
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Immunol. , 12 September 2022
Sec. Inflammation
Volume 13 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1011789
This article is a correction to:
The Cholesterol-Binding Sequence in Monomeric C-Reactive Protein Binds to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain and Blocks Interaction With Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2
by Li H-y, Gao N, Liu C-y, Liu X-l, Wu F, Dai N, Han J and Li Q-y (2022) Front. Immunol. 13:918731. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.918731
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 5D as published. The positive control of Figure 5D was misplaced. The positive control of Figure 5D has been replaced with the correct version. The corrected Figure 5D and its caption appear below.
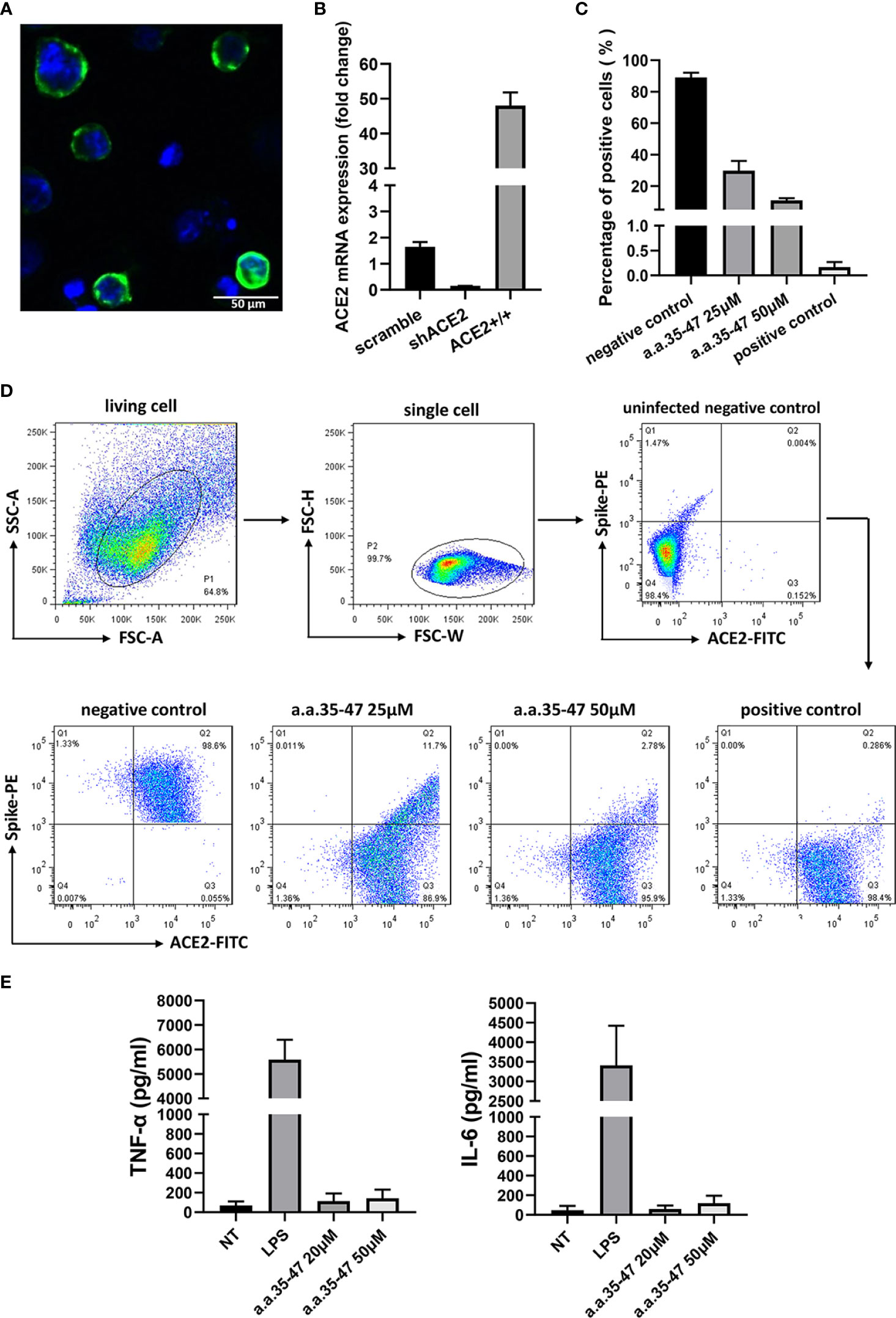
Figure 5 CBS inhibits the spike RBD from binding to cell surface ACE2. (A) Immunofluorescence of the A549 cells stably expressing ACE2. Green fluorescence indicates ACE2-mNEOGreen and blue indicates DAPI. (B) mRNA expression of ACE2-overexpressing (ACE2+/+) and knockdown (shACE2) cell lines (n = 3). (C) Results of flow cytometry showing that CBS inhibits the interaction between the spike RBD and ACE2 at the cellular level (n = 3). Lomefloxacin acted as the positive control and untreated cells served as the negative control. (D) Schematic showing the flow cytometry gating process and typical flow cytometry diagrams of different concentrations of CBS-treated cells and controls. (E) CBS itself did not induce the release of cytokines from immune cells. Immortalized bone marrow-derived macrophages (iBMDM) were stimulated with different concentrations of CBS, and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was used as the positive control (n = 3). Results showed that the CBS itself did not stimulate cells. All results are presented as means ± S.E.M.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2, monomeric C-reactive protein, pattern recognition receptor, ACE2, cholesterol-binding sequence
Citation: Li H-y, Gao N, Liu C-y, Liu X-l, Wu F, Dai N, Han J and Li Q-y (2022) Corrigendum: The cholesterol-binding sequence in monomeric C-reactive protein binds to the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain and blocks interaction with Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. Front. Immunol. 13:1011789. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1011789
Received: 04 August 2022; Accepted: 16 August 2022;
Published: 12 September 2022.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Alok Agrawal, East Tennessee State University, United StatesCopyright © 2022 Li, Gao, Liu, Liu, Wu, Dai, Han and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qiu-yu Li, bGlxaXV5dTAwQGJqbXUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.