- 1Faculty of Health Sciences, Division of Immunology and South African Medical Research Council (SAMRC) Immunology of Infectious Diseases, Institute of Infectious Diseases and Molecular Medicine (IDM), University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa
- 2International Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB), Cape Town, South Africa
- 3Department of Molecular and Cell Biology Faculty of Science, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa
The interleukin (IL)-4 receptor alpha (IL-4Rα), ubiquitously expressed on both innate and adaptive immune cells, controls the signaling of archetypal type 2 immune regulators; IL-4 and IL-13, which elicit their signaling action by the type 1 IL-4Rα/gamma common and/or the type 2 IL-4Rα/IL-13Rα complexes. Global gene-deficient mouse models targeting IL-4, IL-13, or the IL-4Rα chain, followed by the development of conditional mice and generation of important cell-type-specific IL-4Rα-deficient mouse models, were indeed critical to gaining in-depth understanding of detrimental T helper (Th) 2 mechanisms in type 1-controlled diseases. A primary example being cutaneous leishmaniasis, which is caused by the protozoan parasite Leishmania major, among others. The disease is characterized by localized self-healing cutaneous lesions and necrosis for which, currently, not a single vaccine has made it to a stage that can be considered effective. The spectrum of human leishmaniasis belongs to the top 10 infectious diseases according to the World Health Organization. As such, 350 million humans are at risk of infection and disease, with an incidence of 1.5–2 million new cases being reported annually. A major aim of our research is to identify correlates of host protection and evasion, which may aid in vaccine design and therapeutic interventions. In this review, we focus on the immune-regulatory role of the IL-4Rα chain from innate immune responses to the development of beneficial type 1 and detrimental type 2 adaptive immune responses during cutaneous Leishmania infection. We discuss the cell-specific requirements of the IL-4Rα chain on crucial innate immune cells during L. major infection, including, IL-4Rα-responsive skin keratinocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils, as well as dendritic cells (DCs). The latter, contributing to one of the paradigm shifts with respect to the role of IL-4 instructing DCs in vivo, to promote Th1 responses against L. major. Finally, we extend these innate responses and mechanisms to control of adaptive immunity and the effect of IL-4Rα-responsiveness on T and B lymphocytes orchestrating the development of CD4+ Th1/Th2 and B effector 1/B effector 2 B cells in response to L. major infection in the murine host.
Introduction
Human leishmaniasis, ranging from localized ulcerating lesions (cutaneous) to disseminated (mucocutaneous) and fatal infection (visceral), presents a global health concern, with over 12 million people currently infected and an additional 350 million humans at risk of infection and disease (1, 2). It is therefore not surprising that infection rates surpass 1.5 million new cases annually (3). Despite a concerted effort to develop a vaccine against the parasite, not a single candidate has been proven effective, and current therapeutic approaches are unable to achieve a sterile cure (2, 3). A thorough understanding of the mechanisms by which Leishmania spp. evade or exploit host immune mechanisms, to persist and establish disease, is paramount to identifying new and improved strategies for effective management of the disease. To address this, experimental models of cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL), which is the most common form of the disease, was established. In this model, disease is induced by infecting mice subcutaneously with Leishmania major. The L. major mouse model provided an excellent system for investigating the mechanisms underlying T helper (Th) 1 and Th2 cell differentiation relating to resistance and susceptibility to intracellular infection (4–6). This model, in global gene-deficient mice, established that the archetypal Th2 cytokines, interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-13 (IL-13), are susceptibility factors during L. major infection in BALB/c mice, counter-regulating a protective Th1 response, and induce their biological functions through a common receptor, the interleukin-4 receptor alpha (IL-4Rα) chain (7–9). However, IL-4Rα-deficient BALB/c mice remain susceptible to L. major infection in chronic stages (9, 10), indicating that IL-4/IL-13 may induce protective responses depending on which cell/s the IL-4/IL-13 ligand/s interact with during disease (11). Given the ubiquitous expression of the IL-4Rα signaling receptor on both innate and adaptive immune cells (12), cell-type-specific IL-4Rα-deficient mice were introduced to dissect the cell-specific roles of IL-4/IL-13 in CL. While these studies exemplified the role of IL-4Rα signaling on specific immune cells (10, 11, 13), it also questioned whether the Th1/Th2 paradigm of resistance/susceptibility to infection was in fact still relevant, considering that in certain disease settings, IL-4/IL-13 signaling essentially instructed a beneficial Th1 response (5, 11). Collectively, these reports highlight that the interplay between resistance and susceptibility to murine L. major infection involves a complex, dynamic interaction between the IL-4Rα chain and various innate and adaptive immune cells, with different clinical and immunological outcomes. In this review, we focus on the cell-specific requirements of the IL-4Rα chain signaling on crucial cells mediating innate and adaptive immunity to CL, relating primarily to L. major infection in mouse models.
The IL-4Rα Chain: Common Receptor for IL-4 and IL-13 Signaling
Interleukin-4
Interleukin-4 plays a critical role in initiating and regulating Th2-type immune responses (14). In mice, IL-4 is a 14–19 kDa glycoprotein localized on chromosome 11, together with the genes for IL-5 and IL-13. During the innate immune response, evidence suggests that early IL-4-producers include basophils (15, 16), mast cells (17), eosinophils (18), natural killer (NK) T cells (19, 20), and innate-like skin keratinocytes (21). T and B lymphocytes orchestrating adaptive immunity, specifically CD4+ Th2 cells (22), B effector 2 (Be2) B cells (23, 24), and γ/δ T cells (25), also secrete IL-4. Apart from regulating the differentiation of Th2 cells, IL-4 also controls immunoglobulin class switching in activated B cells, specifying human B cells to switch to the expression of IgE and IgG4 (26), while in mice, to IgE and IgG1, with the concomitant suppression of IgM, IgG2a, and IgG2b (27, 28). Moreover, alternatively activated macrophages are activated by IL-4 signaling through the IL-4Rα chain (29). Importantly, IL-4 inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression thereby inhibiting IFN-γ-induced classically activated macrophages and induction of a type 1 response. As a whole, IL-4 counter-regulates the expression of IFN-γ (12) and increases the expression of MHC II molecules (30), co-stimulatory molecules CD80 and CD86 (31), and the IL-4 receptor (32). Reports have also indicated that dendritic cells (DCs) can respond to IL-4 in vivo and in vitro and become alternatively activated, in a manner similar to that described for alternatively activated macrophages, by upregulating multiple alternative activation markers such as mannose receptor and RELM-α (33). Moreover, although IL-4 has been shown to be the primary inducer of Th2 responses, studies have reported IL-4-independent Th2 differentiation, Th2 cytokine production, IL-4Rα signaling, and STAT6 regulation (34–41).
Interleukin-13
Murine IL-13 is an immunoregulatory cytokine with a molecular weight of 10–14 kDa (42), also localized on chromosome 11, together with the genes for IL-4 and IL-5. Similar to IL-4, murine IL-13 also promotes upregulation of MHC II antigens, co-stimulatory (CD80/CD86) and adhesion molecules. However, unlike IL-4, murine IL-13 has been shown not to affect Th2 differentiation, B cell switching or upregulation of the low-affinity IgE receptor (CD23), likely due to the absence of a functional IL-13 receptor on those cells in mice. By contrast, human B lymphocytes do respond to IL-13 (34). Innate mast cells, basophils, DCs, NK cells, activated CD4+ Th2 cells, Be2 B cells, and NK T cells are IL-13-producers (34, 43–45). In fact, IL-13 is responsible for activating mast cells, modulating eosinophil function (42), and alternatively activating macrophages in conjunction with IL-4 (29). IL-13 also has immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory effects on macrophages and monocytes, including suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. In addition, nitric oxide (NO) production, along with antibody-mediated cytotoxicity, is inhibited by IL-13.
The IL-4 and IL-13 Receptor Complexes
The overlapping biological functions of IL-4 and IL-13 on certain cell-types could be partly attributed to the shared IL-4Rα component of natively distinct receptors (34). This theory was initially demonstrated in competitive studies in which treatment of mice with IL-4 antagonists or anti-IL-4Rα antibodies inhibited both IL-4- and IL-13-mediated responses (46–48). The IL-4Rα chain (CD124) is a 140 kDa heterodimeric complex, serving as a common monomer in both the type 1 and type 2 receptor complexes (Figure 1). It is ubiquitously expressed in fairly low numbers on hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells (12). IL-4Rα interacts with the gamma common (γc) chain to form the type 1 IL-4 receptor and interacts with the 65–70 kDa IL-13-binding receptor alpha 1 (IL-13Rα1) chain to form the type 2 IL-4/IL-13 receptor (Figure 1) (12). The former is also shared by the receptors for IL-2, IL-7, IL-9, and IL-15. IL-4 binds the IL-4Rα chain with high affinity. By contrast, IL-13 binds the IL-13Rα1 chain with low affinity. However, when paired with the IL-4Rα chain, IL-13 binds the IL-13Rα1 chain with high affinity forming an active signaling unit (49). Expression of IL-13Rα1 is absent on human or murine T cells but constitutively expressed on B cells, epithelial cells and monocytes in both mice and humans (50, 51). In comparison, IL-13 shows a higher binding affinity for the α2 chain of the IL-13 receptor (IL-13Rα2), which is a 55–60 kDa protein (Figure 1). IL-13Rα2 was originally considered a decoy receptor for IL-13, devoid of signal transduction, since its short cytoplasmic domain was not reported to contain any binding motifs for signaling molecules (52). However, well-designed reports have demonstrated a signaling pathway for IL-13 through the IL-13Rα2 chain, which induces the production of TGF-β1 and mediates fibrosis (53). In addition to cell-surface localization, soluble forms of both IL-4Rα and IL-13Rα2 exist (Figure 1), which are capable of binding IL-4 and IL-13 with high affinity as non-signaling monomers. In doing so, the soluble receptors can act as competitive inhibitors of both IL-4 and IL-13 and modulate their effector responses (54, 55).
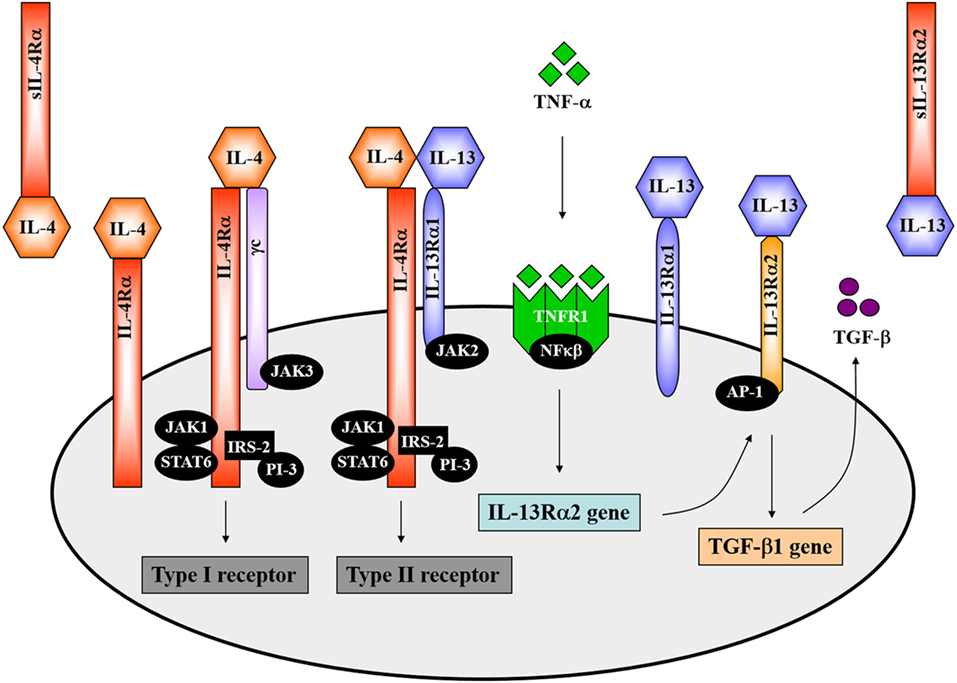
Figure 1. The interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-13 (IL-13) receptor complexes. IL-4 interacts with the interleukin-4 receptor alpha (IL-4Rα) chain in combination with either the gamma common (γc) chain to form the type 1 receptor or with the IL-13-binding receptor alpha 1 (IL-13Rα1) to form the type 2 receptor complex. The IL-4Rα chain signals via the JAK1/STAT6 pathway. Definitively, JAK3 associates with the γc chain and JAK2 with the IL-13Rα1. IL-13 interacts with the type II receptor complex (through IL-13Rα1) or with the α2 chain of the IL-13 receptor (IL-13Rα2). A signaling pathway for IL-13 via IL-13Rα2 has recently been identified. TNF-α induces upregulation of IL-13Rα2 expression. IL-13 then binds to the IL-13Rα2, which activates AP-1 to induce gene expression and secretion of soluble TGF-β. Illustration adapted and redrawn from previous publications (12, 34, 42, 52, 56).
Mechanisms of IL-4 and IL-13 Signaling through the IL-4Rα Chain
Both IL-4 and IL-13 signal transduction via the IL-4Rα chain involves activation of the Janus-family kinases (JAK). JAK1 interacts with the IL-4Rα chain whereas JAK3 interacts with the γc chain and JAK2 with the IL-13Rα1 (Figure 1) (12, 57, 58). IL-4 engagement with the IL-4Rα chain results in tyrosine phosphorylation of the IL-4Rα chain itself as well as phosphorylation of STAT6 and insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS-2) by JAKs, which then associates with the phosphoinositol-3 kinase (PI-3) (Figure 1) (12, 34). STAT6-deficient mice presented impaired IL-13-mediated functions, which confirmed that IL-13 also uses the JAK/STAT6 pathway for signal transduction (Figure 1) (34, 59). IL-13 signaling through the IL-13Rα2 requires initial engagement of the IL-13Rα1/IL-4Rα complexes in conjunction with TNF-α signaling, which increases surface expression of IL-13Rα2. IL-13 then binds to the IL-13Rα2 and, through activation of the transcription factor AP-1, drives secretion of TGF-β (Figure 1) (52, 53).
Cutaneous Leishmanisis
Cell-Mediated Host Immune Responses to L. major
The Leishmania parasite has a complex digenetic life cycle alternating between two distinct stages; the promastigote form found in the female Phlebotomus sandfly vector and the amastigote form replicating within phagolysosomes of host macrophages and DCs. Ironically, macrophages (and DCs) being the primary immune cells involved in the eradication of Leishmania in a mammalian host, are the preferred host cells of the parasite (3, 11, 60, 61). Early pioneering studies focused on the modulation of cytokine signaling as a means to alter immune cell activation and Th cell differentiation. These studies were conducted in an attempt to understand the mechanisms by which Leishmania are able to survive and flourish in these hostile environments while also capitalizing on host defense mechanisms to favor the establishment of disease. These mouse models, involving experimental infection with L. major, established the Th1/Th2 paradigm of resistance/susceptibility to intracellular infection (5, 6). Upon infection with L. major, genetically resistant C57BL/6 mice develop a healing phenotype associated with an IL-12-driven protective Th1/type 1 immune response, upregulation of IFN-γ and classical activation of macrophages for subsequent killing of intracellular parasites by effector NO production (Figure 2) (13, 62–66). IL-18 augments IL-12 activity, both of which interact with the IL-12 receptor β2-chain (IL-12Rβ2) in activated Th1 cells (67) and protects against L. major infections (68). CD8+ T cells and NK cells enhance this protective response by secreting IFN-γ that activates macrophages for parasite clearance. By contrast, the lack of healing in genetically susceptible BALB/c mice is associated with a Th2/type 2 response characterized by the secretion of IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-10, and IL-13, high type 2 anti-Leishmania antibody titers, and alternative activation of macrophages, which altogether promotes parasite survival and growth (Figure 2) (7, 8, 69–71). BALB/c mice present with lower levels of IL-12. Evidence suggests that this might be due to sustained IL-4 expression by Vβ4+Vα8+ CD4+ T cells, mast cells and eosinophils at the inoculation site and draining lymph node (LN) (Figure 2), which delays secretion of IL-12. Alternatively, reduced expression of the IL-12Rβ2 chain on activated Th2 cells lead to a loss in responsiveness to IL-12. In addition, maintenance of inflammatory neutrophils at the site of parasite inoculation (72) and regulatory T cells (Tregs), constituting a source of IL-10, favors the persistence of parasites in leishmanial skin lesions (Figure 2) (73, 74).
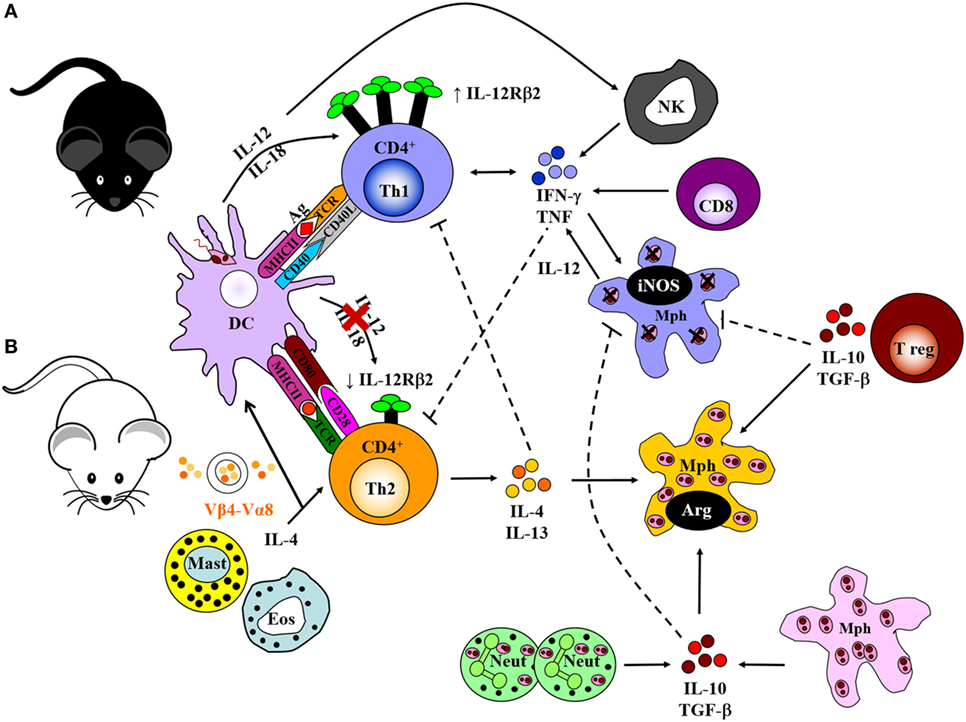
Figure 2. Cell-mediated immune response to Leishmania major in resistant and susceptible mice. (A) Upon interaction with L. major parasites, activated dendritic cells (DCs) process and present parasite antigen and produce IL-12 and IL-18, which interact with the IL-12 receptor β2-chain (IL-12Rβ2) in activated Th1 cells. Together, a dominant Th1 response is generated by the production of IFN-γ and TNF-α. These cytokines upregulate the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and activate infected macrophages for intracellular killing. CD8+ T cells and natural killer (NK) cells control infection by producing IFN-γ and effector killing by macrophages leading to parasite control as observed in C57BL/6 mice. (B) By contrast, parasite persistence in BALB/c mice is due to the failure of an IL-12-dependent redirection of the early Th2 response. This may be due to continued expression of early interleukin-4 (IL-4) from Vβ4+Vα8+ CD4+ T cells, mast cells, and eosinophils at the inoculation site and draining lymph nodes. This delays secretion of IL-12, or loss of responsiveness to IL-12 due to reduced expression of the IL-12Rβ2 chain on activated Th2 cells. IL-4 and IL-13 suppress Th1 responses and inhibit intracellular killing by macrophages. This leads to arginase production by macrophages that favor parasite growth. Sustained neutrophil recruitment to the site of infection and regulatory T cells may promote susceptibility and inhibit Th1 responses by the production of IL-10 and TGF-β that inhibit activation of macrophages. Solid lines represent activation, and broken lines represent inhibition. Illustration drawn from previous publications (6, 75, 76).
The early IL-4 response to L. major is confined to CD4+ T cells expressing a Vβ4+Vα8+ T cell receptor that recognizes the Leishmania antigen LACK (Leishmania homolog of receptors for activated C kinase) (14, 77), in addition to mast cells and eosinophils at the site of infection and draining LN. Both BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice secrete IL-4 early after infection; however, production of IL-4 is sustained in susceptible BALB/c mice and transient in resistant C57BL/6 mice (78). The resistant mice redirect the early Th2 response in an IL-12-dependent mechanism toward a beneficial Th1 response, whereas in susceptible mice, the Th2 response persists and dominates the disease outcome by suppressing effector mechanisms essential for parasite killing (6, 79).
IL-4/IL-13 and IL-4Rα Signaling in CL
Since both IL-4 and IL-13 share a common signaling pathway through the IL-4Rα chain, collectively modulating type 2 immunity, IL-4Rα-mediated mechanisms became our primary research interest, in cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis (7–9, 80) and extending to acute schistosomiasis (81–83), nematode infections (84–86), and allergic airway disease (87, 88). Deletion of the IL-4Rα component impairs downstream signaling of both IL-4 and IL-13 responses via transcription factor STAT6 (Figure 1). This has been established in animal studies during L. major infection in which susceptible BALB/c mice deficient for IL-4 (7), IL-13 (8), IL-4Rα (9, 36), or STAT6 (89) were able to control disease progression. Initial control of L. major during the acute phase of infection in IL-4−/−-deficient mice (7) and IL-4Rα−/−-deficient (9) BALB/c mice is equivalent, with both strains of mice showing reduced footpad swelling (Figure 3), parasite loads and type 1 antibody responses (9). However, in contrast to IL-4−/− mice, IL-4Rα−/− mice developed progressive disease and necrotic footpad lesions during the chronic phase of infection (Figure 3). Thus, the absence of IL-13-mediated functions in IL-4Rα−/− mice implicated IL-13 as a susceptibility factor in chronic L. major infection (9). This was confirmed in IL-13 transgenic C57BL/6 mice, which developed a susceptible phenotype to acute leishmaniasis with impaired IL-12 and IFN-γ production, whereas IL-13-deficient BALB/c mice remained comparatively resistant (8, 90). This was attributed to IL-13 promoting susceptibility by activating alternative macrophages and suppressing secretion of NO, IL-12, and/or IL-18 (8, 90).
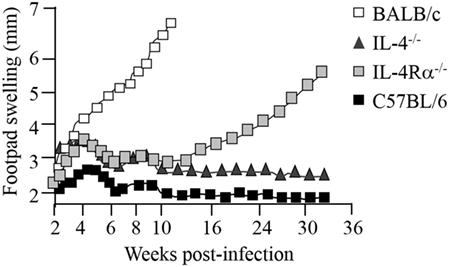
Figure 3. Disease progression in Leishmania major-infected-IL-4−/− and IL-4Rα−/− mice. BALB/c mice deficient for interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-4 receptor alpha (IL-4Rα) were infected with L. major LV39 strain and footpad swelling monitored weekly as an indication of disease progression. Illustration prepared according to published reports (7, 9–11).
The role of IL-4 and IL-4Rα in Leishmania infection in mice is, however, controversial since contradictory reports have suggested that although IL-4 is important, it is not the sole mediator of susceptibility in BALB/c mice. While Kopf et al. and Mohrs et al. demonstrated that IL-4−/− and IL-4Rα−/− mice were able to control CL (7, 9) (Figure 3), Noben-Trauth et al. showed that IL-4−/−- and IL-4Rα−/−-deficient BALB/c mice remained susceptible to disease and could not contain parasites at the site of infection (37, 91). This discrepancy between the two studies and in general, the outcome of L. major infection, may be attributed to a variation of experimental factors, such as the parasite sub-strain used, level of parasite virulence and the embryonic stem cells used to create the knockout mice. Of recent interest, the complex interplay between commensal microbiota in host animals and their vicinity may also be a contributing factor (92). Important to note, despite the absence of IL-4 or IL-4Rα, Th2-cell development and Th2-related cytokines were significantly promoted, although in different Th1/Th2 ratios (7, 37, 91). Subsequently, studies sought to follow IL-4 expression and Th cell development in vivo in L. major-infected IL-4−/− and IL-4Rα−/− BALB/c mice (36, 38, 93). The results revealed that, despite a clear absence of IL-4/IL-13-mediated functions in IL-4−/− and IL-4Rα-deficient mice, unimpaired Th2 polarization and IL-4-producing CD4+ T cells as well as other Th2-related cytokines were still present (7, 34, 36, 38). Accordingly, these pioneering studies confirmed that both IL-4-dependent and IL-4-independent factors contribute to the susceptibility phenotype in L. major-infected BALB/c mice. Together, these findings contradicted the idea that IL-4 is the sole regulator of susceptibility to L. major infection. The body of literature alternatively suggested that the combined action of IL-4/IL-13 heightens susceptibility to L. major, nonetheless, both cytokines may in fact act independently of each other to induce a non-healing response. More importantly, Th2 and type 2 immune responses may be induced independently of IL-4 and IL-13. Thus, at this stage 15 years ago, a definitive role for IL-4/IL-13 in progression of CL remained questionable.
Expression of the IL-4Rα chain reflects the pleiotropic nature of IL-4/IL-13 biology, as this receptor complex is endogenously expressed upon a diverse range of innate and adaptive immune cells in the host. In global gene-deficient mice, the target gene is deficient on all hematopoietic cells. Thus, IL-4- and IL-13-mediated functions at a cellular level remain uncharacterized. Therefore, it is possible that the range of target cells interacting with IL-4 and IL-13, and their order of hierarchical effector function or importance in the host, may account for differential IL-4/IL-13-mediated mechanisms during cutaneous Leishmania infection (4, 5). The emerging principles of innate instruction of adaptive immunity further exemplify that IL-4Rα signaling on innate cells may contribute specific functions that shape the adaptive immune response and outcome of infection.
IL-4Rα Signaling on Specific Innate Immune Cells in CL in Mice
Cre/loxP Targeting to Generate Cell-Specific IL-4Rα-Deficient Mice
To determine the cell-specific requirements for the IL-4Rα and its ligands, in type 1 and type 2-controlled diseases, we established a second generation of knockout mice using conditional IL-4Rα-deficient mice, thus creating novel mice with a cell-specific deletion of the il4rα gene. This was achieved by the bacteriophage-derived Cre/loxP genetic recombination system under control of specific loci (Figure 4). In this system, cyclization recombinase (Cre) inserted downstream of a cell-specific promoter recognizes a pair of loxP sequences flanking the gene of interest (specifically, Exon 7 to Exon 9 of IL-4Rα). Cre-recombinase removes the intervening DNA by bringing the two loxP sites together (94). Transgenic Cre mice (Zcre) are backcrossed to BALB/c or C57BL/6 for nine generations, then intercrossed with global IL-4Rα (IL-4Rα−/−) BALB/c (9) mice to generate ZcreIL-4Rα−/− BALB/c mice. Littermate mice are then subsequently intercrossed with floxed IL-4Rα (IL-4Rαflox/flox) BALB/c mice (Exon 6 to Exon 8 flanked by loxP) (82) to yield cell-specific IL-4Rα-deficient mice (or ZcreIL-4Rα−/lox) (10, 82, 84). With this strategy, we increase the efficiency of Cre-recombination by reducing the LoxP substrate for Cre-recombinase by 50%, thereby avoiding early aberrant non-Mendelian Cre recombination (10, 82).
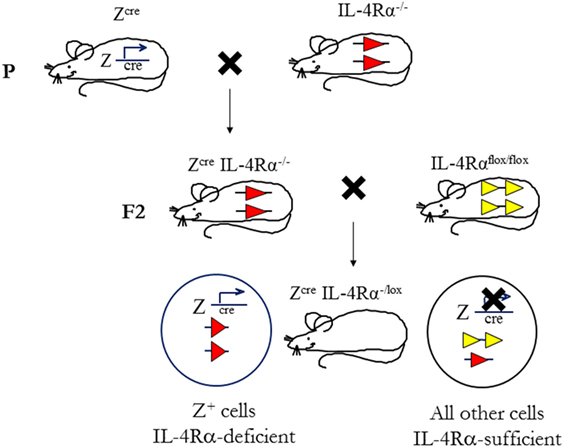
Figure 4. Mouse breeding strategy to create cell-specific interleukin-4 receptor alpha (IL-4Rα)-deficient mice. IL-4Rαflox/flox BALB/c mice were intercrossed with transgenic mice expressing Cre-recombinase under control of a cell-specific promoter (Zcre) and IL-4Rα−/− BALB/c mice to generate ZcreIL-4Rα−/lox mice. The “loxed” IL-4Rα allele, yellow arrows; deleted allele, red arrows. Illustration adapted and redrawn from previous publications (10, 11, 82).
IL-4Rα-Responsive Innate-Like Skin Keratinocytes in Murine CL
In CL, the skin represents the site of primary infection between the sandfly, parasites and the mammalian host. It is therefore probable that this immunologic organ may provide decisive signals for the development of a Th response early after infection. In addition to 20 billion T cells (95), the skin also contains innate and innate-like cells such as keratinocytes, melanocytes, and Langerhans cells in the epidermis, and dermal DCs, plasmacytoid DCs, phagocytes as well as lymphoid cells in the dermis (96). Keratinocytes are the most abundant cells in the epidermal layer (~90%) capable of differentiating harmful pathogens from harmless commensal organisms, and directing an appropriate immune response against it. The latter is due to their expression of distinct pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that recognize signature pathogen-specific molecular patterns. Biological activities of keratinocytes range from secretion of antimicrobial peptides to recruitment of host immune cells and notably, modulation of cytokine production (96–98). An immunomodulatory role for keratinocytes during L. major infection became evident when it was found that these cells secreted an array of cytokines, such as IL-12, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, within the first few hours after infection. The release of keratinocyte-specific inflammatory cytokines following Leishmania exposure implies the involvement of Toll-like receptor (TLR) activation on these cells since TLR recognition is often associated with the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (99). Of interest however, besides the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, IL-4 was also found to be produced by keratinocytes of both BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice (21). While the general consensus is that IL-4 acts as a canonical Th2 cytokine to induce a detrimental Th2/type 2 response, there have been studies demonstrating that early production of IL-4 at the site of infection may essentially drive a beneficial Th1 response, under the instruction of DCs secreting IL-12 (11, 100, 101). Importantly, direct uptake of L. major parasites by keratinocytes seems unlikely because of the subcutaneous infection and because keratinocytes have been reported not to take up L. major in vitro (21). Nevertheless, these reports suggested that keratinocytes may be the source of the early IL-4 that instructs DCs to drive a protective Th1/type 1 response. This is supported by the fact that keratinocytes express surface IL-4Rα predisposing the cells to possible autocrine stimulation by keratinocyte-derived IL-4 and IL-13, which may also influence DCs in a paracrine manner. Of note, Ehrchen et al. (21) did not identify strain-specific differences in the expression of IL-13 in the skin or specifically by keratinocytes. These cells can, however, secrete and signal IL-13 (97, 102). We therefore investigated if the autocrine action of IL-4 and IL-13, signaling on keratinocytes via the IL-4Rα complex, contributes to type 2 responses during CL. To address this, we generated keratinocyte-specific-IL-4Rα deficient (KRT14creIL-4Rα−/lox) mice on a BALB/c background using the cre/loxP system (Figure 4) under control of the keratinocyte 14 (krt14) locus. Considering that the strain of Leishmania initiating infection has a relevant influence on T cell-priming during infection, we incorporated experimental CL with L. major LV39 and IL81 strains by subcutaneous injection in the footpad. Surprisingly, despite minor immunological changes, KRT14creIL-4Rα−/lox mice on the BALB/c background developed non-healing disease similar to the littermate control mice following infection in the footpad. Moreover, the default Th2/type 2-driven cellular and humoral immune response characteristic of BALB/c mice, developed independently of IL-4Rα-responsive keratinocytes following L. major LV39 and IL81 infection in the footpad (Figure 5A) (submitted manuscript). Overall, our data and the reports above suggests that cytokine and chemokine-secreting skin keratinocytes might be involved in amplifying the L. major-induced inflammatory tissue signal by mobilizing leukocytes to the infection site following recognition of L. major parasites by keratinocyte-specific PRRs.
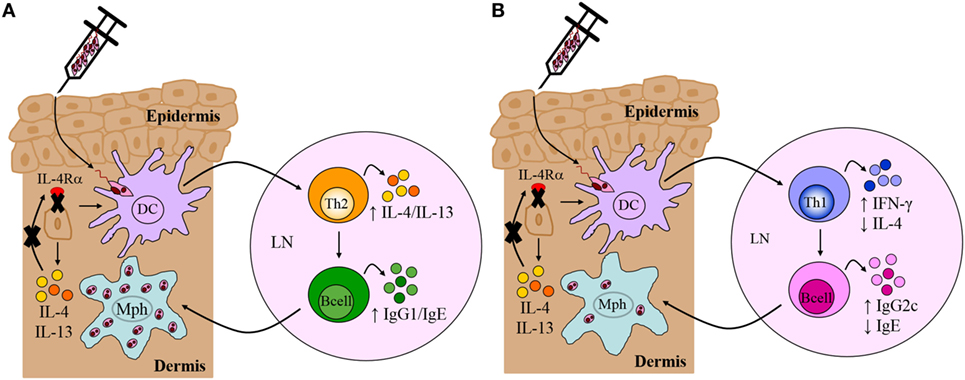
Figure 5. Immune response in Leishmania major-infected BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice deficient for interleukin-4 receptor alpha (IL-4Rα)-responsive keratinocytes. (A) Th2/Type 2-mediated susceptibility in BALB/c mice deficient for IL-4Rα-responsive keratinocytes. KRT14creIL-4Rα−/lox BALB/c mice, generated by cre/loxP targeting, developed non-healing disease to experimental L. major LV39 and IL81 infection in the footpad, characterized by substantial interleukin-4 (IL-4)/interleukin-13 (IL-13) production and IgG1/IgE production, similar to littermate control BALB/c mice. Model prepared using information from submitted manuscript. (B) Th1/Type 1-mediated protective immunity in C57BL/6 mice deficient for IL-4Rα-responsive keratinocytes. Similar to control C57BL/6 mice, KRT14creIL-4Rα−/lox C57BL/6 mice, generated by cre/loxP targeting, controlled lesion development upon L. major LV39 and IL81 infection in the footpad or ear dermis, characterized by strong IFN-γ and IgG2c production and concomitantly reduced IL-4 and IgE (103). DC, dendritic cells; Mph, macrophage; LN, lymph node; Th1, T helper 1; Th2, T helper 2.
In contrast to our original hypothesis, this suggested that IL-4Rα-responsive keratinocytes may not play a role in regulating the default Th2 polarized response during L. major infection in BALB/c mice. Nevertheless, given that Ehrchen et al. (21) reported a higher secretion of keratinocyte-derived IL-4 in C57BL/6 mice, as opposed to BALB/c, this suggested that the absence of IL-4 on keratinocytes in C57BL/6 mice might have a pronounced effect on Th1 polarization. As above and in Figure 4, the cre/loxP system was therefore used to generate KRT14creIL-4Rα−/lox mice on a C57BL/6 background. The use of both L. major LV39 and IL81 strains, injected subcutaneously in the footpad and ear, once again revealed unexpected results. In the absence of IL-4Rα-responsive keratinocytes, C57BL/6 mice controlled the development of inflammatory lesions upon infection with L. major LV39 and IL-81, which correlated with reduced parasite burdens and the expansion of Th1/type 1 cellular and humoral immune responses (Figure 5B) (103). Collectively, the data obtained in both KRT14creIL-4Rα−/lox BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice mitigate an autocrine role for IL-4/IL-13 signaling on keratinocytes in the development of a non-healing Th2/type 2 or protective Th1/type 1 immune response, respectively, following experimental infection with L. major LV39 and IL-81 in mice.
IL-4Rα-Responsive Macrophages and Neutrophils in Murine CL
Following Leishmania infection in the skin, innate macrophages, neutrophils and DCs are recruited to the site of inoculation, which can become infected and as a result, have specific and important roles in shaping CD4+ Th cell-dependent immune responses to infection. Considering that each of these cell-types express the surface IL-4Rα complex, we investigated cell-specific requirements for the IL-4Rα and its ligands on macrophages, neutrophils, and DCs. Studies have demonstrated that Leishmania-derived molecules activate TLRs, such as TLR2, TLR4, and TLR9, on these professional phagocytes to initiate the innate response. However, the consequences of such activation are complex and depend on the nature of the TLR, the cell type, the parasite species, the timing in which these events occur and the cytokine milieu surrounding the infected cells (104). Concerning macrophages, it is now well-accepted that these cells can be activated by different stimuli, with IFN-γ leading to classically activated macrophages, while signaling of IL-4/IL-13, via the IL-4Rα complex, results in alternative macrophage activation. The former mediates secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and killing of intracellular Leishmania, while the latter favors growth and survival of the parasites. Importantly, iNOS-mediated NO production is counter-regulated by IL-4Rα-dependent mechanisms through depletion of l-arginine, the substrate utilized by iNOS, leading to arginase I-expressing alternatively activated macrophages. Therefore, we postulated that the absence of IL-4Rα-responsive macrophages at the site of infection would induce signals that lead to a polarized protective Th1 response due to the absence of alternatively activated macrophages. Accordingly, LysMcreIL-4Rα−/lox mice on a susceptible BALB/c genetic background were generated, by cre/loxP targeting under control of the lysosome (lysm) locus (Figure 4), showing selective deficiency of IL-4Rα on macrophages and neutrophils.
In the context of Leishmania infection, neutrophils rapidly recruited to the site of inoculation (105) mediate persistence of parasites in skin lesions (72, 106). By contrast, it has also been shown that neutrophils mediate killing of intracellular Leishmania by neutrophil extracellular traps (107) or via activation of killing effector functions in macrophages through recruitment of TLR4 by neutrophil elastase (104, 108). However, the importance of type 2 signaling on macrophages and neutrophils during the early stages of L. major infection was undefined. The LysMcreIL-4Rα−/lox BALB/c strain therefore provided an attractive model to interrogate the combined contribution of Th2/type 2 responses via the IL-4Rα on macrophages and neutrophils in vivo in progression of CL. Hölscher et al. (13) revealed that in the absence of IL-4Rα on macrophages and neutrophils, BALB/c showed a significant control of disease progression up to 13 weeks after infection with L. major, despite sufficient Th2 and type 2 immune responses similar to littermate controls (Figure 6). Delayed disease progression in L. major-infected LysMcreIL-4Rα−/lox BALB/c mice was attributed to inhibition of alternative activation of macrophages and improved macrophage leishmanicidal activities due to NO production by classically activated macrophages (Figure 6). However, following 13 weeks of infection, LysMcreIL-4Rα−/lox mice developed fulminant CL with increasing footpad swelling, accompanied by ulceration and necrosis concomitant with elevated parasite burdens requiring termination of the experiment by week 18. The action of macrophages and neutrophils appear to complement each other as both population of cells are rapidly recruited to the site of infection and capable of phagocytosing Leishmania parasites following TLR stimulation. Accordingly, TLR4 was shown to be required for efficient leishmanicidal activity as the absence thereof led to increased arginase-derived urea and reduced formation of NO, probably via the activity of iNOS. The latter requires IL-12 secretion by antigen-presenting cells (APCs), and this cytokine can be activated by TLR9 (109). Thus, once could speculate that enhanced TLR4/TLR9 activation might have contributed to early control of disease in LysMcreIL-4Rα−/lox mice. Altogether, our study showed that IL-4Rα-mediated effects on macrophages and neutrophils seem to be involved in the development of early disease progression after L. major infection. The authors postulated that the transient effect of IL-4Rα-deficiency on macrophages/neutrophils after L. major infection may be that production of IL-4 and/or immunosuppressive cytokines by CD4+ T cells abolished the initial protective immune responses observed. Concurrently, an alternate hypothesis on IL-4Rα-dependent protective mechanisms emerged. Macrophage-derived IL-12 production was shown to be inhibited upon engagement of the IL-4Rα complex (82). Thus, Hölscher et al. (13) postulated that IL-4-mediated instruction of DCs may produce IL-12 (100), which indeed has been shown to promote resistance in L. major-infected BALB/c mice.
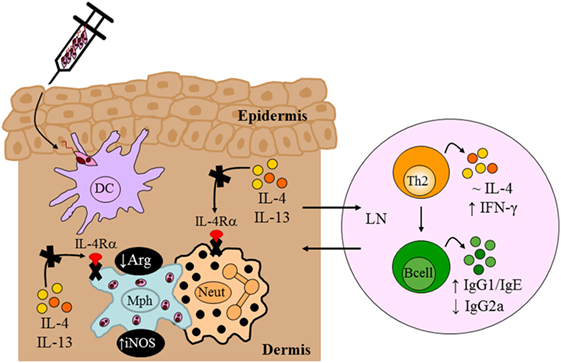
Figure 6. Immune response in BALB/c mice deficient for interleukin-4 receptor alpha (IL-4Rα)-responsive macrophages/neutrophils. Despite delayed disease progression in the footpads of L. major LV39-infected LysMcreIL-4Rα−/lox mice, unimpaired Th2/type II responses and reduced IgG2a were detected, similar to control BALB/c mice. The absence of IL-4Rα-responsive macrophages led to increased inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and reduced arginase, reflecting a shift to classically-activated macrophages likely as a consequence of increased IFN-γ compared to littermate control BALB/c mice. Illustration prepared from Hölscher et al. (13). DC, dendritic cells; Mph, macrophage; LN, lymph node; Th2, T helper 2.
IL-4Rα-Responsive DCs in Murine CL
Evidence from in vitro and in vivo studies began to contradict the detrimental role of IL-4 in susceptibility to L. major infection and the following observations proved critical: first, recombinant IL-4 was shown to promote IL-12 production by bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs) upon stimulation with specific ligands; second, IL-4, not IL-13, enhanced the production of IL-12 via signaling through the type 1 IL-4R complex; third, exogenous IL-4-administered in vivo during the period of DC activation in a murine model of L. major infection upregulated DC-derived il-12 transcripts leading to a protective Th1 response and healing in otherwise susceptible BALB/c mice, and fourth, administration of exogenous IL-4 in vivo during the period of T cell priming resulted in the default Th2 pathway and progressive disease in L. major-infected BALB/c mice. A follow-up study demonstrated that IL-4-mediated instruction was limited to DCs, excluding other APCs, and the mechanism responsible was inhibition of IL-10 by IL-4, leading to protective IL-12-driven Th1 responses (110). Altogether, the reports alluded to above portrayed IL-4 signaling on DCs as a double-edged sword in murine CL, emphasizing that the release of DC-derived IL-12 and the outcome of L. major infection in BALB/c mice depends on the timing of the IL-4Rα chain interacting with target cells. DCs are those innate cells that most acutely reflect innate control of adaptive immunity (111) as these sentinels of the immune system transition innate to adaptive immune responses owing to their proficient antigen-presenting function and migratory capacity (112).
To investigate a role for IL-4Rα-responsive DCs in resistance to L. major infection, we generated CD11ccreIL-4Rα−/lox BALB/c mice, in which dendritic-cell specific deletion of the il4rα gene was achieved by the Cre/loxP system under control of the cd11c locus (Figure 4). Infection studies with L. major LV39 and IL81 in the footpad revealed that IL-4-mediated instruction of DCs occurs in vivo with biological quantities of IL-4 acting on DCs to promote protective immunity. In the absence of IL-4Rα-responsive DCs, BALB/c mice became hypersusceptible to disease, when compared with littermate control mice, showing exacerbated lesion development and earlier tissue necrosis. This correlated with uncontrolled parasite replication at the infection site and a shift to Th2/type 2 cellular and humoral immune responses (Figure 7). Notably, CD11ccreIL-4Rα−/lox BALB/c mice displayed a striking increase in parasite dissemination from the site of infection to the draining LN and peripheral organs, including the brain of infected animals. Collectively, the data appeared to suggest that impaired NO-mediated killing effector functions in IL-4Rα-unresponsive DCs (and macrophages) facilitated a safe haven for parasite multiplication and dissemination of parasites. Accordingly, secretion of IL-12 by IL-4Rα-deficient DCs was severely impaired whereas IL-10 production was increased thereby confirming the mechanism behind impaired DC instruction in vivo. Interestingly, efficient TLR ligation on DCs disposes a potent negative signal for Th2 cell development (113). Thus, an alternate mechanism for the heightened susceptibility in CD11ccreIL-4Rα−/lox BALB/c might involve impaired TLR-mediated activation of DCs. In agreement, induction of BMDC-IL-12 following L. major infection was shown to be dependent on TLR9 activation (114). This might suggest a combined involvement of IL-4 and the TLR pathway in activating DC-derived IL-12 in this protective anti-L. major response. However, further research is required to elucidate a functional relationship.
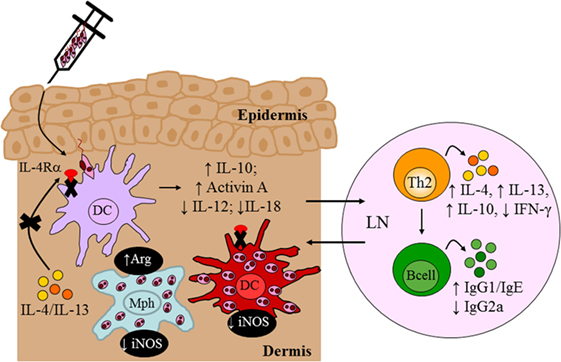
Figure 7. Immune response in BALB/c mice deficient for interleukin-4 receptor alpha (IL-4Rα)-responsive DCs. Absence of interleukin-4 (IL-4)/interleukin-13 (IL-13) signaling on DCs led to hypersusceptibility in BALB/c mice upon Leishmania major LV39 and IL81 infection in the footpad, characterized by a shift to Th2/type II immune responses and alternatively activated macrophages stronger than that usually observed in littermate BALB/c mice. Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in DCs was also dramatically reduced with increased arginase (Arg) compared to littermate mice providing a safe haven for L. major growth, survival, and dissemination to peripheral organs. Illustration prepared from Hurdayal et al. (11). DC, dendritic cells; Mph, macrophage; LN, lymph node; Th2, T helper 2.
In a parallel study, we explored the efficacy of IL-4 as an adjuvant in DC-mediated vaccination as in the context of visceral leishmaniasis, IL-4 mediates protective immunity and has been shown to instruct successful chemotherapy and vaccination responses (80). Accordingly, IL-4Rα-deficient BMDCs, with reduced IL-12 and increased IL-10 secretion, failed to vaccinate BALB/c animals against acute leishmaniasis, while IL-4-sufficient BMDCs producing increased IL-12 and reduced IL-10 successfully immunized BALB/c mice against infection (115). These observations unveiled yet another paradigm, suggesting that Leishmania vaccines should potentially incorporate IL-4 as an adjuvant, rather than IL-12, to induce protective IFN-γ responses.
IL-4Rα Signaling on Specific Adaptive Immune Cells in CL in Mice
IL-4Rα-Responsive CD4+ Th Cells in Murine CL
Recognition of Leishmania-specific molecular patterns by the PRRs of early innate immune cells provides the necessary signals that determine the choice of effector response in adaptive immunity, mediated primarily by T and B lymphocytes. Indeed, the central role of T cells during L. major infection was established early on (116); however, the contradictory roles of IL-4 (7, 91) questioned whether IL-4 counter-regulated a protective Th1 response to promote susceptibility to infection. In an attempt to reconcile these observations, we focused on specific abrogation of IL-4-responsive CD4+ T cells by deletion of the IL-4Rα subunit in BALB/c mice (LckcreIL-4Rα−/lox). In contrast to littermate control BALB/c mice, which developed ulcerating, necrotic lesions following infection with L. major LV39 and IL81, lack of IL-4-responsive CD4+ T cells led to a healing phenotype similar to that of the resistant C57BL/6 mice (10). Resistance to L. major in LckcreIL-4Rα−/lox BALB/c mice correlated with early il-12p35 mRNA transcription leading to increased IFN-γ production, elevated iNOS expression and enhanced memory responses, similar to C57BL/6 mice (Figure 8). In contrast to global IL-4Rα−/− mice, LckcreIL-4Rα−/lox BALB/c mice maintained chronic control of L. major infection. Collectively, the data demonstrated that CD4+ T cell-specific IL-4Rα-mediated signaling drives susceptibility to L. major infection, altogether highlighting a protective role for IL-4/IL-13 signaling on non-CD4+ T cells in L. major-infected BALB/c mice. Follow-up studies further demonstrated that iLckcreIL-4Rα−/lox BALB/c mice, with IL-4Rα deficiency on all T cell populations (CD4+, CD8+, natural killer T, and γδ+ T cells) were also able to resolve lesion development, correlating with reduced parasite replication, IFN-γ-mediated protective delayed type hypersensitivity responses and downregulated L. major-specific IgG1, similar to LckcreIL-4Rα−/lox and C57BL/6 mice (Figure 8). As expected, the non-healing littermate BALB/c control mice developed severe footpad swelling and increased parasite burdens (81). Taken together, these studies concluded that absence of IL-4Rα-responsive non-CD4+, in addition to CD4+ T cells, does not further affect transformation of BALB/c mice to a healer phenotype.
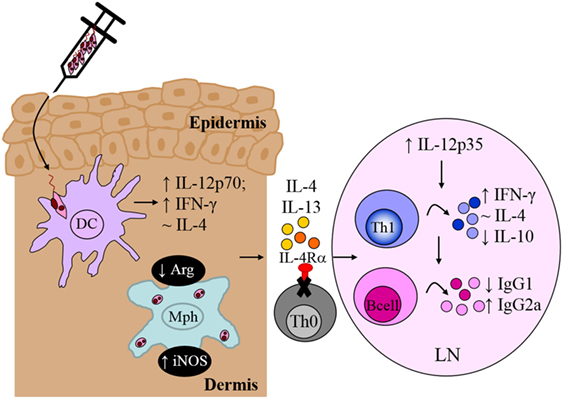
Figure 8. CD4+ T cell-specific interleukin-4 receptor alpha (IL-4Rα)-deficient mice develop a polarized Th1/type I immune response. In the absence of interleukin-4 (IL-4)-responsive T cells, normally susceptible BALB/c mice developed a healing phenotype upon experimental infection in the footpad, characterized by increased IFN-γ and IgG2a and concomitantly reduced IL-10 and IgG1 compared to littermate BALB/c mice. Interestingly, CD4+ T cell-specific IL-4Rα-deficient mice maintained equivalent IL-4 production to control littermate BALB/c mice. Illustration prepared from Radwanska et al. (10). DC, dendritic cells; Mph, macrophage; LN, lymph node; Th0, naive T cell; Th1, T helper 1.
CD4+ Th17 and Tregs in CL in Relation to IL-4 and IL-4Rα Signaling
Apart from the Th1 and Th2 lineage of CD4+ T cells, naive CD4+ T cells may differentiate into additional lineages including CD4+ IL-17-producing cells (Th17) and Tregs. Th17 cells are characterized by the production of IL-17 and require retinoic acid-related orphan receptor gamma t, in addition to STAT3 and IL-23, for differentiation and maintenance (117). Various experimental models have linked the combined activity of Th17 cells, IL-17 and neutrophils to the pathogenesis of CL (118–120). A recent study indicated a link between IL-4 and the commitment of Th17 cells via the activation of IL-23 (121). In a model of cell-mediated inflammation, the authors demonstrated that IL-4 abrogates Th17 cells by selectively silencing IL-23 in APCs (121). Concurrently, IL-4 completely abrogates IL-23 to induce the IL-12-producing capacity of DCs. Altogether, the role of IL-4 and IL-4Rα signaling on this lineage of cells in CL would be an exciting avenue to investigate considering that in the study above, IL-12-dependent Th1 responses remained unaltered upon IL-4-mediated IL-23/Th17 silencing (121), and as already established, the former is needed for host protection to CL.
The ability for the host to maintain long-term immunity against Leishmania infection suggests that the parasite persists in an immune privileged site by a balance between CD4+ effector and Tregs that downregulate parasite-specific immunity (122). Differentiation of Tregs requires activation of forkhead box protein 3 (Foxp3) leading to the production of IL-10, TGF-β, and IL-4 (117, 123). In susceptible BALB/c mice, Tregs play a significant disease controlling role by regulating the biased Th2 response (ideally they suppress excessive Th2 responses) since the absence of CD4+CD25+ Treg cells dramatically increases IL-4 levels and exacerbates L. major infection (124, 125). In resistant C57BL/6 mice, CD4+CD25+ Tregs control protective Th1 responses by an IL-10-dependent mechanism mediating parasite persistence and latent infection (74). Of considerable interest, however, Pillemer et al. revealed that IL-4 signaling via the IL-4Rα–STAT6 axis was required to maintain Foxp3 expression in Tregs and promote their proliferation (123). Thus, while global depletion of Treg cells yielded informative and differing results in cutaneous disease, it provided little insight into the underlying mechanisms by which Tregs suppress or enhance Th2 responses via the IL-4/IL-4Rα axis (and the corresponding effects on Th1 immunity). The identification of Foxp3 as the crucial inducer of Tregs and our Cre/loxP technology enables us to provide further insight into this field. Consequently, we have generated BALB/c mice with a cell-specific deletion of the IL-4Rα chain on Tregs under control of the foxp3 locus. Experimental studies in murine models are currently underway to elucidate the contribution of IL-4-signaling on Tregs in the infectious process caused by L. major.
IL-4Rα-Responsive B Cells in Murine CL
Apart from CD4+ T cells, independent researchers began to unravel the contribution of B lymphocytes in host protection or susceptibility to CL. Initial proof-of-concept studies provided evidence that B cells may play a role in susceptibility to infection with L. major (126, 127). Nevertheless, the use of mice genetically deficient for B cells (μMT or JHD) demonstrated that B lymphocytes play a limited role in Th2-mediated susceptibility to Leishmania infection, as the absence of B cells in BALB/c mice did not critically alter disease outcome (128, 129). This conclusion changed dramatically when it became evident that B cells could also secrete cytokines that potentially modulate both pathologic or protective functions, independent of their antibody-secreting and antigen-presenting functions (130). This was further supported by several lines of evidence showing that B cells assist in regulating the quality and quantity of both primary and memory CD4+ Th cell responses (130). However, up until this point, the contribution of cytokine-producing B cells in the context of inflammation, infection, and autoimmunity, which were conventionally dependent on CD4+ T cells, was an unexplored aspect. A hallmark study employing both in vitro and in vivo methods characterized the subdivision of B cells into distinct cytokine-producing “effector” subsets. Defined effector B cells producing cytokines such as IFN-γ, IL-12p40, TNF-α, and IL-6 were termed B effector 1 (Be1) cells, whereas Be2 B cells secreted copious amounts of IL-2, IL-4, and IL-13 (23). The profiles of Be1 and Be2 cells closely resembled that of CD4+ Th1 and Th2 cells, which altogether led to a renaissance in this field of B cell biology. To date, cytokine-producing B cells have been reported in various models of parasitic and bacterial infection (23, 131, 132) and autoimmune diseases (133, 134). Collectively, the evidence provided by these studies were inclined to suggest that, in response to antigen, cytokine-producing B cells might function to initiate and/or maintain the magnitude and quality of CD4+ Th1/Th2-dependent immune responses.
Of interest to our team, it was reported that the differentiation of naive B cells into IL-4-expressing Be2 cells was critically dependent upon Th2 signals and the IL-4/IL-4Rα signaling pathway (24). This led to the generation of a novel mouse strain lacking IL-4Rα expression specifically on B cells, mb1creIL-4Rα−/lox BALB/c mice, generated by cre/loxP under control of the mb1 locus (56). As murine lymphocytes are not responsive to IL-13, this mouse model provided an invaluable tool to investigate a role for IL-4-responsive B cells during infection with L. major. Infection studies with L. major LV39 and IL-81 in B cell-specific IL-4Rα-deficient BALB/c mice revealed a beneficial role for IL-4Rα-unresponsive B cells in host-protective immunity and concomitantly, a detrimental role for IL-4Rα-responsive B cells in the non-healing response to L. major (135). In the absence of IL-4 signaling on B cells, BALB/c mice effectively controlled progression of lesion development and parasite replication as a consequence of enhanced Th1/type 1 immunity and improved leishmanicidal effector functions (Figure 9), resembling a similar phenotype to CD4+ T cell-specific IL-4Rα-deficient BALB/c (10). Mechanistic studies further revealed that the healing phenotype in mb1creIL-4Rα−/lox BALB/c mice was due to reduced il-4 and increased ifn-γ transcripts in IL-4Rα-unresponsive B cells as early as Day 1 postinfection. Furthermore, mixed-bone marrow chimeras were instrumental in confirming that IL-4-producing B cells are crucial in driving the non-healing susceptible type 2 immune response characteristic of BALB/c mice during L. major infection (135). Recent evidence has indicated innate-like activation of B cells following recognition of foreign antigens (136, 137), via B cell receptor-independent mechanisms, leading to early B cell cytokine secretion. The efficient antigen-presenting function of B cells (138, 139) allows the cell to present the antigen it acquires and in lieu of its cytokine secretion, induce paracrine activation of neighboring cells, such as CD4+ T cells. These reports and our current data appear to suggest a model in which early IL-4Rα-responsive B cells producing IL-4 after infection are capable of influencing early Th polarization toward detrimental Th2 responses that drive L. major-induced CL (135).
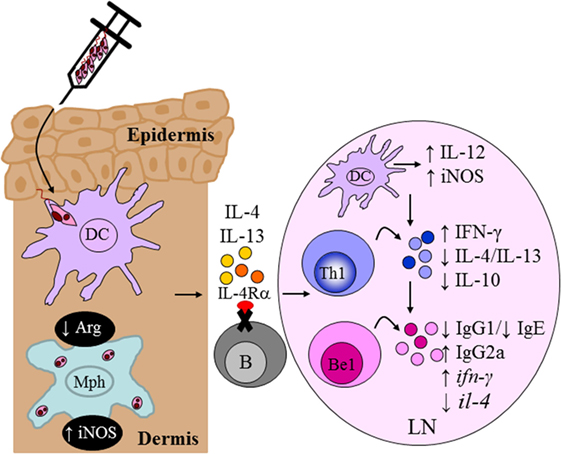
Figure 9. Absence of interleukin-4 (IL-4)-responsive B cells transforms non-healer BALB/c mice to a healer phenotype. Mb1creIL-4Rα−/lox mice developed an IL-12-induced protective Th1/type I immune response compared to littermate control BALB/c mice following Leishmania major LV39 and IL81 infection in the footpad. IL-4Rα-deficient B cells secreted increased ifn-γ and reduced il-4 transcripts, as early as day 1 postinfection, resembling a B effector 1 phenotype in comparison to IL-4Rα-sufficient B cells. This in turn led to improved macrophage leishmanicidal functions and control of parasite replication at the site of infection. Illustration prepared from Hurdayal et al. (135). DC, dendritic cells; Mph, macrophage; LN, lymph node; B, B cells; Be1, B effector 1 B cells; Th1, T helper 1.
Conclusion
Collectively, the development of conditional mice and generation of important immune cell-type-specific IL-4Rα-deficient mouse models have been critical in our understanding of Th2/type 2-mediated mechanisms in innate and adaptive immune cells during disease with the causative agent of CL, L. major. Our data show that the hierarchical importance of target cells interacting with the IL-4Rα and its ligands (IL-4 and IL-13) is a dynamic interaction, largely influenced by cytokines secreted in the vicinity of target and non-target cells, heterogenous CD4+ T cell populations, autocrine versus paracrine signaling, the Leishmania species/strain initiating infection, and the timing of the immune response.
This is especially relevant when considering the full spectrum of human leishmaniasis and strain-specific roles of the IL-4Rα chain and its ligands. Visceral leishmaniasis, initiated by intravenous injection of Leishmania donovani amastigotes in mouse models, is quite idiosyncratic in this regard. Similar to L. major infection in BALB/c mice, protective immunity against L. donovani is dependent on IL-12-induced-IFN-γ production for classical activation of macrophages and NO-induced killing of intracellular parasites (140). However, early studies in both humans and mice demonstrated that control of visceral disease was independent of the differential production of Th1 and Th2-derived cytokines (141). Thus, the overall evidence suggested that the Th2 response did not counteract immunological control of visceral leishmaniasis (142, 143).
On the contrary, the introduction of gene-deficient mice revealed surprisingly protective roles for IL-4, IL-13 and IL-4Rα signaling, during primary L. donovani infection (144–146). In addition, the IL-4/IL-13 signaling cascade was reported to play a significant role in successful drug treatment with sodium stibogluconate (80, 145) and augmenting vaccination responses (147). These reports added immense value to our understanding of the Th2 response in remarkably, control of visceral leishmaniasis, improved chemotherapy and vaccination. However, it could not tell us which IL-4/IL-13-signaling cells were important in mediating protective immunity, in lieu of the global gene deficiency in these models. Consequently, current research within our team is aimed at unraveling IL-4 and IL-13 signaling on specific target immune cells during visceral leishmaniasis using our cell-type-specific IL-4Rα-deficient mouse models. Our initial studies have indicated that control of primary L. donovani infection, granuloma maturation, and chemotherapeutic efficacy is independent of IL-4Rα-responsive macrophages and neutrophils in BALB/c mice (144). This raises intriguing questions regarding the modes of action of IL-4 and IL-13 on other cellular targets such as CD4+ T cells, Treg cells, DCs, and B cells, which are currently under investigation.
Author Contributions
RH and FB contributed equally to the design and writing of the present review.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Miss. Shandré Pillay, Miss. Rebeng Maine, Miss. Amy Graham, and Dr. Suraj Parihar, for their contributions to editing this review. FB and RH are supported by grants from the South African Medical Research Council (Unit on Immunology of Infectious Diseases), National Research Foundation (NRF), South African Research Chair Initiative (SARCHi), and the University of Cape Town.
References
1. Kaye P, Scott P. Leishmaniasis: complexity at the host-pathogen interface. Nat Rev Microbiol (2011) 9(8):604–15. doi:10.1038/nrmicro2608
2. Savoia D. Recent updates and perspectives on leishmaniasis. J Infect Dev Ctries (2015) 9(6):588–96. doi:10.3855/jidc.6833
3. Gupta G, Oghumu S, Satoskar AR. Mechanisms of immune evasion in leishmaniasis. Adv Appl Microbiol (2013) 82:155–84. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-407679-2.00005-3
4. Alexander J, Brombacher F. T helper1/T helper2 cells and resistance/susceptibility to Leishmania infection: is this paradigm still relevant? Front Immunol (2012) 3:80. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2012.00080
5. Hurdayal R, Brombacher F. The role of IL-4 and IL-13 in cutaneous leishmaniasis. Immunol Lett (2014) 161(2):179–83. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2013.12.022
6. Sacks D, Noben-Trauth N. The immunology of susceptibility and resistance to Leishmania major in mice. Nat Rev Immunol (2002) 2(11):845–58. doi:10.1038/nri933
7. Kopf M, Brombacher F, Köhler G, Kienzle G, Widmann KH, Lefrang K, et al. IL-4-deficient Balb/c mice resist infection with Leishmania major. J Exp Med (1996) 184(3):1127–36. doi:10.1084/jem.184.3.1127
8. Matthews DJ, Emson CL, McKenzie GJ, Jolin HE, Blackwell JM, McKenzie AN. IL-13 is a susceptibility factor for Leishmania major infection. J Immunol (2000) 164(3):1458–62. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.164.3.1458
9. Mohrs M, Ledermann B, Köhler G, Dorfmüller A, Gessner A, Brombacher F. Differences between IL-4- and IL-4 receptor alpha-deficient mice in chronic leishmaniasis reveal a protective role for IL-13 receptor signaling. J Immunol (1999) 162(12):7302–8.
10. Radwanska M, Cutler AJ, Hoving JC, Magez S, Holscher C, Bohms A, et al. Deletion of IL-4Ralpha on CD4 T cells renders BALB/c mice resistant to Leishmania major infection. PLoS Pathog (2007) 3(5):e68. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.0030068
11. Hurdayal R, Nieuwenhuizen NE, Revaz-Breton M, Smith L, Hoving JC, Parihar SP, et al. Deletion of IL-4 receptor alpha on dendritic cells renders BALB/c mice hypersusceptible to Leishmania major infection. PLoS Pathog (2013) 9(10):e1003699. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1003699
12. Nelms K, Keegan AD, Zamorano J, Ryan JJ, Paul WE. The IL-4 receptor: signaling mechanisms and biologic functions. Annu Rev Immunol (1999) 17:701–38. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.17.1.701
13. Hölscher C, Arendse B, Schwegmann A, Myburgh E, Brombacher F. Impairment of alternative macrophage activation delays cutaneous leishmaniasis in nonhealing BALB/c mice. J Immunol (2006) 176(2):1115–21. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.176.2.1115
14. Himmelrich H, Launois P, Maillard I, Biedermann T, Tacchini-Cottier F, Locksley RM, et al. In BALB/c mice, IL-4 production during the initial phase of infection with Leishmania major is necessary and sufficient to instruct Th2 cell development resulting in progressive disease. J Immunol (2000) 164(9):4819–25. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.164.9.4819
15. Min B, Prout M, Hu-Li J, Zhu J, Jankovic D, Morgan ES, et al. Basophils produce IL-4 and accumulate in tissues after infection with a Th2-inducing parasite. J Exp Med (2004) 200(4):507–17. doi:10.1084/jem.20040590
16. van Panhuys N, Prout M, Forbes E, Min B, Paul WE, Le Gros G. Basophils are the major producers of IL-4 during primary helminth infection. J Immunol (2011) 186(5):2719–28. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1000940
17. Plaut M, Pierce JH, Watson CJ, Hanley-Hyde J, Nordan RP, Paul WE. Mast cell lines produce lymphokines in response to cross-linkage of Fc epsilon RI or to calcium ionophores. Nature (1989) 339(6219):64–7. doi:10.1038/339064a0
18. Sabin EA, Kopf MA, Pearce EJ. Schistosoma mansoni egg-induced early IL-4 production is dependent upon IL-5 and eosinophils. J Exp Med (1996) 184(5):1871–8. doi:10.1084/jem.184.5.1871
19. Yoshimoto T, Paul WE. CD4pos, NK1.1pos T cells promptly produce interleukin 4 in response to in vivo challenge with anti-CD3. J Exp Med (1994) 179(4):1285–95. doi:10.1084/jem.179.4.1285
20. Akbari O, Stock P, Meyer E, Kronenberg M, Sidobre S, Nakayama T, et al. Essential role of NKT cells producing IL-4 and IL-13 in the development of allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity. Nat Med (2003) 9(5):582–8. doi:10.1038/nm851
21. Ehrchen JM, Roebrock K, Foell D, Nippe N, von Stebut E, Weiss JM, et al. Keratinocytes determine Th1 immunity during early experimental leishmaniasis. PLoS Pathog (2010) 6(4):e1000871. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000871
22. Launois P, Ohteki T, Swihart K, MacDonald HR, Louis JA. In susceptible mice, Leishmania major induce very rapid interleukin-4 production by CD4+ T cells which are NK1.1. Eur J Immunol (1995) 25(12):3298–307. doi:10.1002/eji.1830251215
23. Harris DP, Haynes L, Sayles PC, Duso DK, Eaton SM, Lepak NM, et al. Reciprocal regulation of polarized cytokine production by effector B and T cells. Nat Immunol (2000) 1(6):475–82. doi:10.1038/82717
24. Harris DP, Goodrich S, Mohrs K, Mohrs M, Lund FE. Cutting edge: the development of IL-4-producing B cells (B effector 2 cells) is controlled by IL-4, IL-4 receptor alpha, and Th2 cells. J Immunol (2005) 175(11):7103–7. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.175.11.7103
25. Ferrick DA, Schrenzel MD, Mulvania T, Hsieh B, Ferlin WG, Lepper H. Differential production of interferon-gamma and interleukin-4 in response to Th1- and Th2-stimulating pathogens by gamma delta T cells in vivo. Nature (1995) 373(6511):255–7. doi:10.1038/373255a0
26. Gascan H, Gauchat JF, Roncarolo MG, Yssel H, Spits H, de Vries JE. Human B cell clones can be induced to proliferate and to switch to IgE and IgG4 synthesis by interleukin 4 and a signal provided by activated CD4+ T cell clones. J Exp Med (1991) 173(3):747–50. doi:10.1084/jem.173.3.747
27. Coffman RL, Ohara J, Bond MW, Carty J, Zlotnik A, Paul WE. B cell stimulatory factor-1 enhances the IgE response of lipopolysaccharide-activated B cells. J Immunol (1986) 136(12):4538–41.
28. Snapper CM, Finkelman FD, Stefany D, Conrad DH, Paul WE. IL-4 induces co-expression of intrinsic membrane IgG1 and IgE by murine B cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol (1988) 141(2):489–98.
29. Classen A, Lloberas J, Celada A. Macrophage activation: classical versus alternative. Methods Mol Biol (2009) 531:29–43. doi:10.1007/978-1-59745-396-7_3
30. Noelle R, Krammer PH, Ohara J, Uhr JW, Vitetta ES. Increased expression of Ia antigens on resting B cells: an additional role for B-cell growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (1984) 81(19):6149–53. doi:10.1073/pnas.81.19.6149
31. Stack RM, Lenschow DJ, Gray GS, Bluestone JA, Fitch FW. IL-4 treatment of small splenic B cells induces costimulatory molecules B7-1 and B7-2. J Immunol (1994) 152(12):5723–33.
32. Ohara J, Paul WE. Receptors for B-cell stimulatory factor-1 expressed on cells of haematopoietic lineage. Nature (1987) 325(6104):537–40. doi:10.1038/325537a0
33. Cook PC, Jones LH, Jenkins SJ, Wynn TA, Allen JE, MacDonald AS. Alternatively activated dendritic cells regulate CD4+ T-cell polarization in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2012) 109(25):9977–82. doi:10.1073/pnas.1121231109
34. Brombacher F. The role of interleukin-13 in infectious diseases and allergy. Bioessays (2000) 22(7):646–56. doi:10.1002/1521-1878(200007)22:7<646::AID-BIES7>3.3.CO;2-0
35. Cunningham AF, Serre K, Toellner KM, Khan M, Alexander J, Brombacher F, et al. Pinpointing IL-4-independent acquisition and IL-4-influenced maintenance of Th2 activity by CD4 T cells. Eur J Immunol (2004) 34(3):686–94. doi:10.1002/eji.200324510
36. Mohrs M, Holscher C, Brombacher F. Interleukin-4 receptor alpha-deficient BALB/c mice show an unimpaired T helper 2 polarization in response to Leishmania major infection. Infect Immun (2000) 68(4):1773–80. doi:10.1128/IAI.68.4.1773-1780.2000
37. Noben-Trauth N, Paul WE, Sacks DL. IL-4- and IL-4 receptor-deficient BALB/c mice reveal differences in susceptibility to Leishmania major parasite substrains. J Immunol (1999) 162(10):6132–40.
38. Noben-Trauth N, Shultz LD, Brombacher F, Urban JF Jr, Gu H, Paul WE. An interleukin 4 (IL-4)-independent pathway for CD4+ T cell IL-4 production is revealed in IL-4 receptor-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (1997) 94(20):10838–43. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.20.10838
39. Ritz SA, Cundall MJ, Gajewska BU, Alvarez D, Gutierrez-Ramos JC, Coyle AJ, et al. Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor-driven respiratory mucosal sensitization induces Th2 differentiation and function independently of interleukin-4. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol (2002) 27(4):428–35. doi:10.1165/rcmb.4824
40. Finkelman FD, Morris SC, Orekhova T, Mori M, Donaldson D, Reiner SL, et al. Stat6 regulation of in vivo IL-4 responses. J Immunol (2000) 164(5):2303–10. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.164.5.2303
41. Jankovic D, Kullberg MC, Noben-Trauth N, Caspar P, Paul WE, Sher A. Single cell analysis reveals that IL-4 receptor/Stat6 signaling is not required for the in vivo or in vitro development of CD4+ lymphocytes with a Th2 cytokine profile. J Immunol (2000) 164(6):3047–55. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.164.6.3047
42. Hershey GK. IL-13 receptors and signaling pathways: an evolving web. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2003) 111(4):677–90. doi:10.1067/mai.2003.1333
43. de Saint-Vis B, Fugier-Vivier I, Massacrier C, Gaillard C, Vanbervliet B, Aït-Yahia S, et al. The cytokine profile expressed by human dendritic cells is dependent on cell subtype and mode of activation. J Immunol (1998) 160(4):1666–76.
44. Hoshino T, Winkler-Pickett RT, Mason AT, Ortaldo JR, Young HA. IL-13 production by NK cells: IL-13-producing NK and T cells are present in vivo in the absence of IFN-gamma. J Immunol (1999) 162(1):51–9.
45. McKenzie AN, Culpepper JA, de Waal Malefyt R, Brière F, Punnonen J, Aversa G, et al. Interleukin 13, a T-cell-derived cytokine that regulates human monocyte and B-cell function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (1993) 90(8):3735–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.8.3735
46. Aversa G, Punnonen J, Cocks BG, de Waal Malefyt R, Vega F Jr, Zurawski SM, et al. An interleukin 4 (IL-4) mutant protein inhibits both IL-4 or IL-13-induced human immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) and IgE synthesis and B cell proliferation: support for a common component shared by IL-4 and IL-13 receptors. J Exp Med (1993) 178(6):2213–8. doi:10.1084/jem.178.6.2213
47. Hilton DJ, Zhang JG, Metcalf D, Alexander WS, Nicola NA, Willson TA. Cloning and characterization of a binding subunit of the interleukin 13 receptor that is also a component of the interleukin 4 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (1996) 93(1):497–501. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.1.497
48. Zurawski SM, Vega F Jr, Huyghe B, Zurawski G. Receptors for interleukin-13 and interleukin-4 are complex and share a novel component that functions in signal transduction. EMBO J (1993) 12(7):2663–70.
49. LaPorte SL, Juo ZS, Vaclavikova J, Colf LA, Qi X, Heller NM, et al. Molecular and structural basis of cytokine receptor pleiotropy in the interleukin-4/13 system. Cell (2008) 132(2):259–72. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.030
50. Gauchat JF, Schlagenhauf E, Feng NP, Moser R, Yamage M, Jeannin P, et al. A novel 4-kb interleukin-13 receptor alpha mRNA expressed in human B, T, and endothelial cells encoding an alternate type-II interleukin-4/interleukin-13 receptor. Eur J Immunol (1997) 27(4):971–8. doi:10.1002/eji.1830270425
51. Graber P, Gretener D, Herren S, Aubry JP, Elson G, Poudrier J, et al. The distribution of IL-13 receptor alpha1 expression on B cells, T cells and monocytes and its regulation by IL-13 and IL-4. Eur J Immunol (1998) 28(12):4286–98. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199812)28:12<4286::AID-IMMU4286>3.0.CO;2-H
52. MacDonald TT. Decoy receptor springs to life and eases fibrosis. Nat Med (2006) 12(1):13–4. doi:10.1038/nm0106-13
53. Fichtner-Feigl S, Strober W, Kawakami K, Puri RK, Kitani A. IL-13 signaling through the IL-13alpha2 receptor is involved in induction of TGF-beta1 production and fibrosis. Nat Med (2006) 12(1):99–106. doi:10.1038/nm1332
54. Jung T, Schrader N, Hellwig M, Enssle KH, Neumann C. Soluble human interleukin-4 receptor is produced by activated T cells under the control of metalloproteinases. Int Arch Allergy Immunol (1999) 119(1):23–30. doi:10.1159/000024171
55. Zhang JG, Hilton DJ, Willson TA, McFarlane C, Roberts BA, Moritz RL, et al. Identification, purification, and characterization of a soluble interleukin (IL)-13-binding protein. Evidence that it is distinct from the cloned Il-13 receptor and Il-4 receptor alpha-chains. J Biol Chem (1997) 272(14):9474–80. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.14.9474
56. Hoving JC. Investigating the Role of IL-4/IL-13 and Their Receptors in Ulcerative Colitis. Cape Town: University of Cape Town (2010). Doctor of Philosophy.
57. Murata T, Noguchi PD, Puri RK. IL-13 induces phosphorylation and activation of JAK2 Janus kinase in human colon carcinoma cell lines: similarities between IL-4 and IL-13 signaling. J Immunol (1996) 156(8):2972–8.
58. Yin T, Tsang ML, Yang YC. JAK1 kinase forms complexes with interleukin-4 receptor and 4PS/insulin receptor substrate-1-like protein and is activated by interleukin-4 and interleukin-9 in T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem (1994) 269(43):26614–7.
59. Takeda K, Kamanaka M, Tanaka T, Kishimoto T, Akira S. Impaired IL-13-mediated functions of macrophages in STAT6-deficient mice. J Immunol (1996) 157(8):3220–2.
60. Lu F, Huang S. The roles of mast cells in parasitic protozoan infections. Front Immunol (2017) 8:363. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2017.00363
61. De Trez C, Magez S, Akira S, Ryffel B, Carlier Y, Muraille E. iNOS-producing inflammatory dendritic cells constitute the major infected cell type during the chronic Leishmania major infection phase of C57BL/6 resistant mice. PLoS Pathog (2009) 5(6):e1000494. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000494
62. Güler ML, Gorham JD, Hsieh CS, Mackey AJ, Steen RG, Dietrich WF, et al. Genetic susceptibility to Leishmania: IL-12 responsiveness in TH1 cell development. Science (1996) 271(5251):984–7. doi:10.1126/science.271.5251.984
63. Heinzel FP, Schoenhaut DS, Rerko RM, Rosser LE, Gately MK. Recombinant interleukin 12 cures mice infected with Leishmania major. J Exp Med (1993) 177(5):1505–9. doi:10.1084/jem.177.5.1505
64. Park AY, Hondowicz B, Kopf M, Scott P. The role of IL-12 in maintaining resistance to Leishmania major. J Immunol (2002) 168(11):5771–7. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.168.11.5771
65. Stenger S, Donhauser N, Thuring H, Rollinghoff M, Bogdan C. Reactivation of latent leishmaniasis by inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase. J Exp Med (1996) 183(4):1501–14. doi:10.1084/jem.183.4.1501
66. Stenger S, Thuring H, Rollinghoff M, Bogdan C. Tissue expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase is closely associated with resistance to Leishmania major. J Exp Med (1994) 180(3):783–93. doi:10.1084/jem.180.3.783
67. Yoshimoto T, Takeda K, Tanaka T, Ohkusu K, Kashiwamura S, Okamura H, et al. IL-12 up-regulates IL-18 receptor expression on T cells, Th1 cells, and B cells: synergism with IL-18 for IFN-gamma production. J Immunol (1998) 161(7):3400–7.
68. Monteforte GM, Takeda K, Rodriguez-Sosa M, Akira S, David JR, Satoskar AR. Genetically resistant mice lacking IL-18 gene develop Th1 response and control cutaneous Leishmania major infection. J Immunol (2000) 164(11):5890–3. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.164.11.5890
69. Arendse B, Van Snick J, Brombacher F. IL-9 is a susceptibility factor in Leishmania major infection by promoting detrimental Th2/type 2 responses. J Immunol (2005) 174(4):2205–11. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.174.4.2205
70. Iniesta V, Gómez-Nieto LC, Molano I, Mohedano A, Carcelén J, Mirón C, et al. Arginase I induction in macrophages, triggered by Th2-type cytokines, supports the growth of intracellular Leishmania parasites. Parasite Immunol (2002) 24(3):113–8. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3024.2002.00444.x
71. Locksley RM, Scott P. Helper T-cell subsets in mouse leishmaniasis: induction, expansion and effector function. Immunol Today (1991) 12(3):A58–61. doi:10.1016/S0167-5699(05)80017-9
72. Tacchini-Cottier F, Zweifel C, Belkaid Y, Mukankundiye C, Vasei M, Launois P, et al. An immunomodulatory function for neutrophils during the induction of a CD4+ Th2 response in BALB/c mice infected with Leishmania major. J Immunol (2000) 165(5):2628–36. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.165.5.2628
73. Belkaid Y, Piccirillo CA, Mendez S, Shevach EM, Sacks DL. CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells control Leishmania major persistence and immunity. Nature (2002) 420(6915):502–7. doi:10.1038/nature01152
74. Belkaid Y, Hoffmann KF, Mendez S, Kamhawi S, Udey MC, Wynn TA, et al. The role of interleukin (IL)-10 in the persistence of Leishmania major in the skin after healing and the therapeutic potential of anti-IL-10 receptor antibody for sterile cure. J Exp Med (2001) 194(10):1497–506. doi:10.1084/jem.194.10.1497
75. Liu D, Uzonna JE. The early interaction of Leishmania with macrophages and dendritic cells and its influence on the host immune response. Front Cell Infect Microbiol (2012) 2:83. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2012.00083
77. Launois P, Maillard I, Pingel S, Swihart KG, Xénarios I, Acha-Orbea H, et al. IL-4 rapidly produced by V beta 4 V alpha 8 CD4+ T cells instructs Th2 development and susceptibility to Leishmania major in BALB/c mice. Immunity (1997) 6(5):541–9. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80342-8
78. Morris L, Troutt AB, Handman E, Kelso A. Changes in the precursor frequencies of IL-4 and IFN-gamma secreting CD4+ cells correlate with resolution of lesions in murine cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Immunol (1992) 149(8):2715–21.
79. Sypek JP, Chung CL, Mayor SE, Subramanyam JM, Goldman SJ, Sieburth DS, et al. Resolution of cutaneous leishmaniasis: interleukin 12 initiates a protective T helper type 1 immune response. J Exp Med (1993) 177(6):1797–802. doi:10.1084/jem.177.6.1797
80. Alexander J, Carter KC, Al-Fasi N, Satoskar A, Brombacher F. Endogenous IL-4 is necessary for effective drug therapy against visceral leishmaniasis. Eur J Immunol (2000) 30(10):2935–43. doi:10.1002/1521-4141(200010)30:10<2935::AID-IMMU2935>3.0.CO;2-Q
81. Dewals B, Hoving JC, Leeto M, Marillier RG, Govender U, Cutler AJ, et al. IL-4Ralpha responsiveness of non-CD4 T cells contributes to resistance in Schistosoma mansoni infection in pan-T cell-specific IL-4Ralpha-deficient mice. Am J Pathol (2009) 175(2):706–16. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2009.090137
82. Herbert DR, Hölscher C, Mohrs M, Arendse B, Schwegmann A, Radwanska M, et al. Alternative macrophage activation is essential for survival during schistosomiasis and downmodulates T helper 1 responses and immunopathology. Immunity (2004) 20(5):623–35. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(04)00107-4
83. Mountford AP, Hogg KG, Coulson PS, Brombacher F. Signaling via interleukin-4 receptor alpha chain is required for successful vaccination against schistosomiasis in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun (2001) 69(1):228–36. doi:10.1128/IAI.69.1.228-236.2001
84. Horsnell WG, Cutler AJ, Hoving JC, Mearns H, Myburgh E, Arendse B, et al. Delayed goblet cell hyperplasia, acetylcholine receptor expression, and worm expulsion in SMC-specific IL-4Ralpha-deficient mice. PLoS Pathog (2007) 3(1):e1. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.0030037
85. Schmidt S, Hoving JC, Horsnell WG, Mearns H, Cutler AJ, Brombacher TM, et al. Nippostrongylus-induced intestinal hypercontractility requires IL-4 receptor alpha-responsiveness by T cells in mice. PLoS One (2012) 7(12):e52211. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0052211
86. Urban JF Jr, Noben-Trauth N, Donaldson DD, Madden KB, Morris SC, Collins M, et al. IL-13, IL-4Ralpha, and Stat6 are required for the expulsion of the gastrointestinal nematode parasite Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. Immunity (1998) 8(2):255–64. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80477-X
87. Kirstein F, Nieuwenhuizen NE, Jayakumar J, Horsnell WG, Brombacher F. Role of IL-4 receptor alpha-positive CD4(+) T cells in chronic airway hyperresponsiveness. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2016) 137(6):1852–62.e9. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2015.10.036
88. Nieuwenhuizen NE, Kirstein F, Jayakumar J, Emedi B, Hurdayal R, Horsnell WG, et al. Allergic airway disease is unaffected by the absence of IL-4Ralpha-dependent alternatively activated macrophages. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2012) 130(3):743–50.e8. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.03.011
89. Stamm LM, Räisänen-Sokolowski A, Okano M, Russell ME, David JR, Satoskar AR. Mice with STAT6-targeted gene disruption develop a Th1 response and control cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Immunol (1998) 161(11):6180–8.
90. McKenzie GJ, Emson CL, Bell SE, Anderson S, Fallon P, Zurawski G, et al. Impaired development of Th2 cells in IL-13-deficient mice. Immunity (1998) 9(3):423–32. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80625-1
91. Noben-Trauth N, Kropf P, Muller I. Susceptibility to Leishmania major infection in interleukin-4-deficient mice. Science (1996) 271(5251):987–90. doi:10.1126/science.271.5251.987
92. Belkaid Y, Hand TW. Role of the microbiota in immunity and inflammation. Cell (2014) 157(1):121–41. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.011
93. Kropf P, Schopf LR, Chung CL, Xu D, Liew FY, Sypek JP, et al. Expression of Th2 cytokines and the stable Th2 marker ST2L in the absence of IL-4 during Leishmania major infection. Eur J Immunol (1999) 29(11):3621–8. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199911)29:11<3621::AID-IMMU3621>3.3.CO;2-Q
94. Nagy A. Cre recombinase: the universal reagent for genome tailoring. Genesis (2000) 26(2):99–109. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1526-968X(200002)26:2<99::AID-GENE1>3.0.CO;2-B
95. Clark RA. Skin-resident T cells: the ups and downs of on site immunity. J Invest Dermatol (2010) 130(2):362–70. doi:10.1038/jid.2009.247
96. Nestle FO, Di Meglio P, Qin JZ, Nickoloff BJ. Skin immune sentinels in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol (2009) 9(10):679–91. doi:10.1038/nri2622
97. Grone A. Keratinocytes and cytokines. Vet Immunol Immunopathol (2002) 88(1–2):1–12. doi:10.1016/S0165-2427(02)00136-8
98. Pivarcsi A, Kemeny L, Dobozy A. Innate immune functions of the keratinocytes. A review. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung (2004) 51(3):303–10. doi:10.1556/AMicr.51.2004.3.8
99. Miller LS. Toll-like receptors in skin. Adv Dermatol (2008) 24:71–87. doi:10.1016/j.yadr.2008.09.004
100. Biedermann T, Zimmermann S, Himmelrich H, Gumy A, Egeter O, Sakrauski AK, et al. IL-4 instructs TH1 responses and resistance to Leishmania major in susceptible BALB/c mice. Nat Immunol (2001) 2(11):1054–60. doi:10.1038/ni725
101. Hochrein H, O’Keeffe M, Luft T, Vandenabeele S, Grumont RJ, Maraskovsky E, et al. Interleukin (IL)-4 is a major regulatory cytokine governing bioactive IL-12 production by mouse and human dendritic cells. J Exp Med (2000) 192(6):823–33. doi:10.1084/jem.192.6.823
102. Akaiwa M, Yu B, Umeshita-Suyama R, Terada N, Suto H, Koga T, et al. Localization of human interleukin 13 receptor in non-haematopoietic cells. Cytokine (2001) 13(2):75–84. doi:10.1006/cyto.2000.0814
103. Descatoire M, Hurrell BP, Govender M, Passelli K, Martinez-Salazar B, Hurdayal R, et al. IL-4Rα signaling in keratinocytes and early IL-4 production are dispensable for generating a curative T helper 1 response in Leishmania major-infected C57BL/6 mice. Front Immunol (2017) 8:1265. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2017.01265
104. Faria MS, Reis FC, Lima AP. Toll-like receptors in Leishmania infections: guardians or promoters? J Parasitol Res (2012) 2012:930257. doi:10.1155/2012/930257
105. Peters NC, Egen JG, Secundino N, Debrabant A, Kimblin N, Kamhawi S, et al. In vivo imaging reveals an essential role for neutrophils in leishmaniasis transmitted by sand flies. Science (2008) 321(5891):970–4. doi:10.1126/science.1159194
106. Hurrell BP, Schuster S, Grün E, Coutaz M, Williams RA, Held W, et al. Rapid sequestration of Leishmania mexicana by neutrophils contributes to the development of chronic lesion. PLoS Pathog (2015) 11(5):e1004929. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004929
107. Rochael NC, Guimarães-Costa AB, Nascimento MT, DeSouza-Vieira TS, Oliveira MP, Garcia e Souza LF, et al. Classical ROS-dependent and early/rapid ROS-independent release of neutrophil extracellular traps triggered by Leishmania parasites. Sci Rep (2015) 5:18302. doi:10.1038/srep18302
108. Ribeiro-Gomes FL, Moniz-de-Souza MC, Alexandre-Moreira MS, Dias WB, Lopes MF, Nunes MP, et al. Neutrophils activate macrophages for intracellular killing of Leishmania major through recruitment of TLR4 by neutrophil elastase. J Immunol (2007) 179(6):3988–94. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.179.6.3988
109. Li Y, Ishii K, Hisaeda H, Hamano S, Zhang M, Nakanishi K, et al. IL-18 gene therapy develops Th1-type immune responses in Leishmania major-infected BALB/c mice: is the effect mediated by the CpG signaling TLR9? Gene Ther (2004) 11(11):941–8. doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3302240
110. Yao Y, Li W, Kaplan MH, Chang CH. Interleukin (IL)-4 inhibits IL-10 to promote IL-12 production by dendritic cells. J Exp Med (2005) 201(12):1899–903. doi:10.1084/jem.20050324
111. Iwasaki A, Medzhitov R. Control of adaptive immunity by the innate immune system. Nat Immunol (2015) 16(4):343–53. doi:10.1038/ni.3123
112. Banchereau J, Briere F, Caux C, Davoust J, Lebecque S, Liu YJ, et al. Immunobiology of dendritic cells. Annu Rev Immunol (2000) 18:767–811. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.767
113. Sun J, Pearce EJ. Suppression of early IL-4 production underlies the failure of CD4 T cells activated by TLR-stimulated dendritic cells to differentiate into Th2 cells. J Immunol (2007) 178(3):1635–44. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.178.3.1635
114. Liese J, Schleicher U, Bogdan C. TLR9 signaling is essential for the innate NK cell response in murine cutaneous leishmaniasis. Eur J Immunol (2007) 37(12):3424–34. doi:10.1002/eji.200737182
115. Masic A, Hurdayal R, Nieuwenhuizen NE, Brombacher F, Moll H. Dendritic cell-mediated vaccination relies on interleukin-4 receptor signaling to avoid tissue damage after Leishmania major infection of BALB/c mice. PLoS Negl Trop Dis (2012) 6(7):e1721. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0001721
116. Scott P, Natovitz P, Coffman RL, Pearce E, Sher A. Immunoregulation of cutaneous leishmaniasis. T cell lines that transfer protective immunity or exacerbation belong to different T helper subsets and respond to distinct parasite antigens. J Exp Med (1988) 168(5):1675–84.
117. Zhu J, Yamane H, Paul WE. Differentiation of effector CD4 T cell populations (*). Annu Rev Immunol (2010) 28:445–89. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-030409-101212
118. Lopez Kostka S, Dinges S, Griewank K, Iwakura Y, Udey MC, von Stebut E. IL-17 promotes progression of cutaneous leishmaniasis in susceptible mice. J Immunol (2009) 182(5):3039–46. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0713598
119. Gonzalez-Lombana C, Gimblet C, Bacellar O, Oliveira WW, Passos S, Carvalho LP, et al. IL-17 mediates immunopathology in the absence of IL-10 following Leishmania major infection. PLoS Pathog (2013) 9(3):e1003243. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1003243
120. Pedraza-Zamora CP, Delgado-Dominguez J, Zamora-Chimal J, Becker I. Th17 cells and neutrophils: close collaborators in chronic Leishmania mexicana infections leading to disease severity. Parasite Immunol (2017) 39(4):12420. doi:10.1111/pim.12420
121. Guenova E, Skabytska Y, Hoetzenecker W, Weindl G, Sauer K, Tham M, et al. IL-4 abrogates T(H)17 cell-mediated inflammation by selective silencing of IL-23 in antigen-presenting cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2015) 112(7):2163–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.1416922112
122. Peters N, Sacks D. Immune privilege in sites of chronic infection: Leishmania and regulatory T cells. Immunol Rev (2006) 213:159–79. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.2006.00432.x
123. Pillemer BB, Qi Z, Melgert B, Oriss TB, Ray P, Ray A. STAT6 activation confers upon T helper cells resistance to suppression by regulatory T cells. J Immunol (2009) 183(1):155–63. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0803733
124. Aseffa A, Gumy A, Launois P, MacDonald HR, Louis JA, Tacchini-Cottier F. The early IL-4 response to Leishmania major and the resulting Th2 cell maturation steering progressive disease in BALB/c mice are subject to the control of regulatory CD4+CD25+ T cells. J Immunol (2002) 169(6):3232–41. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.169.6.3232
125. Xu D, Liu H, Komai-Koma M, Campbell C, McSharry C, Alexander J, et al. CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells suppress differentiation and functions of Th1 and Th2 cells, Leishmania major infection, and colitis in mice. J Immunol (2003) 170(1):394–9. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.170.1.394
126. Hoerauf A, Solbach W, Lohoff M, Rollinghoff M. The Xid defect determines an improved clinical course of murine leishmaniasis in susceptible mice. Int Immunol (1994) 6(8):1117–24. doi:10.1093/intimm/6.8.1117
127. Sacks DL, Scott PA, Asofsky R, Sher FA. Cutaneous leishmaniasis in anti-IgM-treated mice: enhanced resistance due to functional depletion of a B cell-dependent T cell involved in the suppressor pathway. J Immunol (1984) 132(4):2072–7.
128. Miles SA, Conrad SM, Alves RG, Jeronimo SM, Mosser DM. A role for IgG immune complexes during infection with the intracellular pathogen Leishmania. J Exp Med (2005) 201(5):747–54. doi:10.1084/jem.20041470
129. Ronet C, Voigt H, Himmelrich H, Doucey MA, Hauyon-La Torre Y, Revaz-Breton M, et al. Leishmania major-specific B cells are necessary for Th2 cell development and susceptibility to L. major LV39 in BALB/c mice. J Immunol (2008) 180(7):4825–35. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.180.7.4825
130. Fillatreau S. Cytokine-producing B cells as regulators of pathogenic and protective immune responses. Ann Rheum Dis (2013) 72(Suppl 2):ii80–4. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202253
131. Wojciechowski W, Harris DP, Sprague F, Mousseau B, Makris M, Kusser K, et al. Cytokine-producing effector B cells regulate type 2 immunity to H. polygyrus. Immunity (2009) 30(3):421–33. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2009.01.006
132. Ganapamo F, Dennis VA, Philipp MT. CD19(+) cells produce IFN-gamma in mice infected with Borrelia burgdorferi. Eur J Immunol (2001) 31(12):3460–8. doi:10.1002/1521-4141(200112)31:12<3460::AID-IMMU3460>3.0.CO;2-X
133. Fillatreau S, Sweenie CH, McGeachy MJ, Gray D, Anderton SM. B cells regulate autoimmunity by provision of IL-10. Nat Immunol (2002) 3(10):944–50. doi:10.1038/ni833
134. Barr TA, Shen P, Brown S, Lampropoulou V, Roch T, Lawrie S, et al. B cell depletion therapy ameliorates autoimmune disease through ablation of IL-6-producing B cells. J Exp Med (2012) 209(5):1001–10. doi:10.1084/jem.20111675
135. Hurdayal R, Ndlovu HH, Revaz-Breton M, Parihar SP, Nono JK, Govender M, et al. IL-4-producing B cells regulate T helper cell dichotomy in type 1- and type 2-controlled diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2017) 114(40):E8430–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.1708125114
136. Bao Y, Liu X, Han C, Xu S, Xie B, Zhang Q, et al. Identification of IFN-gamma-producing innate B cells. Cell Res (2014) 24(2):161–76. doi:10.1038/cr.2013.155
137. Silva-Barrios S, Smans M, Duerr CU, Qureshi ST, Fritz JH, Descoteaux A, et al. Innate immune B cell activation by Leishmania donovani exacerbates disease and mediates hypergammaglobulinemia. Cell Rep (2016) 15(11):2427–37. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2016.05.028
138. Pape KA, Catron DM, Itano AA, Jenkins MK. The humoral immune response is initiated in lymph nodes by B cells that acquire soluble antigen directly in the follicles. Immunity (2007) 26(4):491–502. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2007.02.011
139. Chen X, Jensen PE. The role of B lymphocytes as antigen-presenting cells. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) (2008) 56(2):77–83. doi:10.1007/s00005-008-0014-5
140. Kaye PM, Svensson M, Ato M, Maroof A, Polley R, Stager S, et al. The immunopathology of experimental visceral leishmaniasis. Immunol Rev (2004) 201:239–53. doi:10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.00188.x
141. Kaye PM, Curry AJ, Blackwell JM. Differential production of Th1- and Th2-derived cytokines does not determine the genetically controlled or vaccine-induced rate of cure in murine visceral leishmaniasis. J Immunol (1991) 146(8):2763–70.
142. Miralles GD, Stoeckle MY, McDermott DF, Finkelman FD, Murray HW. Th1 and Th2 cell-associated cytokines in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. Infect Immun (1994) 62(3):1058–63.
143. Murray HW, Flanders KC, Donaldson DD, Sypek JP, Gotwals PJ, Liu J, et al. Antagonizing deactivating cytokines to enhance host defense and chemotherapy in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. Infect Immun (2005) 73(7):3903–11. doi:10.1128/IAI.73.7.3903-3911.2005
144. McFarlane E, Carter KC, McKenzie AN, Kaye PM, Brombacher F, Alexander J. Endogenous IL-13 plays a crucial role in liver granuloma maturation during Leishmania donovani infection, independent of IL-4Ralpha-responsive macrophages and neutrophils. J Infect Dis (2011) 204(1):36–43. doi:10.1093/infdis/jir080
145. Stager S, Alexander J, Carter KC, Brombacher F, Kaye PM. Both interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-4 receptor alpha signaling contribute to the development of hepatic granulomas with optimal antileishmanial activity. Infect Immun (2003) 71(8):4804–7. doi:10.1128/IAI.71.8.4804-4807.2003
146. Satoskar A, Bluethmann H, Alexander J. Disruption of the murine interleukin-4 gene inhibits disease progression during Leishmania mexicana infection but does not increase control of Leishmania donovani infection. Infect Immun (1995) 63(12):4894–9.
Keywords: interleukin-4 receptor alpha, interleukin-4/interleukin-13, murine cutaneous leishmaniasis, innate cells, adaptive cells
Citation: Hurdayal R and Brombacher F (2017) Interleukin-4 Receptor Alpha: From Innate to Adaptive Immunity in Murine Models of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis. Front. Immunol. 8:1354. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01354
Received: 21 July 2017; Accepted: 03 October 2017;
Published: 10 November 2017
Edited by:
Uwe Ritter, University of Regensburg, GermanyReviewed by:
Tiago W. P. Mineo, Federal University of Uberlandia, BrazilRicardo Silvestre, Instituto de Pesquisa em Ciências da Vida e da Saúde (ICVS), Portugal
Copyright: © 2017 Hurdayal and Brombacher. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Frank Brombacher, YnJvbWJhY2hlcmZyYW5rQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Ramona Hurdayal
Ramona Hurdayal Frank Brombacher
Frank Brombacher