
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Immunol. , 02 July 2024
Sec. T Cell Biology
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1446350
This article is a correction to:
CD8 T cell response and its released cytokine IFN-γ are necessary for lung alveolar epithelial repair during bacterial pneumonia
 Xiaoying Zhang1
Xiaoying Zhang1 Mir Ali1
Mir Ali1 Morgan Alexandra Pantuck1
Morgan Alexandra Pantuck1 Xiaofeng Yang2
Xiaofeng Yang2 Chih-Ru Lin3
Chih-Ru Lin3 Karim Bahmed3
Karim Bahmed3 Beata Kosmider3
Beata Kosmider3 Ying Tian1*
Ying Tian1*A Corrigendum on
CD8 T cell response and its released cytokine IFN-γ are necessary for lung alveolar epithelial repair during bacterial pneumonia
By Zhang X, Ali M, Pantuck MA, Yang X, Lin C-R, Bahmed K, Kosmider B and Tian Y (2023). Front. Immunol. 14:1268078. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1268078
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 1C as published. In Figure 1, “2 dpi” and “7 dpi” were intended to depict separate cells. However, an overlapping region was mistakenly included. The corrected version of Figure 1 and its caption appear below.
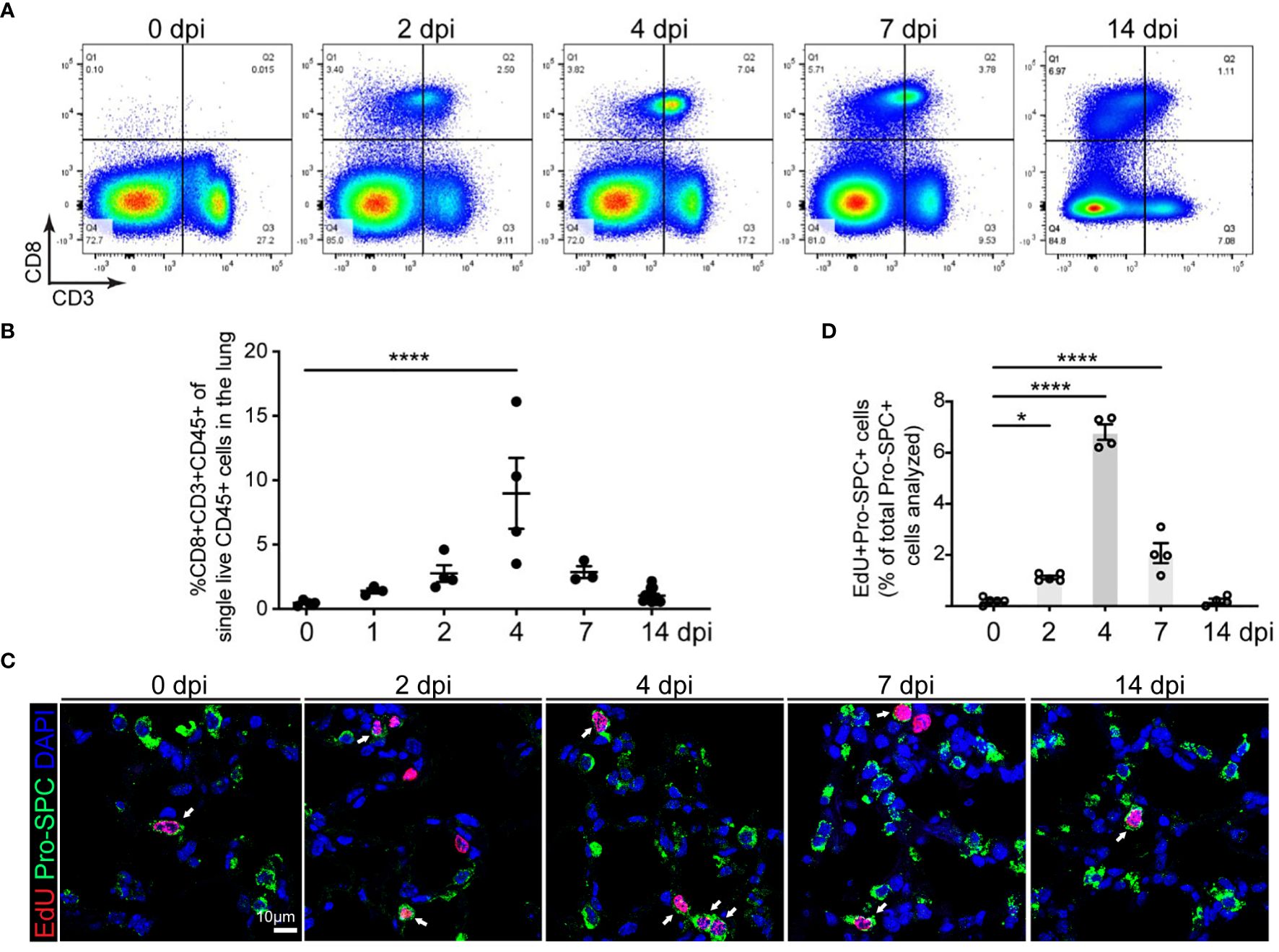
Figure 1 Correlation of CD8 T cell accumulation in the lung and AT2 cell proliferation in SpT4-infected mice. Lung tissues were collected at 0, 1, 2, 4, 7 and 14 days post SpT4 infection (dpi). (A) Flow cytometry analysis on dissociated lung cells at 0, 2, 4, 7 and 14 dpi. (B) Quantification of flow cytometry data showing the percentage of CD8+CD3+CD45+ cells of total live CD45+ cells in the lung at indicated time points. (C) Confocal images of lung sections at 0, 2, 4, 7, and 14 dpi. AT2 cells in DNA synthesis-phase were detected using Click-iT EdU Alexa Fluor (red) and co-immunostaining with antibody against Pro-SPC (green) to detect AT2 cells. Cell nuclear was stained with DAPI (blue). Arrows point to regions double positive for EdU and Pro- SPC. Scale bar: 10 μm. (D) Quantification of EdU+Pro-SPC+ cells as percentage of total Pro- SPC+ cells analyzed (≥10 randomly selected fields per mouse). (B, D) 3-8 mice per time point. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. P values were calculated using one-way ANOVA. * P < 0.05; **** P < 0.0001.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: CD8 T-cell, IFN-γ, alveolar epithelial cells, repair, acute lung injury
Citation: Zhang X, Ali M, Pantuck MA, Yang X, Lin C-R, Bahmed K, Kosmider B and Tian Y (2024) Corrigendum: CD8 T cell response and its released cytokine IFN-γ are necessary for lung alveolar epithelial repair during bacterial pneumonia. Front. Immunol. 15:1446350. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1446350
Received: 09 June 2024; Accepted: 24 June 2024;
Published: 02 July 2024.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Narendra Prasad Singh, University of South Carolina, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Zhang, Ali, Pantuck, Yang, Lin, Bahmed, Kosmider and Tian. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ying Tian, eWluZy50aWFuQHRlbXBsZS5lZHU=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.