
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Immunol. , 21 March 2023
Sec. Alloimmunity and Transplantation
Volume 14 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1183969
This article is a correction to:
The mast cell: A Janus in kidney transplants
 G. van der Elst1
G. van der Elst1 H. Varol1
H. Varol1 M. Hermans2
M. Hermans2 C. C. Baan3
C. C. Baan3 J. P. Duong-van Huyen4
J. P. Duong-van Huyen4 D. A. Hesselink3
D. A. Hesselink3 R. Kramann3,5,6
R. Kramann3,5,6 M. Rabant4
M. Rabant4 M. E. J. Reinders3
M. E. J. Reinders3 J. H. von der Thüsen1
J. H. von der Thüsen1 T. P. P. van den Bosch1†
T. P. P. van den Bosch1† M. C. Clahsen-van Groningen1,5*†
M. C. Clahsen-van Groningen1,5*†A Corrigendum on
The mast cell: A Janus in kidney transplants
By van der Elst G, Varol H, Hermans M, Baan CC, Duong-van Huyen JP, Hesselink DA, Kramann R, Rabant M, Reinders MEJ, von der Thüsen JH, van den Bosch TPP and Clahsen-van Groningen MC (2023) 14:1122409. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1122409
In the published article, there was an error in the legend for Figures 1, 2 as published. The legends of Figures 1, 2 were switched. The corrected legend appears below.
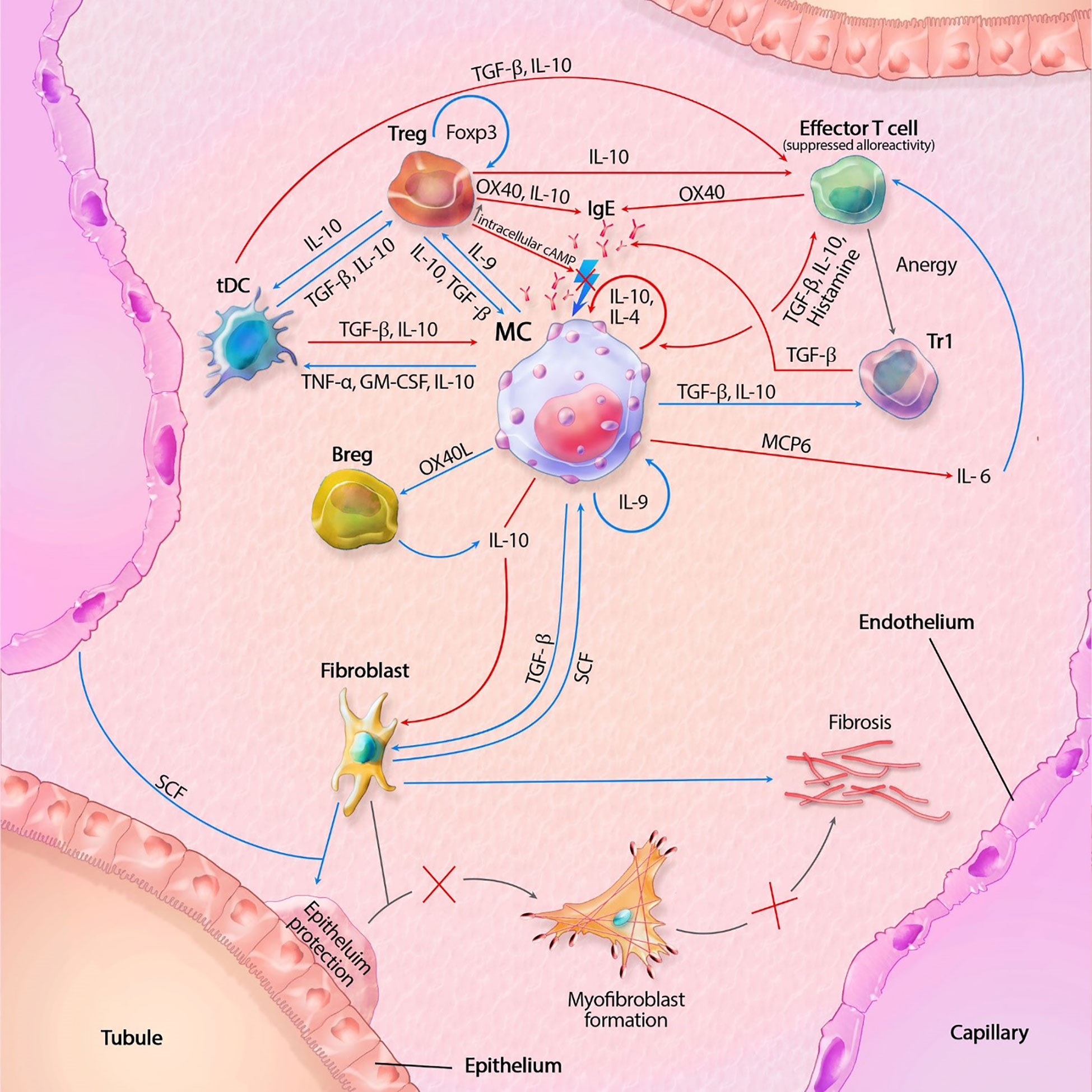
Figure 1 Mast cell (MC) interactions within the transplant during tolerance. FcϵRI activity is inhibited by TGF-β, IL-10 and OX40 ligation. Tregs also inhibit degranulation by lowering intracellular Ca2+ levels through increased cAMP. IL-10 suppresses alloreactivity within CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and promote anergy and regulatory functions of CD4+ T cells. IL-10 mediated inhibition of fibroblasts also inhibit subsequent formation of myofibroblasts. IL-10 with co-stimulation of IL-4 decrease MC proliferation, while IL-9 increases proliferation. GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IL, interleukin; MCP6, mat cell protease 6; SCF, stem cell factor; tDC, tolerogenic dendritic cell; TGF-β, tissue growth factor beta; TNF-α, tissue necrotic factor alpha; Tr1, regulatory T cell type 1 (induced); Treg, regulatory T cell (natural); Blue lines symbolize activating pathways, red lines inhibitory pathways, gray lines symbolize subsequent events. Lighting icons are used in the most profound activation patterns, which are inhibited in tolerogenic environments.
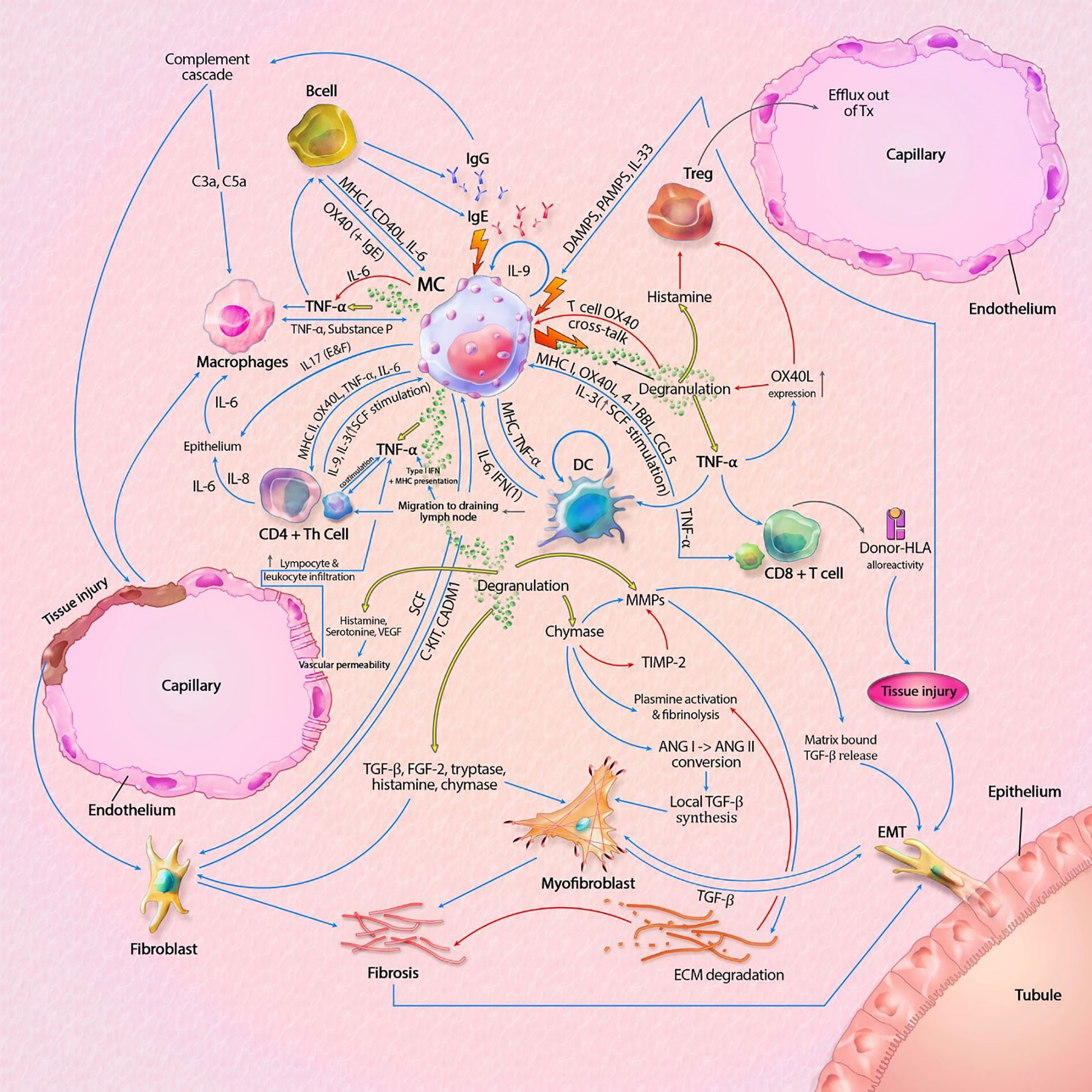
Figure 2 Mast cell (MC) interactions within the graft during rejection. Pathways can include both cytokines (like TNF-α) and membrane bound interaction (like MHC I-TLR interaction). MC-T cell interaction through OX40L-OX40 cross-linking inhibits MC degranulation, represented by the inhibitory pathway towards degranulation. Innate immune cells can also result in tissue injury, which is not shown in this model. Interaction between APCs, T cells and B cells, resulting in antigen production is also not shown in this model. The model shows almost no inhibitory pathways, explaining the progressive state of fibrosis within KTx even when immunosuppressive drugs are taken. Detailed description of the model can be found within the text. ANG, angiotensin; C3a/C5a, complement component; ECM, extracellular matrix; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; FGF-2; fibroblast growth factor-2; Ig, immunoglobulin; IL, interleukin; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinase; SCF, stem cell factor; tDC, tolerogenic dendritic cell; TGF-β, tissue growth factor beta; Th cell, T helper cell; TIMP-2, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2; TNF-α, tissue necrotic factor alpha; Treg, regulatory T cell (natural); VEGF, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Blue lines symbolize activating pathways, red lines inhibitory pathways, yellow lines represent pre-formed mediators within MCs. Grey lines represent subsequent events. Lighting icons are used in the most profound activation patterns.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: mast cell (MC), kidney transplant, rejection, fibrosis, tolerance
Citation: van der Elst G, Varol H, Hermans M, Baan CC, Duong-van Huyen JP, Hesselink DA, Kramann R, Rabant M, Reinders MEJ, von der Thüsen JH, van den Bosch TPP and Clahsen-van Groningen MC (2023) Corrigendum: The mast cell: A Janus in kidney transplants. Front. Immunol. 14:1183969. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1183969
Received: 10 March 2023; Accepted: 13 March 2023;
Published: 21 March 2023.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2023 van der Elst, Varol, Hermans, Baan, Duong-van Huyen, Hesselink, Kramann, Rabant, Reinders, von der Thüsen, van den Bosch and Clahsen-van Groningen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: M. C. Clahsen-van Groningen, bS5jbGFoc2VuLXZhbmdyb25pbmdlbkBlcmFzbXVzbWMubmw=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share senior authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.