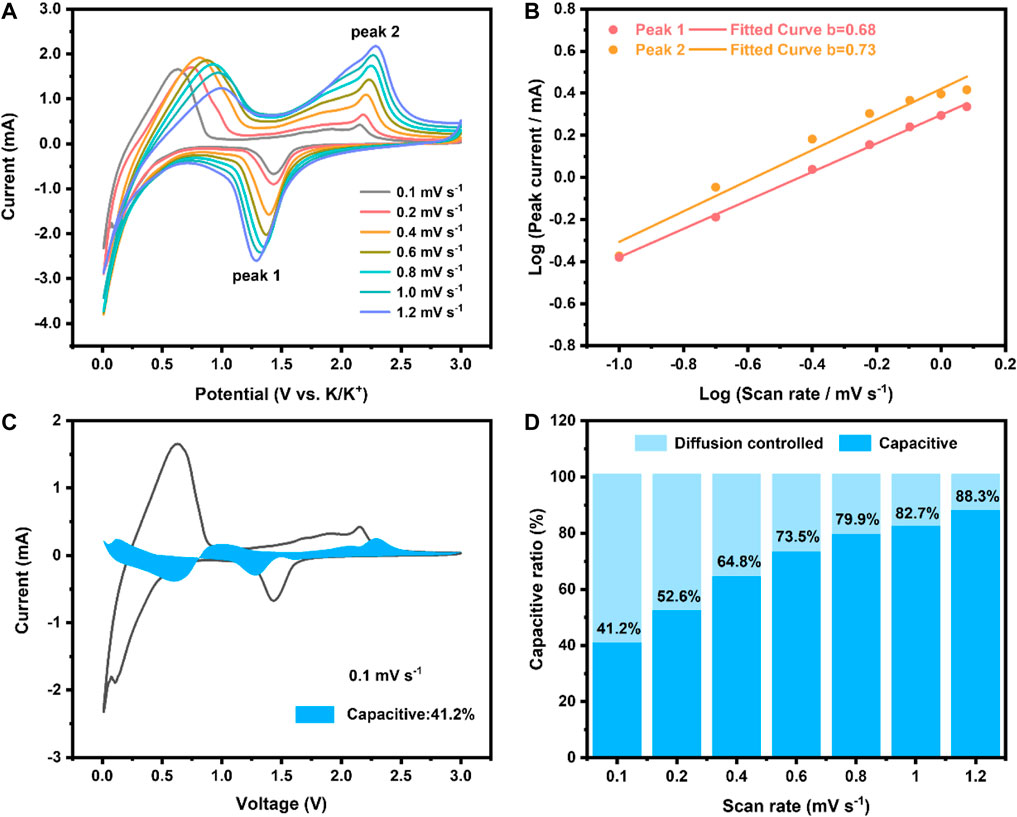
FIGURE 5. (A) CV curves of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC anode at different scan rates, (B) Plots for b-value determination, (C) Sketch view of the capacitive behavior of the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC anode at 1.0 mV s−1, and (D) Contribution rate of pseudocapacitance and diffusion control at different scan rates.
Conclusion
In summary, the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC were successfully fabricated by coating the polymer layer of polyphosphazene on the surfaces of NiCo2O4/CC followed by selenization and carbonization. The polyphosphazene-derived SPNC layer effectively alleviates the volume expansion of NiCo2Se4 and is beneficial to increase more active sites for the storage of K+ ions. Based on the effective combination of the SPNC and NiCo2Se4, the binder-free NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC anode shows a high reversible capacity of 880.9 mA h·g−1 at a current density of 0.1 A g−1 as well as good rate performance. Also, the NiCo2Se4⊂SPNC/CC anode could maintain a high reversible capacity of 268.1 mA h·g−1 after 500 cycles, at a current density of 0.5 A g−1. We have reason to believe that the anode materials of multiheteroatoms co-doped bimetallic selenides will show great potential application in PIB batteries.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author Contributions
JF: Supervision, Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing original draft. YZ: Writing–review and editing. ZZ: Methodology, Data curation, Investigation. WG: Visualization, Investigation. SZ: Supervision, writing–review and editing.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 22072088). This work was also sponsored by Shanghai Rising-Star Program (no. 19QA1404100). This work was financially supported by the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (20ZR1421400 and 19DZ2271100).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmats.2022.875684/full#supplementary-material.
References
Chen, K.-T., Chong, S., Yuan, L., Yang, Y.-C., and Tuan, H.-Y. (2021). Conversion-alloying Dual Mechanism Anode: Nitrogen-Doped Carbon-Coated Bi2Se3 Wrapped with Graphene for Superior Potassium-Ion Storage. Energ. Storage Mater. 39, 239–249. doi:10.1016/j.ensm.2021.04.019
Chong, X., Liu, C., Wang, C., Yang, R., and Zhang, B. (2021). Integrating Hydrogen Production and Transfer Hydrogenation with Selenite Promoted Electrooxidation of α‐Nitrotoluenes to E ‐Nitroethenes. Angew. Chem. 133, 22181–22187. doi:10.1002/ange.202108666
Cui, R. C., Xu, B., Dong, H. J., Yang, C. C., and Jiang, Q. (2020). N/O Dual‐Doped Environment‐Friendly Hard Carbon as Advanced Anode for Potassium‐Ion Batteries. Adv. Sci. 7, 1902547. doi:10.1002/advs.201902547
Ge, J., Fan, L., Wang, J., Zhang, Q., Liu, Z., Zhang, E., et al. (2018). MoSe2/N-Doped Carbon as Anodes for Potassium-Ion Batteries. Adv. Energ. Mater. 8, 1801477. doi:10.1002/aenm.201801477
Guan, C., Sumboja, A., Zang, W., Qian, Y., Zhang, H., Liu, X., et al. (2019). Decorating Co/CoNx Nanoparticles in Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanoarrays for Flexible and Rechargeable Zinc-Air Batteries. Energ. Storage Mater. 16, 243–250. doi:10.1016/j.ensm.2018.06.001
Hou, L., Shi, Y., Wu, C., Zhang, Y., Ma, Y., Sun, X., et al. (2018). Monodisperse Metallic NiCoSe2 Hollow Sub-Microspheres: Formation Process, Intrinsic Charge-Storage Mechanism, and Appealing Pseudocapacitance as Highly Conductive Electrode for Electrochemical Supercapacitors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1705921. doi:10.1002/adfm.201705921
Hu, Z., Liu, Q., Chou, S. L., and Dou, S. X. (2017). Advances and Challenges in Metal Sulfides/Selenides for Next‐Generation Rechargeable Sodium‐Ion Batteries. Adv. Mater. 29, 1700606. doi:10.1002/adma.201700606
Huang, H., Cui, J., Liu, G., Bi, R., and Zhang, L. (2019). Carbon-Coated MoSe2/MXene Hybrid Nanosheets for Superior Potassium Storage. ACS Nano 13, 3448–3456. doi:10.1021/acsnano.8b09548
Huang, M., Wang, X., Meng, J., Liu, X., Yao, X., Liu, Z., et al. (2020). Ultra-fast and High-Stable Near-Pseudocapacitance Intercalation Cathode for Aqueous Potassium-Ion Storage. Nano Energy 77, 105069. doi:10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.105069
Li, K., Chen, S., Chen, S., Liu, X., Pan, W., and Zhang, J. (2019). Nitrogen, Phosphorus Co-doped Carbon Cloth as Self-Standing Electrode for Lithium-Iodine Batteries. Nano Res. 12, 549–555. doi:10.1007/s12274-018-2251-1
Li, L., Zhao, J., Zhu, Y., Pan, X., Wang, H., and Xu, J. (2020). Bimetallic Ni/Co-ZIF-67 Derived NiCo2Se4/N-Doped Porous Carbon Nanocubes with Excellent Sodium Storage Performance. Electrochim. Acta 353, 136532. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136532
Liu, Y., Lu, Y. X., Xu, Y. S., Meng, Q. S., Gao, J. C., Sun, Y. G., et al. (2020). Pitch‐Derived Soft Carbon as Stable Anode Material for Potassium Ion Batteries. Adv. Mater. 32, 2000505. doi:10.1002/adma.202000505
Luo, M., Yu, H., Hu, F., Liu, T., Cheng, X., Zheng, R., et al. (2020). Metal Selenides for High Performance Sodium Ion Batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 380, 122557. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2019.122557
Qian, Y., Jiang, S., Li, Y., Yi, Z., Zhou, J., Li, T., et al. (2019). In Situ Revealing the Electroactivity of P-O and P-C Bonds in Hard Carbon for High‐Capacity and Long‐Life Li/K‐Ion Batteries. Adv. Energ. Mater. 9, 1901676. doi:10.1002/aenm.201901676
Qiu, L.-C., Wang, Q.-C., Yue, X.-Y., Qiu, Q.-Q., Li, X.-L., Chen, D., et al. (2020). NiCo2Se4 as an Anode Material for Sodium-Ion Batteries. Electrochemistry Commun. 112, 106684. doi:10.1016/j.elecom.2020.106684
Rajagopalan, R., Tang, Y., Ji, X., Jia, C., and Wang, H. (2020). Advancements and Challenges in Potassium Ion Batteries: A Comprehensive Review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 1909486. doi:10.1002/adfm.201909486
Shen, H., Gracia-Espino, E., Ma, J., Zang, K., Luo, J., Wang, L., et al. (2017). Synergistic Effects between Atomically Dispersed Fe−N−C and C−S−C for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Acidic Media. Angew. Chem. 129, 13988–13992. doi:10.1002/ange.201706602
Xie, S., Gou, J., Liu, B., and Liu, C. (2019). Nickel-cobalt Selenide as High-Performance and Long-Life Electrode Material for Supercapacitor. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 540, 306–314. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2019.01.030
Xu, C., Märker, K., Lee, J., Mahadevegowda, A., Reeves, P. J., Day, S. J., et al. (2020). Bulk Fatigue Induced by Surface Reconstruction in Layered Ni-Rich Cathodes for Li-Ion Batteries. Nat. Mater. 20, 84–92. doi:10.1038/s41563-020-0767-8
Xu, Y., Wang, C., Niu, P., Li, Z., Wei, L., Yao, G., et al. (2021). Tuning the Nitrogen-Doping Configuration in Carbon Materials via Sulfur Doping for Ultrastable Potassium Ion Storage. J. Mater. Chem. A. 9, 16150–16159. doi:10.1039/d1ta03811g
Yu, P., Wang, L., Sun, F., Xie, Y., Liu, X., Ma, J., et al. (2019). Co Nanoislands Rooted on Co-N-C Nanosheets as Efficient Oxygen Electrocatalyst for Zn-Air Batteries. Adv. Mater. 31, 1901666. doi:10.1002/adma.201901666
Zeng, Y., Meng, Y., Lai, Z., Zhang, X., Yu, M., Fang, P., et al. (2017). An Ultrastable and High-Performance Flexible Fiber-Shaped Ni-Zn Battery Based on a Ni-NiO Heterostructured Nanosheet Cathode. Adv. Mater. 29, 1702698. doi:10.1002/adma.201702698
Zhang, Y., Li, T., Cao, S.-A., Luo, W., and Xu, F. (2020). NiCo2Se4 Hierarchical Microflowers of Nanosheets and Nanorods as Pseudocapacitive Mg-Storage Materials. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 8, 2964–2972. doi:10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b07592
Zhang, W., Yin, J., Wang, W., Bayhan, Z., and Alshareef, H. N. (2021). Status of Rechargeable Potassium Batteries. Nano Energy 83, 105792. doi:10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.105792
Zhao, Z., Gao, C., Fan, J., Shi, P., Xu, Q., and Min, Y. (2021). Dual Confinement of CoSe2 Nanorods with Polyphosphazene-Derived Heteroatom-Doped Carbon and Reduced Graphene Oxide for Potassium-Ion Batteries. ACS Omega 6, 17113–17125. doi:10.1021/acsomega.1c02649
Zheng, J., Wu, Y., Sun, Y., Rong, J., Li, H., and Niu, L. (2021). Advanced Anode Materials of Potassium Ion Batteries: From Zero Dimension to Three Dimensions. Nano-micro Lett. 13, 1–37. doi:10.1007/s40820-020-00541-y
Zhou, C., Zhang, P., Liu, J., Zhou, J., Wang, W., Li, K., et al. (2021). Hierarchical NiCo2Se4 Nanoneedles/nanosheets with N-Doped 3D Porous Graphene Architecture as Free-Standing Anode for superior Sodium Ion Batteries. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 587, 260–270. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2020.12.015
Zhu, S., Li, Q., Wei, Q., Sun, R., Liu, X., An, Q., et al. (2017). NiSe2 Nanooctahedra as an Anode Material for High-Rate and Long-Life Sodium-Ion Battery. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 9, 311–316. doi:10.1021/acsami.6b10143
Keywords: potassium-ion batteries, bimetallic selenides, tri-doped carbon, carbon cloth, binder-free anode
Citation: Fan J, Zheng Y, Zhao Z, Guo W and Zhu S (2022) Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur Tri-doped Carbon A Coated NiCo2Se4 Needle Arrays Grown on Carbon Cloth as Binder-free Anode for Potassium-Ion Batteries. Front. Mater. 9:875684. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2022.875684
Received: 14 February 2022; Accepted: 23 February 2022;
Published: 09 March 2022.
Edited by:
Likun Pan, East China Normal University, ChinaCopyright © 2022 Fan, Zheng, Zhao, Guo and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sheng Zhu, emh1c2hlbmdAc2hpZXAuZWR1LmNu
 Jinchen Fan
Jinchen Fan Yujun Zheng2
Yujun Zheng2 Sheng Zhu
Sheng Zhu