
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Immunol. , 06 January 2022
Sec. Alloimmunity and Transplantation
Volume 12 - 2021 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.825243
This article is a correction to:
Non-Invasive Diagnosis for Acute Rejection Using Urinary mRNA Signature Reflecting Allograft Status in Kidney Transplantation
 Jung-Woo Seo1,2
Jung-Woo Seo1,2 Yu-Ho Lee2
Yu-Ho Lee2 Dong Hyun Tae3
Dong Hyun Tae3 Seon Hwa Park2
Seon Hwa Park2 Ju-Young Moon2,4
Ju-Young Moon2,4 Kyung Hwan Jeong4
Kyung Hwan Jeong4 Chan-Duck Kim5
Chan-Duck Kim5 Byung Ha Chung6
Byung Ha Chung6 Jae Berm Park7
Jae Berm Park7 Yeong Hoon Kim8
Yeong Hoon Kim8 Junhee Seok3
Junhee Seok3 Sun Hyung Joo9
Sun Hyung Joo9 Seung Hwan Lee9
Seung Hwan Lee9 Jong Soo Lee10
Jong Soo Lee10 Sang-Ho Lee2,4*
Sang-Ho Lee2,4*A Corrigendum on:
Non-Invasive Diagnosis for Acute Rejection Using Urinary mRNA Signature Reflecting Allograft Status in Kidney Transplantation
by Seo J-W, Lee YH, Tae DH, Park SH, Moon J-Y, Jeong KH, Kim C-D, Chung BH, Park JB, Kim YH, Seok J, Joo SH, Lee SH, Lee JS and Lee S-H. (2021). Front. Immunol. 12:656632. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.656632
In the original article, we neglected to include “This work was supported by the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant no. HI13C1232) and by the National Research Foundation of Korea Grant funded by the Korean government, Ministry of Science, and ICT (grant no. 2018M3A9E8078807)”.
In the original article, there was a mistake in the legend for Figure 2A as published. Incorrect word use in the legend changed the meaning of the statement. The correct legend appears below.
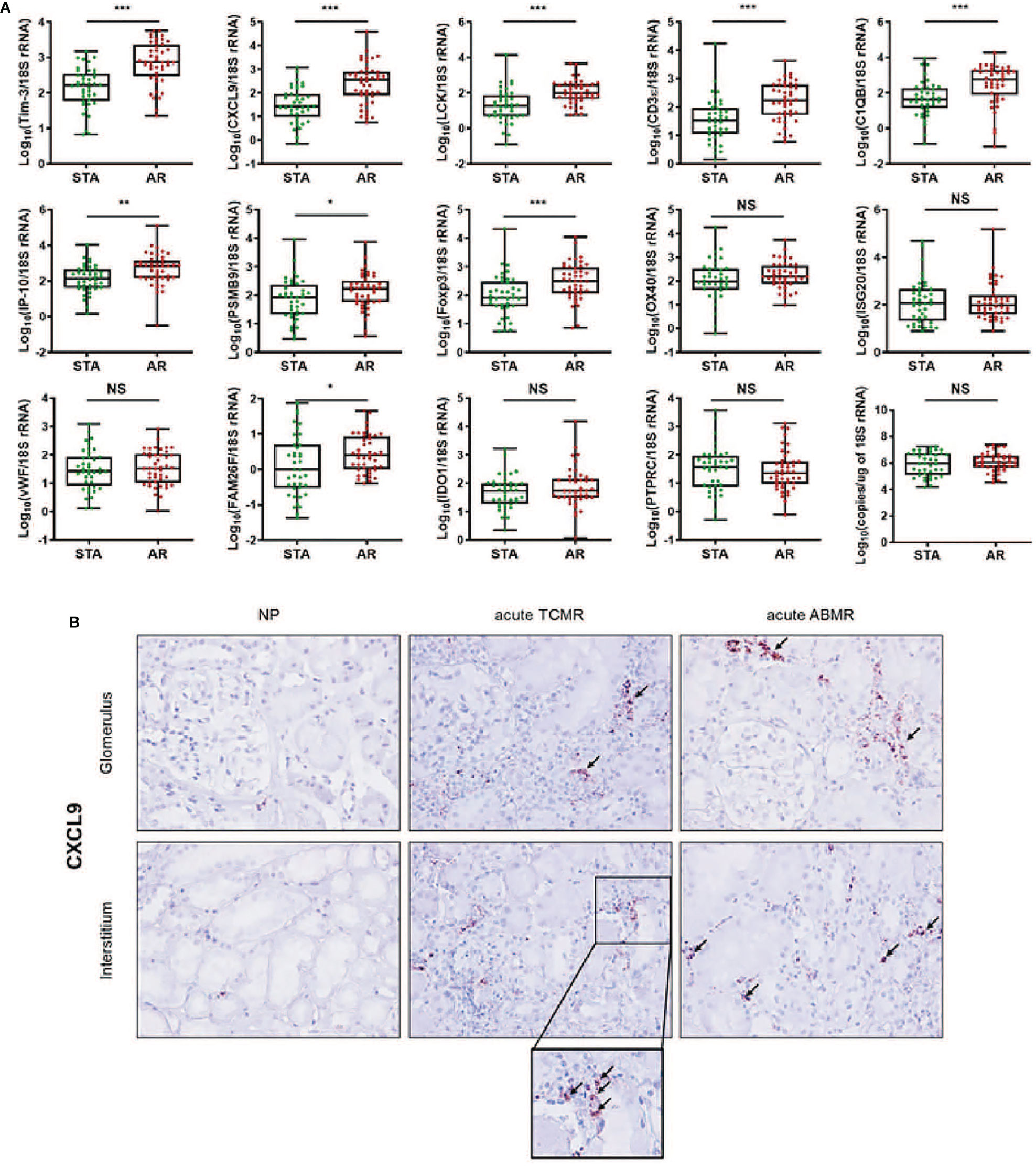
Figure 2 The expression levels of each mRNA between STA (n=45) and AR (n=58) were analyzed using absolute quantitative qPCR without pre-amplification. Each mRNA level was log10-transformed after each mRNA copy number was normalized with 18S rRNA copies (x10-6) in the QC-passed samples (STA, n=40; AR, n=44). (A) The levels of CXCL9, IP-10, C1QB, PSMB9, LCK, CD3ε, Foxp3, FAM26F, and Tim-3 mRNAs were significantly elevated in AR compared to STA, and for OX40, ISG20, vWF, IDO1, and PTPRC mRNAs, there was no difference. In the 18s rRNA used as an endogenous control, there was no difference between AR and STA. P values by the non-parametric Mann-Whitney test were expressed as the mean ± SE. NS: not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 versus STA. Although LCK, Foxp3, and FAM26F mRNAs were statistically significant, these mRNAs were not detected in more than 10% of the QC-passed samples. Therefore, we excluded these mRNAs for further analysis. (B) CXCL9 mRNA expression in kidney biopsy tissues of NP, acute TCMR and acute ABMR groups was examined by ISH (original magnification x400). CXCL9 was distinctly expressed in the damaged tubules in kidney allografts of acute TCMR and predominantly in the peritubular capillary area in ABMR groups (black arrows). Scale bars: 50 μm.
In the published article, there was an error in affiliation 1. Instead of “Department of Core Research Laboratory, Medical Science Institute, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, South Korea”, it should be “Core Research Laboratory, Medical Science Institute, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, South Korea”.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that they do not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: kidney, transplantation, non-invasive diagnosis, acute rejection, urinary mRNA
Citation: Seo J-W, Lee Y-H, Tae DH, Park SH, Moon J-Y, Jeong KH, Kim C-D, Chung BH, Park JB, Kim YH, Seok J, Joo SH, Lee SH, Lee JS and Lee S-H (2022) Corrigendum: Non-Invasive Diagnosis for Acute Rejection Using Urinary mRNA Signature Reflecting Allograft Status in Kidney Transplantation. Front. Immunol. 12:825243. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.825243
Received: 30 November 2021; Accepted: 13 December 2021;
Published: 06 January 2022.
Edited and reviewed by:
Xianding Wang, Sichuan University, ChinaCopyright © 2022 Seo, Lee, Tae, Park, Moon, Jeong, Kim, Chung, Park, Kim, Seok, Joo, Lee, Lee and Lee. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sang-Ho Lee, bHNoa2lkbmV5QGtodS5hYy5rcg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.