- 1LKS Faculty of Medicine, School of Public Health, University of Hong Kong, Pokfulam, Hong Kong SAR, China
- 2School of Public Health and Health Policy, City University of New York, New York, NY, United States
by Liang, Y., Luo, S., Schooling, C. M., and Au Yeung, S. L. (2021). Front. Genet. 12:699455. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.699455
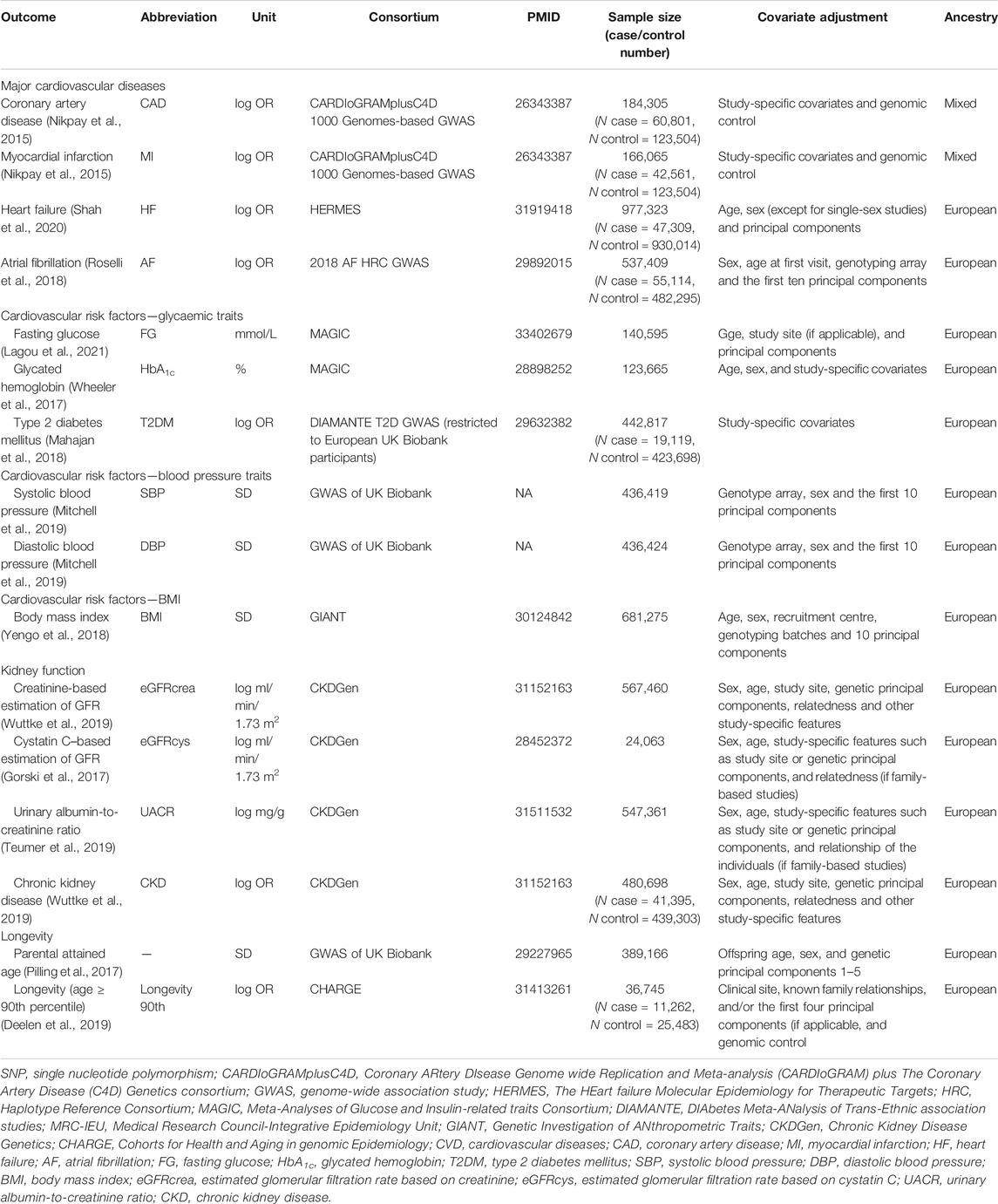
In the original article, there was an error where the description of Type 2 Diabetes Miletus (T2DM) under Data Sources, Outcomes was not clear. In this study, the T2DM data “restricted to European UK Biobank participants” was used.
A correction has been made to Data Sources, Outcomes:
“We also included cardiovascular risk factors as secondary outcomes, including blood pressure [systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP) (Mitchell et al., 2019)], body mass index (BMI) (Yengo et al., 2018), glycaemic traits [fasting glucose (FG) (Lagou et al., 2021), glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) (Wheeler et al., 2017)], and T2DM (restricted to European UK Biobank participants) (Mahajan et al., 2018),”
In addition, there were mistakes in Table 1, Supplementary Table S6, and Supplementary Figure S1 as published when describing the genetic data used for T2DM. The sample size number of T2DM (restricted to European UK Biobank participants) including case and control number was incorrect. The corrected Table 1, Supplementary Table S6, and Supplementary Figure S1 appear below.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2021.699455/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure S1 | Study design of this Mendelian randomization study of genetically predicted FGF23 and cardiovascular diseases, their risk factors, kidney function and longevity. SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; LD, linkage disequilibrium; CARDIoGRAMplusC4D, Coronary ARtery DIsease Genome wide Replication and Meta-analysis (CARDIoGRAM) plus The Coronary Artery Disease (C4D) Genetics consortium; GWAS, genome-wide association study; HERMES, The Heart Failure Molecular Epidemiology for Therapeutic Targets; HRC, Haplotype Reference Consortium; MAGIC, Meta-Analyses of Glucose and Insulin-related traits Consortium; DIAMANTE, DIAbetes Meta-ANalysis of Trans-Ethnic association studies; MRC-IEU, Medical Research Council-Integrative Epidemiology Unit; GIANT, Genetic Investigation of ANthropometric Traits; CKDGen, Chronic Kidney Disease Genetics; CHARGE, Cohorts for Health and Aging in genomic Epidemiology; CVD, cardiovascular diseases; CAD, coronary artery disease; MI, myocardial infarction; HF, heart failure; AF, atrial fibrillation; FG, fasting glucose; HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; BMI, body mass index; eGFRcrea, estimated glomerular filtration rate based on creatinine; eGFRcys, estimated glomerular filtration rate based on cystatin C; UACR, urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio; CKD, chronic kidney disease.
Supplementary Table S6 | Participant overlap between the FGF23 genome wide association studies (GWAS) and the outcome GWAS.
References
Deelen, J., Evans, D. S., Arking, D. E., Tesi, N., Nygaard, M., Liu, X., et al. (2019). A Meta-Analysis of Genome-wide Association Studies Identifies Multiple Longevity Genes. Nat. Commun. 10, 3669–3714. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-11558-2
Gorski, M., Van Der Most, P. J., Teumer, A., Chu, A. Y., Li, M., Mijatovic, V., et al. (2017). 1000 Genomes-Based Meta-Analysis Identifies 10 Novel Loci for Kidney Function. Sci. Rep. 7, 45040. doi:10.1038/srep45040
Lagou, V., Mägi, R., Hottenga, J.-J., Grallert, H., Perry, J. R., Bouatia-Naji, N., et al. (2021). Sex-dimorphic Genetic Effects and Novel Loci for Fasting Glucose and Insulin Variability. Nat. Commun. 12, 1–18.
Liang, Y., Luo, S., Schooling, C. M., and Au Yeung, S. L. (2021). Genetically Predicted Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Major Cardiovascular Diseases, Their Risk Factors, Kidney Function, and Longevity: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Genet. 12, 699455. doi:10.3389/fgene.2021.699455
Mahajan, A., Wessel, J., Willems, S. M., Zhao, W., Robertson, N. R., Chu, A. Y., et al. (2018). Refining the Accuracy of Validated Target Identification through Coding Variant fine-mapping in Type 2 Diabetes. Nat. Genet. 50, 559–571. doi:10.1038/s41588-018-0084-1
Mitchell, R., Elsworth, B., Mitchell, R., Raistrick, C., Paternoster, L., and Hemani, G. (2019). MRC IEU UK Biobank GWAS Pipeline Version 2. University of Bristol. doi:10.5523/bris.2fahpksont1zi26xosyamqo8rr
Nikpay, M., Goel, A., Won, H. H., Hall, L. M., Willenborg, C., Kanoni, S., et al. (2015). A Comprehensive 1,000 Genomes-Based Genome-wide Association Meta-Analysis of Coronary Artery Disease. Nat. Genet. 47, 1121–1130. doi:10.1038/ng.3396
Pilling, L. C., Kuo, C.-L., Sicinski, K., Tamosauskaite, J., Kuchel, G. A., Harries, L. W., et al. (2017). Human Longevity: 25 Genetic Loci Associated in 389,166 UK Biobank Participants. Aging 9, 2504–2520. doi:10.18632/aging.101334
Roselli, C., Chaffin, M. D., Weng, L. C., Aeschbacher, S., Ahlberg, G., Albert, C. M., et al. (2018). Multi-ethnic Genome-wide Association Study for Atrial Fibrillation. Nat. Genet. 50, 1225–1233. doi:10.1038/s41588-018-0133-9
Shah, S., Henry, A., Roselli, C., Lin, H., Sveinbjörnsson, G., Fatemifar, G., et al. (2020). Genome-wide Association and Mendelian Randomisation Analysis Provide Insights into the Pathogenesis of Heart Failure. Nat. Commun. 11, 163–212. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-13690-5
Teumer, A., Li, Y., Ghasemi, S., Prins, B. P., Wuttke, M., Hermle, T., et al. (2019). Genome-wide Association Meta-Analyses and fine-mapping Elucidate Pathways Influencing Albuminuria. Nat. Commun. 10, 4130–4219. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-11576-0
Wheeler, E., Leong, A., Liu, C. T., Hivert, M. F., Strawbridge, R. J., Podmore, C., et al. (2017). Impact of Common Genetic Determinants of Hemoglobin A1c on Type 2 Diabetes Risk and Diagnosis in Ancestrally Diverse Populations: A Transethnic Genome-wide Meta-Analysis. Plos Med. 14, e1002383. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002383
Wuttke, M., Li, Y., Li, M., Sieber, K. B., Feitosa, M. F., Gorski, M., et al. (2019). A Catalog of Genetic Loci Associated with Kidney Function from Analyses of a Million Individuals. Nat. Genet. 51, 957–972. doi:10.1038/s41588-019-0407-x
Keywords: FGF23, cardiovascular disease, cardiovascular risk factor, type 2 diabetes mellitus, longevity, kidney disease, Mendelian randomization
Citation: Liang Y, Luo S, Schooling CM and Au Yeung SL (2021) Corrigendum: Genetically Predicted Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Major Cardiovascular Diseases, Their Risk Factors, Kidney Function, and Longevity: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Genet. 12:794246. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.794246
Received: 13 October 2021; Accepted: 20 October 2021;
Published: 11 November 2021.
Edited and reviewed by:
Hui-Qi Qu, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, United StatesCopyright © 2021 Liang, Luo, Schooling and Au Yeung. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shiu Lun Au Yeung, YXlzbHJ5YW5AaGt1Lmhr
 Ying Liang
Ying Liang Shan Luo
Shan Luo C. Mary Schooling
C. Mary Schooling Shiu Lun Au Yeung
Shiu Lun Au Yeung