
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Immunol. , 25 April 2023
Sec. T Cell Biology
Volume 14 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1201876
This article is a correction to:
Intrahepatic infiltration of activated CD8+ T cells and mononuclear phagocyte is associated with idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury
 Hyun Yang1,2
Hyun Yang1,2 Ji Won Han1,3
Ji Won Han1,3 Jae Jun Lee1
Jae Jun Lee1 Ahlim Lee1,2
Ahlim Lee1,2 Sung Woo Cho1
Sung Woo Cho1 Pu Reun Rho1
Pu Reun Rho1 Min-Woo Kang1
Min-Woo Kang1 Jeong Won Jang1,3
Jeong Won Jang1,3 Eun Sun Jung4
Eun Sun Jung4 Jong Young Choi1,3
Jong Young Choi1,3 Pil Soo Sung1,3*
Pil Soo Sung1,3* Si Hyun Bae1,2*
Si Hyun Bae1,2*A Corrigendum on
Intrahepatic infiltration of activated CD8+ T cells and mononuclear phagocyte is associated with idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury
by Yang H, Han JW, Lee JJ, Lee A, Cho SW, Rho PR, Kang M-W, Jang JW, Jung ES, Choi JY, Sung PS and Bae SH (2023) Front. Immunol. 14:1138112. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1138112
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 3A as published. The X-axis and Y-axis labels of the sixth panel from the top and sixth panel from the bottom in Figure 3A were incorrectly displayed as “FSC-H” and “SSC-A”, respectively.
The correct labels for these panels should be “HLA-DR” and “CD38”, respectively. The corrected Figure 3A and its caption appear below.
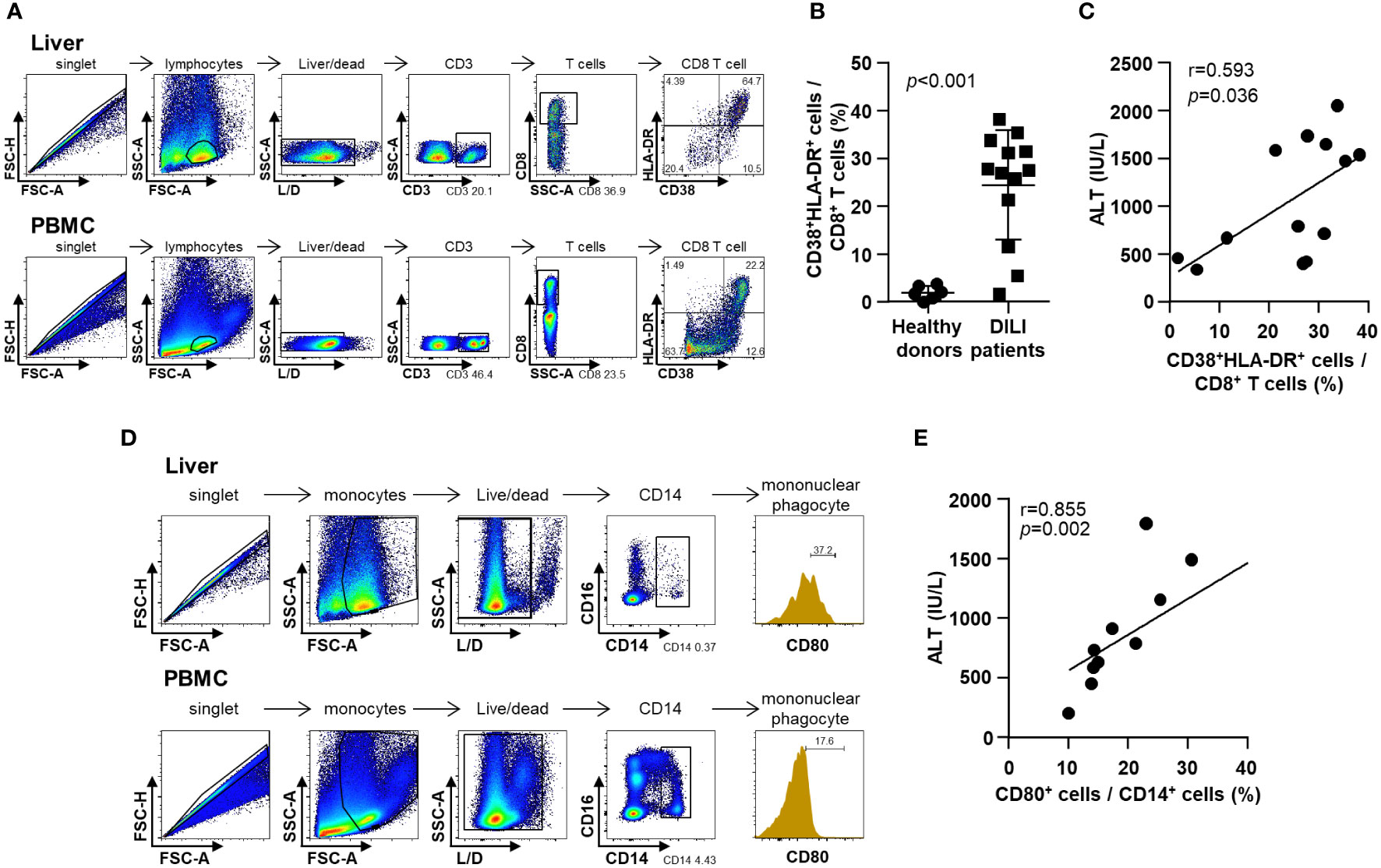
Figure 3 Phenotypes of infiltrative immune cells in the DILI livers. (A) Representative flow cytometry result of intrahepatic T cell activation in a patient with DILI. (B) Frequency of activated (CD38+HLA-DR+) CD8+ T cells in patients with DILI was significantly higher than that in healthy donors (p < 0.001). (C) Percentage of activated (CD38+HLA-DR+) CD8+ T cells in DILI livers was positively correlated with serum ALT (r = 0.593, p = 0.036). (D) Representative flow cytometry result of intrahepatic mononuclear phagocyte activation in a patient with DILI. (E) Percentage of activated (CD80+) CD14+ mononuclear phagocytes in the DILI livers was positively correlated with serum ALT (r = 0.855, p = 0.002). Correlations between variables were analyzed using Spearman or Pearson coefficients. PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; ALT, alanine aminotransferase.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: drug-induced liver injury, T cell, mononuclear phagocyte, flow cytometry, steroid
Citation: Yang H, Han JW, Lee JJ, Lee A, Cho SW, Rho PR, Kang M-W, Jang JW, Jung ES, Choi JY, Sung PS and Bae SH (2023) Corrigendum: Intrahepatic infiltration of activated CD8+ T cells and mononuclear phagocyte is associated with idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Front. Immunol. 14:1201876. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1201876
Received: 07 April 2023; Accepted: 13 April 2023;
Published: 25 April 2023.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Jing Wang, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, ChinaCopyright © 2023 Yang, Han, Lee, Lee, Cho, Rho, Kang, Jang, Jung, Choi, Sung and Bae. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Pil Soo Sung, cHNzdW5nQGNhdGhvbGljLmFjLmty; Si Hyun Bae, YmFlc2hAY2F0aG9saWMuYWMua3I=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.