
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Genet. , 28 February 2024
Sec. Livestock Genomics
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2024.1372841
This article is part of the Research Topic Omics Applied to Livestock Genetics,volume II View all 16 articles
This article is a correction to:
Genome-wide survey reveals the genetic background of Xinjiang Brown cattle in China
 Xiao Wang1,2
Xiao Wang1,2 Zhen Ma3
Zhen Ma3 Liang Gao2
Liang Gao2 Lixin Yuan3
Lixin Yuan3 Zhibing Ye3
Zhibing Ye3 Fanrong Cui3
Fanrong Cui3 Xiaoping Guo4
Xiaoping Guo4 Wujun Liu1*
Wujun Liu1* Xiangmin Yan3*
Xiangmin Yan3*A Corrigendum on
Genome-wide survey reveals the genetic background of Xinjiang Brown cattle in China
by Wang X, Ma Z, Gao L, Yuan L, Ye Z, Cui F, Guo X, Liu W and Yan X (2024). Front. Genet. 14:1348329. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1348329
In the published article, there was an error in the legend for Figure 4 as published. In the phrase “(B) Principal component analysis for the first two PCs of the 178 studied cattle”, 178 needs to be replaced with 177 in order to be consistent with the numbers in the text. The corrected legend appears below.
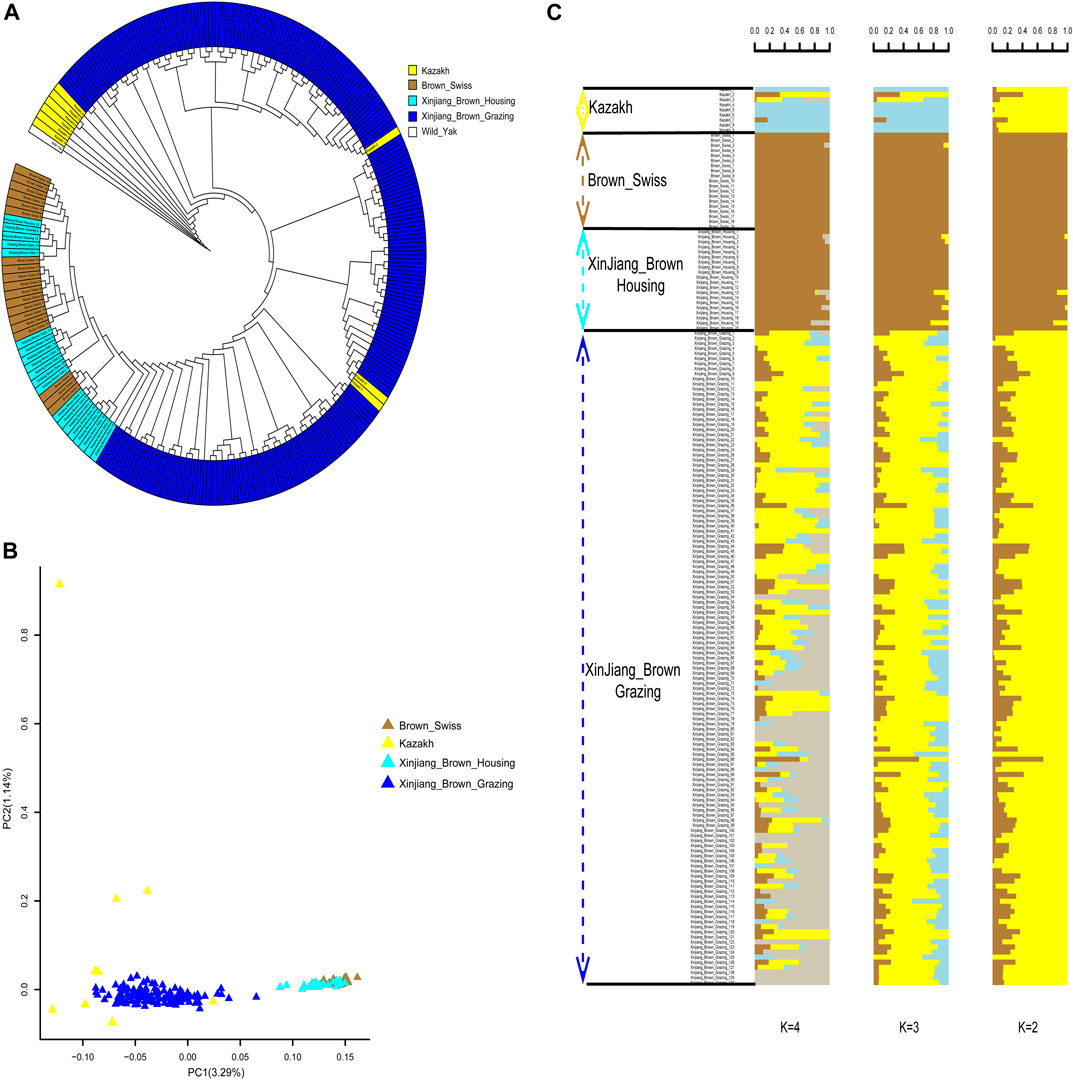
FIGURE 4. Phylogenetic relationship and population structure of the Xinjiang Brown cattle-grazing type (XBG) cattle and the other three breeds evaluated in this study. (A) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree constructed from single-nucleotide variant data among four populations. (B) Principal component analysis for the first two PCs of the 177 studied cattle. (C) ADMIXTURE analysis with four presumed ancestral groups to two presumed ancestral groups (K = from 2 to 4).
“Figure 4. Phylogenetic relationship and population structure of the Xinjiang Brown cattle-grazing type (XBG) cattle and the other three breeds evaluated in this study. (A) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree constructed from single-nucleotide variant data among four populations. (B) Principal component analysis for the first two PCs of the 177 studied cattle. (C) ADMIXTURE analysis with four presumed ancestral groups to two presumed ancestral groups (K = from 2 to 4).”
In the published article, there was an error in the legend for Figure 5 as published. In the phrase “Ancestry proportion of the 130 XBG and 20 XBH individuals inferred using RFMix, as based on the reference panels of Kazakh and Brown Swiss cattle”, 130 needs to be replaced with 129, in order to be consistent with the numbers in the text. The corrected legend appears below.
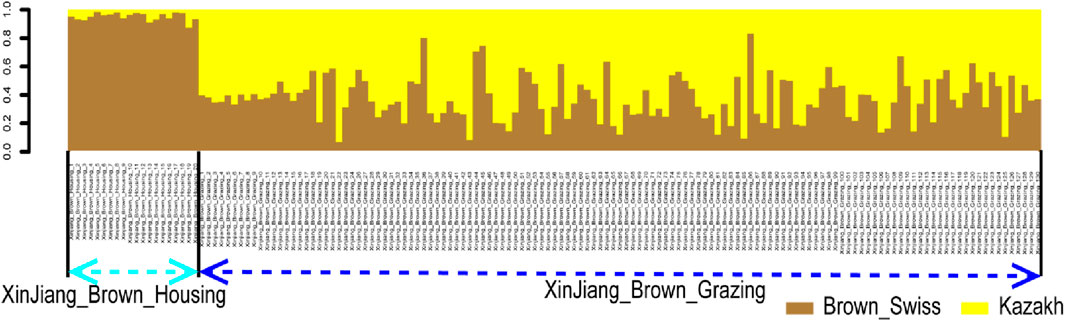
FIGURE 5. Ancestry proportion of the 129 XBG and 20 XBH individuals inferred using RFMix, as based on the reference panels of Kazakh and Brown Swiss cattle.
“Figure 5. Ancestry proportion of the 129 XBG and 20 XBH individuals inferred using RFMix, as based on the reference panels of Kazakh and Brown Swiss cattle.”
In the published article, there was an error in the Funding. “National Agricultural Science and Technology Special Project of China (No. NK2022130302)” is a secret item and its number needs to be deleted. The correct Funding statement appears below.
“The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Science and Technology Major Project (No. 2022A02001-1), Xinjiang Brown Cattle Joint Breeding Group Improvement and Enhancement Action Plan Issues (No. 2023XJHN-14), and Xinjiang Agriculture Research System (No. XJARS-XM-08).”
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: Xinjiang Brown cattle, specific-locus amplified fragment-sequencing, genetic structure, genetic diversity, candidate genes, ancestry proportion
Citation: Wang X, Ma Z, Gao L, Yuan L, Ye Z, Cui F, Guo X, Liu W and Yan X (2024) Corrigendum: Genome-wide survey reveals the genetic background of Xinjiang Brown cattle in China. Front. Genet. 15:1372841. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1372841
Received: 18 January 2024; Accepted: 01 February 2024;
Published: 28 February 2024.
Edited and reviewed by:
Lucas Lima Verardo, Universidade Federal dos Vales do Jequitinhonha e Mucuri (UFVJM), BrazilCopyright © 2024 Wang, Ma, Gao, Yuan, Ye, Cui, Guo, Liu and Yan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wujun Liu, bHdqX3dzQDE2My5jb20=; Xiangmin Yan, eWFueGlhbmdtaW4xMDE0QHNvaHUuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.