- 1Laboratory for Marine Fisheries Science and Food Production Processes, Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Qingdao, China
- 2Key Lab of Sustainable Development of Marine Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture, Qingdao, China
Introduction
Many animals (including human) belonged to Bilateria and their external shapes showed left-right symmetry (Palmer, 1996), while the internal organs developed asymmetrically during embryonic development (Levin, 2005). Previous studies have shown that ciliary motility were critical for left-right asymmetry in embryonic development (Tisler et al., 2016). Ciliary motility could lead to asymmetric distribution of Hedgehog (Hh) proteins, which in turn leaded to asymmetric expression of downstream genes resulting in embryonic left-right asymmetry (Zhu et al., 2020). Cilia- and flagella-associated protein 53 (cfap53) played an important role in ciliary rotation, and could regulate the left and right asymmetry of human internal organs (Narasimhan et al., 2015; Noel et al., 2016; Gur et al., 2017). The breaking mechanism of its left-right asymmetry had always been one of the important fundamental issues in developmental biology research (Sutherland and Ware, 2009).
Having an asymmetrical skull with both eyes on the same side was the most typical feature of flatfish, which was one of the most asymmetrical body shape among vertebrates. (Schreiber, 2006; Friedman, 2008; Bao et al., 2011; Li et al., 2013; Schreiber, 2013). The study on the mechanism of left-right asymmetry in flatfish was helpful to deepen the understanding of the mechanism of left-right axis establishment. For flatfish metamorphosis, Shao et al. found that thyroid hormone and retinoic acid signal transduction, as well as the phototransduction process, played important roles in flatfish metamorphosis (Shao et al., 2017). Meanwhile, they also found that retinoic acid inhibited eye migration by interfering with thyroid hormone heterodimerization on retinoic acid receptor/thyroid hormone receptor formation. Lü et al. through comparative genomic analysis found that some genes of the retinoic acid and WNT signaling pathways related to body axis development in the flatfish genome were significant changes (Lu et al., 2021). In vertebrates such as humans and zebrafish, mutations in these genes often caused asymmetry in craniofacial tissue and body development (Juriloff et al., 2006; Marini et al., 2019), which indicated that they played crucial roles in the development of the asymmetric body axis of the flatfish. At the same time, they further analyzed the transcriptome data and found that some core genes of the RA and WNT signaling pathways also expressed asymmetrically during the metamorphosis of the flatfish, which may be related to eye migration. To date, flatfish had made great progress in the problem of eye migration. However, flatfish could be divided into two types based on eye migration: right eye migration caused both eyes on the left side of the body (sinistral) and left eye migration caused both eyes on the right side of the body (dextral) (Bergstrom, 2007; Munroe, 2014). The regulatory mechanism of left eye migration or right eye migration was currently unclear. Through breeding experiments found that the left eye migration or the right eye migration of flatfish was controlled by genetics (Hashimoto et al., 2002; Russo et al., 2012), but its specific regulatory mechanism remains to further studied.
V. variegatus was a dextral flatfish, mainly distributed in the western Pacific coast, such as northern China, South Korea and Japan (Wada et al., 2004; Tian et al., 2008; Sekino et al., 2011). Since records were first started in the 1980s, the V. variegatus wild resources have decreased dramatically due to overfishing (Wada et al., 2011). The high commercial price of V. variegatus made it widely regarded as a promising candidate to enhance aquaculture and fishery resources in North Asia (Xu et al., 2012). Here, we used three generations of sequencing data to obtain high-quality genome of V. variegatus, which will help to promote the cultivation of its improved varieties. Then, through comparative genomics analysis with sinistral flatfish, we could excavate some genes related to eye migration of V. variegatus, which provide valuable gene resources for studying the mechanism of dextral flatfish eyes migration.
Materials and methods
DNA sampling and sequencing
A male adult V. variegate were collected and used for DNA sequencing. The male adult weighted 427g with the full length of 33cm. DNA of V. variegate was extracted from muscle tissues. The genomic DNA from male muscle was used to construct Illumina and PacBio libraries, while the genomic DNA from female muscle was used to construct Hi-C libraries.
For PacBio sequencing, the genomic DNA was fragmented and fragments with approximately 20kb were filtered using the BluePippin Size Selection system (Sage Science). After DNA damage repair and DNA ends repair, DNA fragments were ligated to blunt hairpins. DNA polymerase was bound to the annealed SMRTbell templates. The library was sequenced using the PacBio SEQUEL platform.
A paired-end (PE) Illumina library with 300bp insert sizes was produced using Nextera DNA Flex Library Prep Kit. The library was sequenced using Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform.
For Hi-C sequencing, approximately 2g weight of muscle tissue was cross-linked with 37% formaldehyde in serum-free DMEM, homogenized and incubated at room temperature for 15 min. Glycine was added to a final concentration of 0.25M to stop the cross-linking reaction. Cells were further lysed and the chromatin was digested, labeled and ligated with biotin (Lieberman-Aiden et al., 2009). The cross-linked DNA was extracted and digested with Mbol restriction enzyme. The sticky ends of the digested products were marked with biotin and ligated. After the removal of the protein and biotinylated free-ends, DNA was purified and ultrasonically sheared to a size of 350bp. The biotin-labelled DNA fragments were enriched and prepared for the Hi-C sequencing library. The library was sequenced using Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform.
RNA sampling and sequencing
The V. variegate used in genome sequencing were also dissected into a number of tissues. Kidney, brain, gonad, and spleen from the female adult, and muscle and gonad from the male adult were used for RNA extraction using TRIzol reagents. The cDNA libraries were constructed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations and paired-end sequenced with 150 bp using the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform.
Estimation of genome size
The male V. variegatus PE libraries Illumina sequencing data were used to estimate V. variegatus genome size and heterozygosity rate. We first used jellyfish v2.3.0 (Marcais and Kingsford, 2011) (-C -m 21 -s 1000000000) to calculate k-mer spectrum. Then Genomescope (Vurture et al., 2017) (k = 21; length = 100; max coverage = 1000) was used to measure the V. variegatus genome size and heterozygosity rate using the k-mer spectrum.
Genome assembly
We first used Canu v1.8 (Koren et al., 2017) to correct the PacBio subreads, and then used Flye v2.6 (Kolmogorov et al., 2019) to assemble the genome based on the corrected PacBio data. And redundant sequences were removed by purge_dups v1.0.0 (Guan et al., 2020).
The purged contigs were subsequently polished using the PacBio and Illumina sequencing data. First, we used pbmm2 (SMRT Link v8.0) with default parameters to realign the raw PacBio data back to the assembled genome, and used gcpp (SMRT Link v8.0) with default parameters to polish genome. Then we used bwa v0.7.17 (Li, 2013) with default parameters to align the Illumina data to the genome, and used pilon v1.23 (Walker et al., 2014) with default parameters to further polish the genome. After two rounds of gcpp and pilon polishing, we had obtained high accuracy V. variegatus contigs.
For chromosome-level scaffolds, juicer v1.6.2 (Durand et al., 2016) with default parameters was used to align the Hi-C data to assembled contigs, and then 3D-DNA (Dudchenko et al., 2017) with default parameters was used to anchor the V. variegatus contigs to chromosomes.
Genome quality evaluation
Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs (BUSCO v4.0.5) (Seppey et al., 2019) were used to evaluation the completeness of the genome assembly by searching against actinopterygii_odb10 database. And we used the following procedure to further assess the accuracy of the V. variegatus genome: (1) bwa v0.7.17 with default parameters was used to map the PE libraries Illumina data to the assembled genome, and then used the samtools flagstat function (SAMtools v1.9) (Li et al., 2009) to count basic statistics. (2) samtools depth was used to calculate the coverage depth of all bases. (3) Freebays v1.3.2 (Garrison and Marth, 2012) were used to call genome SNPs using PE libraries Illumina data.
Repeat annotation
Tandem repeats and transposable elements (TEs) were identified in the assembled genome. Tandem Repeats Finder (Benson, 1999) was used to identify tandem repeat sequences. For transposable elements (TEs), we identified by combination of homology-based and de novo methods. For the homology-based approach, at the nucleotide level, we used RepeatMasker v4.0.9 with the parameters “-a -nolow -no_is -norna -s” to identify known TEs using the Repbase TE library. At the protein level, we used RepeatProteinMask with the parameters “-noLowSimple -pvalue 0.0001 -engine wublast” to search the TE protein database. To further identify the TEs in the assembled genome, RepeatModeler v2.0 (Flynn et al., 2020) was used to construct a specific V. variegatus TE library, consisting of the following steps, (1) We used RepeatModeler to de novo predict TEs in the V. variegatus genome. (2) We used blastx to map the TEs collected by RepeatModeler to the vertebrate protein database (ftp://ftp.uniprot.org/pub/databases/uniprot/current_release/knowledgebase/taxonomic_divisions/uniprot_sprot_vertebrates.dat.gz). (3) We used protExcluder with default parameters to exclude TE come from gene fragments. After excluding putative gene fragments, we got the final de novo identification TE library, RepeatMasker used this TE library to further identify V. variegatus TEs.
Gene structure and functional annotation
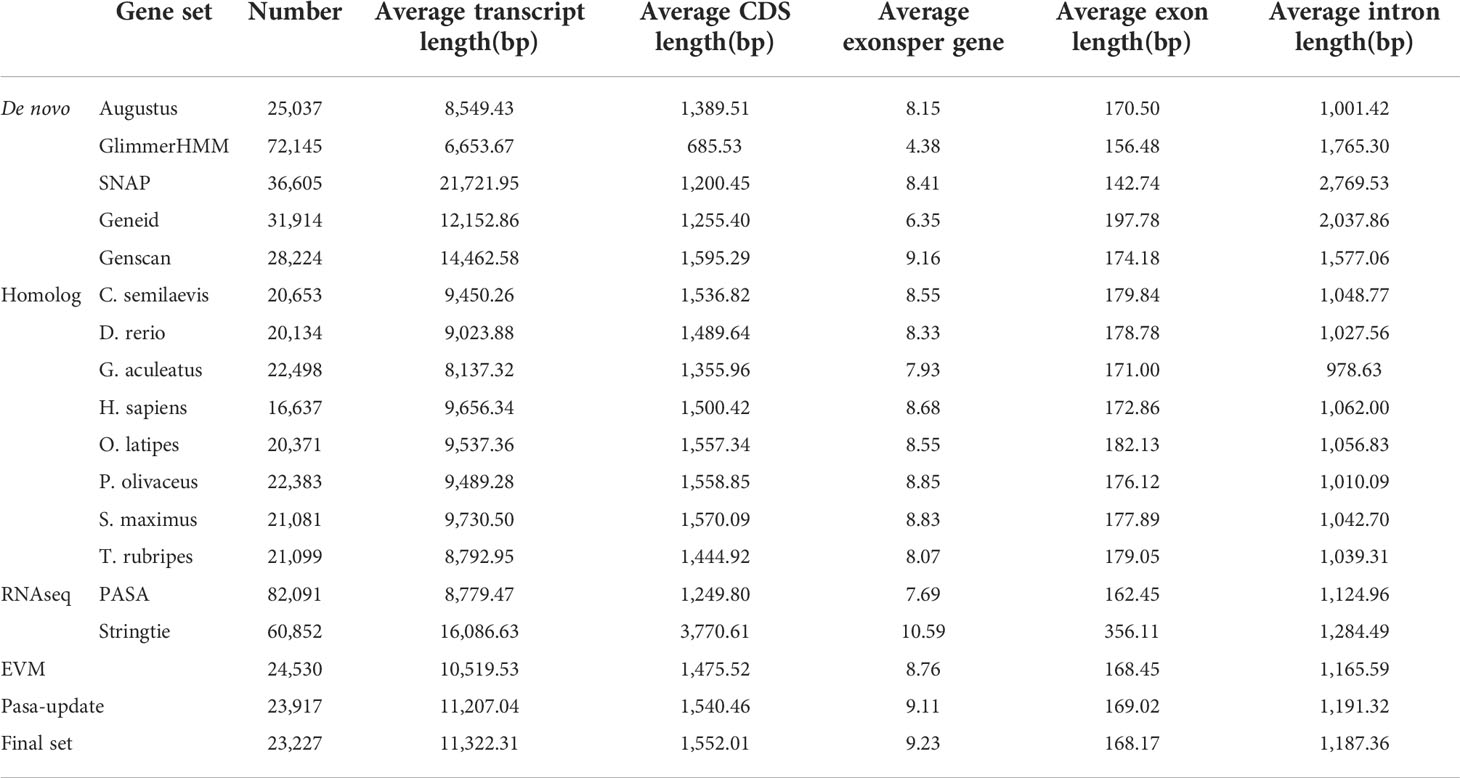
We used de novo, homology-based, and RNA-seq based methods to annotate genes in the V. variegatus genome. For RNA-seq data, we first used HISAT v2.1.0 (Kim et al., 2015) with default parameters to align RNA-seq data to V. variegatus genome and then used StringTie v2.0 (Pertea et al., 2015) with default parameters to reconstruct transcripts. After using RepeatMasker to mask TEs of the assembled genome, five de novo gene predictors, including Augustus (Stanke et al., 2008), GlimmerHMM (Majoros and Salzberg, 2004), SNAP (Korf, 2004), Geneid (Alioto et al., 2018) and Genscan (Burge and Karlin, 1998), were used for gene prediction. For the homology-based prediction, proteins sequences of Homo sapiens, Danio rerio, Oryzias latipes, Takifugu rubripes, Cynoglossus semilaevis, Scophthalmus maximus and Gasterosteus aculeatus were downloaded from Ensembl (release 98), Paralichthys olivaceus proteins were downloaded from NCBI, then we used Exonerate v2.2 (Slater and Birney, 2005) (identity>80%) to map the proteins sequences to V. variegatus genome for conduct homology-based gene prediction. Finally, all the identifiable gene Structures from homology-based, de novo methods and RNA-seq data were combined into consensus gene models by EVidenceModeler (EVM) (Haas et al., 2008a) and PASA (Haas et al., 2008a).
Gene functions were assigned based on the best match obtained by aligning the protein-coding sequence to the National Center for Biotechnology Information nonredundant protein (NR) and SwissProt databases using BLASTP (-e 1e-5). InterProScan v5 (Jones et al., 2014) was also used to identify gene function, motifs and domains it contained. KEGG Automatic Annotation Server (KAAS) with bi-directional best hit (BBH) method was used to assign KEGG orthologs.
Gene family construction and comparative genomic analysis
In order to construct gene family among 12 teleost fish, the longest protein sequence of Homo sapiens, Danio rerio, Oryzias latipes, Takifugu rubripes, Cynoglossus semilaevis, Scophthalmus maximus and Gasterosteus aculeatus, Oreochromis niloticus, Lates calcarifer, and Lepisosteus oculatus were used to build gene family by OrthoFinder v2.3.8 (Emms and Kelly, 2019). Proteins sequences of D. rerio, O. latipes, T. rubripes, C. semilaevis, S. maximus, G. aculeatus, O. niloticus, L. calcarifer, H. comes and L. oculatus were downloaded from Ensembl (release 98) (Cunningham et al., 2019). P. olivaceus proteins were downloaded from NCBI.
For positive selection gene identification, we used GUIDANCE2 (–msaProgram PRANK) to perform multiple sequence alignment of single-copy gene families, then CODEML from the PAML V4.9j (Yang, 2007) with branch-site model was used to detect positive selection genes. TBtools (Chen et al., 2020) was used to perform GO and KEGG enrichment analysis.
Phylogenetic analysis and species divergence time estimation
For phylogenetic analysis, we extracted single copy gene families from OrthoFinder results. For each single-copy gene family, we used mafft v7.429 (Katoh and Standley, 2016) for multiple sequence alignment, and GUIDANCE V2.02 (Sela et al., 2015) used multiple sequence alignment information to construct supperMSA. Then we used IQ-TREE v2.0-rc1 (Minh et al., 2020) to build the evolution tree. Finally, we used MCMCTree from the PAML v4.9j (Yang, 2007) to estimate the divergence time between 12 lineages, three calibration points (Benton and Donoghue, 2007) based on fossil records were used to calibrate the substitution rate, including Gasterosteus aculeatus (97.8-150.9Mya), Oryzias latipes (97.8-150.9Mya), Danio rerio (149.85-165.2Mya).
Results and discussion
Genome assembly
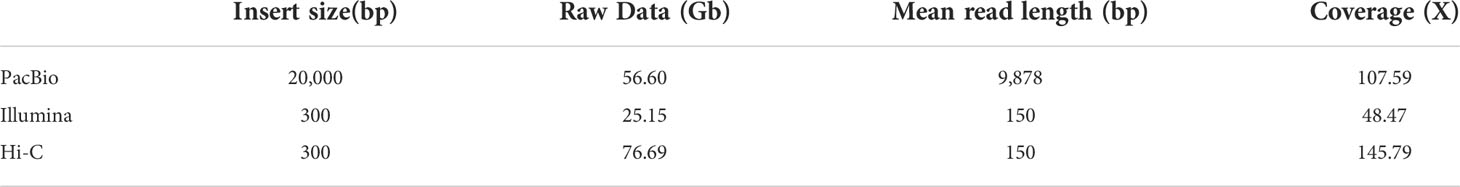
For genome assembly, we sequenced the male V. variegatus with long and short-reads sequencing technology, respectively. We used PacBio Sequel platform to generate 56.60 Gb male V. variegatus PacBio sequencing data. At the same time, we used the Illumina Novaseq platform to generate 25.15 Gb male PE library data and 76.69 Gb Hi-C sequencing data (Table 1).
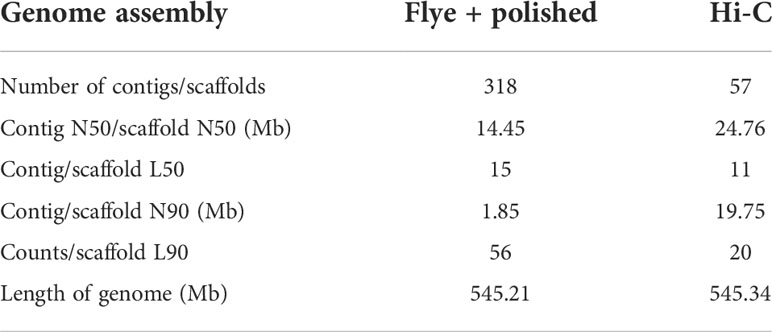
Before genome assembly, GenomeScope was used to estimate genome size and heterozygosity rate. We used male Illumina sequencing data to estimate the genome size was 526.05Mb and the heterozygosity rate was 0.3%, which means that the V. variegatus genome has a low complexity (Figure 1A). Then PacBio subreads were used to assemble V. variegatus genome sequence according to the assembly pipeline of Figure 1B. We first used Canu to correct the PacBio subreads and then used Flye to assemble the genome. Then we used purge_dups to remove redundant sequences based on sequence similarity and reads depth information. After polishing the assembled genome using PacBio and Illumina sequencing data, we obtained 545.21Mb male contigs, with a contig N50 of 14.45 Mb (Table 2).
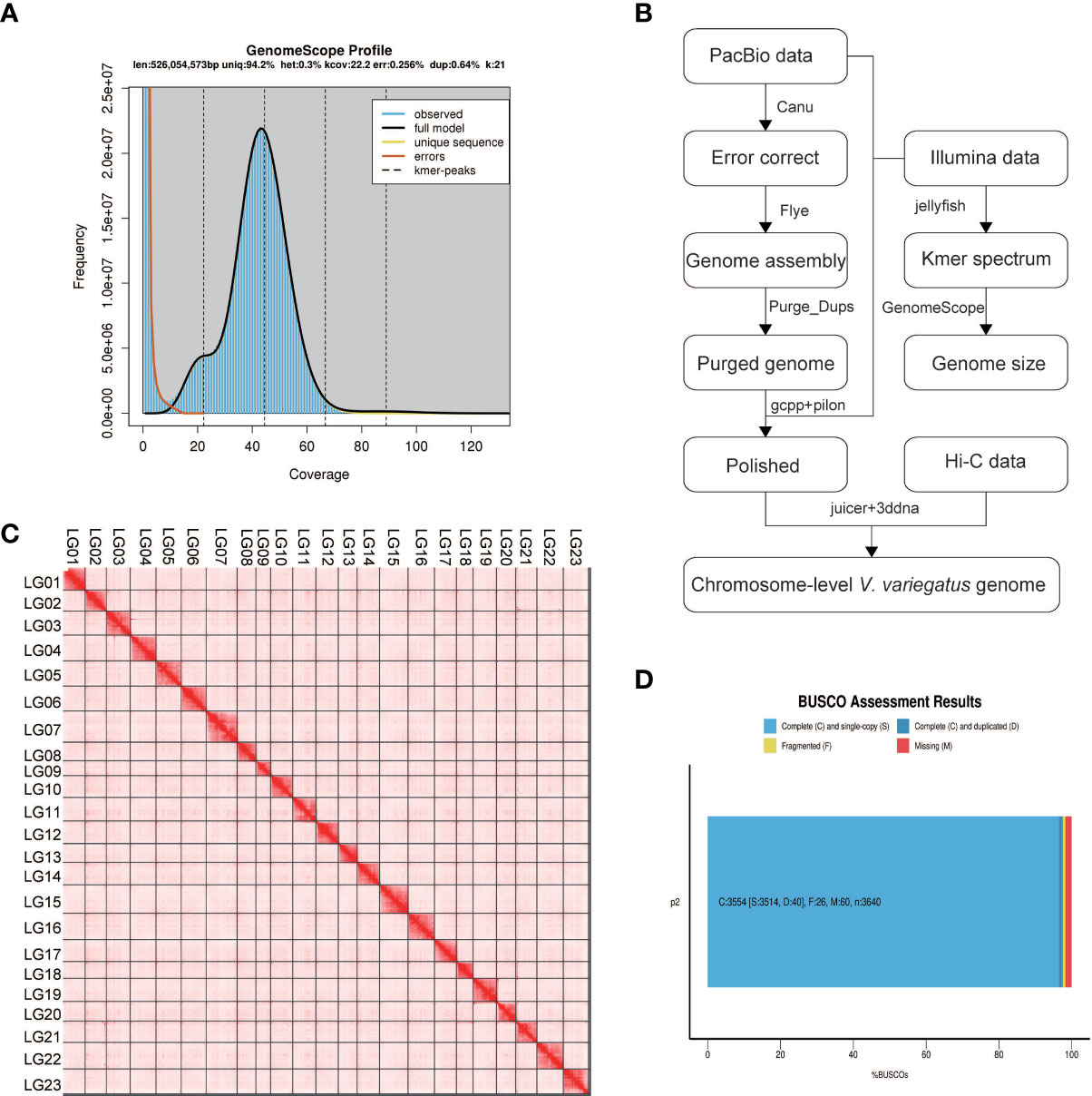
Figure 1 Genome assembly information. (A) Schematic illustration of the Verasper variegatus genome assembly pipeline (B) 21-mer estimates of genome size. The x-axis is the depth (X) and the y-axis is the representative the kmer frequency. The estimated size of the genome is 526.05Mb, and the heterozygosity is 0.3%; (C) Verasper variegatus genome contig contact Heatmap using Hi‐C data. LG 01-23 representing the 23 pseudo-chromosomes. The color bar illuminates the contact density from red (high) to white (low); (D) BUSCO evaluation results, 3554 (97.6%) complete and 26 (0.7%) fragmented BUSCOs were present in Verasper variegatus genome. 60 BUSCOs were not found in Verasper variegatus genome.
Several approaches were used to validate the completeness and accuracy of the assembled male genome: (1) 97.6% (3554) complete Actinopterygii BUSCOs were presented in the assembled genome, including 96.5% (3514) single-copy Actinopterygii BUSCOs and 1.1% (40) duplicated Actinopterygii BUSCOs, which indicating that the assembly of the V. variegatus genome was highly complete (Figure 1D, Supporting information Table S2). (2) 99.54% of the PE library Illumina sequencing reads could be mapped to the assembled genome and 98.49% of the reads were properly aligned to the genome with their pairs (Supporting information, Table S3, Figure S1). (3) With the exception for the gap areas, over 99.92% of the genomic regions have a coverage depth greater than 5. (5) 2217 homozygous SNVs were found in the assembled genome, the genome accuracy at the base level could reach 99.99996%. In conclusion, these results supported the conclusion that we had obtained a high-quality V. variegatus genome.
In order to generate chromosome-scale scaffolds, 76.69 Gb Hi-C sequencing dada were obtained and used to anchor male contigs to chromosomes. 99.91% of the male genome sequences were anchored to 23 pseudo-chromosomes (Figure 1C, Supporting information Table S1).
Genome annotation
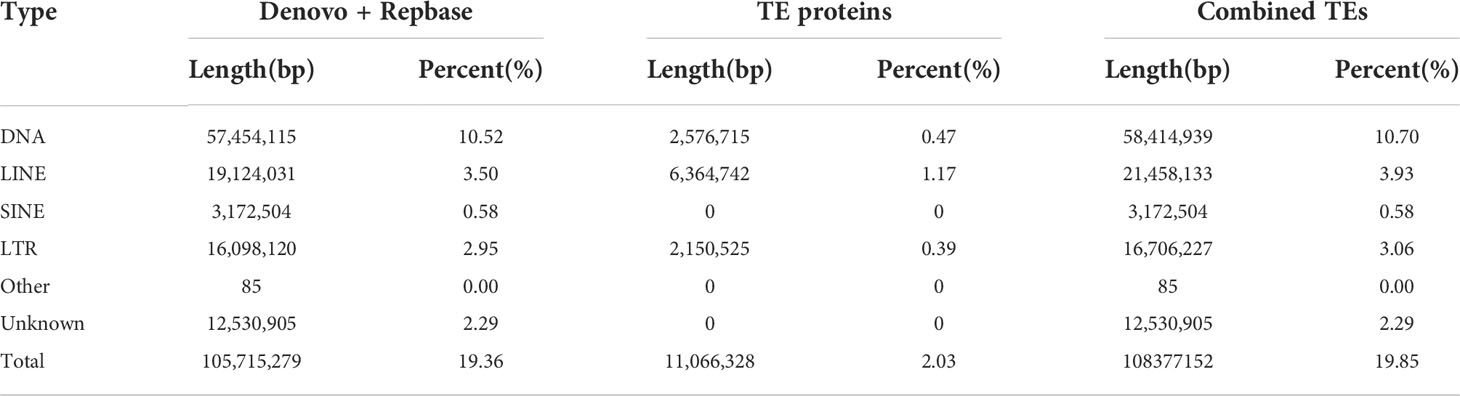
Approximately 105.72 Mb (~19.85%) of the V. variegatus genome was composed of TEs (Table 3, Figure 2), which was much higher than the content of TEs in other published flatfish genomes (87.8 Mb in S. maximus, 56.2 Mb in P. olivaceus and 20.3 Mb in C. semilaevis). Maybe it was the advantage of PacBio subreads length that allowed us to successfully assemble more TEs in the V. variegatus genome (Lee et al., 2016). Among these, the top three categories of repetitive elements were DNA transposons (10.70%), long terminal repeats (LTRs, 3.06%) and long interspersed nuclear elements (LINEs, 3.93%) (Figure 3A).
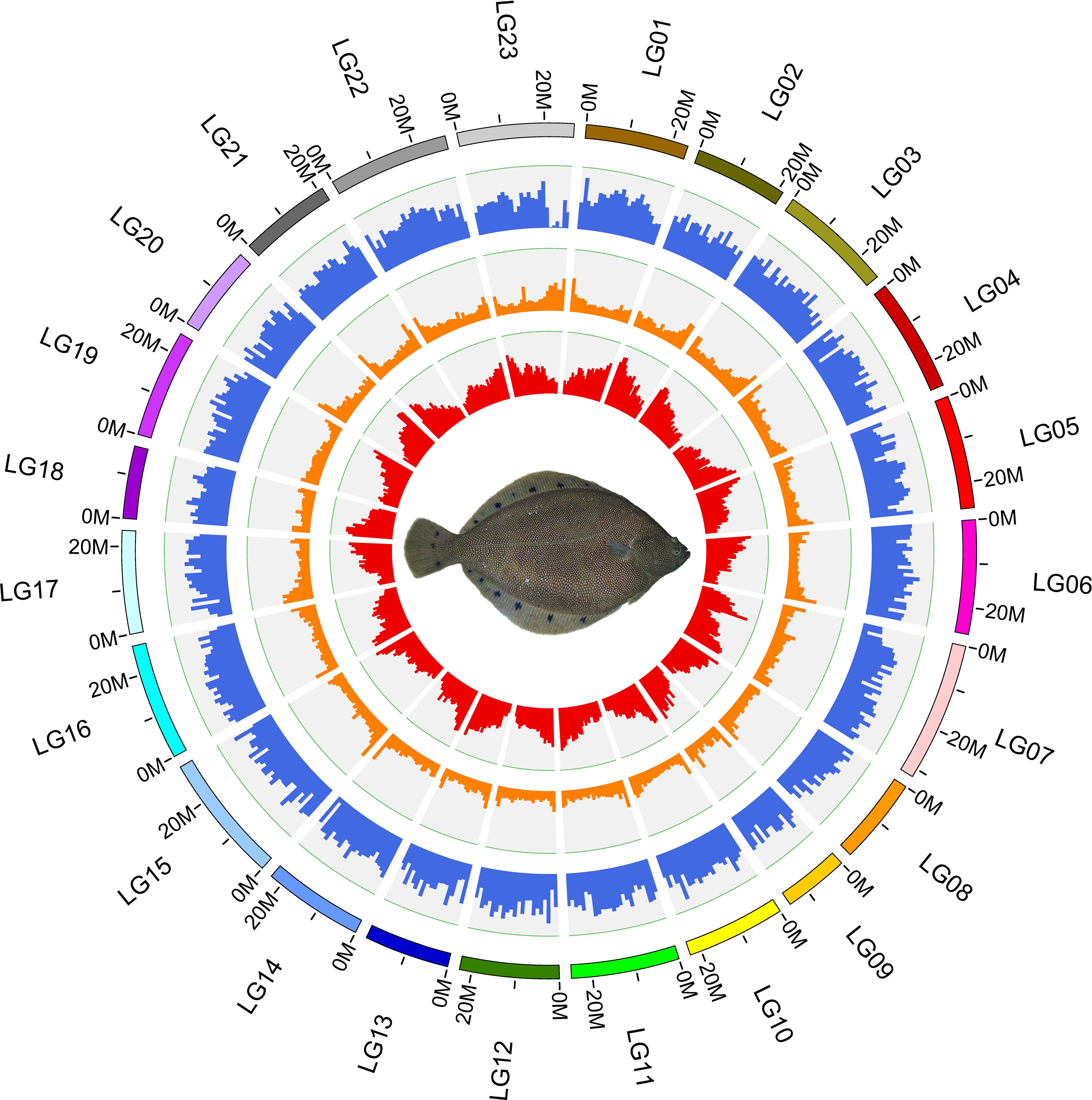
Figure 2 Circos plot basic characteristics of the reference genome of Verasper variegatus, from outside to inside circles indicate: the gene density, repeat content, GC content.
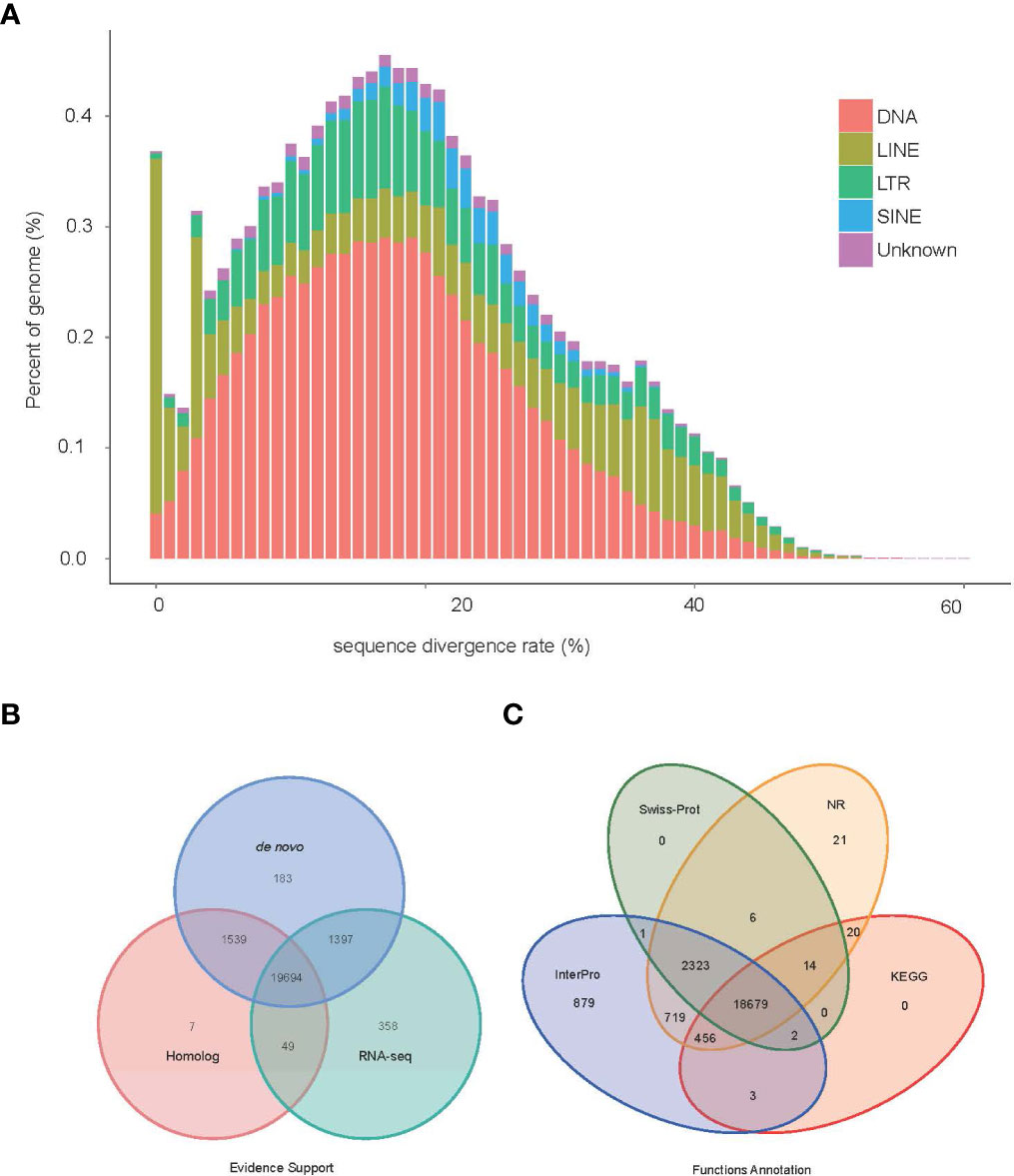
Figure 3 Genome annotation information (A) TE divergence distribution, the x-axis is the degree of divergence between the annotated TE sequence in the genome and the corresponding sequence in Repbase. The y-axis is the percentage of TE sequence in the genome. (B) Statistics supported by evidence for protein-coding gene sets. (C) Statistical results of gene function annotation.
By using the EVidenceModeler (EVM) genome annotation pipeline combined with ab initio prediction, homology-based approaches and RNA-Seq transcripts, a total of 23,227 high-confidence protein-coding gene sets of the V. variegatus genome had been identified (Figure 3B). The average length of V. variegatus transcript was 11,322.31 bp, the exon average length was 168.17 bp and the average number of exons per gene was 9.23 (Table 4). Then we used several approaches to functionally annotate the predicted genes in the V. variegatus genome Overall, 99.6% of the V. variegatus genes were function annotated based on known proteins in public databases, including SwissProt, NR, KEGG, InterPro databases, etc. Of these annotated genes, 21,444 (92.3%) genes had GO annotations and 19174 (82.6%) genes could be assigned to KEGG pathways (Figure 3C, Supporting information Table S4).
Gene family identifications and comparative genomic analysis
A total of 9745 core gene families and 796 species-specific gene families were identified in 12 fish genomes by OrthoFinder2. For V. variegatus, 21069 (90.7%) genes could be assigned to corresponding gene families, including 107 genes belonging to 48 V. variegatus-specific gene families. And there were 2158 genes cannot be assigned to any gene family (Figure S2).
Changes in the size of gene families may be the basis for many important morphological, physiological and behavioral differences between species (Demuth and Hahn, 2009). We used cafe4 (Han et al., 2013) to screen 69 expansion gene families and 33 contraction gene families in the V. variegatus genome (Figure 4A). KEGG enrichment analysis of the V. variegatus expanded gene families demonstrated that they were mainly assigned in “Hippo signaling pathway”, “Calcium signaling pathway”, “Axon guidance” pathways, which related to organ development and nervous system (Figure 4B). Some extended gene families may played important roles in flatfish metamorphosis. The homeodomain‐interacting protein kinase (HIPK) family played an important role in eye development, and could affect eye development through multiple signaling pathways such as TGF-beta, BMP, Notch and Wnt signaling pathways (Hofmann et al., 2003; Jia et al., 2007; Lee et al., 2009a; Lee et al., 2009b; Inoue et al., 2010). For the dynein heavy chain family, mutations on DNAH5 could cause randomization of left and right asymmetry (Olbrich et al., 2002), which may be related to eye migration of V. variegatus.
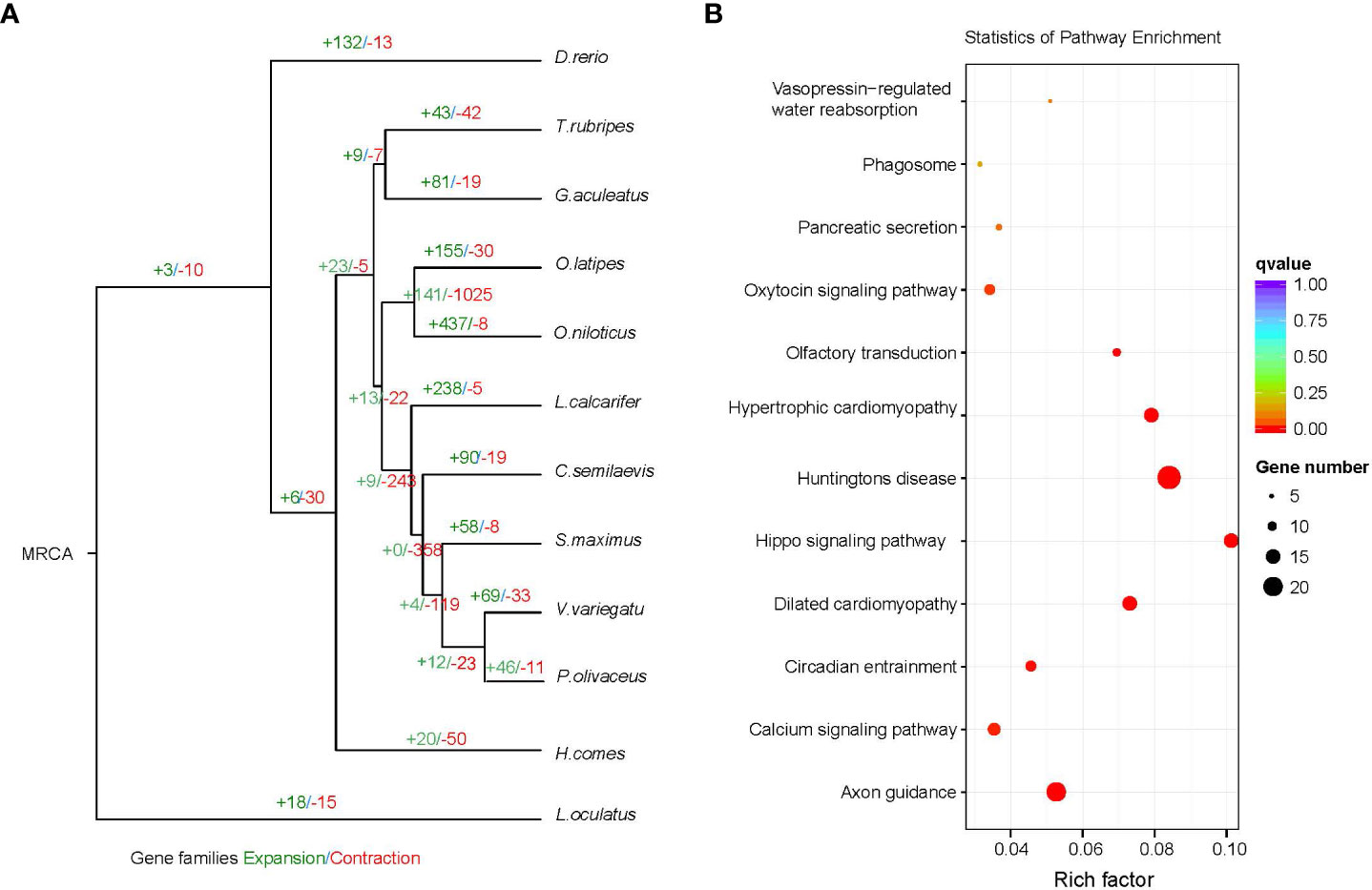
Figure 4 Gene family comparison. (A) Gene family size change analysis, including the number of expanded gene families (+) and contracted gene families (-). (B) KEGG enrichment analysis of expanded gene families.
To further explore the evolutionary genetic resources, we used PAML to identify 311 positively selected genes (PSGs) in the V. variegatus genome. Some V. variegatus PSGs associated with skin development and pigmentation (vps18, ippk, dhcr24, ngfr, acp1, myb, Ino80, ebna1, bp2, ctr9, acp1), thyroid hormone receptor (nr1h4 and prox1), mlanosomal transporters (slc45a1), retinoic acid metabolism (cyp26a1), otolith and pineal (otomp), retinal contrast adaptation and visual function in the retinal circuit (irx5, gja10). The V. variegatus PSGs and expanded gene families provide valuable genetic resources for the study of various physiological and morphological changes associated with flatfish metamorphosis and adaptation.
To further explore the difference of Darwinian selection between sinistral flatfish and dextral flatfish, we used PAML to detect parallel selection genes in dextral flatfish, with dextral flatfish as foreground branch and sinistral flatfish as background branch. 193 positive selection genes were identified in dextral flatfish. Among them, some genes related to cell proliferation, apoptosis and cilia formations received different selections in sinistral flatfish and dextral flatfish. Such as WD repeat-containing protein 11 (wdr11) of dextral flatfish contained two positive selection sites: Gln450→THr, Cys1120→Ile. Wdr11 was essential for normal cilia formation and is involved in a variety of life processes through the Hedgehog (Hh) signalling pathway (Kim et al., 2018). Another ciliary movement related parallel selection gene was cfap53, which played an important role in the establishment of organ laterality during embryogenesis. Some genes (xkr8, tctp) related to cell proliferation and apoptosis were also subjected to parallel selection in dextral flatfish. Cell proliferation and apoptosis play important roles in flounder eye migration and frontal bone deformation (Sun et al., 2015). The V. variegatus parallel selection genes provide valuable genetic resources for the study of flatfish left eye migration.
Phylogenetic analysis
For phylogenetic analysis, a total of 4704 single-copy gene families were obtained from OrthoFinder2 results and used as input to GUIDANCE2. GUIDANCE2 used MAFFT V7.429 to align each gene family and generate SuperMSA separately. Subsequently, IQ-TREE was used to reconstruct the phylogenetic tree using SuperMSA. Then MCMCTree from the PAML software package was used to estimate the divergence time of the V. variegate, three calibration points based on fossil records obtained from the TimeTree database were used to calibrate the substitution rate, including Gasterosteus aculeatus (97.8-150.9Mya), Oryzias latipes (97.8-150.9Mya), Danio rerio (149.85-165.2Mya).
Our analysis suggests that V. variegate, C. semilaevis, S. maximus, P. olivaceus and L. calcarifer were in a clade. V. variegate and P. olivaceus had a closer evolutionary relationship and likely shared a common ancestor around 20.4-50.4 million years ago (Figure 5).
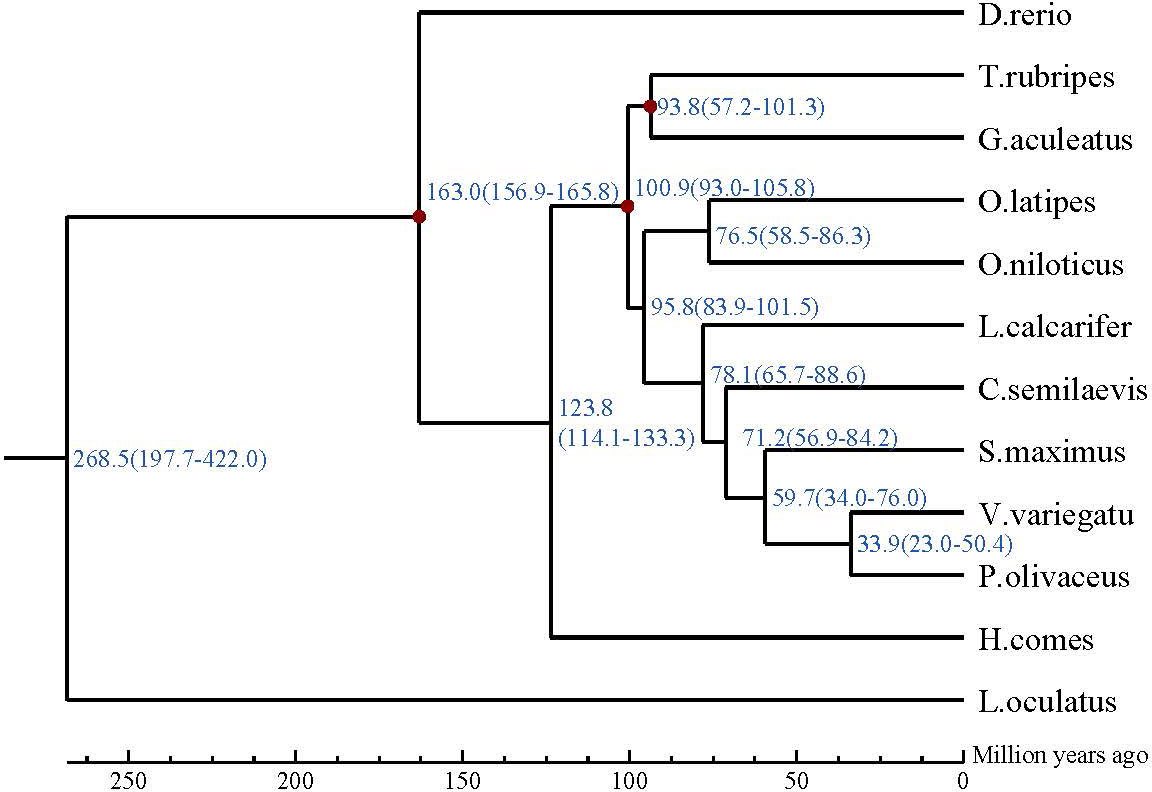
Figure 5 The phylogenetic relationship of Verasper variegatus with other 12 fish species. The divergence time was estimated using three fossil calibration points (red circles). The lower coordinate shows the estimated divergence time (Mya).
Conclusion
In present study, we successfully assembled a high-quality V variegatus genome using long and short sequencing data. The 545.34Mb V variegatus genome assembly consists of 315 contigs with contig N50 length of 15.16 Mb, and 99.91% of contigs could be mounted on chromosomes. Then we performed comparative genomic analysis and found that some genes related to cell proliferation, apoptosis and cilia formation were under parallel selection in dextral flatfish, which may be related to the migration of the left eye of V. variegatus. The high quality chromosome-level V. variegatus genomes will provide valuable resources for studying the molecular mechanism of metamorphosis of flatfish.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, GCA_013332515.1 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, SRR11838598, SRR11838599, SRR11838600, SRR11838601, SRR11838602, SRR11838603, SRR11838604, SRR11851925, SRR11846737, SRR11846738, SRR11846739, SRR11846740, SRR11846741, SRR11846742.
Author contributions
SC conceived and designed the research. ZC, CL, X-WX, and WX performed the genome sequencing. X-WX, ZC, CL, HX, and WX performed the data analyses. ZC, CL and HX performed sample preparation. X-WX, ZC, WX, and SC wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD0900201), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32102791), the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS (NO.2020TD20), AoShan Talents Cultivation Program Supported by Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (No.2017ASTCP-OS15), the Taishan Scholar Climbing Project Fund of Shandong, China. The Central Public-interest Scientific Institute Basal Research Fund, CAFS (No.2020TD19).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2022.1045052/full#supplementary-material
References
Alioto T., Blanco E., Parra G., Guigo R. (2018). Using geneid to identify genes. Curr. Protoc. Bioinf. 64 (1), e56. doi: 10.1002/cpbi.56
Bao B., Ke Z., Xing J., Peatman E., Liu Z., Xie C., et al. (2011). Proliferating cells in suborbital tissue drive eye migration in flatfish. Dev. Biol. 351 (1), 200–207. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.12.032
Benson G. (1999). Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 27 (2), 573–580. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.2.573
Benton M. J., Donoghue P. C. (2007). Paleontological evidence to date the tree of life. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24 (1), 26–53. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msl150
Bergstrom C. A. (2007). Morphological evidence of correlational selection and ecological segregation between dextral and sinistral forms in a polymorphic flatfish, platichthys stellatus. J. Evol. Biol. 20 (3), 1104–1114. doi: 10.1111/j.1420-9101.2006.01290.x
Burge C. B., Karlin S. (1998). Finding the genes in genomic DNA. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 8 (3), 346–354. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(98)80069-9
Chen C., Chen H., Zhang Y., Thomas H. R., Frank M. H., He Y., et al. (2020). TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 13 (8), 1194–1202. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
Cunningham F., Achuthan P., Akanni W., Allen J., Amode M. R., Armean I. M., et al. (2019). Ensembl 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 47 (D1), D745–D751. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1113
Demuth J. P., Hahn M. W. (2009). The life and death of gene families. Bioessays 31 (1), 29–39. doi: 10.1002/bies.080085
Dudchenko O., Batra S. S., Omer A. D., Nyquist S. K., Hoeger M., Durand N. C., et al. (2017). De novo assembly of the aedes aegypti genome using Hi-c yields chromosome-length scaffolds. Science 356 (6333), 92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.aal3327
Durand N. C., Shamim M. S., Machol I., Rao S. S., Huntley M. H., Lander E. S., et al. (2016). Juicer provides a one-click system for analyzing loop-resolution Hi-c experiments. Cell Syst. 3 (1), 95–98. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2016.07.002
Emms D. M., Kelly S. (2019). OrthoFinder: Phylogenetic orthology inference for comparative genomics. Genome Biol. 20 (1), 238. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1832-y
Flynn J. M., Hubley R., Goubert C., Rosen J., Clark A. G., Feschotte C., et al. (2020). RepeatModeler2 for automated genomic discovery of transposable element families. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 117 (17), 9451–9457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1921046117
Friedman M. (2008). The evolutionary origin of flatfish asymmetry. Nature 454 (7201), 209–212. doi: 10.1038/nature07108
Garrison E., Marth G. (2012). Haplotype-based variant detection from short-read sequencing. arXiv e-prints. arXiv:1207.3907.
Guan D., McCarthy S. A., Wood J., Howe K., Wang Y., Durbin R. (2020). Identifying and removing haplotypic duplication in primary genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 36 (9), 2896–2898. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa025
Gur M., Cohen E. B., Genin O., Fainsod A., Perles Z., Cinnamon Y. (2017). Roles of the cilium-associated gene CCDC11 in left-right patterning and in laterality disorders in humans. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 61 (3-4-5), 267–276. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.160442yc
Haas B. J., Salzberg S. L., Zhu W., Pertea M., Allen J. E., Orvis J., et al. (2008a). Automated eukaryotic gene structure annotation using EVidenceModeler and the program to assemble spliced alignments. Genome Biol. 9 (1), R7. doi: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-1-r7
Han M. V., Thomas G. W., Lugo-Martinez J., Hahn M. W. (2013). Estimating gene gain and loss rates in the presence of error in genome assembly and annotation using CAFE 3. Mol. Biol. Evol. 30 (8), 1987–1997. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst100
Hashimoto H., Mizuta A., Okada N., Suzuki T., Tagawa M., Tabata K., et al. (2002). Isolation and characterization of a Japanese flounder clonal line, reversed, which exhibits reversal of metamorphic left-right asymmetry. Mech. Dev. 111 (1), 17–24. doi: 10.1016/S0925-4773(01)00596-2
Hofmann T. G., Stollberg N., Schmitz M. L., Will H. (2003). HIPK2 regulates transforming growth factor-beta-induced c-jun NH(2)-terminal kinase activation and apoptosis in human hepatoma cells. Cancer Res. 63 (23), 8271–8277.
Inoue T., Kagawa T., Inoue-Mochita M., Isono K., Ohtsu N., Nobuhisa I., et al. (2010). Involvement of the hipk family in regulation of eyeball size, lens formation and retinal morphogenesis. FEBS Lett. 584 (14), 3233–3238. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.06.020
Jia J., Lin M., Zhang L., York J. P., Zhang P. (2007). The notch signaling pathway controls the size of the ocular lens by directly suppressing p57Kip2 expression. Mol. Cell Biol. 27 (20), 7236–7247. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00780-07
Jones P., Binns D., Chang H. Y., Fraser M., Li W., McAnulla C., et al. (2014). InterProScan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 30 (9), 1236–1240. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu031
Juriloff D. M., Harris M. J., McMahon A. P., Carroll T. J., Lidral A. C. (2006). Wnt9b is the mutated gene involved in multifactorial nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in A/WySn mice, as confirmed by a genetic complementation test. Birth Defects Res. A Clin. Mol. Teratol. 76 (8), 574–579. doi: 10.1002/bdra.20302
Katoh K., Standley D. M. (2016). A simple method to control over-alignment in the MAFFT multiple sequence alignment program. Bioinformatics 32 (13), 1933–1942. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw108
Kim D., Langmead B., Salzberg S. L. (2015). HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 12 (4), 357–360. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3317
Kim Y. J., Osborn D. P., Lee J. Y., Araki M., Araki K., Mohun T., et al. (2018). WDR11-mediated hedgehog signalling defects underlie a new ciliopathy related to kallmann syndrome. EMBO Rep. 19 (2), 269–289. doi: 10.15252/embr.201744632
Kolmogorov M., Yuan J., Lin Y., Pevzner P. A. (2019). Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs. Nat. Biotechnol. 37 (5), 540–546. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0072-8
Koren S., Walenz B. P., Berlin K., Miller J. R., Bergman N. H., Phillippy A. M. (2017). Canu: scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 27 (5), 722–736. doi: 10.1101/gr.215087.116
Lee W., Andrews B. C., Faust M., Walldorf U., Verheyen E. M. (2009a). Hipk is an essential protein that promotes notch signal transduction in the drosophila eye by inhibition of the global co-repressor groucho. Dev. Biol. 325 (1), 263–272. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.10.029
Lee H., Gurtowski J., Yoo S., Nattestad M., Marcus S., Goodwin S., et al. (2016). Third-generation sequencing and the future of genomics. bioRxiv 048603. doi: 10.1101/048603
Lee W., Swarup S., Chen J., Ishitani T., Verheyen E. M. (2009b). Homeodomain-interacting protein kinases (Hipks) promote Wnt/Wg signaling through stabilization of beta-catenin/Arm and stimulation of target gene expression. Development 136 (2), 241–251. doi: 10.1242/dev.025460
Levin M. (2005). Left-right asymmetry in embryonic development: A comprehensive review. Mech. Dev. 122 (1), 3–25. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2004.08.006
Li H. (2013). Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv e-prints. arXiv:1303.3997.
Lieberman-Aiden E., van Berkum N. L., Williams L., Imakaev M., Ragoczy T., Telling A., et al. (2009). Comprehensive mapping of long-range interactions reveals folding principles of the human genome. Science 326 (5950), 289–293. doi: 10.1126/science.1181369
Li H., Handsaker B., Wysoker A., Fennell T., Ruan J., Homer N., et al. (2009). The sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25 (16), 2078–2079. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Li L., Zheng J., Bao B., Berendzen P. B. (2013). Change of eye shape during metamorphosis in two flatfishes, paralichthys olivaceus and solea senegalensis, with comparison of eye shape within the pleuronectiformes. Ichthyological Res. 60 (2), 178–183. doi: 10.1007/s10228-012-0332-9
Lu Z., Gong L., Ren Y., Chen Y., Wang Z., Liu L., et al. (2021). Large-Scale sequencing of flatfish genomes provides insights into the polyphyletic origin of their specialized body plan. Nat. Genet. 53 (5), 742–751. doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00836-9
Majoros W. H., Salzberg S. L. (2004). An empirical analysis of training protocols for probabilistic gene finders. BMC Bioinf. 5, 206. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-5-206
Marcais G., Kingsford C. (2011). A fast, lock-free approach for efficient parallel counting of occurrences of k-mers. Bioinformatics 27 (6), 764–770. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr011
Marini N. J., Asrani K., Yang W., Rine J., Shaw G. M. (2019). Accumulation of rare coding variants in genes implicated in risk of human cleft lip with or without cleft palate. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 179 (7), 1260–1269. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.61183
Minh B. Q., Schmidt H. A., Chernomor O., Schrempf D., Woodhams M. D., von Haeseler A., et al. (2020). IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 37 (5), 1530–1534. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaa015
Munroe T. A. (2014). “Systematic diversity of the pleuronectiformes,” in: Flatfishes, ed. Gibson RN, Nash RDM, Geffen AJ, Veer der van HW. (FL: Wiley Online Library press.), 13–51.
Narasimhan V., Hjeij R., Vij S., Loges N. T., Wallmeier J., Koerner-Rettberg C., et al. (2015). Mutations in CCDC11, which encodes a coiled-coil containing ciliary protein, causes situs inversus due to dysmotility of monocilia in the left-right organizer. Hum. Mutat. 36 (3), 307–318. doi: 10.1002/humu.22738
Noel E. S., Momenah T. S., Al-Dagriri K., Al-Suwaid A., Al-Shahrani S., Jiang H., et al. (2016). A zebrafish loss-of-Function model for human CFAP53 mutations reveals its specific role in laterality organ function. Hum. Mutat. 37 (2), 194–200. doi: 10.1002/humu.22928
Olbrich H., Haffner K., Kispert A., Volkel A., Volz A., Sasmaz G., et al. (2002). Mutations in DNAH5 cause primary ciliary dyskinesia and randomization of left-right asymmetry. Nat. Genet. 30 (2), 143–144. doi: 10.1038/ng817
Palmer A. R. (1996). From symmetry to asymmetry: phylogenetic patterns of asymmetry variation in animals and their evolutionary significance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 93 (25), 14279–14286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.25.14279
Pertea M., Pertea G. M., Antonescu C. M., Chang T. C., Mendell J. T., Salzberg S. L. (2015). StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 33 (3), 290–295. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3122
Russo T., Pulcini D., Costantini D., Pedreschi D., Palamara E., Boglione C., et al. (2012). “Right” or “wrong”? insights into the ecology of sidedness in european flounder, platichthys flesus. J. Morphol. 273 (3), 337–346. doi: 10.1002/jmor.11027
Schreiber A. M. (2006). Asymmetric craniofacial remodeling and lateralized behavior in larval flatfish. J. Exp. Biol. 209 (Pt 4), 610–621. doi: 10.1242/jeb.02056
Schreiber A. M. (2013). Flatfish: An asymmetric perspective on metamorphosis. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 103, 167–194. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385979-2.00006-X
Sekino M., Saitoh K., Shimizu D., Wada T., Kamiyama K., Gambe S., et al. (2011). Genetic structure in species with shallow evolutionary lineages: A case study of the rare flatfish verasper variegatus. Conserv. Genet. 12 (1), 139–159. doi: 10.1007/s10592-010-0128-2
Sela I., Ashkenazy H., Katoh K., Pupko T. (2015). GUIDANCE2: accurate detection of unreliable alignment regions accounting for the uncertainty of multiple parameters. Nucleic Acids Res. 43 (W1), W7–14. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv318
Seppey M., Manni M., Zdobnov E. M. (2019). BUSCO: Assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness. Methods Mol. Biol. 1962, 227–245. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9173-0_14
Shao C., Bao B., Xie Z., Chen X., Li B., Jia X., et al. (2017). The genome and transcriptome of Japanese flounder provide insights into flatfish asymmetry. Nat. Genet. 49 (1), 119–124. doi: 10.1038/ng.3732
Slater G. S., Birney E. (2005). Automated generation of heuristics for biological sequence comparison. BMC Bioinf. 6, 31. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-31
Stanke M., Diekhans M., Baertsch R., Haussler D. (2008). Using native and syntenically mapped cDNA alignments to improve de novo gene finding. Bioinformatics 24 (5), 637–644. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn013
Sun M., Wei F., Li H., Xu J., Chen X., Gong X., et al. (2015). Distortion of frontal bones results from cell apoptosis by the mechanical force from the up-migrating eye during metamorphosis in paralichthys olivaceus. Mech. Dev. 136, 87–98. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2015.01.001
Sutherland M. J., Ware S. M. (2009). Disorders of left-right asymmetry: Heterotaxy and situs inversus. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 151C (4), 307–317. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.30228
Tian Y. S., Chen S. L., Ji X. S., Zhai J. M., Sun L. J., Chen C., et al. (2008). Cryopreservation of spotted halibut (Verasper variegatus) sperm. Aquaculture 284 (1), 268–271. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.07.047
Tisler M., Wetzel F., Mantino S., Kremnyov S., Thumberger T., Schweickert A., et al. (2016). Cilia are required for asymmetric nodal induction in the sea urchin embryo. BMC Dev. Biol. 16 (1), 28. doi: 10.1186/s12861-016-0128-7
Vurture G. W., Sedlazeck F. J., Nattestad M., Underwood C. J., Fang H., Gurtowski J., et al. (2017). GenomeScope: Fast reference-free genome profiling from short reads. Bioinformatics 33 (14), 2202–2204. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx153
Wada T., Aritaki M., Tanaka M. (2004). Effects of low-salinity on the growth and development of spotted halibut verasper variegatus in the larva-juvenile transformation period with reference to pituitary prolactin and gill chloride cells responses. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 308 (1), 113–126. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2004.02.015
Wada T., Kamiyama K., Shimamura S., Matsumoto I., Mizuno T., Nemoto Y. (2011). Habitat utilization, feeding, and growth of wild spotted halibut verasper variegatus in a shallow brackish lagoon: Matsukawa-ura, northeastern Japan. Fish. Sci. 77 (5), 785–793. doi: 10.1007/s12562-011-0385-0
Walker B. J., Abeel T., Shea T., Priest M., Abouelliel A., Sakthikumar S., et al. (2014). Pilon: An integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLos One 9 (11), e112963. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112963
Xu Y. J., Liu X. Z., Liao M. J., Wang H. P., Wang Q. Y. (2012). Molecular cloning and differential expression of three GnRH genes during ovarian maturation of spotted halibut, verasper variegatus. J. Exp. Zool A Ecol. Genet. Physiol. 317 (7), 434–446. doi: 10.1002/jez.1736
Yang Z. (2007). PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24 (8), 1586–1591. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msm088
Keywords: Verasper variegatus, genome sequencing, genome assembly, genome annotation, comparative genomic analysis
Citation: Xu X-w, Chen Z, Liu C, Xu W, Xu H and Chen S (2022) Chromosome-level genome assembly of the Verasper variegatus provides insights into left eye migration. Front. Mar. Sci. 9:1045052. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.1045052
Received: 16 September 2022; Accepted: 18 October 2022;
Published: 27 October 2022.
Edited by:
Li Gong, Zhejiang Ocean University, ChinaReviewed by:
Xidong Mu, Pearl River Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, ChinaZhengfei Wang, Yancheng Teachers University, China
Copyright © 2022 Xu, Chen, Liu, Xu, Xu and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Songlin Chen, Y2hlbnNsQHlzZnJpLmFjLmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xi-wen Xu
Xi-wen Xu Zhangfan Chen
Zhangfan Chen Changlin Liu1†
Changlin Liu1† Wenteng Xu
Wenteng Xu Songlin Chen
Songlin Chen