- 1Medawar Building for Pathogen Research, Nuffield Department of Medicine, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom
- 2Department of Infectious Diseases and Microbiology, Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford, United Kingdom
- 3Oxford BRC, John Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford, United Kingdom
- 4Nuffield Department of Medicine, Big Data Institute, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom
Chronic viral hepatitis infections are a major public health concern, with an estimated 290 million individuals infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) globally. This virus has been a passenger in human populations for >30,000 years, and remains highly prevalent in some settings. In order for this endemic pathogen to persist, viral adaptation to host immune responses is pre-requisite. Here, we focus on the interplay between HBV infection and the CD8+ T cell response. We present the evidence that CD8+ T cells play an important role in control of chronic HBV infection and that the selective pressure imposed on HBV through evasion of these immune responses can potentially influence viral diversity, chronicity, and the outcome of infection, and highlight where there are gaps in current knowledge. Understanding the nature and mechanisms of HBV evolution and persistence could shed light on differential disease outcomes, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, and help reach the goal of global HBV elimination by guiding the design of new strategies, including vaccines and therapeutics.
Introduction
Within hosts, viruses with high mutation rates can rapidly adapt to the selection pressures placed upon them, including natural and vaccine induced immune responses, and antiviral therapy. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) represents a substantial international public health challenge, with an estimated 290 million people chronically infected globally (1). In this review, we explore the evidence for HBV escape from the CD8+ T cell response and examine the influence this process could have on infection outcomes.
Hepatitis B virus belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family of small, enveloped, primarily hepatotropic viruses. At only 3,200 bp, HBV has one of the smallest genomes of all known pathogenic viruses. The partially double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) circular genome consists of four genes, X, Polymerase (P), Core (C), and Surface (S), and a high proportion of the genome is encoded on overlapping open reading frames (Figure 1). During transcription, the partially dsDNA genome is “completed” to form a fully dsDNA molecule, which is subsequently supercoiled to form covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA). This cccDNA is reverse transcribed by HBV reverse transcriptase (RT), an enzyme lacking 3′–5′ exonuclease proof-reading capacity, and therefore introducing mutations into the HBV genome during each round of replication [in duck hepadnavirus, the mutation rate is estimated at between 0.8 × 10−5 and 4.5 × 10−5 substitutions per nucleotide per replication (2)]. The mutations generated result in a viral quasispecies, comprised of dominant genotype(s) surrounded by clouds of closely related HBV variants.
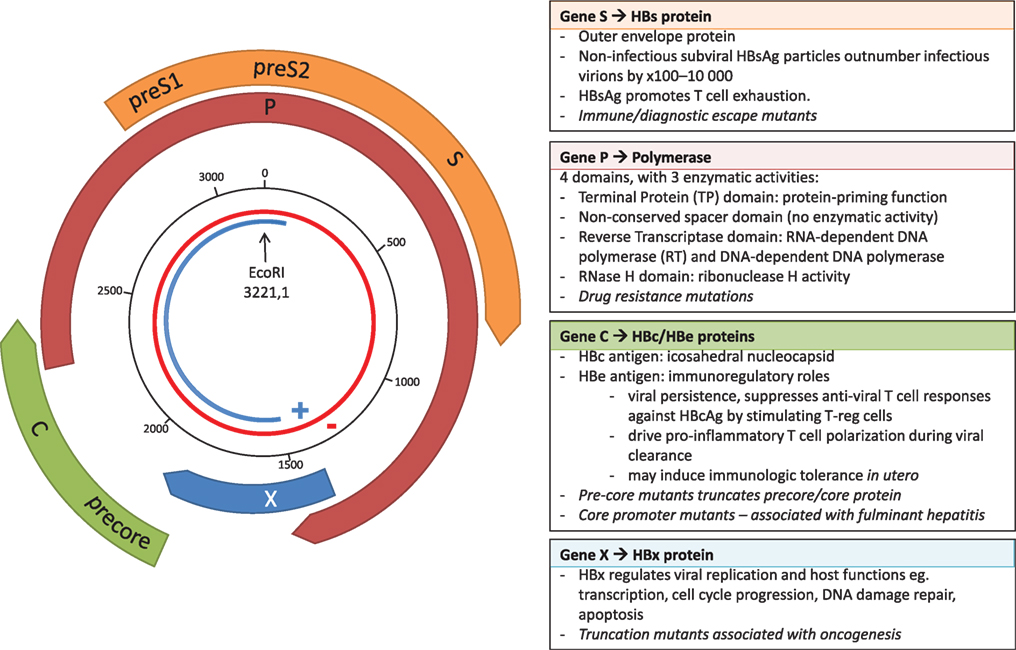
Figure 1. The overlapping genome structure of hepatitis B virus (HBV). The partially double-stranded circular DNA genome is shown with the negative strand in red and the positive strand in blue. The black numbered circle indicates the nucleotide position. The four genes, X, Polymerase (P), Core (C), and Surface (S) are represented by the thick colored arrows, with the main functional roles of the four genes shown in the boxes, and key impact of mutations shown in italics.
The error prone RT, coupled with high rates of HBV replication [estimated at between 200 and 1,000 virions/hepatocyte/day at the peak of infection (3)] results in the production of a large number of virions harboring mutations. The vast majority of mutations are likely to be deleterious, some are neutral, and a minority provide the virus with a potential selective advantage, such as escape from CD8+ T cell-mediated responses. However, HBV polymorphisms are constrained by the overlapping reading frame structure of the genome, since the majority of mutations can simultaneously affect multiple genes [these have been described as “mirror” mutations (4), Figure 2]. Mutations that are neutral or beneficial for one protein might be detrimental for another. Accordingly, overlapping regions of the HBV genome generally have less diversity compared to non-overlapping regions (5) and the within-host rate of evolution at overlapping regions is about half that of non-overlapping regions (6).
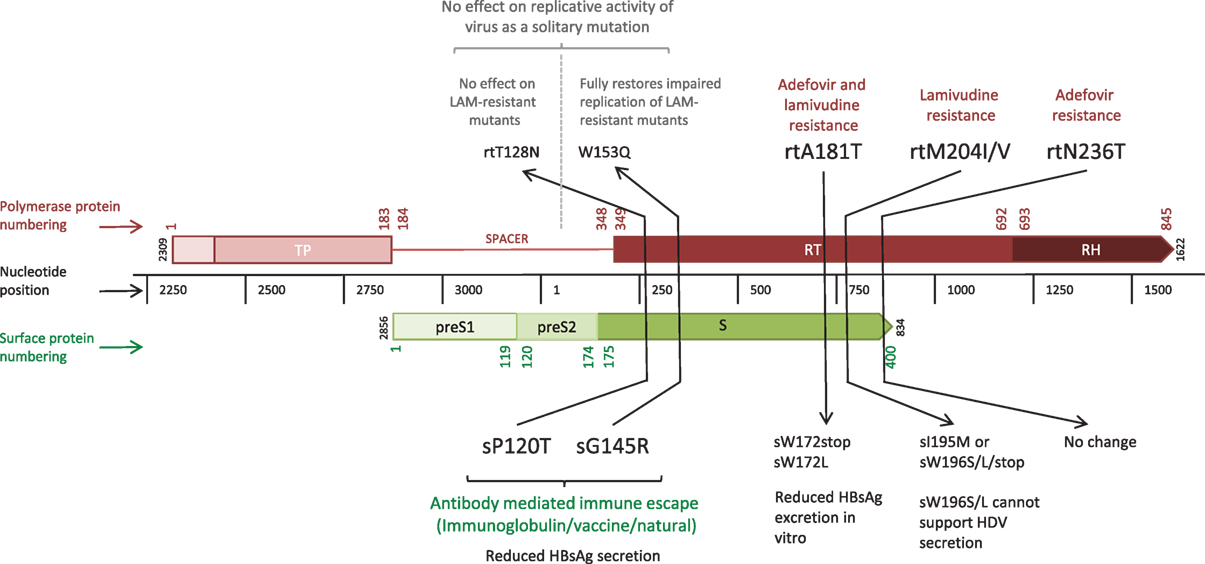
Figure 2. Linear depiction of overlapping reading frames of the Polymerase (P) and Surface (S) genes, highlighting five “mirror mutations” (4) where a nucleotide substitution influences amino acids in both S and P proteins. Gene lengths are given in nucleotides (black central bar); protein numbering based on the HBVdb X02763 amino acid sequence (7) is shown in color (Polymerase in red, Surface in green) for the whole protein. Mutations are given in amino acid positions in the affected gene segment, with the mutations in bold indicating the primary mutation with functional effect, and those in regular text indicating the secondary mirror mutation with any incidental functional effect.
Current vaccination and treatment approaches are hindered by poor diagnosis and access to treatment, drug and vaccine escape mutants, viral rebound on treatment cessation or immunosuppression, and lack of curative therapy (8). To make a significant impact on HBV prevalence, parallel improvements in diagnostics, treatment, and prevention are required; ultimately, new immunotherapeutic strategies may be key to the success of elimination. Developing a more robust picture of the extent, nature, and significance of the interplay between the virus and the host CD8+ T cell response is an important avenue of enquiry, enabling us to predict and tailor therapeutic interventions that may be beneficial in mediating control or clearance of chronic infection.
A robust body of data has been assimilated over the past few decades for HIV and HCV, informing significant understanding of the nature and impact of CD8+ T cell-mediated immune control and escape (Table 1). For HBV, there is a relative paucity of such evidence but the field could be advanced by similar approaches. We have therefore set out to assimilate the evidence for viral adaptation to the host CD8+ T cell response in HBV infection, and to consider the significance of this adaptation both to viral fitness and function, and to host outcomes. Finally, we highlight gaps in our current understanding and knowledge, in order to provide foundations for ongoing research efforts.
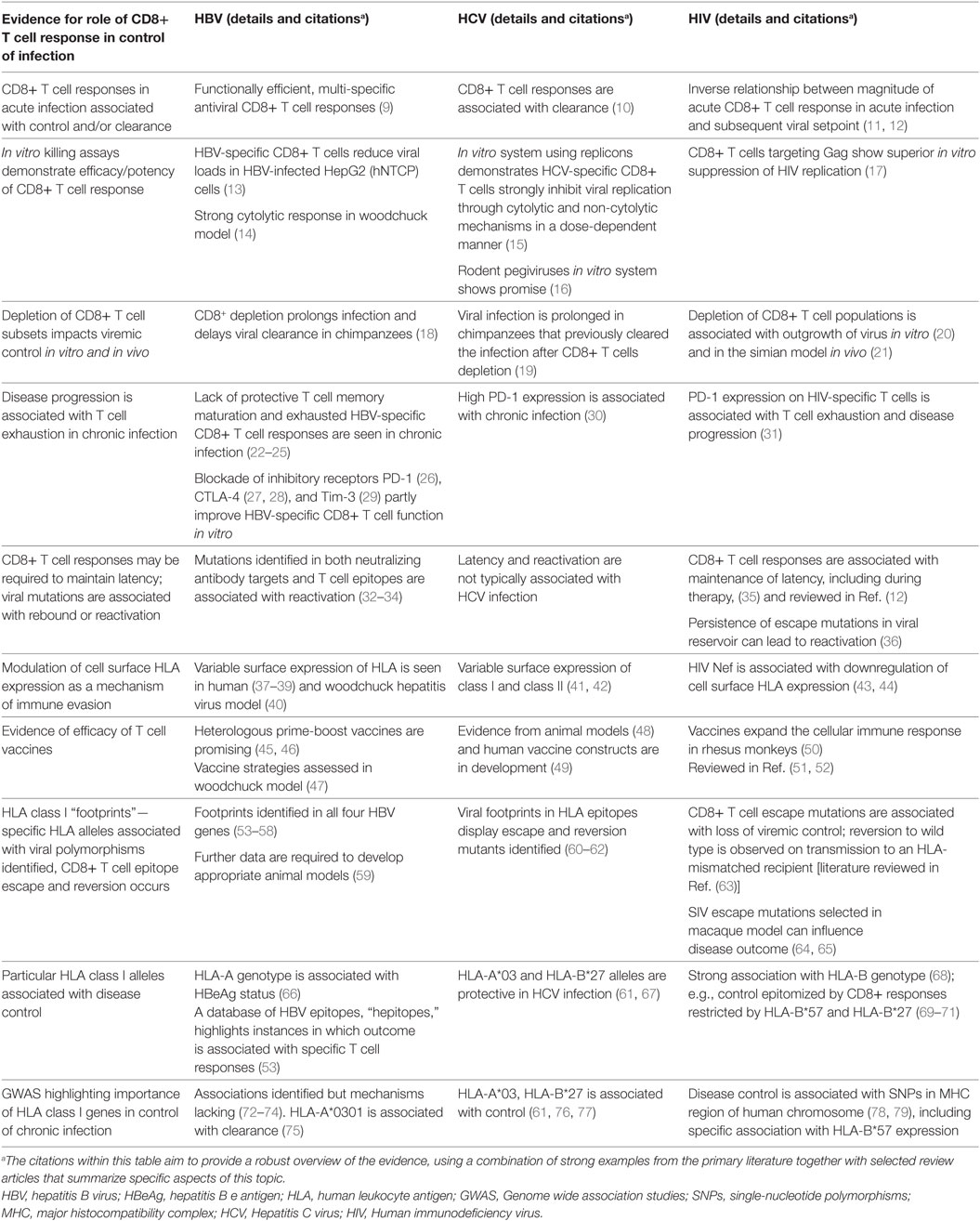
Table 1. Strands of evidence for the significance of the CD8+ T cell response in control/clearance of infection with blood-borne viruses.
The Immunological Basis for Escape
Acute and chronic HBV infections are associated with functionally different CD8+ T cell responses (Table 1). Acute, self-resolving infections are characterized by functionally efficient, multi-specific antiviral CD8+ T cell responses which are sustained after viral clearance (9). Both non-cytolytic and cytolytic mechanisms have been implicated (22). In contrast, chronic infection is typically characterized by a lack of protective T cell memory maturation and exhausted HBV-specific CD8+ T cell responses (22–24).
Th1-polarized CD4+ T cells regulate and maintain CD8+ T cell responses and contribute to HBV clearance (80). Genome wide association studies (GWAS) have linked a range of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class II alleles with disease outcomes. CD4+ responses are associated with vaccine responses (81) and clearance of acute infection (82, 83). Host HLA class II genotype has also been linked to treatment response (84) and to risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (85). CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells suppress the activation, proliferation, and interferon-γ production of both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in chronic HBV infection (86, 87).
The highly polymorphic HLA class I genes are thought to be an important host factor for viral control, contributing to differences in HBV outcome observed globally. Host HLA polymorphisms and different HBV genotypes have been demonstrated to influence the rate of disease progression and the long-term outcome of HBV infection (66, 88, 89). However, HBV can subvert various multiple steps of the CD8+ T cell antigen processing and presentation pathway to evade detection by the host (Figure 3, boxes 1–5). Thus, while all individuals with chronic HBV infection are at risk of increased progression to cirrhosis and HCC, individual outcomes depend on the interplay between host, viral, and environmental factors. In addition to HLA genes, other factors are implicated in disease outcome including age and duration of infection, other host genetic factors (90), and exposure to hepatotoxins (91).
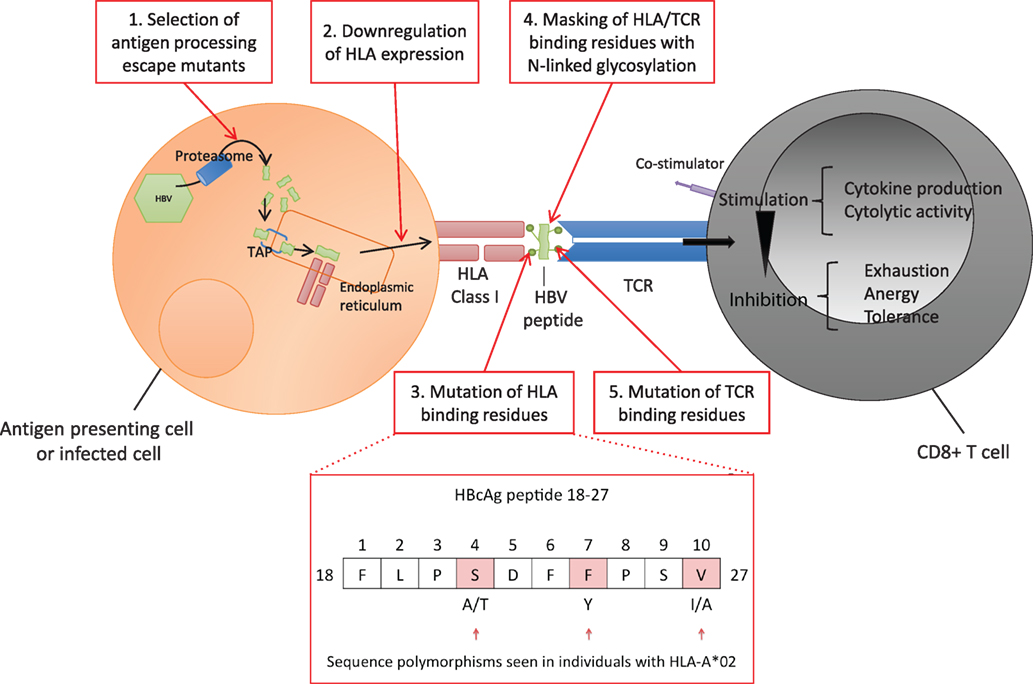
Figure 3. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) evasion of the host CD8+ T cell-mediated immune response. Viral peptides are processed into 7–12 mers by proteasomal degradation and are transported via the Transporter associated with Antigen Processing (TAP) into the endoplasmic reticulum. Peptides containing an appropriate motif are bound by human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I molecules and transported to the cell surface for expression (92). Each T cell receptor (TCR) binds a range of specific HLA-peptide combinations. TCRs are concentrated on the cell surface over time at an “immunological synapse” triggering intracellular signaling (93). HBV can potentially escape the host CD8+ response at a number of points. 1. Evading antigen processing, 2. Downregulating presentation (37–40), 3. Altering HLA binding residues (54–56, 94), 4. Masking HLA epitope with N-linked glycosylation (NLG) sites (32, 95), 5. Altering TCR binding residues of the epitope (10, 96–99). Examples of polymorphic sites in HBV core antigen HLA-A*02 restricted FV10 epitope (residues 18–27) are highlighted (54).
Mechanisms of HBV Escape from CD8+ T Cell Responses
Antigen-Processing Escape Mutants
The amino acids flanking viral epitopes are important for effective antigen processing; mutations in these regions may impair proteasomal processing of the epitopes and are recognized in both HCV and HIV as a mechanism of CD8+ T cell escape (100, 101). Likewise, mutations altering the processing of HBV epitopes could be relevant for HBV escape from the CD8+ T cell-mediated immune response (Figure 3, box 1), however, none have been identified at present, potentially due to the focus on mutations lying within HLA-restricted epitopes rather than in the flanking regions.
Virus Peptides Regulate Surface HLA Expression
Virus-induced changes in HLA class I surface expression play an important role in viral pathogenesis and persistence (Figure 3, box 2). CD8+ T cells recognize HBV-infected hepatocytes through presentation of HLA class I HBV epitopes on the cell surface (13), however, this expression can be upregulated or downregulated. Decreased presentation of class I MHC molecules on hepatocytes and lymphoid cells is described in the woodchuck hepatitis virus model (40). Changes in surface HLA have also been described in human HBV infection (37), for example, lower HLA class I has been associated with hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg)-positive vs HBeAg-negative status (38, 39). Interestingly, these studies are three decades old and have not been replicated in the more recent literature. Downregulation of HLA class II molecules by pre-core mutants has also been described during chronic HBV infection (102). Mutations altering the processing or presentation of HBV HLA class I epitopes, although not conclusively demonstrated, could hypothetically be relevant for escape from the CD8+ T cell-mediated immune response in human infection (Figure 3, box 2).
Selective Mutation of HLA-Binding Residues
Immune escape by selective mutation of HLA-binding residues within HBV CD8+ epitopes is one of the most commonly identified mechanisms for viral CD8+ immune escape (Table 1; Figure 3, box 3). Evidence of this escape mechanism in HBV has emerged through the identification of HLA class I “footprints” (94), mutations that are significantly enriched in patients with certain HLA class I alleles. Older literature was conflicting regarding the frequency and significance of such footprints in HBV (96, 103), but HLA footprints have subsequently been identified in all four HBV genes and mapped to known or predicted HLA epitopes [Table 1 (53)]. In some cases, these mutations result in altered peptide-HLA binding scores, providing a plausible mechanism for HBV immune escape, but have so far only been identified using cross-sectional data (54, 55, 96). However, the pattern of escape is consistent across populations with divergent HLA haplotypes and different HBV genotypes, for example, genotypes B and C in a cohort of Chinese-origin patients (56), New Zealand-resident Tongans with chronic HBV genotype C3 infections (57) and Iranian patients with genotype D infection (58). Importantly, core mutants in patients with chronic genotype A or D infection have been confirmed to impair CD8+ T cell IFN-γ secretion in vitro (54), indicating that these mutants could play an in vivo role in immune escape. These studies are limited by the sequencing methods (in which a pre-defined number of variants is typically selected for cloning and sequencing) reducing sensitivity for detection of low-abundance variant detection compared to newer ultra-deep sequencing methods.
Further studies have focused on identifying regions of the HBV genome with high within-host nucleotide diversity, and high rates of nonsynonymous substitutions, to determine which regions may be under strong HLA-mediated selection pressure. In a longitudinal study of eight HBeAg-negative asymptomatic HBV carriers, followed over 25 years, the ratio of synonymous to nonsynonymous mutations (dS/dN) in the core gene was low, suggesting high rates of positive selection, although no specific HLA-restricted epitopes were identified (104). Another study demonstrated low dS/dN ratios in patients with sustained vs unsustained viral control following treatment, with specific surface antigen polymorphisms lying within HLA class I epitopes identified [sV14G, sF20S, sT45I, sI213L (105)], although this was not confirmed either with HLA genotyping or through demonstration of a functional impact on T cell recognition.
Epitope Masking With N-Linked Glycosylation (NLG)
N-linked glycosylation is a post-translational modification that plays an established role in the antigenicity and infectivity of viruses (106, 107). NLG can mask immunogenic epitopes, interfering with antibody recognition of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), leading to immune and diagnostic escape (32, 95). It can also impact on HBV virion secretion, likely by altering the ability of envelope proteins to interact with the capsid surface (108–110). The number of NLG sites correlates with disease state, with increased NLG reported in patients with reactivated HBV vs chronic infection, and in those with sustained vs unsustained response off treatment (32, 111). Although the role of NLG in HBV evasion of CD8+-mediated T cell immunity is yet to be determined, it could potentially provide another strategy for immune escape by interfering with the binding of an HBV epitope to an HLA molecule, or the binding of an HLA-antigen complex to a cognate T cell receptor (TCR) (Figure 3, box 4).
Alteration of TCR Recognition
Engagement of the TCR with HLA class I/peptide complexes on antigen-presenting cells is key to activating CD8+ T cells; therefore, mutations in the TCR contact residues of an epitope can lead to immune escape. Immunodominance of viral epitopes is not simply determined by the amino acid sequence of the peptide and its binding affinity, but also depends on the peptide concentration and T cell clone, with the same HBV peptide able to induce different signaling cascades in different CD8+ T cell clones (97). Antagonist functions may provide HBV with a means of immune escape (Figure 3, box 5). Specifically, certain CD8+ T cell epitopes in hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg) (97) and HBsAg (98) act as TCR antagonists, binding the TCR and inhibiting the CD8+ T cell response. HBeAg may promote HBV chronicity by inducing CD8+ T cell tolerance. However, the underlying mechanisms driving this immune state in humans remain to be elucidated. Indeed, the mechanism may not involve presentation of an HLA class I-restricted epitope, as currently no epitopes have been identified that are unique to the pre-core sequence of HBeAg (a ~29 amino acid stretch not shared with HBcAg) (112).
Chronic HBV infection is characterized by an exhausted CD8+ T cell phenotype associated with reduced cytotoxic activity and enhanced expression of inhibitory markers. TCR binding in the presence of high HBsAg levels induces T cell exhaustion, characterized by poor effector cytotoxic activity, impaired cytokine production and sustained expression of multiple inhibitory receptors. A hierarchy of co-inhibitory receptors, dominated by PD-1, act synergistically to promote CD8+ tolerance. The degree of T cell impairment also depends on suppressive cytokines, interaction with other T cell subsets, and stage of T cell differentiation (113–117). T cell exhaustion is (at least partly) reversible; blockade of inhibitory receptors including PD-1 (26, 117), CTLA-4 (27), and Tim-3 (29) partly improve HBV-specific CD8+ T cell function in vitro. In addition, therapy with nucleot(s)ide analogs may lead to a modest reconstitution of HBV-specific T cell function (118). Although this restoration is transient (119), these CD8+ T cells can be associated with viral control upon therapy cessation (120).
Escape Over Space and Time
Kinetics of Escape
Evidence of immune-mediated selection has been found in HBV infection (53–56), although the kinetics of immune escape are yet to be robustly delineated. Longitudinal samples from the same individuals form the ideal dataset to address questions about the changes in viral sequence and diversity over time, but this has rarely been undertaken for HBV infection. One longitudinal study of HBV evolution following acquisition from a single source demonstrated an expansion and contraction of HBV diversity, with maximum diversity coinciding with peak viremia, and a predominance of nonsynonymous mutations with greatest diversity in the core gene (3). Further longitudinal data are required to unpick the timing and kinetics of viral evolution.
An area of HBV kinetics that has received some attention is the scenario of HBeAg loss. It is hypothesized that the change from HBeAg-positive to HBeAg-negative occurs by one of two mechanisms:
(i) Antibody-mediated control (121, 122) usually associated with low HBV DNA levels. This situation is most likely to be characterized by low viral sequence diversity, although the low viral loads make this difficult to study given the limits of sensitivity of next generation sequencing approaches.
(ii) Selection of pre-core and promotor mutations (123), reducing or eliminating HBeAg production. In this case, HBeAg-negative status is associated with an increase in evolutionary rate and therefore with increased sequence diversity (6, 54, 56, 57, 104, 111, 124–126). The cause/effect relationship between the increased evolutionary rate and the shift in immune activity is unclear. The higher viral mutation rate could lead to the occurrence of stochastic mutations, generating new T cell epitopes that disrupt immune tolerance, or could be the consequence of increased immune reactivity driving escape mutants.
Compartment-Specific Evolution
Compartment-specific evolution has been described for chronic viruses, including HIV (127, 128) and HCV (129, 130), although the evidence for HBV is very limited to date. The practical barriers to sampling tissue compartments longitudinally from the same patient make it difficult to assess the co-evolution of genetically distinct subpopulations over time [as is likely the case for HIV in the genital tract (131)].
Although hepadnaviruses are characteristically hepatotropic, HBV DNA is also found in a range of other tissues, including lymphatic cells. In the woodchuck model, life-long replication- and transmission-competent viruses persist in lymphocytes (132). However, it is difficult to demonstrate that hepatitis B virions isolated from different compartments in humans are replication and transmission competent, without a viable method of culturing autologous virus. There are some data to suggest that peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs) can support viral replication (133), but secretion of HBeAg and HBsAg from liver macrophages has not been detected [Lucifora, unpublished data, referred to in (134)].
HBV may undergo independent evolution in different tissue compartments, leading to compartmentalization of viral subpopulations (135–137); for example, HBV variants isolated from PBLs may be specifically adapted to this environment (137), potentially harboring relevant immune-escape mutants (135, 137). It has been hypothesized that compartment-specific mutants may serve as a source of reactivation or transmission and have been implicated in reinfection post liver transplant (138), mother to child transmission (137, 139), fulminant hepatic failure in the context of HIV co-infection (140), and antiviral escape (141).
Further work is required to confirm whether HBV does harbor replication and transmission competent viruses in cells other than hepatocytes. If this is confirmed, understanding host-virus dynamics at the compartmental level, studying the emergence of immune and antiviral escape mutants and the factors contributing to persistence and transmission will be crucial for developing improved therapeutics for HBV control.
Functional Impact of Escape Mutations on HBV
The primary functional impact of mutations within HLA class I-restricted T cell epitopes is to alter the frequency and/or functionality of the CD8+ T cell immune response. These mutations may have additional impact on the viral replication cycle and treatment response in the following ways:
(i) Altered structure/function of the viral protein containing the mutated immune epitope (Figure 2). This is seen in HBV escape from B cell immunity in which mutations within the S gene are associated with diagnostic failure (HBsAg mutants are not detected by the immunological assay) and treatment failure due to changes in assembly and secretion, virion formation and HBV infectivity (109, 142, 143).
(ii) Effects of a “mirror” escape mutation on the overlapping gene (Figure 2). A mutation leading to amino acid substitutions in both the P and S genes, can simultaneously affect replicative capacity, drug resistance, and immunogenicity (142–145). Furthermore, deletions in regions such as the spacer region of Pol, neutral to Pol function, may lead to loss of immune epitopes in the overlapping preS1-preS2 region.
(iii) Impact of compensatory mutations mitigating for (i) and (ii). This is seen in replication deficient CD8+ immune escape mutants in HCV (146) and HIV (147, 148) but has not yet been identified in HBV.
The full range of functional impacts of HBV CD8+ immune escape mutants has not been comprehensively explored. Understanding the functional impact of mirror and compensatory mutations that are associated with CD8+ T cell-mediated selection may lead to further insights into the host–virus interaction.
Clinical Impact of Virus and Host Polymorphisms on Host Outcome
Impact of HBV Mutations on Reactivation
Hepatitis B virus reactivation as a consequence of immunosuppression has emerged as an important issue across a wide range of clinical settings [as previously reviewed (149, 150)]. Reactivation is seen secondary to immunosuppressive therapy for cancer, in particular in the context of therapy with rituximab and fludarabine (33, 151), solid organ transplantation (150), bone marrow transplantation (152), and autoimmune disease [especially with infliximab treatment (153–155)], highlighting that HBV reactivation is associated with a general defect of HBV-specific T cell control. Reactivation has also been documented in immunocompetent patients despite the presence of neutralizing antibodies (156).
Specific mutations associated with HBV reactivation have been identified in both neutralizing antibody targets and T cell epitopes (32–34). In a study of 29 patients with HBV reactivation, 75% of HBV-reactivated patients (vs 3% of chronic HBV controls) carried HBsAg mutations localized in immune-active HBsAg regions, and 5 of 13 identified HBsAg mutations were localized in HLA-restricted T cell epitopes [either class I (sC48G, sV96A, sL175S, and sG185E) or class II (sS171F)] (32). This suggests that in addition to an iatrogenic trigger for reactivation during immunosuppressive therapy, viral sequence can be a contributory factor as a result of CD8+ immune escape mutants.
Impact of Host HLA Class I Haplotype on HBV Infection Outcome
GWAS approaches have linked various single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the HLA class II region with a range of infection outcomes, but there is a lack of such robust evidence for the involvement of HLA class I genes (72, 73, 75). One study identified a relationship between class I HLA-A genotype and HBeAg status (66), suggesting a role for genes at this locus in control of infection. However, confirmation of HLA associations can be difficult due to the variability in study design and methodologies and the small, heterogeneous populations sampled. Furthermore, the mechanisms for these HLA class I associations with disease outcome are poorly understood. Differences in antigen presentation, TCR binding leading to changes in T cell activation, and altered cytokine production may be responsible, either individually or in combination. Effects of linkage disequilibrium with other important neighboring loci, such as HLA class II or killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptors genes, cannot be excluded. Functional studies are required to determine the basis for these associations.
Impact of HBV Adaptation on Control Strategies
It is likely that to achieve elimination in line with global public health goals (157), new therapies targeting either the host immune system or the HBV replication cycle will be needed. Specific immunotherapies are under development, targeting both the innate and adaptive immune system, which aim to eliminate (or stably suppress) HBV replication (158).
T cell-based immune therapies are attractive options for HBV control (159). Strategies broadly take two approaches, either aiming to restore functionality and increase the quantity of existing defective host T cells with vaccines and checkpoint inhibitors, or to mimic the T cell response mounted during naturally resolving acute HBV infection by the adoptive transfer of HBV-specific T cells. Adoptive T cell therapy renders T cells HBV-specific by expression of natural HLA-restricted TCRs or HLA-independent chimeric antigen receptors on the T cell surface. Although natural TCRs have the advantage of activating the T cell response in a physiological way, therapy is potentially complicated by the need to match TCR to host HLA alleles, although some cross-reactivity may occur (160).
Given that HBV is able to evade natural immunity (32, 149, 156, 161, 162), vaccine-induced immunity (163, 164), and antiviral therapy (145, 165–169), it should be anticipated that HBV has the potential to mutate and escape from immunotherapeutic control. This is a vital consideration in the development of new HBV control strategies, and good knowledge of the full range of escape strategies should allow us to predict and potentially mitigate this. Care must be taken when developing T cell immunotherapies and polyepitope vaccines as immunodominance is a complex function of the nature and context of the epitope within the peptide, the TCR, the T cell clone, and the environment (98). The HBV literature is skewed toward the investigation of certain populations with specific HBV genotypes and HLA haplotypes, as highlighted in the “Hepitopes” database, a catalog of HLA class I epitopes in HBV, in which a disproportionate 44% of reported CD8+ T cell epitopes are HLA-A*02 restricted (53). The effect of using a polyepitope vaccine or re-directing T cells against peptides presented by discordant HLA alleles needs to be considered. This might inadvertently occur by using a vaccine or T cell-based immunotherapy based on key epitopes from a different genotype to that prevalent in the population to which it is delivered, and may produce functionally incompetent T cells, unable to recognize the infectious virus strain when used, or potentially lead to immunopathology. Since knowledge about certain host/virus interactions is under-represented, further studies will be required to define the full range of CD8+ T cell epitopes presented by HLA alleles, the antiviral functions of the corresponding CD8+ T cells in each compartment, the potential for generation of immune escape mutants and the impact these have on the immune response.
Challenges
The understanding of HBV escape from the CD8+ immune response is lagging behind that of HIV and HCV. The field struggles with a lack of comprehensive literature, small datasets that can lead to conflicting results, differences in approaches to classifying patient groups into poor/outdated descriptions of “phases” of infection, over-reliance on serostatus, and lack of longitudinal follow-up and deep sequence data. Establishing the role of compartmentalization in infection is complex, with clinical samples scarce due to the risk associated with liver biopsy. These challenges are exacerbated by an under-resourcing of clinical and research approaches in many of the settings where HBV is endemic (8).
Future Focus
There are many unanswered questions in the field of HBV and CD8+ immunity. In Table 2, we highlight gaps in our current understanding and knowledge, suggest desirable methods to develop, datasets to collate, and questions to be answered in order to provide foundations for ongoing research efforts.
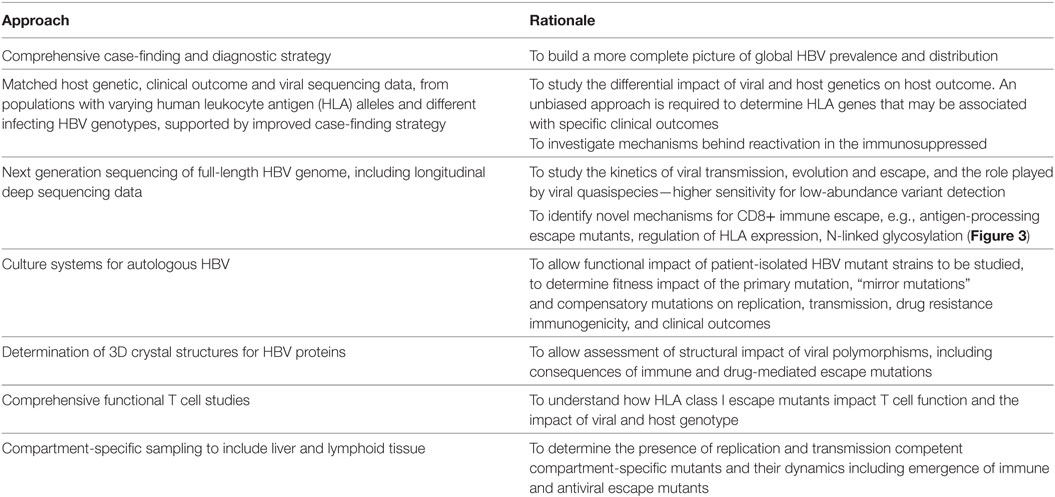
Table 2. Areas for future focus in determining the nature and characteristics of the CD8+ T cell response to hepatitis B virus (HBV).
Summary
Hepatitis B virus is a complicated, unique virus, which has evolved together with Homo sapiens over millennia; it has evolved a range of mechanisms that favor transmission and persistence which include the capacity to evade the CD8+ T cell response. By focusing on understanding the evolutionary interplay between host and virus, we can develop better insights into areas where we can target viral “Achilles heels.” The need for novel anti-HBV strategies should drive a deeper exploration of this host–pathogen interaction. Future research will be strengthened by comprehensive cross-sectional and longitudinal studies on HLA-typed hosts with clinical details, across a range of host ethnicities and HBV genotypes, with high quality serological and whole genome HBV deep sequencing data. This will provide a more comprehensive understanding of the nature and mechanisms of HBV evolution and persistence, helping us to reach the goal of global HBV eradiation by guiding the design of new strategies, including vaccines and therapeutics.
Author Contributions
SL undertook the primary literature review and drafted the manuscript; all authors had substantial input into revisions.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The handling Editor declared a past co-authorship with one of the authors PK.
Funding
SL is funded by the National Institute for Health Research. PM is funded by the Wellcome Trust (grant number 110110). KL is funded by the Wellcome Trust (grant number 107652/Z15/Z) and The Royal Society. PK is funded by the Wellcome Trust (WT109965MA) and National Institute for Health Research Biomedical Research Centre, Oxford.
Abbreviations
C HBV, core gene; CARs, chimeric antigen receptors; cccDNA, covalently closed circular DNA; GWAS, genome wide association studies; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HBcAg, hepatitis B core antigen; HBeAg, hepatitis B e antigen; HBsAg, hepatitis B surface antigen; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; KIR, killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptors; NLG, N-linked glycosylation; ORF, open reading frame; P HBV, polymerase gene; PBL, peripheral blood lymphocyte; RT, reverse transcriptase; S HBV, surface gene; SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism; TCR, T cell receptor; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; HIV, Human immunodeficiency virus; HCV, Hepatitis C virus.
References
1. Polaris Observatory Collaborators. Global prevalence, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in 2016: a modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol (2018) 3(6):383–403. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(18)30056-6
2. Pult I, Abbott N, Zhang YY, Summers J. Frequency of spontaneous mutations in an avian hepadnavirus infection. J Virol (2001) 75(20):9623–32. doi:10.1128/JVI.75.20.9623-9632.2001
3. Whalley SA, Murray JM, Brown D, Webster GJ, Emery VC, Dusheiko GM, et al. Kinetics of acute hepatitis B virus infection in humans. J Exp Med (2001) 193:847–54. doi:10.1084/jem.193.7.847
4. Sheldon J, Soriano V. Hepatitis B virus escape mutants induced by antiviral therapy. J Antimicrob Chemother (2008) 61(4):766–8. doi:10.1093/jac/dkn014
5. Mizokami M, Orito E, Ohba K, Ikeo K, Lau JYN, Gojobori T. Constrained evolution with respect to gene overlap of hepatitis B virus. J Mol Evol (1997) 44(1 Suppl):83–90. doi:10.1007/PL00000061
6. Harrison A, Lemey P, Hurles M, Moyes C, Horn S, Pryor J, et al. Genomic analysis of hepatitis B virus reveals antigen state and genotype as sources of evolutionary rate variation. Viruses (2011) 3(2):83–101. doi:10.3390/v3020083
7. Hayer J, Jadeau F, Deléage G, Kay A, Zoulim F, Combet C. The Hepatitis B Virus Database (HBVdb) – X02763 [Internet]. Available from: https://hbvdb.ibcp.fr (Accessed: April, 2018).
8. O’Hara GA, McNaughton AL, Maponga T, Jooste P, Ocama P, Chilengi R, et al. Hepatitis B virus infection as a neglected tropical disease. PLoS Negl Trop Dis (2017) 11(10):e0005842. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0005842
9. Rehermann B, Fowler P, Sidney J, Person J, Redeker A, Brown M, et al. The cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to multiple hepatitis B virus polymerase epitopes during and after acute viral hepatitis. J Exp Med (1995) 181(3):1047–58. doi:10.1084/jem.181.3.1047
10. Chen MT, Billaud J-N, Sällberg M, Guidotti LG, Chisari FV, Jones J, et al. A function of the hepatitis B virus precore protein is to regulate the immune response to the core antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2004) 101(41):14913–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.0406282101
11. Streeck H, Nixon DF. T cell immunity in acute HIV-1 infection. J Infect Dis (2010) 202(Suppl 2):S302–8. doi:10.1086/655652
12. McBrien JB, Kumar NA, Silvestri G. Mechanisms of CD8(+) T cell-mediated suppression of HIV/SIV replication. Eur J Immunol (2018) 48(6):898–914. doi:10.1002/eji.201747172
13. Hoh A, Heeg M, Ni Y, Schuch A, Binder B, Hennecke N, et al. HBV-infected HepG2hNTCP cells serve as a novel immunological tool to analyze the antiviral efficacy of CD8+ T cells in vitro. J Virol (2015) 89(14):7433–8. doi:10.1128/JVI.00605-15
14. Frank I, Budde C, Fiedler M, Dahmen U, Viazov S, Lu M, et al. Acute resolving woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV) infection is associated with a strong cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response to a single WHV core peptide. J Virol (2007) 81(13):7156–63. doi:10.1128/JVI.02711-06
15. Jo J, Aichele U, Kersting N, Klein R, Aichele P, Bisse E, et al. Analysis of CD8+ T-cell-mediated inhibition of hepatitis C virus replication using a novel immunological model. Gastroenterology (2009) 136(4):1391–401. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.12.034
16. Billerbeck E, Wolfisberg R, Fahnøe U, Xiao JW, Quirk C, Luna JM, et al. Mouse models of acute and chronic hepacivirus infection. Science (2017) 357(6347):204–8. doi:10.1126/science.aal1962
17. Julg B, Williams KL, Reddy S, Bishop K, Qi Y, Carrington M, et al. Enhanced anti-HIV functional activity associated with gag-specific CD8 T-cell responses. J Virol (2010) 84(11):5540–9. doi:10.1128/JVI.02031-09
18. Thimme R, Wieland S, Steiger C, Ghrayeb J, Reimann KA, Purcell RH, et al. CD8(+) T cells mediate viral clearance and disease pathogenesis during acute hepatitis B virus infection. J Virol (2003) 77(1):68–76. doi:10.1128/JVI.77.1.68-76.2003
19. Shoukry NH, Grakoui A, Houghton M, Chien DY, Ghrayeb J, Reimann KA, et al. Memory CD8+ T cells are required for protection from persistent hepatitis C virus infection. J Exp Med (2003) 197(12):1645–55. doi:10.1084/jem.20030239
20. Leitman EM, Palmer CD, Buus S, Chen F, Riddell L, Sims S, et al. Saporin-conjugated tetramers identify efficacious anti-HIV CD8+ T-cell specificities. PLoS One (2017) 12(10):e0184496. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0184496
21. Jin X, Bauer DE, Tuttleton SE, Lewin S, Gettie A, Blanchard J, et al. Dramatic rise in plasma viremia after CD8(+) T cell depletion in simian immunodeficiency virus-infected macaques. J Exp Med (1999) 189(6):991–8. doi:10.1084/jem.189.6.991
22. Bertoletti A, Ferrari C. Adaptive immunity in HBV infection. J Hepatol (2016) 64(1):S71–83. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2016.01.026
23. Boni C, Fisicaro P, Valdatta C, Amadei B, Di Vincenzo P, Giuberti T, et al. Characterization of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-specific T-cell dysfunction in chronic HBV infection. J Virol (2007) 81(8):4215–25. doi:10.1128/JVI.02844-06
24. Chang JJ, Thompson AJV, Visvanathan K, Kent SJ, Cameron PU, Wightman F, et al. The phenotype of hepatitis B virus-specific T cells differ in the liver and blood in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology (2007) 46(5):1332–40. doi:10.1002/hep.21844
25. Phillips S, Chokshi S, Riva A, Evans A, Williams R, Naoumov NV. CD8(+) T cell control of hepatitis B virus replication: direct comparison between cytolytic and noncytolytic functions. J Immunol (2010) 184(1):287–95. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0902761
26. Fisicaro P, Valdatta C, Massari M, Loggi E, Biasini E, Sacchelli L, et al. Antiviral intrahepatic T-cell responses can be restored by blocking programmed death-1 pathway in chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology (2010) 138(2):682–93. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2009.09.052
27. Cao H, Zhang R, Zhang W. CTLA4 interferes with the HBV specific T cell immune response (review). Int J Mol Med (2018) 42(2):703–12. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2018.3688
28. Schurich A, Khanna P, Lopes AR, Han KJ, Peppa D, Micco L, et al. Role of the coinhibitory receptor cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 on apoptosis-prone CD8 T cells in persistent hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology (2011) 53(5):1494–503. doi:10.1002/hep.24249
29. Wu W, Shi Y, Li S, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Wu Y, et al. Blockade of Tim-3 signaling restores the virus-specific CD8 + T-cell response in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Eur J Immunol (2012) 42(5):1180–91. doi:10.1002/eji.201141852
30. Rutebemberwa A, Ray SC, Astemborski J, Levine J, Liu L, Dowd KA, et al. High-programmed death-1 levels on hepatitis C virus-specific T cells during acute infection are associated with viral persistence and require preservation of cognate antigen during chronic infection. J Immunol (2008) 181(12):8215–25. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.181.12.8215
31. Day CL, Kaufmann DE, Kiepiela P, Brown JA, Moodley ES, Reddy S, et al. PD-1 expression on HIV-specific T cells is associated with T-cell exhaustion and disease progression. Nature (2006) 443(7109):350–4. doi:10.1038/nature05115
32. Salpini R, Colagrossi L, Bellocchi MC, Surdo M, Becker C, Alteri C, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen genetic elements critical for immune escape correlate with hepatitis B virus reactivation upon immunosuppression. Hepatology (2015) 61(3):823–33. doi:10.1002/hep.27604
33. Hayashi K, Ishigami M, Ishizu Y, Kuzuya T, Honda T, Tachi Y, et al. Clinical characteristics and molecular analysis of hepatitis B virus reactivation in hepatitis B surface antigen-negative patients during or after immunosuppressive or cytotoxic chemotherapy. J Gastroenterol (2016) 51(11):1081–9. doi:10.1007/s00535-016-1187-z
34. Ando T, Kojima K, Isoda H, Eguchi Y, Honda T, Ishigami M, et al. Reactivation of resolved infection with the hepatitis B virus immune escape mutant G145R during dasatinib treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia. Int J Hematol (2015) 102(3):379–82. doi:10.1007/s12185-015-1788-y
35. Cartwright EK, Spicer L, Smith SA, Lee D, Fast R, Paganini S, et al. CD8(+) lymphocytes are required for maintaining viral suppression in SIV-infected macaques treated with short-term antiretroviral therapy. Immunity (2016) 45(3):656–68. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2016.08.018
36. Deng K, Pertea M, Rongvaux A, Wang L, Durand CM, Ghiaur G, et al. Broad CTL response is required to clear latent HIV-1 due to dominance of escape mutations. Nature (2015) 517(7534):381–5. doi:10.1038/nature14053
37. Pignatelli M, Waters J, Brown D, Lever A, Iwarson S, Schaff Z, et al. HLA class I antigens on the hepatocyte membrane during recovery from acute hepatitis B virus infection and during interferon therapy in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology (1986) 6(3):349–53. doi:10.1002/hep.1840060303
38. Chu CM, Shyu WC, Kuo RW, Liaw YF. HLA class I antigen display on hepatocyte membrane in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: its role in the pathogenesis of chronic type B hepatitis. Hepatology (1987) 8(3):712–7. doi:10.1002/hep.1840080358
39. Montanto L, Miescher GC, Goodall AH, Wiedmann KH, Janossy G, Thomas HC. Hepatitis B virus and HLA antigen display in the liver during chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology (1982) 2(5):557S–61S. doi:10.1002/hep.1840020508
40. Michalak TI, Hodgson PD, Churchill ND. Posttranscriptional inhibition of class I major histocompatibility complex presentation on hepatocytes and lymphoid cells in chronic woodchuck hepatitis virus infection. J Virol (2000) 74(10):4483–94. doi:10.1128/JVI.74.10.4483-4494.2000
41. Saito K, Ait-Goughoulte M, Truscott SM, Meyer K, Blazevic A, Abate G, et al. Hepatitis C virus inhibits cell surface expression of HLA-DR, prevents dendritic cell maturation, and induces interleukin-10 production. J Virol (2008) 82(7):3320–8. doi:10.1128/JVI.02547-07
42. Kang W, Sung PS, Park S-H, Yoon S, Chang D-Y, Kim S, et al. Hepatitis C virus attenuates interferon-induced major histocompatibility complex class I expression and decreases CD8+ T cell effector functions. Gastroenterology (2014) 146(5):1351–4. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2014.01.054
43. Schwartz O, Maréchal V, Le Gall S, Lemonnier F, Heard JM. Endocytosis of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules is induced by the HIV-1 Nef protein. Nat Med (1996) 2(3):338–42. doi:10.1038/nm0396-338
44. Mwimanzi P, Markle TJ, Ueno T, Brockman MA. Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I down-regulation by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 negative factor (HIV-1 Nef): what might we learn from natural sequence variants? Viruses (2012) 4(9):1711–30. doi:10.3390/v4102014
45. Backes S, Jäger C, Dembek CJ, Kosinska AD, Bauer T, Stephan AS, et al. Protein-prime/modified vaccinia virus Ankara vector-boost vaccination overcomes tolerance in high-antigenemic HBV-transgenic mice. Vaccine (2016) 34(7):923–32. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.12.060
46. Buchmann P, Dembek C, Kuklick L, Jäger C, Tedjokusumo R, von Freyend MJ, et al. A novel therapeutic hepatitis B vaccine induces cellular and humoral immune responses and breaks tolerance in hepatitis B virus (HBV) transgenic mice. Vaccine (2013) 31(8):1197–203. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.12.074
47. Kosinska AD, Zhang E, Johrden L, Liu J, Seiz PL, Zhang X, et al. Combination of DNA prime – adenovirus boost immunization with entecavir elicits sustained control of chronic hepatitis B in the woodchuck model. PLoS Pathog (2013) 9(6):e1003391. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1003391
48. Wijesundara DK, Gummow J, Li Y, Yu W, Quah BJ, Ranasinghe C, et al. Induction of genotype cross-reactive, hepatitis C virus-specific cell-mediated immunity in DNA-vaccinated mice. J Virol (2018) 92(8):e02133-17. doi:10.1128/JVI.02133-17
49. von Delft A, Donnison TA, Lourenço J, Hutchings C, Mullarkey CE, Brown A, et al. The generation of a simian adenoviral vectored HCV vaccine encoding genetically conserved gene segments to target multiple HCV genotypes. Vaccine (2018) 36(2):313–21. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.10.079
50. Barouch DH, O’Brien KL, Simmons NL, King SL, Abbink P, Maxfield LF, et al. Mosaic HIV-1 vaccines expand the breadth and depth of cellular immune responses in rhesus monkeys. Nat Med (2010) 16(3):319–23. doi:10.1038/nm.2089
51. Mcmichael AJ, Koff WC. Vaccines that stimulate T cell immunity to HIV-1: the next step. Nat Immunol (2014) 15(4):319–22. doi:10.1038/ni.2844
52. Streeck H. Designing optimal HIV-vaccine T-cell responses. Curr Opin HIV AIDS (2016) 11(6):593–600. doi:10.1097/COH.0000000000000313
53. Lumley S, Noble H, Hadley MJ, Callow L, Malik A, Chua YY, et al. Hepitopes: a live interactive database of HLA class I epitopes in hepatitis B virus. Wellcome Open Res (2016) 1:9. doi:10.12688/wellcomeopenres.9952.1
54. Kefalakes H, Budeus B, Walker A, Jochum C, Hilgard G, Heinold A, et al. Adaptation of the hepatitis B virus core protein to CD8 + T-cell selection pressure. Hepatology (2015) 62(1):47–56. doi:10.1002/hep.27771
55. Nitschke K, Luxenburger H, Kiraithe MM, Thimme R, Neumann-Haefelin C. CD8+ T-cell responses in hepatitis B and C: the (HLA-) A, B, and C of hepatitis B and C. Dig Dis (2016) 34(4):396–409. doi:10.1159/000444555
56. Desmond CP, Gaudieri S, James IR, Pfafferott K, Chopra A, Lau GK, et al. Viral adaptation to host immune responses occurs in chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, and adaptation is greatest in HBV e antigen-negative disease. J Virol (2012) 86(2):1181–92. doi:10.1128/JVI.05308-11
57. Abbott WGH, Tsai P, Leung E, Trevarton A, Ofanoa M, Hornell J, et al. Associations between HLA class I alleles and escape mutations in the hepatitis B virus core gene in New Zealand-resident Tongans. J Virol (2010) 84(1):621–9. doi:10.1128/JVI.01471-09
58. Khedive A, Norouzi M, Ramezani F, Karimzadeh H, Alavian SM, Malekzadeh R, et al. Hepatitis B virus surface protein mutations clustered mainly in CTL immune epitopes in chronic carriers: results of an Iranian nationwide study. J Viral Hepat (2013) 20(7):494–501. doi:10.1111/jvh.12045
59. Nassal M, Dallmeier K, Schultz U, Sun D. Phenotyping hepatitis B virus variants: from transfection towards a small animal in vivo infection model. J Clin Virol (2005) 34(Suppl 1):S89–95. doi:10.1016/S1386-6532(05)80017-4
60. Gaudieri S, Rauch A, Park LP, Freitas E, Herrmann S, Jeffrey G, et al. Evidence of viral adaptation to HLA class I-restricted immune pressure in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J Virol (2006) 80(22):11094–104. doi:10.1128/JVI.00912-06
61. Fitzmaurice K, Petrovic D, Ramamurthy N, Simmons R, Merani S, Gaudieri S, et al. Molecular footprints reveal the impact of the protective HLA-A*03 allele in hepatitis C virus infection. Gut (2011) 60(11):1563–71. doi:10.1136/gut.2010.228403
62. Ruhl M, Knuschke T, Schewior K, Glavinic L, Neumann-Haefelin C, Chang DI, et al. CD8+ T-cell response promotes evolution of hepatitis c virus nonstructural proteins. Gastroenterology (2011) 140(7):2064–73. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.02.060
63. Kloverpris HN, Leslie A, Goulder P. Role of HLA adaptation in HIV evolution. Front Immunol (2015) 6:665. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2015.00665
64. Martins MA, Tully DC, Cruz MA, Power KA, Veloso de Santana MG, Bean DJ, et al. Vaccine-induced simian immunodeficiency virus-specific CD8+ T-cell responses focused on a single Nef epitope select for escape variants shortly after infection. J Virol (2015) 89(21):10802–20. doi:10.1128/JVI.01440-15
65. Harris M, Burns CM, Becker EA, Braasch AT, Gostick E, Johnson RC, et al. Acute-phase CD8 T cell responses that select for escape variants are needed to control live attenuated simian immunodeficiency virus. J Virol (2013) 87(16):9353–64. doi:10.1128/JVI.00909-13
66. Matthews PC, Carlson JM, Beloukas A, Malik A, Jooste P, Ogwu A, et al. HLA-A is a predictor of hepatitis B e antigen status in HIV-positive African adults. J Infect Dis (2016) 213(8):1248–52. doi:10.1093/infdis/jiv592
67. McKiernan SM, Hagan R, Curry M, McDonald GSA, Kelly A, Nolan N, et al. Distinct MHC class I and II alleles are associated with hepatitis C viral clearance, originating from a single source. Hepatology (2004) 40(1):108–14. doi:10.1002/hep.20261
68. Kiepiela P, Leslie AJ, Honeyborne I, Ramduth D, Thobakgale C, Chetty S, et al. Dominant influence of HLA-B in mediating the potential co-evolution of HIV and HLA. Nature (2004) 432(7018):769–75. doi:10.1038/nature03113
69. Martinez-Picado J, Prado JG, Fry EE, Pfafferott K, Leslie A, Chetty S, et al. Fitness cost of escape mutations in p24 Gag in association with control of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol (2006) 80(7):3617–23. doi:10.1128/JVI.80.7.3617-3623.2006
70. Kiepiela P, Ngumbela K, Thobakgale C, Ramduth D, Honeyborne I, Moodley E, et al. CD8+T-cell responses to different HIV proteins have discordant associations with viral load. Nat Med (2007) 13(1):46–53. doi:10.1038/nm1520
71. Frater AJ, Brown H, Oxenius A, Gunthard HF, Hirschel B, Robinson N, et al. Effective T-cell responses select human immunodeficiency virus mutants and slow disease progression. J Virol (2007) 81(12):6742–51. doi:10.1128/JVI.00022-07
72. Singh R, Kaul R, Kaul A, Khan K. A comparative review of HLA associations with hepatitis B and C viral infections across global populations. World J Gastroenterol (2007) 13(12):1770–87. doi:10.3748/wjg.v13.i12.1770
73. Wang L, Zou ZQ, Wang K. Clinical relevance of HLA gene variants in HBV infection. J Immunol Res (2016) 2016:9069375. doi:10.1155/2016/9069375
74. Li X, Liu W, Wang H, Jin X, Fang S, Shi Y, et al. The influence of HLA alleles and HBV subgenotyes on the outcomes of HBV infections in Northeast China. Virus Res (2012) 163(1):328–33. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2011.10.020
75. Thio CL, Thomas DL, Karacki P, Gao X, Marti D, Kaslow RA, et al. Comprehensive analysis of class I and class II HLA antigens and chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Virol (2003) 77(22):12083–7. doi:10.1128/JVI.77.22.12083-12087.2003
76. Ansari MA, Pedergnana V, Ip C LC, Magri A, Von Delft A, Bonsall D, et al. Genome-to-genome analysis highlights the effect of the human innate and adaptive immune systems on the hepatitis C virus. Nat Genet (2017) 49(5):666–73. doi:10.1038/ng.3835
77. Neumann-Haefelin C, Oniangue-Ndza C, Kuntzen T, Schmidt J, Nitschke K, Sidney J, et al. Human leukocyte antigen B27 selects for rare escape mutations that significantly impair hepatitis C virus replication and require compensatory mutations. Hepatology (2011) 54(4):1157–66. doi:10.1002/hep.24541
78. Fellay J, Shianna KV, Ge D, Colombo S, Ledergerber B, Weale M, et al. A whole-genome association study of major determinants for host control of HIV-1. Science (2007) 317(5840):944–7. doi:10.1126/science.1143767
79. International HIV Controllers Study, Pereyra F, Jia X, McLaren PJ, Telenti A, De Bakker PIW, et al. The major genetic determinants of HIV-1 control affect HLA class I peptide presentation. Science (2010) 330(6010):1551–7. doi:10.1126/science.1195271
80. Penna A, Del Prete G, Cavalli A, Bertoletti A, D’Elios MM, Sorrentino R, et al. Predominant T-helper 1 cytokine profile of hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid-specific T cells in acute self-limited hepatitis B. Hepatology (1997) 25(4):1022–7. doi:10.1002/hep.510250438
81. Nishida N, Sugiyama M, Sawai H, Nishina S, Sakai A, Ohashi J, et al. Key HLA-DRB1-DQB1 haplotypes and role of the BTNL2 gene for response to a hepatitis B vaccine. Hepatology (2018). doi:10.1002/hep.29876
82. Hu Z, Liu Y, Zhai X, Dai J, Jin G, Wang L, et al. New loci associated with chronic hepatitis B virus infection in Han Chinese. Nat Genet (2013) 45(12):1499–503. doi:10.1038/ng.2809
83. Kamatani Y, Wattanapokayakit S, Ochi H, Kawaguchi T, Takahashi A, Hosono N, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies variants in the HLA-DP locus associated with chronic hepatitis B in Asians. Nat Genet (2009) 41(5):591–5. doi:10.1038/ng.348
84. Hosaka T, Suzuki F, Kobayashi M, Fukushima T, Kawamura Y, Sezaki H, et al. HLA-DP genes polymorphisms associate with hepatitis B surface antigen kinetics and seroclearance during nucleot(s)ide analogue therapy. Liver Int (2015) 35(4):1290–302. doi:10.1111/liv.12652
85. Jiang D-K, Sun J, Cao G, Liu Y, Lin D, Gao Y-Z, et al. Genetic variants in STAT4 and HLA-DQ genes confer risk of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet (2013) 45(1):72–5. doi:10.1038/ng.2483
86. Stoop JN, Van Der Molen RG, Baan CC, Van Der Laan LJW, Kuipers EJ, Kusters JG, et al. Regulatory T cells contribute to the impaired immune response in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology (2005) 41(4):771–8. doi:10.1002/hep.20649
87. Feng I-C, Koay L-B, Sheu M-J, Kuo H-T, Sun C-S, Lee C, et al. HBcAg-specific CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells modulate immune tolerance and acute exacerbation on the natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Biomed Sci (2007) 14(1):43–57. doi:10.1007/s11373-006-9129-z
88. Lin C-L, Kao J-H. Natural history of acute and chronic hepatitis B: the role of HBV genotypes and mutants. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol (2017) 31(3):249–55. doi:10.1016/j.bpg.2017.04.010
89. Fung SK, Lok ASF. Hepatitis B virus genotypes: do they play a role in the outcome of HBV infection? Hepatology (2004) 40(4):790–2. doi:10.1002/hep.20455
90. Matsuura K, Isogawa M, Tanaka Y. Host genetic variants influencing the clinical course of hepatitis B virus infection. J Med Virol (2016) 88(3):371–9. doi:10.1002/jmv.24350
91. El-Serag HB. Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology (2012) 142(6):1264–73. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.061
92. Cresswell P, Ackerman AL, Giodini A, Peaper DR, Wearsch PA. Mechanisms of MHC class I-restricted antigen processing and cross-presentation. Immunol Rev (2005) 207:145–57. doi:10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00316.x
93. Bromley SK, Burack WR, Kenneth G, Somersalo K, Sims TN, Sumen C, et al. The immunological synapse. Annu Rev Immunol (2001) 19:375–96. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.375
94. Klenerman P, McMichael A. AIDS/HIV. Finding footprints among the trees. Science (2007) 315(5818):1505–7. doi:10.1126/science.1140768
95. Yu DM, Li XH, Mom V, Lu ZH, Liao XW, Han Y, et al. N-glycosylation mutations within hepatitis B virus surface major hydrophilic region contribute mostly to immune escape. J Hepatol (2014) 60(3):515–22. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2013.11.004
96. Bertoletti A, Costanzo A, Chisari FV, Levrero M, Artini M, Sette A, et al. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to a wild type hepatitis B virus epitope in patients chronically infected by variant viruses carrying substitutions within the epitope. J Exp Med (1994) 180(3):933–43. doi:10.1084/jem.180.3.933
97. Bertoletti A, Sette A, Chisari FV, Penna A, Levrero M, De Carli M, et al. Natural variants of cytotoxic epitopes are T-cell receptor antagonists for antiviral cytotoxic T cells. Nature (1994) 369(6479):407–10. doi:10.1038/369407a0
98. Nayersina R, Fowler P, Guilhot S, Missale G, Cerny A, Schlicht HJ, et al. HLA A2 restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses to multiple hepatitis B surface antigen epitopes during hepatitis B virus infection. J Immunol (1993) 150(10):4659–71.
99. Chen M, Sällberg M, Hughes J, Jones J, Guidotti LG, Chisari FV, et al. Immune tolerance split between hepatitis B virus precore and core proteins. J Virol (2005) 79(5):3016–27. doi:10.1128/JVI.79.5.3016-3027.2005
100. Kimura Y, Gushima T, Rawale S, Kaumaya P, Walker CM. Escape mutations alter proteasome processing of major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted epitopes in persistent hepatitis C virus infection. J Virol (2005) 79(8):4870–6. doi:10.1128/JVI.79.8.4870-4876.2005
101. Allen TM, Altfeld M, Yu XG, O’Sullivan KM, Lichterfeld M, Le Gall S, et al. Selection, transmission, and reversion of an antigen-processing cytotoxic T-lymphocyte escape mutation in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Virol (2004) 78(13):7069–78. doi:10.1128/JVI.78.13.7069-7078.2004
102. Mohamadkhani A, Sotoudeh M, Bowden S, Poustchi H, Jazii FR, Sayehmiri K, et al. Downregulation of HLA class II molecules by G1896A pre-core mutation in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Viral Immunol (2009) 22(5):295–300. doi:10.1089/vim.2009.0031
103. Rehermann B, Pasquinelli C, Mosier SM, Chisari FV. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) sequence variation of cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitopes is not common in patients with chronic HBV infection. J Clin Invest (1995) 96(3):1527–34. doi:10.1172/JCI118191
104. Osiowy C, Giles E, Tanaka Y, Mizokami M, Minuk GY. Molecular evolution of hepatitis B virus over 25 years. J Virol (2006) 80(21):10307–14. doi:10.1128/JVI.00996-06
105. Chen L, Gan QR, Zhang DQ, Yao LF, Lin RS, Li Q, et al. Increased intrahepatic quasispecies heterogeneity correlates with off-treatment sustained response to nucleos(t)ide analogues in e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B patients. Clin Microbiol Infect (2016) 22(2):201–7. doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2015.10.007
106. Vigerust DJ, Shepherd VL. Virus glycosylation: role in virulence and immune interactions. Trends Microbiol (2007) 15(5):211–8. doi:10.1016/j.tim.2007.03.003
107. Anjum S, Wahid A, Afzal MS, Albecka A, Alsaleh K, Ahmad T, et al. Additional glycosylation within a specific hypervariable region of subtype 3a of hepatitis C virus protects against virus neutralization. J Infect Dis (2013) 208(11):1888–97. doi:10.1093/infdis/jit376
108. Kwei K, Tang X, Lok AS, Sureau C, Garcia T, Li J, et al. Impaired virion secretion by hepatitis B virus immune escape mutants and its rescue by wild-type envelope proteins or a second-site mutation. J Virol (2013) 87(4):2352–7. doi:10.1128/JVI.02701-12
109. Ito K, Qin Y, Guarnieri M, Garcia T, Kwei K, Mizokami M, et al. Impairment of hepatitis B virus virion secretion by single-amino-acid substitutions in the small envelope protein and rescue by a novel glycosylation site. J Virol (2010) 84(24):12850–61. doi:10.1128/JVI.01499-10
110. Julithe R, Abou-Jaoude G, Sureau C. Modification of the hepatitis B virus envelope protein glycosylation pattern interferes with secretion of viral particles, infectivity, and susceptibility to neutralizing antibodies. J Virol (2014) 88(16):9049–59. doi:10.1128/JVI.01161-14
111. Sede M, Lopez-Ledesma M, Frider B, Pozzati M, Campos RH, Flichman D, et al. Hepatitis B virus depicts a high degree of conservation during the immune-tolerant phase in familiarly transmitted chronic hepatitis B infection: deep-sequencing and phylogenetic analysis. J Viral Hepat (2014) 21(9):650–61. doi:10.1111/jvh.12196
112. Milich D, Liang TJ. Exploring the biological basis of hepatitis B e antigen in hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology (2003) 38(5):1075–86. doi:10.1053/jhep.2003.50453
113. Ye B, Liu X, Li X, Kong H, Tian L, Chen Y. T-cell exhaustion in chronic hepatitis B infection: current knowledge and clinical significance. Cell Death Dis (2015) 6:e1694. doi:10.1038/cddis.2015.42
114. Webster GJM, Reignat S, Brown D, Ogg GS, Jones L, Seneviratne SL, et al. Longitudinal analysis of CD8+ T cells specific for structural and nonstructural hepatitis B virus proteins in patients with chronic hepatitis B: implications for immunotherapy. J Virol (2004) 78(11):5707–19. doi:10.1128/JVI.78.11.5707-5719.2004
115. Kondo Y, Ninomiya M, Kakazu E, Kimura O, Shimosegawa T. Hepatitis B surface antigen could contribute to the immunopathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection. ISRN Gastroenterol (2013) 2013:935295. doi:10.1155/2013/935295
116. Whalley SA, Brown D, Webster GJM, Jacobs R, Reignat S, Bertoletti A, et al. Evolution of hepatitis B virus during primary infection in humans: transient generation of cytotoxic T-cell mutants. Gastroenterology (2004) 127(4):1131–8. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2004.07.004
117. Bengsch B, Martin B, Thimme R. Restoration of HBV-specific CD8+ T cell function by PD-1 blockade in inactive carrier patients is linked to T cell differentiation. J Hepatol (2014) 61(6):1212–9. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2014.07.005
118. Boni C, Laccabue D, Lampertico P, Giuberti T, Viganò M, Schivazappa S, et al. Restored function of HBV-specific T cells after long-term effective therapy with nucleos(t)ide analogues. Gastroenterology (2012) 143(4):963–73.e9. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2012.07.014
119. Boni C, Penna A, Bertoletti A, Lamonaca V, Rapti I, Missale G, et al. Transient restoration of anti-viral T cell responses induced by lamivudine therapy in chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol (2003) 39(4):595–605. doi:10.1016/S0168-8278(03)00292-7
120. Rivino L, Le Bert N, Gill US, Kunasegaran K, Cheng Y, Tan DZM, et al. Hepatitis b virus–specific t cells associate with viral control upon nucleos(t)ide-analogue therapy discontinuation. J Clin Invest (2018) 128(2):668–81. doi:10.1172/JCI92812
121. Chu CM, Liaw YF. Chronic hepatitis B virus infection acquired in childhood: special emphasis on prognostic and therapeutic implication of delayed HBeAg seroconversion. J Viral Hepat (2007) 14(3):147–52. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2893.2006.00810.x
122. Chen Y-C, Chu C-M, Liaw Y-F. Age-specific prognosis following spontaneous hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology (2010) 51(2):435–44. doi:10.1002/hep.23348
123. Okamoto H, Tsuda F, Akahane Y, Sugai Y, Yoshiba M, Moriyama K, et al. Hepatitis B virus with mutations in the core promoter for an e antigen-negative phenotype in carriers with antibody to e antigen. J Virol (1994) 68(12):8102–10.
124. Wang H-Y, Chien M-H, Huang H-P, Chang H-C, Wu C-C, Chen P-J, et al. Distinct hepatitis B virus dynamics in the immunotolerant and early immunoclearance phases. J Virol (2010) 84(7):3454–63. doi:10.1128/JVI.02164-09
125. Hannoun C, Horal P, Lindh M. Long-term mutation rates in the hepatitis B virus genome. J Gen Virol (2000) 81(Pt 1):75–83. doi:10.1099/0022-1317-81-1-75
126. Bozkaya H, Akarca US, Ayola B, Lok ASF. High degree of conservation in the hepatitis B virus core gene during the immune tolerant phase in perinatally acquired chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol (1997) 26(3):508–16. doi:10.1016/S0168-8278(97)80415-1
127. Philpott S, Burger H, Tsoukas C, Foley B, Anastos K, Kitchen C, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genomic RNA sequences in the female genital tract and blood: compartmentalization and intrapatient recombination. J Virol (2005) 79(1):353–63. doi:10.1128/JVI.79.1.353-363.2005
128. Schnell G, Price RW, Swanstrom R, Spudich S. Compartmentalization and clonal amplification of HIV-1 variants in the cerebrospinal fluid during primary infection. J Virol (2010) 84(5):2395–407. doi:10.1128/JVI.01863-09
129. Roque-Afonso AM, Ducoulombier D, Di Liberto G, Kara R, Gigou M, Dussaix E, et al. Compartmentalization of hepatitis C virus genotypes between plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Virol (2005) 79(10):6349–57. doi:10.1128/JVI.79.10.6349-6357.2005
130. Russelli G, Pizzillo P, Iannolo G, Barbera F, Tuzzolino F, Liotta R, et al. HCV replication in gastrointestinal mucosa: potential extra-hepatic viral reservoir and possible role in HCV infection recurrence after liver transplantation. PLoS One (2017) 12(7):e0181683. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0181683
131. Bull ME, Heath LM, McKernan-Mullin JL, Kraft KM, Acevedo L, Hitti JE, et al. Human immunodeficiency viruses appear compartmentalized to the female genital tract in cross-sectional analyses but genital lineages do not persist over time. J Infect Dis (2013) 207(8):1206–15. doi:10.1093/infdis/jit016
132. Michalak TI. Occult persistence and lymphotropism of hepadnaviral infection: insights from the woodchuck viral hepatitis model. Immunol Rev (2000) 174:98–111. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0528.2002.017406.x
133. Mason A, Wick M, White H, Perrillo R. Hepatitis B virus replication in diverse cell types during chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology (1993) 18(4):781–9. doi:10.1002/hep.1840180406
134. Faure-Dupuy S, Durantel D, Lucifora J. Liver macrophages: friend or foe during hepatitis B infection? Liver Int (2018). doi:10.1111/liv.13884
135. Coffin CS, Mulrooney-Cousins PM, Van Marle G, Roberts JP, Michalak TI, Terrault NA. Hepatitis B virus quasispecies in hepatic and extrahepatic viral reservoirs in liver transplant recipients on prophylactic therapy. Liver Transpl (2011) 17(8):955–62. doi:10.1002/lt.22312
136. Coffin CS, Osiowy C, Gao S, Nishikawa S, van der Meer F, van Marle G. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) variants fluctuate in paired plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells among patient cohorts during different chronic hepatitis B (CHB) disease phases. J Viral Hepat (2015) 22(4):416–26. doi:10.1111/jvh.12308
137. Datta S, Panigrahi R, Biswas A, Chandra PK, Banerjee A, Mahapatra PK, et al. Genetic characterization of hepatitis B virus in peripheral blood leukocytes: evidence for selection and compartmentalization of viral variants with the immune escape G145R mutation. J Virol (2009) 83(19):9983–92. doi:10.1128/JVI.01905-08
138. Brind A, Jiang J, Samuel D, Gigou M, Feray C, Bréchot C, et al. Evidence for selection of hepatitis B mutants after liver transplantation through peripheral blood mononuclear cell infection. J Hepatol (1997) 26(2):228–35. doi:10.1016/S0168-8278(97)80035-9
139. Chakravarty R, Neogi M, Roychowdhury S, Panda CK. Presence of hepatitis B surface antigen mutant G145R DNA in the peripheral blood leukocytes of the family members of an asymptomatic carrier and evidence of its horizontal transmission. Virus Res (2002) 90(1–2):133–41. doi:10.1016/S0168-1702(02)00147-8
140. Bagaglio S, Albarello L, Biswas P, Uberti-Foppa C, Fortis C, Morsica G. Virological pattern of hepatitis B infection in an HIV-positive man with fatal fulminant hepatitis B: a case report. J Med Case Rep (2009) 3:110. doi:10.1186/1752-1947-3-110
141. Gao S, Duan Z-P, Chen Y, van der Meer F, Lee SS, Osiowy C, et al. Compartmental HBV evolution and replication in liver and extrahepatic sites after nucleos/tide analogue therapy in chronic hepatitis B carriers. J Clin Virol (2017) 94:8–14. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2017.06.009
142. Wu C, Zhang X, Tian Y, Song J, Yang D, Roggendorf M, et al. Biological significance of amino acid substitutions in hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) for glycosylation, secretion, antigenicity and immunogenicity of HBsAg and hepatitis B virus replication. J Gen Virol (2010) 91(Pt 2):483–92. doi:10.1099/vir.0.012740-0
143. Torresi J. The virological and clinical significance of mutations in the overlapping envelope and polymerase genes of hepatitis B virus. J Clin Virol (2002) 25:97–106. doi:10.1016/S1386-6532(02)00049-5
144. Delaney WE, Yang H, Westland CE, Das K, Arnold E, Gibbs CS, et al. The hepatitis B virus polymerase mutation rtV173L is selected during lamivudine therapy and enhances viral replication in vitro. J Virol (2003) 77(21):11833–41. doi:10.1128/JVI.77.21.11833-11841.2003
145. Mokaya J, McNaughton AL, Hadley M, Beloukas A, Geretti A-M, Goedhals D, et al. A systematic review of hepatitis B virus (HBV) drug and vaccine escape mutations in Africa: a call for urgent action. bioRxiv (2018). doi:10.1101/258350
146. Oniangue-Ndza C, Kuntzen T, Kemper M, Berical A, Wang YE, Neumann-Haefelin C, et al. Compensatory mutations restore the replication defects caused by cytotoxic T lymphocyte escape mutations in hepatitis C virus polymerase. J Virol (2011) 85(22):11883–90. doi:10.1128/JVI.00779-11
147. Peyerl FW, Bazick HS, Newberg MH, Barouch DH, Sodroski J, Letvin NL. Fitness costs limit viral escape from cytotoxic T lymphocytes at a structurally constrained epitope. J Virol (2004) 78(24):13901–10. doi:10.1128/JVI.78.24.13901-13910.2004
148. Brockman MA, Schneidewind A, Lahaie M, Schmidt A, Miura T, DeSouza I, et al. Escape and compensation from early HLA-B57-mediated cytotoxic T-lymphocyte pressure on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gag alter capsid interactions with cyclophilin A. J Virol (2007) 81(22):12608–18. doi:10.1128/JVI.01369-07
149. Hoofnagle JH. Reactivation of hepatitis B. Hepatology (2009) 49(5 Suppl):S156–65. doi:10.1002/hep.22945
150. Loomba R, Liang TJ. Hepatitis B reactivation associated with immune suppressive and biological modifier therapies: current concepts, management strategies, and future directions. Gastroenterology (2017) 152(6):1297–309. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.02.009
151. Sugauchi F, Tanaka Y, Kusumoto S, Matsuura K, Sugiyama M, Kurbanov F, et al. Virological and clinical characteristics on reactivation of occult hepatitis B in patients with hematological malignancy. J Med Virol (2011) 83(3):412–8. doi:10.1002/jmv.21995
152. Kempinska A, Kwak EJ, Angel JB. Reactivation of hepatitis B infection following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in a hepatitis B-immune patient: case report and review of the literature. Clin Infect Dis (2005) 41(9):1277–82. doi:10.1086/496924
153. Mok MY, Ng WL, Yuen MF, Wong RW, Lau CS. Safety of disease modifying anti-rheumatic agents in rheumatoid arthritis patients with chronic viral hepatitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol (2000) 18(3):363–8.
154. Ito S, Nakazono K, Murasawa A, Mita Y, Hata K, Saito N, et al. Development of fulminant hepatitis B (precore variant mutant type) after the discontinuation of low-dose methotrexate therapy in a rheumatoid arthritis patient. Arthritis Rheum (2001) 44(2):339–42. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(200102)44:2<339::AID-ANR51>3.0.CO;2-Q
155. Esteve M, Saro C, Gonzalez-Huix F, Suarez F, Forne M, Viver JM. Chronic hepatitis B reactivation following infliximab therapy in Crohn’s disease patients: need for primary prophylaxis. Gut (2004) 53(9):1363–5. doi:10.1136/gut.2004.040675
156. Kajiwara E, Tanaka Y, Ohashi T, Uchimura K, Sadoshima S, Kinjo M, et al. Hepatitis B caused by a hepatitis B surface antigen escape mutant. J Gastroenterol (2008) 43(3):243–7. doi:10.1007/s00535-007-2150-9
157. World Health Organization. Global Hepatitis Report 2017. Geneva: World Health Organization (2017).
158. Bertoletti A, Bert NL. Immunotherapy for chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Gut Liver (2018). doi:10.5009/gnl17233
159. Bertoletti A, Tan AT, Koh S. T-cell therapy for chronic viral hepatitis. Cytotherapy (2017) 19(11):1317–24. doi:10.1016/j.jcyt.2017.07.011
160. Wisskirchen K, Metzger K, Schreiber S, Asen T, Weigand L, Dargel C, et al. Isolation and functional characterization of hepatitis B virus-specific T-cell receptors as new tools for experimental and clinical use. PLoS One (2017) 12(8):e0182936. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0182936
161. Rehermann B, Ferrari C, Pasquinelli C, Chisari FV. The hepatitis B virus persists for decades after patients’ recovery from acute viral hepatitis despite active maintenance of a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response. Nat Med (1996) 2(10):1104–8. doi:10.1038/nm1096-1104
162. Kaymakoglu S, Baran B, Onel D, Badur S, Atamer T, Akyuz F. Acute hepatitis B due to immune-escape mutations in a naturally immune patient. Acta Gastroenterol Belg (2014) 77(2):262–5.
163. Ye Q, Shang S-Q, Li W. A new vaccine escape mutant of hepatitis B virus causes occult infection. Hum Vaccin Immunother (2015) 11(2):407–10. doi:10.4161/21645515.2014.994461
164. Mendy M, D’Mello F, Kanellos T, Oliver S, Whittle H, Howard CR. Envelope protein variability among HBV-Infected asymptomatic carriers and immunized children with breakthrough infections. J Med Virol (2008) 80(9):1537–46. doi:10.1002/jmv.21221
165. Zhang M, Ge G, Yang Y, Cai X, Fu Q, Cai J, et al. Decreased antigenicity profiles of immune-escaped and drug-resistant hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) double mutants. Virol J (2013) 10:292. doi:10.1186/1743-422X-10-292
166. Lacombe K, Boyd A, Gozlan J, Lavocat F, Girard P-M, Zoulim F. Drug-resistant and immune-escape HBV mutants in HIV-infected hosts. Antivir Ther (2010) 15(3 Pt B):493–7. doi:10.3851/IMP1495
167. Sloan RD, Ijaz S, Moore PL, Harrison TJ, Teo CG, Tedder RS. Antiviral resistance mutations potentiate hepatitis B virus immune evasion through disruption of its surface antigen a determinant. Antivir Ther (2008) 13(3):439–47.
168. Baxa DM, Thekdi AD, Golembieski A, Krishnan PV, Sharif O, Kizy A, et al. Evaluation of anti-HBV drug resistant mutations among patients with acute symptomatic hepatitis B in the United States. J Hepatol (2013) 58(2):212–6. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2012.09.014
Keywords: hepatitis B virus, evolution, adaptation, diversity, CD8+ T cells, adaptive immunity, human leukocyte antigen
Citation: Lumley SF, McNaughton AL, Klenerman P, Lythgoe KA and Matthews PC (2018) Hepatitis B Virus Adaptation to the CD8+ T Cell Response: Consequences for Host and Pathogen. Front. Immunol. 9:1561. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01561
Received: 12 April 2018; Accepted: 25 June 2018;
Published: 16 July 2018
Edited by:
Gkikas Magiorkinis, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, GreeceReviewed by:
Antonio Bertoletti, Duke-NUS Medical School, SingaporeJoerg Timm, Heinrich-Heine Universität Düsseldorf, Germany
Robert Thimme, Albert Ludwigs Universität Freiburg, Germany
Copyright: © 2018 Lumley, McNaughton, Klenerman, Lythgoe and Matthews. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Philippa C. Matthews, cGhpbGlwcGEubWF0dGhld3NAbmRtLm94LmFjLnVr
 Sheila F. Lumley
Sheila F. Lumley Anna L. McNaughton
Anna L. McNaughton Paul Klenerman
Paul Klenerman Katrina A. Lythgoe
Katrina A. Lythgoe Philippa C. Matthews
Philippa C. Matthews