
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Immunol. , 04 October 2023
Sec. Molecular Innate Immunity
Volume 14 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1259246
This article is part of the Research Topic Mesenchymal and Immune cell Crosstalk in Fibrotic Diseases View all 6 articles
 Rajani Kandhi1
Rajani Kandhi1 Mehdi Yeganeh1
Mehdi Yeganeh1 Akihiko Yoshimura2
Akihiko Yoshimura2 Alfredo Menendez3
Alfredo Menendez3 Sheela Ramanathan1
Sheela Ramanathan1 Subburaj Ilangumaran1*†
Subburaj Ilangumaran1*†Introduction: Hepatic stellate cells (HSC) become activated, differentiate to myofibroblasts and produce extracellular fibrillar matrix during liver fibrosis. The hepatic fibrogenic response is orchestrated by reciprocal interactions between HSCs and macrophages and their secreted products. SOCS1 can regulate several cytokines and growth factors implicated in liver fibrosis. Here we investigated the role of SOCS1 in regulating HSC activation.
Methods: Mice lacking SOCS1 in HSCs (Socs1ΔHSC) were generated by crossing Socs1fl/fl and LratCre mice. Liver fibrosis was induced by carbon tetrachloride and evaluated by Sirius red staining, hydroxyproline content and immunostaining of myofibroblasts. Gene expression of pro-fibrogenic factors, cytokines, growth factors and chemokines were quantified by RT-qPCR. The phenotype and the numbers of intrahepatic leukocyte subsets were studied by flow cytometry. The impact of fibrosis on the development of diethyl nitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma was evaluated.
Results: Socs1ΔHSC mice developed more severe liver fibrosis than control Socs1fl/fl mice that was characterized by increased collagen deposition and myofibroblast differentiation. Socs1ΔHSC mice showed a significant increase in the expression of smooth muscle actin, collagens, matrix metalloproteases, cytokines, growth factors and chemokines in the liver following fibrosis induction. The fibrotic livers of Socs1ΔHSC mice displayed heightened inflammatory cell infiltration with increased proportion and numbers of Ly6ChiCCR2+ pro-inflammatory macrophages. This macrophage population contained elevated numbers of CCR2+CX3CR1+ cells, suggesting impaired transition towards restorative macrophages. Fibrosis induction following exposure to diethyl nitrosamine resulted in more numerous and larger liver tumor nodules in Socs1ΔHSC mice than in Socs1fl/fl mice.
Discussion: Our findings indicate that (i) SOCS1 expression in HSCs is a critical to control liver fibrosis and development of hepatocaellular carcinoma, and (ii) attenuation of HSC activation by SOCS1 regulates pro-inflammatory macrophage recruitment and differentiation during liver fibrosis.
Liver fibrosis is a leading cause of global morbidity and mortality (1). Liver fibrosis also promotes the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a major cause of cancer related mortality (2, 3). Hepatocyte damage caused by viral pathogens, toxic chemicals and metabolites and metabolic overload induce an inflammatory response in the liver to contain and repair the damage (4–6). Mediators released by stressed and dying hepatocytes and cellular debris activate hepatic stellate cells (HSC) and Kupffer cells to initiate an inflammatory response. Monocyte-derived macrophages and other recruited immune cells dynamically participate in liver inflammation and tissue repair (7, 8). The tissue repair process requires production of extracellular matrix (ECM) components such as collagens by myofibroblasts, which arise mainly from HSCs, to aid hepatocyte proliferation and tissue regeneration. However, the hepatic fibrogenic response can become exaggerated with persistent hepatocyte damage, resulting in chronic inflammation, myofibroblast proliferation, excess ECM production and replacement of the liver parenchyma with fibrous connective tissue. Even though liver fibrosis is reversible at early stages, progressive liver fibrosis can lead to liver cirrhosis and loss of vital hepatic functions. HCC predominantly arises in cirrhotic livers, as compensatory hepatocyte proliferation within the prevailing inflammatory milieu facilitates acquisition of genetic lesions and neoplastic transformation (9, 10). Given the clinical significance of liver fibrosis and HCC, intense efforts are being made to halt the progression of liver fibrosis towards cirrhosis and HCC through greater understanding of the cellular and molecular mediators and the underlying mechanisms (11–14). Various animal models of experimental liver fibrosis and HCC induction have made immense contributions to this endeavor (15–17).
HSCs are central players in liver fibrosis development and progression, first as a sensor of mediators released by damaged hepatocytes and activated macrophages, and second as the main source of matrix-producing myofibroblasts (14). HSCs are situated in the space of Disse in close contact with hepatocytes on one side and endothelial cells and the associated Kupffer cells on the sinusoidal side (18). In normal livers, HSCs are maintained in a non-proliferative quiescent state and function as the principal cell type for storing retinyl esters as cytoplasmic lipid droplets. Upon activation, HSCs lose these vitamin A droplets and transdifferentiate to contractile myofibroblasts that proliferate, express fibrogenic genes and deposit ECM proteins. The activation state of HSCs is perpetuated by several chemokines, cytokines, growth factors and other soluble mediators produced by stressed hepatocytes, biliary epithelial cells, Kupffer cells, recruited proinflammatory macrophages, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and platelets, whereas IFNγ produced by natural killer (NK) and NKT cells inhibits HSC activation (14, 19). Upon cessation of the inflammatory stimuli, pro-resolution macrophages play a crucial role in reversing the fibrotic changes by inhibiting HSC activation and by producing enzymes that clear the fibrillar matrix. Fibrosis resolution also involves clearance of activated HSCs through cellular senescence and apoptosis. Targeting the cytokines, chemokines and growth factors that promote HSC activation is a promising strategy for therapeutic intervention of liver fibrosis (12, 20).
Cytokines and growth factors that activate HSCs are mainly regulated by mechanisms that control their signaling (21). Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1) is an indispensable regulator of IFNγ signaling and can also inhibit signaling by many other cytokines and growth factors (22, 23). SOCS1 is also critical to control the production of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines such as IL-6, TNFα and MCP-1/CCL2 by activated macrophages (24). Low SOCS1 expression correlates with increased fibrosis in human patients with chronic liver disease, and Socs1 haplo-insufficient mice display increased susceptibility to fibrosis induction by dimethynitrosamine (25). We have shown that whole body SOCS1-deficient mice in an IFNγ-deficient background are highly susceptible to liver fibrosis induction following carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced necro-inflammatory chemical injury (26). We have also shown that selective ablation of SOCS1 in myeloid cells results in heightened sensitivity to liver fibrosis, indicating a key role of SOCS1 in regulating cytokine responses in macrophages during hepatic fibrogenic response (27). As macrophages release many cytokines and growth factors that directly impact HSCs during liver fibrosis (8, 14), we ablated the Socs1 gene selectively in HSCs using the Cre recombinase expressed under the promoter of lecithin retinol acyltransferase (LRAT) involved in retinol storage in HSCs (28, 29). In the current study, we show that HSC-specific SOCS1 deletion worsens liver fibrosis via enhancing HSC activation and by promoting the accumulation of proinflammatory macrophages, which suggest that SOCS1 expression in HSCs is crucial to control the reciprocal crosstalk between activated HSCs and macrophages.
Socs1fl/fl mice (30) were backcrossed to C57BL/6 mice obtained from Charles River Laboratories for more than ten generations. LratCre mice were obtained from Dr. C. Österreicher (University of Vienna) (29) and rederived by cesarian section into the specific pathogen-free facility in our animal colony. R26ZsGreen reporter mice (Jax mice: 007906; B6. Cg-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm6(CAG-ZsGreen1) Hze/J; also known as Ai6 mouse) (31) were obtained from the Jackson Laboratory. The R26ZsGreen reporter mouse harbors a targeted mutation at the Rosa 26 locus (Gt (ROSA)26S) with a loxP-flanked STOP cassette, which prevents the transcription of a CAG promoter-driven enhanced green fluorescent protein ZsGreen1. LratCre mice were bred with the R26ZsGreen reporter to verify LratCre-induced ZsGreen expression in HSCs. Socs1fl/fl mice were bred with LratCre mice to generate Socs1fl/flLratCre mice lacking SOCS1 expression in HSCs (Socs1ΔHSC). Mice were housed in ventilated cages with 12 hours day/night cycle and fed with normal chow ad libitum. All experiments on mice were carried out during daytime with the approval of the Université de Sherbrooke Ethics Committee for Animal Care and Use (Protocol ID: 2018-2083).
To induce liver fibrosis, carbon tetrachloride (CCl4; Sigma-Aldrich, Oakville, ON) diluted at 1:3 ratio in corn oil was administered via intra-peritoneal route (0.5 μL/g body weight) in 8-10-week-old mice twice a week for five weeks (32). Only male mice were used in this study due to the protective effect of estrogens on inflammatory cytokine production in female mice (33–35). Three days after the last injection, mice were euthanized, and serum and liver tissues were collected. Liver tissues were processed for histology, protein and mRNA expression and flow cytometry analyses of intrahepatic leukocytes, as detailed below.
Serum alanine transferase (ALT) levels were measured using a kinetic assay kit from Pointe Scientific Inc. (Brussels, Belgium) following manufacturer’s instructions. Hydroxyproline content in liver tissue homogenates was measured as described previously (26).
Pieces of liver tissues were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde overnight and stored in 70% ethanol until they were processed for paraffin embedding following standard methods. Sections of formalin-fixed paraffin embedded liver tissues (5 µm) were deparaffinized, rehydrated, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) or Sirius red as previously described (26). Digital images of stained sections were acquired using a Nanozoomer Digital Pathology (NDP) slide scanner and analyzed using the NDP.view2 software (Hamamatsu Photonics, Japan). Quantification of Sirius red staining areas was done using the Image J software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA) from twenty randomly selected fields from three to five mice in each group.
Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of liver sections for alpha smooth muscle actin (αSMA) was done as previously described to detect myofibroblasts (26) (Supplementary Table S1). Macrophages were detected by immunofluorescence (IF) staining. Deparaffinized tissue sections were incubated overnight with CD68 antibody (Supplementary Table S1) followed by a AlexaFluor-488-conjugated secondary antibody (Invitrogen/ThermoFisher Scientific) for 1 h at room temperature in the dark. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342 (Thermo Fisher; Cat# 62249) for 5 min at room temperature. The stained slides were washed and mounted in Vectashield (Vector Laboratories; Cat# H-1900) antifading medium. IHC images were captured using the NDP slide scanner and IF images acquired using Axioskop 2 fluorescence microscope (Carl Zeiss Canada Ltd, Toronto, Canada). Staining intensity of αSMA and the proportion of CD68 positive cells were quantified in three randomly selected fields from three to five mice in each group using the NIH ImageJ software.
RNA extraction, cDNA preparation and gene expression analysis by RT-qPCR were carried out as described previously (26). All RT-qPCR primers (Supplementary Table S2) showed more than 90% efficiency and displayed a single melting curve. Expression levels of specific genes were normalized for the housekeeping gene Rplp0 (36B4) within each experimental group and expressed as fold induction compared to the control group.
Liver tissue lystaes were prepared from snap frozen samples using a tissue homogenizer bead mill (MM 400; Retsch, Hann, Germany) and protein concentration determined as previously described (26). Thirty μg of total protein from each sample were separated on SDS-polyacrylamide gels, blotted on to PVDF membrane and probed for the indicated proteins using the primary antibodies listed in Supplementary Table S3. HRP-conjugated mouse and rabbit secondary antibodies and enhanced chemiluminescence reagents (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Pittsburg, PA) were used to reveal the western blot bands. Images were captured using the VersaDOC 5000 imaging system (Bio-Rad).
HSCs were isolated from 12-weeks old mice by equilibrium density gradient centrifugation of liver cells released by collagenase digestion, following published methods with some modifications (36, 37). Mice were anesthetized by intraperitoneal administration of Ketamine-Xylazine mixture (Ketamine-87 mg/kg; Xylazine-13 mg/kg - in normal saline), placed on supine position, the liver was exposed and the inferior vena cava canulated as described by Mederacke et al. (37). The livers were perfused with 0.5 mM EGTA in HEPES-buffered Hank’s balanced salt solution (HHBSS: NaCl 140 mM, KCl 5.4 mM, Na2HPO4 0.34 mM, NaHCO3 4.2 mM, KH2PO4 0.44 mM; MgCl2 0.4 mM, HEPES 10 mM, D-glucose 100 mg/L) without calcium, maintained at 42°C in a water bath, for 2 min using a peristaltic pump, with the portal vein severed to flush out erythrocytes. The liver parenchyma was digested by perfusion with freshly prepared Type IV collagenase (Worthington Biochemical; Cat # LS004186; 18 mg of 325 collagen digestion units) in 50 mL of prewarmed HHBSS containing 1.5 mM CaCl2 (wash buffer). Tissue digestion was stopped when the liver became amorphous and collapsed (~7 min). The digested liver was carefully removed and aseptically transferred to a Petri dish. The liver tissue was teased apart using forceps to release cells into suspension, which was passed through 70 μm nylon filter strainer (BD Falcon) to remove tissue debris. Hepatocytes were sedimented by centrifuging the cell suspension at 50 g for 5 min at 4°C. Nonparenchymal cells were pelleted down by centrifuging the supernatant at 500 g for 10 min at 4°C. The cell pellet was resuspended in 5 mL 20% OptiPrep™ (Axis Shield; 60% stock diluted with wash buffer), transferred to a 15 mL tube, slowly overlaid with 5 mL 11.5% OptiPrep and then 2 mL wash buffer, and centrifuged at 1500 g for 17 min at 4°C without brake. An opaque layer formed at the interface between 11.5% OptiPrep and the wash buffer was carefully collected with a Pasteur pipette and the cells were washed at 500 g for 5 min at 4°C. The cells were resuspended in DMEM containing 10% FCS and counted.
For IF microscopy, HSCs were seeded on coverslips in a 12 well plate at 1 ×105 cells/well in DMEM-10% FCS and cultured with the indicated cytokines and growth factors. Control and stimulated cells on coverslips were washed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), fixed in ice-cold methanol for 5 min at room temperature, followed by washing in PBS three times each for 5 min. The coverslips were incubated in PBST (PBS with 0.2% Triton X-100) containing 5% BSA for 1 h to block non-specific Ab binding. This was followed by incubation with primary Ab diluted in PBST-1% BSA in a humidified chamber for 1 h at room temperature or overnight at 4°C. Subsequent steps were similar to those described for IF microscopy of tissue sections.
For gene expression studies, control HSCs were lysed immediately after isolation in RNAlater (ThermoFisher Scientific). For stimulation with cytokines and growth factors, primary HSCs were cultured in 35 mm Petri dishes (0.5 ×106 cells/well) and cultured in DMEM-10% FCS in the presence of IL-6 (10 ng/mL), TGFβ (5 ng/mL) or PDGFB (20 ng/mL) (all from R&D Sytems, Minniapolis, MN). After for 24 h incubation, the cells were lysed in RNAlater for gene expression analysis as previously described (26).
IHLs were isolated by a four steps protocol involving (i) controlled collagenase digestion of minced liver tissue using the GentleMACS tissue dissociator device (Miltenyi Biotech), (ii) microfiltration and sedimentation of hepatocytes and IHLs by differential centrifugation, (iii) Percoll gradient centrifugation of sedimented IHLs to remove fatty debris, and (iv) magnetic selection of hematopoietic cells using anti-CD45 antibody to clarify the resuspended Percoll-sedimented cells as detailed elsewhere (38). This IHL isolation procedure developed for fatty liver tissues is applicable to fibrotic and normal livers. The cells were resuspended in PBS containing 2% fetal bovine serum (FBS) for flow cytometry analysis.
Aliquots of IHLs were incubated in 100 μL of Fc Block diluted in PBS-2%FBS for 10 min on ice. After washing in PBS-2%FBS, the cells are incubated with a panel of fluorochrome conjugated antibodies (Supplementary Table S4) diluted in PBS-2%FBS. The cells were washed and fluorescence data were acquired using the CytoFlex flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter). The data was analyzed using the FlowJo software (BD Biosciences).
To induce HCC, 2 weeks old male mice were injected via intra peritoneal route diethylnitrosamine (DEN; Millipore-Sigma; 25 mg/Kg body weight) followed by bi-weekly injections of CCl4 (0.5 ml/Kg) starting at 8 weeks of age for 14 consecutive weeks (39). Mice were euthanized after 22 weeks and tumor development assessed by counting the number of nodules and measuring the liver/body weight ratio.
The data were compiled on an Excel spreadsheet (Microsoft 365) and Prism V9.3.1 software (GraphPad, La Jolla, CA, USA) was used to plot graphs and for statistical analysis. p values <0.05 were considered significant.
Cytokines and growth factors produced by stressed hepatocytes and activated macrophages are the key drivers of liver fibrosis and represent potential therapeutic targets (4, 12). The loss of SOCS1, a key regulator of inflammatory cytokine and growth factor signaling in the liver, promotes liver fibrosis (25, 26, 40). Primary HSCs isolated from SOCS1-deficient mice display increased proliferation in response to IL-6, PDGF, EGF, TGFα and HGF, suggesting a cell-intrinsic role of SOCS1 in regulating HSC activation (26). To directly assess the role of SOCS1 in regulating HSCs responses during liver fibrosis, we crossed Socs1fl/fl mice with LratCre deleter mice, which ablates floxed genes specifically in HSCs in the liver (28, 29). We confirmed the expression of Lrat promoter driven Cre expression in HSCs using the ROSA26-ZsGreen reporter mice (31). Cryosections of livers from LratCreROSA26-ZsGreen mice showed a ZsGreen expression pattern that is consistent with the distribution of HSCs (Supplementary Figure S1A), which was confirmed by immunostaining for the HSC marker desmin (Supplementary Figure S1B) as well as by verifying ZsGreen expression in primary HSCs (Supplementary Figure S1C-E).
Liver fibrosis was induced in Socs1ΔHSC and Socs1fl/fl control mice by intraperitoneal administration of CCl4 twice a week for 5 weeks. Sirius red staining of the liver sections of these mice showed increased collagen deposition with prominent bridging fibrosis pattern compared to limited septal fibrosis observed in Socs1fl/fl control mice (Figure 1A). Quantification of the staining area and intensity showed significantly elevated levels of collagen deposition in HSC-specific SOCS1-deficient mice livers that was confirmed by hepatic hydroxyproline content (Figure 1B, C), Masson’s trichrome staining and western blot (Supplementary Figure S2 and Figure 1D). However, the increase in serum ALT levels following CCl4 treatment was comparable between Socs1ΔHSC and Socs1fl/fl control mice (Figure 1E), suggesting that increased fibrosis in Socs1ΔHSC mice resulted from increased fibrogenic response caused by the loss of SOCS1 in HSCs rather than from increased liver damage. This was confirmed by immunohistochemical staining of αSMA in myofibroblasts, which showed intense staining and significantly increased staining area in Socs1ΔHSC mice compared to Socs1fl/fl controls (Figure 1F, G). Consistent with this data, CCl4-treated Socs1ΔHSC mice livers showed increased expression of Acta2 and Col1a1 genes and αSMA and collagen 1 protein expression (Figure 1H, D). The fibrotic livers of Socs1ΔHSC mice showed significantly elevated expression of Col3a1, the antifibrotic matrix metalloproteinase 2 (Mmp2) (41) and tissue inhibitor of MMPs 1 (Timp1) genes compared to Socs1fl/fl mice livers (Figure 1H). Moreover, expression of genes coding for proinflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IL-1β, profibrogenic TGFβ and the myofibroblast growth factor PDGFB, which were markedly induced in Socs1fl/fl mice livers, was significantly elevated in the fibrotic livers of Socs1ΔHSC mice (Figure 1I). These data indicated that SOCS1 expression in HSCs plays a crucial role in regulating hepatic fibrogenic response induced by chemical agents.
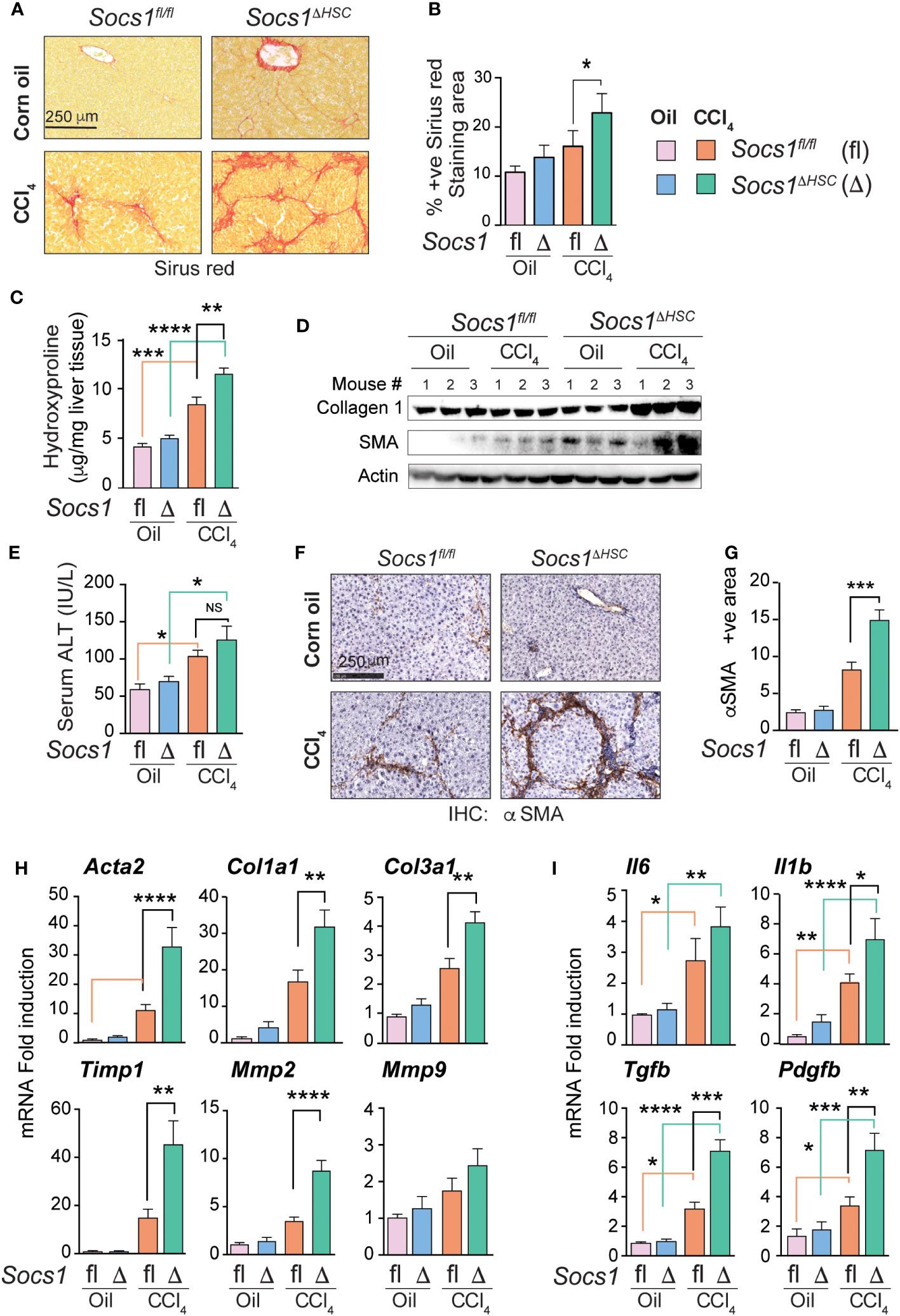
Figure 1 SOCS1 deficiency in HSCs increases the severity of liver fibrosis induced by CCl4. Eight weeks old male Socs1ΔHSC and sex matched Socs1fl/fl littermate controls were treated with CCl4 or vehicle (corn oil) twice a week for five weeks and euthanized three days later. (A) Sirius red staining for collagen deposition. Representative data from at least three mice for each group are shown. (B) Quantification of sirius red staining areas. Mean ± standard error of mean (SE) from three to six mice per group for two independent experiments. (C) Hydroxy proline content of liver tissues. Mean ± SE from five to eight mice per group from two experiments. (D) Western blot evaluation of collagen 1 and αSMA proteins in the liver tissues from three mice in each group. Beta actin was used as a loading control. (E) Serum ALT levels from four mice per group from two different experiments are shown (mean ± SE). (F) IHC staining of αSMA in representative liver sections. Representative data from at least three mice in each group are shown. (G) Quantification of αSMA staining area. Mean ± SE from three to five mice per group from two experiments. (H, I) RT-qPCR evaluation of the expression of genes associated with hepatic fibrogenic response (H), cytokines and growth factors (I). n = 6-8 mice per group from a minimum of two separate experiments. Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. ns, not significant; * p <0.05, ** p <0.01, *** p <0.001; **** p <0.0001.
As TGFβ is a key driver of ECM deposition (42, 43), we examined TGFβ signaling pathway components in the fibrotic livers of Socs1ΔHSC and Socs1fl/fl mice. Socs1ΔHSC mice displayed increased phosphorylation of SMAD2 and SMAD3 in both CCl4 and oil treated groups (Figure 2A). On the other hand, increased SMAD3 phosphorylation was observed in the livers of Socs1fl/fl mice only after CCl4 treatment, whereas SMAD2 phosphorylation level was not altered (Figure 2A). Similarly, phosphorylation of the MAP kinase ERK1/2 was prominent in both in both CCl4 and oil treated groups of Socs1ΔHSC mice but occurred only after CCl4 treatment in control mice (Figure 2A). These observations suggested increased responsiveness of SOCS1-deficient HSCs to TGFβ and growth factor signaling that promoted their fibrogenic response. To test this possibility, primary HSCs enriched from Socs1ΔHSC and Socs1fl/fl mice were exposed to inflammatory (IL-6), fibrogenic (TGFβ) and growth stimulating (PDGFB) cytokines and the induction genes that promote myofibroblast differentiation (Acta2) and matrix production (Col1a1) and remodelling (Mmp2, Timp1) was evaluated. TGFβ strongly induced Acta2, Col1a1, Mmp2 and Timp1 genes in control HSCs and the induction of all but Mmp2 were further amplified significantly by SOCS1 deficiency (Figure 2B). Whereas IL-6 caused a discernible increase in the expression of Acta2, Col1a1 and Mmp2 genes in control and SOCS1-deficient HSCs, PDGFB, the most potent growth factor for HSCs (18, 44), did not change the expression of these fibrogenic genes. Notably, SOCS1-deficient HSCs showed discernibly elevated basal expression of Acta2 and Timp1 genes (Figure 2B), suggesting production of autocrine fibrogenic mediators in SOCS1-deficient HSCs. Indeed, TGFβ stimulation upregulated Tgfb and Pdgfb genes in control HSCs that was significantly amplified by SOCS1 deficiency (Figure 2B). Immunofluorescence staining of αSMA following TGFβ stimulation showed profound increase in SOCS1-deficient HSCs compared to control HSCs (Figure 2C). These results indicated that SOCS1 is a critical to regulator of HSC activation by limiting their responsiveness to TGFβ stimulation and TGFβ-induced autocrine mediator production.
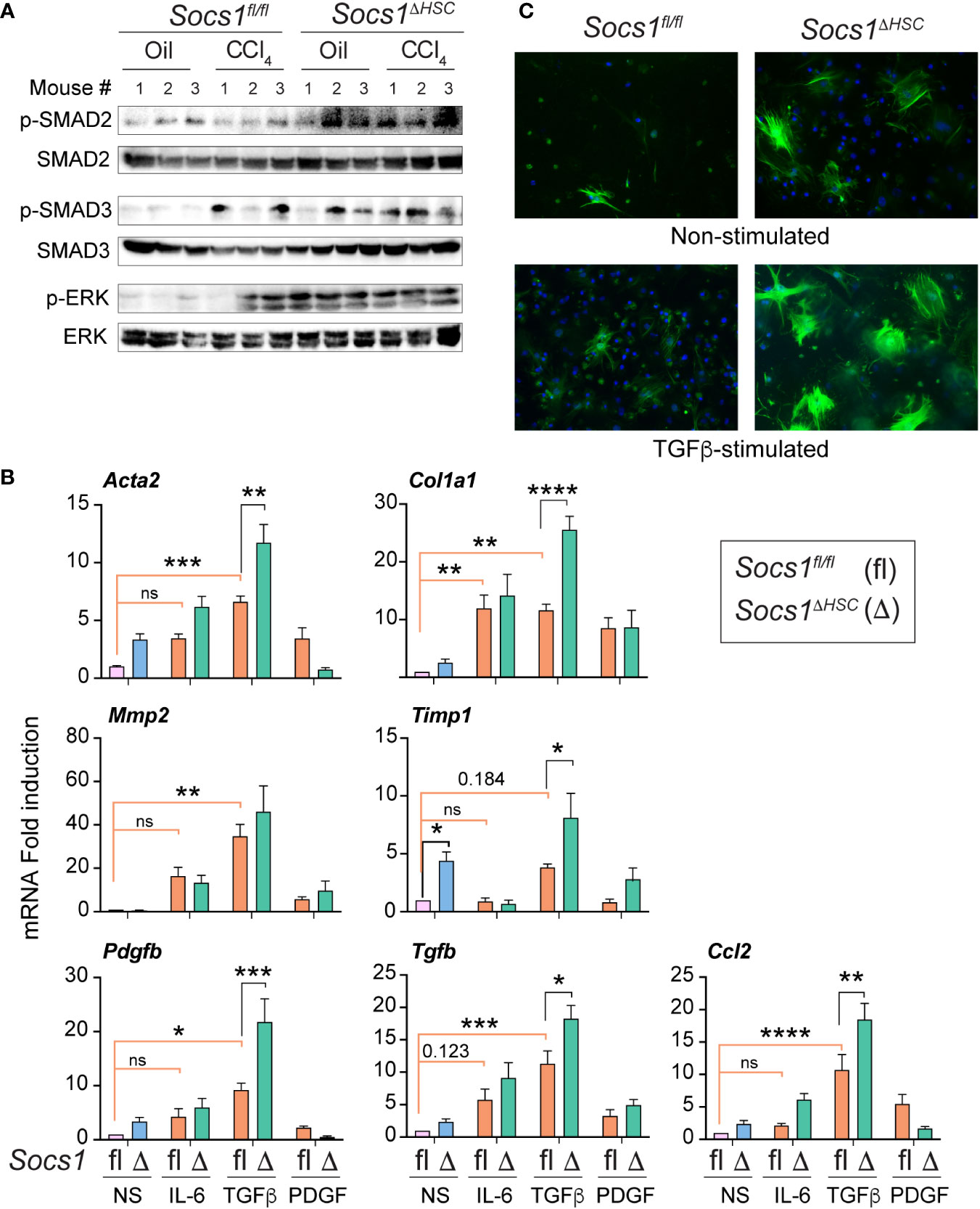
Figure 2 Primary HSCs from Socs1ΔHSC mice show increased responsiveness to TGFβ stimulation. (A) Phosphorylated and total SMAD2, SMAD3 and ERK1/2 protein levels in the liver tissues from three mice in the indicated groups. (B) RT-qPCR evaluation of the expression of genes associated with hepatic fibrogenic response following stimulation with IL-6 (10 ng/mL), TGFβ (5 ng/mL) or PDGFB (20 ng/mL) for 24 h. Mean ± SE of data was pooled from in triplicate cultures from two experiments were compared by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. * p <0.05, ** p <0.01, *** p <0.001; **** p <0.0001. ns, not significant. (C) IF evaluation of αSMA expression in four days old primary HSC cultures from Socs1fl/fl and Socs1ΔHSC mice without or with TGFβ stimulation (5 ng/mL) for 24 h. Representative images from two experiments are shown.
Hematoxylin and eosin-stained liver sections of CCl4-treated mice revealed increased inflammatory cell infiltration in Socs1ΔHSC mice in the periportal area and around the central vein compared to Socs1fl/fl controls (Figure 3A). This observation suggested that SOCS1 deficiency in HSCs enhances hepatic inflammatory response during fibrogenesis. In support of this notion, the expression of the Ccl2 chemokine gene, which is strongly induced by CCL4 treatment in control mice, was further increased in HSC-specific SOCS1-deficient mice (Figure 3B). However, the induction of Ccl5 (RANTES) and Cx3cl1 (Fractalkine) genes was comparable between Socs1ΔHSC and Socs1fl/fl mice livers. We also observed that TGFβ strongly induced the Ccl2 gene in primary HSCs that was significantly elevated in SOCS1-deficient HSCs (Figure 2B). As Ccl2 encodes the macrophage chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP1/CCL2), we examined the distribution of macrophages in the CCL4-treated livers. The fibrotic livers of Socs1fl/fl mice harbored significantly more CD68+ cells, possibly representing Kupffer cells arising from recruited macrophages (45), and their numbers increased further in Socs1ΔHSC mice compared to Socs1fl/fl mice (Figure 3C, D). Flow cytometry analysis of intrahepatic leukocytes revealed that the proportion and number of total CD45+CD11b+ myeloid cells and CD11b+Ly6G+ polymorphonuclear neutrophils, which were comparable between vehicle-treated Socs1ΔHSC and Socs1fl/fl mice, significantly increased following fibrosis induction and this increase was further augmented by SOCS1 deficiency in HSCs (Figure 3E–G). These data indicated that SOCS1 expression in HSCs is crucial to control immune cell recruitment and to regulate fibrosis-associated inflammatory response during liver fibrosis.
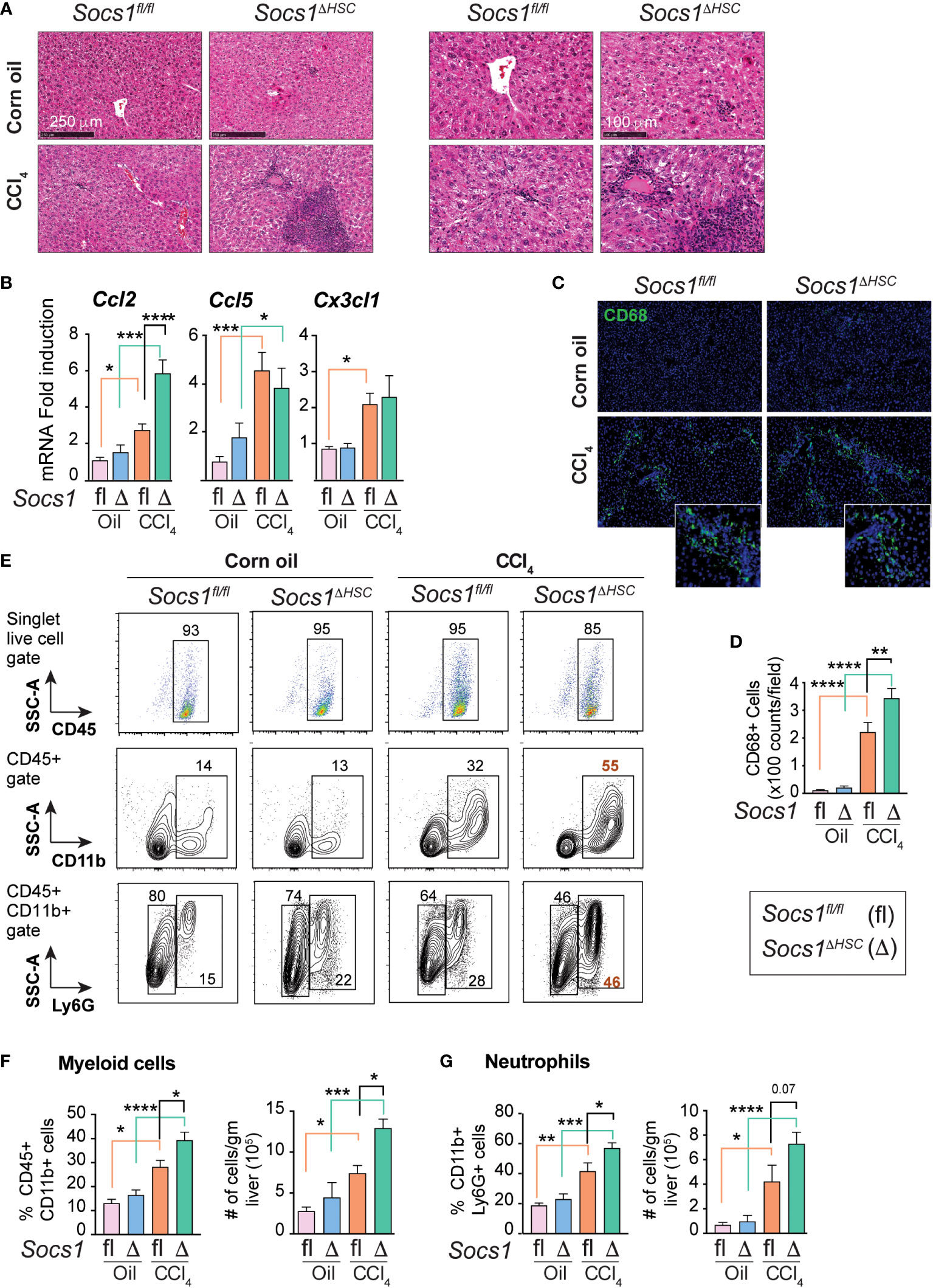
Figure 3 Fibrotic livers of HSC-specific SOCS1 deficient mice show increased innate immune cell infiltration. (A) Representative hematoxylin and eosin-stained liver sections of Socs1fl/fl and Socs1ΔHSC mice treated with corn oil or CCl4 at lower (left panels) and higher (right panels) magnification. (B) RT-qPCR evaluation of chemokine gene expression in liver tissues. Mean ± SE from 6-8 mice per group from at least two separate experiments (C) CD68 IF staining of representative liver sections. Insets show magnified images for CCl4-treated mice livers. (D) Quantification of CD68+ cells. Mean ± SE quantified from 8-10 fields from 3-4 mice/group. (E) Immunophenotyping of IHLs from corn oil or CCl4 treated mice groups by flow cytometry. Representative zebra blots showing distribution of CD45+, CD45+CD11b+ and CD45+CD11b+Ly6G+ cells. Numbers inside the plots indicate the proportion of cells within the gated cell populations. (F, G) Proportions and absolute counts of CD45+CD11b+ myeloid cells (F) and CD45+CD11b+Ly6G+ polymorphonuclear cells (G) in the indicated groups of mice. Pooled data from 5-7 mice per group from two different experiments are shown (mean ± SE). One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. * p <0.05, ** p <0.01, *** p <0.001; **** p <0.0001.
The increased numbers of myeloid cells (Figure 3E, F) and the heightened induction of Il6, Il1b, Tgfb and Pdgfb genes in CCl4-treated livers of Socs1ΔHSC mice (Figure 1I), suggested potent activation of monocyte-derived macrophages. To test this hypothesis, we evaluated the expression level of proinflammatory macrophage marker Ly6C (45) on CD45+CD11b+ cells (Figure 4A). The fibrotic livers of Socs1fl/fl mice livers harbored increased proportion and number of Ly6Chi proinflammatory macrophages that were further increased in the livers of Socs1ΔHSC mice (Figure 4B). Even though Ly6Clo anti-inflammatory macrophages were significantly reduced in frequency in the fibrotic livers of both Socs1fl/fl and Socs1ΔHSC mice, absolute number of this macrophage subset was not significantly altered (Figure 4C). Proinflammatory macrophages are also characterized by the upregulation the chemokine receptor CCR2 (45, 46). When the expression of CCR2 and Ly6C was examined on CD11b+Ly6G- cells, we observed a significant increase in the proportion and number of Ly6ChiCCR2+ cells in CCl4-treated livers of Socs1fl/fl mice that was further increased in Socs1ΔHSC mice (Figure 4D, E). The proportion of Ly6Chi cells that did not express CCR2 significantly decreased in both Socs1fl/fl and Socs1ΔHSC mice, although their absolute numbers of were not significantly affected (Figure 4F).
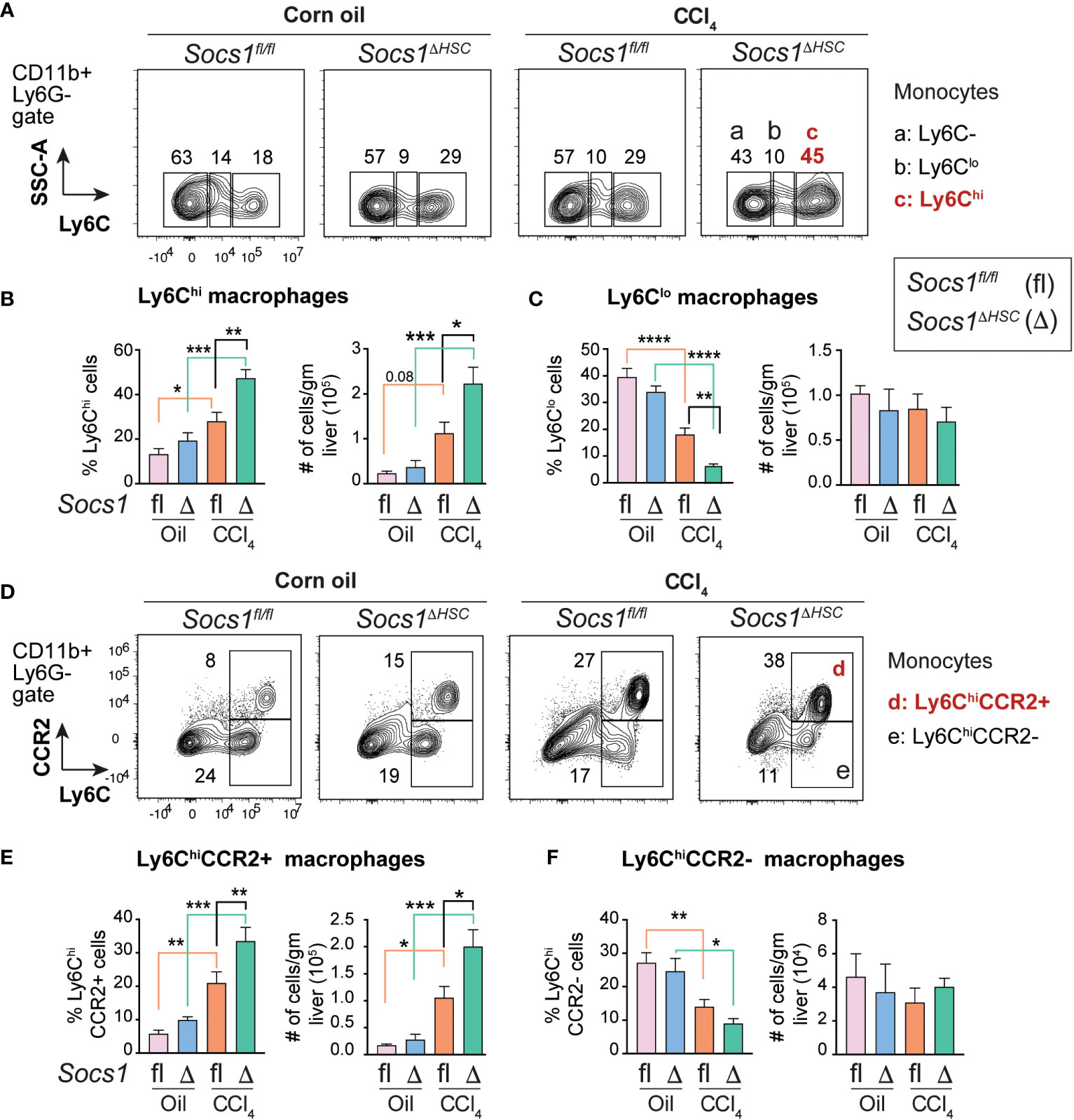
Figure 4 Increased inflammatory macrophage infiltration in the fibrotic livers of HSC-specific SOCS1 deficient mice. (A) Representative density blots showing expression of the proinflammatory monocyte marker Ly6C within the CD45+CD11b+Ly6G− cells in the livers of Socs1ΔHSC and Socs1fl/fl control mice. Gates represented by alphabets identify (a) Ly6C− (b) Ly6Clo and (c) Ly6Chi macrophage populations, and the numbers indicate their proportions within the gates. (B, C) Proportions and absolute counts of Ly6G−Ly6Chi proinflammatory macrophages compared to the Ly6G−Ly6Clo subset. (D) Representative zebra blots showing expression of the proinflammatory macrophage marker CCR2 within the CD45+CD11b+Ly6G−Ly6Chi macrophage population in the livers of Socs1ΔHSC and Socs1fl/fl control mice. Gates represented by alphabets identify (d) CCR2+ and (e) CCR2− cell populations, and the numbers indicate their proportions within the gates. (E, F) Proportions and absolute counts of Ly6ChiCCR2+ and Ly6ChiCCR2− subsets. Mean ± SE data was pooled from 5-7 mice per group from two different experiments and compared by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. * p <0.05, ** p <0.01, *** p <0.001; **** p <0.0001.
During fibrosis progression proinflammatory macrophages transition to restorative macrophages that promote tissue repair and fibrosis resolution after cessation of the inflammatory stimuli (45). The pro-resolution macrophages are characterized by the expression of the CX3CR1 chemokine receptor. Segregation of the macrophage population based on the expression of Ly6C and CX3CR1 revealed that the proportion of Ly6CloCX3CR1+ pro-resolution macrophages did not change in the livers of CCl4-treated Socs1fl/fl and Socs1ΔHSC mice although their numbers showed a discernible, though not significant, increase in both groups (Figure 5A, B). On the other hand, the proportion and number of Ly6Chi cells that also expressed CX3CR1 was markedly upregulated in the fibrotic livers of Socs1fl/fl and Socs1ΔHSC mice, with a significant increase in both frequency and number (Figure 5A, C). Next, we analyzed the co-expression of CCR2 and CX3CR1 within CD11b+Ly6G−Ly6Chi pro-inflammatory macrophage population. We observed a marked increase in the frequency of Ly6ChiCCR2+CX3CR1+ cells in both Socs1fl/fl and Socs1ΔHSC mice with significantly elevated number of these cells in Socs1ΔHSC mice (Figure 5D, E). These results suggest that the increased inflammatory response in Socs1ΔHSC mice prevents these intermediate or transitional macrophages from acquiring the CX3CR1+Ly6CloCCR2− restorative macrophage phenotype.
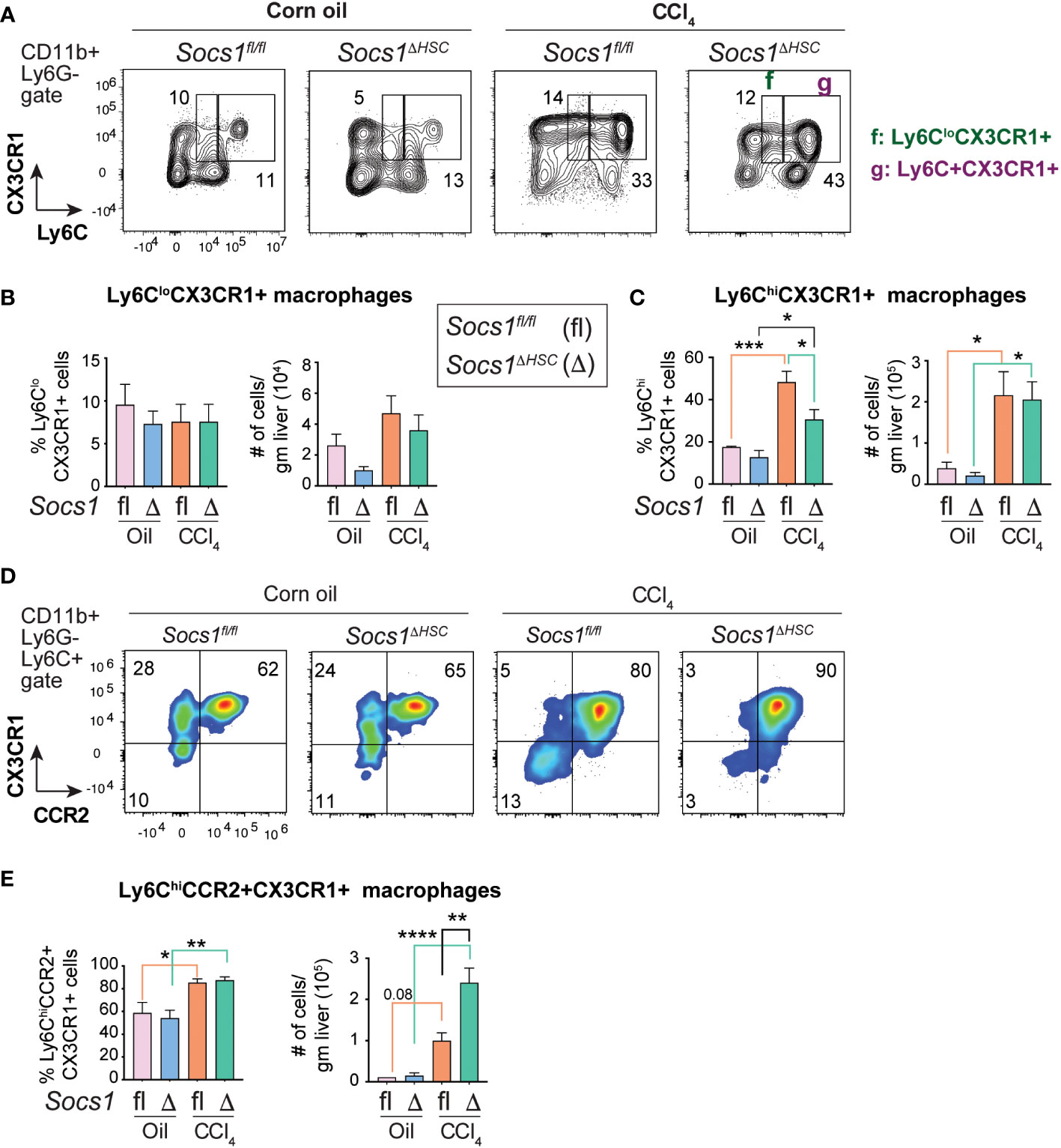
Figure 5 Fibrotic livers of HSC-specific SOCS1 deficient mice accumulate macrophages expressing both CCR2 and CX3CR1. (A) Representative zebra blots showing the expression of Ly6C and CX3CR1 within the CD45+CD11b+Ly6G− cells in the livers of Socs1ΔHSC and Socs1fl/fl control mice. Gates represented by alphabets identify (f) Ly6CloCX3CR1+ and (g) Ly6ChiCX3CR1+ macrophage populations, and the numbers indicate their proportions within the gates. (B, C) Proportions and absolute counts of) Ly6CloCX3CR1+ pro-resolution macrophages compared to the Ly6C+CX3CR1+ proinflammatory subset. (D) Representative density blots showing the expression of CCR2 and CX3CR1 within the CD45+CD11b+Ly6C+ cells in the fibrotic livers of Socs1ΔHSC and Socs1fl/fl control mice. (E) Proportions and absolute counts of Ly6C+CCR2+CX3CR1+ macrophages. Pooled data from 4-6 mice per group from two different experiments are shown (mean ± SEM). One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. * p <0.05, ** p <0.01, *** p <0.001, **** p <0.0001.
The fibrotic livers of Socs1ΔHSC mice also contained an increased frequency and number of CD11b+CD11c+ myeloid dendritic cells (DC), whereas the number of plasmacytoid DCs were not affected (Supplementary Figure S3). The livers of CCl4-treated Socs1ΔHSC mice also harbored an elevated number of CD8+ T lymphocytes that displayed an activated effector (CD69+), effector memory (CD44hiCD62Llo) and central memory (CD44hiCD62Lhi) phenotype, whereas the numbers of CD4 T and NK cells and the activation status of CD4+ T cells were not affected (Supplementary Figures S4, S5).
Liver fibrosis driven by activated HSC and the associated inflammation driven by macrophages are important drivers of HCC development and progression (10, 47, 48). To determine if increased liver fibrosis in Socs1ΔHSC mice promotes HCC development, we administered DEN to 2 weeks old mice followed by CCl4 treatment beginning at 8 weeks of age and continued for 14 weeks to induce and sustain liver fibrosis (Figure 6A). Examination of the livers at the end of this treatment period revealed increased liver body weight ratio in Socs1ΔHSC mice than in control mice, with increased number of liver tumor nodules that showed histological features of hepatocellular carcinoma (Figure 6B–D).
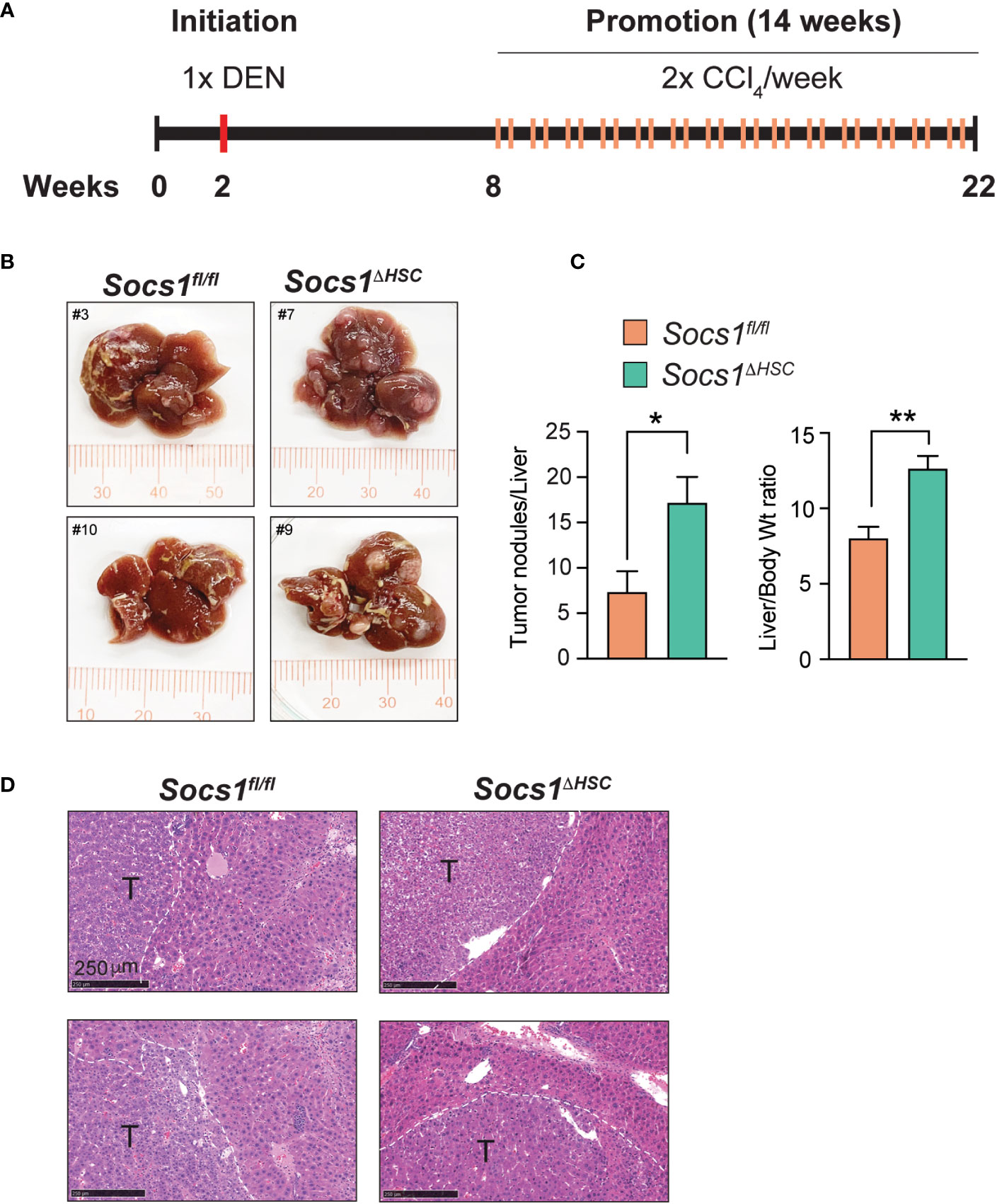
Figure 6 SOCS1 deficiency in HSCs enhances hepatocarcinogenesis in fibrotic livers. (A) Schematic representation of hepatocellular carcinoma induction. Two weeks old Socs1fl/flLratCre mice (n=8) and Socs1fl/fl controls (n=7) were injected with DEN (25 mg/kg BW, i.p.). Six weeks later, the mice were administered CCl4 (0.5 ml/kg BW, i.p.), weekly for 14 weeks, and euthanized at the age of 22 weeks. (B) Representative images of livers showing HCC nodules. (C) Liver to body weight ratio and the number of surface liver nodules per mouse. Data shown as Mean ± SE from 6-7 mice per group were compared by two-tailed unpaired t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. (D) Representative H&E sections of the tumor bearing livers. T, tumor nodule.
Myofibroblasts that differentiate from HSCs are key pathogenic mediators of hepatic fibrosis that can progress towards HCC and thus are considered a key therapeutic target (10, 20, 47). Genetic targeting of HSCs has been widely used to gain deeper understanding of the molecular basis of HSC activation, differentiation and fibrogenic functions. These efforts to track HSCs or modulate their gene expression have employed mice expressing the Cre recombinase under diverse promoters such as collagens, glial fibrillary acidic protein (Gfap), Pdgfb and Lrat (28, 49–53). Among these, LRAT is expressed selectively in HSCs and not in hepatocytes, cholangiocytes and endothelial cells in the liver. Thus, the LratCre deleter mouse has provided a valuable tool for deeper understanding of the physiopathology of liver fibrosis and HCC development (28, 29, 48, 54–58). In the current study, we ablated the Socs1 gene using the LratCre deleter to understand the role of SOCS1 in regulating HSC activation. Our findings reveal a non-redundant cell-intrinsic role of SOCS1 in HSCs that controls HSC activation by TGFβ and amplification of the hepatic inflammatory response in liver fibrosis (Figure 7).
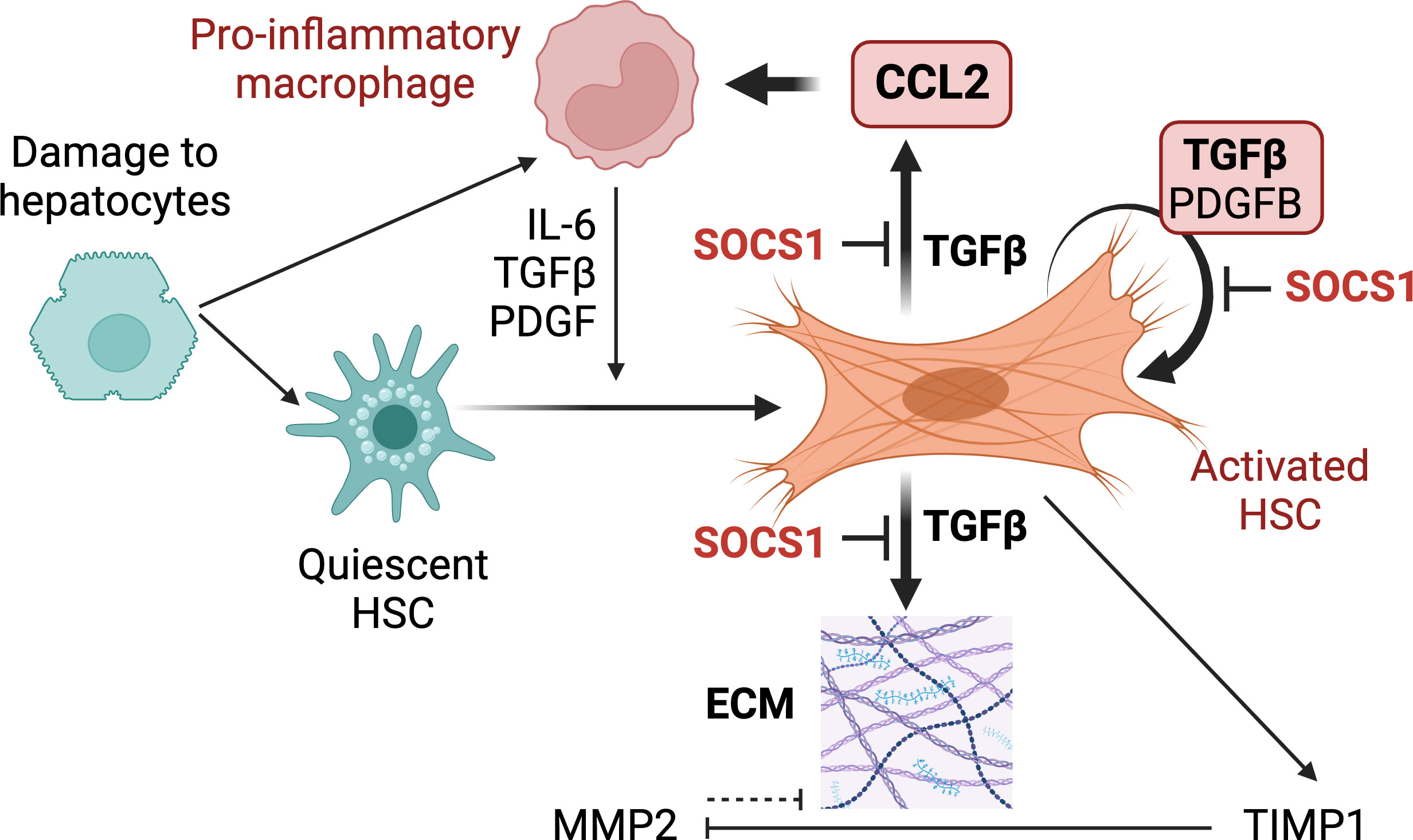
Figure 7 Proposed functions of SOCS1 in HSCs. Following hepatocyte damage, quiescent HSCs become activated and differentiate towards myofibroblasts to repair tissue damage. Liver resident and recruit macrophages contribute to HSC activation via secreting TGFβ, PDGF, chemokines and inflammatory cytokines. Activated HSCs produce autocrine TGFβ, which induces fibrogenic genes that promote synthesis and accumulation of ECM. TGFβ also induces autocrine PDGFB that promotes myofibroblast proliferation and induces CCL2 gene expression in HSCs that recruits macrophages and other inflammatory cells. During liver fibrosis, SOCS1 plays a crucial cell-intrinsic regulatory role in HSCs to control TGFβ-induced expression of fibrogenic and chemokine genes and autocrine TGFβ and PDGFB production.
SOCS1 expression can attenuate several cytokines that signal via the canonical JAK-STAT pathway as well as many growth factors that signal via receptor tyrosine kinases (22, 23, 59). Our finding that Socs1ΔHSC mice develop severe fibrosis compared to control mice indicates that SOCS1 regulates cytokines and growth factors that promote HSC activation. PDGFB, which signals via the PDGFRα and PDGFRβ receptor tyrosine kinases and activates ERK and AKT signaling pathways, is a potent paracrine and autocrine mitogen for HSCs (60). Whereas transgenic expression of PDGFB in the liver under albumin promoter increased collagen deposition and promoted CCl4-induced liver fibrosis, ablation of PDGFRβ in HSCs attenuated liver fibrosis (44, 61). SOCS1 was reported to interact with PDGFR (62). PDGF stimulation of primary HSCs from Socs1ΔHSC mice did not alter the expression of the fibrogenic genes (Figure 2B). However, we have shown that primary HSCs from whole body SOCS1 deficient mice display increased proliferation to PDGF stimulation (26), suggesting a role for SOCS1 in regulating HSC proliferation in liver fibrosis. In support of this notion, we observed increased induction of ERK1/2 phosphorylation in the livers of Socs1ΔHSC (Figure 2A), suggesting deregulated PDGFR signaling in SOCS1-deficient HSCs. However, further studies using Socs1ΔHSC primary HSCs are needed to determine potential contribution of other growth factors such as EGF, as it is also mitogenic to HSCs and SOCS1 can attenuate EGFR signaling (63–65).
Among the cytokines that signal via the JAK-STAT pathway, IL-6 could be involved in liver fibrosis via amplifying the intercellular communication between stressed hepatocytes, HSCs and macrophages (12). IL-6 was also reported to stimulate the expression of Acta2 and Col1a expression in human HSCs (66). As SOCS1 was initially discovered as a negative regulator of the inflammatory cytokine IL-6 signaling (67), loss of SOCS1 could amplify IL-6 signaling and promote liver fibrosis. Earlier studies using whole body Il6 knockout mice reported an anti-fibrotic role of IL-6 although another study has reported potential pro-fibrotic effects (68–70). Given that IL-6 is critical for hepatocyte survival and liver regeneration, it was postulated that decreased hepatocyte survival in the absence of IL-6 resulted in sustained hepatocyte damage, contributing to increased fibrosis in Il6-deficient mice rather than a direct anti-fibrotic role of IL-6 (69, 71). In support of this possibility, we did not observe any significant increase in the induction of fibrogenic genes in primary HSCs from Socs1ΔHSC mice following IL-6 stimulation (Figure 2B), possibly because SOCS3, which is a more potent regulator of IL-6 signaling than SOCS1 and is necessary to control IL-6 signaling in vivo (72), is intact in SOCS1-deficient HSCs.
A direct effect of SOCS1 deficiency in HSCs was the elevated expression of the fibrogenic genes Acta2, Col1a1 and Timp1, Pdgfb coding for PDGFB and autocrine Tgfb induction following TGFβ stimulation (Figure 2B), suggesting deregulated TGFβ signaling in SOCS1-deficient HSCs. This idea is supported by increased SMAD3 phosphorylation in the fibrotic livers of Socs1ΔHSC mice (Figure 2A). SMAD3 is considered more crucial for the pro-fibrogenic effect of TGFβ (43, 73, 74). SOCS1 deficiency might potentiate TGFβ signaling in HSCs by multiple mechanisms: In quiescent HSCs, the TGFβ-induced canonical SMAD2/3 pathway is attenuated by the TGFβ pseudoreceptor BAMBI, which is downmodulated by NF-κB that is activated by lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from the gut microbiota via the toll like receptor 4 (TLR4) (75). SOCS1 is a key regulator of TLR4 signaling in macrophages (76, 77). SOCS1 controls LPS-induced NF-κB signaling by virtue of its ability to function as a substrate adaptor for protein ubiquitination. SOCS1 attenuates TLR4 signaling by promoting ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of a key signaling adaptor the Toll/Interleukin-1 receptor domain containing adaptor protein (TIRAP, also called MAL) (78). Besides, SOCS1 promotes ubiquitination-dependent degradation of p65RelA component of NF-κB itself (79, 80). In addition to the canonical SMAD2/SMAD3 signaling pathway, TGFβ activates JAK1-STAT3 signaling that synergizes with the SMAD3 pathway (81). This pathway can potentially be regulated by SOCS1 via inhibition of JAK1. Clearly, further studies are needed to elucidate the mechanistic basis of SOCS1-dependent regulation of TGFβ signaling in HSCs.
TGFβ stimulation of SOCS1-deficient HSCs increased the induction of Ccl2, which is a target gene of NF-κB and encodes MCP-1/CCL2. CCL2 is a key chemoattractant for macrophages, plays a crucial role in liver fibrosis and a potential therapeutic target (12, 82, 83). The fibrotic livers of Socs1ΔHSC mice also showed elevated expression of Ccl2 and increased numbers of macrophages (Figure 3). Macrophages play a key role in liver homeostasis (45, 84). The normal liver harbors a large reservoir of tissue resident Kupffer cells distributed along the liver sinusoids and monocyte-derived macrophages that are mainly located in the periportal regions. However, hepatic tissue injury causes a large influx of monocyte-derived macrophages that are Ly6C+, express CCR2 and are pro-inflammatory in function. These inflammatory macrophages secrete mediators that attract immune cells, activate HSCs to become myofibroblasts and modulate the ECM, all functions aimed at containing the tissue damage (13). Subsequently, these inflammatory macrophages transition to restorative macrophages that downregulate Ly6C and CCR2 levels, upregulate the chemokine receptor CX3CR1 expression and help clear the ECM and apoptotic HSCs (45). Strikingly, macrophages that express CX3CR1 without downmodulating Ly6C or CCR2 (Ly6ChiCCR2+CX3CR1+) accumulate in the fibrotic livers of Socs1ΔHSC mice (Figure 5). These cells likely represent intermediate, transitional state cells that would eventually become pro-restorative Ly6CloCCR2−CX3CR1+ macrophages upon cessation of the fibrotic stimuli. The fact that these cells are discernibly increased in number in the fibrotic livers of control Socs1fl/fl mice suggests that increased inflammatory response in the livers of Socs1ΔHSC mice, originating from deregulated cytokine and growth factor signaling in HSCs, hampers this transition. Transcriptomic and proteomic studies on studies on purified HSCs and macrophages from the control and fibrotic livers of Socs1fl/fl Socs1ΔHSC mice and co-culture experiments using purified HSCs and macrophages would be needed to fully understand how SOCS1-HSCs modulate macrophage phenotype and functions.
Inflammation associated with liver fibrosis is a key driver of HCC development and progression (10, 47, 48). Deletion of Lim homeobox domain 2 (Lhx2), a repressor of HSC activation, in HSCs was shown to shift these cells from cytokine-producing phenotype towards the persistently myofibroblastic phenotype and promote HCC development (48). We observed a similarly increased susceptibility of Socs1ΔHSC mice to liver fibrosis and HCC development. Overall, our findings show that SOCS1 regulates HSC activation by TGFβ and thereby controls liver fibrosis and HCC development at least partly via attenuating pro-inflammatory macrophage recruitment and promoting their transition to restorative macrophages.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
The animal study was approved by Université de Sherbrooke Ethics Committee for Animal Care and Use. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
RK: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. MY: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. AY: Writing – review & editing, Resources. AM: Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision. SR: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Resources, Validation. SI: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by a Project grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) to SI (PJT-153255).
RK was a recipient of a doctoral fellowship from Fonds de Recherche du Québec-Santé (FRQS). Figure 7 was created with BioRender.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1259246/full#supplementary-material
ALT, alanine transferase; CCl4, carbon tetrachloride; ECM, extracellular matrix; LF, Liver fibrosis; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NDP, nanozoomer Digital Pathology; SOCS, suppressor of cytokine signaling; SMA, smooth muscle actin; TIMP, tissue inhibitor of MMP.
1. Gines P, Krag A, Abraldes JG, Sola E, Fabrellas N, Kamath PS. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet (2021) 398:1359–76. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01374-X
2. Llovet JM, Montal R, Sia D, Finn RS. Molecular therapies and precision medicine for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol (2018) 15:599–616. doi: 10.1038/s41571-018-0073-4
3. Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, Singal AG, Pikarsky E, Roayaie S, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers (2021) 7:6. doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-00240-3
5. Hernandez-Gea V, Friedman SL. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol (2011) 6:425–56. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130246
6. Chiang DJ, Pritchard MT, Nagy LE. Obesity, diabetes mellitus, and liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol (2011) 300:G697–702. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00426.2010
7. Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology (2008) 134:1655–69. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.003
8. Pellicoro A, Ramachandran P, Iredale JP, Fallowfield JA. Liver fibrosis and repair: immune regulation of wound healing in a solid organ. Nat Rev Immunol (2014) 14:181–94. doi: 10.1038/nri3623
9. Farazi PA, DePinho RA. Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis: from genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer (2006) 6:674–87. doi: 10.1038/nrc1934
10. Zhang DY, Friedman SL. Fibrosis-dependent mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology (2012) 56:769–75. doi: 10.1002/hep.25670
11. Lee YA, Wallace MC, Friedman SL. Pathobiology of liver fibrosis: a translational success story. Gut (2015) 64:830–41. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-306842
12. Trautwein C, Friedman SL, Schuppan D, Pinzani M. Hepatic fibrosis: Concept to treatment. J Hepatol (2015) 62:S15–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.02.039
13. Tacke F. Targeting hepatic macrophages to treat liver diseases. J Hepatol (2017) 66:1300–12. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.02.026
14. Tsuchida T, Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol (2017) 14:397–411. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.38
15. Liedtke C, Luedde T, Sauerbruch T, Scholten D, Streetz K, Tacke F, et al. Experimental liver fibrosis research: update on animal models, legal issues and translational aspects. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair (2013) 6:19. doi: 10.1186/1755-1536-6-19
16. Delire B, Starkel P, Leclercq I. Animal models for fibrotic liver diseases: what we have, what we need, and what is under development. J Clin Transl Hepatol (2015) 3:53–66. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2014.00035
17. Bao YL, Wang L, Pan HT, Zhang TR, Chen YH, Xu SJ, et al. Animal and organoid models of liver fibrosis. Front Physiol (2021) 12:666138. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.666138
18. Friedman SL. Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol Rev (2008) 88:125–72. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00013.2007
19. Seki E, Schwabe RF. Hepatic inflammation and fibrosis: functional links and key pathways. Hepatology (2015) 61:1066–79. doi: 10.1002/hep.27332
20. Higashi T, Friedman SL, Hoshida Y. Hepatic stellate cells as key target in liver fibrosis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev (2017) 121:27–42. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2017.05.007
21. Yoshimura A, Ito M, Chikuma S, Akanuma T, Nakatsukasa H. Negative regulation of cytokine signaling in immunity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol (2018) 10(7):a028571. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028571
22. Alexander WS. Suppressors of cytokine signalling (SOCS) in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol (2002) 2:410–6. doi: 10.1038/nri818
23. Kazi JU, Kabir NN, Flores-Morales A, Ronnstrand L. SOCS proteins in regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci: CMLS (2014) 71:3297–310. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1619-y
24. Sachithanandan N, Graham KL, Galic S, Honeyman JE, Fynch SL, Hewitt KA, et al. Macrophage deletion of SOCS1 increases sensitivity to LPS and palmitic acid and results in systemic inflammation and hepatic insulin resistance. Diabetes (2011) 60:2023–31. doi: 10.2337/db11-0259
25. Yoshida T, Ogata H, Kamio M, Joo A, Shiraishi H, Tokunaga Y, et al. SOCS1 is a suppressor of liver fibrosis and hepatitis-induced carcinogenesis. J Exp Med (2004) 199:1701–7. doi: 10.1084/jem.20031675
26. Kandhi R, Bobbala D, Yeganeh M, Mayhue M, Menendez A, Ilangumaran S. Negative regulation of the hepatic fibrogenic response by suppressor of cytokine signaling 1. Cytokine (2016) 82:58–69. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.12.007
27. Mafanda EK, Kandhi R, Bobbala D, Khan MGM, Nandi M, Menendez A, et al. Essential role of suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1) in hepatocytes and macrophages in the regulation of liver fibrosis. Cytokine (2019) 124:154501. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.07.032
28. Mederacke I, Hsu CC, Troeger JS, Huebener P, Mu X, Dapito DH, et al. Fate tracing reveals hepatic stellate cells as dominant contributors to liver fibrosis independent of its aetiology. Nat Commun (2013) 4:2823. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3823
29. Österreicher CH, Lemberger UJ, Mahon R, Rülicke T, Trauner M, Casanova E. O147 Hepatic Stellate cells are the major source of collagen in murine models of liver fibrosis. J Hepatol (2014) 60:S61.
30. Tanaka K, Ichiyama K, Hashimoto M, Yoshida H, Takimoto T, Takaesu G, et al. Loss of suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 in helper T cells leads to defective Th17 differentiation by enhancing antagonistic effects of IFN-gamma on STAT3 and Smads. J Immunol (2008) 180:3746–56. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.6.3746
31. Madisen L, Zwingman TA, Sunkin SM, Oh SW, Zariwala HA, Gu H, et al. A robust and high-throughput Cre reporting and characterization system for the whole mouse brain. Nat Neurosci (2010) 13:133–40. doi: 10.1038/nn.2467
32. Scholten D, Trebicka J, Liedtke C, Weiskirchen R. The carbon tetrachloride model in mice. Lab Anim (2015) 49:4–11. doi: 10.1177/0023677215571192
33. Naugler WE, Sakurai T, Kim S, Maeda S, Kim K, Elsharkawy AM, et al. Gender disparity in liver cancer due to sex differences in MyD88-dependent IL-6 production. Science (2007) 317:121–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1140485
34. Shimizu I, Ito S. Protection of estrogens against the progression of chronic liver disease. Hepatol Res (2007) 37:239–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2007.00032.x
35. Romualdo GR, Prata GB, da Silva TC, Fernandes AAH, Moreno FS, Cogliati B, et al. Fibrosis-associated hepatocarcinogenesis revisited: Establishing standard medium-term chemically-induced male and female models. PloS One (2018) 13:e0203879. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203879
36. Chang W, Yang M, Song L, Shen K, Wang H, Gao X, et al. Isolation and culture of hepatic stellate cells from mouse liver. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) (2014) 46:291–8. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmt143
37. Mederacke I, Dapito DH, Affo S, UChinami H, Schwabe RF. High-yield and high-purity isolation of hepatic stellate cells from normal and fibrotic mouse livers. Nat Protoc (2015) 10:305–15. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2015.017
38. Kandhi R, Variya B, Ramanathan S, Ilangumaran S. An improved method for isolation and flow cytometric characterization of intrahepatic leukocytes from fatty and fibrotic liver tissues. Anat Rec (Hoboken) (2022) 306(5):1011–30. doi: 10.1002/ar.25039
39. Uehara T, Pogribny IP, Rusyn I, The DEN. and CCl4 -induced mouse model of fibrosis and inflammation-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Protoc Pharmacol (2014) 66:14 30 1–14 30 10. doi: 10.1002/0471141755.ph1430s66
40. Khan MGM, Ghosh A, Variya B, Santharam MA, Kandhi R, Ramanathan S, et al. Hepatocyte growth control by SOCS1 and SOCS3. Cytokine (2019) 121:154733. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.154733
41. Giannandrea M, Parks WC. Diverse functions of matrix metalloproteinases during fibrosis. Dis Model Mech (2014) 7:193–203. doi: 10.1242/dmm.012062
42. George J, Roulot D, Koteliansky VE, Bissell DM. In vivo inhibition of rat stellate cell activation by soluble transforming growth factor beta type II receptor: a potential new therapy for hepatic fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (1999) 96:12719–24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.22.12719
43. Dewidar B, Meyer C, Dooley S, Meindl-Beinker AN. TGF-beta in hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrogenesis-updated 2019. Cells (2019) 8(11):1419. doi: 10.3390/cells8111419
44. Czochra P, Klopcic B, Meyer E, Herkel J, Garcia-Lazaro JF, Thieringer F, et al. Liver fibrosis induced by hepatic overexpression of PDGF-B in transgenic mice. J Hepatol (2006) 45:419–28. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2006.04.010
45. Krenkel O, Tacke F. Liver macrophages in tissue homeostasis and disease. Nat Rev Immunol (2017) 17:306–21. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.11
46. Geissmann F, Jung S, Littman DR. Blood monocytes consist of two principal subsets with distinct migratory properties. Immunity (2003) 19:71–82. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(03)00174-2
47. Thompson AI, Conroy KP, Henderson NC. Hepatic stellate cells: central modulators of hepatic carcinogenesis. BMC Gastroenterol (2015) 15:63. doi: 10.1186/s12876-015-0291-5
48. Filliol A, Saito Y, Nair A, Dapito DH, Yu LX, Ravichandra A, et al. Opposing roles of hepatic stellate cell subpopulations in hepatocarcinogenesis. Nature (2022) 610:356–65. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05289-6
49. Yang L, Jung Y, Omenetti A, Witek RP, Choi S, Vandongen HM, et al. Fate-mapping evidence that hepatic stellate cells are epithelial progenitors in adult mouse livers. Stem Cells (2008) 26:2104–13. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2008-0115
50. Kisseleva T, Cong M, Paik Y, Scholten D, Jiang C, Benner C, et al. Myofibroblasts revert to an inactive phenotype during regression of liver fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America (2012) 109:9448–53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1201840109
51. Lujambio A, Akkari L, Simon J, Grace D, Tschaharganeh DF, Bolden JE, et al. Non-cell-autonomous tumor suppression by p53. Cell (2013) 153:449–60. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.03.020
52. Henderson NC, Arnold TD, Katamura Y, Giacomini MM, Rodriguez JD, McCarty JH, et al. Targeting of alphav integrin identifies a core molecular pathway that regulates fibrosis in several organs. Nat Med (2013) 19:1617–24. doi: 10.1038/nm.3282
53. Greenhalgh SN, Conroy KP, Henderson NC. Cre-ativity in the liver: transgenic approaches to targeting hepatic nonparenchymal cells. Hepatology (2015) 61:2091–9. doi: 10.1002/hep.27606
54. Zhang R, Kikuchi AT, Nakao T, Russell JO, Preziosi ME, Poddar M, et al. Elimination of wnt secretion from stellate cells is dispensable for zonation and development of liver fibrosis following hepatobiliary injury. Gene Expr (2019) 19:121–36. doi: 10.3727/105221618X15373858350141
55. Poole LG, Pant A, Cline-Fedewa HM, Williams KJ, Copple BL, Palumbo JS, et al. Liver fibrosis is driven by protease-activated receptor-1 expressed by hepatic stellate cells in experimental chronic liver injury. Res Pract Thromb Haemost (2020) 4:906–17. doi: 10.1002/rth2.12403
56. Liu X, Xu J, Rosenthal S, Zhang LJ, McCubbin R, Meshgin N, et al. Identification of lineage-specific transcription factors that prevent activation of hepatic stellate cells and promote fibrosis resolution. Gastroenterology (2020) 158:1728–1744 e14. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.01.027
57. Hamberger F, Mederacke YS, Mederacke I. An inducible model for genetic manipulation and fate-tracing of PDGFRbeta-expressing fibrogenic cells in the liver. Sci Rep (2023) 13:7322. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34353-y
58. Min K, Yenilmez B, Kelly M, Echeverria D, Elleby M, Lifshitz LM, et al. Lactate transporter MCT1 in hepatic stellate cells promotes fibrotic collagen expression in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. bioRxiv (2023). doi: 10.1101/2023.05.03.539244
59. Trengove MC, Ward AC. SOCS proteins in development and disease. Am J Clin Exp Immunol (2013) 2:1–29.
60. Bonner JC. Regulation of PDGF and its receptors in fibrotic diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev (2004) 15:255–73. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2004.03.006
61. Kocabayoglu P, Lade A, Lee YA, Dragomir AC, Sun X, Fiel MI, et al. beta-PDGF receptor expressed by hepatic stellate cells regulates fibrosis in murine liver injury, but not carcinogenesis. J Hepatol (2015) 63:141–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.01.036
62. De Sepulveda P, Okkenhaug K, Rose JL, Hawley RG, Dubreuil P, Rottapel R. Socs1 binds to multiple signalling proteins and suppresses steel factor- dependent proliferation. EMBO J (1999) 18:904–15. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.4.904
63. Fuchs BC, Hoshida Y, Fujii T, Wei L, Yamada S, Lauwers GY, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition attenuates liver fibrosis and development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology (2014) 59:1577–90. doi: 10.1002/hep.26898
64. Liang D, Chen H, Zhao L, Zhang W, Hu J, Liu Z, et al. Inhibition of EGFR attenuates fibrosis and stellate cell activation in diet-induced model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis (2018) 1864:133–42. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.10.016
65. Xia L, Wang L, Chung AS, Ivanov SS, Ling MY, Dragoi AM, et al. Identification of both positive and negative domains within the epidermal growth factor receptor COOH-terminal region for signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) activation. J Biol Chem (2002) 277:30716–23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M202823200
66. Kagan P, Sultan M, Tachlytski I, Safran M, Ben-Ari Z, Both MAPK. and STAT3 signal transduction pathways are necessary for IL-6-dependent hepatic stellate cells activation. PloS One (2017) 12:e0176173. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176173
67. Starr R, Willson TA, Viney EM, Murray LJ, Rayner JR, Jenkins BJ, et al. A family of cytokine-inducible inhibitors of signalling. Nature (1997) 387:917–21. doi: 10.1038/43206
68. Natsume M, Tsuji H, Harada A, Akiyama M, Yano T, Ishikura H, et al. Attenuated liver fibrosis and depressed serum albumin levels in carbon tetrachloride-treated IL-6-deficient mice. J Leukoc Biol (1999) 66:601–8. doi: 10.1002/jlb.66.4.601
69. Bansal MB, Kovalovich K, Gupta R, Li W, Agarwal A, Radbill B, et al. Interleukin-6 protects hepatocytes from CCl4-mediated necrosis and apoptosis in mice by reducing MMP-2 expression. J Hepatol (2005) 42:548–56. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2004.11.043
70. Kovalovich K, DeAngelis RA, Li W, Furth EE, Ciliberto G, Taub R. Increased toxin-induced liver injury and fibrosis in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Hepatology (2000) 31:149–59. doi: 10.1002/hep.510310123
71. Cressman DE, Greenbaum LE, DeAngelis RA, Ciliberto G, Furth EE, Poli V, et al. Liver failure and defective hepatocyte regeneration in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Science (1996) 274:1379–83. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5291.1379
72. Croker BA, Krebs DL, Zhang JG, Wormald S, Willson TA, Stanley EG, et al. SOCS3 negatively regulates IL-6 signaling in vivo. Nat Immunol (2003) 4:540–5. doi: 10.1038/ni931
73. Uemura M, Swenson ES, Gaca MD, Giordano FJ, Reiss M, Wells RG. Smad2 and Smad3 play different roles in rat hepatic stellate cell function and alpha-smooth muscle actin organization. Mol Biol Cell (2005) 16:4214–24. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-02-0149
74. Zhang L, Liu C, Meng XM, Huang C, Xu F, Li J. Smad2 protects against TGF-beta1/Smad3-mediated collagen synthesis in human hepatic stellate cells during hepatic fibrosis. Mol Cell Biochem (2015) 400:17–28. doi: 10.1007/s11010-014-2258-1
75. Seki E, De Minicis S, Osterreicher CH, Kluwe J, Osawa Y, Brenner DA, et al. TLR4 enhances TGF-beta signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat Med (2007) 13:1324–32. doi: 10.1038/nm1663
76. Kinjyo I, Hanada T, Inagaki-Ohara K, Mori H, Aki D, Ohishi M, et al. SOCS1/JAB is a negative regulator of LPS-induced macrophage activation. Immunity (2002) 17:583–91. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(02)00446-6
77. Nakagawa R, Naka T, Tsutsui H, Fujimoto M, Kimura A, Abe T, et al. SOCS-1 participates in negative regulation of LPS responses. Immunity (2002) 17:677–87. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(02)00449-1
78. Mansell A, Smith R, Doyle SL, Gray P, Fenner JE, Crack PJ, et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 negatively regulates Toll-like receptor signaling by mediating Mal degradation. Nat Immunol (2006) 7:148–55. doi: 10.1038/ni1299
79. Ryo A, Suizu F, Yoshida Y, Perrem K, Liou YC, Wulf G, et al. Regulation of NF-kappaB signaling by Pin1-dependent prolyl isomerization and ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of p65/RelA. Mol Cell (2003) 12:1413–26. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(03)00490-8
80. Strebovsky J, Walker P, Lang R, Dalpke AH. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1) limits NFkappaB signaling by decreasing p65 stability within the cell nucleus. FASEB J (2011) 25:863–74. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-170597
81. Tang LY, Heller M, Meng Z, Yu LR, Tang Y, Zhou M, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) directly activates the JAK1-STAT3 axis to induce hepatic fibrosis in coordination with the SMAD pathway. J Biol Chem (2017) 292:4302–12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.773085
82. Seki E, de Minicis S, Inokuchi S, Taura K, Miyai K, van Rooijen N, et al. CCR2 promotes hepatic fibrosis in mice. Hepatology (2009) 50:185–97. doi: 10.1002/hep.22952
83. Ehling J, Bartneck M, Wei X, Gremse F, Fech V, Mockel D, et al. CCL2-dependent infiltrating macrophages promote angiogenesis in progressive liver fibrosis. Gut (2014) 63:1960–71. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-306294
Keywords: alanine transferase (ALT), carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), extracellular matrix (ECM), liver fibrosis (LF), matrix metalloproteinase (MMP), nanozoomer Digital Pathology (NDP), suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)
Citation: Kandhi R, Yeganeh M, Yoshimura A, Menendez A, Ramanathan S and Ilangumaran S (2023) Hepatic stellate cell-intrinsic role of SOCS1 in controlling hepatic fibrogenic response and the pro-inflammatory macrophage compartment during liver fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 14:1259246. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1259246
Received: 15 July 2023; Accepted: 18 September 2023;
Published: 04 October 2023.
Edited by:
Jagadeesh Bayry, Indian Institute of Technology Palakkad, IndiaReviewed by:
Jingwei Mao, Dalian Medical University, ChinaCopyright © 2023 Kandhi, Yeganeh, Yoshimura, Menendez, Ramanathan and Ilangumaran. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Subburaj Ilangumaran, U3ViYnVyYWouSWxhbmd1bWFyYW5AVXNoZXJicm9va2UuY2E=
†ORCID: Subburaj Ilangumaran, orcid.org/0000-0002-7563-576X
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.