
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Immunol. , 15 June 2023
Sec. Comparative Immunology
Volume 14 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1222662
This article is a correction to:
Edwardsiella piscicida infection reshapes the intestinal microbiome and metabolome of big-belly seahorses: mechanistic insights of synergistic actions of virulence factors
 Lele Zhang1,2†
Lele Zhang1,2† Fang Wang3†
Fang Wang3† Longwu Jia1,2
Longwu Jia1,2 Hansheng Yan1,2
Hansheng Yan1,2 Longkun Gao1,2
Longkun Gao1,2 Yanan Tian1,2
Yanan Tian1,2 Xiaolei Su1,2
Xiaolei Su1,2 Xu Zhang1,2
Xu Zhang1,2 Chunhui Lv1,2
Chunhui Lv1,2 Zhenhao Ma1,2
Zhenhao Ma1,2 Yuanyuan Xue1,2
Yuanyuan Xue1,2 Qiang Lin4
Qiang Lin4 Kai Wang1,2*
Kai Wang1,2*by Zhang L, Wang F, Jia L, Yan H, Gao L, Tian Y, Su X, Zhang X, Lv C, Ma Z, Xue Y, Lin Q and Wang K (2023) Front. Immunol. 14:1135588. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1135588
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 2A as published. E9 1-4 and E21 1-4 should be changed to E9D 1-4 and E21D 1-4, respectively. The corrected Figure 2 and its caption appear below.
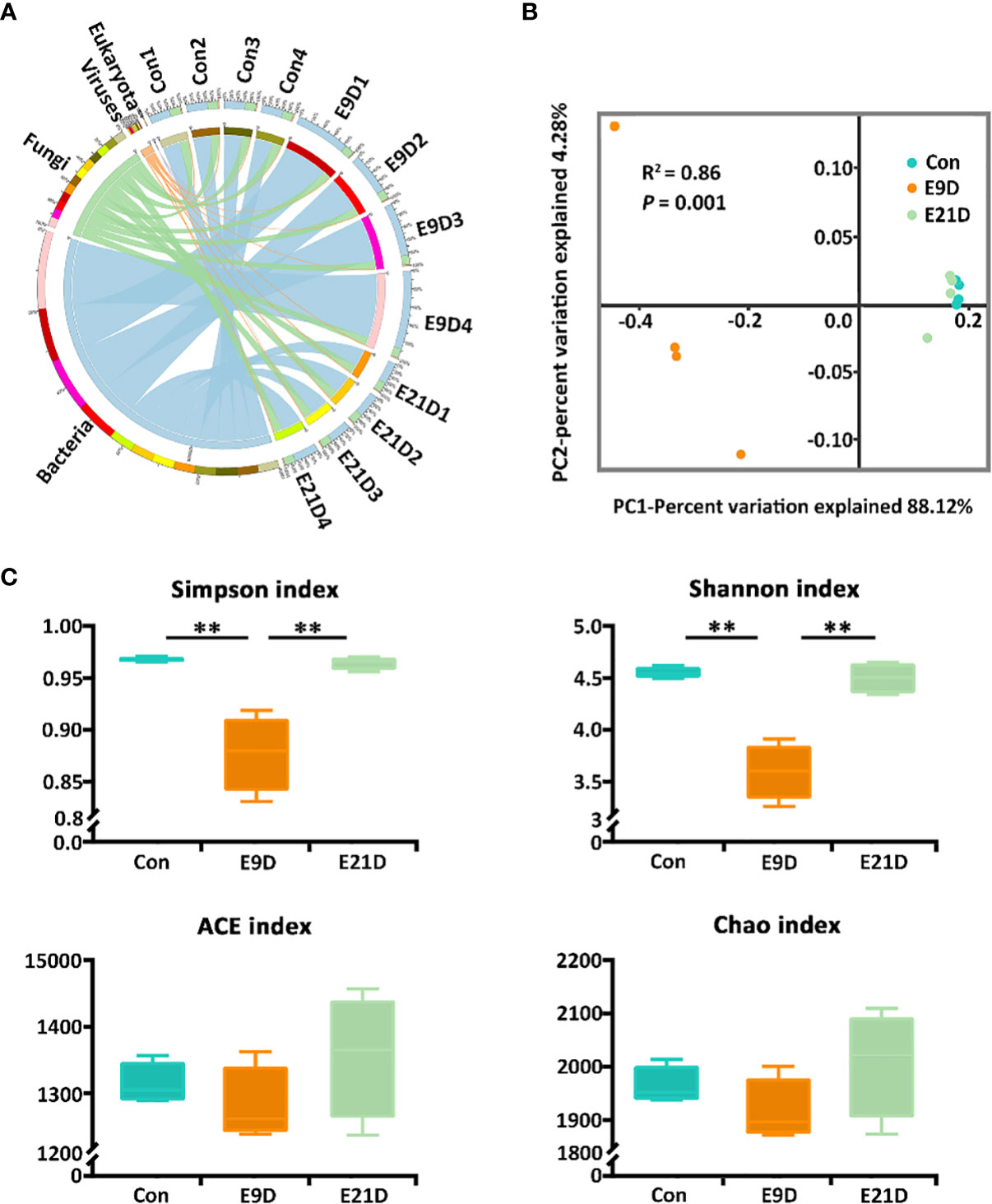
Figure 2 Effects of Edwardsiella piscicida infection on kingdom-level composition (A), structure (B), and diversity (C) of intestinal microbiota in big-belly seahorses. (B, C) represent bacterial intestinal microbiota at the species level. Con represents healthy controls (4.1–4.5 g, PSS); E9D and E21D represent the samples collected on days 9 and 21 of E. piscicida- challenged group (4.1–4.5 g, 1 × 105 cfu/mL), respectively (similarly hereinafter). **P < 0.01.
Figure 2. Effects of Edwardsiella piscicida infection on kingdom-level composition (A), structure (B), and diversity (C) of intestinal microbiota in big-belly seahorses. (B, C) represent bacterial intestinal microbiota at the species level. Con represents healthy controls (4.1–4.5 g, PSS); E9D and E21D represent the samples collected on days 9 and 21 of E. piscicida- challenged group (4.1–4.5 g, 1 × 105 cfu/mL), respectively (similarly hereinafter). ** P < 0.01.
In the published article, there was an error. A repeated and wrong sentence was found in the last paragraph of the Results section.
A correction has been made to 3 Results, 3.6 Molecular pathogenesis of E. piscicida-induced enteritis. This sentence previously stated: “In addition, seven of the eight KMBs L-Malic acid and L-Glutamate significantly decreased (P < 0.05) (Figures 7A; 4D left panel; 5C). In addition, seven of the eight KMBs with central roles were enriched and significantly negatively correlated with two key intestinal microbiota functions, TCS and ABC transporters (P < 0.05).”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“In addition, seven of the eight KMBs with central roles were enriched and significantly negatively correlated with two key intestinal microbiota functions, TCS and ABC transporters (P < 0.05).”
The authors apologize for these errors and state that they do not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: Edwardsiella piscicida, metagenome, metabolome, virulence factor, big-belly seahorse, pathogenesis
Citation: Zhang L, Wang F, Jia L, Yan H, Gao L, Tian Y, Su X, Zhang X, Lv C, Ma Z, Xue Y, Lin Q and Wang K (2023) Corrigendum: Edwardsiella piscicida infection reshapes the intestinal microbiome and metabolome of big-belly seahorses: mechanistic insights of synergistic actions of virulence factors. Front. Immunol. 14:1222662. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1222662
Received: 15 May 2023; Accepted: 05 June 2023;
Published: 15 June 2023.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Chou Min Chong, Putra Malaysia University, MalaysiaCopyright © 2023 Zhang, Wang, Jia, Yan, Gao, Tian, Su, Zhang, Lv, Ma, Xue, Lin and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kai Wang, d2FuZ2t5dEAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.