Identification of m6A modification patterns and development of m6A–hypoxia prognostic signature to characterize tumor microenvironment in triple-negative breast cancer
- 1Department of Head and Neck Oncology and Department of Radiation Oncology, Cancer Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 2Department of Breast Oncology, Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Translational Research (Ministry of Education), Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, China
By Shen X, Zhong J, He J, Han J and Chen N (2022). Front. Immunol. 13:978092. doi: .10.3389/fimmu.2022.978092
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 9F as published. After checking the original paper, the images of Figure 9F were mistakenly included. The corrected Figure 9 and its caption Figure 9 Nomogram and detection of MHPS gene expression. appear below.
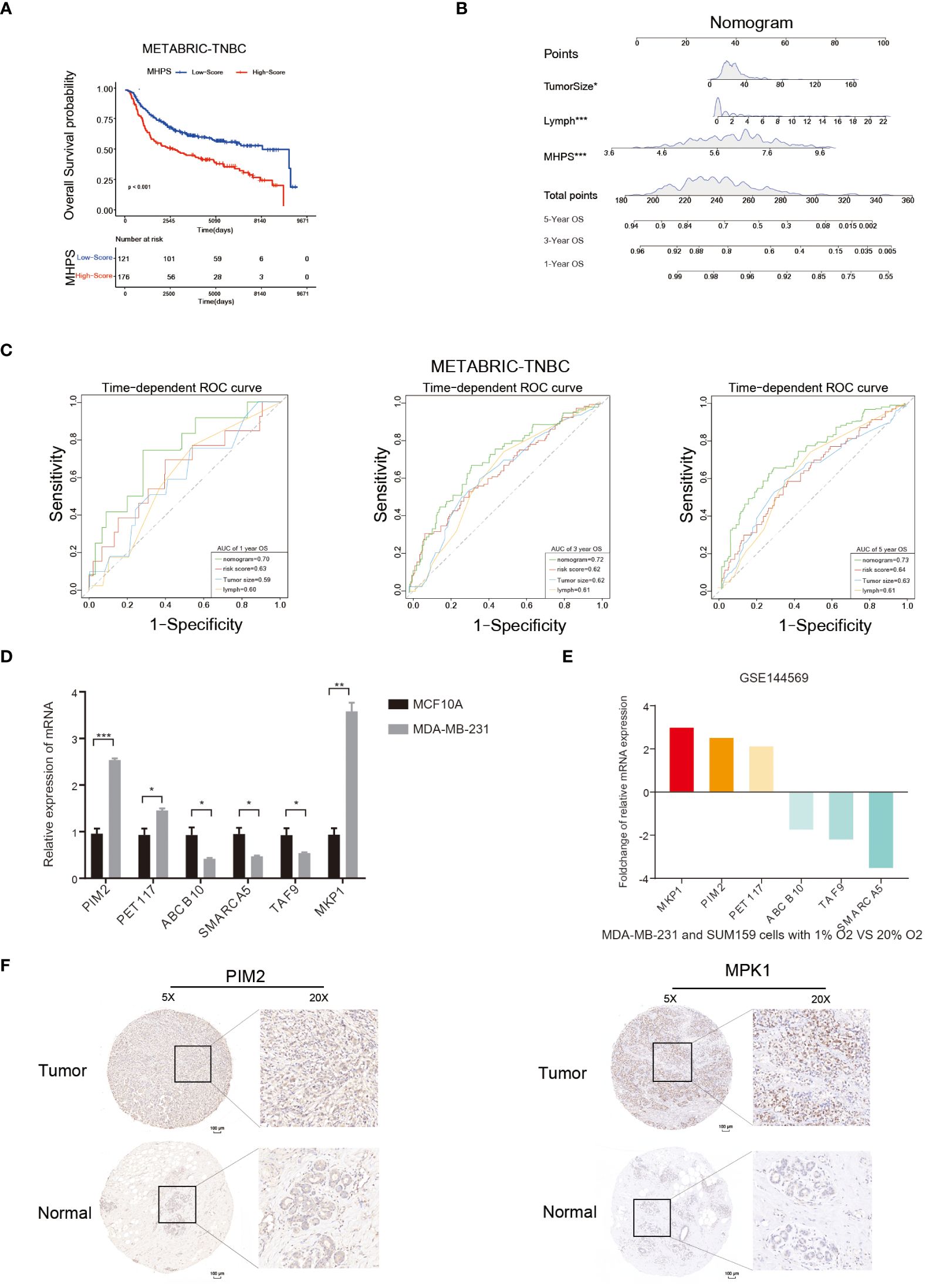
Figure 9 Nomogram and detection of MHPS gene expression. (A) Kaplan-Meier analysis of patients with high or low MHPS risk socre in METABRIC-TNBC cohort. (B) Construction of nomogram scoring system to predict patient survival at 1-, 3- and 5- years. Each clinical factor in the nomogram system corresponds to a score, and all scores are summed to obtain a total point, which can predict the survival rate of patients at 1-, 3- and 5- years. (C) Time-dependent ROC for the nomogram, MHPS, tumor size, lymph node in the METABRIC cohort (for predicting 1, 3, and 5-years OS). (D) Comparison of mRNA expression of hub genes in normal breast and TNBC cell lines. (E) Different expression of hub genes in normoxia and hypoxia cultured TNBC cells based on GSE144569 dataset. (F) IHC staining to detect protein expression of PIM2 and MKP1 in normal and tumor tissues. Scale bar:100μm.(*P< 0.05,**P< 0.01, and ***P< 0.001). ns, not significant.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: Triple-negative breast cancer, m6A RNA methylation, m6A-hypoxia signature, tumor microenvironment, immune cell infiltration
Citation: Shen X, Zhong J, He J, Han J and Chen N (2024) Corrigendum: Identification of m6A modification patterns and development of m6A–hypoxia prognostic signature to characterize tumor microenvironment in triple-negative breast cancer. Front. Immunol. 15:1441843. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1441843
Received: 31 May 2024; Accepted: 27 June 2024;
Published: 05 July 2024.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Haitao Wang, National Cancer Institute (NIH), United StatesCopyright © 2024 Shen, Zhong, He, Han and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Nianyong Chen, bl95Y2hlbkBob3RtYWlsLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xi Shen
Xi Shen Jianxin Zhong
Jianxin Zhong Jinlan He1
Jinlan He1 Nianyong Chen
Nianyong Chen