
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Genet. , 06 January 2025
Sec. Livestock Genomics
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2024.1503148
This article is part of the Research Topic Insights in Livestock Genomics View all 6 articles
 Yumei Shi1,2†
Yumei Shi1,2† Xini Wang1†
Xini Wang1† Shaokang Chen3
Shaokang Chen3 Yanhui Zhao2
Yanhui Zhao2 Yan Wang2
Yan Wang2 Xihui Sheng2
Xihui Sheng2 Xiaolong Qi2
Xiaolong Qi2 Lei Zhou1
Lei Zhou1 Yu Feng1
Yu Feng1 Jianfeng Liu1
Jianfeng Liu1 Chuduan Wang1
Chuduan Wang1 Kai Xing1*
Kai Xing1*Intramuscular fat (IMF) is an important indicator for evaluating meat quality. Transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) is widely used for the study of IMF deposition. Machine learning (ML) is a new big data fitting method that can effectively fit complex data, accurately identify samples and genes, and it plays an important role in omics research. Therefore, this study aimed to analyze RNA-seq data by ML method to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) affecting IMF deposition in pigs. In this study, a total of 74 RNA-seq data from muscle tissue samples were used. A total of 155 DEGs were identified using a limma package between the two groups. 100 and 11 significant genes were identified by support vector machine recursive feature elimination (SVM-RFE) and random forest (RF) models, respectively. A total of six intersecting genes were in both models. KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of the intersecting genes revealed that these genes were enriched in pathways associated with lipid deposition. These pathways include α-linolenic acid metabolism, linoleic acid metabolism, ether lipid metabolism, arachidonic acid metabolism, and glycerophospholipid metabolism. Four key genes affecting intramuscular fat deposition, PLA2G6, MPV17, NUDT2, and ND4L, were identified based on significant pathways. The results of this study are important for the elucidation of the molecular regulatory mechanism of intramuscular fat deposition and the effective improvement of IMF content in pigs.
Intramuscular fat is one of the most important determinants of pork quality (Zhang et al., 2021) and affects the sensory qualities of pork, such as tenderness, flavor, and juiciness (Fernandez et al., 1999). Intramuscular fat content is influenced by several factors (Malgwi et al., 2022), among which genetic factors play a decisive role in intramuscular fat content (Hamill et al., 2012). The genes that have been studied and found to affect intramuscular fat deposition are ROBO2 (Sato et al., 2017), HS6ST3 (Jiang et al., 2011), PLIN5 (Puig-Oliveras et al., 2014) and NR4A1 (Qin et al., 2018), and so on.
RNA-seq technology is widely used in the field of genetic breeding in livestock production. In the field of animal husbandry, numerous studies have utilized transcriptomics to uncover the intrinsic connection between gene expression and economic traits. For instance, researchers have revealed the rules of muscle development during the embryonic stage of Chengkou pheasants through transcriptomic analysis (Ren et al., 2021); identified the potential regulatory genes associated with heat tolerance in Holstein dairy cows (Liu et al., 2020); and determined the genes related to the growth and development of skeletal muscles by comparing the transcriptomic differences among different duck breast muscle tissues and among different pigeon breast muscle tissues (Wang Z. et al., 2021; Ding et al., 2021). In recent years, there have been many reports on transcriptomic studies of traits related to intramuscular fat deposition in pigs by RNA-seq technology. Li et al. analyzed transcriptomic data from the longissimus dorsi muscle (LDM) of Wei and Yorkshire pigs and found that many differentially expressed lncRNAs may influence the developmental process of IMF by regulating its potential target genes (Li et al., 2020). Cho et al. compared IMF in western and Korean native pig breeds with LDM and identified the MYH3 on pig chromosome 12 as a causal gene affecting intramuscular fat deposition, which can inhibit myogenic regulatory factor binding and thus promote intramuscular fat deposition through a structural variation of 6-bp deletion on the promoter (Cho et al., 2019). Huang et al. analyzed IMF using Laiwu pig and Large White pig and identified a total of 513 mRNAs and 55 lncRNAs differentially expressed between the two pig breeds and identified 31 key lncRNAs by co-expression network construction and cis- and trans-regulated target gene analysis (Huang W. et al., 2018). Through transcriptomic studies, several candidate genes have been identified to affect the process of intramuscular fat deposition in pigs, such as LEP (Li et al., 2010), FASN (Crespo-Piazuelo et al., 2020) ACACA (Piórkowska et al., 2020), and so on. Although the transcriptome provides an efficient tool for the genetic resolution of important traits, transcriptome sequencing analysis is difficult for later functional validation and has a high false positive rate due to the small sample size. Current transcriptome data analysis methods mainly focus on the processing of a small number of samples from a single experiment, and the data from different samples cannot be integrated, which is not deep enough for data mining. Gene expression exhibits temporal specificity and spatial specificity. Spatial specificity implies that in multicellular organisms at specific growth and development stages, the same gene is expressed differently in various tissues and organs. The spatial distributional differences manifested by gene expression along the sequence of time or stage are actually determined by the distribution of cells in organs. Hence, the spatial specificity of gene expression is also known as cell specificity or tissue specificity. Due to the significant influence of both space and time on gene expression and the considerable variations in the samples employed in different studies, it becomes challenging to discover the major effector genes that universally regulate fat deposition.
ML, as an important component in the field of artificial intelligence, provides a new strategy for the study of histology. Currently, the method has been widely used in many areas of multi-omics research (Hashimoto et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2021). The classification function of ML in cancer genome classification or typing can be used to discover new biomarkers, new drug targets, and a deep understanding of cancer-induced genes (Huang S. et al., 2018). They have also been applied to genome selection in animal husbandry and have slightly improved their accuracy compared to traditional methods (Waldmann et al., 2020). For transcriptomic data, the large number of expressed genes determines the high complexity of the model, and ML, a new big data fitting method, can effectively fit complex data and accurately identify samples and genes (Waldmann et al., 2020). In addition, the small number of individual study samples affects the accuracy of machine learning analysis; therefore, multiple datasets need to be integrated to accurately predict and mine key genes with machine learning algorithms. SVM-RFE effectively reduces the feature dimension through recursive feature elimination and is suitable for high-dimensional small sample data. RF offers gene importance scores, can capture nonlinear relationships and feature interactions, and demonstrates robustness against noise and outliers. By contrast, KNN, K-means, neural networks, and naive Bayes are not appropriate for feature selection: KNN lacks a feature evaluation mechanism; K-means is not suitable for identifying differential genes; neural networks require a large quantity of data; and naive Bayes assumes feature independence, which is inconsistent with the characteristics of gene data (Sheth et al., 2022). In this study, the two methods of SVM-RFE and RF were chosen to screen differentially expressed genes mainly because they possess certain advantages in feature selection and handling high-dimensional data.
Therefore, this study collected the longissimus dorsi muscle tissue samples transcriptome datasets from pigs with different IMF content including our study and NCBI’s Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database. Two machine learning methods RF and SVM-RFE were used for identifying key genes affecting IMF content. The findings are helpful for further exploring the molecular regulatory mechanisms of intramuscular fat deposition in pigs.
In this study, 53 Songliao Black sows and 132 Long White sows were selected from the Tianjin Ninghe Original Breeding Pig Farm. These pigs were reared under the identical feeding conditions. When the pigs were raised to approximately 100 kg, the backfat thickness was determined using the HONGDA HS-1500 veterinary B ultrasound machine (between the second-to-last and fourth ribs, 5 cm from the dorsal midline) (Suzuki et al., 2009). To avoid the influence of different genetic backgrounds, three pairs of individuals from each breed with extreme differences in backfat thickness were slaughtered and the longissimus dorsi muscle tissues were collected. One portion was analyzed for the IMF content of the samples using the FOSSDSCAN near-infrared rapid analyzer for food components, while the other portion was preserved in liquid nitrogen for RNA extraction.
Total RNA was extracted from the longissimus dorsi muscle tissue using the Trizol kit according to the product instructions, and a total of 12 samples were extracted. The extracted RNA was diluted with 1% DEPC water and denatured for 2 min at 70°C. The quality of the RNA was checked by Agilent 2100, and the library was constructed by Illumina TruSeqTM RNA kit. The constructed libraries were sequenced by the Illumina Hiseq 2000 sequencing platform with pair ends (PE). In this study, eight datasets were also downloaded from the SRA database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/) under NCBI, namely PRJNA776032, PRJNA302287, PRJNA359473, PRJNA480676, PRJNA695218, PRJNA387276, PRJNA743884, and PRJNA604841. A total of 62 samples with an equal number of samples in high and low intramuscular fat groups in each dataset, including muscle tissue samples from Min, Wannanhua, Diannan Small-ear, Tibetan, Landrace, Large White, Iberian, Nanyang Black, Wei, and Dingyuan pigs.
A total of 74 samples were collected and these data were processed by the same method, and the raw data were quality-controlled using fastp software (Chen et al., 2018) to remove sequences with connectors and low-quality sequences (reads with Q ≤ 20). High-quality sequences were aligned to the pig reference genome Sus scrofa 11.1 using HISAT2 software (Kim et al., 2019) and annotated, and the expression of genes in different samples was calculated by HTSeq software (Anders et al., 2015). After obtaining gene expression profiles all data sets were integrated and samples were grouped according to phenotypic indicators (backfat thickness and intramuscular fat content) (Table 1). The downloaded data categorized lean pigs as the high IMF group and local pigs as the low IMF group.
To make the data comparable across studies, all data were converted to fragments per thousand bases of transcripts per million mapped reads (FPKM). The genes were screened with the following criteria: (1) removal of genes without symbol names; (2) removal of genes expressed in less than 10 samples. Before analyzing the data this study adjusted for batch effect, processed by the combat function of the sva package of the R-4.2.2 package, and visualized the gene expression data before and after the batch effect adjustment. Sva is a commonly used batch effect adjustment method that removes the batch effect by identifying and adjusting for potential influencing factors while preserving the biological differences in the data and avoiding biological conclusions.
In this study, differential expression analysis was performed using the algorithm provided by the limma program package of the R-4.2.2 software packages (Ritchie et al., 2015). The data of the high intramuscular fat group was compared with the low intramuscular fat group, and the data were screened at P < 0.05, |log2 FC| > 1 to select genes with significance. The occurrence of false positives in differential expression analysis was controlled in our study by adjusting the batch effect with the ComBat function. The DEGs were visualized by volcano plot. The samples were clustered using DEGs through the Microsign online analysis cloud platform (www.bioinformatics.com.cn).
To further identify the candidate genes affecting intramuscular fat deposition in pigs, machine-learning models were constructed based on the results of differential expression analysis. The expression levels of each DEG were scaled to the [0–1] interval using the maximum-minimum normalization method, to unify the weights of features and improve model accuracy. The data set is divided into a training set and a validation set with 74 samples, of which 75% of the samples were used as the training set to build the model, and the remaining 25% were used as the validation set to validate the performance of the model (Figures 1A, B). Two supervised learning classifiers, including SVM-RFE (Sahran et al., 2018)and RF (Zhao et al., 2018) models, were tested in this study. The e1071 program package of the R-4.2.2 package (https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/e1071/index.html) was used to implement SVM-RFE for differentially expressed gene screening, while RF was done using the randomForest program package (https://www.stat.berkeley.edu/∼breiman/RandomForests/). To avoid overfitting the constructed models, the models were validated using a fivefold cross-validation to adjust the suitable parameters (Figure 1C).
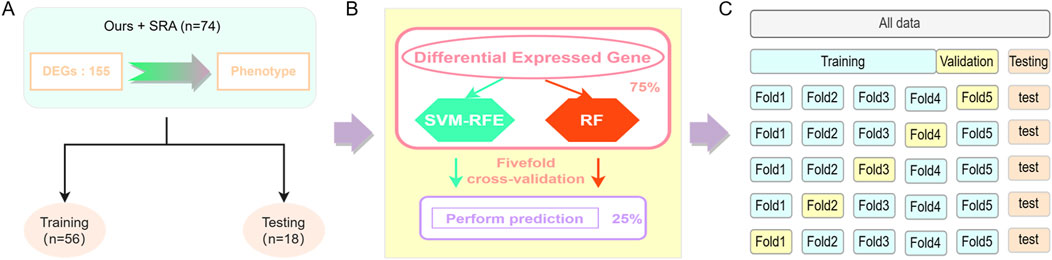
Figure 1. Model construction. (A) Data set division, (B) Classifier construction, (C) Fivefold cross-validation.
To understand the functions of the genes screened by the machine learning model, biological functional analysis and their visualization were performed. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis of the identified significant genes was performed through Omicshare Kidio Bioinformatics Cloud Platform (https://www.omicshare.com/).
By analyzing the quality of the raw sequencing data, it was found that the data quality was all as expected (Additional file 1: Supplementary Table S1). The quality-controlled high-quality reads were compared to the reference genome of pigs, and the mapping rates were found to be above 90% (Additional file 2: Supplementary Table S2). The data are reliable and can be analyzed in the next step.
The initially obtained gene expression profiles had a total of 31,908 genes, and after retaining the genes with symbol names and those expressed in at least 10 samples, 9,675 genes remained. The remaining data were subjected to the batch effect adjustment, and the box plot shows that the range of gene expression values in the samples decreased after the batch effect adjustment, indicating a reduction in outliers (Figures 2A, B). After principal component analysis, it was found that before the batch effect adjustment, the samples were divided into three groups, indicating heterogeneity among the samples, and after the batch effect adjustment. The samples clustered together, indicating similarity among the samples (Figures 2C, D).
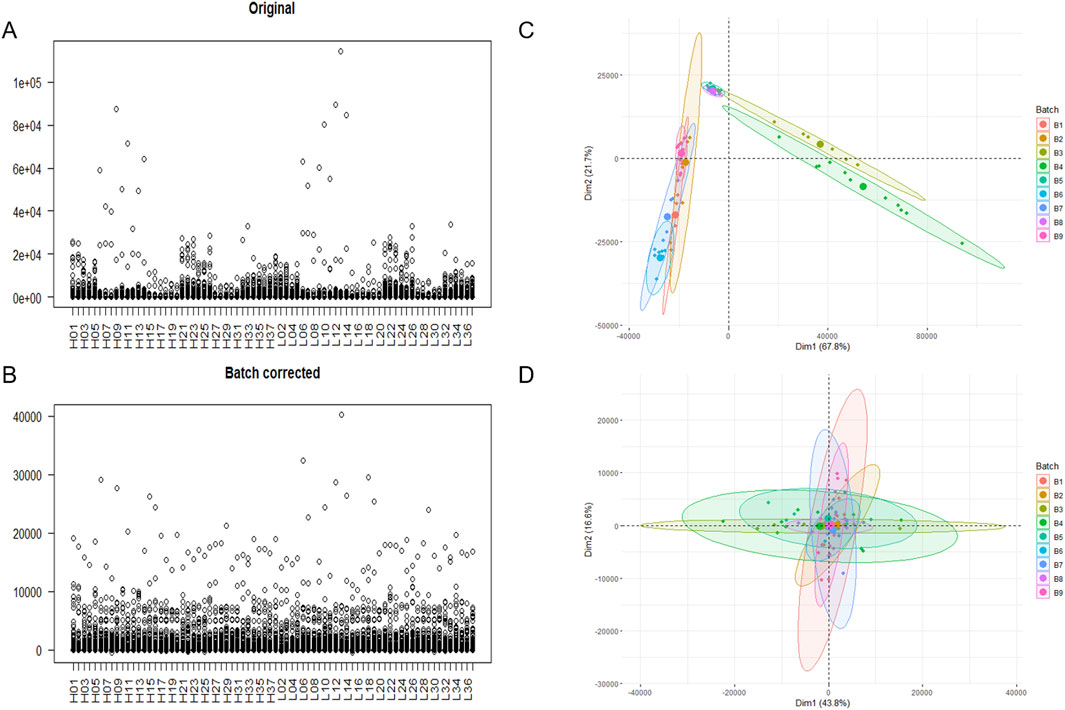
Figure 2. Mapping before and after removal of the batch effect. (A) Box line plot before batch effect adjustment. (B) Box line plot after batch effect adjustment. (C) PCA plot before batch effect adjustment. (D) PCA plot after batch effect adjustment.
The sample clustering heat map further showed that the samples were more homogeneous after adjusting the batch effect (Figure 3).
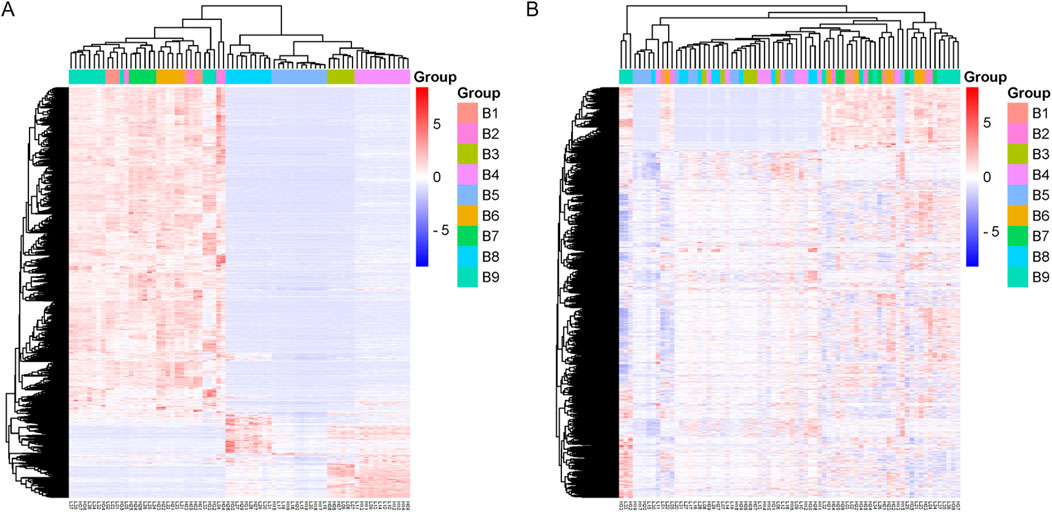
Figure 3. Sample clustering heat map. (A) The heat map of clustering before batch effect adjustment. (B) The heat map of clustering after batch effect adjustment.
The limma package was used to perform differential expression analysis on the nine datasets, and 180, 1,526, 315, 365, 1,097, 570, 1,452, 452, and 358 genes were identified, respectively. No common differential genes were found among these datasets (Supplementary F S1). This indicates that it is difficult to find genes that regulate fat deposition with generalizability by aggregating DEGs between different datasets.
Using the limma package, differential expression analysis was performed on the integrated dataset, and 155 DEGs were screened. Among them, 99 genes were highly expressed in the high intramuscular fat group, and 56 genes were highly expressed in the low intramuscular fat group (Figure 4A). In addition, these screened genes can effectively separate the high intramuscular fat group from the low intramuscular fat group (Figure 4B).
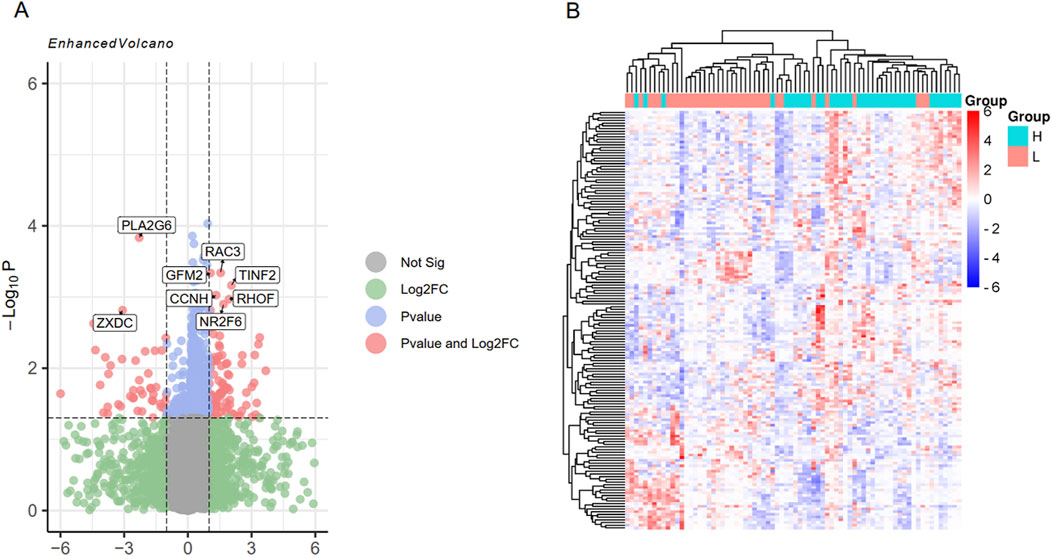
Figure 4. Differential expression analysis of the integrated data set. (A) represents a volcano plot of DEGs, which shows the eight genes with the most significant P values; (B) represents the sample clustering heat map of DEGs.
The SVM-RFE model screened 100 significant genes (Additional file 3: Supplementary Table S3), RF screened 11 significant genes, and Table 2 shows the top 15 ranked genes screened by the SVM-RFE model. A total of six common important features were screened by both models (Figure 5). Area Under Curve (AUC) is defined as the area beneath the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve. Given that the ROC curve is typically located above the line y = x, the range of AUC values lies between 0.5 and 1. The AUC value is equivalent to the probability that a randomly chosen positive example is ranked higher than a randomly chosen negative example (Fawcett, 2006). Thus, the larger the AUC value, the more likely the current classification algorithm is to rank the positive sample before the negative sample, indicating a better classification performance.
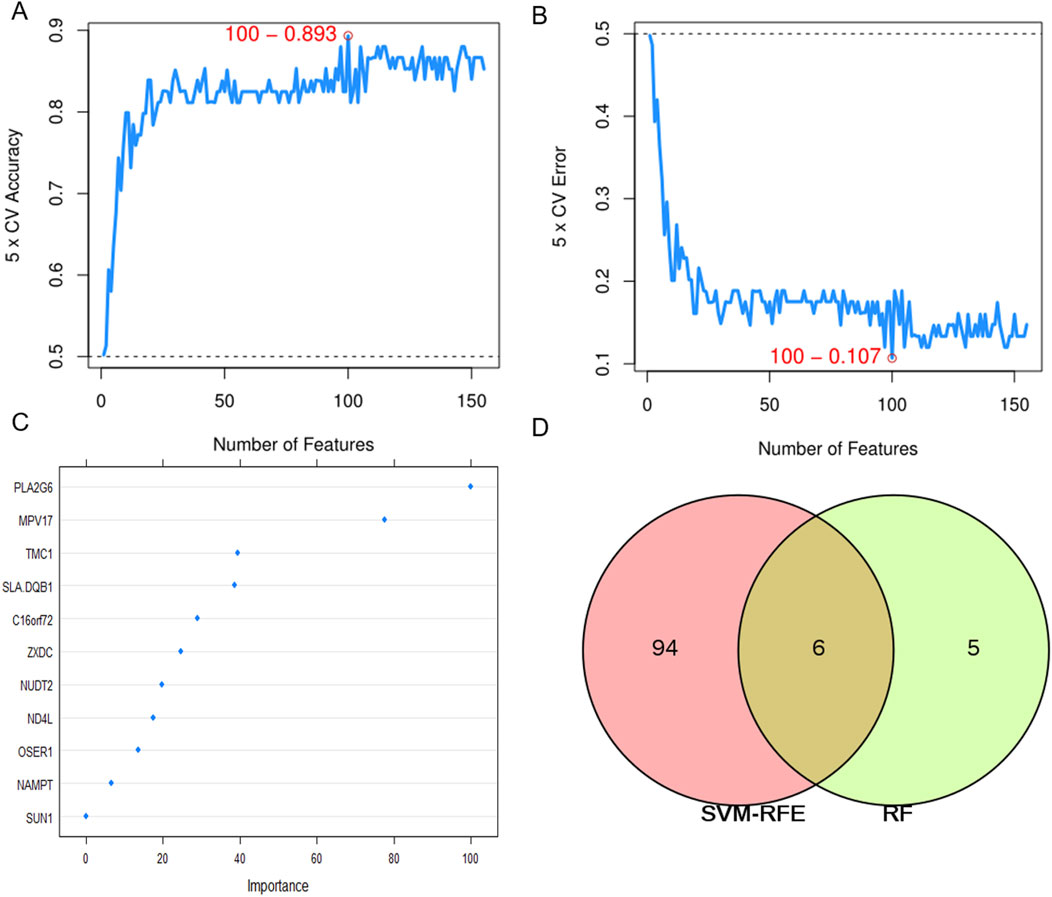
Figure 5. Two algorithms are used for feature selection. (A) the accuracy of the SVM-RFE model. (B) error rate of SVM-RFE model. (C) importance ranking of genes identified by random forest. (D) The intersection feature selection between SVM-RFE and RF algorithms.
Visualized by ROC curves, AUC of SVM-RFE and RF are 0.893 and 0.86, respectively (Supplementary Figure S2), indicating that the former technique is superior to the latter.
In addition, this study identified 10 genes associated with fat deposition from the 100 genes screened by SVM-RFE, namely APP, CTSZ, EIF4EBP1, FABP4, FAM184B, ID1, PLA2G6, SELENOF, SRGN, and TSPO, and these genes are associated with fat deposition (Table 3).
Among them, eight genes were highly expressed in the high intramuscular fat group compared to the low intramuscular fat group, and only EIF4EBP1HE and PLA2G6 were highly expressed in the low intramuscular fat group. Moreover, there was mainly a positive correlation between these genes (Figure 6).
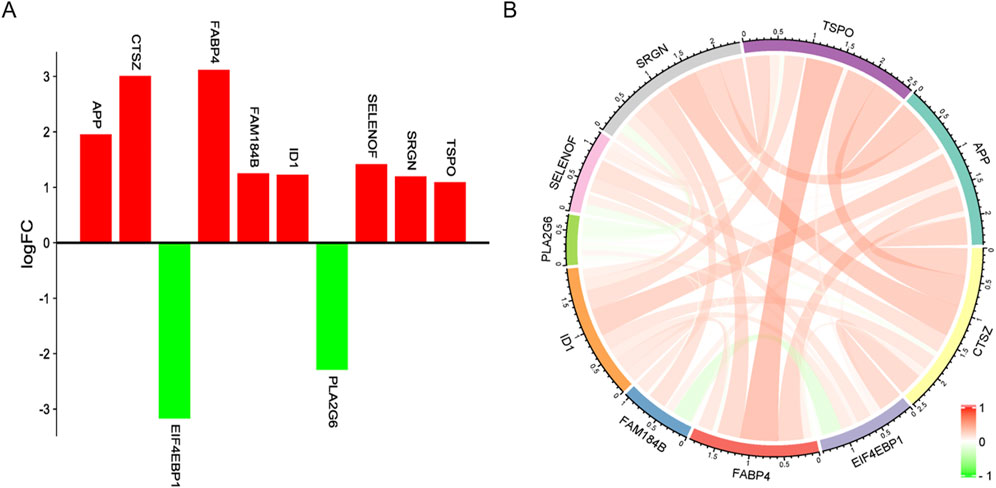
Figure 6. Gene expression profile. (A) Red represents upregulation and green represents downregulation. (B) The color, and width of the ribbon correlate with the correlation of gene expression, where red indicates a positive correlation and green indicates a negative correlation.
To visualize the distribution of samples in the high intramuscular fat group and the low intramuscular fat group, the distribution of samples was visualized using a 3D scatter plot. The green triangles in Figure 7 represent the high intramuscular fat group and the red triangles represent the low intramuscular fat group, and the top three most important genes were selected as coordinates. It can be seen from the figure that the distribution of the two groups of samples is very different (Additional file 4: Supplementary Table S4), and therefore, the model this study constructed can effectively distinguish the high intramuscular fat group from the low intramuscular fat group. (Figure 7).
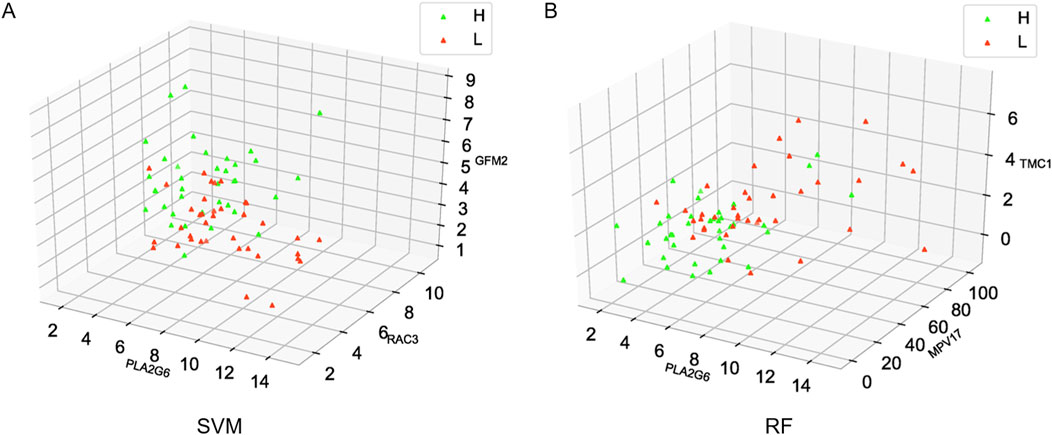
Figure 7. Distribution of high and low group samples. (A) Distribution of SVM-RFE samples, (B) Distribution of RF samples.
Six intersecting genes screened using two models were subjected to KEGG pathway enrichment analysis, and it was found that these genes were enriched in a total of 20 pathways. Among them, there are 10 significantly enriched pathways, and most of them are related to fat deposition, such as α- Linoleic acid metabolism, linoleic acid metabolism, ether lipid metabolism, glycerophospholipid metabolism, and arachidonic acid metabolism, etc. (Figure 8). Four genes related to fat deposition were screened based on significant pathways, namely PLA2G6, MPV17, NUDT2, and ND4L.
The four important genes were PLA2G6, MPV17, NUDT2, and ND4L, where PLA2G6 and MPV17 were upregulated in the high intramuscular fat group, and NUDT2 and ND4L were downregulated in the high intramuscular fat group compared to the low intramuscular fat group (Figure 9).
The integration of data from different transcriptomic studies is important for improving the reliability and generalizability of the results, allowing access to valid information that is not available from individual studies (Lazar et al., 2013; Mooney and Mcweeney, 2014). In our study, this was confirmed by screening the DEGs in each of the nine datasets using traditional differential analysis methods, and as a result, no common gene was found in these datasets. In contrast, when this study integrated multiple transcriptomic datasets for differential expression analysis, a common set of DEGs was found, and the results of this study are biologically significant.
When integrating the dataset, the batch effect needs to be adjusted to unify the data from different studies. This is because the data this study acquired may lead to errors due to differences in sample collection time, sequencing platform and pig breed, tissue, age and sex, and so on. So that the DEGs this study eventually found are not the genes that differ, resulting in false positives.
In this study, the large dataset was initially screened by traditional variance analysis methods, and then machine learning algorithms were utilized to further identify DEGs. A total of two classification algorithms, SVM-RFE and RF, were trained, and a set of key predictors was obtained for each classifier. The intersection of important genes was screened by these classifiers and functional annotation of these genes yielded key candidate genes affecting fat deposition. This study finally screened a total of four important genes, PLA2G6, MPV17, NUDT2, and ND4L. PLA2G6 is a lipid regulator that catalyzes the hydrolysis of fatty acids in glycerophospholipids (Baburina and Jackowski, 1999). MPV17 is a mitochondrial inner membrane protein that forms oligomers in lipid bilayers (Sperl and Hagn, 2021), and it has also been shown that low levels of MPV17 expression are associated with quiescence in energy metabolism. The results indicate that MPV17 influences the resting energy metabolism by exerting an impact on the mitochondrial respiratory chain and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) (Jacinto et al., 2021). Diadenosine polyphosphates (e.g., Ap4A) are physiologically released compounds, and the roles of their receptors as well as their function as second messengers influencing insulin release have been demonstrated. It has been shown that glucose levels in the blood increase and plasma insulin decreases after Ap4A administration in rats (Verspohl et al., 2003a; Verspohl et al., 2003b), and NUDT2 is thought to be a major factor in maintaining low intracellular Ap4A levels (Mclennan et al., 1995; Abdelghany et al., 2001; Carmi-Levy et al., 2008). ND4L is involved in the composition of the electron transport chain during oxidative phosphorylation, and dysfunction of this gene leads to metabolic disorders (Dashti et al., 2021), and it is considered to be a major predisposing factor for the development of metabolic syndrome (Perks et al., 2017). In addition, functional annotation of these genes after the KEGG pathway revealed that these genes are enriched in pathways related to lipid deposition such as α-linolenic acid metabolism, linoleic acid metabolism, ether lipid metabolism, and glycerophospholipid metabolism. Based on these results, it was concluded that these four genes play important roles in fat deposition in pigs, and these genes and pathways are not commonly found in traditional analysis methods but are some potential candidates that may affect fat deposition in pigs. This indicates that through machine learning methods were able to find some important information that could not be found by traditional differential analysis methods. This study further confirms the significance of integrating transcriptomic data from different sources (Liu et al., 2022) and shows that machine learning models can provide further technical support for traditional differential analysis methods (Veiner et al., 2022).
There is no single machine learning method that can be applied to all types of samples and different algorithms should be chosen based on the sample characteristics of different studies (Mirza et al., 2019). In this study, after evaluating the performance of both classifiers, it was found that the SVM-RFE model is more accurate than the RF model. Support vector machine algorithm, as a supervised cluster analysis algorithm, has achieved good results in the classification of high-dimensional small sample data with good generalization ability (Cherkassky, 1997), which has been favored by many researchers and is widely used in various fields of research (Zheng Y. et al., 2020; Lin et al., 2021; Shang et al., 2021; Song et al., 2021). The random forest belongs to an integrated algorithm, which itself has better accuracy than most individual algorithms and performs well in many cases (Lam et al., 2021), so it is also widely used in various fields of research (He et al., 2019; Toth et al., 2019; Bi et al., 2020). The choice of the classifier depends on the amount of data and the complexity of the problem, but there are many cases where support vector machines outperform random forests in terms of predictive effectiveness (Caruana and Niculescu-Mizil, 2006). For this study, the number of samples is relatively small and the complexity of the sample information is high, and the SVM-RFE model shows better performance compared to the RF model. This further indicates that different algorithms for different sample characteristics should be chosen, which is the only way to ensure the accuracy of the classification and the reliability of the results.
This study integrated transcriptomic datasets from different studies to identify important genes by combining traditional gene expression analysis and machine learning methods and finally screened a total of four important genes, PLA2G6, MPV17, NUDT2, and ND4L. At the same time, some important pathways were identified. This study screened consistent key genes affecting intramuscular fat deposition from different breeds of pigs, providing new reference information for the study of molecular regulatory mechanisms of porcine fat deposition.
Both original dataset and publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/, accession numbers PRJNA1043865, PRJNA776032, PRJNA302287, PRJNA359473, PRJNA480676, PRJNA695218, PRJNA387276, PRJNA743884 and PRJNA604841.
The animal studies were approved by The Ethics Committee of Beijing University of Agriculture. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent was obtained from the owners for the participation of their animals in this study.
YS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing–original draft. XW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing–original draft. SC: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Writing–original draft. YZ: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Writing–original draft. YW: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Writing–original draft. XS: Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. XQ: Formal Analysis, Software, Visualization, Writing–original draft. LZ: Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. YF: Formal Analysis, Software, Visualization, Writing–original draft. JL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing–original draft. CW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Resources, Writing–original draft. KX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the earmarked fund for Biological Breeding-National Science and Technology Major Project(No.2023ZD04046), CARS (No. 35) and the 2115 Talent Development Program of China Agricultural University.
We thank the Livestock and Poultry Biological Breeding and Reproductive Physiology team for their help in this study.
Author SC was employed by Beijing Animal Husbandry Station.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2024.1503148/full#supplementary-material
Abdelghany, H. M., Gasmi, L., Cartwright, J. L., Bailey, S., Rafferty, J. B., and McLennan, A. G. (2001). Cloning, characterisation and crystallisation of a diadenosine 5′,5′′′-P(1),P(4)-tetraphosphate pyrophosphohydrolase from Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1550 (1), 27–36. doi:10.1016/s0167-4838(01)00263-1
Alecu, I., and Bennett, S. A. L. (2019). Dysregulated lipid metabolism and its role in α-synucleinopathy in Parkinson's disease. Front. Neurosci. 13, 328. doi:10.3389/fnins.2019.00328
Anders, S., Pyl, P. T., and Huber, W. (2015). HTSeq--a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 31 (2), 166–169. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu638
Baburina, I., and Jackowski, S. (1999). Cellular responses to excess phospholipid. J. Biol. Chem. 274 (14), 9400–9408. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.14.9400
Bi, X. A., Hu, X., Wu, H., and Wang, Y. (2020). Multimodal data analysis of alzheimer's disease based on clustering evolutionary random forest. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 24 (10), 2973–2983. doi:10.1109/JBHI.2020.2973324
Carmi-Levy, I., Yannay-Cohen, N., Kay, G., Razin, E., and Nechushtan, H. (2008). Diadenosine tetraphosphate hydrolase is part of the transcriptional regulation network in immunologically activated mast cells. Mol. Cell Biol. 28 (18), 5777–5784. doi:10.1128/MCB.00106-08
Caruana, R., and Niculescu-Mizil, A. (2006). An empirical comparison of supervised learning algorithms. ICML 06, 161–168. doi:10.1145/1143844.1143865
Cheng, F., Liang, J., Yang, L., Lan, G., Wang, L., and Wang, L. (2021). Systematic identification and comparison of the expressed profiles of lncRNAs, miRNAs, circRNAs, and mRNAs with associated Co-expression networks in pigs with low and high intramuscular fat. Anim. (Basel) 11 (11), 3212. doi:10.3390/ani11113212
Chen, S., Zhou, Y., Chen, Y., and Gu, J. (2018). fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34 (17), i884–i890. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
Cherkassky, V. (1997). The nature of statistical learning theory∼. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 8 (6), 1564. doi:10.1109/TNN.1997.641482
Cho, I. C., Park, H. B., Ahn, J. S., Han, S. H., Lee, J. B., Lim, H. T., et al. (2019). A functional regulatory variant of MYH3 influences muscle fiber-type composition and intramuscular fat content in pigs. PLoS Genet. 15 (10), e1008279. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1008279
Crespo-Piazuelo, D., Criado-Mesas, L., Revilla, M., Castelló, A., Noguera, J. L., Fernández, A. I., et al. (2020). Identification of strong candidate genes for backfat and intramuscular fatty acid composition in three crosses based on the Iberian pig. Sci. Rep. 10 (1), 13962. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-70894-2
Dashti, M., Alsaleh, H., Rodriguez-Flores, J. L., Eaaswarkhanth, M., Al-Mulla, F., and Thanaraj, T. A. (2021). Mitochondrial haplogroup J associated with higher risk of obesity in the Qatari population. Sci. Rep. 11 (1), 1091. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-80040-7
Ding, H., Lin, Y., Zhang, T., Chen, L., Zhang, G., Wang, J., et al. (2021). Transcriptome analysis of differentially expressed mRNA related to pigeon muscle development. Anim. (Basel) 11 (8), 2311. doi:10.3390/ani11082311
Fawcett, T. (2006). An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 27 (8), 861–874. doi:10.1016/j.patrec.2005.10.010
Fernandez, X., Monin, G., Talmant, A., Mourot, J., and Lebret, B. (1999). Influence of intramuscular fat content on the quality of pig meat - 2. Consumer acceptability of m. longissimus lumborum. Meat Sci. 53 (1), 67–72. doi:10.1016/s0309-1740(99)00038-8
Hamill, R. M., Mcbryan, J., Mcgee, C., Mullen, A. M., Sweeney, T., Talbot, A., et al. (2012). Functional analysis of muscle gene expression profiles associated with tenderness and intramuscular fat content in pork. Meat Sci. 92 (4), 440–450. doi:10.1016/j.meatsci.2012.05.007
Hashimoto, D. A., Witkowski, E., Gao, L., Meireles, O., and Rosman, G. (2020). Artificial intelligence in anesthesiology: current techniques, clinical applications, and limitations. Anesthesiology 132 (2), 379–394. doi:10.1097/ALN.0000000000002960
He, S., Chen, W., Liu, H., Li, S., Lei, D., Dang, X., et al. (2019). Gene pathogenicity prediction of Mendelian diseases via the random forest algorithm. Hum. Genet. 138 (6), 673–679. doi:10.1007/s00439-019-02021-9
Huang, S., Cai, N., Pacheco, P. P., Narrandes, S., Wang, Y., and Xu, W. (2018b). Applications of support vector machine (SVM) learning in cancer genomics. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 15 (1), 41–51. doi:10.21873/cgp.20063
Huang, W., Zhang, X., Li, A., Xie, L., and Miao, X. (2018a). Genome-Wide analysis of mRNAs and lncRNAs of intramuscular fat related to lipid metabolism in two pig breeds. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 50 (6), 2406–2422. doi:10.1159/000495101
Jacinto, S., Guerreiro, P., De Oliveira, R. M., Cunha-Oliveira, T., Santos, M. J., Grazina, M., et al. (2021). MPV17 mutations are associated with a quiescent energetic metabolic profile. Front. Cell Neurosci. 15, 641264. doi:10.3389/fncel.2021.641264
Jiang, Z., Michal, J. J., Wu, X. L., Pan, Z., and MacNeil, M. D. (2011). The heparan and heparin metabolism pathway is involved in regulation of fatty acid composition. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 7 (5), 659–663. doi:10.7150/ijbs.7.659
Kim, D., Paggi, J. M., Park, C., Bennett, C., and Salzberg, S. L. (2019). Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 37 (8), 907–915. doi:10.1038/s41587-019-0201-4
Kim, S., Kim, N., Park, S., Jeon, Y., Lee, J., Yoo, S. J., et al. (2020). Tanycytic TSPO inhibition induces lipophagy to regulate lipid metabolism and improve energy balance. Autophagy 16 (7), 1200–1220. doi:10.1080/15548627.2019.1659616
Lam, C., Calvert, J., Siefkas, A., Barnes, G., Pellegrini, E., Green-Saxena, A., et al. (2021). Personalized stratification of hospitalization risk amidst COVID-19: a machine learning approach. Health Policy Technol. 10 (3), 100554. doi:10.1016/j.hlpt.2021.100554
Lazar, C., Meganck, S., Taminau, J., Steenhoff, D., Coletta, A., Molter, C., et al. (2013). Batch effect removal methods for microarray gene expression data integration: a survey. Brief. Bioinform 14 (4), 469–490. doi:10.1093/bib/bbs037
Lee, Y. H., Tharp, W. G., Maple, R. L., Nair, S., Permana, P. A., and Pratley, R. E. (2008). Amyloid precursor protein expression is upregulated in adipocytes in obesity. Obes. (Silver Spring) 16 (7), 1493–1500. doi:10.1038/oby.2008.267
Lee, Y. W., Choi, J. W., and Shin, E. H. (2021). Machine learning model for predicting malaria using clinical information. Comput. Biol. Med. 129, 104151. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.104151
Li, X. J., Zhou, J., Liu, L. Q., Qian, K., and Wang, C. L. (2016). Identification of genes in longissimus dorsi muscle differentially expressed between Wannanhua and Yorkshire pigs using RNA-sequencing. Anim. Genet. 47 (3), 324–333. doi:10.1111/age.12421
Lin, J., Lu, Y., Wang, B., Jiao, P., and Ma, J. (2021). Analysis of immune cell components and immune-related gene expression profiles in peripheral blood of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J. Transl. Med. 19 (1), 319. doi:10.1186/s12967-021-02991-3
Li, Q., Huang, Z., Zhao, W., and Li, M. (2020). Transcriptome analysis reveals Long intergenic non-coding RNAs contributed to intramuscular fat content differences between Yorkshire and Wei pigs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (5), 1732. doi:10.3390/ijms21051732
Liu, S., Yue, T., Ahmad, M. J., Hu, X., Zhang, X., Deng, T., et al. (2020). Transcriptome analysis reveals potential regulatory genes related to heat tolerance in Holstein dairy cattle. Genes(Basel) 11 (1), 68. doi:10.3390/genes11010068
Liu, H., Xing, K., Jiang, Y., Liu, Y., Wang, C., and Ding, X. (2022). Using machine learning to identify biomarkers affecting fat deposition in pigs by integrating multisource transcriptome information. J. Agric. Food Chem. 70 (33), 10359–10370. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.2c03339
Li, X., Kim, S. W., Choi, J. S., Lee, Y. M., Lee, C. K., Choi, B. H., et al. (2010). Investigation of porcine FABP3 and LEPR gene polymorphisms and mRNA expression for variation in intramuscular fat content. Mol. Biol. Rep. 37 (8), 3931–3939. doi:10.1007/s11033-010-0050-1
Malgwi, I. H., Halas, V., GrüNVALD, P., Carnier, P., and Schiavon, S. (2022). Genes related to fat metabolism in pigs and intramuscular fat content of pork: a focus on nutrigenetics and nutrigenomics. Anim. (Basel) 12 (2), 215. doi:10.3390/ani12020215
Mclennan, A. G., Mayers, E., Walker-Smith, I., and Chen, H. (1995). Lanterns of the firefly Photinus pyralis contain abundant diadenosine 5′,5′′′-P1,P4-tetraphosphate pyrophosphohydrolase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 270 (8), 3706–3709. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.8.3706
Mirza, B., Wang, W., Wang, J., Choi, H., Chung, N. C., and Ping, P. (2019). Machine learning and integrative analysis of biomedical big data. Genes (Basel) 10 (2), 87. doi:10.3390/genes10020087
Mooney, M., and Mcweeney, S. (2014). Data integration and reproducibility for high-throughput transcriptomics. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 116, 55–71. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-801105-8.00003-5
MuñOZ, M., GarcíA-Casco, J. M., Caraballo, C., Fernández-Barroso, M. Á., Sánchez-Esquiliche, F., Gómez, F., et al. (2018). Identification of candidate genes and regulatory factors underlying intramuscular fat content through longissimus dorsi transcriptome analyses in heavy iberian pigs. Front. Genet. 9, 608. doi:10.3389/fgene.2018.00608
Patil, M., Sharma, B. K., Elattar, S., Chang, J., Kapil, S., Yuan, J., et al. (2017). Id1 promotes obesity by suppressing Brown adipose thermogenesis and white adipose browning. Diabetes 66 (6), 1611–1625. doi:10.2337/db16-1079
Perks, K. L., Ferreira, N., Richman, T. R., Ermer, J. A., Kuznetsova, I., Shearwood, A. M. J., et al. (2017). Adult-onset obesity is triggered by impaired mitochondrial gene expression. Sci. Adv. 3 (8), e1700677. doi:10.1126/sciadv.1700677
PióRKOWSKA, K., Małopolska, M., Ropka-Molik, K., Szyndler-Nędza, M., Wiechniak, A., Żukowski, K., et al. (2020). Evaluation of SCD, ACACA and FASN mutations: effects on pork quality and other production traits in pigs selected based on RNA-seq results. Anim. (Basel) 10 (1), 123. doi:10.3390/ani10010123
Puig-Oliveras, A., Ramayo-Caldas, Y., Corominas, J., Estellé, J., Pérez-Montarelo, D., Hudson, N. J., et al. (2014). Differences in muscle transcriptome among pigs phenotypically extreme for fatty acid composition. PLoS One 9 (6), e99720. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0099720
Qin, D. D., Yang, Y. F., Pu, Z. Q., Liu, D., Yu, C., Gao, P., et al. (2018). NR4A1 retards adipocyte differentiation or maturation via enhancing GATA2 and p53 expression. J. Cell Mol. Med. 22 (10), 4709–4720. doi:10.1111/jcmm.13715
Ren, L., Liu, A., Wang, Q., Wang, H., and Dong, D. (2021). Transcriptome analysis of embryonic muscle development in Chengkou Mountain Chicken. BMC Genomics 22 (1), 431. doi:10.1186/s12864-021-07740-w
Ritchie, M. E., Phipson, B., Wu, D., Hu, Y., Law, C. W., Shi, W., et al. (2015). Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 43 (7), e47. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv007
Russo, V., Fontanesi, L., Scotti, E., Beretti, F., Davoli, R., Nanni Costa, L., et al. (2008). Single nucleotide polymorphisms in several porcine cathepsin genes are associated with growth, carcass, and production traits in Italian Large White pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 86 (12), 3300–3314. doi:10.2527/jas.2008-0920
Sahran, S., Albashish, D., Abdullah, A., Shukor, N. A., and Hayati Md Pauzi, S. (2018). Absolute cosine-based SVM-RFE feature selection method for prostate histopathological grading. Artif. Intell. Med. 87, 78–90. doi:10.1016/j.artmed.2018.04.002
Sato, S., Uemoto, Y., Kikuchi, T., Egawa, S., Kohira, K., Saito, T., et al. (2017). Genome-wide association studies reveal additional related loci for fatty acid composition in a Duroc pig multigenerational population. Anim. Sci. J. 88 (10), 1482–1490. doi:10.1111/asj.12793
Savedoroudi, P., Bennike, T. B., Kastaniegaard, K., Talebpour, M., Ghassempour, A., and Stensballe, A. (2019). Serum proteome changes and accelerated reduction of fat mass after laparoscopic gastric plication in morbidly obese patients. J. Proteomics 203, 103373. doi:10.1016/j.jprot.2019.05.001
Shang, Z., Sun, J., Hui, J., Yu, Y., Bian, X., Yang, B., et al. (2021). Construction of a support vector machine-based classifier for pulmonary arterial hypertension patients. Front. Genet. 12, 781011. doi:10.3389/fgene.2021.781011
Sheth, V., Tripathi, U., and Sharma, A. (2022). A comparative analysis of machine learning algorithms for classification purpose. Procedia Comput. 215, 422–431. doi:10.1016/j.procs.2022.12.044
Song, X., Zheng, Y., Xue, W., Li, L., Shen, Z., Ding, X., et al. (2021). Identification of risk genes related to myocardial infarction and the construction of early SVM diagnostic model. Int. J. Cardiol. 328, 182–190. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.12.007
Sperl, L. E., and Hagn, F. (2021). NMR structural and biophysical analysis of the disease-linked inner mitochondrial membrane protein MPV17. J. Mol. Biol. 433 (15), 167098. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167098
Suzuki, K., Inomata, K., Katoh, K., Kadowaki, H., and Shibata, T. (2009). Genetic correlations among carcass cross-sectional fat area ratios, production traits, intramuscular fat, and serum leptin concentration in Duroc pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 87 (7), 2209–2215. doi:10.2527/jas.2008-0866
Toth, R., Schiffmann, H., Hube-Magg, C., Büscheck, F., Höflmayer, D., Weidemann, S., et al. (2019). Random forest-based modelling to detect biomarkers for prostate cancer progression. Clin. Epigenetics 11 (1), 148. doi:10.1186/s13148-019-0736-8
Tsukiyama-Kohara, K., Poulin, F., Kohara, M., DeMaria, C. T., Cheng, A., Wu, Z., et al. (2001). Adipose tissue reduction in mice lacking the translational inhibitor 4E-BP1. Nat. Med. 7 (10), 1128–1132. doi:10.1038/nm1001-1128
Veiner, M., Morimoto, J., Leadbeater, E., and Manfredini, F. (2022). Machine learning models identify gene predictors of waggle dance behaviour in honeybees. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 22 (6), 2248–2261. doi:10.1111/1755-0998.13611
Verspohl, E. J., Blackburn, G. M., Hohmeier, N., Hagemann, J., and Lempka, M. (2003a). Synthetic, nondegradable diadenosine polyphosphates and diinosine polyphosphates: their effects on insulin-secreting cells and cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Med. Chem. 46 (8), 1554–1562. doi:10.1021/jm011070z
Verspohl, E. J., Hohmeier, N., and Lempka, M. (2003b). Diadenosine tetraphosphate (Ap4A) induces a diabetogenic situation: its impact on blood glucose, plasma insulin, gluconeogenesis, glucose uptake and GLUT-4 transporters. Pharmazie 58 (12), 910–915. doi:10.1021/jm011070z
Waldmann, P., Pfeiffer, C., and MéSZáROS, G. (2020). Sparse convolutional neural networks for genome-wide prediction. Front. Genet. 11, 25. doi:10.3389/fgene.2020.00025
Wang, Z., Liang, W., Yan, D., Tian, H., Dong, B., Zhao, W., et al. (2021). Identification of genes related to growth traits from transcriptome profiles of duck breast muscle tissue. Anim. Biotechnol. 34, 1239–1246. doi:10.1080/10495398.2021.2018333
Wang, L., Zhang, Y., Zhang, B., Zhong, H., Lu, Y., and Zhang, H. (2021). Candidate gene screening for lipid deposition using combined transcriptomic and proteomic data from Nanyang black pigs. BMC Genomics 22 (1), 441. doi:10.1186/s12864-021-07764-2
Wang, Z., Li, Q., Chamba, Y., Zhang, B., Shang, P., Zhang, H., et al. (2015). Identification of genes related to growth and lipid deposition from transcriptome profiles of pig muscle tissue. PLoS One 10 (10), e0141138. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0141138
Xu, J., Wang, C., Jin, E., Gu, Y., Li, S., and Li, Q. (2018). Identification of differentially expressed genes in longissimus dorsi muscle between Wei and Yorkshire pigs using RNA sequencing. Genes Genomics 40 (4), 413–421. doi:10.1007/s13258-017-0643-3
Yuan, Z., Sunduimijid, B., Xiang, R., Behrendt, R., Knight, M. I., Mason, B. A., et al. (2021). Expression quantitative trait loci in sheep liver and muscle contribute to variations in meat traits. Genet. Sel. Evol. 53 (1), 8. doi:10.1186/s12711-021-00602-9
Zappaterra, M., Gioiosa, S., Chillemi, G., Zambonelli, P., and Davoli, R. (2020). Muscle transcriptome analysis identifies genes involved in ciliogenesis and the molecular cascade associated with intramuscular fat content in Large White heavy pigs. PLoS One 15 (5), e0233372. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0233372
Zhang, P., Li, Q., Wu, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, B., and Zhang, H. (2022). Identification of candidate genes that specifically regulate subcutaneous and intramuscular fat deposition using transcriptomic and proteomic profiles in Dingyuan pigs. Sci. Rep. 12 (1), 2844. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-06868-3
Zhang, Y., Sun, Y., Wu, Z., Xiong, X., Zhang, J., Ma, J., et al. (2021). Subcutaneous and intramuscular fat transcriptomes show large differences in network organization and associations with adipose traits in pigs. Sci. China Life Sci. 64 (10), 1732–1746. doi:10.1007/s11427-020-1824-7
Zhao, X., Wu, Y., Lee, D. L., and Cui, W. (2018). iForest: interpreting random forests via visual analytics. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph 25, 407–416. doi:10.1109/TVCG.2018.2864475
Zheng, X., Ren, B., Li, X., Yan, H., Xie, Q., Liu, H., et al. (2020a). Selenoprotein F knockout leads to glucose and lipid metabolism disorders in mice. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 25 (7), 1009–1022. doi:10.1007/s00775-020-01821-z
Zheng, Y., Fang, Z., Xue, Y., Zhang, J., Zhu, J., Gao, R., et al. (2020b). Specific gut microbiome signature predicts the early-stage lung cancer. Gut Microbes 11 (4), 1030–1042. doi:10.1080/19490976.2020.1737487
Keywords: machine learning, pig, transcriptome, intramuscular fat, key genes
Citation: Shi Y, Wang X, Chen S, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Sheng X, Qi X, Zhou L, Feng Y, Liu J, Wang C and Xing K (2025) Identification of key genes affecting intramuscular fat deposition in pigs using machine learning models. Front. Genet. 15:1503148. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1503148
Received: 28 September 2024; Accepted: 09 December 2024;
Published: 06 January 2025.
Edited by:
Johann Sölkner, University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences Vienna, AustriaReviewed by:
Zhiyan Zhang, Jiangxi Agricultural University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Shi, Wang, Chen, Zhao, Wang, Sheng, Qi, Zhou, Feng, Liu, Wang and Xing. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kai Xing, eGtAY2F1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.