- Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Pathology, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, United States
Background: Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) complex (MTBC) includes ten species that affect mammals and pose a significant global health concern. Upon infection, Mtb induces various stages in the host, including early bacterial elimination, which may or may not involve memory responses. Deciphering the role of innate immune responses during MTBC infection is crucial for understanding disease progression or protection. Over the past decade, there has been growing interest in the innate immune response to Mtb, with new preclinical models emerging.
Methods: We conducted a systematic review following PRISMA guidelines, focused on innate immune mediators linked to protection or disease progression in animal models of MTBC infection. We searched two databases: National Library of Medicine and Web of Science. Two researchers independently extracted data based on specific inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Results: Eighty-three articles were reviewed. Results were categorized in four groups: MTBC species, animal models, soluble factors and innate pathways, and other molecules (metabolites and drugs). Mtb and M. bovis were the only species studied. P2X7R receptor's role in disease progression and higher macrophage recruitment were observed differentially after infection with hypervirulent Mtb strains. Mice and non-human primates (NHPs) were the most used mammals, with emerging models like Galleria mellonella and planarians also studied. NHPs provided insights into age-dependent immunity and markers for active tuberculosis (ATB). Key innate immune factors/pathways identified included TNF-α, neutrophil recruitment, ROS/RNS responses, autophagy, inflammasomes, and antimicrobial peptides, with homologous proteins identified in insects. Metabolites like vitamin B5 and prostaglandin E2 were associated with protection. Immunomodulatory drugs targeting autophagy and other mechanisms were studied, exhibiting their potential as therapeutic alternatives.
Conclusion: Simpler, physiologically relevant, and ethically sound models, such as G. mellonella, are needed for studying innate responses in MTBC infection. While insects lack adaptive immunity, they could provide insights into “pure” innate immune responses. The dissection of “pure,” “sustained” (later than 7 days post-infection), and trained innate immunity presents additional challenges that require high-resolution temporospatial analytical methods. Identifying early innate immune mediators and targetable pathways in the blood and affected tissues could identify biomarkers for immunization efficiency, disease progression, and potential synergistic therapies for ATB.
1 Introduction
In recent decades, there has been an increasing interest in the innate response mediators against members of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) complex (MTBC). MTBC groups ten genetically related species of the Mycobacterium genus that cause tuberculosis (TB) in different mammal species. Within MTBC, Mtb and M. bovis are the most significant species for human health to date (1, 2). Mtb is the leading infectious killer for humans, which generated an estimated close to 1.3 million deaths worldwide in 2023 (3). On the other hand, M. bovis is the primary causative agent of bovine TB and represents a risk for humans and other mammal species due to its ability to infect a broad spectrum of hosts (4, 5).
Innate immunity is the body’s first line of defense against pathogens, present from birth, and characterized by non-specific responses that do not involve genetic rearrangement (6). It aims to control infections either directly through effector responses or by activating adaptive immunity (7, 8). While much of our knowledge about innate immune responses to MTBC comes from in vitro and ex vivo studies, some findings have been inconsistent, for instance the role of neutrophils and the vitamin D during Mtb infection (9–11). Neutrophils’ ability to kill Mtb varies, depending on the cell of origin (mouse vs. human) or other unidentified factors (11). Besides these inconsistencies, these short-lived cells present significant challenges during in vitro or ex vivo assays (11–13). Similarly, although vitamin D inhibits Mtb growth in vitro, its clinical use in TB treatment has not shown substantial improvement in patient outcomes (9). These discrepancies highlight the difficulties in translating in vitro findings to clinical settings.
Early innate responses to Mtb are critical in determining the infection’s outcome in humans, with only 20-25% of individuals exhibiting signs of infection after being exposed to this pathogenic bacterium (14). In some individuals, a combination of innate and adaptive immunity, or in others, the action of mostly (or solely) innate immunity are proposed to control the infection (15–18). For instance, close contacts of TB patients (exposed to the bacterium) never develop disease or exhibit delayed hypersensitive type IV response (PPD-negative). These “self-controlling” TB cases and non-infected contacts drive the hypothesis that some Mtb-infected people develop innate responses with a sterilizing activity against the bacterium (19). This hypothesis has yet to be fully confirmed since recent studies have not found a protective innate response among PPD-negative contacts. However, this still does not exclude the possibility of unknown innate markers associated with early Mtb elimination and even “innate memory” responses that help in this matter (20, 21). While adaptive responses (led by T-cell immunity) are well-studied, they do not fully explain protection against TB, highlighting the importance of further research into innate immunity to find markers of protection or disease control.
Various preclinical animal models, including mice, non-human primates (NHP), and other vertebrates, have been used to study Mtb-host interactions. However, ethical concerns around animal research as well as the high cost and infrastructure associated, have led to increasing interest in alternative models, such as invertebrates. These invertebrate models hold potential for providing new insights into the Mtb-host interaction and expanding research options while acknowledging ethical concerns. Considering the importance of animal models in pre-clinical studies, we conducted a systematic review of recent findings towards innate responses found exclusively during in vivo infection with members of the MTBC, exploring the evolution and some limitations observed.
2 Methods
2.1 Study design
This systematic review aims to comprehensively analyze published peer-reviewed articles within the last decade to determine the molecules and pathways associated with innate responses in animal models infected with MTBC. We adopted the PICO (Population: animal models, Intervention: infection with an MTBC strain in the laboratory setting; Comparation: Group of non-infected animals, Outcome: innate response molecules associated with protection or disease progression) framework (22) to formulate the central question: What type of innate immune mediators (soluble factors and innate pathways) are commonly identified among different animal models that are either associated with protection or disease progression after MTBC infection? The collection of experimental studies and the analysis of their findings were focused on experimentally infected animals only and provided the most common and recently used animal models for MTBC infection. Our review also includes the description of novel host molecules associated with an early antibacterial response and potential limitations in this field. This review aims to provide state of the art information about the preclinical models used to study innate responses against Mtb and other members of the MTBC complex, extracting some commonalities, advantages and disadvantages, as well as some valuable findings in the most novel models used.
2.2 Search strategy and selection criteria
For the systematic search, two databases were consulted: the National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health (PUBMED) and the Web of Science (WOS). The Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms selected were “Innate Immune Response,” “Mycobacterium tuberculosis,” and “Animal Model,” separated by the Boolean operator AND. The initial search was conducted on July 18, 2023, and the inclusion criteria were articles that:
1. were published in the last ten years,
2. described experimental data on animals,
3. reported animals infected with members of MTBC complex, and
4. evaluated innate responses.
We excluded articles focused only on in vitro, ex vivo, clinical studies, other infections (including other species of the Mycobacterium genera), studies that did not use live bacteria to infect the animals, reviews, opinions, meeting reports, and perspectives.
2.3 Study selection and data extraction
Two researchers (LMNR and CM) conducted the article search independently using the MeSH terms described above and extracted the articles obtained using Zotero and Endnote, respectively, following the referred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (23). The search was evaluated for duplicate entries, and every abstract was then analyzed for an initial application of the inclusion/exclusion criteria listed in the previous section. For most cases, the whole article was assessed in the initial screening, looking for the innate immune response findings derived from animal infections only. The total list was revised twice to manually extract all the information used in the qualitative and frequency analysis of four different categories: (i) MTBC species, (ii) animals used, (iii) soluble and membrane-associated factors and innate pathways, and (iv) other relevant molecules.
3 Results
3.1 Results of the search
After removing duplicates and applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, we initially selected 76 articles for the review, out of 274 articles collected for analysis. While reviewing the selected articles, we found seven additional publications that meet the inclusion criteria (some were part of the references in the initial selection), giving us 83 articles to review (Figure 1; Supplementary Table 1).
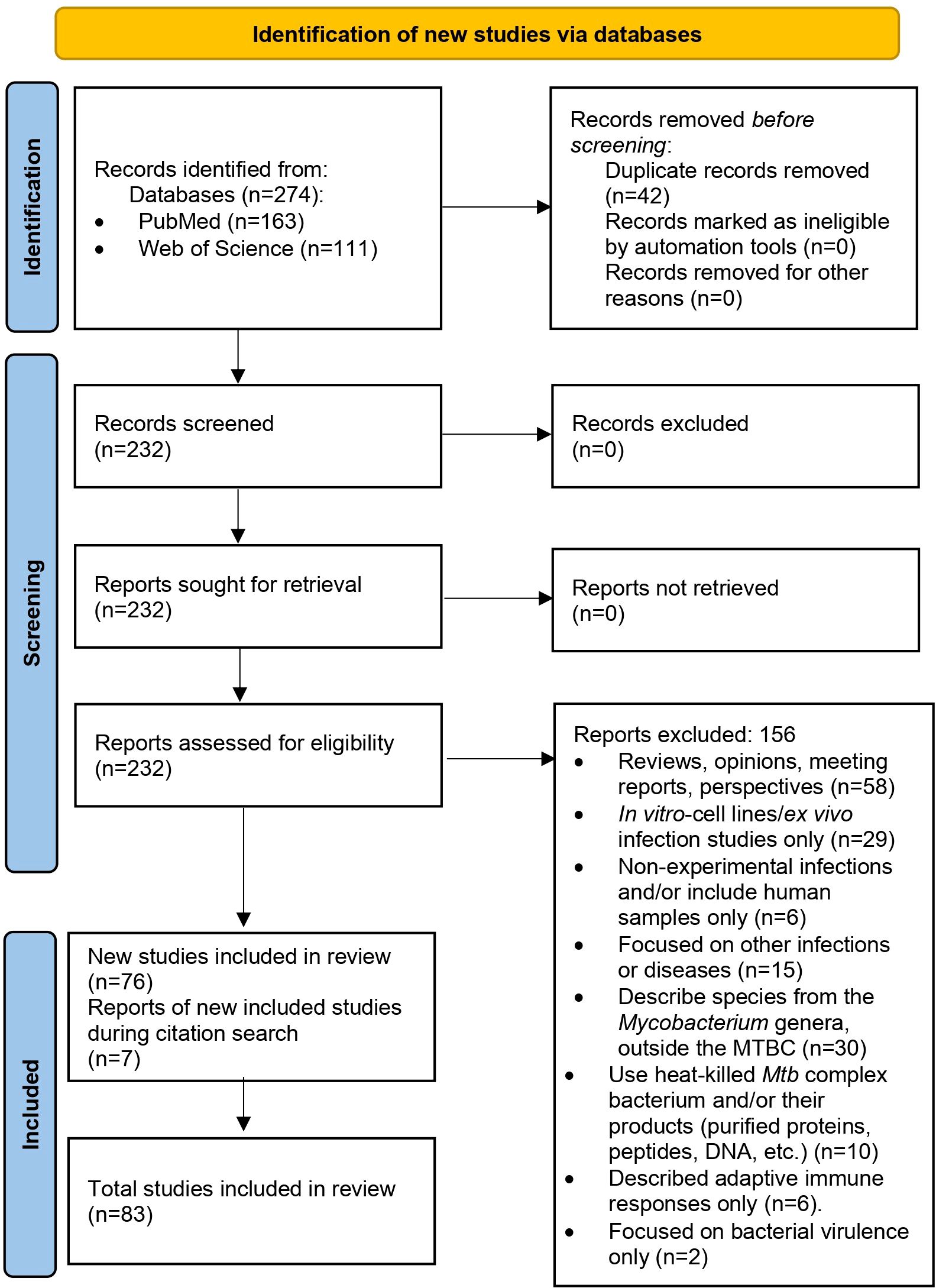
Figure 1. PRISMA 2020 flow diagram used in this systematic review (23).
3.2 Synthesis and analysis of the reviewed articles
During the data extraction process, we focused specifically on innate immune responses observed in vivo following infection with live bacteria, excluding studies that used mixed approaches (like infecting animals and then evaluating responses only after ex-vivo stimulation of specific cell types). As an initial step, we identify the infecting bacteria, the animals and infection routes used to ensure the validity of the findings in the context of our PICO question (Figure 2). This review concentrates on early innate responses, as defined by innate immunity, but also included studies that measured responses weeks or even years after infection, particularly for investigating memory-like or trained immunity responses (24, 25). Long-term innate responses have been described in chronic aseptic and septic conditions, including atherosclerosis and HIV respectively (26–28). Therefore, it is not surprising to see active innate-associated pathways persisting overtime in a chronic infection like TB. We differentiated major “early” and “sustained” innate immunity responses, using the seven days break point [prior to induction of adaptive immunity (29)] to differentiate these two responses (Figure 3A). In Figure 3B, we also separated those innate responses specifically induced after BCG vaccination and after infection in the vaccinated animals.
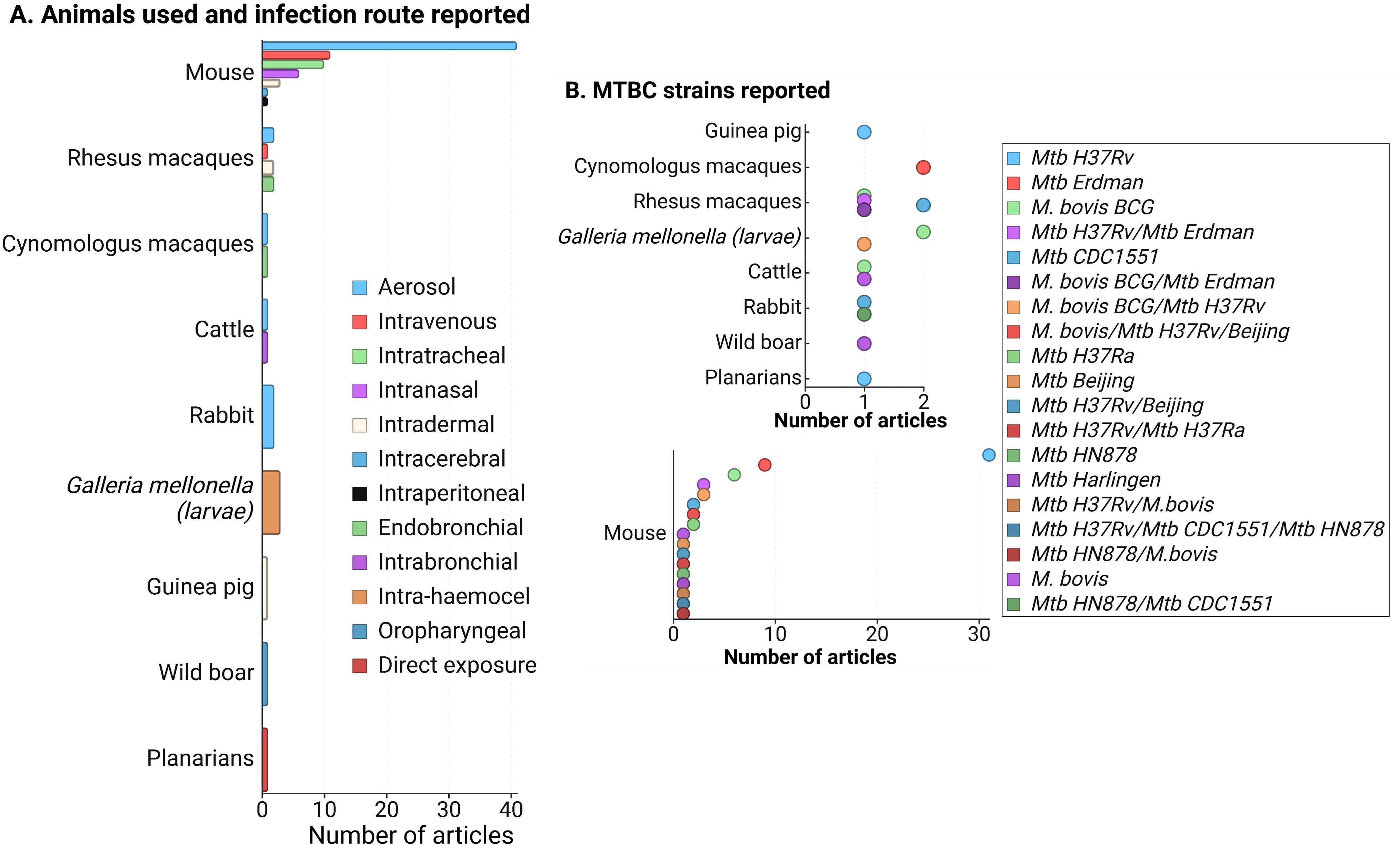
Figure 2. (A) Frequency of animals used in innate response studies against members of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC), along with the infection routes reported for each animal model. (B) MTBC strains used in the reviewed articles, categorized by animal models. Since mice were the most commonly reported model, the lower section of the figure focuses specifically on MTBC strains used in mice. A total of 83 articles were evaluated. Note that some articles utilized more than one animal model (primarily mice and non-human primates), infection route, or strain, but no studies involving mixed infections were included. Figure created with Biorender.
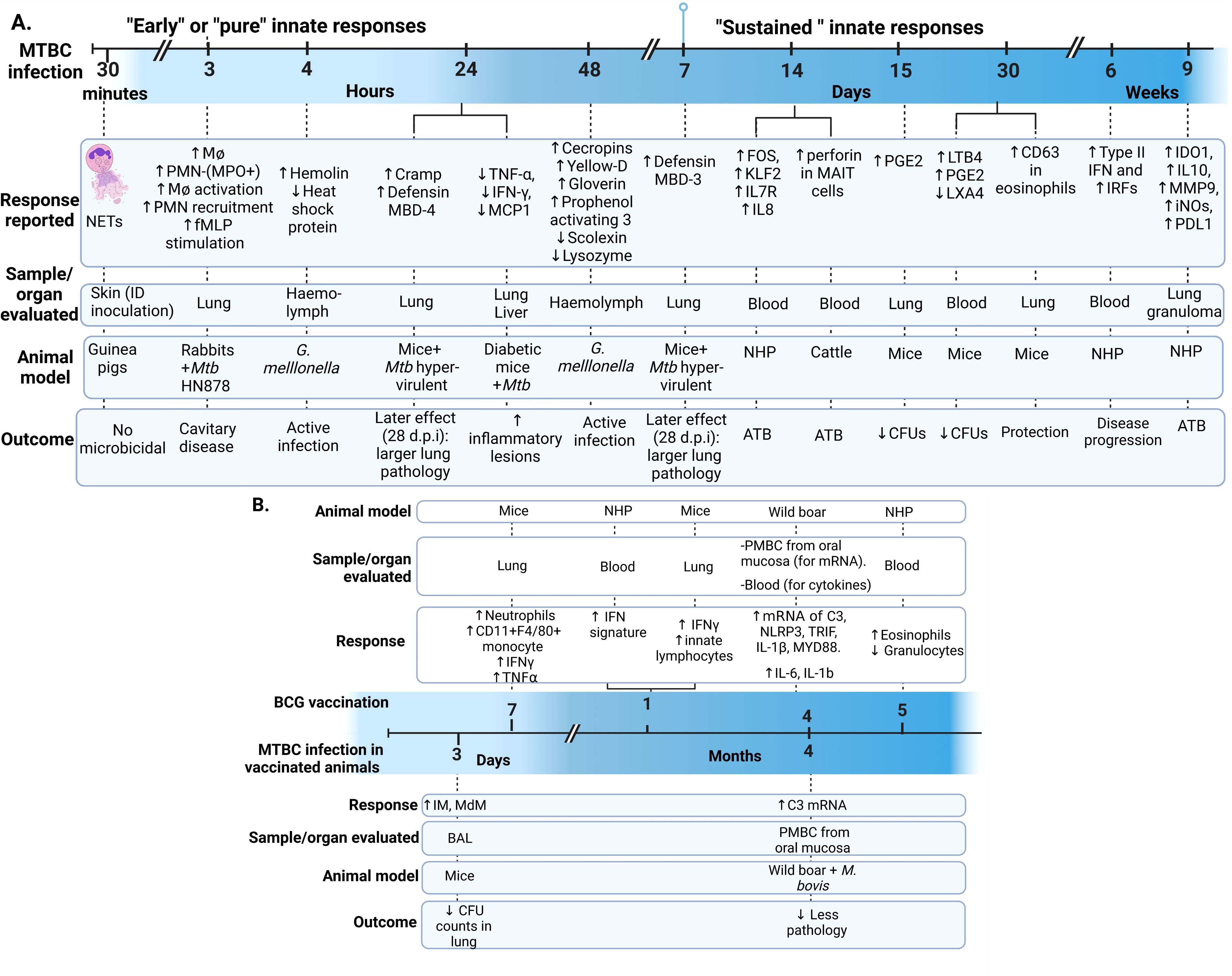
Figure 3. Early and sustained innate responses found in animals with active TB. (A) Main responses associated with active disease. (B) Responses observed after immunization and after Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC) infection in immunized animals (29–33). Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). ID, intradermal; PMN, Polymorphonuclear leukocyte; fMLP, N-formyl-Methionyl-Leucyl-Phenylalanine; MPO, Myeloperoxidase; Cramp, Cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide; ATB, active TB; TNF, Tumoral necrosis factor; IFN, Interferon; MCP-1, monocyte chemotactic protein-1; FOS, Finkel-Biskis-Jinkins osteosarcoma, member of the AP-1 (activator protein-1) family of inducible transcription factors; KLF2, Kruppel-like factor 2; IL, Interleukin; NHP, Non-human primate; MAIT, mucosal-associated invariant T; (PGE2, Prostaglandin E2; LTB4, Leukotriene B4; LXA4, Lipoxin A4; IRF, Interferon regulatory factors; IDO1, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; MMP-9, matrix metallopeptidase 9; iNOs, inducible nitric oxide synthase; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; IM, interstitial macrophages; MdM, monocyte-derived macrophages; BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage; PBMC, Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells; C3, Complement 3 protein; NLP3, “NOD-like” receptor (NLR) pyrin domain-containing protein 3; TRIF, Toll/IL-1R domain-containing adaptor-inducing IFN-β; MYD88, myeloid differentiation primary-response 88 protein; d.p.i, days postinfection.
Trained immunity occurs when pathogens or their components [pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs)] induce epigenetic changes, such as histone methylation, leading to non-permanent changes in inflammatory gene expression (34). This results in a more robust immune response upon subsequent infection (24, 30, 31, 34). These epigenetic changes associated with memory responses have been reported in monocytes and hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) after BCG vaccination, leading to increased anti-mycobacterial responses (29, 35). Interestingly, virulent Mtb strains can suppress this process by reprogramming HSCs via type I interferon (IFN), in contrast to the type II IFN pathway induced by BCG, which demonstrates that trained immunity also depends on the infecting bacterial species or strain (36). We included four articles that explicitly described trained immunity in mice and calves (29–32), Other articles reported the effects of BCG protection in wild boars (37) or their potential in trained immunity in non-human primates (NHP) (33).
The present review does not intend to provide a hierarchy classification of the animal models studied based on which could be more relevant to replicating human ATB. Rather, it intends to provide major applications and limitations observed within each study type. Also, following our PICO question, we evaluate the main findings in terms of molecules and innate pathways, as well as their association with the clinical presentation of the disease.
3.2.1 MTBC species
The reviewed articles focused on two species from the MTBC: Mtb and M. bovis, including various genotypes, attenuated or hypervirulent mutants, and clinical isolates (Figure 2B). Additional searches for other MTBC members, such as M. africanum, M. canetti, M. caprae, M. microti, M. mungi, M. orygis, M. pinnipedii, and M. suricattae, did not yield any result. Mtb H37Rv, mostly used to infect mice, was the most frequent strain reported, followed by Mtb Erdman and M. bovis BCG. Thirty articles were excluded because they reported infections with species outside the MTBC, primarily M. marinum. While M. marinum is often used to study host-pathogen interactions in zebrafish (which develop granuloma-like structures similar to those in human TB) (38), it is not a member of the MTBC and, therefore, did not meet the inclusion criteria for this review.
Different Mtb strains, such as H37Rv, CDC1551, and W-Beijing, were evaluated for their role in infections. Hypervirulent strains like W-Beijing, for instance, are known to cause severe pathology, including significant neutrophil infiltration and higher levels of necrosis (39). Amaral et al. showed that mice lacking the purinergic P2X7 receptor (P2X7R), which detects extracellular ATP, experience reduced myeloid cell infiltration in the lungs and less severe disease when infected with W-Beijing or the pathogenic M. bovis strain MP287/03, but not so much with H37Rv. This suggests that the innate receptor P2X7R plays a key role in contributing to the clinical presentation of the more aggressive forms of TB (Table 1) (47). Additionally, rabbits infected with different Mtb strains (Beijing HN878 or CDC1551) exhibited strain-specific patterns of interleukin (IL)-17 (additional information can be found in the section 3.2.3.11) (55).
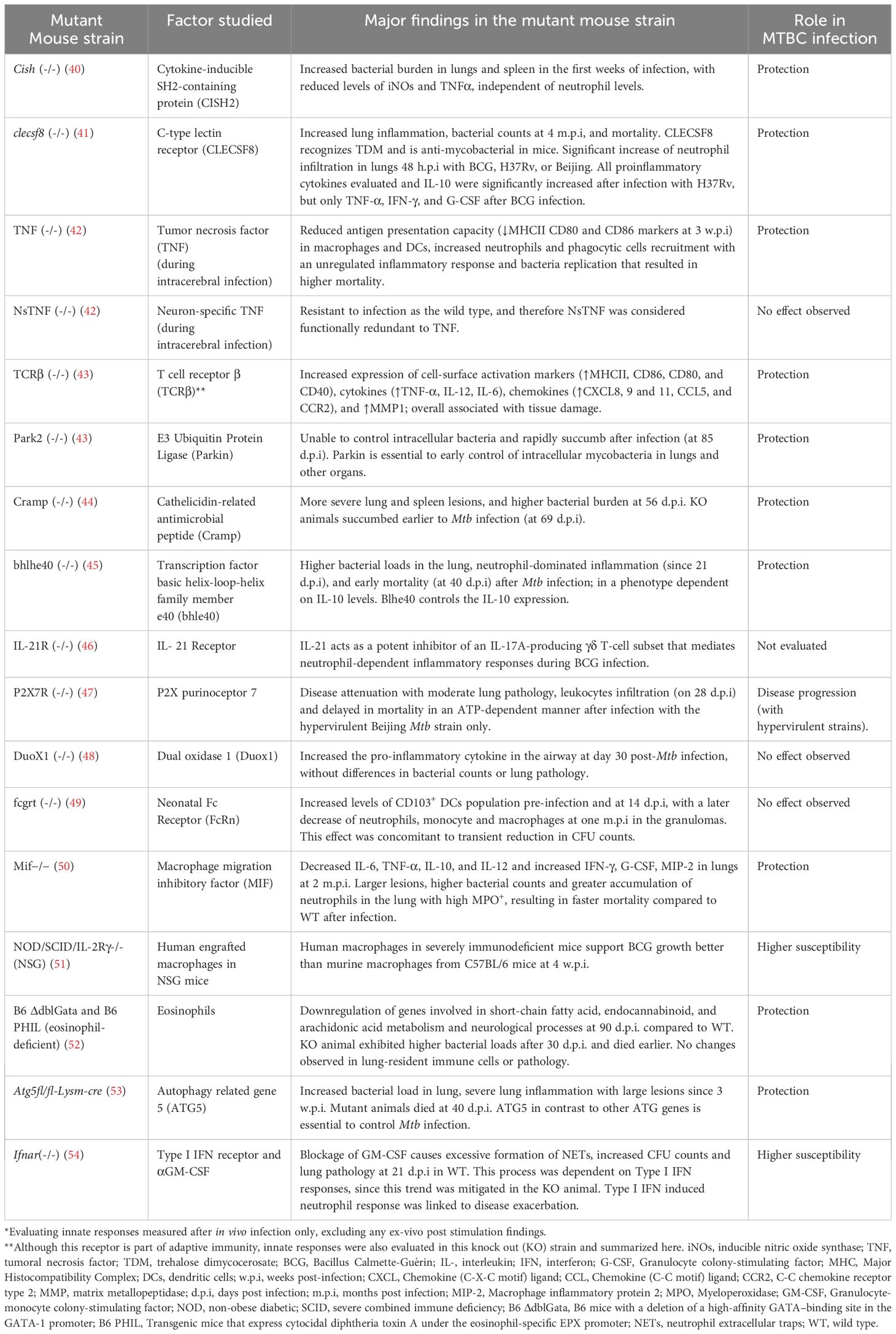
Table 1. Examples of genetically modified mouse strains used for the evaluation of innate responses against Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC)*.
Strain-specific responses were also observed in BCG-vaccinated C3Heb/FeJ mice subsequently infected with the Mtb Beijing strain. Henao-Tamayo et al. found a significant reduction in granulocytic influx to the lungs 25-50 days post-infection, which was accompanied by lower bacterial counts and less lung necrosis at the same time points (56).
3.2.2 Animals used and significant findings in each model
Animal models used in the 83 evaluated articles are summarized in Figure 2A, highlighting mammalian species as the most frequently used. Similarly to previous reviews focused on animal models of MTBC infection (57–60), most of our findings are dominated by the responses observed in mice and NHP. The aerosol route was highly reported among infected mammals (except for the wild boar that was infected via the oropharyngeal route only) (Figure 2A), which is related to the need to use animal models that better replicate the infection route for human infection, especially for the case of Mtb. The infection route was a relevant variable (especially for mammals), since that could also determine some of the evaluated tissues and the type of host response expected.
3.2.2.1 Mouse
Many important discoveries in the innate response against Mtb (i.e., role of TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-12, among others) have been obtained in the mouse model (61). Mice have also been used to study the most recently described role of micro-RNAs (like miR-223 and miR-155) (62, 63) and sensing pathways for bacterial nucleic acids in MTBC (64). Similarly, innate receptors such as TLR2, TLR9, the complement system, and other conserved immunological pathways in mammalians have been studied in the mouse model. Although they do not entirely mimic the human TB infection, mice provide similar infection routes to humans, cost-effective use of several biological replicates, and the availability to explore different genetic and immunological tools (65). Recent studies have shown that lower bacterial doses in mice, like the ultra-low dose (1-3 founding bacteria, measured using DNA-barcoded strains) can more successfully mimic human infection (61, 66).
Under the mouse background (BALB/c, C57BL/6, and C3HeB/FeJ, also known as Kramnik), transgenic and knock-out strains for specific genes have been used as models to evaluate different innate immune response mediators in the articles reviewed (Table 1). These different genetic mice also reflect different degrees of susceptibility to Mtb infection. C57BL/6 mice are generally considered more resistant to Mtb infection than BALB/c mice, and both mice do not develop necrotic lung lesions, a pathology hallmark of human TB (67). On the contrary, C3HeB/FeJ mice are highly susceptible and fail in controlling Mtb infection, displaying a more severe disease progression with characteristics closer to human TB, including the development of large, caseous lung necrotic lesions (68–70).
3.2.2.1.1 Study of innate immune responses in the context of metabolic comorbidities
The mouse model was used to evaluate chronic comorbidities, specifically type 2 diabetes (T2D), which negatively impacts Mtb infection outcomes in humans (51, 71, 72). In this review, we found an overall similar cytokine profile in lung and liver from diabetic mice infected with Mtb and M. bovis intravenously, with earlier and stronger responses after Mtb infection (Figure 3A, Table 2) (71, 72). A systemic increase in pro-inflammatory cytokines characterizes T2D (107). The results observed in this review highlight the bi-directional relationship between T2D and susceptibility to TB, associated with a dysregulated cytokine profile (71, 72). The similar cytokine trend reported post-Mtb and M. bovis infection in this mouse model does not exclude additional innate responses differentially induced by these two species that could be explored deeper, for instance using a discovery mass spectrometry approach (108, 109).
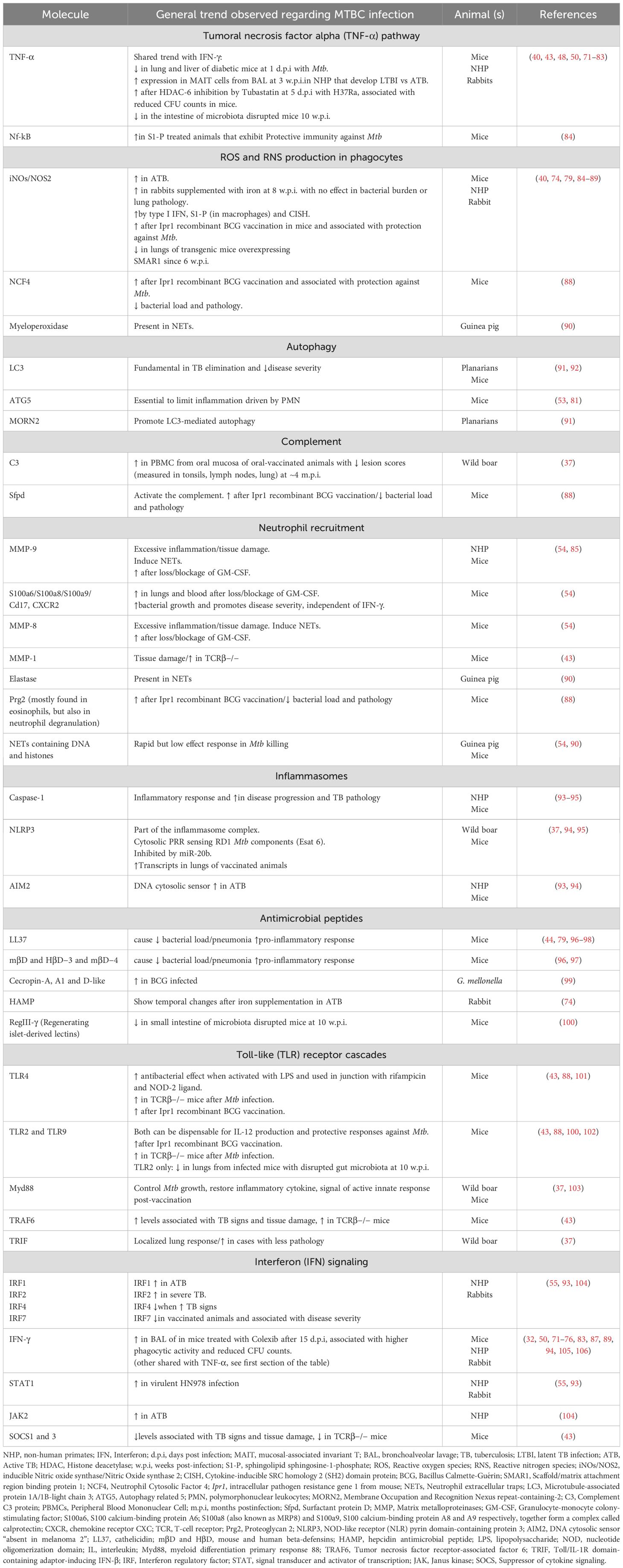
Table 2. Molecules associated with main innate pathways reviewed during Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC) infection.
3.2.2.1.2 Trained immunity
Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor (NOD)-associated trained immunity response was studied in mice by Bricket et al. and was not associated with the early anti-mycobacterial mechanisms induced by BCG. In this study, mice were infected 7 days after receiving the BCG vaccine, detecting similar reductions in lung bacterial counts in both NOD1 and NOD2 deficient mice, as well as in wild-type (WT) mice. At 7 days post-vaccination, higher levels of circulating monocytes (CD11b+F4/80+) and neutrophils were recruited to the lungs, and these were sufficient to control the infection in live-BCG vaccinated mice. This response was accompanied by increased levels of TNF-α and IFN-γ in the lungs. However, the protective innate immune response was independent of natural killer (NK) cells and IFN-γ levels and was instead dependent on neutrophils (29).
Steigler et alfound significant increased levels of innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) secreting high levels of IFN-γ in the lungs, four weeks after intranasal BCG vaccination. The immune response found using the intranasal vaccination was stronger compared to other administration routes, such as intradermal vaccination (32). This finding is relevant for mucosa-associated trained immunity due to the ability of ILCs to induce memory responses (110). D’Agostino et al. showed a rapid increase of interstitial (IM) and monocyte-derived macrophages (MdM) in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) as early as three days post-Mtb infection in previously immunized mice, while >90% of the cells in BAL were alveolar macrophages (AM) in unimmunized mice. These findings confirmed that airway macrophages (mostly represented by IM and MdM) were associated with protection (lower CFU counts) during early Mtb infection and their role in trained immunity (Figure 3B) (30). Importantly, none of the articles mentioned above describe any epigenetic or a specific biochemical mechanism associated with the innate-induced memory response.
Additional knock-out (KO) mouse strains allowed the study of specific mediators, either soluble molecules or receptors, to validate their roles in the innate response against MTBC in pulmonary or cerebral infection. Table 1 summarizes the main findings for some of these KO mouse strains.
3.2.2.2 Non-human primates
Macaca mulatta (rhesus macaques, RM) and Macaca fascicularis (cynomolgus macaques, CM), were the second most used models to study TB, due to their ability to closely mimic human TB and immune responses. NHPs are the preferred model to investigate TB vaccines and pathogenesis. While NHP models are highly informative, they have limitations, including high costs, specialized infrastructure, and ethical concerns (66). In our review, five articles used RM (33, 52, 73, 85, 93) and two used CM (104, 111). There are notable differences between NHP species in their response to Mtb infection. Although both RM and CM are highly susceptible to Mtb, RM are generally more vulnerable to severe TB than CM (66, 112). This increased susceptibility in RM may be linked to differences in their innate immune responses. RM display an anti-inflammatory profile in peripheral monocytes even before infection, with reduced IFN-γ secretion, whereas CM show a stronger pro-inflammatory response, particularly the release of TNF-α, during early infection (113). Most of our reviewed articles using NHP focused on cellular responses and blood transcriptomic profiles, which we differentiated by NHP species (Table 3).
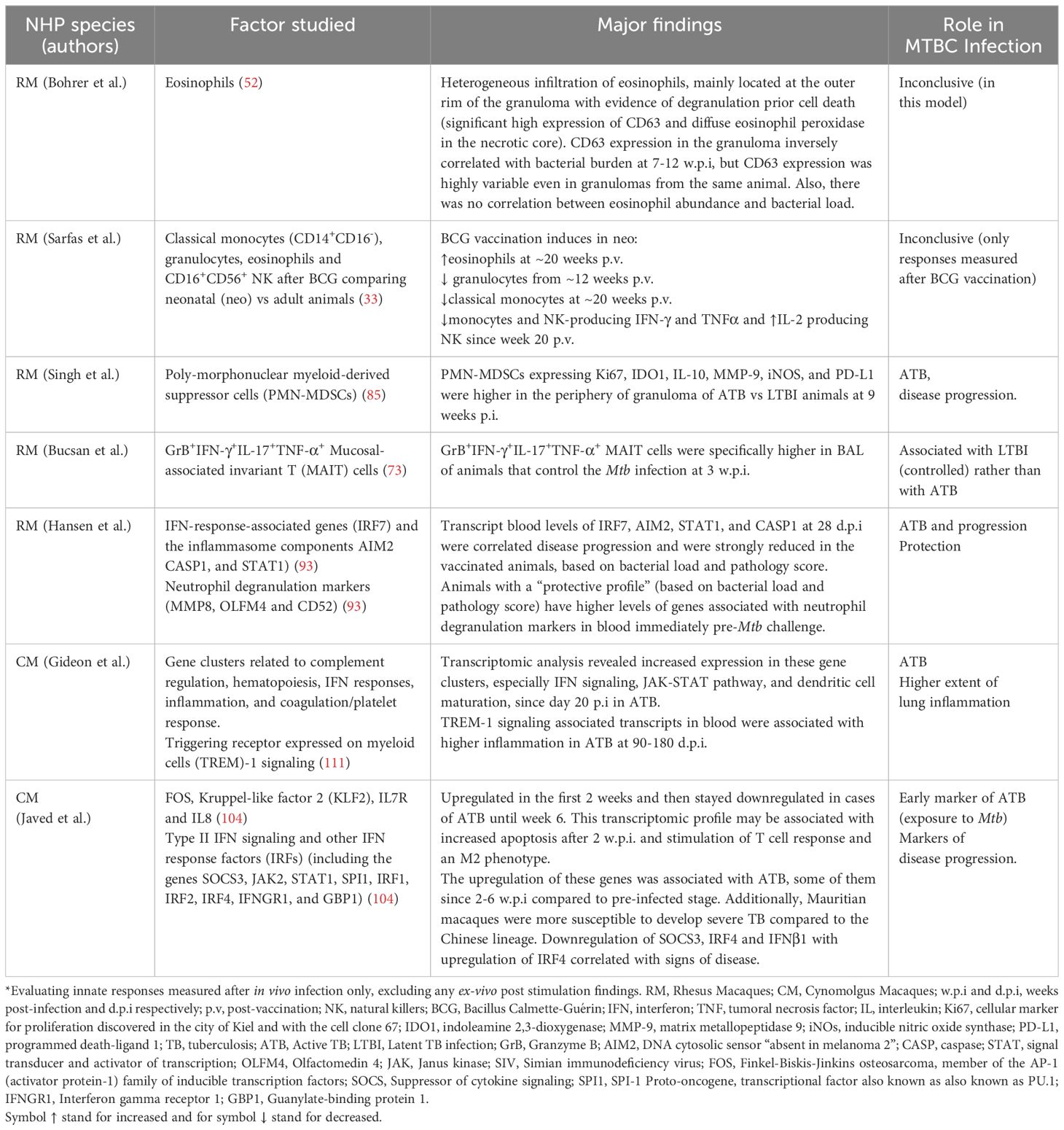
Table 3. Reviewed non-human primate (NHP) innate responses after Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC) infection*.
3.2.2.2.1 Innate responses in NHP with ATB vs LTBI
The NHP model is valuable for studying innate immune responses in the context of active TB (ATB) and latent TB infection (LTBI) (73, 85, 111). Singh et al. found that RM with ATB had a higher proportion of granulocytic polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells (PMN-MDSCs) in lung granulomas, particularly in the periphery near the lymphocyte core, compared to RM with LTBI. These PMN-MDSCs in ATB showed elevated expressions of markers associated with immunosuppression, such as, IL-10, Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1), Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP-9), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and programmed death-ligand 1(PD-L1). The researchers suggested that these cells, due to their localization within the lymphocytic regions of granulomas, could suppress anti-mycobacterial immune responses, making them a potential marker for ATB (85). However, the translation of this finding into the clinical setting as part of a diagnostic tool is still unclear. On the other hand, a rapid but non-significant increase of a specific population of mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells was more associated with LTBI than ATB in RM. These MAIT cells reported by Bucsan et al, were detected in the blood and BAL at three w.p.i (Table 3) (73).
ATB and LTBI outcome in CM were associated with early differences in the blood transcriptomic profile. Gideon et al. reported an increased transcriptomic blood signature in CM as early as 20-30 days d.p.i. that was linked to ATB (Table 3). Interestingly, LTBI animals showed an early increased IFN response at 7 d.p.i., which was reversed by 30 d.p.i. Overall, the transcriptomic profiles of ATB and LTBI in CM were similar to those observed in humans, though LTBI profiles in CM were more heterogeneous and less intense (111). Confirming the findings from Gideon et al. (111)., Hansen et al., demonstrated the association between increased IFN transcripts in the blood of CM with ATB. They also revealed the protective effect of blood markers pre Mtb-challenge that were associated with neutrophil degranulation (Table 3) (93).
Javed et al. reported a temporal gene expression analysis in the blood of CM following Mtb infection, using a human genomic oligonucleotide microarray to identify biomarkers for ATB. This group identified gene clusters based on expression changes between pre-infected and infected animals over a 6-week period, described in Table 3 (104). They also found that CM’s susceptibility to Mtb varied by animals’ origin, with Mauritian animals being more susceptible than Chinese ones. This was attributed to intrinsic differences in type II IFN gene expression among other genes (Table 3). Finally, the authors cautioned that differences in blood transcriptomics should be interpreted carefully, as they could reflect cell migration to the infection site or be influenced by higher cell death rates in specific cell types (104).
3.2.2.2.2 Innate responses following BCG vaccination discriminated by age
Sarfas et al. evaluated the immune responses of neonatal-vaccinated (neo-BCG) RM versus adult-vaccinated (ad-BCG) RM. They assessed systemic responses from 12 weeks to 3 years post-vaccination in neonatally vaccinated animals and at 20 weeks post-vaccination (p.v) in adults (33). Time dependent differences in the frequency of specific subpopulation of circulating NK, monocytes, and eosinophils, as well as the levels of IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2 produced by these cells were reported (33). These differences in immune cell populations and cytokine responses led the authors suggest that neonatal BCG vaccination may induce distinct innate-protective responses in infants, indicating also the induction of trained immunity at this age. They also recommended that future vaccine efficacy studies in non-human primates (NHPs) should include evaluations at neonatal ages (33). Unfortunately, these responses were not further evaluated after in vivo infection in vaccinated animals (Table 3).
Interestingly, eosinophils were also studied in the context of MTBC infection in RM and mice (52). Although eosinophils were not infected with Mtb, active and early recruitment of these cells positive for CD63 (degranulation marker) was observed in the lung tissue of both animal models. A protective role for these cells in the control of Mtb infection was established by Bohrer et al., in an eosinophil-deficient KO mouse model (Table 1), but a more heterogeneous response was observed in RM (Table 3).
3.2.2.3 Other mammals
Rabbits were reported by two articles that evaluated pathological features and transcriptional differences in innate-associated genes after external stimuli (74) or in response to Mtb strains with different virulence profiles (55). Kolloli et al. concluded that iron supplementation induces different transcriptomic changes, depending on the evaluated tissue, without affecting bacterial burden or disease pathology. For instance, a systemic downregulation of IFNG, TNFA, and IL1B and upregulation of IL6 and SMAD6 was reported four weeks p.i (w.p.i). In the lungs, IL6 is downregulated similarly to the transcriptional regulators SMAD6 and SMAD7, while IL10, NOS2, IFNG, and TNFA are upregulated simultaneously. SMAD6 and SMAD7 are involved in the expression of the hepcidin antimicrobial peptide (HAMP) (74).
Subbian et al. found transcriptional differences in 14 genes at 3 hours post-infection with greater recruitment of macrophages and polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) (with higher myeloperoxidase activity) and cavitary disease more like human active TB in the lungs of rabbits infected with HN878 compared to those infected with CDC1551. Overall, pathways involved in macrophage activation, fMLP (N-formyl-Methionyl-Leucyl-Phenylalanine)-stimulation or PMN recruitment and activation were upregulated after HN878 versus CDC1551 infection (Figure 3A). Some of the genes with increased expression include TNF, CXCL10, STAT1, IL1A, SPP1, CCL4, CCL2, IRF5, CD38, while reduced expression of IL4R, CAV1, TGFB2, IL18, and CD36 were observed (66). That early signature profile was relatively constant at four w.p.i and proposed to determine long-term Mtb infection in rabbits (55).
Cattle infected with either M. bovis BCG or AF2122/97 were used as a model to study trained immunity (31) or MAIT cells (114), respectively. In the study by Guerra-Maupome et al., calves did not exhibit differences in the number of monocytes expressing CD14+, CD11b+, or TLR-4 at four weeks post-BCG-vaccination, compared to unvaccinated animals (31) as opposed to the increased trend observed in BCG-vaccinated humans (115, 116). Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC) from the aerosol vaccinated compared to the unvaccinated cattle showed increased levels of IL-6, IL-1β, and TNFα, but only after ex-vivo stimulation with LPS or Pam3CSK4. The latter allowed the authors to conclude that the innate immune system of calves can be “trained” and could be used as an immunomodulatory strategy (31). However, they did not explore the trained immunity effect after the animals were re-infected with M. bovis.
The second article by Edmans et al. revealed a MAIT cell population in the blood that showed higher perforin expression two-weeks after M. bovis infection without changes in the number of these cells. This high perforin expression was seen mainly in animals with TB lesions (114).
Guinea pigs develop necrotic core granulomas, and their macrophages exhibit surface CD1b and CD1c, making them a beneficial small animal model for replicating human TB (67). This animal has been widely studied for host-pathogen interactions in metabolic co-morbidities (such as diabetes and malnutrition) and mainly adaptive responses against MTBC (117). However, only one article focused on innate responses in the guinea pig was found during our review, specifically studying the neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) (chromatin webs). Although this was one of the earliest responses observed, it was not microbicidal (90).
Wild boars were orally vaccinated with a heat-inactivated M. bovis strain and then infected with the same (viable) strain. Beltrán-Beck et al. evaluated the transcriptomic responses post-vaccination in the PMN of the oral mucosa and serum and then after infection in vaccinated animals. Some differences were noted in the complement and inflammasome responses post-vaccination, but only C3 mRNA levels remained after M. bovis infection, which was associated with reduced pathology (Figure 3B) (37).
3.2.2.4 Invertebrates
In recent years, invertebrate animal models such as the insect Galleria mellonella (99, 118, 119) and planarians (Dugesia japonica and Schmidtea mediterranea) (91) have been used to study TB. These smaller models are advantageous for high-throughput evaluation of innate immune responses and align with animal research’s 3Rs principles (Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement) (120). Invertebrates, which lack a well-developed adaptive immune system, rely primarily on robust innate immunity to defend against pathogens and other stressors, making them valuable for studying innate immune responses against bacteria, including MTBC (121). Insect models, for example, have contributed significantly to understanding innate immunity and facilitated the discovery of mediators, such as the Toll-like receptors (TLRs). Conserved immune responses across insects and mammals include phagocytosis, opsonization, oxidative stressors, and eicosanoid synthesis, among others yet to be characterized (121, 122).
3.2.2.4.1 Galleria mellonella
The larvae of Galleria mellonella (greater wax moth) were used to assess infection by injecting the bacteria into the hemocoel(Figure 2A). This model has a simple body structure and ability to tolerate human body temperature, which allows the identification of components of innate responses that are shared with more complex animals, including cells, soluble factors, cell receptors, physical barriers, and processes (like phagocytosis, cell adhesion, redox responses, and others) (123, 124). Despite the advantages, the model lacks relevance for exploring human-specific infection routes and the interplay between innate and adaptive immunity. However, the lack of adaptive responses and the relatively short time as a larvae could be exploited to study “pure” early innate or “sustained” responses (up to 6 weeks approximately, when the next pupa stage start to develop) (125).
Pathologically, G. mellonella larvae exhibit granuloma-like structures (called nodules) in their fat body with infected hemocytes (insect immune cells) (122). Hemocytes are phagocytic cells (similar to human macrophages and neutrophils) and were described in two out of three articles reporting infecting insects (118, 119). Different subtypes of hemocytes have been described (i.e., granulocytes, spherulocytes, plasmatocytes, prohemocytes, coagulocytes, and oenocytoids) (126, 127) with the identification of distinct cell markers (128, 129). However, the specific roles of different hemocyte subtypes in the immune response against MTBC remain unclear (118). Additionally, this model has potential for studying “trained immunity,” as BCG vaccination improves survival in larvae, hinting at its relevance for exploring innate induced memory in TB (99).
3.2.2.4.2 Planarian species
Planarian species, specifically D. japonica and S. mediterranea, were explored as a novel model for studying Mtb infection. These planarians were infected directly by exposing them to liver homogenates mixed with Mtb. However, the study found that planarians could resist Mtb infection, as no viable bacteria were recovered after nine days post-infection (91). A fundamental limitation of this model is that temperatures above 30°C are lethal for these planarians (130), which does not match the optimal growth temperature of Mtb (37°C). This temperature difference may have impacted the growth and survival of Mtb during infection. Specific findings regarding this model were focused on autophagy, which will be discussed in section 3.2.3 under the subsection “Autophagy-related proteins.”
3.2.3 Soluble and membrane-associated factors distributed in innate pathways
This section aims to provide information about the different factors (soluble and membrane-associated) studied by classifying them in different immunological pathways. Some pathways contain mediators acting on both innate and adaptive responses, like IL-21 or IFN-γ. However, only specific findings in the evaluation of innate responses were selected. For instance, IL-21 was evaluated as part of γδ T-cell response (46).
3.2.3.1 Tumoral necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) pathway
One of the central and most frequently identified factors in these reviewed articles was the cytokine TNF-α that was reported in articles using mice (40, 43, 48, 50, 71, 72, 75–83, 131), NHP (73), and rabbits (74). This pathway is responsible for multiple biological functions, including inflammation, cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis (132). TNF-α is a cytokine produced by immune and non-immune cells and has a crucial role in TB protection (9). Signaling involves different molecules, such as the transcriptional factor Nf-kB. Nf-kB was increased in animals treated with sphingolipid sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1-P) that exhibited protection to Mtb (84). Most of the trends reported for TNF-α, were similarly reported for IFN- γ, except for one study in which the Mif-/- animals were used (Table 1). Significant trends identified in this pathway are described in the first section of Table 2, while those obtained in KO mice strains and NHP are summarized in Tables 1 and 3, respectively.
3.2.3.2 ROS and RNS production in phagocytes
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitrogen species (RNS) are essential components of the antimicrobial system, produced mainly by macrophages (9, 133). iNOs was one of the most frequently reported proteins in this category. iNOs was higher in ATB in different mammals evaluated (Table 2). Different articles described the role of iNOs during anti-mycobacterial defense, being stimulated by type-I IFN (86), S1-P (84), and cytokine-inducible SRC homology 2 (SH2) domain protein (CISH) (40). Conversely, overexpression of scaffold/matrix attachment region binding protein 1 (SMAR1) induced a significant reduction of iNOS expression in the lungs of infected mice at six w.p.i (87). In the same article, increased levels of IFN-γ and IL-12 in lung homogenates at four w.p.i were also reported, suggesting responses associated with adaptive immunity and potentially “sustained” innate immunity. These findings highlight the need to not only evaluate the kinetics of release, but also identify the cell where those innate responses are originating in vivo.
Neutrophil cytosolic factor 4 (NCF4) is a component of the NADPH oxidase complex, which is predicted to be involved in the production of O2-, via NADPH oxidase 2 (134). Increased NCF4 levels were related to reduced bacterial load and a protective response in animals immunized with an Ipr1-modified BCG vaccine (a BCG carrying the mouse gene Ipr1-intracellular pathogen resistance 1) (88). Other proteins and their trends are also summarized in Table 2.
Lastly, the production of ROS by lung-residing myeloid cells (primarily PMN and AM) in mice was hampered by the early action of platelets that reduced the availability of these cells by forming aggregates in the lung by 21 d.p.i (independently of their canonical activation, by cyclooxygenase (COX)-1, glycoprotein IIb/IIIa or the ADP-receptor P2Y12). This effect was confirmed by reduced bacterial load and lung pathology, as well as increased survival following platelet depletion around the onset of inflammation at seven d.p.i, but not before the infection (135). Increased early platelet response has been also reported in human patients that progress to ATB (136).
3.2.3.3 IFN signaling
There are three types of IFNs: Type I (mainly IFN-α, -β, and others), Type II (IFN-γ), and Type III (IFN-λ). Reduced levels of IFN-γ were reported in diabetic mice as early as 24 h.p.i, that were exhibiting a dysregulated immune response with increased bacterial burden and inflammatory lesions (Figure 3A) (71, 72). In NHP, type I and type II IFN transcriptomic signatures were associated with ATB as early as two w.p.i (Table 3) (104). Additional molecules and associated articles are summarized in Table 2. Also, the interaction between this pathway and the neutrophil response was studied in the deficient IFNγR−/− mice (Table 1).
IFN regulatory factors (IRF 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 7) showed a diverse response during Mtb infection. IRF7, among other innate transcriptional signatures from PMB cells in the blood, were correlated with the extent of disease and were strongly reduced in the vaccinated RM that exhibited Mtb control and reduced pathology (Table 3) (93). In the article by Javed et al., IRF1 was highlighted among the early blood transcriptomic biomarkers in active TB that was also shared between human and macaque pathways as part of the type II IFN signaling, with sustained upregulation from the second through the 12th-w.p.i. Other IRFs, such as IRF2 and 4, were expressed differently, depending on the time point evaluated and the lineage of the infected animal (either Chinese or Mauritian macaque lines) (Table 3) (104).
3.2.3.4 Neutrophil recruitment
Neutrophils can internalize bacteria and activate inflammatory and effector responses, by the action of mediators like myeloperoxidase, elastase, and the production of NETs. As it was discussed earlier, neutrophils generate one of the earliest responses in the guinea pig (Figure 3, Table 2); however, they were ineffective at eliminating Mtb (90). Other publications concluded that the role of neutrophils is not necessarily bactericidal but perhaps in initiating inflammatory responses (29). Das et al. and Moreira-Texeira et al. concluded that neutrophil accumulation without a macrophage response leads to higher bacterial burden, increased disease severity, and greater lethality. This macrophage-reduced response was observed in MIF deficient mice (simultaneous to reduced macrophage innate cytokines: IL-6 TNF-α, IL-12, IL-10) (50, 54).
Other proteins also associated with this pathway are described in Table 2. Among those, proteolytic matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) participate in the degradation of the lung extracellular matrix components, with the subsequent Mtb spread. These proteins have been proposed as biomarkers of ATB disease (137). During our review, we found enhanced MMP-1, 8, and 9 levels in blood and lungs during active TB that was responsible for excessive inflammation and tissue damage in mouse-susceptible strains (54). MMPs were also highly expressed during neutrophil activation and recruitment and induced neutrophil responses such as the NETs (43, 54, 85).
The dual role of neutrophil described in the reviewed articles is represented by excessive inflammation in acute phase after infection (probably bacterial dose/strain-dependent) (56) and protection in “sustained” or trained immunity after BCG vaccination in mice (29). In humans, neutrophil degranulation and NETs markers are also increased early in patients that progress to ATB (136). In RM, a higher expression of neutrophil degranulation makers was seen before exposure to Mtb that resulted in reduced lung pathology and bacterial load after infection, and therefore categorized as a protection marker (pre-infection) (Table 3) (93). This protective role of neutrophils may be driven by a specific subpopulation that could be induced since early developmental stages in the bone marrow after BCG immunization (29, 35).
3.2.3.5 Inflammasomes
The inflammasome is a complex consisting of a sensor (such as a cytosolic pattern recognition receptor or PRR), an adaptor, and an effector (pro-caspase-1) proteins that, when activated, cleaves pro-inflammatory cytokines essential for MTBC control (138, 139). We found articles describing two types of inflammasome receptors: “NOD-like” receptor (NLR) pyrindomain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) and the DNA cytosolic sensor “absent in melanoma 2” (AIM2) (Table 2). In mice, NLRP3 interacts with the Mtb Esat-6 protein and influences the expression of IL-18 and IFN-γ (94). In addition to mice (94, 95), the inflammasome complex NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-1β was reported in wild boars (37). In that model, mRNA levels of these inflammasome-associated molecules were increased in the PBMC from oral mucosa after oral vaccination with BCG (Figure 3B) (37). On the other hand, NLRP3 was shown to be mitigated by miR-20b binding to the 3’-UTR of NLRP3 mRNA, inducing M2 macrophage polarization in the mouse (Figure 4) (95).
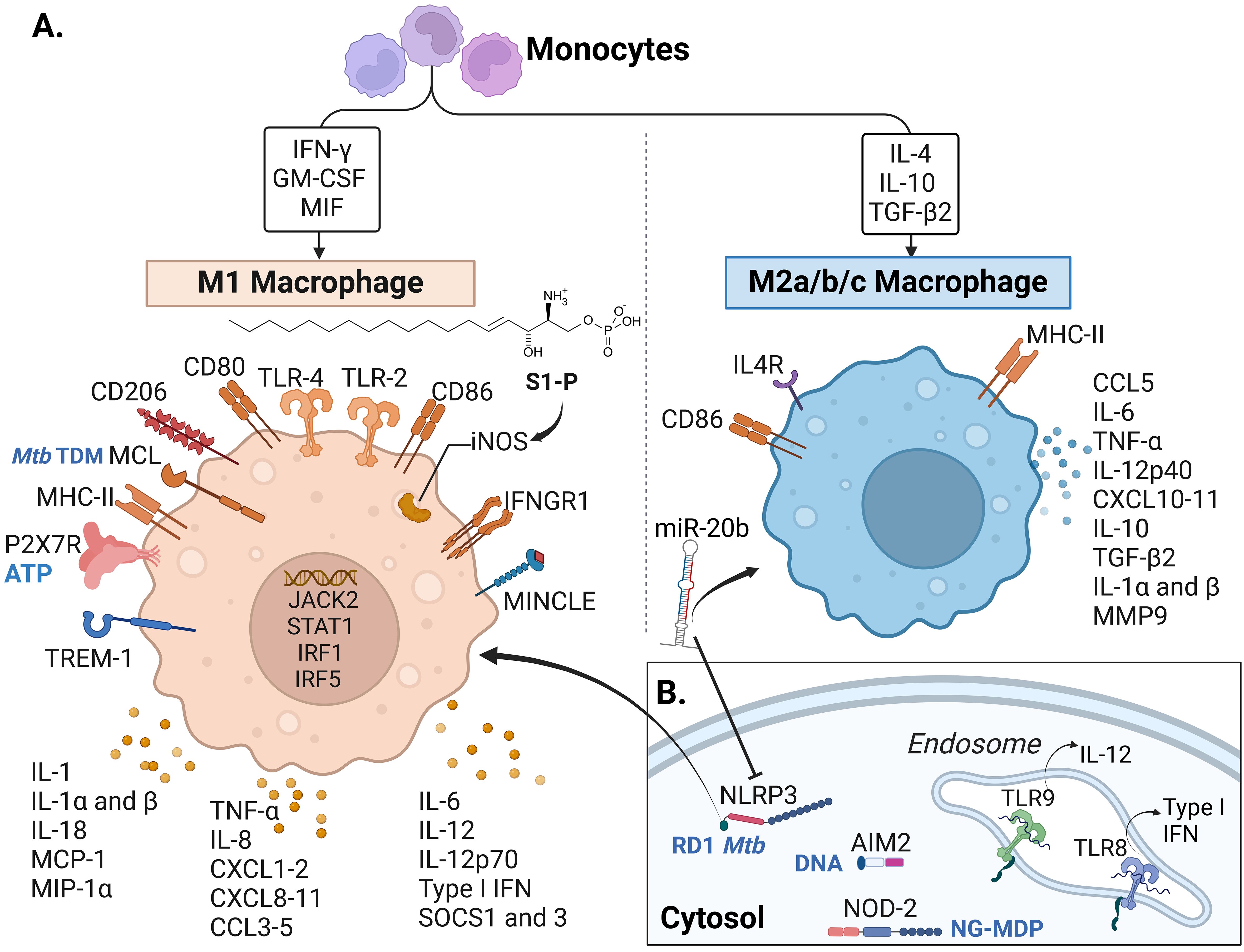
Figure 4. Macrophage receptors and soluble factors identified in response to Mtb complex in the reviewed articles.A. Cytokines, chemokines and receptors identified in the reviewed articles mostly associated with M1 macrophages. (B) Intracellular and endosomal receptors. Some of the recognized molecules (from Mtb or the host) are written in blue in panels (A, B), including TDM: trehalose dimycocerosate (Mtb), ATP: Adenosine triphosphate released from host damaged cells, RD-1 Mtb: region of difference 1, present in virulent Mtb strains, DNA: self (host) and bacterial DNA, NG-MDP: Mycobacterial N-glycolylated muramyl dipeptide. IFN, Interferon; GM-CSF, Granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor; MIF, Macrophage migration inhibitory factor; IL, interleukin; TGF, Transforming Growth Factor; S1-P, sphingolipid sphingosine-1-phosphate; TLR, Toll-like receptor; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; IFNGR, Interferon-gamma receptor; MINCLE, Macrophage inducible C-type lectin, also known as CLEC4E; TREM, Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells; P2X7R, P2X purinoceptor 7; MHC, Major histocompatibility complex; MCL, macrophage C-type lectin; MCP-1, monocyte chemotactic protein-1; MIP-1α, Macrophage inflammatory protein-1α; CXCL, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand; CCL, C-C chemokine ligand; SOCS, Suppressor of cytokine signaling; MMP, Matrix metalloproteinase; miR-20b, microRNA 20b; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor (NLR) pyrin domain-containing protein 3; AIM2, DNA cytosolic sensor “absent in melanoma 2”; NOD, Nucleotide oligomerization domain. Macrophage phenotype classification done following (140–143). Created with BioRender.com.
Another inflammasome-related PRR is the AIM2-like receptor. Kuptz et al. demonstrated that NLRP3 rather than AIM2 was involved in the activation of IL-18 in mice (94). In NHP (RM), AIM2 was increased in animals with active TB and reduced in vaccinated animals that showed Mtb control (no signs of granulomatous disease) (Table 3) (93).
3.2.3.6 Autophagy
More than 30 autophagy-related genes (ATGs) and other players, such as the microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3 (LC3), perform this innate protein degradation and regulatory mechanism in mammals. The activation of these proteins results in the membrane invagination of the bacteria, its products, or even damaged self-organelles. There is also a non-canonical autophagy known as LC3-associated phagocytosis (LAP), with the participation of PRR, independently of autophagosome formation (144). Deficient ATG5 mice exhibit more severe inflammation and succumb earlier to the infection (Table 1) (53). More recently, Kinsella et al. reported that ATG5 was required in CD11c+ cells (lung macrophages and DCs) to control the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines and avoid neutrophil recruitment (81).
LC3 participates in the autophagosome maturation and has two recognized isoforms: a cytosolic (LC-I) and a membrane-associated isoform (LC3-II, that is LC-3 conjugated to phosphatidylethanolamine) (145). LC3-II, regularly measured as marker of autophagic activity, was found increased in M. bovis infected mice after treatment with nilotinib (also discussed in section 3.2.5) (92). LC3 was evaluated also in planarians. LC3 co-localization with Mtb in mature phagolysosomes and LAP was fundamental for Mtb elimination in planarians. Finally, the Membrane Occupation and Recognition Nexus repeat-containing-2 (MORN2) transcript promoted both LC3 processes, and Mtb phagocytosis in planarians and humans (91).
3.2.3.7 Antimicrobial peptides
Increased antimicrobial peptides were reported in the early response to MTBC infection, which was more prominent when a hypervirulent strain infected the host (96, 99). Cecropins increased 48 hours post BCG infection in the insect model (99), while hypervirulent bacteria induced higher cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide (Cramp) and defensins response in the mouse model as soon as one d.p.i compared to the levels induced by H37Rv (Figure 3A) (96). In other cases, the antimicrobial activity of these peptides was evaluated in the mouse model as a potential therapeutic alternative (79, 97). For instance, Ramos-Espinosa et al. evaluated the use of recombinant adenovirus as a delivery strategy for antimicrobial peptides [Human β-defensin 3 (HβD3) or cathelicidin (LL37)]. This treatment strategy resulted in reduced bacterial load and pneumonia with higher expression of proinflammatory cytokines and a synergistic effect with anti-TB drugs (97). In line with this, KO mice for Cramp (LL37 mouse homolog) were unable to control Mtb and succumbed earlier after infection (44) (Table 1).
In the rabbit, the antimicrobial peptide HAMP was studied, which is also known to regulate systemic iron. In this study, HAMP levels in the lung were upregulated after 8 weeks post-Mtb infection in animals supplemented with iron without affecting bacterial load (74). Although antimicrobial peptides are mainly produced by epithelial cells and macrophages (96), none of the reviewed articles evaluated the epithelial cells in vivo during an MTBC infection. Lastly, lower expression of the gene RegIII γ, involved in defense peptide production in the intestine, was found in mice with antibiotic induced-intestinal dysbiosis. This trend was more intense after the mice were infected with H37Rv and in the infected animals that were treated with Isoniazid (INH) (Table 2) (76).
3.2.3.8 C-type lectin receptors
These groups of PRR were represented in the reviewed articles mainly by the Macrophage inducible C-type lectin receptor (MINCLE) and macrophage C-type lectin (MCL). Macrophages and DCs express MCL that recognize Mtb TDM (Trehalose 6,6’-dimycolate). Reduced MCL levels were linked to increased inflammation, bacterial burdens, and mortality in the mouse model (Table 1) (41). These receptors exert non-redundant anti-Mtb function, facilitating the uptake of the bacteria and the signaling towards proinflammatory responses (41, 131). Gut microbiota dysbiosis reduces the expression of MINCLE in DCs that induces adaptive T cell CD4+ responses, demonstrating a strong relationship between gut microbiota and DCs with subsequent Mtb elimination (146). Gut microbiota disruption also reduces the expression of other innate receptors, such as NOD2, MHC-II, and TLR2 in pulmonary DCs that participate in anti-Mtb responses in the mouse model (76, 100, 146).
3.2.3.9 Toll like receptor
We found three TLRs in our reviewed articles: TLR2, 4, and 9. Significant findings related to these TLRs and other molecules participating in this innate pathway are described in Table 2. The activation of TLR4 can be dependent or independent of myeloid differentiation primary-response protein 88 (MyD88). MyD88 is fundamental to clear MTBC infection. The reactivation of MyD88 signaling in myeloid cells (macrophages and DCs) during M. bovis BCG infection is sufficient to control pathogen growth and reinstate local inflammatory cytokine production (IL-12p40, IFN-γ, and IL-1β in lungs) in mice (103). Before Mtb infection, Myd88 and the Toll/IL-1R domain-containing adaptor-inducing IFN-β (TRIF) transcripts were higher in vaccinated wild boars than in unvaccinated wild boars, as a sign of activation of the innate response and reduced pathology (Figure 3B) (37). Another mediator in TLR4-mediated responses is the tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6). TRAF6 was associated with TB signs and tissue damage in the TCRβ deficient mice (Table 1) (43).
3.2.3.10 Fc gamma receptors (FCGRs)-dependent phagocytosis
This phagocytic receptor binds to the Fc portion of immunoglobulin G (IgG). One article evaluated the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) in a KO mutant mouse strain (Table 1). Mtb-infected mice lacking FcRn had a reduced neutrophil infiltration in Mtb-infected lungs, concomitant to reduced bacterial burden and pathology. Because of the absence of FcRn reduced the capacity of CD103+ DCs to eliminate bacteria, other phagocytic cells may be driving the Mtb elimination and contributing to the low pathology profile observed (49).
3.2.3.11 Immunoregulatory interactions between lymphoid and non-lymphoid cells
In this pathway, we have grouped the different IL observed in four mammalian species (Table 4) and the triggering receptors expressed on myeloid cells (TREM)-1. A high frequency of articles reporting IL and other cytokines and chemokines could be explained by their relevance in the inflammatory responses generated after MTBC infection, the availability of analytical methods (ELISA, Luminex®, flow cytometry), and reagents that allow the multiplexed study of these molecules, particularly in the mouse model. In the remaining animal models, IL and other cytokines were primarily studied using gene expression analysis, either by using qRT-PCR (40, 87), whole transcriptomic studies, or a combination of both (55, 104). The increase of acute-phase cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, or anti-inflammatory IL-10 in serum or different tissues of mammals depended mainly on the specific factor being studied (KO mouse strains, ATB vs LTBI, etc.) and how those induce early or “sustained” changes in innate responses (Tables 1, 3; Figure 3, section 3.2.2). Some of the articles included in this review evaluated these innate cytokines in response to different factors, such as the use of hypervirulent strains (55, 147). For instance, IL-17 is required for early protective immunity against the hypervirulent Mtb HN878, but not much against Mtb H37Rv or CDC1551 (147).
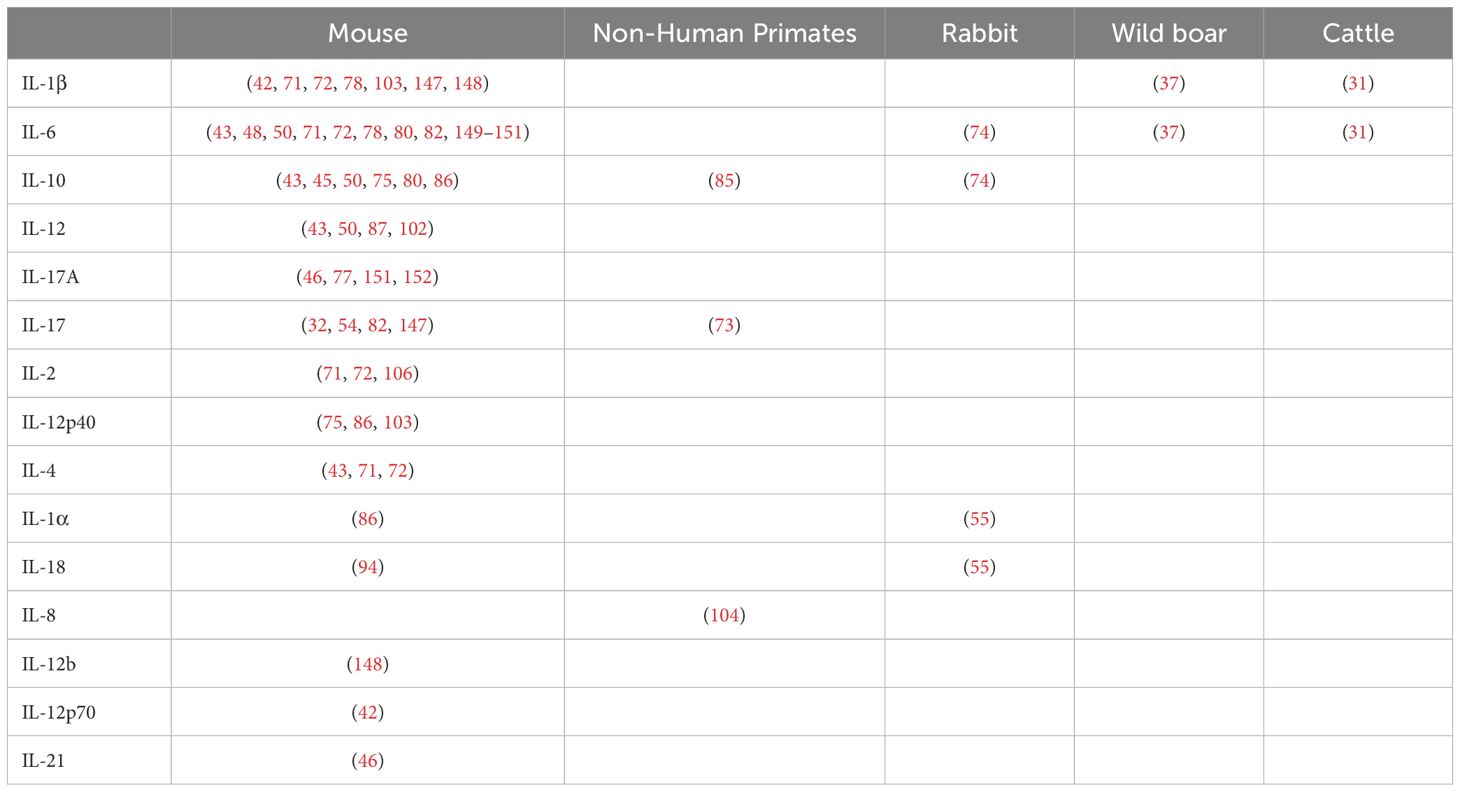
Table 4. Reported interleukins (IL) associated with innate responses against Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC) differentiated by animal models.
Besides myeloid cells, TREM-1 is highly expressed in Vδ2 T cells of human patients with ATB and is involved in inflammation (153). In our review, increased TREM-1 signature-associated transcripts were associated with higher inflammation and disease severity in NHP at the time of diagnosis (90-180 d.p.i), similarly observed in human studies (111).
3.2.3.12 Eicosanoids and enzymes that participate in their synthesis
Eicosanoids are lipid mediators derived from arachidonic acid, produced by cyclooxygenases (COXs) and lipoxygenases (LOs), among other enzymes. These mediators include prostaglandins, resolvins, lipoxins, and leukotrienes (154–159). Eicosanoids have protective functions in innate and adaptive responses after Mtb infection (9, 155, 160). The most frequently reported eicosanoid, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), generated by COX1, limits tissue damage and bacteria growth in the mouse lungs at 15 d.p.i (105). Mayer-Barber et al. similarly showed that PGE2 induced anti-Mtb activity and was stimulated by IL-1 during infection in mice, resulting in reduced CFU in the lung four w.p.i (86). During TB progression in susceptible mice, increased serum levels of leukotriene B4 (LTB4) and PGE2, as well as decreased levels of lipoxin A4 (LXA4) were seen in the first 30 d.p.i. LTB4 increases susceptibility to Mtb. Therefore, a balanced PGE2/LTB4 response influences the severity of Mtb infection (82). The other eicosanoid-producing enzyme, 5-LO, generates LTB4 and LXA4. In mice, 5-LO is negatively associated with protection against Mtb, since its absence led to higher levels of PGE2, low bacterial counts, and rearrangement of the profile of cells recruited to the lung (favoring CD11c+, CD19+, and CD3+/CD4+ cells) after Mtb infection (105).
3.2.4 Proteins exclusively present in insects
Despite being mentioned only by Asai et al., several insect proteins were described in a discovery-mass spectrometry-based approach (Table 5) (99). Proteomic analyses in G. mellonella infected with BCG strain identified proteins like serpins (serine protease inhibitors), which play a role in innate immune responses in both insects and mammals. This and other major identified proteins with potential or known homologues in mammals are described in Table 5. In insects, serpins are associated with the regulation of the TLR pathway and other unique immune processes like melanization (169). Although serpin sequences between insects and vertebrates are not similar, they are known to participate in defense responses in both animal species (170). Serpins in mice regulate the structure of hypoxic granulomas by inhibiting the activity of cysteine and serine proteases, which in turn will prevent excessive tissue damage and death of Mtb–infected macrophages (171). Serpins were elevated in response to BCG injection after 48 hours.
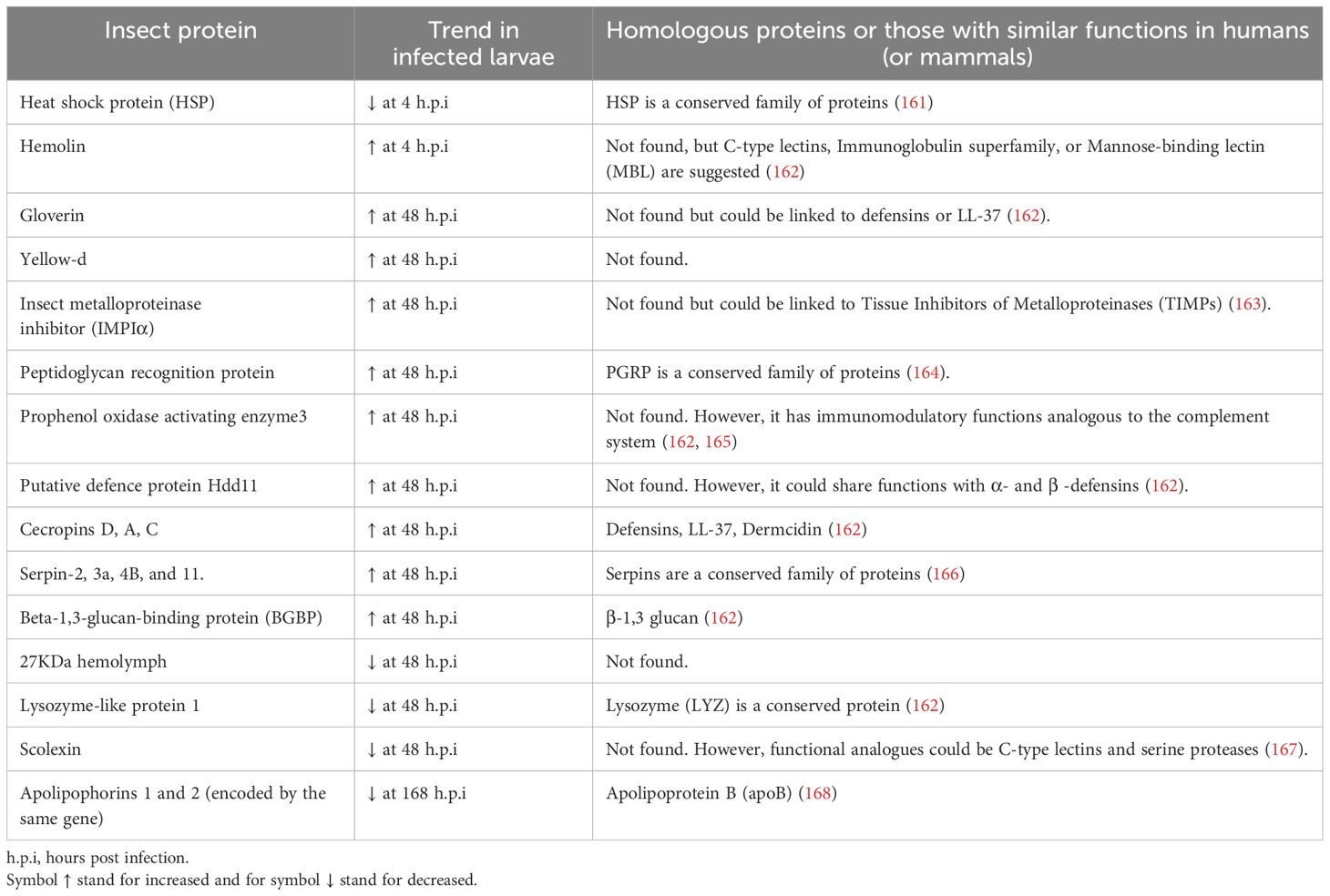
Table 5. Insect proteins found in BCG-infected Galleria mellonella hemolymph compared to uninfected larvae (99) and their suggested human homologous protein.
Additionally, the protein scolexin, involved in coagulation, was reduced at the same time point (99), a contrasting trend reported in response to different infections in other insect models (167). Scolexin has shown lectin properties in other insects, which could be interesting to evaluate in the context of MTBC infection. These lectin properties are relevant due to the known interaction between the mycobacterial mannose residues and C-type lectin receptors in mammals that facilitate bacterial adhesion to cells, uptake, and intracellular persistence (172). Some of the proteins reported after BCG infection, such as the putative defense protein Hdd11, were similarly altered in invasive aspergillosis in the G. mellonella infection model. Hdd11 shares domains with an insect protein involved in nodulation, a process similar to granuloma formation in mammals (173). Interestingly, a similar reduction was observed for the 27 kDa hemolymph protein and Lysozyme–like protein 1 after BCG and Aspergillus fumigatus infection in this insect. However, the changes were 24 hours earlier in the fungal infection (173).
3.2.5 Other relevant molecules
3.2.5.1 Metabolites
This review explores the role of various metabolites that influence the early immune response to MTBC infection. Vitamin B5 has shown promise by reducing bacterial load, promoting macrophage maturation, and increasing pro-inflammatory cytokine levels (TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-17) in mice as early as one-week postinfection (83). In contrast, vitamin B6 did not appear to affect the innate immune response in mice (149), and iron supplementation did not significantly alter bacterial burden or disease progression in rabbits (74). Additionally, S1-P induced M1 macrophage polarization, iNOS expression in the lungs and protection against infection (84). This review summarizes other factors influencing M1 and M2 macrophage polarization, shown in Figure 4. Recent findings have demonstrated that the classification into M1 and M2 macrophages is rather simplistic in explaining the events happening during infection in vivo; however, it is still helpful to describe an inflammatory or anti-inflammatory profile (174).
Another metabolite examined is 5-OP-RU ((5-(2-oxopropylideneamino)-6-D-ribitylaminouracil), an intermediate in bacterial riboflavin biosynthesis, which has demonstrated contrasting effects in vitro and in vivo. In vitro, 5-OP-RU activates MAIT cells, but in vivo, it requires co-stimulation with the TLR2/6 agonist Pam2Cys to promote pulmonary MAIT cell expansion in mice (89). In NHP infected with Mtb, treatment with 5-OP-RU activated MAIT cells, but did not expand them, nor did it help control the infection. In some cases, animals treated with 5-OP-RU developed acute respiratory symptoms, prompting the authors to reconsider its therapeutic potential (175). Effects of metabolites (including eicosanoids) in innate immunity should be evaluated as a sole factor, but also in combination with others (metabolites and proteins), due to the reactive nature of these molecules, their half-life and their co-stimulatory and antagonistic effect observed with other molecules. For example, the co-stimulatory activity described between 5-OP-RU and Pam2Cys (89) and the antagonistic effect observed for PGE2 and LTB4 (82). Moreover, while 5-OP-RU showed minimal impact on the intestinal microbiota in NHPs (175), its effects on the respiratory tract microbiota remain an area for further investigation.
3.2.5.2 Drugs as potential modulators of innate responses
We found several drug treatments with the potential for modulating the innate immune response and inhibiting Mtb or M. bovis growth, all of them evaluated in the mouse model. Biapenem and tubastatin A activated DCs and macrophages, reducing Mtb growth and suggesting new therapeutic avenues that stimulate the innate immune response (75, 176). Additionally, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin and ibuprofen, particularly when administered in later infection stages, reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines, alleviated lung pathology, and decreased bacterial load (80, 82).
Hussain et al. also reported that nilotinib induced both parkin and LC3-II proteins in the lung of M. bovis infected animals at 63 d.p.i. In a natural infection, M. bovis leads to the overexpression of the Abelson tyrosine kinase (Abl), that inhibits parkin, which is crucial to promote ubiquitin accumulation around the bacilli for its elimination (92). Nilotinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that promotes parking activity by inhibiting Abl (177). A protective role of parkin was also described in the KO mouse model (Table 1). The LC3-II increased after Nilotinib treatment also suggests the induction of autophagy, an antibacterial process described in section 3.2.4 (145). Targeting these pathways with Nilotinib resulted in reduced pathology, bacterial counts in lung and spleen, and higher survival of M. bovis-infected animals, highlighting its potential therapeutic benefits (92, 178).
Pharmacological inhibition of COX-2, administering Celecoxib shortly before and daily after infection, significantly reduced bacterial load in the lungs of infected mice (105). These findings highlight the potential of various pharmacological approaches to combat MTBC and possibly other non-tuberculous mycobacteria, warranting further evaluation in clinical settings.
Pretreatment with anti-TB drugs like INH and pyrazinamide (but not rifampicin) disrupted the mouse microbiota, leading to an increase in the Firmicutes phylum and reduced MHC-II expression in AM at five d.p.i, which worsened lung and extrapulmonary pathology (100). Additionally, pretreatment with a broad-spectrum antibiotic cocktail exacerbated this effect, decreasing MHC-II and CD86 expression in lung myeloid dendritic cells and likely impairing antigen presentation. Disruption of gut microbiota also resulted in higher levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β, IL-12) and lower levels of IL-10, further hindering the antibacterial efficacy of the subsequent INH treatment and leading to higher bacterial loads and more severe lung pathology compared to control mice (76).
4 Conclusions
Our review highlights a wide range of innate immune pathways activated during MTBC infections, specifically those caused by Mtb and M. bovis. Many of these pathways are highly conserved across mammals, and some, such as phagocytosis, oxidative stress responses, and antimicrobial peptide production, are also found in insects. Larvae of G. mellonella was proposed as a cost-effective and ethical model to study MTBC-host interactions relevant to human disease. The lack of adaptive immunity in insects (and other invertebrates), may offer valuable insights into “pure” innate immune responses. On the other hand, mice, though less susceptible to MTBC infections, are commonly used to study innate immune responses. The use of more susceptible strains and KO mouse mutants has led to discoveries of key immune mechanisms, such as trained immunity, the impact of metabolic co-morbidities (diabetes), and the early protection induced by specific soluble mediators (such as Cish, Parkin, Atg5, transcription factors like Bhlhe40, among others), eosinophils and receptors (CLECSF8).
Interestingly, the study of innate responses to MTBC also depends on the bacterial strain. For example, early protective factors against hypervirulent strains, like the Beijing strain, include IL-17 while a detrimental role was reported for the P2X7R receptor. Strains like HN878 lead to higher early recruitment of macrophages and PMN in rabbits, contributing to the formation of cavitary lesions.
The complexity of TB as a chronic disease makes it challenging to track time-dependent innate responses, especially as adaptive immune responses emerge after seven d.p.i. We must emphasize that these late “sustained” innate mediators were mainly evaluated after BCG vaccination and in the context of trained immunity. Articles explicitly describing trained immunity in mice and calves highlight the role of airway macrophages (IM and MdM) and neutrophils and the independence of NOD1 and 2 receptors and NK. The protective effect of many of the “sustained” innate responses driven by BCG vaccination in mammals and insects should be evaluated in the context of a later in vivo infection, in addition to ex-vivo experiments. Epigenetic changes associated with these memory-innate responses should be confirmed in vivo in different cell types using high-resolution methods to explore temporospatial histone, DNA, and RNA modifications (179).
One of the earliest innate responses observed occurs within 30 minutes of MTBC infection and involves neutrophils. Neutrophil activation emerged as one of the most frequently studied pathways, though it was often linked to excessive inflammation and disease severity. Interestingly, neutrophils were also found to have a protective role in early infection in BCG vaccinated mice. A key factor in this response was prg2 (Table 2), which is also involved in the eosinophil response. The protective role of eosinophils was further evaluated in mice and NHP.
Finally, recent research has expanded our understanding of the gut microbiota’s role in impairing innate immune responses towards MTBC and how the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics (pre-infection) can modulate these responses by altering gut microbiota composition. Additionally, the identification of specific innate pathways or mediators could help us to identify early or “sustained” responses associated with disease severity or protective responses. These biomarkers could be relevant in the evaluation of disease progression or immunization efficiency. Protective responses could be dynamic, as immunization could induce different responses depending on the age at which the vaccine is administered. One limitation of this review is its exclusive focus on in vivo studies, which excludes valuable findings from in vitro or organoid models. Due to the extent of this topic and the PICO question we established for the systematic review, we could not explore some of the mechanisms behind the responses measured in greater detail. Moreover, the role of sex differences in immune responses was not addressed, which represents a critical area for future research.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
LN: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CM: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. KD: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study used internal discretionary research funds provided to Dobos laboratory.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the Colorado State University Libraries for their support during the collection of the reviewed articles.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1467016/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Bespiatykh D, Bespyatykh J, Mokrousov I, Shitikov E. A comprehensive map of mycobacterium tuberculosis complex regions of difference. mSphere. (2021) 6. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00535-21
2. Zhang H, Liu M, Fan W, Sun S, Fan X. The impact of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in the environment on one health approach. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:994745. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.994745
4. Dawson KL, Bell A, Kawakami RP, Coley K, Yates G, Collins DM. Transmission of Mycobacterium orygis (M. tuberculosis Complex Species) from a Tuberculosis Patient to a Dairy Cow in New Zealand. J Clin Microbiol. (2012) 50:3136–8. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01652-12
5. Adesokan HK, Akinseye VO, Streicher EM, Van Helden P, Warren RM, Cadmus SI. Reverse zoonotic tuberculosis transmission from an emerging Uganda I strain between pastoralists and cattle in South-Eastern Nigeria. BMC Vet Res. (2019) 15:437. doi: 10.1186/s12917-019-2185-1
6. Carpenter S, O’Neill LAJ. From periphery to center stage: 50 years of advancements in innate immunity. Cell. (2024) 187:2030–51. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.03.036
7. Sankar P, Mishra BB. Early innate cell interactions with Mycobacterium tuberculosis in protection and pathology of tuberculosis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1260859. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1260859
8. Marshall JS, Warrington R, Watson W, Kim HL. An introduction to immunology and immunopathology. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. (2018) 14:49. doi: 10.1186/s13223-018-0278-1
9. Ravesloot-Chávez MM, Van Dis E, Stanley SA. The innate immune response to mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Annu Rev Immunol. (2021) 39:611–37. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-093019-010426
10. Sia JK, Rengarajan J. Immunology of mycobacterium tuberculosis infections. Microbiol Spectr. (2019) 7. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0022-2018
11. Lowe DM, Redford PS, Wilkinson RJ, O’Garra A, Martineau AR. Neutrophils in tuberculosis: friend or foe? Trends Immunol. (2012) 33:14–25. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2011.10.003
12. Connelly AN, Huijbregts RPH, Pal HC, Kuznetsova V, Davis MD, Ong KL, et al. Optimization of methods for the accurate characterization of whole blood neutrophils. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:3667. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07455-2
13. Blanter M, Gouwy M, Struyf S. Studying neutrophil function in vitro: cell models and environmental factors. J Inflammation Res. (2021) 14:141–62. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S284941
14. Kontsevaya I, Cabibbe AM, Cirillo DM, DiNardo AR, Frahm N, Gillespie SH, et al. Update on the diagnosis of tuberculosis. Clin Microbiol Infection. (2024) 30:1115–22. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2023.07.014
15. Pai M, Behr MA, Dowdy D, Dheda K, Divangahi M, Boehme CC, et al. Tuberculosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2016) 2:16076. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.76
16. Cadena AM, Fortune SM, Flynn JL. Heterogeneity in tuberculosis. Nat Rev Immunol. (2017) 17:691–702. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.69
17. Drain PK, Bajema KL, Dowdy D, Dheda K, Naidoo K, Schumacher SG, et al. Incipient and subclinical tuberculosis: a clinical review of early stages and progression of infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. (2018) 31. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00021-18
18. Tiemersma EW, van der Werf MJ, Borgdorff MW, Williams BG, Nagelkerke NJD. Natural history of tuberculosis: duration and fatality of untreated pulmonary tuberculosis in HIV negative patients: A systematic review. PloS One. (2011) 6:e17601. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017601
19. Jalbert E, Liu C, Mave V, Lang N, Kagal A, Valvi C, et al. Comparative immune responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis in people with latent infection or sterilizing protection. iScience. (2023) 26:107425. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107425
20. Zeng G, Zhang G, Chen X. Th1 cytokines, true functional signatures for protective immunity against TB? Cell Mol Immunol. (2018) 15:206–15. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2017.113
21. Sher A, Flynn JL. Sterilizing immunity: New opportunities for rational TB vaccine design. J Exp Med. (2021) 218. doi: 10.1084/jem.20210454
22. Hooijmans CR, de Vries RBM, Ritskes-Hoitinga M, Rovers MM, Leeflang MM, IntHout J, et al. Facilitating healthcare decisions by assessing the certainty in the evidence from preclinical animal studies. PloS One. (2018) 13:e0187271. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187271
23. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
24. Divangahi M, Aaby P, Khader SA, Barreiro LB, Bekkering S, Chavakis T, et al. Trained immunity, tolerance, priming and differentiation: distinct immunological processes. Nat Immunol. (2021) 22:2–6. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-00845-6
25. Sherwood ER, Burelbach KR, McBride MA, Stothers CL, Owen AM, Hernandez A, et al. Innate immune memory and the host response to infection. J Immunol. (2022) 208:785–92. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2101058
26. Christ A, Bekkering S, Latz E, Riksen NP. Long-term activation of the innate immune system in atherosclerosis. Semin Immunol. (2016) 28:384–93. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2016.04.004
27. Aronova A, Tosato F, Naser N, Asare Y. Innate immune pathways in atherosclerosis—From signaling to long-term epigenetic reprogramming. Cells. (2023) 12:2359. doi: 10.3390/cells12192359
28. Boasso A, Shearer GM. Chronic innate immune activation as a cause of HIV-1 immunopathogenesis. Clin Immunol. (2008) 126:235–42. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2007.08.015
29. Bickett TE, McLean J, Creissen E, Izzo L, Hagan C, Izzo AJ, et al. Characterizing the BCG induced macrophage and neutrophil mechanisms for defense against mycobacterium tuberculosis. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1202. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01202
30. D’Agostino MR, Lai R, Afkhami S, Khera A, Yao Y, Vaseghi-Shanjani M, et al. Airway Macrophages Mediate Mucosal Vaccine–Induced Trained Innate Immunity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Early Stages of Infection. J Immunol. (2020) 205:2750–62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000532
31. Guerra-Maupome M, Vang DX, McGill JL. Aerosol vaccination with Bacille Calmette-Guerin induces a trained innate immune phenotype in calves. PloS One. (2019) 14. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212751
32. Steigler P, Daniels NJ, McCulloch TR, Ryder BM, Sandford SK, Kirman JR. BCG vaccination drives accumulation and effector function of innate lymphoid cells in murine lungs. Immunol Cell Biol. (2018) 96:379–89. doi: 10.1111/imcb.12007
33. Sarfas C, White AD, Sibley L, Morrison AL, Gullick J, Lawrence S, et al. Characterization of the infant immune system and the influence and immunogenicity of BCG vaccination in infant and adult rhesus macaques. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:754589. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.754589
34. Netea MG, Quintin J, van der Meer JWM. Trained immunity: A memory for innate host defense. Cell Host Microbe. (2011) 9:355–61. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2011.04.006
35. Kaufmann E, Sanz J, Dunn JL, Khan N, Mendonça LE, Pacis A, et al. BCG educates hematopoietic stem cells to generate protective innate immunity against tuberculosis. Cell. (2018) 172:176–190.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.031
36. Khan N, Downey J, Sanz J, Kaufmann E, Blankenhaus B, Pacis A, et al. M. tuberculosis reprograms hematopoietic stem cells to limit myelopoiesis and impair trained immunity. Cell. (2020) 183:752–770.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.062
37. Beltrán-Beck B, de la Fuente J, Garrido JM, Aranaz A, Sevilla I, Villar M, et al. Oral vaccination with heat inactivated Mycobacterium bovis activates the complement system to protect against tuberculosis. PloS One. (2014) 9. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098048
38. Stinear TP, Seemann T, Harrison PF, Jenkin GA, Davies JK, Johnson PDR, et al. Insights from the complete genome sequence of Mycobacterium marinum on the evolution of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Genome Res. (2008) 18:729–41. doi: 10.1101/gr.075069.107
39. de Oliveira FM, Procopio VO, Menezes G de L, da Silva RA, Kipnis A, Junqueira-Kipnis AP. Mycobacterium bovis pknG R242P mutation results in structural changes with enhanced virulence in the mouse model of infection. Microorganisms. (2022) 10. doi: 10.3390/MICROORGANISMS10040673
40. Carow B, Gao Y, Terán G, Yang XO, Dong C, Yoshimura A, et al. CISH controls bacterial burden early after infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice. Tuberculosis. (2017) 107:175–80. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2017.09.007
41. Wilson GJ, Marakalala MJ, Hoving JC, Van Laarhoven A, Drummond RA, Kerscher B, et al. The C-type lectin receptor CLECSF8/CLEC4D is a key component of anti-mycobacterial immunity. Cell Host Microbe. (2015) 17:252–9. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.01.004
42. Francisco NM, Hsu NJ, Keeton R, Randall P, Sebesho B, Allie N, et al. TNF-dependent regulation and activation of innate immune cells are essential for host protection against cerebral tuberculosis. J Neuroinflamm. (2015) 12. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0345-1
43. Pal L, Nandani R, Kumar P, Swami B, Roy G. Macrophages are the key players in promoting hyper-inflammatory response in a mouse model of TB-IRIS. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:775177. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.775177
44. Gupta S, Winglee K, Gallo R, Bishai WR. Bacterial subversion of cAMP signalling inhibits cathelicidin expression, which is required for innate resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Pathol. (2017) 242:52–61. doi: 10.1002/path.4878
45. Huynh JP, Lin CC, Kimmey JM, Jarjour NN, Schwarzkopf EA, Bradstreet TR, et al. Bhlhe40 is an essential repressor of IL-10 during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J Exp Med. (2018) 215:1823–38. doi: 10.1084/jem.20171704
46. Huang Y, Matsumura Y, Hatano S, Noguchi N, Murakami T, Iwakura Y, et al. IL-21 inhibits IL-17A-producing γδ T-cell response after infection with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin via induction of apoptosis. Innate Immun. (2016) 22:588–97. doi: 10.1177/1753425916664125
47. Amaral EP, Ribeiro SCM, Lanes VR, Almeida FM, de Andrade MRM, Bomfim CCB, et al. Pulmonary infection with hypervirulent mycobacteria reveals a crucial role for the P2X7 receptor in aggressive forms of tuberculosis. PloS Pathog. (2014) 10. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004188
48. Gupta T, Sarr D, Fantone K, Ashtiwi NM, Sakamoto K, Quinn FD, et al. Dual oxidase 1 is dispensable during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in mice. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1044703. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1044703
49. Vogelzang A, Lozza L, Reece ST, Perdomo C, Zedler U, Hahnke K, et al. Neonatal Fc receptor regulation of lung immunoglobulin and CD103+ dendritic cells confers transient susceptibility to tuberculosis. Infect Immun. (2016) 84:2914–21. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00533-16
50. Das R, Koo MS, Kim BH, Jacob ST, Subbian S, Yao J, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is a critical mediator of the innate immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2013) 110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1301128110
51. Lee J, Brehm MA, Greiner D, Shultz LD, Kornfeld H. Engrafted human cells generate adaptive immune responses to Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection in humanized mice. BMC Immunol (2013) 14:53. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-14-53
52. Bohrer AC, Castro E, Hu Z, Queiroz ATL, Tocheny CE, Assmann M, et al. Eosinophils are part of the granulocyte response in tuberculosis and promote host resistance in mice. J Exp Med. (2021) 218. doi: 10.1084/jem.20210469
53. Kimmey JM, Huynh JP, Weiss LA, Park S, Kambal A, Debnath J, et al. Unique role for ATG5 in neutrophil-mediated immunopathology during M. tuberculosis infection. Nat. (2015) 528:565–9. doi: 10.1038/nature16451
54. Moreira-Teixeira L, Stimpson PJ, Stavropoulos E, Hadebe S, Chakravarty P, Ioannou M, et al. Type I IFN exacerbates disease in tuberculosis-susceptible mice by inducing neutrophil-mediated lung inflammation and NETosis. Nat Commun. (2020) 11. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19412-6
55. Subbian S, Bandyopadhyay N, Tsenova L, O’Brien P, Khetani V, Kushner NL, et al. Early innate immunity determines outcome of Mycobacterium tuberculosis pulmonary infection in rabbits. Cell Communication Signaling. (2013) 11. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-11-60
56. Henao-Tamayo M, Obregón-Henao A, Creissen E, Shanley C, Orme I, Ordway DJ. Differential Mycobacterium bovis BCG vaccine-derived efficacy in C3Heb/FeJ and C3H/HeOuJ mice exposed to a clinical strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Clin Vaccine Immunol. (2015) 22:91–8. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00466-14
57. Williams A, Orme IM. Animal models of tuberculosis: an overview. Microbiol Spectr. (2016) 4. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.TBTB2-0004-2015
58. Li H, Li H. “Animal models of tuberculosis.,”. In: Vaccines for neglected pathogens: strategies, achievements and challenges. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2023). p. 139–70. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-24355-4_7
59. Dharmadhikari AS, Nardell EA. What animal models teach humans about tuberculosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2008) 39:503–8. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0154TR
60. Singh A, Gupta U. Animal models of tuberculosis: Lesson learnt. Indian J Med Res. (2018) 147:456. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_554_18
61. Plumlee CR, Duffy FJ, Gern BH, Delahaye JL, Cohen SB, Stoltzfus CR, et al. Ultra-low dose aerosol infection of mice with mycobacterium tuberculosis more closely models human tuberculosis. Cell Host Microbe. (2021) 29:68–82.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.10.003
62. Soldevilla P, Vilaplana C, Cardona P-J. Mouse models for mycobacterium tuberculosis pathogenesis: show and do not tell. Pathogens. (2022) 12:49. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12010049
63. Behrouzi A, Alimohammadi M, Nafari AH, Yousefi MH, Riazi Rad F, Vaziri F, et al. The role of host miRNAs on Mycobacterium tuberculosis. ExRNA. (2019) 1:40. doi: 10.1186/s41544-019-0040-y
64. Cheng Y, Schorey JS. Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced IFN-β production requires cytosolic DNA and RNA sensing pathways. J Exp Med. (2018) 215:2919–35. doi: 10.1084/jem.20180508
66. Laddy DJ, Bonavia A, Hanekom WA, Kaushal D, Williams A, Roederer M, et al. Toward tuberculosis vaccine development: recommendations for nonhuman primate study design. Infect Immun. (2018) 86. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00776-17
67. Orme IM. The mouse as a useful model of tuberculosis. Tuberculosis. (2003) 83:112–5. doi: 10.1016/S1472-9792(02)00069-0
68. Bouté M, Carreras F, Rossignol C, Doz E, Winter N, Epardaud M. The C3HeB/FeJ mouse model recapitulates the hallmark of bovine tuberculosis lung lesions following Mycobacterium bovis aerogenous infection. Vet Res. (2017) 48:73. doi: 10.1186/s13567-017-0477-7
69. Driver ER, Ryan GJ, Hoff DR, Irwin SM, Basaraba RJ, Kramnik I, et al. Evaluation of a Mouse Model of Necrotic Granuloma Formation Using C3HeB/FeJ Mice for Testing of Drugs against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (2012) 56:3181–95. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00217-12
70. Coppola M, Jurion F, van den Eeden SJF, Tima HG, Franken KLMC, Geluk A, et al. In-vivo expressed Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens recognised in three mouse strains after infection and BCG vaccination. NPJ Vaccines. (2021) 6:81. doi: 10.1038/s41541-021-00343-2
71. Alim MA, Sikder S, Sathkumara H, Kupz A, Rush CM, Govan BL, et al. Dysregulation of key cytokines may contribute to increased susceptibility of diabetic mice to Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection. Tuberculosis. (2019) 115:113–20. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2019.02.005
72. Alim MA, Kupz A, Sikder S, Rush C, Govan B, Ketheesan N. Increased susceptibility to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in a diet-induced murine model of type 2 diabetes. Microbes Infect. (2020) 22:303–11. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2020.03.004
73. Bucsan AN, Rout N, Foreman TW, Khader SA, Rengarajan J, Kaushal D. Mucosal-activated invariant T cells do not exhibit significant lung recruitment and proliferation profiles in macaques in response to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis CDC1551. Tuberculosis. (2019) 116:S11–8. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2019.04.006
74. Kolloli A, Singh P, Marcela Rodriguez G, Subbian S. Effect of iron supplementation on the outcome of non-progressive pulmonary Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J Clin Med. (2019) 8. doi: 10.3390/jcm8081155
75. Wang X, Tang X, Zhou Z, Huang Q. Histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor enhances resistance to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection through innate and adaptive immunity in mice. Pathog Dis. (2018) 76. doi: 10.1093/femspd/fty064
76. Negi S, Pahari S, Bashir H, Agrewala JN. Intestinal microbiota disruption limits the isoniazid mediated clearance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice. Eur J Immunol. (2020) 50:1976–87. doi: 10.1002/eji.202048556
77. Umemura M, Okamoto-Yoshida Y, Yahagi A, Touyama S, Nakae S, Iwakura Y, et al. Involvement of IL-17A-producing TCR γδ T cells in late protective immunity against pulmonary mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Immun Inflammation Dis. (2016) 4:401–12. doi: 10.1002/iid3.121
78. Chen Y, Xiao JN, Li Y, Xiao YJ, Xiong YQ, Liu Y, et al. Mycobacterial lipoprotein Z triggers efficient innate and adaptive immunity for protection against Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:3190. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03190
79. Ramos-Espinosa O, Hernández-Bazán S, Francisco-Cruz A, Mata-Espinosa D, Barrios-Payán J, Marquina-Castillo B, et al. Gene therapy based in antimicrobial peptides and proinflammatory cytokine prevents reactivation of experimental latent tuberculosis. Pathog Dis. (2016) 74. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftw075
80. Kroesen VM, Rodríguez-Martínez P, García E, Rosales Y, Díaz J, Martín-Céspedes M, et al. A beneficial effect of low-dose aspirin in a murine model of active tuberculosis. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:798. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00798
81. Kinsella RL, Kimmey JM, Smirnov A, Woodson R, Gaggioli MR, Chavez SM, et al. Autophagy prevents early proinflammatory responses and neutrophil recruitment during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection without affecting pathogen burden in macrophages. PloS Biol. (2023) 21:e3002159. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002159
82. Marzo E, Vilaplana C, Tapia G, Diaz J, Garcia V, Cardona P-J. Damaging role of neutrophilic infiltration in a mouse model of progressive tuberculosis. Tuberculosis. (2014) 94:55–64. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2013.09.004
83. He W, Hu S, Du X, Wen Q, Zhong X-P, Zhou X, et al. Vitamin B5 Reduces Bacterial Growth via Regulating Innate Immunity and Adaptive Immunity in Mice Infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:365. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00365
84. Nadella V, Sharma L, Kumar P, Gupta P, Gupta UD, Tripathi S, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S-1P) promotes differentiation of naive macrophages and enhances protective immunity against mycobacterium tuberculosis. Front Immunol. (2020) 10:3085. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03085
85. Singh B, Singh DK, Ganatra SR, Escobedo RA, Khader S, Schlesinger LS, et al. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Mediate T Cell Dysfunction in Nonhuman Primate TB Granulomas. mBio (2021) 12:e03189–21. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03189-21
86. Mayer-Barber KD, Andrade BB, Oland SD, Amaral EP, Barber DL, Gonzales J, et al. Host-directed therapy of tuberculosis based on interleukin-1 and type i interferon crosstalk. Nature. (2014) 511:99–103. doi: 10.1038/nature13489
87. Yadav B, Malonia SK, Majumdar SS, Gupta P, Wadhwa N, Badhwar A, et al. Constitutive expression of SMAR1 confers susceptibility to mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in a transgenic mouse model. Indian J Med Res. (2015) 142:732–41. doi: 10.4103/0971-5916.174566
88. Wang Y, Yang C, He Y, Zhan X, Xu L. Ipr1 modified BCG as a novel vaccine induces stronger immunity than BCG against tuberculosis infection in mice. Mol Med Rep. (2016) 14:1756–64. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5447
89. Vorkas CK, Levy O, Skular M, Li K, Aubé J, Glickman MS. Efficient 5-OP-RU-induced enrichment of mucosa-associated invariant T cells in the murine lung does not enhance control of aerosol mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Infect Immun. (2020) 89. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00524-20
90. Filio-Rodríguez G, Estrada-García I, Arce-Paredes P, Moreno-Altamirano MM, Islas-Trujillo S, Ponce-Regalado MD, et al. In vivo induction of neutrophil extracellular traps by Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a Guinea pig model. Innate Immun. (2017) 23:625–37. doi: 10.1177/1753425917732406
91. Abnave P, Mottola G, Gimenez G, Boucherit N, Trouplin V, Torre C, et al. Screening in planarians identifies MORN2 as a key component in LC3-associated phagocytosis and resistance to bacterial infection. Cell Host Microbe. (2014) 16:338–50. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.08.002
92. Hussain T, Zhao D, Shah SZA, Sabir N, Wang J, Liao Y, et al. Nilotinib: A tyrosine kinase inhibitor mediates resistance to intracellular mycobacterium via regulating autophagy. Cells. (2019) 8:506. doi: 10.3390/cells8050506
93. Hansen SG, Zak DE, Xu G, Ford JC, Marshall EE, Malouli D, et al. Prevention of tuberculosis in rhesus macaques by a cytomegalovirus-based vaccine. Nat Med. (2018) 24:130–43. doi: 10.1038/nm.4473
94. Kupz A, Zedler U, Stäber M, Perdomo C, Dorhoi A, Brosch R, et al. ESAT-6-dependent cytosolic pattern recognition drives noncognate tuberculosis control in vivo. J Clin Invest. (2016) 126:2109–22. doi: 10.1172/JCI84978
95. Lou J, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Qiu W. MiR-20b inhibits mycobacterium tuberculosis induced inflammation in the lung of mice through targeting NLRP3. Exp Cell Res. (2017) 358:120–8. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.06.007
96. Montoya-Rosales A, Provvedi R, Torres-Juarez F, Enciso-Moreno JA, Hernandez-Pando R, Manganelli R, et al. lysX gene is differentially expressed among Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains with different levels of virulence. Tuberculosis. (2017) 106:106–17. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2017.07.005
97. Ramos-Espinosa O, Mata-Espinosa D, Francisco-Cruz A, López-Torres MO, Hernández-Bazán S, Barrios-Payán J, et al. Immunotherapeutic effect of adenovirus encoding antimicrobial peptides in experimental pulmonary tuberculosis. J Leukoc Biol. (2021) 110:951–63. doi: 10.1002/JLB.4MA0920-627R
98. López V, Villar M, Queirós J, Vicente J, Mateos-Hernández L, Díez-Delgado I, et al. Comparative proteomics identifies host immune system proteins affected by infection with mycobacterium bovis. PloS Negl Trop Dis. (2016) 10. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004541
99. Asai M, Sheehan G, Li Y, Robertson BD, Kavanagh K, Langford PR, et al. Innate Immune Responses of Galleria mellonella to Mycobacterium bovis BCG Challenge Identified Using Proteomic and Molecular Approaches. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2021) 11:619981. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.619981
100. Khan N, Mendonca L, Dhariwal A, Fontes G, Menzies D, Xia J, et al. Intestinal dysbiosis compromises alveolar macrophage immunity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Mucosal Immunol. (2019) 12:772–83. doi: 10.1038/s41385-019-0147-3
101. Aqdas M, Maurya SK, Pahari S, Singh S, Khan N, Sethi K, et al. Immunotherapeutic role of NOD-2 and TLR-4 signaling as an adjunct to antituberculosis chemotherapy. ACS Infect Dis. (2021) 7:2999–3008. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00136
102. Gopalakrishnan A, Dietzold J, Salgame P. Vaccine-mediated immunity to experimental Mycobacterium tuberculosis is not impaired in the absence of Toll-like receptor 9. Cell Immunol. (2016) 302:11–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2015.12.009
103. Berod L, Stüve P, Swallow M, Arnold-Schrauf C, Kruse F, Gentilini MV, et al. MyD88 signalling in myeloid cells is sufficient to prevent chronic mycobacterial infection. Eur J Immunol. (2014) 44:1399–409. doi: 10.1002/eji.201344039
104. Javed S, Marsay L, Wareham A, Lewandowski KS, Williams A, Dennis MJ, et al. Temporal expression of peripheral blood leukocyte biomarkers in a Macaca fascicularis infection model of tuberculosis; comparison with human datasets and analysis with parametric/non-parametric tools for improved diagnostic biomarker identification. PloS One. (2016) 11. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154320
105. Sorgi CA, Soares EM, Rosada RS, Bitencourt CS, Zoccal KF, Pereira PAT, et al. Eicosanoid pathway on host resistance and inflammation during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection is comprised by LTB4 reduction but not PGE2 increment. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2020) 1866. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.165574
106. Choi H-G, Choi S, Back YW, Park H-S, Bae HS, Choi CH, et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv2882c Protein Induces Activation of Macrophages through TLR4 and Exhibits Vaccine Potential. PloS One. (2016) 11:e0164458. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164458
107. Donath MY, Shoelson SE. Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol. (2011) 11:98–107. doi: 10.1038/nri2925
108. Nyman TA, Lorey MB, Cypryk W, Matikainen S. Mass spectrometry-based proteomic exploration of the human immune system: focus on the inflammasome, global protein secretion, and T cells. Expert Rev Proteomics. (2017) 14:395–407. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2017.1319768
109. Bennike TB. Advances in proteomics: characterization of the innate immune system after birth and during inflammation. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1254948. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1254948
110. Spits H, Cupedo T. Innate lymphoid cells: Emerging insights in development, lineage relationships, and function. Annu Rev Immunol. (2012) 30:647–75. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-075053
111. Gideon HP, Skinner JA, Baldwin N, Flynn JL, Lin PL. Early whole blood transcriptional signatures are associated with severity of lung inflammation in cynomolgus macaques with mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J Immunol. (2016) 197:4817–28. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601138
112. Flynn JL, Gideon HP, Mattila JT, Lin PL. Immunology studies in non-human primate models of tuberculosis. Immunol Rev. (2015) 264:60–73. doi: 10.1111/imr.12258
113. Dijkman K, Vervenne RAW, Sombroek CC, Boot C, Hofman SO, van Meijgaarden KE, et al. Disparate tuberculosis disease development in macaque species is associated with innate immunity. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:2479. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02479
114. Edmans MD, Connelley TK, Jayaraman S, Vrettou C, Vordermeier M, Mak JYW, et al. Identification and phenotype of MAIT cells in cattle and their response to bacterial infections. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:627173. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.627173
115. Kleinnijenhuis J, Quintin J, Preijers F, Joosten LAB, Ifrim DC, Saeed S, et al. Bacille Calmette-Guérin induces NOD2-dependent nonspecific protection from reinfection via epigenetic reprogramming of monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2012) 109:17537–42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1202870109
116. Kleinnijenhuis J, Quintin J, Preijers F, Joosten LAB, Jacobs C, Xavier RJ, et al. BCG-induced trained immunity in NK cells: Role for non-specific protection to infection. Clin Immunol. (2014) 155:213–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2014.10.005
117. Clark S, Hall Y, Williams A. Animal models of tuberculosis: Guinea pigs. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. (2015) 5:a018572–a018572. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a018572
118. Li Y, Spiropoulos J, Cooley W, Khara JS, Gladstone CA, Asai M, et al. Galleria mellonella-a novel infection model for the mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Virulence. (2018) 9:1126–37. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2018.1491255
119. Asai M, Li Y, Spiropoulos J, Cooley W, Everest DJ, Kendall SL, et al. Galleria mellonella as an infection model for the virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. Virulence. (2022) 13:1543–57. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2119657
120. Prescott MJ, Lidster K. Improving quality of science through better animal welfare: the NC3Rs strategy. Lab Anim (NY). (2017) 46:152–6. doi: 10.1038/laban.1217
121. Kloc M, Halasa M, Kubiak JZ, Ghobrial RM. Invertebrate immunity, natural transplantation immunity, somatic and germ cell parasitism, and transposon defense. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:1072. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021072
122. Smith D FQ, Casadevall A. Fungal immunity and pathogenesis in mammals versus the invertebrate model organism. Galleria mellonella. Pathog Dis. (2021) 79. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftab013
123. Perveen N, Muhammad K, Bin MS, Zaheer T, Munawar N, Gajic B, et al. Host-pathogen interaction in arthropod vectors: Lessons from viral infections. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1061899. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1061899
124. Baxter RHG, Contet A, Krueger K. Arthropod innate immune systems and vector-borne diseases. Biochemistry. (2017) 56:907–18. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00870
125. de Jong AW, van Veldhuizen D, Groot AT, Hagen F. Standardized methods to rear high-quality Galleria mellonella larvae for the study of fungal pathogens. Entomol Exp Appl. (2022) 170:1073–80. doi: 10.1111/eea.13237
126. Senior NJ, Titball RW. Isolation and primary culture of Galleria mellonella hemocytes for infection studies. F1000Res. (2021) 9:1392. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.27504.2
127. Cho Y, Cho S. Hemocyte-hemocyte adhesion by granulocytes is associated with cellular immunity in the cricket, Gryllus bimaculatus. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:18066. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54484-5
128. Gallorini M, Marinacci B, Pellegrini B, Cataldi A, Dindo ML, Carradori S, et al. Immunophenotyping of hemocytes from infected Galleria mellonella larvae as an innovative tool for immune profiling, infection studies and drug screening. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:759. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51316-z
129. Wrońska AK, Kaczmarek A, Sobich J, Grzelak S, Boguś MI. Intracellular cytokine detection based on flow cytometry in hemocytes from Galleria mellonella larvae: A new protocol. PloS One. (2022) 17:e0274120. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274120
130. Hammoudi N, Torre C, Ghigo E, Drancourt M. Temperature affects the biology of Schmidtea mediterranea. Sci Rep. (2018) 8. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33355-5
131. Wu Y, Wu M, Ming S, Zhan X, Hu S, Li X, et al. TREM-2 promotes Th1 responses by interacting with the CD3ζ-ZAP70 complex following Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J Clin Invest. (2021) 131. doi: 10.1172/JCI137407
132. You K, Gu H, Yuan Z, Xu X. Tumor necrosis factor alpha signaling and organogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:727075. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.727075
133. Schorey JS, Schlesinger LS. Innate immune responses to tuberculosis. Microbiol Spectr. (2016) 4. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.tbtb2-0010-2016
134. He C, Luo H, Coelho A, Liu M, Li Q, Xu J, et al. NCF4 dependent intracellular reactive oxygen species regulate plasma cell formation. Redox Biol. (2022) 56:102422. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102422
135. Scheuermann L, Pei G, Domaszewska T, Zyla J, Oberbeck-Müller D, Bandermann S, et al. Platelets restrict the oxidative burst in phagocytes and facilitate primary progressive tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2020) 202:730–44. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201910-2063OC
136. Meier S, Seddon JA, Maasdorp E, Kleynhans L, du Plessis N, Loxton AG, et al. Neutrophil degranulation, NETosis and platelet degranulation pathway genes are co-induced in whole blood up to six months before tuberculosis diagnosis. PloS One. (2022) 17:e0278295. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278295
137. Kathamuthu GR, Kumar NP, Moideen K, Nair D, Banurekha VV, Sridhar R, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases are potential biomarkers of pulmonary and extra-pulmonary tuberculosis. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:419. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00419
138. Broz P, Dixit VM. Inflammasomes: mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. (2016) 16:407–20. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.58
139. Ma J, Zhao S, Gao X, Wang R, Liu J, Zhou X, et al. The Roles of Inflammasomes in Host Defense against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Pathogens. (2021) 10:120. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10020120
140. Chen S, Saeed AFUH, Liu Q, Jiang Q, Xu H, Xiao GG, et al. Macrophages in immunoregulation and therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:207. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01452-1
141. Gao J, Liang Y, Wang L. Shaping polarization of tumor-associated macrophages in cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:888713. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.888713
142. Strizova Z, Benesova I, Bartolini R, Novysedlak R, Cecrdlova E, Foley LK, et al. M1/M2 macrophages and their overlaps – myth or reality? Clin Sci. (2023) 137:1067–93. doi: 10.1042/CS20220531
143. Zheng XF, Hong YX, Feng GJ, Zhang GF, Rogers H, Lewis MAO, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced M2 to M1 macrophage transformation for IL-12p70 production is blocked by candida albicans mediated up-regulation of EBI3 expression. PloS One. (2013) 8. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063967
144. Bah A, Vergne I. Macrophage autophagy and bacterial infections. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:1483. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01483
145. Tanida I, Ueno T, Kominami E. LC3 and Autophagy. Methods Mol Biol. (2008) 445:77–88. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-157-4_4
146. Negi S, Pahari S, Bashir H, Agrewala JN. Gut microbiota regulates mincle mediated activation of lung dendritic cells to protect against mycobacterium tuberculosis. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:1142. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01142
147. Gopal R, Monin L, Slight S, Uche U, Blanchard E, A. Fallert Junecko B, et al. Unexpected Role for IL-17 in Protective Immunity against Hypervirulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis HN878 Infection. PloS Pathog. (2014) 10. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004099
148. Wang J, Ge P, Qiang L, Tian F, Zhao D, Chai Q, et al. The mycobacterial phosphatase PtpA regulates the expression of host genes and promotes cell proliferation. Nat Commun. (2017) 8. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00279-z
149. Gengenbacher M, Vogelzang A, Schuerer S, Lazar D, Kaiser P, Kaufmann SHE. Dietary pyridoxine controls efficacy of vitamin b6-auxotrophic tuberculosis vaccine bacillus calmette-Guérin ΔureC::Hly Δpdx1 in Mice. mBio. (2014) 5. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01262-14
150. Nemeth J, Olson GS, Rothchild AC, Jahn AN, Mai D, Duffy FJ, et al. Contained Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection induces concomitant and heterologous protection. PloS Pathog. (2020) 16:e1008655. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008655
151. Martinot AJ, Blass E, Yu J, Aid M, Mahrokhian SH, Cohen SB, et al. Protective efficacy of an attenuated Mtb ΔLprG vaccine in mice. PloS Pathog. (2020) 16:e1009096. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009096
152. Esparza-Gonzalez SC, Troy AR, Izzo AA. Comparative analysis of Bacillus subtilis spores and monophosphoryl lipid A as adjuvants of protein-based Mycobacterium tuberculosis-based vaccines: Partial requirement for interleukin-17A for induction of protective immunity. Clin Vaccine Immunol. (2014) 21:501–8. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00622-13
153. Hoogendijk AJ, Blok DC, Garcia Laorden MI, Kager LM, Lede IO, Rahman W, et al. Soluble and cell-associated triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 and -2 in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. J Infection. (2015) 71:706–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2015.09.002
154. Dennis EA, Norris PC. Eicosanoid storm in infection and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. (2015) 15:511–23. doi: 10.1038/nri3859
155. Divangahi M, Desjardins D, Nunes-Alves C, Remold HG, Behar SM. Eicosanoid pathways regulate adaptive immunity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nat Immunol. (2010) 11:751–8. doi: 10.1038/ni.1904
156. Kaushal D. Eicosanoids, prostaglandins, and the progression of tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. (2012) 206:1803–5. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis611
157. Morteau O. Prostaglandins and inflammation: the cyclooxygenase controversy. Inflammation. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands (2001). p. 67–81. doi: 10.1007/978-94-015-9702-9_6
158. Harizi H, Corcuff J-B, Gualde N. Arachidonic-acid-derived eicosanoids: roles in biology and immunopathology. Trends Mol Med. (2008) 14:461–9. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2008.08.005
159. Kohli P, Levy BD. Resolvins and protectins: mediating solutions to inflammation. Br J Pharmacol. (2009) 158:960–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00290.x
160. Nore KG, Jørgensen MJ, Dyrhol-Riise AM, Jenum S, Tonby K. Elevated levels of anti-inflammatory eicosanoids and monocyte heterogeneity in mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and disease. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:579849. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.579849
161. Schlesinger MJ. Heat shock proteins. J Biol Chem. (1990) 265:12111–4. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)38314-0
162. Sheehan G, Garvey A, Croke M, Kavanagh K. Innate humoral immune defences in mammals and insects: The same, with differences ? Virulence. (2018) 9:1625–39. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2018.1526531
163. Brew K, Dinakarpandian D, Nagase H. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: evolution, structure and function. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Protein Structure Mol Enzymology. (2000) 1477:267–83. doi: 10.1016/S0167-4838(99)00279-4
164. Kang D, Liu G, Lundström A, Gelius E, Steiner H. A peptidoglycan recognition protein in innate immunity conserved from insects to humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (1998) 95:10078–82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.17.10078
165. Cerenius L, Söderhäll K. Immune properties of invertebrate phenoloxidases. Dev Comp Immunol. (2021) 122:104098. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2021.104098
166. Irving JA. Phylogeny of the serpin superfamily: implications of patterns of amino acid conservation for structure and function. Genome Res. (2000) 10:1845–64. doi: 10.1101/gr.GR-1478R
167. Finnerty CM, Granados RR, Karplus PA. The insect immune protein scolexin is a novel serine proteinase homolog. Protein Sci. (1999) 8:242–8. doi: 10.1110/ps.8.1.242
168. Zhao Y, Liu W, Zhao X, Yu Z, Guo H, Yang Y, et al. Apolipophorin-II/I contributes to cuticular hydrocarbon transport and cuticle barrier construction in locusta migratoria. Front Physiol. (2020) 11:790. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00790
169. Spence MA, Mortimer MD, Buckle AM, Minh BQ, Jackson CJ. A comprehensive phylogenetic analysis of the serpin superfamily. Mol Biol Evol. (2021) 38:2915–29. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab081
170. Meekins DA, Kanost MR, Michel K. Serpins in arthropod biology. Semin Cell Dev Biol. (2017) 62:105–19. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.09.001
171. Reece ST, Loddenkemper C, Askew DJ, Zedler U, Schommer-Leitner S, Stein M, et al. Serine protease activity contributes to control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in hypoxic lung granulomas in mice. J Clin Invest. (2010) 120:3365–76. doi: 10.1172/JCI42796
172. Kolbe K, Veleti SK, Reiling N, Lindhorst TK. Lectins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis – rarely studied proteins. Beilstein J Organic Chem. (2019) 15:1–15. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.15.1
173. Sheehan G, Clarke G, Kavanagh K. Characterisation of the cellular and proteomic response of Galleria mellonella larvae to the development of invasive aspergillosis. BMC Microbiol. (2018) 18:63. doi: 10.1186/s12866-018-1208-6
174. Veglia F, Sanseviero E, Gabrilovich DI. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the era of increasing myeloid cell diversity. Nat Rev Immunol. (2021) 21:485–98. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-00490-y
175. Sakai S, Lora NE, Kauffman KD, Dorosky DE, Oh S, Namasivayam S, et al. Functional inactivation of pulmonary MAIT cells following 5-OP-RU treatment of non-human primates. Mucosal Immunol. (2021) 14:1055–66. doi: 10.1038/s41385-021-00425-3
176. Pahuja I, Verma A, Ghoshal A, Mukhopadhyay S, Kumari A, Shaji A, et al. Biapenem, a carbapenem antibiotic, elicits mycobacteria specific immune responses and reduces the recurrence of tuberculosis. Microbiol Spectr. (2023) 11. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00858-23
177. Clark EH, Vázquez de la Torre A, Hoshikawa T, Briston T. Targeting mitophagy in Parkinson’s disease. J Biol Chem. (2021) 296:100209. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.014294
178. Manzanillo PS, Ayres JS, Watson RO, Collins AC, Souza G, Rae CS, et al. The ubiquitin ligase parkin mediates resistance to intracellular pathogens. Nature. (2013) 501:512–6. doi: 10.1038/nature12566
Keywords: early immunity, preclinical models, in vivo, cytokines, receptors, innate cells, trained immunity
Citation: Nieto Ramirez LM, Mehaffy C and Dobos KM (2025) Systematic review of innate immune responses against Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex infection in animal models. Front. Immunol. 15:1467016. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1467016
Received: 19 July 2024; Accepted: 27 December 2024;
Published: 30 January 2025.
Edited by:
Styliani Karanika, Johns Hopkins Medicine, United StatesReviewed by:
Elena Stylianou, University of Oxford, United KingdomNamrata Anand, University of Chicago Medical Center, United States
Kathirvel Maruthai, Johns Hopkins University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Nieto Ramirez, Mehaffy and Dobos. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Luisa Maria Nieto Ramirez, bHVpc2FtQGNvbG9zdGF0ZS5lZHU=; Karen Marie Dobos, a2FyZW4uZG9ib3NAY29sb3N0YXRlLmVkdQ==
 Luisa Maria Nieto Ramirez
Luisa Maria Nieto Ramirez Carolina Mehaffy
Carolina Mehaffy Karen Marie Dobos
Karen Marie Dobos