Treatment of Surgical Brain Injury by Immune Tolerance Induced by Peripheral Intravenous Injection of Biotargeting Nanoparticles Loaded With Brain Antigens
- 1Graduate School of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China
- 2Tianjin Key Laboratory of Cerebral Vascular and Neurodegenerative Diseases, Tianjin, China
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Tianjin Huanhu Hospital, Tianjin, China
- 4Tianjin Key Laboratory on Technologies Enabling Development of Clinical Therapeutics and Diagnostics (Theranostics), Research Center of Basic Medical Science, School of Pharmacy, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China
by Tian Z, Xu L, Chen Q, Feng R, Lu H, Tan H, Kang J, Wang Y and Yan H (2019) Front. Immunol. 10:743. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00743
In the published article, there was an error in Figures 4 and 5 as published. In Figure 4D, two images were placed in opposite positions. In Figure 5B, we provided a more appropriate picture. The corrected Figures 4 and 5 and its caption appear below.
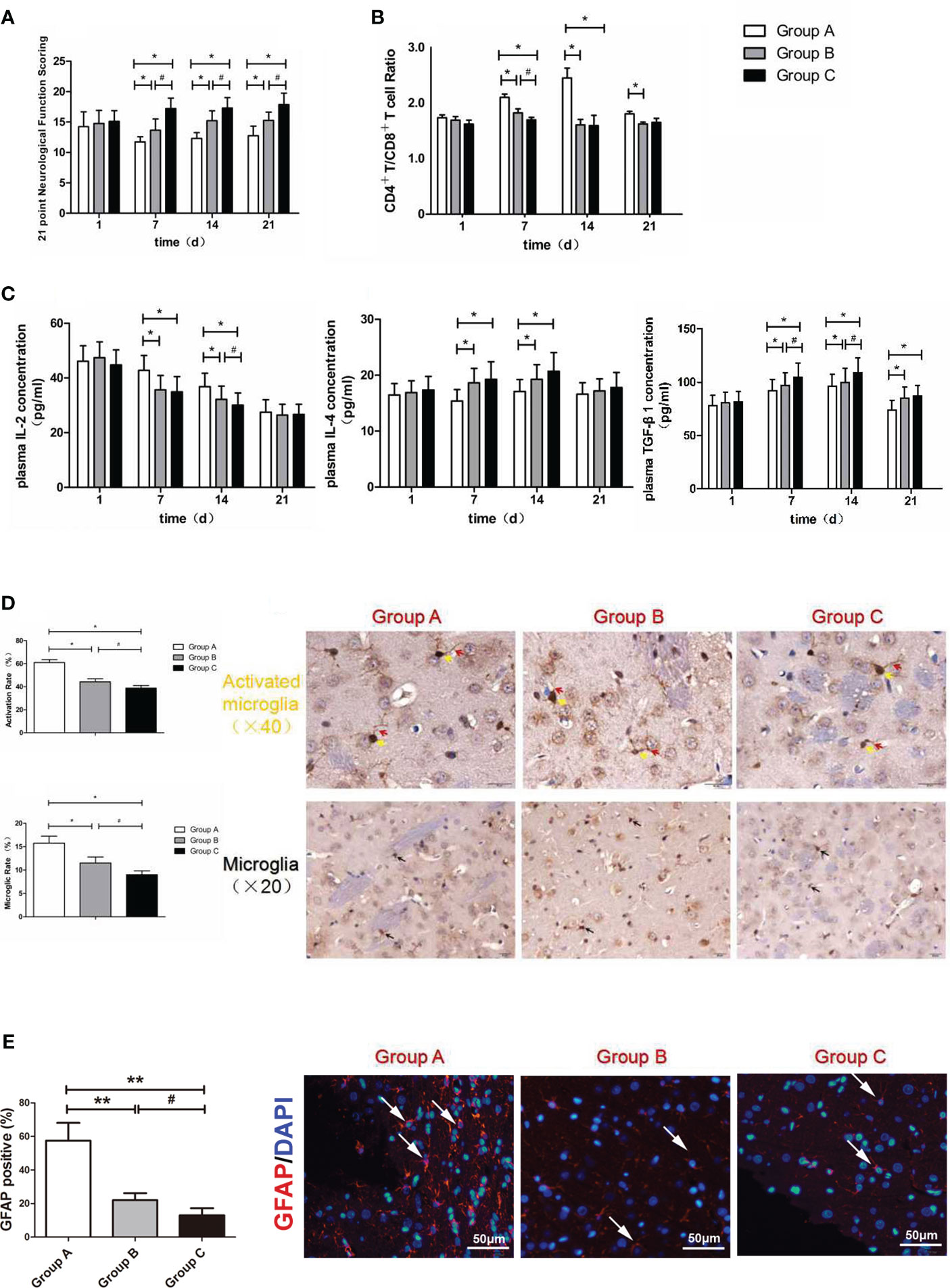
Figure 4 (A) Neurological function scoring histogram. (B) Histogram of peripheral blood CD4+T/CD8+T cell ratios. (C) Histogram of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-2, IL-4 and TGF-β1.*compared with Group A, P < 0.05; #compared with Group B, P < 0.05. (D) Iba-1 expression scoring of microglial cells measured at 21 d after SBI. *compared with Group A, P < 0.05; #compared with Group B, P < 0.05. The brown-positive cells are activated microglial cells, the yellow arrows indicate the somata of the activated microglia, and the red arrows indicate the processes of the activated microglia (x40). The black arrows indicate positive results (the brown cells) (x20). The scale bars are 20μm. (E) GFAP expression scoring of astrocytes measured at 21 d after SBI. *compared with Group A, P < 0.05, **compared with Group A, P < 0.01; #compared with Group B, P < 0.05. The scale bars are 50μm.
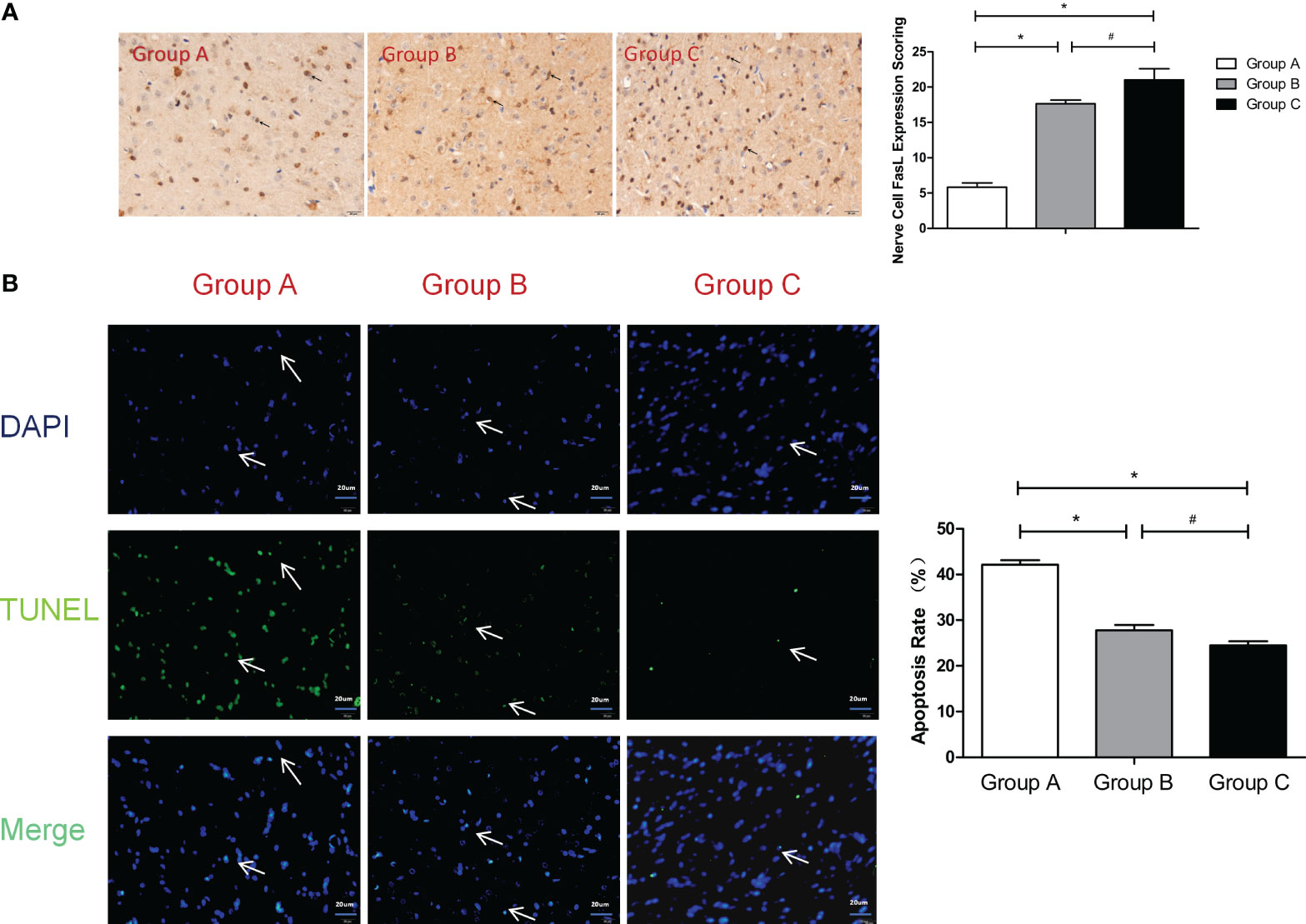
Figure 5 (A) FasL expression scoring of nerve cells measured at 21 d after SBI. *compared with Group A, P < 0.05; #compared with Group B, P < 0.05. The black arrows indicate positive results (the brown cells). (B) TUNEL assay of the nerve cells. *compared with Group A, P < 0.05; # compared with Group B, P < 0.05. DAPI (blue) was used to indicate the nuclei (arrows), and TUNEL (green) was used to indicate the apoptotic signals (arrows). The merge indicates the apoptotic cells (arrows). The scale bars are 20 μm.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: PBAE/PLGA nanoparticles, biotargeting nanoparticles, myelin basic protein, immune tolerance, surgical brain injury
Citation: Tian Z, Xu L, Chen Q, Feng R, Lu H, Tan H, Kang J, Wang Y and Yan H (2023) Corrigendum: Treatment of surgical brain injury by immune tolerance induced by peripheral intravenous injection of biotargeting nanoparticles loaded with brain antigens. Front. Immunol. 14:1335541. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1335541
Received: 09 November 2023; Accepted: 27 November 2023;
Published: 08 December 2023.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Ulises Gomez-Pinedo, Health Research Institute of Hospital Clínico San Carlos, SpainCopyright © 2023 Tian, Xu, Chen, Feng, Lu, Tan, Kang, Wang and Yan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hua Yan, eWFuaHVhMjAwNDIwMDdAc2luYS5jb20=; Yinsong Wang, d2FuZ3lpbnNvbmdAdG11LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Zhen Tian
Zhen Tian Lixia Xu2†
Lixia Xu2† Ruoyang Feng
Ruoyang Feng Hua Yan
Hua Yan