PHLDA1 Suppresses TLR4-Triggered Proinflammatory Cytokine Production by Interaction With Tollip
- 1Department of Cell Biology and Genetics, Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology in High Cancer Incidence Coastal Chao Shan Area of Guang Dong Higher Education Institutes, Shantou University Medical College, Shantou, China
- 2Department of Clinical Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise, China
- 3Department of Pathophysiology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise, China
A Corrigendum on:
PHLDA1 Suppresses TLR4-Triggered Proinflammatory Cytokine Production by Interaction With Tollip
by Peng H, Wang J, Song X, Huang J, Hua H, Wang F, Xu Z, Ma J, Gao J, Zhao J, Nong A, Huang D and Liang B (2022). Front. Immunol. 13:731500. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.731500
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 3 as published. “ERK and JNK” was wrongly written as “ERK1/2 and JNK1/2”. The corrected Figure 3 appears below.
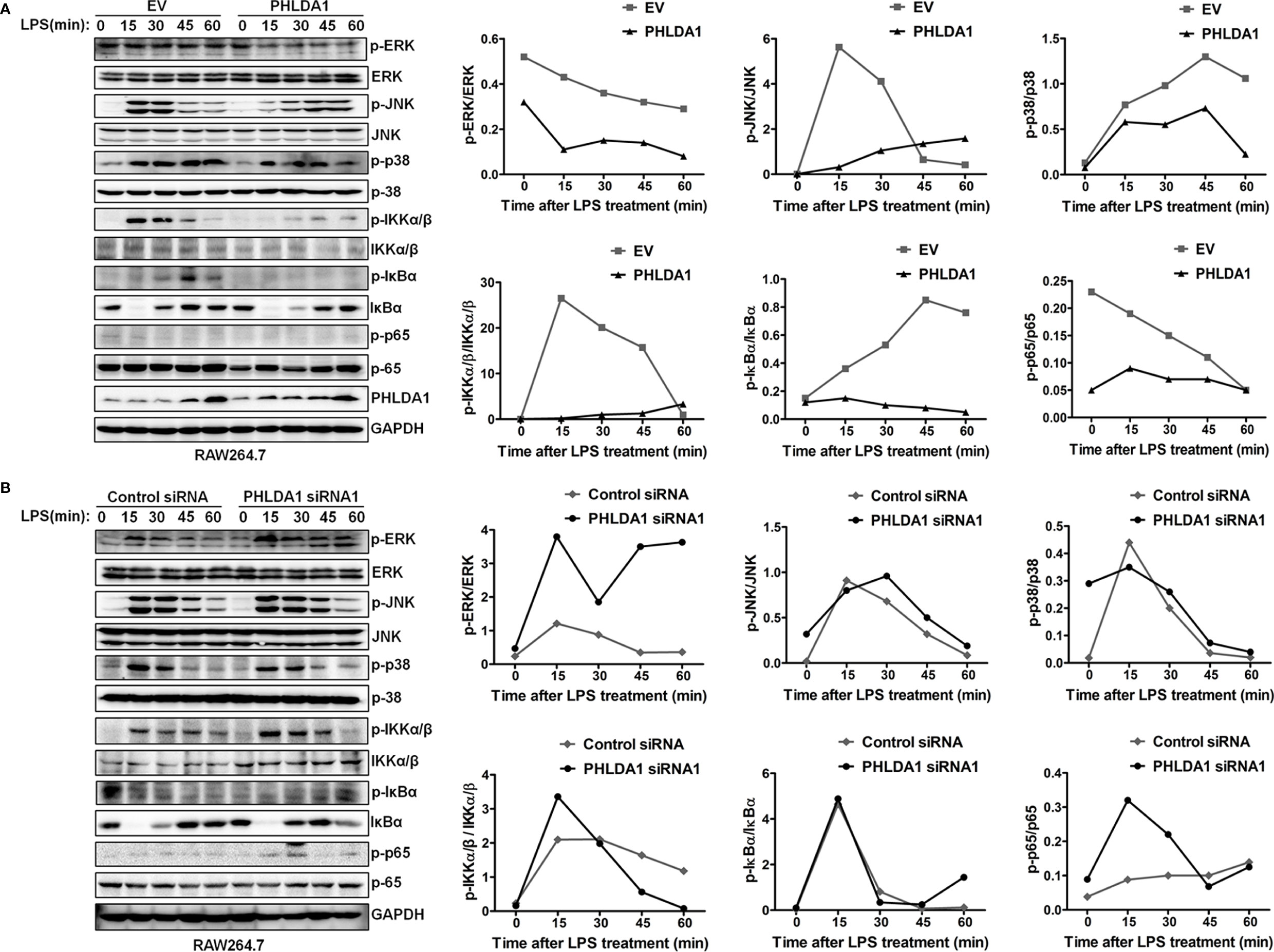
Figure 3 PHLDA1 attenuates the activation of some signal molecules in MyD88-dependent TLR4 signaling pathway. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with EV or PHLDA1 plasmid, and then stimulated with LPS (0.1 μg/ml) for the indicated times. Phosphorylation levels and total protein expressions of important signal molecules (ERK, JNK, p38, IKKα/β, IkBa and p65) in cell lysates were analyzed using Western blot. (B) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with Control siRNA or PHLDA1 siRNA1, and then stimulated with LPS (0.1 μg/ml) for the indicated times. Phosphorylation levels and total protein expressions of the above molecules were analyzed using Western blot. Data shown are presentative of three independent experiments. Phosphorylation levels of the above molecules were quantitated and shown in the right panel. GAPDH was used as a loading control.
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 4 as published. Figures 4B, F were unintentionally flipped over. The corrected Figure 4 appears below.
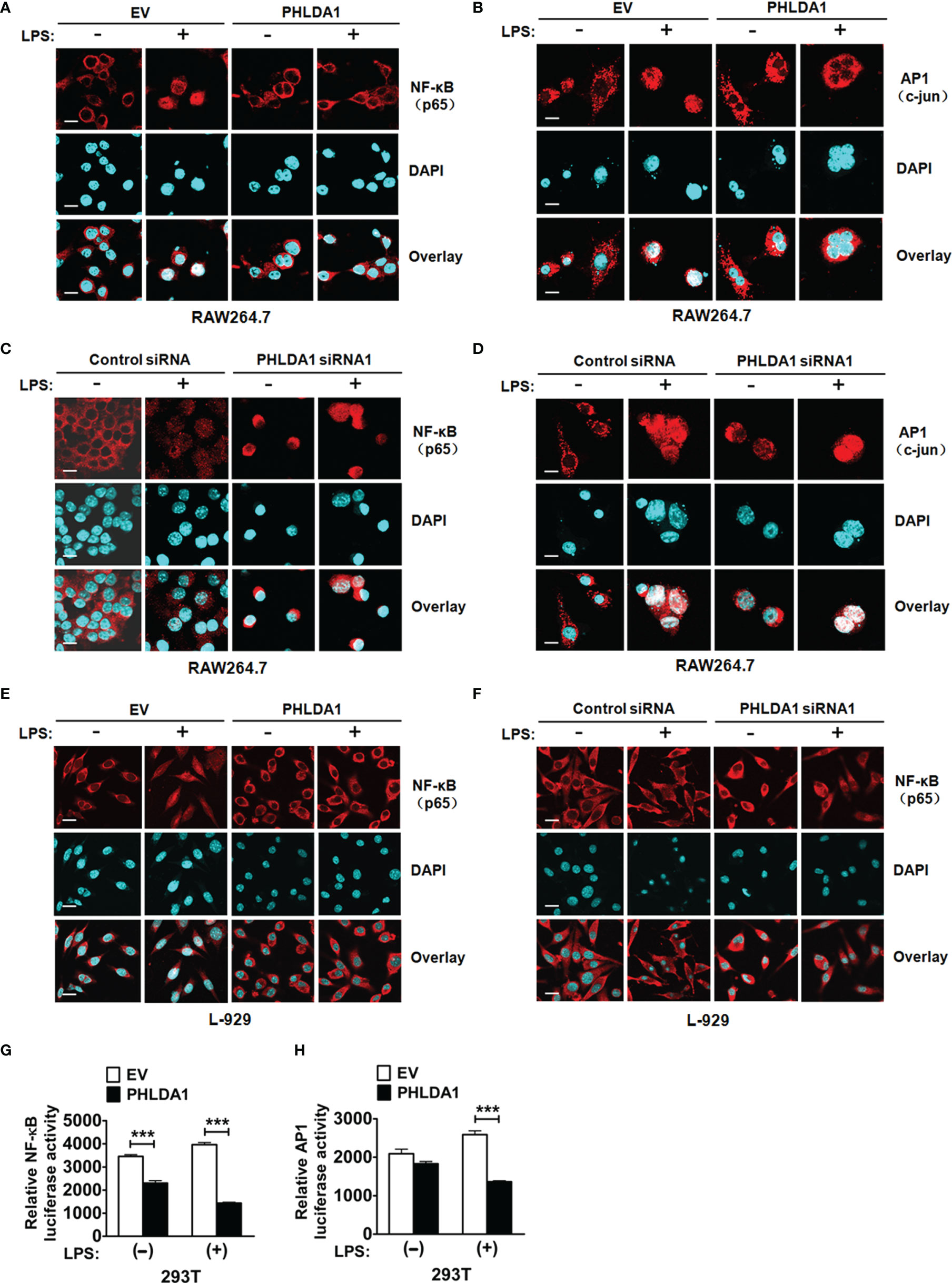
Figure 4 PHLDA1 attenuates LPS-initiated nuclear translocations and responsive element activities of NF-κB and AP1. RAW264.7 cells (A, B) and L-929 cells (E) were transfected with EV or PHLDA1 plasmid, and then stimulated with or without LPS (0.1 μg/ml) for 1 h. Cells were immunostained with anti-NF-κB (p65) antibody or anti-AP1 (c-jun) antibody and Alexa-594-labeled secondary antibodies. The nuclei were stained with DAPI for 15 min. The merged images were captured with a confocal microscope (scale bar, 20 μm). RAW264.7 cells (C, D) and L-929 cells (F) were transfected with Control siRNA or PHLDA1 siRNA1, and then stimulated with or without LPS (0.1 μg/ml) for 1 h. Cells were immunostained with anti-NF- B (p65) antibody or anti-AP1 (c-jun) antibody and Alexa-594-labeled secondary antibodies. The nuclei were stained with DAPI for 15 min. The merged images were captured with a confocal microscope (scale bar, 20 μm). (G, H) EV or PHLDA1 plasmid was transfected into 293T cells together with pTK–Renilla luciferase and NF-κB luciferase reporter plasmids. After 24 h of culture, the cells were incubated with LPS (0.1 μg/ml) for 20 h. The Dual-Luciferase® Reporter (DLR™) Assay System was performed to measure NF-κB or AP1 luciferase activity. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments (***P < 0.001).
The authors apologize for these errors and state that they do not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: PHLDA1, TLR4, suppress, proinflammatory cytokine, Tollip
Citation: Peng H, Wang J, Song X, Huang J, Hua H, Wang F, Xu Z, Ma J, Gao J, Zhao J, Nong A, Huang D and Liang B (2022) Corrigendum: PHLDA1 Suppresses TLR4-Triggered Proinflammatory Cytokine Production by Interaction With Tollip. Front. Immunol. 13:877352. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.877352
Received: 23 February 2022; Accepted: 01 March 2022;
Published: 15 March 2022.
Edited and reviewed by:
Janos G. Filep, Université de Montréal, CanadaCopyright © 2022 Peng, Wang, Song, Huang, Hua, Wang, Xu, Ma, Gao, Zhao, Nong, Huang and Liang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bin Liang, bliang@stu.edu.cn; Dongyang Huang, huangdy@stu.edu.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Hui Peng
Hui Peng Juping Wang3†
Juping Wang3† Anna Nong
Anna Nong Dongyang Huang
Dongyang Huang Bin Liang
Bin Liang