
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Immunol. , 14 March 2023
Sec. Inflammation
Volume 14 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1181215
This article is a correction to:
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote murine skin wound healing by neutrophil and macrophage modulations revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing
 Yuanyuan Liu1,2†
Yuanyuan Liu1,2† Mingwang Zhang3†
Mingwang Zhang3† Yong Liao2
Yong Liao2 Hongbo Chen4
Hongbo Chen4 Dandan Su4
Dandan Su4 Yuandong Tao5
Yuandong Tao5 Jiangbo Li6
Jiangbo Li6 Kai Luo7
Kai Luo7 Lihua Wu7
Lihua Wu7 Xingyue Zhang2‡
Xingyue Zhang2‡ Rongya Yang2*‡
Rongya Yang2*‡by Liu Y, Zhang M, Liao Y, Chen H, Su D, Tao Y, Li J, Luo K, Wu L, Zhang X and Yang R (2023) Front. Immunol. 14:1142088. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1142088
In the published article, there was an error in the legend for Figure 1 as published. The legend for Figure 1A was missing and the legend for Figures 1A–F was misaligned. The corrected legend appears below.
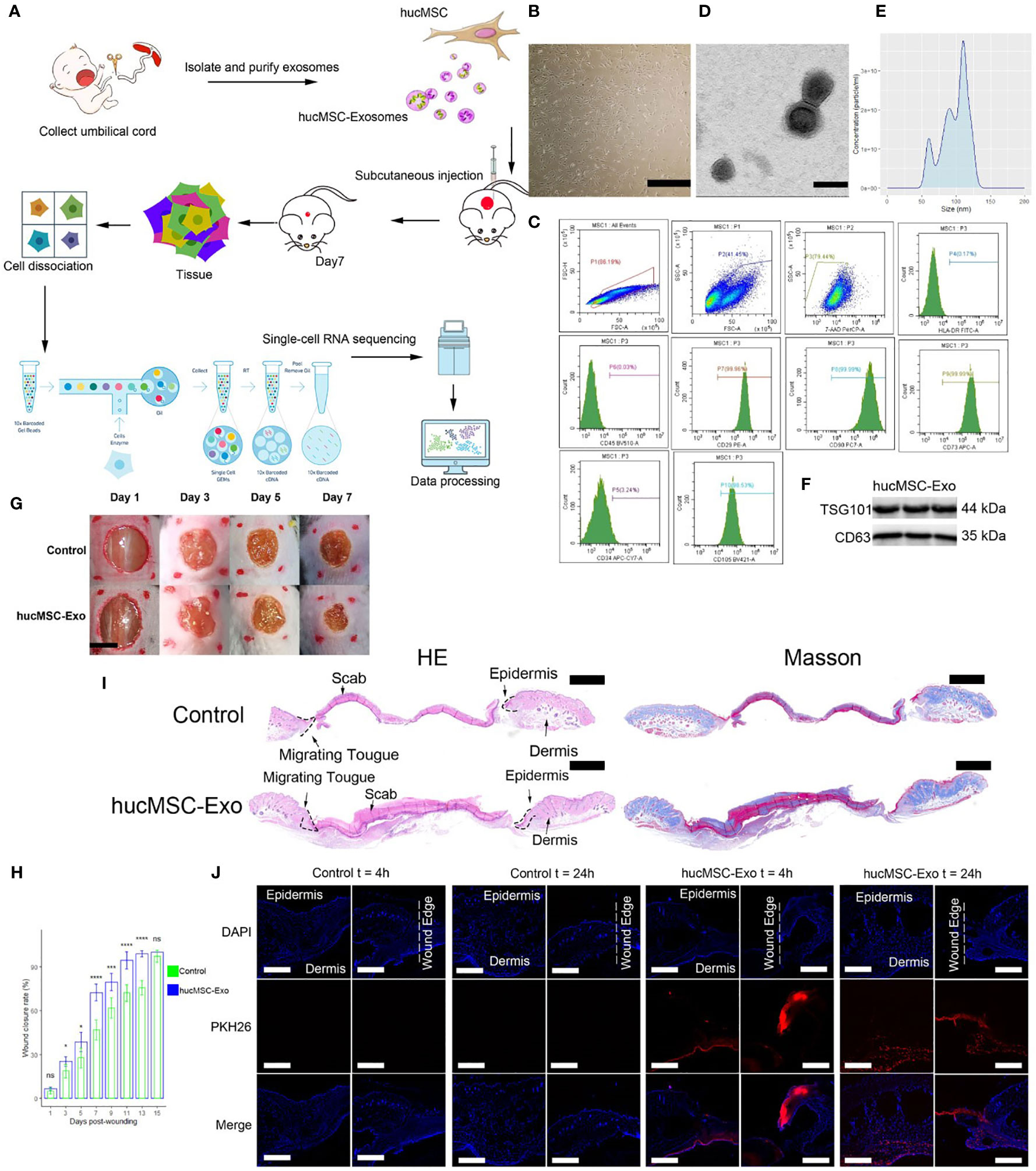
Figure 1 HucMSC-Exosomes accelerate wound healing. (A) Schematic overview of the study design. (B) Microscope image of huc-MSCs. The scale bar is 500 µm. (C) Flow cytometry analysis of HLA, CD29, CD34, CD45, CD73, CD90 and CD105 expression on the huc-MSC surface. (D) Transmission electron microscopy image of hucMSC-Exosomes. Scale bar, 100 nm. (E) Density plot of hucMSC-Exosomes. (F) Western blot of hucMSC-Exosome markers (G) Representative images of wound closure process of hucMSC-Exosomes treatment and PBS control. The scale bar is 4 mm. (H) Wound closure rate of hucMSC-Exosomes treatment and PBS control group. Two-tailed unpaired t-test (n=6). Error bar: mean standard deviation. Ns, not significant, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. (I) H & E and Masson staining of wounds seven days after injury. Scale bar = 1mm. (J) Uptake of hucMSC-Exosome by skin wound in vivo. Scale bar, 500μm.
“HucMSC-Exosomes accelerate wound healing. (A) Schematic overview of the study design. (B) Microscope image of huc-MSCs. The scale bar is 500 µm. (C) Flow cytometry analysis of HLA, CD29, CD34, CD45, CD73, CD90 and CD105 expression on the huc-MSC surface. (D) Transmission electron microscopy image of hucMSC-Exosomes. Scale bar, 100 nm. (E) Density plot of hucMSC-Exosomes. (F) Western blot of hucMSC-Exosome markers (G) Representative images of wound closure process of hucMSC-Exosomes treatment and PBS control. The scale bar is 4 mm. (H) Wound closure rate of hucMSC-Exosomes treatment and PBS control group. Two-tailed unpaired t-test (n=6). Error bar: mean standard deviation. ns, not significant, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. (I) H & E and Masson staining of wounds seven days after injury. Scale bar = 1mm. (J) Uptake of hucMSC-Exosome by skin wound in vivo. Scale bar, 500μm.”
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: exosomes, wound healing, single-cell RNA sequencing, cellular heterogeneity, neutrophils, macrophages
Citation: Liu Y, Zhang M, Liao Y, Chen H, Su D, Tao Y, Li J, Luo K, Wu L, Zhang X and Yang R (2023) Corrigendum: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote murine skin wound healing by neutrophil and macrophage modulations revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing. Front. Immunol. 14:1181215. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1181215
Received: 07 March 2023; Accepted: 08 March 2023;
Published: 14 March 2023.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2023 Liu, Zhang, Liao, Chen, Su, Tao, Li, Luo, Wu, Zhang and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rongya Yang, cm9uZ3lheWFuZzk2MEBvdXRsb29rLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
‡These authors have contributed equally to this work and share last authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.