Humanized Mice for the Evaluation of Novel HIV-1 Therapies
- 1Department of Immunology and Microbiology, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA, United States
- 2The Skaggs Graduate Program in Chemical and Biological Sciences, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA, United States
A Corrigendum on:
Humanized Mice for the Evaluation of Novel HIV-1 Therapies
By Abeynaike S and Paust S (2021). Front. Immunol. 12:636775. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.636775
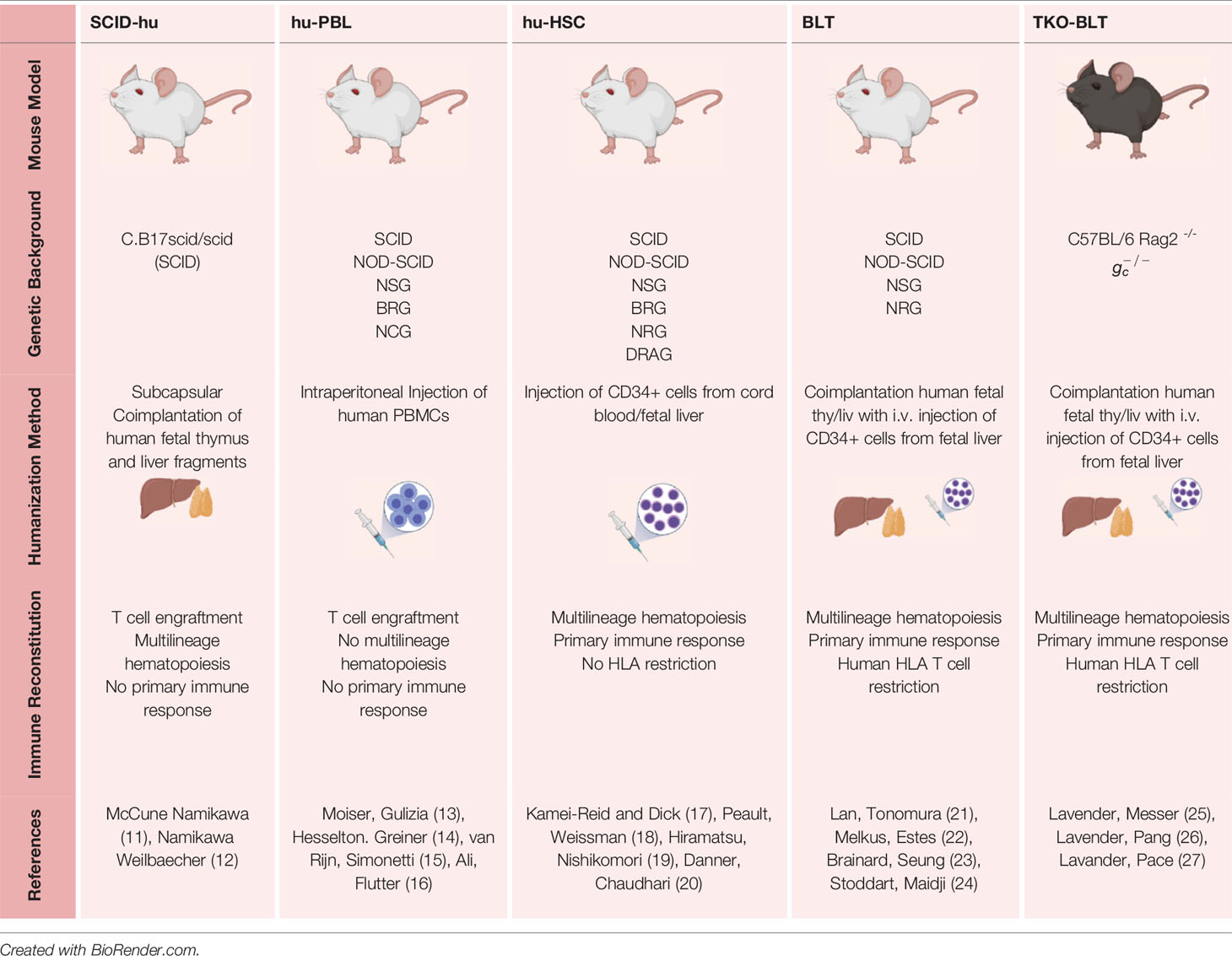
In the original article, there was a mistake in Table 1 as published. The authors incorrectly categorized thy/liv implanted SCID-hu mice as showing no multilineage hematopoeisis. To clarify, Namikawa 1990, showed that SCID mice implanted with both Thy/Liv displayed multilineage hematopoiesis. Specifically, they showed in addition to T cells (CD3, CD4 and CD8), the presence of mature and immature forms of myelomonocytic cells which stained positive for human CD15, as well as progenitors for erythroids and megakaryocytic lineages (1).
The corrected Table 1 appears below.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Reference
Keywords: humanized mice, BLT, DRAG, HIV-1 infection, viral latency, latency reversal, immunotherapy, gene therapy
Citation: Abeynaike S and Paust S (2021) Corrigendum: Humanized Mice for the Evaluation of Novel HIV-1 Therapies. Front. Immunol. 12:808068. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.808068
Received: 03 November 2021; Accepted: 08 November 2021;
Published: 06 December 2021.
Edited and reviewed by:
Qingfeng Chen, Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology (A*STAR), SingaporeCopyright © 2021 Abeynaike and Paust. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Silke Paust, paust@scripps.edu
 Shawn Abeynaike
Shawn Abeynaike Silke Paust
Silke Paust