
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Mater. , 21 November 2016
Sec. Ceramics and Glass
Volume 3 - 2016 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2016.00053
This article is part of the Research Topic Ultrastrong Glasses: Improving Mechanical Properties of Disordered Solids through Topo-Chemical Engineering View all 14 articles
Chemical strengthening of aluminosilicate glasses through K+–Na+ ion exchange has attracted tremendous attentions because of the accelerating demand for high strength and damage resistance glasses. However, a paramount challenge still exists to fabricate glasses with a higher strength and greater depth of ion-exchange layer (DOL). Herein, aluminosilicate glasses with different contents of P2O5 were prepared, and the influence of P2O5 on the increased compressive stress (CS) and DOL was investigated by micro-Raman technique. It was noticed that the hardness, CS, as well as the DOL substantially increased with an increasing concentration of P2O5 varied from 1 to 7 mol%. The obtained micro-Raman spectra confirmed the formation of relatively depolymerized silicate anions that accelerated the ion exchange. Phosphorus-containing aluminosilicate glasses with a lower polymerization degree exhibited a higher strength and deeper DOL, which suggests that the phosphorus-containing aluminosilicate glasses have promising applications in flat panel displays, windshields, and wafer sealing substrates.
The development of ultrathin, high strength, and damage resistance glasses for flat panel displays, windshields, and wafer sealing substrates is an ongoing challenge (Wondraczek et al., 2011; Käfer et al., 2013; Mauro et al., 2016). Traditionally, the practical strength of glasses is two orders of magnitude lower than the theoretical value due to the flaws and defects on the glass surface (Wiederhorn et al., 2013). It is therefore of the outmost importance to eliminate the defects to improve the strength. Various methods of glass strengthening have been developed extensively over the last few decades, such as thermal tempering (Solinov, 2015), chemical strengthening (Olcott, 1963; Karlsson et al., 2010; Varshneya, 2010a,b), and surface crystallization (Donald, 1989). It is noteworthy that chemical strengthening, which is achieved essentially by immersing an alkali-containing glass in a molten salt bath, generates high compressive stress (CS) in thin or irregularly shaped glass objects without measureable optical distortion, making it the leading candidate for strengthening of glasses (Kistler, 1962; Olcott, 1963; Karlsson et al., 2010; Varshneya, 2010a,b). The chemical strengthening properties of glasses are typically characterized by CS and depth of ion-exchange layer (DOL). Moreover, these properties depend much on glass composition and topological restriction (Smedskjaer et al., 2010; Vargheese et al., 2014; Calahoo et al., 2016).
Chemically strengthened aluminosilicate glasses through K+–Na+ ion exchange are currently receiving significant interest due to their excellent mechanical properties (Chang et al., 2014). Previous researches indicated that the DOL of high-alkali aluminosilicate glasses can reach 30–75 μm at 430–490°C for 3–8 h, and the hardness can be enhanced (Wu et al., 2011; Jiang et al., 2013). Because of the increasing demand for high strength and damage resistance glasses, new methods to enhance CS, DOL, and hardness have become a focus of research. Up to now, many investigations on the strengthening process, molten salt, and glass composition have been carried out (Nordberg et al., 1964; Anna and Mauro, 2013; Svenson et al., 2014; Sglavo, 2015). However, the treatment of aluminosilicate glasses was limited in chemical strengthening due to the relatively small DOL. A large value of DOL is required to embed surface flaws and defects in the compressive stress layer. For the glasses designed with a fixed value of DOL, significant cost saving can be achieved by increasing the ion diffusion rate and thus shortening the ion-exchange time. Previous researchers suggested that the addition of P2O5 can accelerate the process of ion exchange and increase the DOL (Burggraaf and Cornelissen, 1964; Zhang et al., 2012; Bookbinder et al., 2013; Chapman et al., 2014). However, it still remains a grand challenge to reveal the underlying mechanism of ion-exchanged aluminosilicate glasses through introducing P2O5.
In this study, the effect of P2O5 on the structure and mechanical properties of ion-exchanged aluminosilicate glasses was systematically investigated. The diffusion coefficient and activation energy Ea of ion-exchanged xP2O5–(100 − x)(0.25Na2O–0.08Al2O3–0.67SiO2) (x = 5) glass treated at 400°C for different ion-exchange times and different ion-exchange temperatures for 6 h were calculated. Then, the hardness, CS, and DOL were measured with the addition of P2O5. Furthermore, the topological structure evolution of phosphorus-containing aluminosilicate glasses was observed by micro-Raman technique to comprehensively analyze the mechanism of ion-exchange strengthening.
A series of xP2O5–(100 − x)(0.25Na2O–0.08Al2O3–0.67SiO2) (x = 1, 3, 5, 6, and 7 mol%, respectively) glass samples were prepared by conventional melt-quenching technique using Na2CO3, SiO2, and Al(OH)3 from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Company and AlPO4 from Aladdin. The starting materials (ca. 20 g) were thoroughly mixed in an agate mortar, and the homogeneous mixture was transferred into a corundum crucible and preheated at 800°C for 30 min before being fully melted at temperatures between 1550 and 1650°C, depending on the composition. The liquid melt was kept at this temperature for an hour to ensure homogenization before it was cooled rapidly in a preheated brass mold to form bulk glasses and annealed at 560°C for 4 h to diminish internal stresses. Then, the glass samples were allowed to cool to room temperature. Such glasses were cut and polished into 2 mm for ion-exchange treatment. In the ion-exchange process, sample 5P2O5-95(0.25Na2O–0.08Al2O3–0.67SiO2) was immersed into a molten KNO3 salt bath at different temperatures (390, 400, 410, 420, and 430°C) for different durations (2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 h). Other samples were treated in a molten KNO3 salt bath by submersion at 400°C for 6 h. Then, the glass specimens were carefully cleaned with deionized water followed by ethanol and stored in a desiccator.
The Vickers hardness value of the polished glasses was determined with micro-indenter (HXD-1000TMC/LCD, Shanghai Taiming Optical Instrument Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China) at room temperature, where the indentation was performed on the surface of each sample at a load of 0.98 N for 10 s. A minimum of 24 indents were measured on each sample. Error bars in the figures all represent the SD across the measured values of hardness. The measurement error for the hardness was less than ±4%. The DOL for each sample was measured on a field-emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) equipped with an energy-dispersive spectrometer (EDS) in line scan mode (S-4800, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan), where the acceleration voltage was 15.0 kV. Based on the potassium and sodium ion concentration profiles in the ion-exchanged glass surface, the DOL was determined when the potassium and sodium ion concentration profiles reached virtually 0 and a constant value, respectively. The CS was measured by using a surface stress meter (FSM-6000LE, Orihara, Tokyo, Japan). Birefringence can be used to directly probe the compressive stress found in the ion-exchange layer because of the compositional gradient. The measurement error for DOL and CS were less than ±5%. Micro-Raman spectra were recorded to investigate the topological structure of glass samples. A Raman spectrometer (INVIA, Renishaw, Gloucestershire, England) with an Ar+-ion laser (514.5 nm) as the irradiation source was employed. Baseline correction was performed using the Wire software program from Renishaw.
The DOL and diffusion coefficients of ion-exchanged xP2O5–(100 − x)(0.25Na2O–0.08Al2O3–0.67SiO2) (x = 5) glass treated at 400°C for different ion-exchange times and different ion-exchange temperatures for 6 h are shown in Figures 1A,B, respectively. Obviously, the DOL is directly related to the ion-exchange time and temperature. With an increasing ion-exchange time and temperature, the DOL drastically increases. It is noteworthy that the DOL for such glasses is higher or comparable with some commercial glasses (Wang et al., 2008; Stavrou et al., 2014), which is desirable for chemically strengthened glasses. To understand the diffusion kinetics of K+ ions in such glasses, the diffusion coefficient and activation energy must be determined. The diffusion coefficient as a function of the local concentration D(C) can be calculated in accordance with the Boltzmann–Matano approach (Matano, 1933; Barton, 1975):
where D(C) is the diffusion coefficient as a function of the local K+ ion concentration, x is the distance from the glass surface, C is the K+ ion concentration, and t is the duration of the diffusion process.
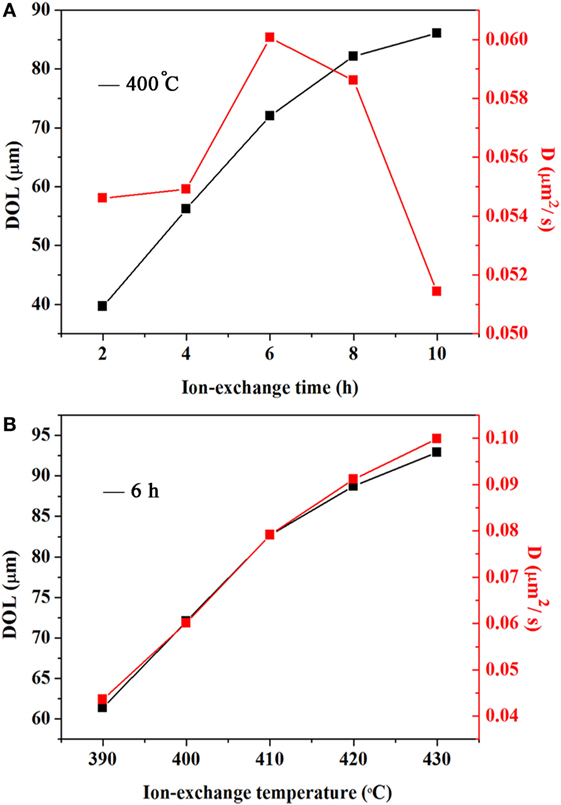
Figure 1. DOL and diffusion coefficient of ion-exchanged xP2O5–(100 − x)(0.25Na2O–0.08Al2O3–0.67SiO2) (x = 5) glass. (A) DOL and diffusion coefficient of the glass treated at 400°C for different ion-exchange durations; (B) DOL and diffusion coefficient of the glass treated at different ion-exchange temperatures for 6 h.
The rate of alkali interdiffusivity depends on the free volume (atomic packing fraction) of the glass network structure (Svenson et al., 2016). And the activation energy has been found to scale with the free volume in the related studies on K+–Na+ interdiffusivity (Potuzak and Smedskjaer, 2014; Smedskjaer et al., 2015). The activation energy Ea (J/mol) for ionic diffusion can be calculated using the Arrhenius equation (Frischat et al., 1975):
where D0 is a constant, Ea is the activation energy for the diffusion process, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is the absolute temperature. Plotting ln D versus T−1 gives the slope k = −Ea/R. The activation energy is assumed to be independent of the temperature.
As shown in Figure 1, the resultant diffusion coefficient increases with an increasing temperature. However, the diffusion coefficient increases with the ion-exchange time until it reaches the maximum of 6 h and then decreases with a longer ion-exchange time. This result may be due to the accumulation of K+ ions in the glass surface that decreases the ion diffusion. The Ea is obtained by fitting the diffusion coefficient data using the Arrhenius equation. The activation energy Ea for ionic diffusion is shown in Figure 2. The red line is the linear fitting result. The calculated Ea value is ca. 80.8 kJ/mol, which is smaller than the values (sodium aluminosilicate glass, 95.4 kJ/mol; soda–lime–silica float glass, 152 kJ/mol) reported in the literature (Shen et al., 2003). The reduced activation energy favors the diffusion of K+–Na+ ions that promote the ion exchange in such phosphorus-containing aluminosilicate glasses.
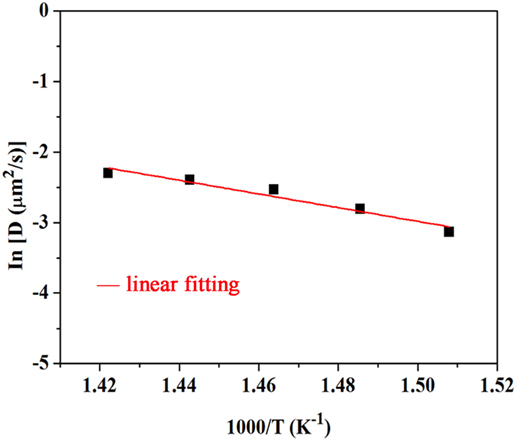
Figure 2. Diffusion coefficient as a function of reciprocal temperature for ion-exchanged xP2O5–(100 − x)(0.25Na2O–0.08Al2O3–0.67SiO2) (x = 5) glass at different ion-exchange temperatures for 6 h.
Moreover, as can be observed from Figure 3, ion exchange of the raw glasses leads to a pronounced increase in hardness. As the ion-exchange time and temperature is increased, the hardness increases until 400°C for 6 h and then decreases. The maximum hardness in the studied glass is up to 5.9 GPa. The increment in hardness is mainly attributed to the formation of surface compression through ion exchange, and the hardness decreases afterward is because of the structural relaxation (Garfinkel and King, 1970; Donald, 1989).
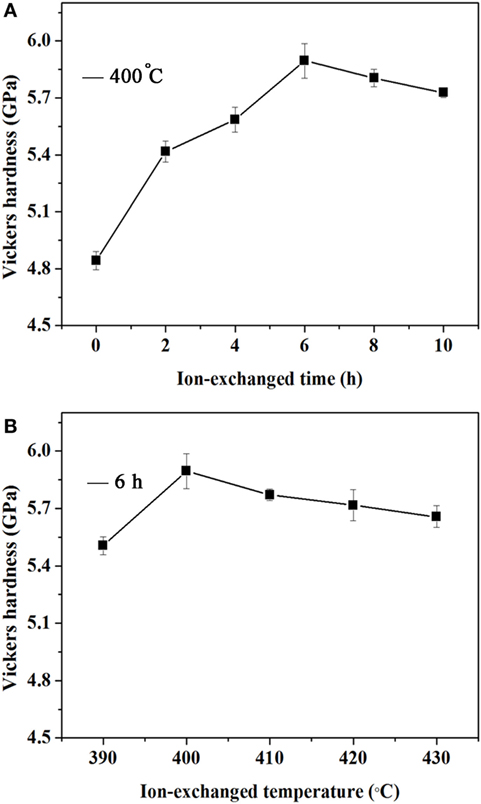
Figure 3. Vickers hardness values of xP2O5–(100 − x)(0.25Na2O–0.08Al2O3–0.67SiO2) (x = 5). (A) Vickers hardness values of the glass treated at 400°C for different ion-exchange durations; (B) Vickers hardness values of the glass treated at different ion-exchange temperatures for 6 h.
Based on the above results, the relatively optimized ion-exchange treatment in xP2O5–(100 − x)(0.25Na2O–0.08Al2O3–0.67SiO2) (x = 1, 3, 5, 6, and 7 mol%, respectively) glasses is performed at 400°C for 6 h. The Vickers hardness values of xP2O5–(100 − x)(0.25Na2O–0.08Al2O3–0.67SiO2) (x = 1, 3, 5, 6, and 7 mol%, respectively) glasses treated at 400°C for 6 h were plotted as a function of the concentration of P2O5 and are shown in Figure 4A. With an increasing concentration of P2O5, the hardness of the untreated glasses decreases from about 5.1 to 4.8 GPa. On the contrary, the hardness of the glass samples with ion exchange significantly increases from 5.5 to 6.1 GPa with an increasing concentration of P2O5, indicating that the addition of P2O5 can enhance the strength through ion exchange. In addition, the result can be further confirmed by the images of the indentations in Figure 4B, which shows that the diagonal length of the indentations (d) becomes smaller with an increasing concentration of P2O5. Because of the slight increase in hardness when x > 5 mol%, the change of indentation is not obvious.
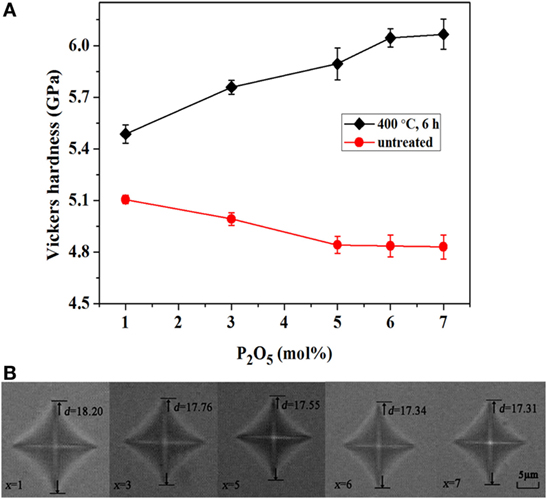
Figure 4. Vickers hardness values of xP2O5–(100 − x)(0.25Na2O–0.08Al2O3–0.67SiO2) (x = 1, 3, 5, 6, and 7 mol%, respectively) glass series treated at 400°C for 6 h. (A) Vickers hardness as a function of the concentration of P2O5 at room temperature before and after ion-exchange treatment; (B) images of the indentations of ion-exchanged glasses after a load of 0.98 N for 10 s.
Ion exchange between K+ and Na+ ions lead to the development of high surface compressive stress. Meanwhile, the strengthening treatment was carried out at a temperature below the annealing range, so that the stress introduced is not removed by relaxation. Figure 5 shows the linear increase of CS and DOL with an increase in P2O5 concentration. It is observed that the CS is monotonically improved when P2O5 concentration was increased, which is basically identical to the tendency of hardness. Additionally, the DOL increases with an increase in P2O5 concentration from 1 to 7 mol%. This is due to the change in atomic packing factor of the glasses with varying P2O5 that promotes the K+–Na+ interdiffusivity. Therefore, it is interesting to note that the presence of P2O5 in aluminosilicate glasses enables the glass to be ion-exchanged more efficiently and to a greater depth that effectively enhance the strength and damage resistance of the glass.
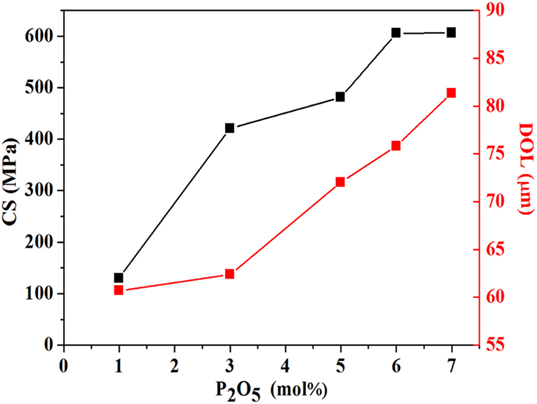
Figure 5. CS and DOL of xP2O5–(100 − x)(0.25Na2O–0.08Al2O3–0.67SiO2) (x = 1, 3, 5, 6, and 7 mol%, respectively) chemically strengthened glasses treated at 400°C for 6 h.
Micro-Raman spectroscopy can be used to determine the structural modifications occurring in the glasses. In Figure 6, spectra are shown as a function of an increasing P2O5 content from 1 to 7 mol% in the range of 400–1500 cm−1. In the following discussion, P(n) represents a [PO4] tetrahedron with n bridging oxygen, and the symbol Si(n) represents a [SiO4] tetrahedron with n bridging oxygen.
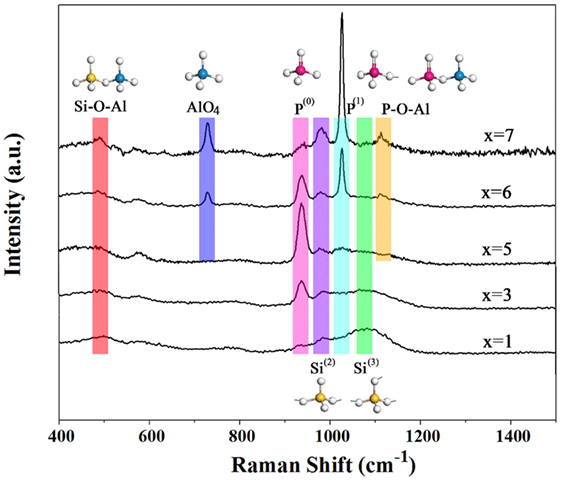
Figure 6. Micro-Raman spectra of aluminosilicate glasses with x mol% P2O5 concentration (x = 1, 3, 5, 6, and 7 mol%, respectively).
The spectra of low-P2O5 glass show four major features centered near 500, 936, 980, and 1090 cm−1, respectively. With an increasing content of P2O5, several new peaks appeared in 730, 1024, and 1120 cm−1. The low-frequency region exhibits a maximum near 500 cm−1 with a shoulder or peak on both the low- and high-frequency side (near 500 and 600 cm−1, respectively) attributes to an oxygen breathing mode of the centers of four- and three-membered rings, respectively, which are contained in a tetrahedral structure (Lazzeri and Mauri, 2003). With an increasing content of P2O5, the shoulder or band frequencies near 500 cm−1 appear insensitive to P2O5 content. The band near 936 cm−1 is assigned to P–O symmetric stretching of non-bridging oxygen ions in orthophosphate units [PO4]−3 or P(0). The high-frequency region (>900 cm−1) of the spectra of P2O5 glass varies significantly with P2O5 content. In the spectra of low-P2O5 glasses, the Raman spectra exhibit a characteristics strong band near 936 cm−1 assigned to P–O stretching in orthophosphate complexes together with a weak band near 1024 cm−1 assigned to bending vibration in pyrophosphate units [PO3O1/2]−2 or P(1) (Mysen, 1996). With an increasing P2O5 content, the Raman spectrum intensity centered near 1024 cm−1 becomes remarkably more intense. The proportion of P(1) initially increased relative to P(0) and was joined by AlPO4 complexes which exhibit a characteristic P–O stretch mode slightly above 1100 cm−1 (Jin et al., 1986). The decrease in P(0)/P(1) with an increasing P2O5 content results in depolymerization of the silicate melts (Mysen, 1998).
The Raman bands observed from 650 to 750 cm−1 are attributed to the presence of Al2O3. Iwamoto et al. (1978) attributed the peak at 700–800 cm−1 to the contribution of AlO4 tetrahedral. And the intensity of AlO4 is related to AlPO4 in 1120 cm−1. With an increasing content of P2O5, the Al–O–P network increases.
The bands located at 980 and 1090 cm−1 contribute to the stretching vibration mode in Si(2) and Si(3), respectively (Aguiar et al., 2009). A further P2O5 increase results in a rapid disappearance of Si(3) and an increase of Si(2) with this region of the spectra gradually becoming dominated by a maximum near 1024 cm−1. So in these glasses, based on the structure change of Si(3) and Si(2), it is clear that both extra non-bridging oxygen ions and positive cations are needed in the transformation process from Si(3) to Si(2). And they could only be scavenged from the original phosphor network. As the phosphor network loses some of non-bridging oxygen ions and positive cations from P(0) to P(1), the peaks of P(0) and Si(3) gradually become less prominent with an increase of P2O5, and the opposite trend is true for the peaks of P(1) and Si(2), following a chemical reaction:
The law for the structure development is consistent with the equilibrium of Le Chatelier’s principle (Chatelier, 1888; Toplis and Schaller, 1998). As the phosphor network loses some non-bridging oxygen ions, the degree of polymerization of silicate network decreases, namely, the formation of relatively depolymerized silicate anions. Therefore, this topological evolution reveals that aluminosilicate glasses with x mol% P2O5 addition (x = 1, 3, 5, 6, and 7 mol%) can accelerate the ion exchange and result in a greater depth of ion exchange.
Additionally, on the basis of the Raman spectroscopic results, we developed a schematic plot of ion exchange process in glass surface at various concentrations of P2O5, as shown in Figure 7. Along with an increasing concentration of P2O5, the network of glass surface is “opened” due to the decrease of polymerization degree of the glass, which is beneficial for the exchange of Na+ with K+ in the glass surface by interdiffusion upon submersion in a liquid molten salt bath (KNO3). This results in the formation of a compressive stress on surface and enhancement of DOL, strength, and damage resistance of the glass.
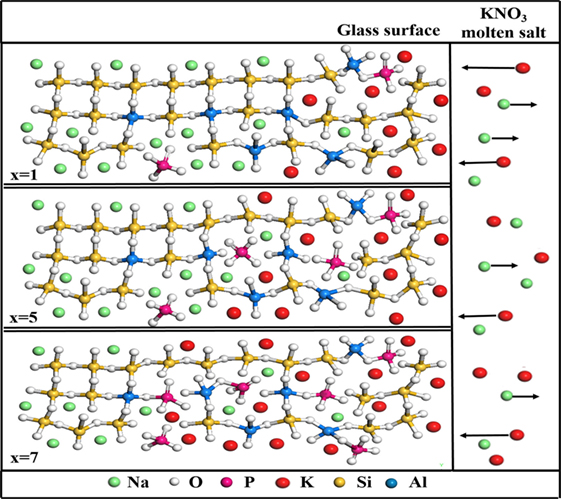
Figure 7. Schematic plot of ion-exchange process in the glass surface at various concentrations of P2O5 (x = 1, 5, and 7 mol%) treated at 400°C for 6 h.
Phosphorus-containing aluminosilicate glasses strengthened by ion exchange were developed, and their mechanical properties and DOL were characterized. The diffusion coefficients and activation energy were calculated by the Boltzmann–Matano approach and the Arrhenius equation. The higher diffusion coefficient and lower activation energy favor the diffusion of K+–Na+ that promotes the ion exchange in these phosphorus-containing aluminosilicate glasses. The increased hardness, DOL, and CS indicate the addition of P2O5 is an appealing approach to improve the strength of ion-exchanged glasses and to a greater depth of ion exchange layer. Furthermore, the obtained micro-Raman spectra show the evidence for the formation of relatively depolymerized silicate anions, indicating a decrease of polymerization degree that accelerates the ion exchange. The schematic of ion exchange at various concentrations of P2O5 is proposed, which suggests that the presence of P2O5 in chemically strengthened aluminosilicate glasses increases the DOL and strength. Because of their convenient manufacturing, such kind of phosphorus-containing aluminosilicate glasses may find promising applications in flat panel displays, windshields, and wafer sealing substrates.
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. HZ and LW designed experiments; LW, FY, and BY carried out experiments; HZ, LW, JC, GC, and LS analyzed the experimental results. HZ and LW wrote the manuscript. All the authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21476083, No. 51572082); the Major Program of Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (No. ZD14521100604); the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. WD1313009), and the Open Fund of the Key Laboratory for Ultrafine Materials of the Ministry of Education at East China University of Science and Technology. Furthermore, we would like to thank Dr. Guangjun Zhang and Dr. Feng He [Schott Glass Technology (Suzhou) Co., Ltd] for helpful discussions on glass structure.
Aguiar, H., Serra, J., González, P., and León, B. (2009). Structural study of sol-gel silicate glasses by IR and Raman spectroscopies. J. Non Cryst. Solids 355, 475–480. doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2009.01.010
Anna, I. F., and Mauro, J. C. (2013). Mutual diffusivity, network dilation, and salt bath poisoning effects in ion-exchanged glass. J. Non Cryst. Solids 363, 199–204. doi:10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2012.12.037
Barton, G. (1975). The mathematics of diffusion. Physics Bullet. 26, 500. doi:10.1088/0031-9112/26/11/044
Bookbinder, D. C., Gross, T. M., and Potuzak, M. (2013). Ion Exchangeable Glass with Deep Compressive Layer and High Damage Threshold. E.P. Patent 2646378 A1.
Burggraaf, A. J., and Cornelissen, J. (1964). The strengthening of glass by ion exchange: part 1. Phys. Chem. Glasses 5, 123–129.
Calahoo, C., Zwanziger, J. W., and Butler, I. S. (2016). Mechanical-structural investigation of ion-exchanged lithium silicate glass using micro-Raman spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 7213–7232. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b01720
Chang, K. C., Tung, L. T., and Liu, Y. C. (2014). The mechanical properties of aluminosilicate glass with chemical strengthening. SID Symp. Digest Technol. Pap. 45, 1226–1229. doi:10.1002/j.2168-0159.2014.tb00320.x
Chapman, C. L., Dejneka, M. J., Gomez, S., and Lamberson, L. A. (2014). Ion Exchangeable Glasses. U.S. Patent 0308526 A1.
Chatelier, H. L. (1888). Recherches expérimentales et théoriques sur les équilibres chimiques. Ann Mines 13, 200.
Donald, I. W. (1989). Review methods for improving the mechanical properties of oxide glasses. J. Mater. Sci. 24, 4177–4208. doi:10.1007/BF00544488
Frischat, G. H., Adda, Y., Le Claire, A. D., Slifkin, L. M., and Wohlbier, F. H. (1975). Ionic Diffusion in Oxide Glasses. Diffusion and Defect Monograph Series. Zurich: Trans Tech Publications.
Garfinkel, H. M., and King, C. B. (1970). Ion concentration and stress in a chemically tempered glass. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 53, 686–691. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1970.tb12043.x
Iwamoto, N., Tsunawaki, Y., Hattori, T., and Mitsuishi, A. (1978). Raman spectra of Na2O-SiO2-Al2O3 and K2O-SiO2-Al2O3 glasses. Phys. Chem. Glasses 19, 141–143.
Jiang, L. B., Guo, X. T., Li, X. Y., Li, L., Zhang, G. L., and Yan, Y. (2013). Different K+-Na+ inter-diffusion kinetics between the air side and tin side of an ion-exchanged float aluminosilicate glass. Appl. Surf. Sci. 265, 889–894. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.11.143
Jin, Y. F., Jiang, D. H., Chen, X. S., Bian, B. Y., and Huang, X. H. (1986). Raman spectrum studies of the glasses in the system Na2O-Al2O3-P2O5. J. Non Crystal. Solids 80, 147–151. doi:10.1016/0022-3093(86)90388-1
Karlsson, S., Jonson, B., and Stalhandske, C. (2010). The technology of chemical glass strengthening – a review. Glass Technol. Eur. J. Glass Sci. Technol. 51, 41–54.
Käfer, D., He, M. Q., Li, J. F., Pambianchi, M. S., Feng, J. W., Mauro, J. C., et al. (2013). Ultra-smooth and ultra-strong ion-exchanged glass as substrates for organic electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23, 3233–3238. doi:10.1002/adfm.201202009
Kistler, S. S. (1962). Stresses in glass produced by nonuniform exchange of monovalent ions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 45, 59–68. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1962.tb11081.x
Lazzeri, M., and Mauri, F. (2003). First-principles calculation of vibrational Raman spectra in large systems: signature of small rings in crystalline SiO2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 036401. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.90.036401
Matano, C. (1933). On the relation between the diffusion coefficients and concentrations of solid metals. Jpn. J Appl. Phys. 8, 109.
Mauro, J. C., Tandia, A., Vargheese, K. D., Mauro, Y. Z., and Smedskjaer, M. M. (2016). Accelerating the design of functional glasses through modeling. Chem. Mater. 28, 4267–4277. doi:10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b01054
Mysen, B. O. (1996). Phosphorus speciation changes across the glass transition in highly polymerized alkali silicate glasses and melts. J. Non Crystal. Solids 81, 1531–1534. doi:10.2138/am-1996-11-1227
Mysen, B. O. (1998). Phosphorus solubility mechanisms in haplogranitic aluminosilicate glass and melt: effect of temperature and aluminum content. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 133, 38–50. doi:10.1007/s004100050435
Nordberg, M. E., Mochel, E. L., Garfinkel, H. M., and Olcott, J. S. (1964). Strengthening by ion exchange. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 47, 215–219. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1964.tb14399.x
Olcott, J. S. (1963). Chemical strengthening of glass. Science 140, 1189–1193. doi:10.1126/science.140.3572.1189
Potuzak, M., and Smedskjaer, M. M. (2014). Alkali diffusivity in alkaline earth sodium boroaluminosilicate glasses. Solid State Ionics. 263, 95–98. doi:10.1016/j.ssi.2014.05.015
Sglavo, V. M. (2015). Chemical strengthening of soda lime silicate float glass: effect of small differences in the KNO3 bath. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 6, 72–82. doi:10.1111/ijag.12101
Shen, J. W., Green, D. J., and Pantano, C. G. (2003). Control of concentration profiles in two step ion exchanged glass. Phys. Chem. Glasses 44, 284–292.
Smedskjaer, M. M., Mauro, J. C., Sen, S., and Yue, Y. Z. (2010). Quantitative design of glassy materials using temperature-dependent constraint theory. Chem. Mater. 22, 5358–5365. doi:10.1021/cm1016799
Smedskjaer, M. M., Mauro, J. C., and Yue, Y. Z. (2015). Cation diffusivity and the mixed network former effect in borosilicate glasses. J. Phys. Chem. B 119, 7106–7115. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcb.5b03520
Solinov, V. F. (2015). Ways to strengthen glass: toughening, ion-exchange. Glass Ceram. 72, 191–193. doi:10.1007/s10717-015-9753-z
Stavrou, E., Palles, D., Kamitsos, E. I., Lipovskii, A., Tagantsev, D., Svirko, Y., et al. (2014). Vibrational study of thermally ion-exchanged sodium aluminoborosilicate glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 401, 232–236. doi:10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2013.12.017
Svenson, M. N., Thirion, L. M., Youngman, R. E., Mauro, J. C., Bauchy, M., Rzoska, S. J., et al. (2016). Effects of thermal and pressure histories on the chemical strengthening of sodium aluminosilicate glass. Front. Mater. 3:14. doi:10.3389/fmats.2016.00014
Svenson, M. N., Thirion, L. M., Youngman, R. E., Mauro, J. C., Rzoska, S. J., Bockowski, M., et al. (2014). Pressure-induced changes in interdiffusivity and compressive stress in chemically strengthened glass. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 10436–10444. doi:10.1021/am5019868
Toplis, M. J., and Schaller, T. (1998). A 31P MAS NMR study of glasses in the system xNa2O-(1-x) Al2O3-2SiO2-yP2O5. J. Non Cryst. Solids 224, 57–68. doi:10.1016/S0022-3093(97)00458-4
Vargheese, K. D., Tandia, A., and Mauro, J. C. (2014). Molecular dynamics simulations of ion-exchanged glass. J. Non Cryst. Solids 403, 107–112. doi:10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2014.07.025
Varshneya, A. K. (2010a). Chemical strengthening of glass: lessons learned and yet to be learned. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 1, 131–142. doi:10.1111/j.2041-1294.2010.00010.x
Varshneya, A. K. (2010b). The physics of chemical strengthening of glass: room for a new view. J. Non Cryst. Solids 356, 2289–2294. doi:10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2010.05.010
Wang, H. F., Han, W. J., and Wang, Y. M. (2008). The effect of ion exchange on glass surface morphology and composition. J. Non Cryst. Solids 354, 1146–1150. doi:10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2006.11.054
Wiederhorn, S. M., Fett, T., Guin, J. P., and Ciccotti, M. (2013). Griffith cracks at the nanoscale. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 4, 76–86. doi:10.1111/ijag.12025
Wondraczek, L., Mauro, J. C., Eckert, J., Kühn, U., Horbach, J., Deubener, J., et al. (2011). Towards ultrastrong glasses. Adv. Mater. 23, 4578–4586. doi:10.1002/adma.201102795
Wu, Z., Shen, X. H., and Tian, Y. L. (2011). High Strength Aluminosilicate Glass and Chemically Toughening Process Thereof. CN101337770.
Keywords: chemical strengthening, ion-exchange layer, compressive stress, P2O5, micro-Raman
Citation: Zeng H, Wang L, Ye F, Yang B, Chen J, Chen G and Sun L (2016) Mechanical–Structural Investigation of Chemical Strengthening Aluminosilicate Glass through Introducing Phosphorus Pentoxide. Front. Mater. 3:53. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2016.00053
Received: 24 September 2016; Accepted: 09 November 2016;
Published: 21 November 2016
Edited by:
Lothar Wondraczek, University of Jena, GermanyReviewed by:
Stefan Karlsson, SP Technical Research Institute of Sweden, SwedenCopyright: © 2016 Zeng, Wang, Ye, Yang, Chen, Chen and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Huidan Zeng, aGR6ZW5nQGVjdXN0LmVkdS5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.